This guide will help traders and investors cautiously respond to market challenges, enhancing trading security and stability.
Key Points
– Understanding Derivatives and Risks: Cryptocurrency derivatives such as futures, options, and swaps offer profit opportunities but come with high volatility, leverage risks, and liquidity challenges.
– Implementing Effective Risk Management: Reduce liquidation risks from market volatility through position control, stop-loss orders, hedging strategies, and asset diversification.
– Ensuring Compliance and Security: Stay informed about regulatory policy changes, choose compliant exchanges, and use cold wallets and secure trading measures to protect assets.
– Maintaining Trading Psychological Stability: Avoid making impulsive decisions due to FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) or panic, follow trading plans, and document trades to optimize strategies.
Cryptocurrencies are rapidly entering the mainstream market, providing unique opportunities for investment, speculation, and hedging. In this emerging field, cryptocurrency derivatives based on digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum have become an important part of the market. These derivatives include futures, options, swaps, and perpetual contracts, allowing traders to profit from market price fluctuations without holding the actual assets.
However, high volatility, complex product structures, and a lack of regulation can turn trading opportunities into significant risks. Therefore, effective risk management is crucial for all cryptocurrency derivatives traders. This guide will provide:
– Overview of Mainstream Derivatives
– Analysis of Key Risk Factors
– Practical Risk Management Strategies
To help traders and investors cautiously respond to market challenges, enhancing trading security and stability.
Table of Contents
Understanding Cryptocurrency Derivatives
Main Risks of Cryptocurrency Derivatives
– Position Planning and Leverage Control
– Stop-Loss Orders and Risk/Reward Ratios
– Hedging Strategies (Options and Arbitrage Trading)
– Asset and Trading Strategy Diversification
– Collateral and Margin Management
– Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Technical and Operational Risk Prevention
Trading Psychology and Emotion Management
– Avoiding FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
– Overcoming Loss Aversion
– Maintaining Trading Records
– Sticking to Trading Plans
Understanding Cryptocurrency Derivatives
Cryptocurrency derivatives allow traders to gain market exposure or execute hedging strategies without directly holding Bitcoin or other digital assets. These tools can amplify returns but also come with higher risks. The main categories are:
Futures
Definition: Buyers and sellers must trade the underlying asset at an agreed price on a specific future date.
Trading Platforms: Regulated exchanges (like CME) and cryptocurrency exchanges (like Binance, XT.COM).
– No Expiration Date: Maintains contract prices close to the spot market through funding rates.
– Suitable for: Traders who wish to hold leveraged positions long-term without needing to roll over contracts.
– Fixed Expiration Date: Positions are settled in cryptocurrency or stablecoins at contract expiration.
– Suitable for: Institutional investors or traders who want a definite settlement time.
Stablecoin Margin vs. Coin-Backed Contracts
– Stablecoin Margin (e.g., BTC/USDT): Uses stablecoins like USDT, USDC as margin to reduce volatility risk of leveraged positions.
– Coin-Backed Contracts (e.g., BTC/USD): Uses cryptocurrencies as margin, with position profits and losses and margin value fluctuating with the market.
Options
Definition: Grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (Call) or sell (Put) cryptocurrency at a specified price before expiration.
Uses:
– Hedging: Prevents significant losses in cryptocurrency assets due to market downturns.
– Income Generation: Earn additional income by selling options (e.g., Covered Call).
– Speculation: Use leverage to gain market direction profits without holding the underlying asset.
Swaps
Definition: Contracts where two parties exchange specific financial returns or obligations.
Perpetual Swaps:
– No Expiration Date: Maintains prices close to the spot market through funding rates.
– Popular in: Exchanges like Binance, OKX, Deribit.
Structured Products
Structured products combine derivatives to offer customized risk/reward structures, favored by institutional investors.
Dual Investment (to be launched on XT.COM)
– No Principal Protection: Users can earn higher returns if market prices do not reach targets at expiration.
– How it Works: If the price is below the target, investors receive the original asset plus additional interest; if the price exceeds the target, the investor's position converts to another asset (e.g., BTC → USDT), potentially missing out on further gains.
– Partial Capital Protection: Returns depend on whether the price remains within a set range.
– Suitable for: Investors seeking stable returns but willing to accept some risk.
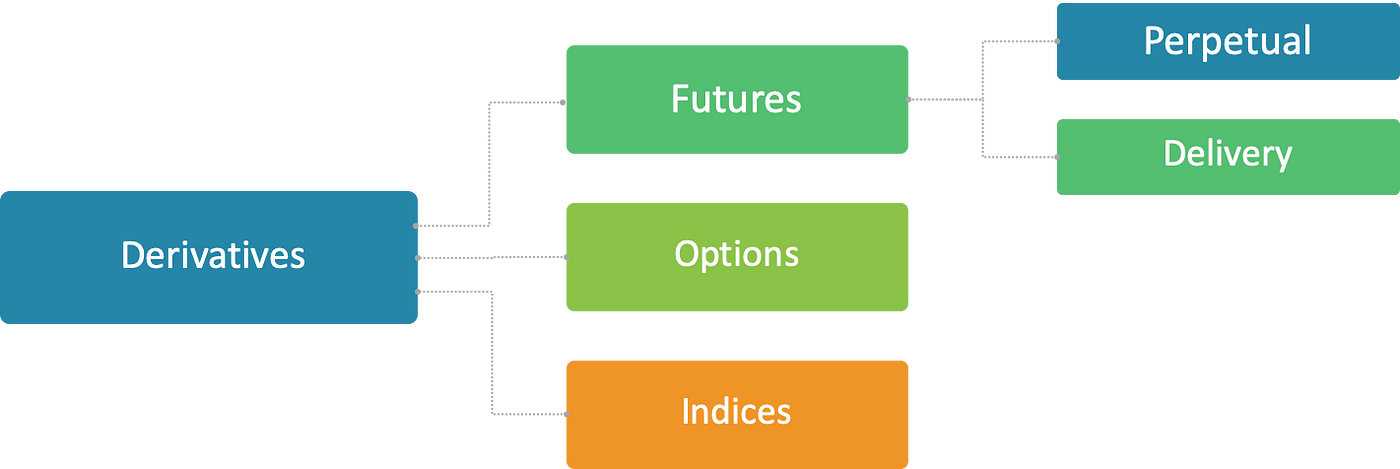
Image Credit: Medium
Main Risks of Cryptocurrency Derivatives
The risks in the cryptocurrency derivatives market are interconnected, and understanding these risks helps traders establish effective protective strategies.
Volatility Risk
– Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile, with daily fluctuations exceeding 80% not uncommon.
– The leverage effect amplifies market volatility, making it easy to trigger forced liquidation if the market moves unfavorably.
Counterparty Risk
– Traders rely on the financial stability and security mechanisms of exchanges.
– If an exchange suffers a hack or bankruptcy, it may result in the loss of margin and unrealized profits.
Liquidity Risk
– Market liquidity is dispersed, especially for small-cap assets, and insufficient trading depth may lead to execution difficulties.
– Low liquidity can cause slippage, making it harder to close positions during market volatility, potentially leading to larger losses.
Regulatory and Legal Risk
– Global cryptocurrency regulations change frequently, with different policies in various regions.
– Regulatory adjustments may affect leverage ratios, margin requirements, and even lead to restrictions or bans on trading in certain areas.
Technology and Operational Risk
– Trading platforms may be subject to hacking, system failures, or server overloads, affecting trading experience and fund security.
– High-frequency trading strategies may fail due to API connection delays or failures, impacting trade execution efficiency and profitability.
Identifying these risks and their severity is key to developing effective risk management strategies.

Image Credit: Insurance Risk Services
Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management requires a combination of quantitative tools, disciplined trading methods, and market research. Here are common strategies:
Position Planning and Leverage Control
Position Planning
– Invest only a portion of funds in a single trade to cope with market fluctuations and control personal risk exposure.
– Over-allocating funds can lead to rapid losses in the portfolio, especially in extreme market conditions.
Leverage Management
– High leverage (e.g., 20x, 50x) can amplify profits but also increases the risk of losses.
– Experienced traders typically use medium to low leverage to reduce liquidation risks.
Stop-Loss Orders and Risk/Reward Ratios
Stop-Loss Orders
– Set stop-loss points to ensure automatic liquidation when market prices reach preset levels, controlling losses.
– A reasonable stop-loss mechanism helps traders maintain discipline and prevent losses from expanding.
Risk/Reward Ratio
– Maintain a healthy risk/reward ratio (e.g., 1:3) to ensure long-term profitability.
– Even if some trades fail, profitable trades can offset losses.
Hedging Strategies
Using Options
– When holding a large amount of cryptocurrency, buying put options can hedge against market crash risks.
– If bearish on the market but concerned about price increases, buying call options can reduce risk.
Arbitrage Trading
– Arbitrage trading reduces risk by holding mutually hedged positions (e.g., going long and short simultaneously).
– This strategy minimizes overall market impact and focuses on price differences between assets.
Diversified Investment
Asset Diversification
– Hold different cryptocurrencies or stablecoins to reduce the impact of a significant drop in a single asset.
– For example, if Bitcoin crashes while Ethereum remains stable, overall losses will be mitigated.
Trading Strategy Diversification
– Use different trading strategies (e.g., trend trading, mean reversion, volatility arbitrage) to adapt to market changes.
– Some strategies may work well in a bullish market but fail in a sideways market, so a multi-strategy approach helps achieve long-term stable profits.
Margin Management
Over-Collateralization
– Keeping extra margin can prevent forced liquidation during severe market fluctuations.
– However, depositing too much capital in a single exchange may increase the risk of exchange bankruptcy or hacking.
Stablecoin Margin
– Using stablecoins (e.g., USDT, USDC, DAI) as margin can reduce additional risks from margin value fluctuations.
– This strategy ensures that a trader's risk is only related to their positions and not affected by market turmoil impacting margin value.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Dynamic Risk Adjustment
– Market conditions are constantly changing, and leverage and stop-loss levels should be adjusted based on current volatility.
– For example, during extreme volatility, reducing leverage and narrowing stop-loss ranges can minimize potential losses.
Risk Analysis and Stress Testing
– Use simulation tools for stress testing to assess the impact of worst-case scenarios like market crashes or exchange failures.
– Adjust position sizes, hedging strategies, and margin management plans based on test results.
These strategies provide traders with a foundational risk management framework, but true success depends on disciplined execution and flexible strategy adjustments based on market changes.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrency derivatives is constantly changing, affecting trading methods and compliance. The U.S. allows regulated Bitcoin futures (CFTC regulated) but imposes strict limits on retail leverage, while some countries completely ban or heavily restrict cryptocurrency derivatives trading.
Compliance in Trading Regions
– Understand the legal regulations in the country where the exchange is located to avoid fines, asset freezes, or legal actions due to violations.
– Different countries have different regulations regarding cryptocurrency derivatives, so it is essential to stay updated on policy changes.
Exchange Due Diligence
– Confirm whether the exchange holds a legitimate license and is supervised by regulatory authorities.
– Assess the financial stability of the exchange to ensure it has sufficient liquidity and security measures for funds.
– Check the security of the exchange and whether it has experienced hacking incidents or asset loss events.
Taxation and Trading Records
– Maintain complete trading records (including entry prices, exit prices, profits, and losses).
– Many countries consider cryptocurrency gains as taxable income, and accurate reporting can help avoid potential legal issues.
KYC and AML Regulations
– Compliant exchanges typically require identity verification (KYC) and trading records to prevent illegal trading.
– Adhering to KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations helps avoid account freezes or regulatory investigations.
By actively managing compliance, traders can reduce legal risks and ensure stable and sustainable trading in the long term.

Image Credit: Financial Crime Academy
Technology and Operational Security Prevention
Cryptocurrency trading relies on robust security measures and sound operational management to ensure fund safety and trading stability.
Fund Security
– Mainstream exchanges store most user funds in cold wallets to prevent hacking.
– Multi-signature mechanisms can enhance security, requiring multiple authorizations for large withdrawals.
Platform Stability
– Exchanges should be equipped with backup servers and failover mechanisms to ensure stable system operation.
– Traders using automated trading tools should check the stability of APIs to avoid trade failures due to system delays or failures.
Operational Risk Management
– Exchanges with comprehensive risk control should be able to respond quickly to hacking attacks or system crashes and restore operations promptly.
– Transparent exchanges often provide proof of reserves and accept third-party audits to enhance user trust.
Understanding the security and operational mechanisms of trading platforms is as important as trading strategies, as a single hacking incident or system failure can lead to devastating losses.
Emotional Management in Trading
Even with good technical skills and trading strategies, emotional influences can still lead to significant losses. The cryptocurrency market is often driven by market speculation and panic, making it easy to trigger erroneous trading decisions based on fear or greed. Maintaining emotional discipline ensures that traders execute trades according to plan rather than being driven by impulses.
Avoiding FOMO
– When prices surge, traders may impulsively enter the market, neglecting risk control, and even buy heavily after the best entry point has passed.
– Adhere to established trading rules and position limits to avoid over-leveraging or missing good entry points due to FOMO.
Overcoming Loss Aversion
– Many traders are reluctant to acknowledge losses, leading to prolonged positions and missed better trading opportunities.
– Early control of small losses helps preserve capital for subsequent more favorable trades.
Keeping a Trading Journal
– Document the decision-making process for each trade (entry/exit prices, reasons for trading, emotions at the time) to help identify error patterns.
– Regularly reviewing the trading journal can help optimize trading strategies and improve discipline.
Sticking to the Trading Plan
– Before entering a trade, clearly set profit targets and stop-loss ranges to ensure each trade has a clear risk management strategy.
– Avoid impulsively adjusting trading strategies due to short-term market fluctuations; necessary adjustments should be based on rational analysis rather than emotional reactions.
Emotional control is key to distinguishing stable, profitable traders from losing traders. Staying calm, strictly executing trading plans, and overcoming psychological barriers are essential for long-term survival and profitability in the cryptocurrency market.
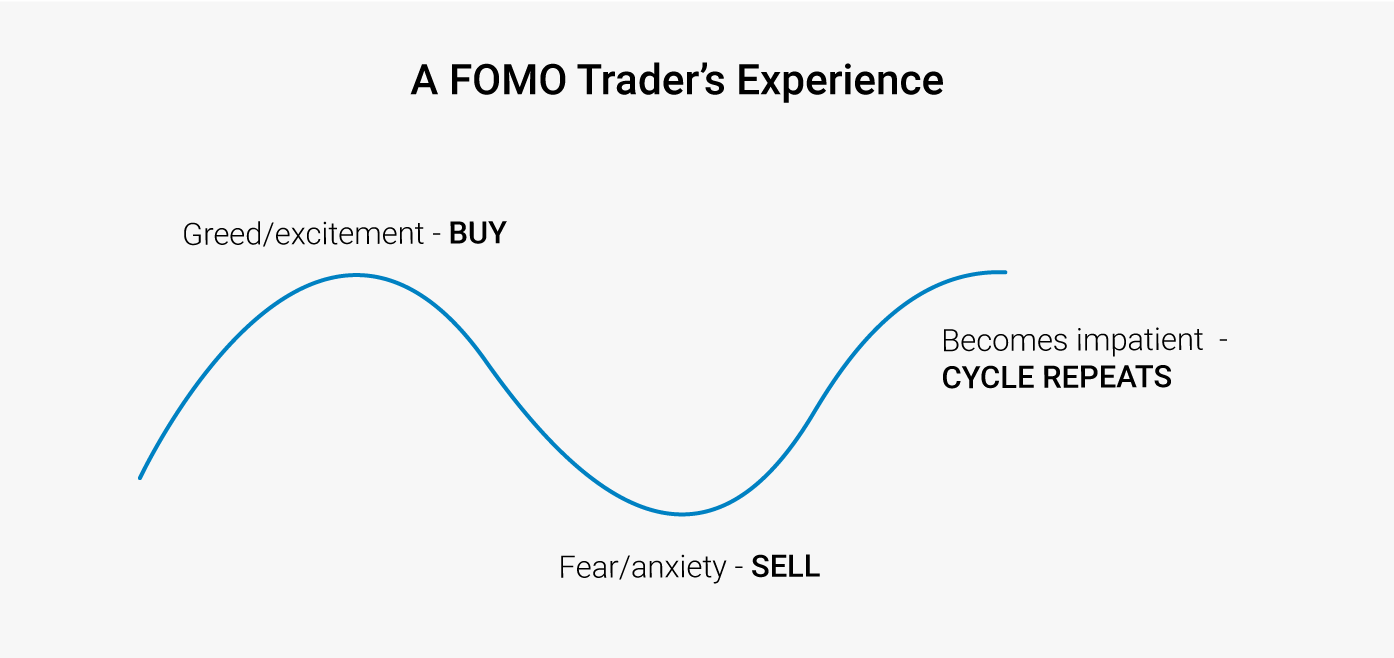
Image Credit: Carl Fajardo
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency derivatives offer high-return opportunities but also come with high volatility and complexity. Successful traders need to effectively manage risks in the following key areas:
– Product Knowledge: Thoroughly understand the mechanisms of futures, options, and swap contracts before trading.
– Risk Control: Use stop-loss orders, reasonable leverage, and hedging strategies to minimize potential losses.
– Trading Security: Ensure the security of exchanges and trading platforms to reduce counterparty risks.
– Regulatory Compliance: Stay updated on KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and tax compliance requirements.
– Emotional Management: Strictly execute trading plans and avoid impulsive decisions driven by market emotions.
As the market continues to evolve, traders must continuously learn and adjust their strategies. While no strategy can completely eliminate risk, a robust approach and strict execution discipline can significantly increase the likelihood of long-term success in the cryptocurrency derivatives market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



