Intent Assets aim to solve the current issue of "TVL stagnation" in the cryptocurrency industry by making new optimizations and upgrades in the profitability, usability, and convenience of assets.
Introduction
The current issue facing the cryptocurrency industry, "TVL stagnation," essentially stems from a lack of sufficient on-chain usability for various cryptocurrency assets, making it difficult to attract users beyond simple airdrop incentives.
To address this problem, dappOS has introduced Intent Assets, which are assets that can both generate returns and be readily available on-chain at any time.
dappOS is an intent execution network that has received investments from top institutions such as Binance Labs and Polychain, with a latest valuation of 300 million USD, making it one of the leading projects in the intent race.
I. Current Industry Issue: Traditional TVL Model Stagnation
TVL (Total Value Locked) is commonly used to measure the total amount of assets locked in a project, reflecting the user participation and market trust of the project. It has been a relatively effective indicator in past cryptocurrency market cycles because TVL represents actual "real money," with a much higher cost of falsification compared to other data indicators such as address quantity and social media attention. Therefore, projects with higher TVL have a clear advantage in market promotion and attracting investors. In this context, many projects attract users by offering high yields and airdrop incentives to quickly increase their TVL data, showcasing the strength and appeal of the project.
However, this approach has revealed some problems in this cycle: after the issuance of coins and listing on exchanges, the TVL of many projects often rapidly declines. This TVL is not contributed by a wide range of cryptocurrency users, but rather by a few large holders or pre-arranged partners through "mining and selling," rapidly increasing the TVL in the short term to cash out. This "stagnant TVL" does not represent the true vitality of the project's ecosystem, but rather achieves short-term data spikes through artificial operations. This phenomenon has led to broader industry issues, such as multiple delays in airdrop distribution or unlocking of user assets for high TVL projects, as there is a concern that once realized, this TVL will quickly dissipate.
As a result, the credibility and effectiveness of TVL as an indicator of the vitality of an on-chain ecosystem have also been questioned.
The reason for the stagnation of TVL is that for ordinary cryptocurrency users, the absolute returns from participating in these projects are limited. Once they encounter market fluctuations, the cost of withdrawing assets or converting them is high, or they need to wait for a long time, potentially missing out on market opportunities. In other words, the opportunity cost of participating in these projects is too high for ordinary users, leading to their low willingness to participate, resulting in TVL being dominated by large holders and becoming a tool for their cashing out.
The introduction of Intent Assets by dappOS is precisely aimed at addressing this issue.
II. dappOS Intent Assets: Making Yield Assets Readily Available on-chain
2.1 What are Intent Assets
Intent Assets are a new type of asset introduced by dappOS, which are assets that offer high asset yield and can be readily available at any time. Whether it is bringing Intent Assets to the exchange in the form of native assets or buying MEME coins, participating in lending, or staking on-chain, users can directly use them. There is no need for additional steps, waiting time, or enduring high slippage.
At first glance, Intent Assets may seem similar to previous financial products like Yu'ebao, both of which have the characteristics of "yield + quick access." However, in terms of usability, liquidity, and security, Intent Assets are far superior to similar previous products. In terms of usability, Yu'ebao and similar products cannot be directly used in dApps and require manual redemption to be used on-chain, and some yield assets even require a long redemption waiting period; in terms of security, the use of Intent Assets is guaranteed by the OMS security mechanism of the dappOS intent execution network, with decentralized and non-custodial underlying assets, making it more secure and trustworthy compared to centralized and opaque "Yu'ebao" products.
2.2 Use Cases of Intent Assets
The first batch of Intent Assets to be launched includes intentBTC, intentETH, and intentUSD.
Here are a few examples to illustrate how Intent Assets are used:
Scenario 1: User wants to redeem their yield assets and convert them to USDT
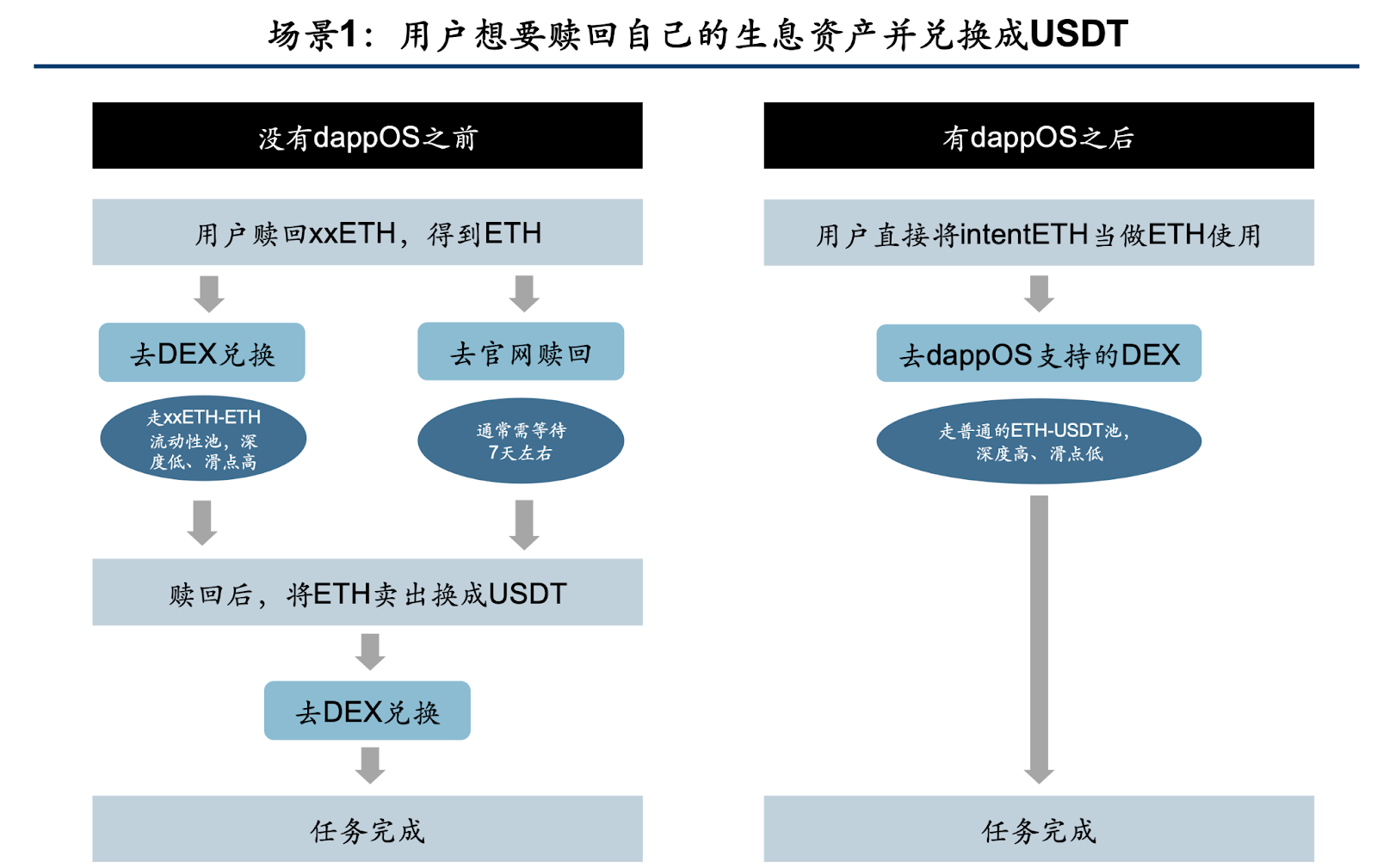
As shown in the image, before the existence of dappOS, if you wanted to redeem your yield assets (such as xxETH), you typically had to choose between redeeming them on a DEX or on the project's official website. If you chose to directly exchange on a DEX, you would need to use a specific xxETH liquidity pool, which could lead to issues such as insufficient liquidity and high slippage, resulting in significant financial losses; when redeeming on the official website, you usually had to wait for around 7 days, which could be very challenging in urgent situations. Additionally, after redemption, you would need to perform additional manual operations to sell ETH and convert it to USDT.
With dappOS, if you hold intentETH, you will find that within the DEX supported by dappOS, intentETH can be directly used as ETH and exchanged for USDT with a single click. The liquidity pool used for the exchange is the high-depth regular ETH-USDT pool, without liquidity or slippage issues.
Scenario 2: User wants to buy token $XXX on the xxL2 chain, but currently has no funds on the xxL2 chain
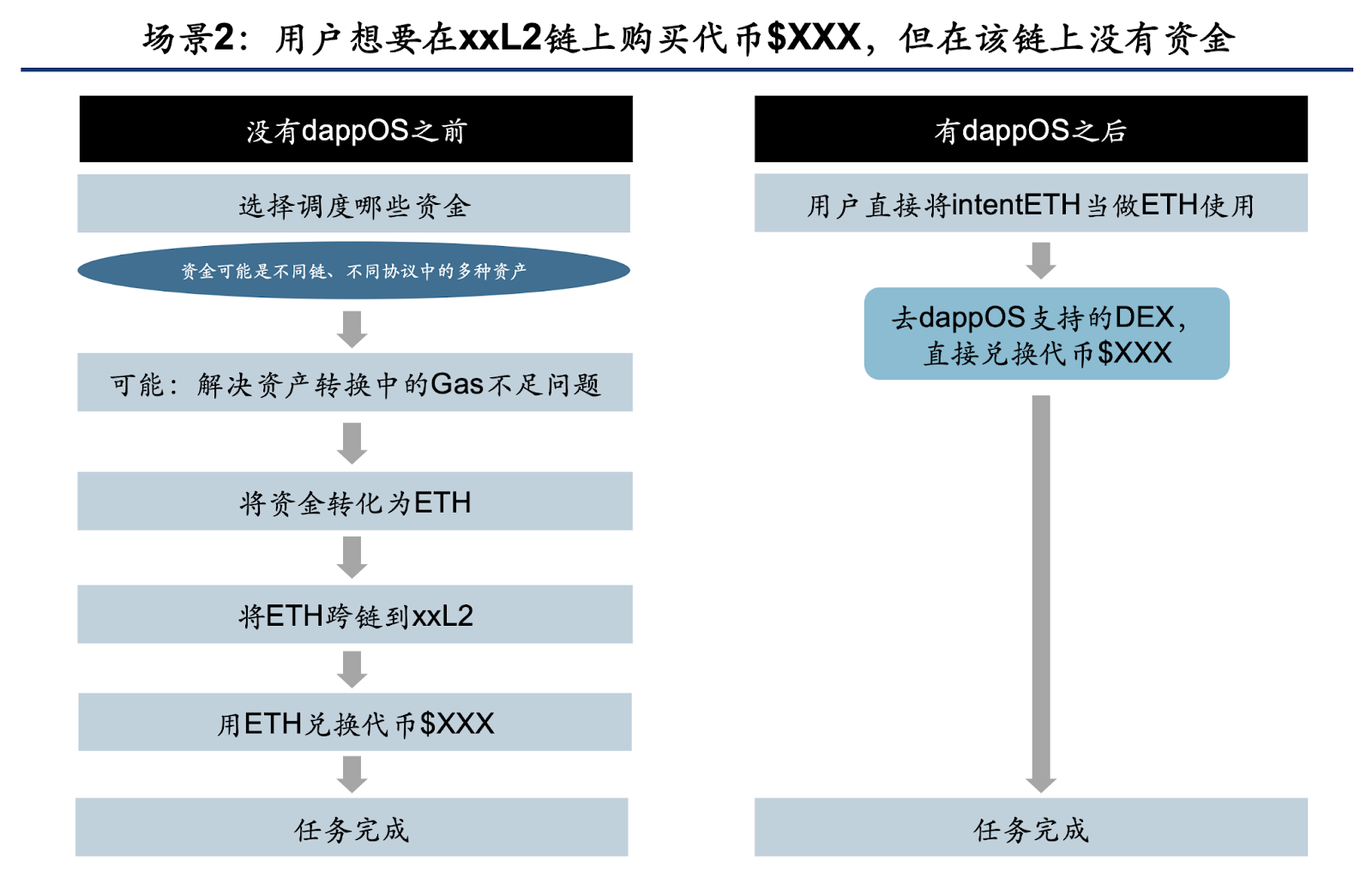
As shown in the image, without dappOS, what seems like a simple operation actually requires a significant amount of planning. For example:
- Fund allocation: Consider which of your funds on which chain is more convenient; some funds may still be in other protocols, and you need to withdraw funds from those protocols.
- Form conversion: Perhaps your funds mainly exist in other forms on other chains, and you need to convert them to ETH, a process that usually involves a trade-off between significant wear and tear and waiting time; if the gas required during the conversion is insufficient, how to supplement the gas, and how to obtain this gas.
- Cross-chain method: Whether to directly use on-chain cross-chain protocols or deposit ETH into an exchange and then withdraw it to the xxL2 chain.
With dappOS, as long as you hold intentETH, you can go to the DEX supported by dappOS on xxL2 to buy tokens. You will find that when using intentETH to buy tokens, it feels no different from using regular ETH. Moreover, you no longer need to plan various operational processes, allowing you to more flexibly use and allocate your on-chain assets in the future. For example, you do not need to keep funds on every L1 and L2 chain "just in case," as holding Intent Assets can meet the temporary interaction needs of various chains.
In summary, when users hold intentETH, they feel no different from using native ETH in (non-yield scenarios), but they can passively earn substantial returns.
III. Working Principle of Intent Assets
3.1 Intent Execution Network
To explain the working principle of Intent Assets, it is necessary to introduce the dappOS intent execution network behind Intent Assets. In dappOS, "intent" can be simply understood as the task that a user wishes to complete.
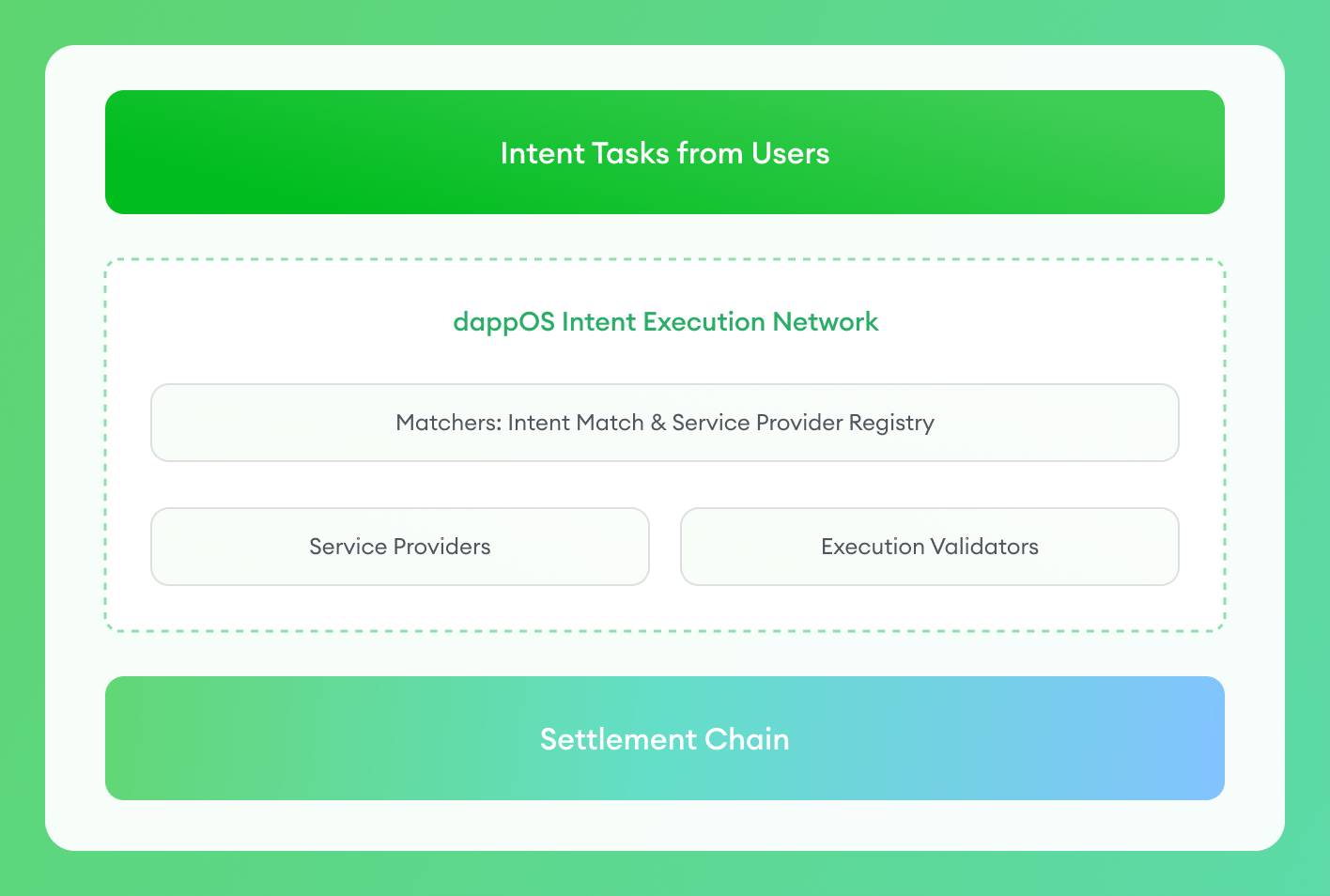
As shown in the above figure, the architecture and functions of the dappOS network are as follows:
- User: Issues intent.
- Service Provider: Executes various intent services. After pledging a certain amount of dappOS tokens as collateral, they can start accepting user intents and earn income.
- Execution Validator: Responsible for verifying the execution of service nodes. If the service node fails to complete the task as required, the validator has the right to vote to penalize the service node.
- Matcher: Responsible for matching the intent of the user and the service provider.
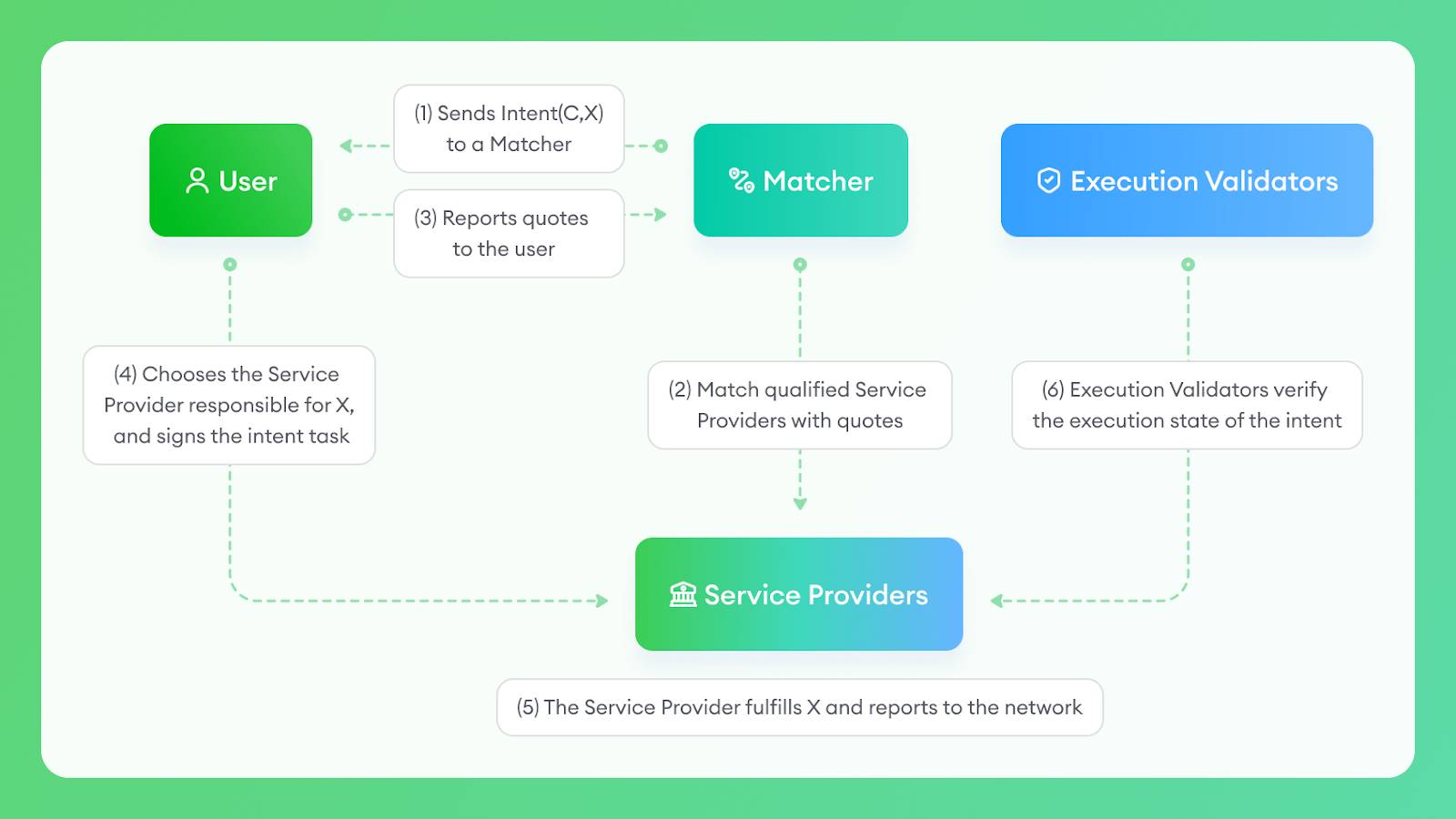
In simple terms, during the specific execution process, the user will send the intent to the matcher through front-end interaction, and then the matcher will inquire with the associated service provider, select the most favorable quote, and offer it to the user. The user can then sign the transaction, transfer the resources required to fulfill the intent to the service provider, and the service provider will execute the user's intent.
After the specified time for the task has passed, if someone finds that the task was not successfully executed, they can challenge the network. The validators of the network will reach a consensus through DPOS voting. If the consensus result is that the task was not successfully executed, the service provider will need to use the collateral to compensate the user.
The core security mechanism of dappOS is the Optimistic Minimum Staking (OMS), which allows service providers to stake slightly more than the total value of the uncompleted intent task to provide services to users (minimum), while allowing service providers to continue executing tasks before the execution results are verified (optimistic). When the validators successfully verify the service node's service results, the service node can successfully receive task income. If the validators find that the task has failed, the system will penalize the service node, and the user can also receive pre-determined compensation. The OMS mechanism aims to achieve a balance between user task efficiency, service provider capital efficiency, and the overall security operation of the system, ensuring the successful completion of user tasks while minimizing the capital cost for service providers.
3.2 Intent Assets
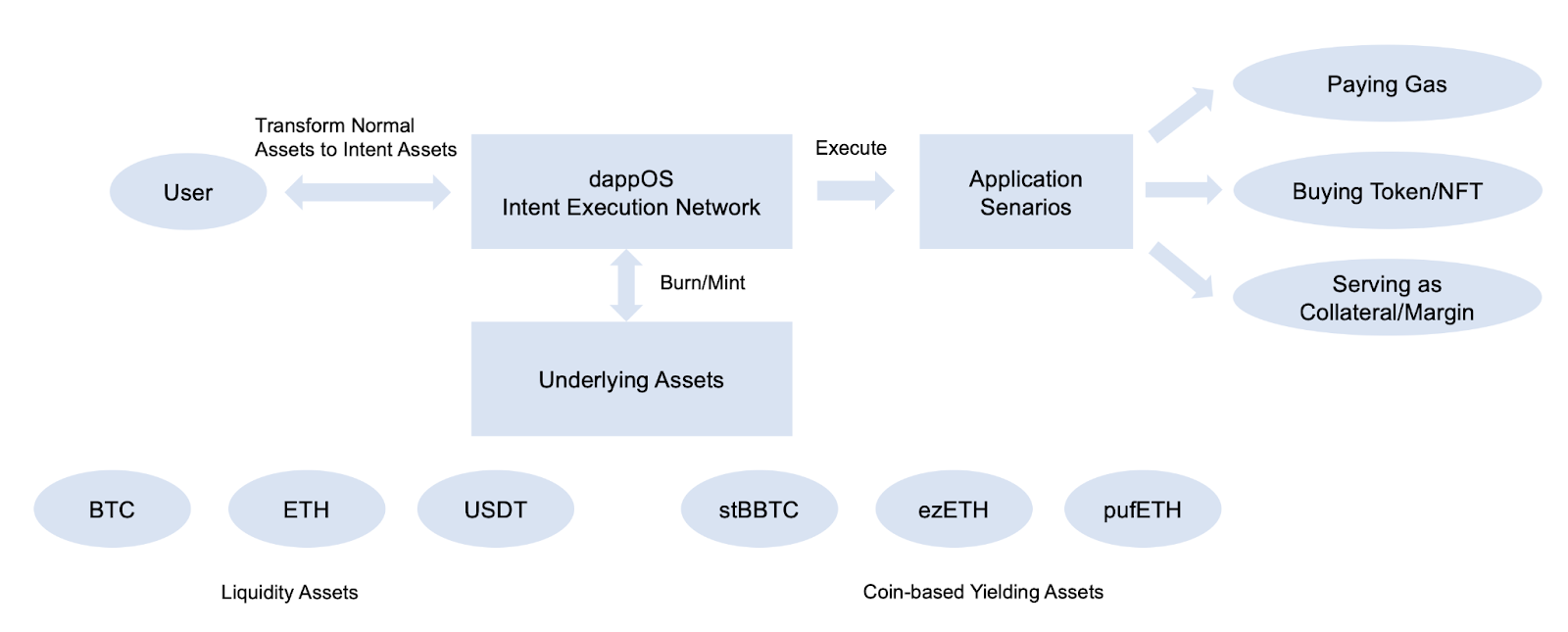
After understanding the working principle of the intent execution network, it is easier to understand the principle of Intent Assets. As shown in the figure above, when a user has the intent to "use Intent Assets directly in a certain scenario," they can directly use Intent Assets with a single click. Essentially, this means submitting the use of Intent Assets as an intent task to the dappOS intent execution network. The user uses the Intent Assets as input, and the specific implementation of the expected results is handled by the service providers in the network. The complexity of various on-chain operations involved in the specific use of Intent Assets will be handled by the service providers in the dappOS network. Due to the significant advantages in cost and speed of professional service providers and their competition with each other, the cost of executing tasks using Intent Assets is low and efficient.
The underlying source of income for Intent Assets comes from yield assets such as LRT/Pendle PT (e.g., wstETH, sUSDe, sDAI, stBBTC). The Intent Assets held by users can be seen as a form of voucher. In theory, without the dappOS intent execution network, users could choose to move assets between different chains and seek methods to generate returns.
However, in practice, users often choose the intent execution network because:
- Users do not want to consider the intermediate process and need operations to be convenient
In current blockchain interactions, users typically need to consider and research many intermediate steps to complete an operation. Using the intent execution network, regardless of how complex the task process is, as long as the result can be clearly verified, it only requires a single confirmation from the user to allow professional service providers to execute the task.
- The intent execution network allows ordinary users to achieve institutional-level cost efficiency
Ordinary users usually cannot compete with professional service providers in terms of cost and efficiency. In the dappOS network, the mutual competition among service providers will drive prices down to the optimal level, allowing users to profit. It empowers ordinary users with institutional-level cost and speed.
For example, to redeem an LRT asset, an ordinary user can only choose between a DEX and a 7-day official redemption period. However, service providers, due to providing a large number of services, have many optimized methods, such as: advancing assets for users and charging interest; offsetting when multiple users have inflows and outflows; merging transactions to reduce gas consumption on Ethereum; and even leveraging scale advantages and deep cooperation with issuers to achieve faster redemption. Similar examples include the task of purchasing tokens, where professional service providers have multiple purchasing channels such as exchanges, with fee advantages, and even direct cooperation with project parties. Even for on-chain operations, service providers have more professional MEV resistance capabilities, which ordinary users cannot achieve.
- The intent execution network provides greater security for Intent Assets
Due to the OMS mechanism of the intent execution network, when a service provider undertakes the task of "using Intent Assets" for a user, the user's assets are actually guaranteed: either the task is successfully executed, or the user receives pre-determined compensation in case of failure. Essentially, users transfer the risks involved in the asset redemption process to service providers with stronger risk-bearing capabilities.
IV. How Intent Assets Solve the Industry Issue of "TVL Stagnation"
At the beginning of this article, it was mentioned that "TVL stagnation" is a major challenge in the industry, caused by the low usability of assets in these TVL projects, leading to high opportunity costs for ordinary users. So why can Intent Assets achieve many things that many TVL projects cannot, such as giving users true on-chain usability for their yield assets?
In fact, various TVL projects have already realized the issue of usability and made some optimization attempts, but with limited effectiveness. These projects mainly provide two channels:
- Direct redemption: Users apply to redeem assets from the project and receive native assets after a certain period.
- Issuance of exchange vouchers: The project issues derivative assets (e.g., xxETH) and establishes liquidity pools for derivative assets (xxETH) and native assets (ETH) on DEX.
Regardless of the method, to ensure a good user liquidity experience, there needs to be sufficient native assets on-chain to support it. This means continuous maintenance costs (as holding native assets may result in loss of yield). In option 1, the project bears the continuous maintenance costs, so users usually need to wait a long time to redeem assets; in option 2, liquidity providers (LP) on DEX bear the continuous maintenance costs, so these pools usually have low depth and high slippage. Especially in high-volatility markets, derivative assets and native assets may have a price difference of over 20%.
In the dappOS intent execution network, there is no longer a need for service providers to provide continuous maintenance costs, and the maintenance costs for usability are dynamically balanced with actual usability needs. Additionally, the maintenance costs of service providers in the intent execution network are significantly lower. This is partly because scaled service providers have stronger professional service capabilities and more channels than ordinary users, and partly because the OMS mechanism allows service providers to execute multiple types of tasks with the same funds. Due to the bidding mechanism, the reduction in costs for these service providers will ultimately be reflected in the user experience.
The ability to solve problems that current product architectures cannot solve is the innovation and charm of the dappOS intent execution network.
V. Conclusion and Outlook
5.1 Summary of Intent Assets Advantages
Intent Assets are a new type of complex assets launched by dappOS, which not only have a high asset yield, but also can be used on-chain at any time. The advantages of Intent Assets can be summarized as follows:
- Enables user assets to generate income and be available on-chain at any time
- Users only need one-click interaction, simple operations, and can achieve institutional-level cost efficiency
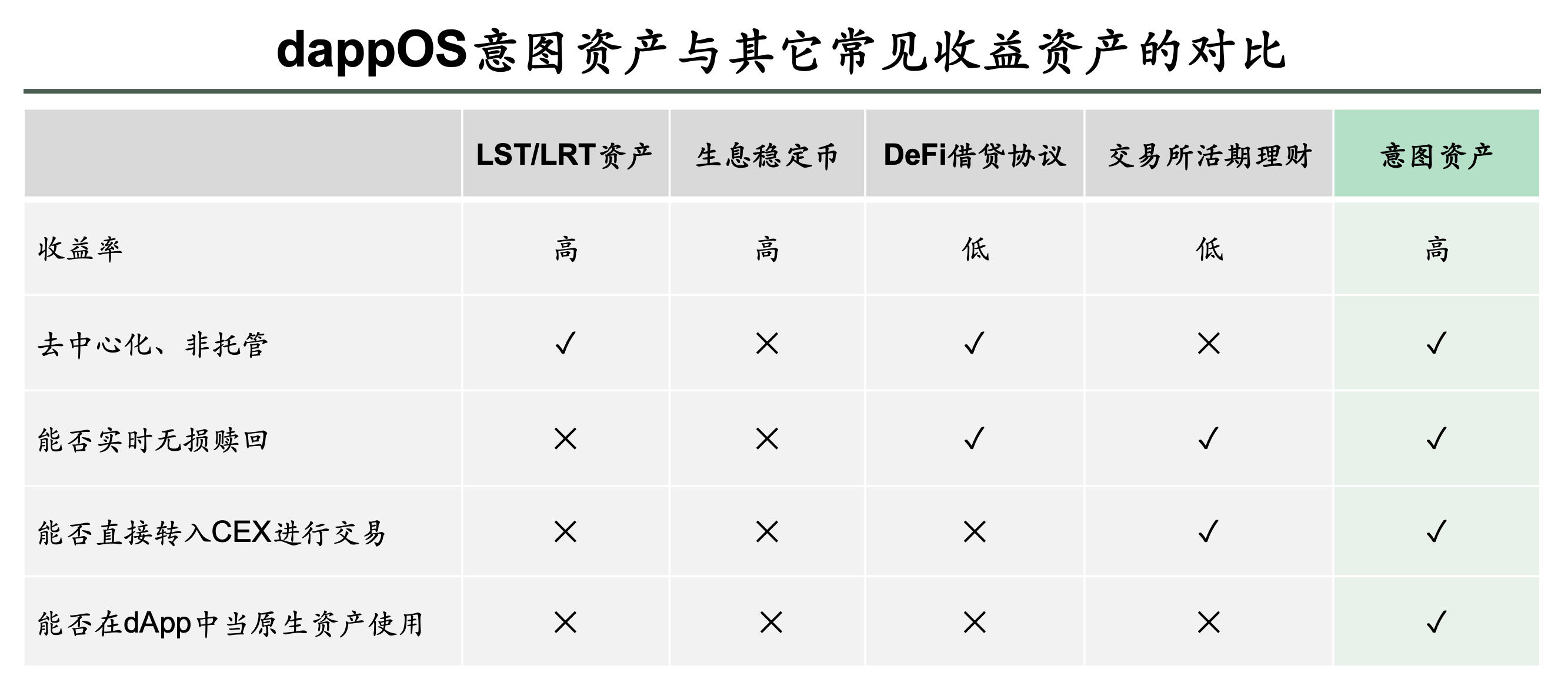
Compared with other typical yield-generating assets, Intent Assets also have relatively obvious relative advantages, summarized in the table below:
5.2 Outlook for Intent Assets
Intent Assets can solve the current "TVL stagnation" problem in the crypto industry, making new optimizations and upgrades in asset profitability, usability, and convenience. Better user experience is the key factor for the crypto industry to attract more users, even reaching hundreds of millions or billions, and moving towards mass adoption.
Currently, the crypto industry is still in its early stages of development. Deep users of the industry may have become accustomed to many "realities," such as various non-interoperable L1/L2 chains, paying gas for each transaction and the possibility of transaction failures, multiple types of USD stablecoins that are not interoperable, etc. However, in the Web2 internet world, these things and even the concepts themselves do not exist. For new users entering the crypto industry, they actually do not want to start by learning "the difference between L1 and L2," or "how to cross-chain," just as they do not want to learn how the interbank clearing system works. What they want is to more directly meet their interaction needs. The significant experience gap in between is what dappOS in the Intent race is constantly striving to bridge.
At the same time, the development and growth of Intent Assets have also gained support from mainstream web3 products. Leading projects in the Web3 field, such as Babylon, Benqi, Berachain, BounceBit, Ether.Fi, GMX, KiloEx, Manta, Puffer, Pendle, QuickSwap, Taiko, Zirkuit, etc., have all joined the Intent Asset network promoted by dappOS, providing application scenarios and returns.
As more mainstream products adopt the Intent Asset standard, a more unified, secure, and user-friendly Web3 asset ecosystem will gradually take shape.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。





