The Federal Reserve is shifting from a flexible inflation target to a strict 2% control, prioritizing price stability. With current inflation exceeding targets and tariffs adding uncertainty, the urgency for a rate cut in September is decreasing. Powell's speech tonight may lean hawkish, emphasizing data dependence, and the crypto market needs to pay attention to changes in liquidity expectations.
1. The Federal Reserve's New Monetary Policy Framework: A Key Shift from "Flexible" to "Strict"
For the crypto market, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy directly impacts global liquidity expectations, and this framework adjustment is a core premise for assessing future funding conditions. The key changes in the new framework focus on four dimensions:
1. Inflation Target: Farewell to FAIT, Anchoring a Strict 2% Target
The flexible average inflation target (FAIT) introduced in 2020 was designed to address the low inflation and low growth environment post-2008—allowing inflation to moderately exceed 2% to compensate for the previous low inflation phase. However, the surge in inflation post-pandemic in 2022 exposed the limitations of this framework: it directly delayed the Federal Reserve's response to inflation in 2021.
Currently, under the pressure of tariffs pushing prices higher, the new framework is likely to abandon or downplay FAIT, re-emphasizing the "strict 2% inflation target." Powell has clearly stated that "the wording from 2020 has become ineffective due to high inflation," directly implying that the Federal Reserve will return to a traditional inflation targeting regime to avoid long-term de-anchoring of inflation expectations.
2. Dual Mandate: The Priority of Price Stability Rises
The 2020 framework prioritized a "broad and inclusive" employment goal, as the Federal Reserve believed that "a strong labor market would not necessarily lead to inflation," based on the experience of low unemployment rates not pushing prices higher before the pandemic.
However, recent data has shattered this perception: the annualized inflation rate reached 2.7% in June 2025 (partly driven by tariffs), and new jobs added in July were only 73,000 (with the previous value revised down), indicating that while the labor market remains robust, signs of cooling are evident. Powell has repeatedly emphasized that "price stability is a prerequisite for the labor market to reach its potential," clearly signaling that "the priority of inflation control is rising."
3. Responding to Uncertainty: A "Wait-and-See" Stance Under Tariffs
The tariff policy of the Trump administration is bringing dual risks: it may push inflation higher while also potentially suppressing economic growth, even leading to "stagflation" (high inflation, high unemployment, low growth). Powell noted that the impact of tariffs on prices "could be a one-time increase or evolve into sustained inflation," and the specific effects still need to be observed.
From the minutes of the July Federal Reserve meeting, policymakers generally held a cautious attitude towards the impact of tariffs, leaning towards "waiting for more data before taking action," and this "wait-and-see" stance will permeate recent policy decisions.
4. Framework Review: Retaining the 2% Target, Simplifying Communication
The Federal Reserve is advancing its five-year framework assessment, ensuring that the framework remains "robust and effective" under different economic conditions through "Fed Listens" events, research meetings, and FOMC discussions. The final new framework will retain the 2% inflation target but may simplify policy tools and communication methods (for example, adjusting the presentation of the "dot plot").
Powell's speech tonight will be a key occasion to elaborate on these changes, expected to emphasize the "flexibility" and "data-driven" decision-making logic.
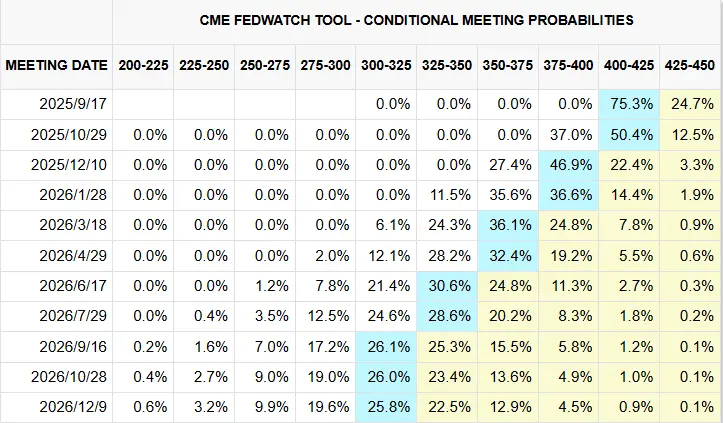
2. The September Rate Cut Under the New Framework: Pulling Factors of Support and Opposition
The Federal Reserve's rate cut decision directly affects market liquidity, which is particularly crucial for the crypto market. Currently, the possibility of a rate cut in September is being tugged back and forth by supporting and opposing factors:
Three Major Factors Supporting a September Rate Cut
- Signs of Cooling in the Labor Market: Only 73,000 new jobs were added in July, with the previous value revised down, and the unemployment rate remains at 4.1% (close to full employment but showing signs of weakness), indicating some relief in labor market pressures, providing some space for a rate cut.
- Strong Market Expectations: According to federal funds futures data, the market currently expects a 70%-83% probability of a 0.25% rate cut in September, reflecting market expectations for "Federal Reserve support for employment," which will also exert some pressure on policy decisions.
- Calls for Easing Within the FOMC: At the July meeting, committee members Waller and Bowman clearly supported a rate cut, indicating an internal tendency towards easing. If subsequent data continues to weaken, it may lead more committee members to shift towards supporting a rate cut.
Three Major Resistances Against a September Rate Cut
- Inflation Continues to Exceed Targets: The annualized inflation rate in June was 2.7%, significantly above the 2% target, and tariffs are still pushing up prices for some goods. Powell is concerned about "long-term inflation expectations becoming unanchored," and currently leans towards maintaining restrictive policies to control inflation.
- Uncertainty of Tariff Impact: It remains unclear whether the impact of tariffs on inflation is "one-time" or "sustained." If the Federal Reserve cuts rates too early, it may exacerbate inflationary pressures, hence they prefer to wait for clearer impact data.
- The Labor Market Remains Robust: Although July's employment data was weak, the unemployment rate at 4.1% is still low, and the labor market has not shown "significant deterioration," which supports the Federal Reserve's "status quo" stance.
3. Powell's Speech Preview Tonight: A Hawkish Tone with "Data Dependence"
Powell's speech will directly set the tone for the Federal Reserve's short-term policy direction, significantly impacting sentiment in the crypto market. Based on current signals, his speech is likely to present a "hawkish but flexible" characteristic:
1. Hawkish Inclination: Driven by Inflation and Framework Goals
Powell's hawkish inclination will primarily revolve around "inflation control": he may reiterate the inflation risks posed by tariffs and the necessity of "anchoring 2% inflation expectations"; at the same time, in line with the new framework's "priority on price stability," he will emphasize that the current interest rate level of 4.25%-4.50% is "moderately restrictive," suitable for addressing the dual risks of current inflation and the labor market.
Statements like "we can wait for clearer data before taking action" and "we can maintain restrictive policies longer" are likely to appear, indicating he will not rush to push for a rate cut in September.
2. Balancing Act: Not Excluding the Possibility of a Rate Cut
To maintain policy flexibility, Powell will not completely close the door on a September rate cut. He may clearly state that if August employment data continues to weaken (e.g., new jobs remain below 100,000) and the labor market significantly deteriorates, the Federal Reserve will "adjust policy in a timely manner to support the economy"—this "data dependence" statement can stabilize market expectations and leave room for future decisions.
Goldman Sachs and Yardeni Research also predict that Powell will maintain a "neutral but cautious" attitude, focusing on "not locking in a specific policy path, but following data changes."
3. Political Context: Upholding Independence
Despite repeated pressure from Trump for the Federal Reserve to cut rates, Powell is likely to emphasize "the independence of the Federal Reserve's policy decisions" in his speech, clearly stating that policy formulation will be based on economic data rather than political pressure. This statement serves to maintain the Federal Reserve's credibility and reinforce the policy's original intent of the "dual mandate (price stability + full employment)."
From a policy perspective, the Federal Reserve is currently in a "cautious hawkish, data-driven" phase: it will neither hastily cut rates due to short-term employment weakness nor excessively tighten due to inflation exceeding expectations. The core approach is to find a balance between "controlling inflation" and "stabilizing employment" through "waiting and data verification," avoiding policy missteps that exacerbate economic uncertainty.
For the crypto market, this means that short-term liquidity easing expectations need to cool down: if Powell confirms a hawkish stance tonight, the market's optimistic expectations for a September rate cut may be revised, and the crypto market could face short-term emotional pressure; however, in the long term, it is still necessary to closely monitor subsequent employment and inflation data—if the data points to "falling inflation + worsening employment," the easing window may still open; conversely, it will need to adapt to the Federal Reserve's "prolonged restrictive policy."
In short, the current Federal Reserve policy has no absolute direction, and "data verification" is the only main thread. The crypto market also needs to shift from "betting on rate cuts" to "adjusting expectations based on data," maintaining a rational response.
The above report data is edited and organized by WolfDAO (x:10xWolfDAO). If you have any questions, please contact us for updates.
Written by: WolfDAO
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




