# I. Outlook
## 1. Macroeconomic Summary and Future Predictions
Last week, the uncertainty surrounding trade policies continued to affect market sentiment, particularly regarding the direction of the Trump administration's tariff policies. The lawsuit filed against the Trump administration's tariff policies by the U.S. International Trade Court, along with the prospects of various trade negotiations, will be key forces influencing market trends.
This week, attention should be focused on the non-farm payroll data for May, which is set to be released on Friday. The results may serve as an important reference for future interest rate cuts.
## 2. Market Movements and Warnings in the Crypto Industry
Last week, Bitcoin faced profit-taking after breaking new highs, leading to some market adjustments. However, there has not yet been a noticeable outflow of large funds, and overall market sentiment remains relatively stable. Meanwhile, Ethereum continues to maintain a high-level consolidation, with its price structure showing no significant breakdown signs, indicating strong support. However, due to limited overall market liquidity, most altcoins experienced deeper corrections last week, putting some investors under short-term pressure.
Moving forward, investors should remain highly cautious and closely monitor subtle changes in macro market sentiment to respond to potential market uncertainties.
## 3. Industry and Sector Hotspots
Driven by AI, the Web3 platform TrendX aims to track trends and promote intelligent trading, helping users formulate smarter investment strategies. The DeFi platform XSY, led by Borderless, simplifies user access to advanced yield strategies through its flagship product Unity ($UTY).
# II. Market Hotspot Sectors and Potential Projects of the Week
## 1. Performance of Potential Sectors
1.1. Analyzing How the AI-Driven Web3 Platform TrendX Helps Users Formulate Smarter Investment Strategies
TrendX is a one-stop platform that leverages artificial intelligence and big data technology to help users discover investment opportunities. Since its establishment in 2022, TrendX has processed over 20TB of on-chain and off-chain data, analyzing billions of data points in real-time to uncover potential investment opportunities. Upholding the philosophy that "change is opportunity," TrendX provides investment advice through an intuitive interface, striving to be at the forefront of the global Web3+AI application ecosystem.
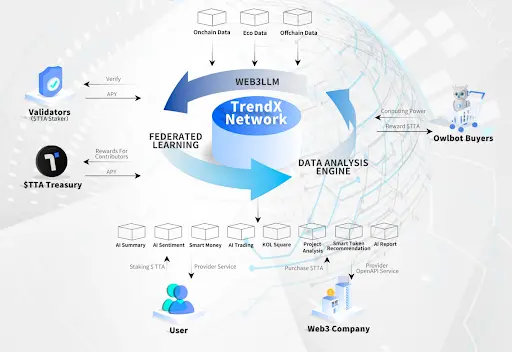
TrendX's distributed computing network, Owlbot, is jointly supported by the TrendX application ecosystem and AI models. It efficiently utilizes idle network resources globally, significantly reducing the actual costs of AI model training and operation. Every computer or smartphone with the TrendX AI program installed contributes computing power to the TrendX network, aiming to build the largest distributed computing network in the industry. This network is widely applied in the Web3 field, providing powerful and sustainable computing services for AI and Web3 companies worldwide.
Architecture Overview
- TrendX Chain
With advanced technology and rich industry experience, TrendX can effectively address the challenges currently faced by the industry. The TrendXChain, scheduled for launch in 2025, will leverage its significant advantages to tackle these pain points:
Rich Data Resources: TrendX possesses a vast amount of on-chain data, community data, and media data focused on Web3, providing a solid foundation for training AI models tailored to the Web3 ecosystem.
Direct Application of AI Models for Web3 Scenarios: TrendX not only has advanced data processing capabilities but also applies them directly to real Web3 scenarios. By integrating smart contracts and automated workflows, the platform supports complex AI operations and real-time decision-making, making it highly suitable for high-frequency trading and automated strategy implementation.
Deep Experience in Web3 and AI: TrendX has been deeply engaged in Web3 and AI for many years, accumulating rich technical strength and industry insights. It has a profound understanding of the needs and challenges of the Web3 ecosystem, enabling it to help enterprises better respond to future trends with innovative technological solutions.
Innovative Decentralized Data Market and Incentive Mechanism: TrendX is committed to building a decentralized data market, employing advanced encryption technology and precise data access control strategies to ensure user privacy and data security. At the same time, it stimulates the vitality and creativity of community members through innovative incentive mechanisms, promoting the sustainable development of the platform.
Solutions:
TrendX addresses the above challenges by launching TrendXChain and implementing Distributed AI Training. TrendXChain focuses not only on data processing and transaction optimization but also solves the challenges of AI training and deployment in decentralized environments through distributed machine learning technology and consensus mechanisms. We adopt Federated Learning, allowing AI models to be trained across multiple nodes, thereby protecting user privacy and reducing the risk of data leakage.
By combining Differential Privacy technology, we further enhance data protection capabilities. By introducing noise in data or model updates, we effectively prevent malicious attackers from extracting personal data from shared information. This hybrid approach is crucial in the AI mining architecture of Web3, ensuring the security and privacy of tasks such as sentiment analysis.
Federated Learning is a key distributed AI training technology that allows model training across multiple distributed devices without centralizing all data on a single server. In the context of Distributed Sentiment Analysis Mining, Federated Learning is essential as it allows training tasks to be collaboratively conducted across multiple devices, thus protecting user privacy and reducing the risk of data leakage. Unlike traditional AI methods that centralize all data on servers or in the cloud, Federated Learning keeps the training process at the data source, avoiding data migration issues. Even if one server has insufficient data, overall training can still be efficiently conducted across multiple nodes.
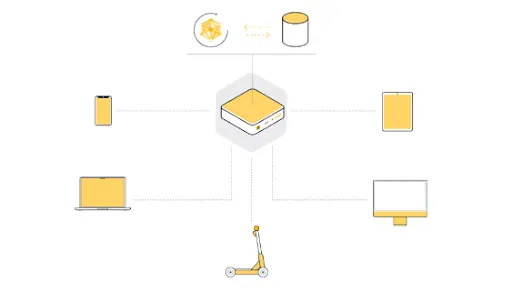
Federated Learning Revolutionizes Traditional Methods
Federated Learning fundamentally disrupts traditional machine learning methods by decentralizing the training process to the location of the data rather than centralizing it at a training hub. This model enables machine learning on distributed datasets. The basic process involves distributing global model parameters to client nodes (such as smartphones or enterprise servers), where each node trains using the same model parameters locally and sends the updated model parameters back to the central server. The server then aggregates model updates from multiple nodes, gradually optimizing the model to ultimately produce a fully trained model.
During this process, participating nodes also receive corresponding incentives to enhance their engagement and contributions to the network.
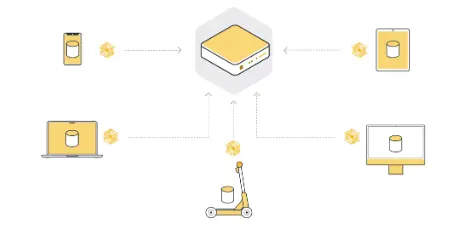
Application Scenarios
- Web3 Large Language Model (Web3 LLM): TrendXChain has built a rich training dataset by collecting 20 million tweets from over 50,000 key opinion leaders (KOLs) in the Web3 industry over the past two years. This model, based on the RoBERTa pre-trained model, is fine-tuned with social media sentiment classification data, enabling efficient sentiment analysis of social media texts and serving as an important tool for sentiment insights in the Web3 field, significantly improving the accuracy and timeliness of sentiment analysis.
- Web3 AI Miners: Web3 AI miners are a decentralized sentiment analysis system that distributes sentiment classification tasks across multiple network nodes (i.e., miners) using distributed computing technology. This architecture enhances the system's security and robustness through blockchain technology while avoiding single points of failure. An innovative incentive mechanism encourages more nodes to join the network, continuously enhancing the training and inference capabilities of the AI model.
Incentive Mechanism
To promote network participation and drive the development of decentralized networks, TrendXChain has designed a blockchain-based incentive mechanism for distributed AI sentiment analysis miners. Miners earn rewards by contributing computing power and completing sentiment classification tasks. These mechanisms not only ensure the healthy operation of the network but also promote the sustainable development of the Web3 ecosystem.
Community Governance
TrendXChain combines a Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism with a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) governance model to achieve efficient and transparent network governance, allowing community members to directly share in the benefits of network development.
By integrating high-performance blockchain technology, innovative AI model training methods, and a decentralized data market, TrendXChain is committed to promoting the widespread application of Web3. It not only provides strong business support for Web3 enterprises but also ensures the security and stability of the entire system through a global distributed AI node network. The vast on-chain data, community data, and media data within the TrendX ecosystem will be used to train large language models tailored specifically for the Web3 field.
2. Web3AI
By tracking the latest developments of over 20,000 Web3 projects and 50,000 industry KOLs, combined with AI big data analysis, TrendX can uncover the social trends and popularity of each project, helping users make more insightful investment decisions.
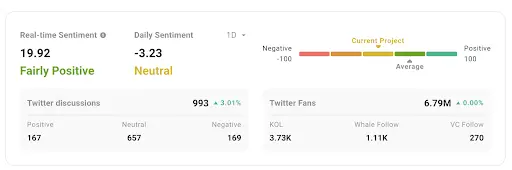
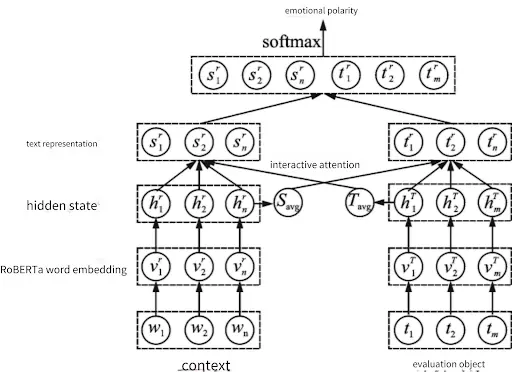
With the help of AI sentiment algorithms, we keep abreast of the latest market trends in real-time, continuously monitoring the latest tweets from all KOLs, recording and comparing daily sentiment scores with price movements, and deeply analyzing the relationship between mention volume and price fluctuations. Users can directly view the daily sentiment overview across Twitter, which serves as a key reference for assessing changes in market sentiment.
AI Sentiment Model Training Process
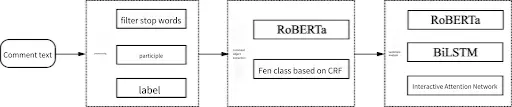
Data Collection
- Using Twitter API: Collecting or scraping over 50,000 tweets related to Web3 industry KOLs through keywords and hashtags (e.g., #Web3, #Blockchain).
- Real-time Monitoring: Establishing a real-time data stream to continuously analyze current sentiment change trends.
Data Preprocessing
- Data Cleaning: Remove noise such as URLs, special characters, and user mentions.
- Language Standardization: Correct spelling errors and unify slang expressions to standardize text formatting.
Model Selection and Training
- Pre-trained Models: Utilize pre-trained language models such as RoBERTa or BERTweet, further fine-tuning them on Web3 domain data.
- Sentiment Classification: Use existing sentiment classification structures (e.g., positive, neutral, negative) and enhance classification accuracy with Web3-specific data.
Fine-tuning and Evaluation
- Data Annotation: Manually annotate a portion of Web3 tweets as the training set.
- Model Fine-tuning: Fine-tune the model on the annotated dataset.
- Performance Evaluation: Evaluate model performance using metrics such as accuracy, recall, and F1 score.
Deployment and Application
- API Deployment: Package the model as an API for easy integration into various applications.
- Real-time Analysis: Integrate into an analysis platform to display real-time sentiment trends.
Visualization and Reporting
- Sentiment Trend Chart: Display a chart showing the trend of sentiment over time.
- Word Cloud: Present high-frequency positive and negative keywords.
Feedback and Optimization
- User Feedback: Collect user feedback to continuously optimize model performance.
- Continuous Learning: Regularly update the model, incorporating the latest tweet data for retraining and optimization.
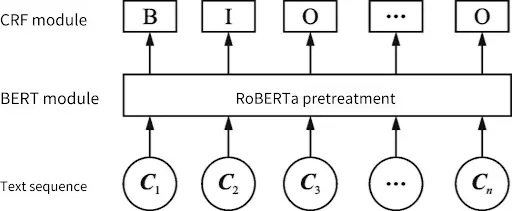
This process ensures the timeliness, accuracy, and application breadth of the sentiment model, making it particularly suitable for real-time monitoring and trend prediction of Web3 market sentiment.
- Owlbot
Owlbot is a key component of the TrendX ecosystem, dedicated to building a global distributed computing system. By deeply integrating with TrendX's powerful Web3 database and functional systems, Owlbot will drive the development of large language models (LLMs) and modular AI models specifically for the Web3 industry.
TrendX users will become providers of AI computing power, fundamentally reducing computing costs and improving operational efficiency. As more users participate, the availability, accuracy, and scalability of AI models will grow exponentially. This mechanism will propel TrendX to achieve a leap in computational efficiency and scale, continuously leading the innovative evolution of Web3 and AI technologies.
Owlbot Core Operating System
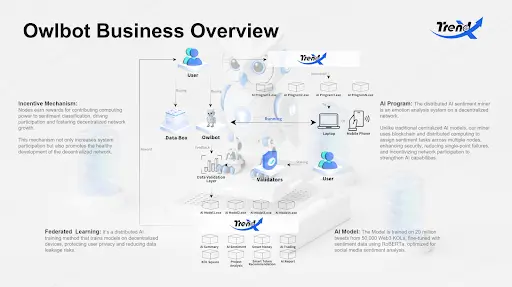
Owlbot's business overview delves into a highly complex and cutting-edge ecosystem that integrates Federated Learning, advanced AI programs, and highly specialized AI models, equipped with dynamic incentive mechanisms to motivate participants and drive continuous innovation.
These elements collectively build a solid framework that not only significantly enhances AI capabilities but also fosters collaboration and growth within the Web3 community. This innovative approach transforms AI robots from mere tools into continuously evolving, vibrant intelligent entities at the forefront of the AI revolution.
Commentary
With its rich Web3 big data resources, advanced AI technology, and innovative distributed computing network Owlbot, TrendX possesses powerful data processing and intelligent analysis capabilities, providing users with precise and timely investment insights and sentiment analysis. Its use of Federated Learning and decentralized incentive mechanisms effectively safeguards user privacy and system security, promoting the sustainable and healthy development of the ecosystem. However, as an emerging platform, TrendX still faces challenges such as high technical complexity, significant resource demands for model training, and intense market competition, necessitating continuous optimization of technology and expansion of its user base to maintain a competitive edge.
1.2. A Brief Analysis of the DeFi Platform XSY, Led by Borderless, Simplifying User Access to Advanced Yield Strategies through Its Flagship Product Unity ($UTY)
XSY is building the next generation of digital synthetic dollars, $UTY, to unlock the dormant potential within the blockchain ecosystem in a structured and scalable manner.
XSY is redefining the future of blockchain liquidity by addressing one of the industry's biggest challenges: the idle capital on-chain. Currently, the vast majority of on-chain assets are underutilized, limiting their potential to drive ecosystem growth. XSY is pioneering a new model that transforms dormant value into productive capital, thereby promoting a more efficient and scalable blockchain economy.
Architecture Overview
- Unity (“UTY”)
$UTY, also known as Unity, is a digital synthetic dollar (DSD). Unity is a Delta-neutral asset that serves as the core synthetic dollar within the XSY decentralized finance product ecosystem.
Whitelisted users can mint $UTY using various assets, with AVAX being the initially supported asset used to build the synthetic Delta-neutral collateral system for $UTY.
Users can utilize $UTY on XSY's DeFi partner platforms (such as Pharaoh and Euler) to receive rewards provided to early $UTY adopters.
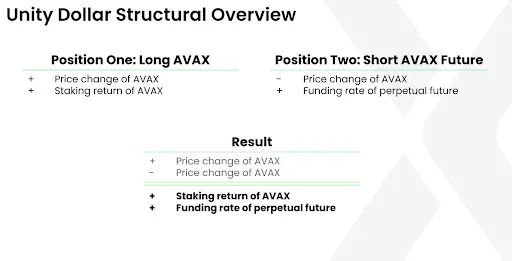
Synthetic Delta-neutral Assets are financial positions constructed through derivatives, making the price changes of the underlying asset have almost no impact on the overall position's value. In the design of Unity, this mechanism is achieved by dividing the collateral assets into two mutually hedging parts:
- A long position in the native protocol asset (e.g., AVAX);
- A short position in perpetual contracts for the native protocol asset.
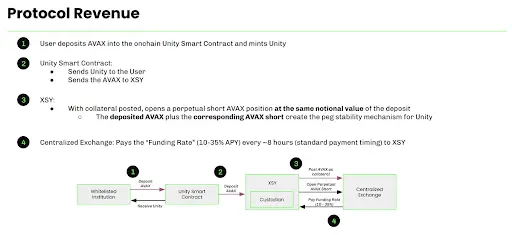
Protocol Revenue Mechanism Explanation:
When users mint $UTY using native protocol assets, for example, Alice mints $UTY worth $1 million using $AVAX worth $1 million.
XSY will open a short position in a perpetual contract for the equivalent of $1 million on centralized exchanges (such as Binance or OKX) to match Alice's $UTY minting operation.
Typically, XSY earns a revenue approximately every 8 hours from holding that short position, known as the "Funding Rate."
The funding rate earned by XSY is variable, depending on the market demand for long or short positions on that native token.
The end result is: Alice receives $UTY worth $1 million, which she can use in partner protocols like Pharaoh or Euler; while XSY holds a neutral hedged position worth $1 million (neither long nor short), which can earn funding fees, thus providing continuous revenue for the protocol.
Underlying Derivative Mechanism Explanation
To maintain the Delta-neutral characteristics of $UTY, the protocol opens a corresponding short position in the derivatives market every time a long position is taken in the spot market. This hedging strategy ensures that the impact of asset price fluctuations is neutralized, thereby stabilizing the fundamental value of the assets used in the system.
Current Derivative Tools Used
To achieve this hedging mechanism, for every $1 of native protocol assets purchased, the protocol simultaneously shorts that asset in the derivatives market for an equivalent nominal amount. The current methods used include:
- Coin/USD perpetual contracts on centralized exchanges
These perpetual contracts allow us to maintain a short position in the native protocol asset without needing to roll over contracts periodically. Current centralized exchanges used for hedging include:
- Binance
- Bybit
- OKX
By executing short positions in these highly liquid derivative markets, the protocol effectively neutralizes directional risk while ensuring efficient capital allocation.
- Open Market Anchored Arbitrage Mechanism
The market value of $UTY is maintained stable through an arbitrage mechanism, where arbitrageurs operate to profit when discrepancies arise between the market price and its relatively fixed mint/redeem price. This process naturally keeps $UTY closely tethered to the $1 price anchor during market fluctuations.
Minting and Redemption Mechanism: Achieved through Issuing Smart Contracts
Authorized users can mint or redeem $UTY at a fixed price of approximately $1 through issuing smart contracts. Although the trading price in the secondary market may fluctuate, this stable mint/redeem mechanism provides opportunities for arbitrageurs, helping to maintain the price stability of $UTY.
Scenario One: Price Below $1 — Arbitrage through Redemption
When the trading price of $UTY on decentralized exchanges (DEX) is below $1, arbitrageurs can profit as follows:
- Purchase $UTY at a discount on the open market;
- Redeem $UTY through a smart contract at a price close to $1;
- Capture the difference between the purchase price and the redemption price as profit while reducing the circulation of $UTY.
This redemption action exerts upward pressure on the market price, prompting it to return to $1.
Scenario Two: Price Above $1 — Arbitrage through Minting
When the market price of $UTY is above $1, arbitrageurs can:
- Mint new $UTY at a fixed price of $1 by issuing a smart contract;
- Sell the newly minted $UTY at a premium on the open market;
- Capture the profit from the difference between the selling price and the minting price while increasing the market circulation of $UTY.
This new supply creates some selling pressure, helping the market price to fall back towards $1.
This arbitrage mechanism is the core means by which $UTY maintains price anchoring stability, leveraging the spontaneous actions of market participants to achieve self-regulating price adjustments.
Summary
The core advantage of XSY lies in the construction of a structured and scalable digital synthetic dollar mechanism through $UTY, effectively activating dormant on-chain capital and achieving liquidity optimization and value reutilization within a decentralized ecosystem. Its innovative delta-neutral hedging model, combined with the CEX derivatives market, continuously generates funding fee revenue for the protocol and stabilizes the $UTY price anchor through an open market arbitrage mechanism, enhancing market confidence and user participation. However, $UTY is currently not open to the public, and its reliance on centralized exchanges may pose systemic risks and regulatory uncertainties to some extent.
2. Detailed Project Focus of the Week
2.1. In-depth Analysis of Layer 1 Protocol N1, Supporting Asynchronous, Unordered Transactions and Achieving Infinite Scalability by Eliminating Consensus
Introduction
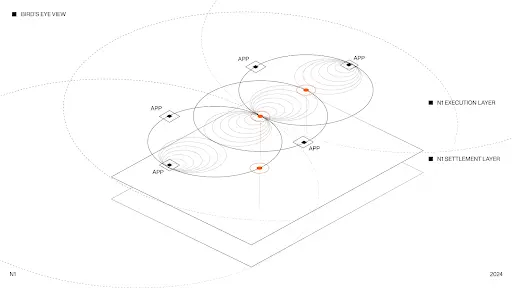
N1 is an L1 blockchain designed from the ground up to natively support applications and horizontal scalability. It can be imagined as an Ethereum vision without historical baggage. Its core innovation lies in avoiding the use of consensus mechanisms in the vast majority of cases—this means that as the number of validators increases, the system can achieve higher scalability.
Unlike traditional approaches, N1 does not rely on consensus to order transactions for all applications; instead, it defaults to unordered and asynchronous processing. Consensus is only introduced when cross-chain interactions occur between applications.
Additionally, N1 natively integrates data availability features and imposes no restrictions on the execution environment, giving developers greater freedom to optimize performance.
Technical Architecture Analysis
- Settlement Layer
The settlement layer of N1 provides the minimum necessary functions for a hosted execution environment and ensures data availability. We introduce a new primitive: unordered set replication, and adopt a hybrid storage model that supports both ordered logs and unordered sets. Before explaining these concepts, let’s illustrate with an example:
Suppose we want to run a zk-rollup providing Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) on N1 while bridging assets both within and outside of N1. To prove to users that the operations are honest, we need to ensure the following for each Ethereum L2 block:
Ensure all users can download the transaction data;
Construct and verify a SNARK proof that the execution of the block is correct;
Prove that the asset bridging operation is correct.
To achieve this, we will use the broadcasting primitive provided by the network. For each block, the operator must complete the following steps:
- Broadcast Transaction Data
The operator broadcasts the transaction data of the current block to the data availability network. The data is encoded using Erasure Coding for efficient sharding storage among validators. This way, the client bandwidth usage is proportional to the block size, ensuring maximum efficiency.
- Collect Data Availability Proofs
The network will continuously ensure data availability. During broadcasting, the operator generates a commitment for the data, binding it to specific data for subsequent verification and recovery. This commitment is included in the state transition proof, and any other client can access and verify this data.
- Execute the Block
Run the block in zkEVM, generating a “receipt” that proves the state transition is correct and that the block data is consistent with the data availability commitment. This step binds the execution result to the data availability in the network.
- Verify and Sign the Receipt
The operator broadcasts the zk proof again and requests validators to verify and sign it. These signatures are aggregated into what is called a “state transition certificate.” During the verification process, validators also check the zkEVM receipt to ensure it matches the data availability commitment and follows the correct fork choice rules, thus preventing the operator from pushing invalid blocks. Only signatures from more than 2/3 of the validators are required.
- Submit the Certificate to the Network
Finally, the operator broadcasts the certificate to the network. Each validator checks whether the signature is consistent with the current set of validators; if correct, it stores the certificate. This certificate can be extracted and verified by any client. This write operation does not have ordering constraints with other clients' write operations, so we refer to it as a write to an “unordered set.” The certificate also includes a withdrawal list, and withdrawals will be pushed to the operator's outbox while updating their account balance.
Core Feature Summary:
The above process constructs a rollup suitable for EVM. You will notice that throughout the process, validators do not need to execute the traditional “two-phase commit protocol (2PC),” which would lead to a quadratic increase in the number of messages. Instead, the operator plays a role similar to a “leader,” responsible for handling the commit logic. Ultimately, the number of messages is linearly related to the number of validators, with a constant delay that does not block the progress of other clients.
The core primitives required by N1 include:
Authenticating and storing state transition certificates;
Ensuring the availability of any data;
Implementing cross-chain asset bridging (with the operator having account control);
The only step that requires global ordering is asset bridging. Since most operations are completed internally in L2, resource competition between different applications is minimal.
Liveness
In a single-operator architecture, how can we ensure the system's liveness? After all, the operator may go down or refuse to generate new blocks.
The solution lies in using L1 blocks as a “clock.” L1 can serve as an “inbox” that enforces the inclusion of transactions and compels the operator to remain active. If the operator stops functioning, the governance mechanism can intervene, take over the operator, and force the extraction of remaining funds. Moreover, we impose no restrictions on how the operator runs: it can also be operated by a decentralized set of nodes to provide stronger liveness guarantees.
Bridging
The network natively supports the verification primitives needed to build cross-chain bridges. We provide a native IBC cross-chain bridge connecting Solana and Ethereum.
- Bridging In: Users can bridge assets to an address controlled by the operator while providing VM-specific metadata indicating how to route the asset within the virtual machine. N1 maintains an “inbox” for bridging assets in its logs, from which the operator consumes data.
- Bridging Out: When bridging out assets, the operator pushes messages to the “outbox,” and these operations are enforced by the state transition function.
- Execution Layer
N1 maintains complete neutrality (agnostic) towards the execution environment. We encourage developers to unleash their creativity and explore specialized paths for performance optimization, such as implementing Lightning Networks or specialized exchanges. Nevertheless, N1 also provides a default execution environment, described as follows.
The default execution environment of N1 is an asynchronous virtual machine network, which we call Processes. Each process can run various virtual machines, such as TypeScript or Solidity, while being able to send and receive messages through ordered channels with other processes in the network.
For example:
- One process might be a perpetual contract exchange built with TypeScript.
- Another process might be a Solidity smart contract.
- Both can interact and collaborate through messages.
The benefits of this architecture include:
- No state contention: Each application runs independently of one another.
- Operates at its own pace: More flexibility to optimize performance and enhance throughput.
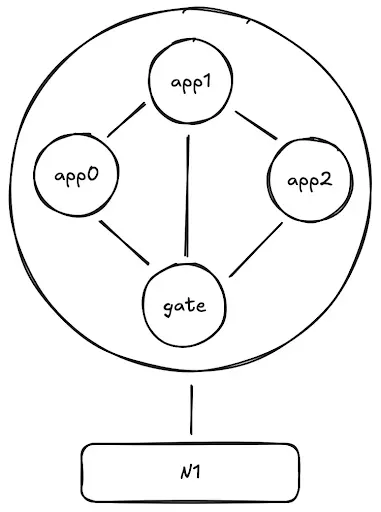
The Gate application is a special program used to handle assets bridged from L1 and route them to the corresponding applications in the L2 network. This greatly simplifies the network's topology and allows for almost instant liquidity between applications.
Unique Properties
You will notice that the default execution network structure of N1 is quite unique. Its design goal is to maximize the capabilities of the underlying Layer 1 and provide a new, high-performance default execution environment. Its core concepts include:
- Dedicated Compute
- Asynchronous Communication
- SNARK Fraud Proofs
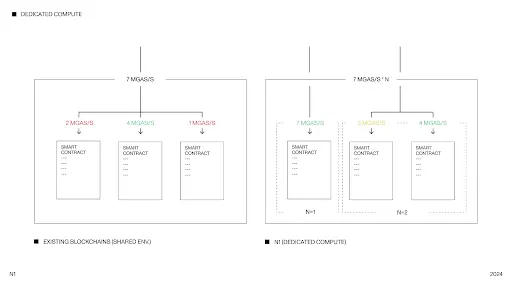
Dedicated Compute
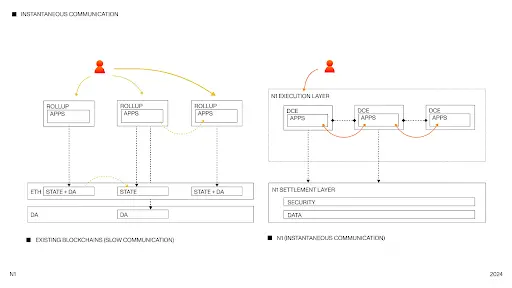
Traditional blockchains run all applications on a shared virtual machine. This structure can lead to state contention, skyrocketing gas fees, and significant fluctuations in latency during load spikes, severely limiting the potential for building complex applications. This is akin to shared database clusters in Web2, which are notoriously poor in scalability.
N1 addresses this bottleneck by introducing a “Dedicated Compute Environment (DCE).” Each application runs in an independent environment with dedicated computing resources, allowing for vertical scaling and fully utilizing the computational resources of its servers to resolve performance bottlenecks.
The process of deploying applications is as simple as mainstream blockchains, if not simpler. N1 lowers the development threshold by being compatible with existing development toolchains:
- Solidity developers can directly use Foundry
- Rust developers can use the standard WASM toolchain
- TypeScript developers can continue using their existing toolset
This significantly enhances the onboarding speed and makes building high-performance applications more efficient.
Instantaneous Communication
Programs communicate with each other through ordered channels in a point-to-point manner, with message content in binary format. Each message triggers the receiving program to execute the payload of that message.
Unlike other messaging solutions, messages here are instantaneous, meaning they are executed as soon as they arrive. This is different from cross-chain bridging on other blockchains, where messages from both parties must wait for some form of verification before either side can trust the message.
(Snark) Fraud Proofs
The uniqueness of N1's execution environment lies in the non-interactive nature of the zero-knowledge proof-based fraud proofs. This means that once a challenger constructs a zero-knowledge proof, they only need to send it to Ethereum to challenge the declared state of N1. This is different from some optimistic rollups that use interactive schemes, which require multiple interactions between the operator (us) and the challenger, leading to withdrawal waiting periods that can last up to 7 days, and necessitating the resolution of compatibility issues between on-chain challenge execution and off-chain normal execution.
The process for validators to detect and report fraud on N1 is as follows:
- Replay: Validators replay the state on their local machines based on the transaction data published on the data availability layer;
- Detection: Validators find that the state root update submitted to Ethereum does not match the state root obtained through data availability replay;
- Proof Generation: Validators execute the program and generate a zero-knowledge proof as a cryptographic credential for the fraud proof;
- On-chain Verification: Validators submit the proof to the on-chain verifier, which verifies the proof based on the program hash;
- State Recovery: If the proof is successfully submitted and proves fraud, the Ethereum contract enters state recovery mode, forcing the operator to roll back the fraudulent state update.
Data Availability
Data availability refers to the N1 network's public disclosure of all transaction data history it has received to nodes, which can use this historical data to reconstruct state transitions and verify the legality of the state on N1. This is key to preventing operators from concealing data to obstruct the generation of fraud proofs. In the case of an invalid state transition, nodes can use the transaction data to construct fraud proofs to roll back the chain state and punish validators who submitted fraudulent state updates.
N1 is built on high-throughput data availability, as the throughput of any program will be bottlenecked by data availability bandwidth. Our modular architecture allows for on-demand allocation of arbitrary bandwidth for specific programs, which is crucial for achieving dedicated compute.
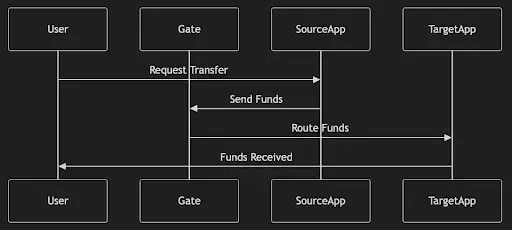
- Transaction Lifecycle
Here are some example lifecycles for deposits and withdrawals. The goal is to demonstrate how transactions involving the most system components operate, thereby helping to understand the overall system architecture. We include processes on both the L1 (Layer 1) and L2 (Layer 2) sides of the system.
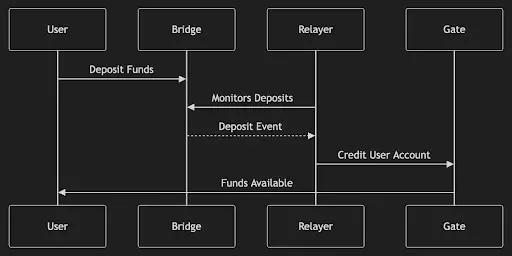
- Deposit
Deposits first go through bridging, then enter the gate application in the network, and are subsequently sent to the designated application.
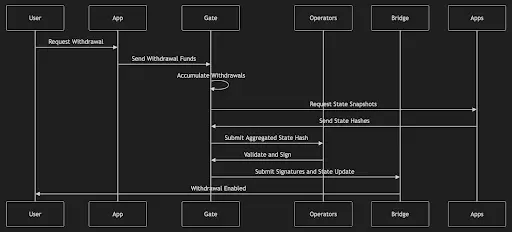
- Withdrawal
Withdrawals must first reach the target application, then go through the gate application, and finally enter the settlement layer during the next settlement.
- Cross-Application Transfer
Cross-application transfers are similar and consist of two transfer operations.
Summary
The advantage of N1 lies in its innovative default design without consensus, significantly enhancing horizontal scalability and performance, supporting asynchronous communication and dedicated compute environments, reducing state contention and latency, and providing flexible execution environment compatibility (such as supporting multiple virtual machines). Additionally, the built-in data availability and SNARK-based fraud proof mechanisms enhance security and trust assurance. However, its optimistic model may rely on the honesty of the operator, and a fully decentralized and efficient SNARK proof system has yet to mature. Bridging and cross-application interactions still require complex coordination, and the overall ecosystem and toolchain are still in development.
### Industry Data Analysis
1. Overall Market Performance
As of November 1 (Eastern Time), the total net outflow of Ethereum spot ETFs was $10,925,600.
1.1. Price Trends of Spot BTC vs ETH
BTC
Analysis
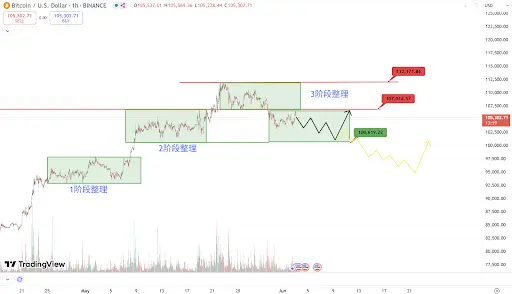
Core: BTC's upward trend that started from $74,000 has been completely destroyed after breaking below the key support of $107,000.
Focus: In the short term, pay attention to whether the rebound can quickly rise above $107,000. If successful, it is expected to test the previous high again; otherwise, it means the price will continue to test the lower edge of the second phase consolidation zone, which is around the support of $100,600.
Conclusion: If it stabilizes above the $100,000 mark and the rebound quickly breaks through $107,000, a mid-term rise is still possible; otherwise, the trend may officially start a downward trend, with prices continuously probing down to the first phase consolidation zone.
ETH
Analysis
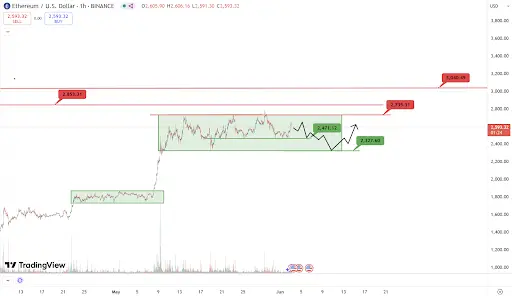
Core: ETH is only in the second phase of consolidation after the upward trend began, and the consolidation from late April to mid-May, combined with the second phase of consolidation from June to now, has accumulated more upward momentum. Therefore, ETH has strong support at $2,320.
Focus: The effectiveness of the support at $2,470 and the second line of support at $2,320.
Conclusion: As long as it stabilizes at $2,320, the medium to long-term outlook remains bullish; otherwise, it will enter a downward range, and the new support area needs to be in the $1,600 to $1,800 range.
2. Public Chain Data
2.1. BTC Layer 2 Summary
Analysis
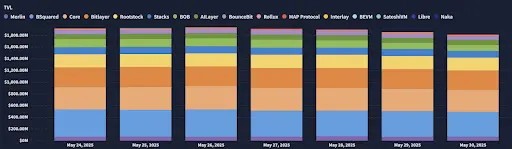
- Stacks (STX)
Stacks continues to maintain its leading position in the Bitcoin smart contract space. Its Nakamoto upgrade, set to launch in 2024, will shorten block times to about 5 seconds and introduce decentralized Bitcoin-pegged assets (sBTC), enhancing integration with the Bitcoin main chain. Currently, Stacks' total value locked (TVL) exceeds $190 million, supporting multiple DeFi platforms and NFT markets such as Velar, Bitflow, and Alex.
- Bitlayer
Bitlayer provides a trustless scaling solution through its BitVM architecture and OP-DLC bridging. The project has established strategic partnerships with multiple networks, including Base, Starknet, and Arbitrum, to promote liquidity for Bitcoin in the multi-chain DeFi ecosystem.
- Mezo
Mezo introduces a "Proof of HODL" consensus mechanism that encourages users to earn rewards by locking BTC. The platform has attracted over 1,059 BTC in deposits and plans to implement a dual-token model (BTC/MEZO) to diversify validator incentives.
2.2. EVM & Non-EVM Layer 1 Summary
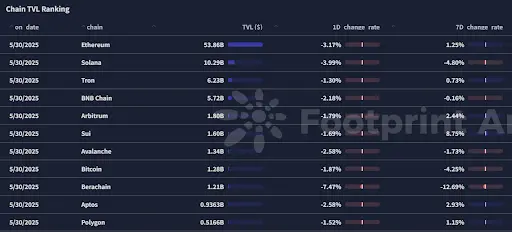
Analysis
EVM Layer 1 Blockchains
Ethereum
Pectra Upgrade: The Ethereum Foundation activated the Pectra upgrade on the Sepolia testnet, an important step to enhance Ethereum's scalability and user experience. The upgrade includes account abstraction (EIP-7702), an increase in validator staking limits (EIP-7251), and improvements to optimize Rollup scalability (EIP-7691).
Base
Flashblocks and Appchains: Base launched Flashblocks to enhance transaction confirmation speed; it also introduced Appchains, allowing developers to create customized Layer 3 solutions, enhancing user engagement and developer flexibility.
Non-EVM Layer 1 Blockchains
Injective
Native EVM Integration: Injective has introduced native Ethereum Virtual Machine support on its Layer 1 blockchain, enabling Ethereum-compatible decentralized applications to run on Injective, enhancing its ecosystem capabilities.
2.3. EVM Layer 2 Summary
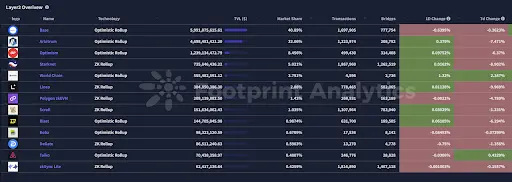
Analysis
Overall Market Performance
- Total Value Locked (TVL): The TVL of the Ethereum L2 ecosystem has surpassed $51 billion, a year-on-year increase of over 205%.
- Active Addresses: The number of weekly active addresses on L2 platforms has reached approximately 10.9 million, about five times that of the Ethereum mainnet.
- Transaction Volume: The annual transaction volume on the Base network has exceeded 10 million, with an average daily transaction count of about 1 million, demonstrating its strong appeal among users and developers.
### 3. Macroeconomic Data Review and Key Data Release Points for Next Week
As of the week ending May 24, the number of initial jobless claims in the United States was 240,000, higher than the expected 230,000, but overall still at a low level. The previous value was 226,000, indicating that the job market remains resilient. The U.S. core PCE price index year-on-year for April was 2.5%, marking a new low since March 2021. This data met market expectations, with the previous value revised from 2.6% to 2.7%.
Important macro data points for this week (June 2 - June 6) include:
June 4: U.S. ADP employment numbers for May
June 5: U.S. initial jobless claims for the week ending May 31
June 6: U.S. unemployment rate for May; U.S. seasonally adjusted non-farm payrolls for May
### Regulatory Policies
United States: Bitcoin Strategic Reserves and Regulatory Reform
- Bitcoin Strategic Reserves: Vice President JD Vance emphasized the strategic role of Bitcoin in U.S.-China competition and reiterated the Trump administration's push to establish a Bitcoin strategic reserve.
- Regulatory Shift: The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has withdrawn its lawsuit against Binance, indicating that the regulatory environment is becoming more cooperative. Meanwhile, the House has introduced the "Digital Asset Market Transparency Act" (CLARITY Act) to establish a formal regulatory framework for crypto assets.
- Stablecoin Legislation: The Senate is promoting the "GENIUS Act," which implements stricter audit requirements and anti-money laundering regulations for stablecoins.
United Kingdom: Plans to Integrate Cryptocurrency into the Mainstream Financial System
- Legislative Proposal: Reform Party leader Nigel Farage announced the "Crypto Revolution" plan, proposing a 10% capital gains tax on cryptocurrency earnings and the establishment of a national Bitcoin reserve at the Bank of England. The party also plans to accept political donations in cryptocurrency.
Pakistan: Establishment of a National Cryptocurrency Committee
- Regulatory Body Formation: Pakistan has established the "Pakistan Crypto Committee" (PCC) aimed at promoting the development of blockchain technology and digital assets, and has released the country's first government-led strategic Bitcoin reserve.
India: Upcoming Release of Cryptocurrency Asset Policy Framework
- Policy Discussion Document: The Indian Ministry of Finance plans to release a discussion document on cryptocurrency asset regulatory policy by June 2025, indicating a robust approach to advancing digital finance.
European Union: Concerns Over Stablecoins and Monetary Sovereignty
- Sovereignty Risk: The rise of stablecoins has raised concerns about monetary sovereignty in Europe. The rapid development of dollar-backed stablecoins internationally, while euro-backed stablecoins remain immature, could exacerbate "dollarization," thereby undermining the monetary sovereignty of the Eurozone.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




