Author: Jessy, Golden Finance
As the regulation of virtual currencies in the United States becomes clearer, DeFi has also become one of the main themes of this bull market.
Currently, when people talk about DeFi under U.S. regulation, they are more often referring to Real World Assets (RWA) on-chain, USD stablecoins, and PayFi, among others. These practices are generally built on Ethereum and its layer two solutions, or some high-performance new public chains. The relationship with Bitcoin seems to be limited to wrapped Bitcoin participating in on-chain financial activities.
To change the previous awkward situation where only wrapped Bitcoin could participate in on-chain finance, BTCFi has emerged. BTCFi refers to the financial service platforms and protocols built around Bitcoin and its ecosystem, combined with decentralized financial technologies, allowing the financial functions of Bitcoin to be expanded.
Specifically, this enables Bitcoin itself to participate in on-chain financial activities, enhancing the previously limited smart contract functionality of Bitcoin. The Bitcoin ecosystem has also developed more complex DeFi protocols similar to those on other public chains, such as centralized exchanges, over-collateralized stablecoins, and re-staking. Additionally, besides BTC itself, some assets related to the BTC ecosystem, such as inscriptions, runes, and RGB++, have also participated in DeFi-related activities.
According to DeFiLlama data, the current total TVL of BTC is $6.545 billion, while Solana's total TVL is $8.297 billion, and Ethereum's total TVL is $68.31 billion. It is evident that BTCFi is still a blue ocean with high development potential.

Currently, BTCFi has given birth to star projects like Babylon, which primarily introduces Bitcoin staking protocols, allowing users to stake Bitcoin on another PoS blockchain and earn rewards without using third-party custody, bridging solutions, or wrapping services. What other projects are worth paying attention to?
Overall Development of BTCFi
According to DeFiLlama data, representative projects in the BTCFi track, such as Babylon, have a total TVL exceeding $5 billion. Among them, lending and re-staking protocols are the two core components of the BTCFi ecosystem, occupying the largest market share.
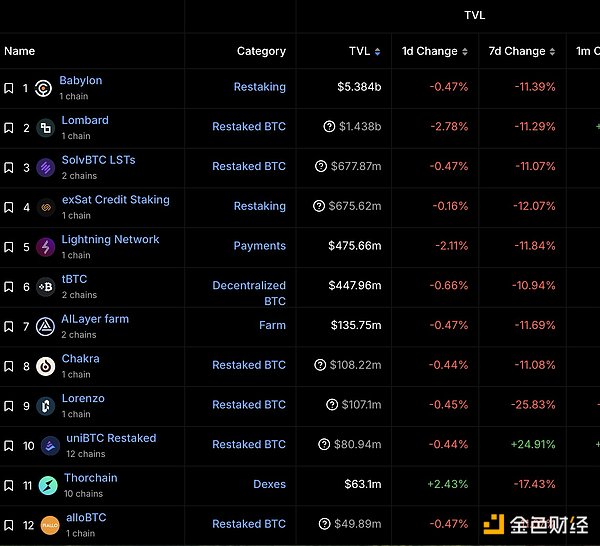
BTCFi Protocol TVL Rankings (Data as of December 24, 2024)
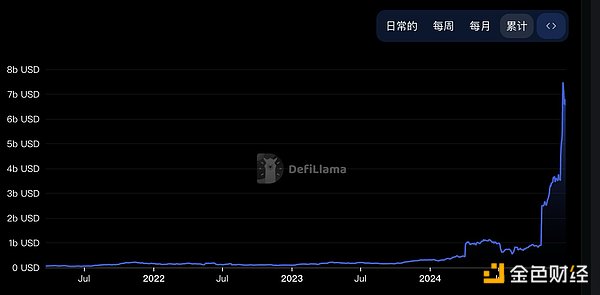
According to DefiLlama's predictions, by 2030, the BTCFi market size will grow to around $1.2 trillion. This year has been a year of rapid development for the BTC ecosystem; at the beginning of 2024, the overall TVL of BTC was $300 million, and by the end of 2024, it had reached $6.5 billion, growing more than 20 times.
In the BTCFi track, lending protocols are one of the most important applications. Traditionally, Bitcoin, as a digital asset, has not participated in the lending market. However, BTCFi protocols enable Bitcoin to be used as collateral for decentralized lending. Notable projects include Liquidium and Shell Finance.
Next are stablecoin protocols, which use Bitcoin and its derivative assets (such as Ordinals and Rune) as collateral to issue stablecoins pegged to the price of Bitcoin. In stablecoin practices, there are Bitcoin-pegged stablecoins from Shell Finance and stablecoins collateralized by Bitcoin from Babylon, among others.
The re-staking mechanism is also an innovation in the current BTCFi ecosystem. This year, these projects have achieved significant results in terms of locked amounts, and there are currently many re-staking protocols in the BTCFi ecosystem. Users can re-stake already staked Bitcoin or other crypto assets to earn additional rewards, such as BounceBit and the Lombard Protocol in the Babylon ecosystem, which both support re-staking.
Introduction to Leading BTCFi Projects
Babylon
When it comes to BTCFi, Babylon is certainly a project that cannot be overlooked. It is the first project in the industry to introduce Bitcoin's own standard staking, essentially a staking, security, and liquidity protocol.
The main innovation lies in the introduction of Bitcoin's own standard staking, achieved through technical upgrades from Bitcoin Improvement Proposals, such as Schnorr signatures, Taproot upgrades, and Tapscript updates, which enhance the efficiency and privacy of staking transactions. This allows Bitcoin holders to lock their BTC assets in the Bitcoin mainnet in a self-custodial manner without third-party custody, and to provide "secure consensus services" on various BTC layer 2s, thereby obtaining rich rewards from other expansion supplies.
Currently, its TVL exceeds $5 billion, and it has a rich ecosystem. According to public information, its ecosystem projects cover seven categories, including Layer 2, DeFi, liquid staking, wallets and custodians, Cosmos, finality providers, and Rollup infrastructure, with a total of 91 projects, including many well-known projects such as BisonLabs and BSquared Network in the Layer 2 field; Kina Finance and LayerBank in the DeFi field; and Bedrock, Chakra, and Lombard in the liquid staking field. These projects have formed a large ecosystem around Babylon, promoting the diversified development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Shell Finance
Shell Finance is the first decentralized lending and stablecoin protocol built on Bitcoin's first layer, aiming to provide decentralized lending and stablecoin protocols for the Bitcoin ecosystem, allowing Bitcoin and related asset holders to manage assets and obtain liquidity more flexibly.
One of its core functions is lending services, where users can use Bitcoin, Ordinals NFTs, BRC-20, Runes, and other Bitcoin ecosystem assets as collateral to borrow a synthetic asset called BTCX. This process does not require trust in third parties and is realized through a unique peer-to-protocol lending mechanism, with Shell Finance acting as the counterparty to the borrower. Unlike traditional lending protocols, Shell Finance charges a one-time loan fee to borrowers instead of continuously charging interest through floating rates, achieving interest-free instant loans and providing unique earning opportunities for inscription holders.
The second core function is stablecoin issuance. Shell Finance is the first decentralized stablecoin protocol on the BTC mainnet, allowing users to obtain stablecoins after collateralizing the aforementioned Bitcoin ecosystem assets. The launch of this stablecoin enhances the liquidity of BTC layer 1 assets and lays the foundation for the development of BTCFi, with plans to expand to networks like Bitcoin Fractal and other UTXO model networks in the future, further broadening the use cases.
Technically, it employs Discreet Log Contracts (DLC) technology and PSBT technology. The former was proposed by Tad Gredryja, a co-creator of the Bitcoin Lightning Network, allowing for a more private, secure, and fully automated contract execution process, such as automatic liquidation to repay loans when the value of staked assets falls below a critical point.
On December 4, 2024, the Shell Finance mainnet was launched.
Liquidium
Liquidium is a lending platform based on the Bitcoin blockchain that allows users to use native ordinals as collateral to borrow and lend native Bitcoin, eliminating the need for intermediaries or custodians.
The product supports various collateral types, not only Bitcoin Ordinals but also plans to support BRC-20 tokens, providing users with more options and further expanding the application scenarios of Bitcoin assets.
Technically, it operates directly on the first layer of the Bitcoin network for all lending operations. The project token LIQUIDIUM was launched on July 22, 2024, and is the first governance token of the rune token standard on Bitcoin. This token aims to decentralize the Liquidium protocol and promote community participation in its governance.
BitSmiley
This project consists of three main components. The first is the over-collateralized stablecoin protocol bitUSD, which is comparable to DAI, allowing users to over-collateralize native BTC to mint the stablecoin bitUSD from the bitSmiley Treasury.
The second is the native trustless lending protocol bitLending, which uses peer-to-peer atomic swap technology to facilitate transaction matching and introduces an insurance system to optimize traditional lending liquidation processes.
The third is the innovative derivatives protocol Credit Default Swaps (CDS), which is essentially a risk transfer tool. On the BitSmiley platform, one party (usually concerned about the risk of debt default) pays a regular fee to another party (willing to take on that risk for a certain return), similar to an insurance premium. If a default event occurs regarding the agreed underlying debt (such as debts arising from borrowing related Bitcoin ecosystem assets), the party assuming the risk must compensate the party paying the fees as agreed, thus managing and hedging the risk of debt default. In operation, it integrates NFT slicing CDS and uses aggregated bidding methods to enhance market efficiency and fairness.
Currently, its token SMILE has been listed on multiple exchanges, such as Bybit, Gate.io, Bitget, and others.
Chakra
Chakra is a Bitcoin re-staking protocol with the following technical innovations: First, self-custodial staking, allowing Bitcoin holders to stake without transferring assets out of their wallets through time-locked scripts, avoiding third-party risks and adhering to the principle of "not your keys, not your coins," ensuring asset security. Second, it employs zero-knowledge proof technology, specifically using Stark to implement the proof system. Bitcoin staking events are verified off-chain through zero-knowledge proofs to access on-chain information without connecting to the Bitcoin network and without trusted setups, enhancing security compared to Snark.
By integrating decentralized Bitcoin liquidity, Chakra provides a more secure and smooth settlement experience. Users can easily stake Bitcoin with one click, utilizing Chakra's advanced settlement network to participate in more liquidity earning opportunities, including LST/LRT projects in the Babylon ecosystem.
Solv Protocol
The Bitcoin staking protocol's core highlight is its collaboration with leading protocols across various ecosystems to provide diverse yield scenarios.
The project has launched SolvBTC, the first BTC product that allows for built-in yield, creating a secure base yield from Bitcoin that would otherwise be idle in users' wallets through staking. SolvBTC captures staking yields from BTC Layer 2, re-staking yields, and DeFi yields from ETH Layer 2, seamlessly integrating various protocols at the application layer to provide rich earning opportunities for Bitcoin holders. Its yields are generated through three strategies: staking, re-staking, and trading strategies.
We can understand it as a unified Bitcoin liquidity matrix, aiming to consolidate the fragmented trillion-dollar liquidity of Bitcoin through SolvBTC. It acts as a yield aggregator for Bitcoin assets, allowing different BTC assets across various chains, such as BTCB, FBTC, MBTC, etc., to be minted into SolvBTC, simplifying the user asset management experience.
This also integrates liquidity opportunities from different Bitcoin assets, with a single SolvBTC traversing the chain to form a unified asset pool, bringing more diversified earning opportunities to holders.
Bedrock
Bedrock is a multi-asset liquidity re-staking protocol.
In the BTCFi space, it uses uniBTC supported by Babylon for re-staking. During the Babylon War, Bedrock performed outstandingly, successfully capturing 297.8 BTC in staking capacity, accounting for nearly 30% of the total initial staking amount in Babylon.
Users of this product can stake wBTC on the Babylon platform using the ETH chain, receiving a 1:1 certificate—uniBTC—in return for their staked WBTC. Babylon provides core technical support in this process. Users who stake wBTC and hold uniBTC can earn Bedrock and Babylon points. By collaborating with Babylon through uniBTC, Bedrock offers liquid staking services to support Babylon's PoS chain. By minting uniBTC, it ensures the stability and security of the Babylon chain and further expands Bedrock products to the BTC chain.
Bouncebit
Bouncebit is dedicated to creating yield infrastructure for Bitcoin, providing institutional-grade yield products, re-staking application scenarios, and CeDeFi services. Its specific business includes:
Bouncebit Protocol: Users deposit BTC and other assets to receive corresponding Liquid Custody Tokens. The assets are managed on the Binance platform through a secure custody account and mirroring mechanism, generating returns for users.
Bouncebit Chain: A Layer 1 blockchain that employs a proof of stake delegation service consensus mechanism and is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine. Users can delegate tokens to validation nodes for staking, and the staking certificates obtained can be used in DApps on the chain.
Share Security Client: Its logic is consistent with Eigenlayer, allowing the security of Bouncebit Chain to be rented out, supporting applications such as Bridge, Oracle, and Sidechain.
Bouncebit launched in early 2024, raising a total of $7.98 million. In May 2024, its native token BB was listed on Binance.
Lorenzo Protocol
A modular Bitcoin L2 infrastructure based on Babylon, designed to provide a liquidity financial layer for Bitcoin.
By utilizing Babylon's Bitcoin staking and timestamp protocols, it lays the foundation for scalable and high-performance Bitcoin applications, enhancing Bitcoin's scalability and enabling the execution of smart contracts and other functions.
The project features an innovative token system, including Liquid Principal Tokens (LPT, such as stBTC) and Yield Accumulation Tokens (YAT). stBTC is pegged 1:1 to the staked BTC, unifying the liquidity of BTC across different ecosystems, allowing holders to redeem their principal after staking ends; YAT has its own re-staking plan, with start and end times, and can be traded or transferred before maturity. Holders can receive POS chain rewards, and YAT from the same staking plan can be exchanged, with its value derived from accumulated yields and speculation on future yields.
The project supports various staking methods, including circular and leveraged staking. Circular staking utilizes partnerships with external DEXs, allowing users to stake BTC, borrow more BTC, and increase staking rewards; leveraged staking simplifies the process by providing internal liquidity, enabling users to apply maximum leverage with a click, improving capital efficiency and optimizing staking returns.
Current Issues in BTCFi
Currently, there are not a few projects in this track, and its total TVL experienced explosive growth in 2024, but the BTCFi track itself has not yet truly sparked a trend in the industry.
At present, the development of this track still faces many issues. The first core issue is that there is often a lack of consensus within the Bitcoin community regarding discussions on certain technological upgrades and innovative solutions, which leads to difficulties in advancing Bitcoin ecosystem-related projects.
On a technical level, there are also significant challenges. First, Bitcoin itself has insufficient block scalability, making it unable to achieve automated financial transactions and complex business logic like Ethereum. Moreover, the interoperability between Bitcoin and other blockchains is limited, with most solutions relying on centralized institutions to achieve cross-chain interactions.
Additionally, the transaction fees for BTCFi projects are relatively high, significantly increasing the costs for participants. For example, Babylon has exposed issues with high transaction fees during the staking process, including skyrocketing miner fees due to FOMO effects, as well as high fees for unlocking and withdrawing after staking.
Insufficient liquidity is also a common issue in this track. On one hand, the liquidity risk of wrapped versions of BTC still exists. For instance, in the Babylon protocol, the wrapped BTC provided by participating staking nodes does not fully match the liquidity of the aggregated native BTC, relying on the credibility of various aggregation platforms to maintain it. On the other hand, the liquidity provision methods for financial activities such as Bitcoin staking and lending are relatively singular, primarily relying on capital borrowing, and have not formed a diversified and efficient liquidity provision mechanism like that in traditional financial markets.
In this context, the total locked value of BTCFi projects is still relatively small compared to mainstream public chains like Ethereum, and the market's acceptance and participation are not high, posing significant challenges for project development and promotion.
Future Outlook
Currently, exchanges like Binance and OKX are collaborating with Babylon, Chakra, Bedrock, B², Solv Protocol, and others to carry out a series of pre-staking, farming, and other activities, allowing users to achieve high returns, which is a very convenient way for ordinary users to participate in BTCFi.
Looking at the projects mentioned above, we find that the current BTCFi ecosystem, in addition to BTC itself, already has a rich variety of asset types participating in BTCFi. For example, inscriptions, runes, and other layer 1 assets based on BTC; RGB++, Taproot assets, and other layer 2 assets based on the BTC network; WBTC on the ETH chain, various LST or LRT certificates representing staked BTC, and other wrap/stake assets. These assets expand the liquidity of BTCFi and enrich the scenarios of BTCFi.
Looking ahead, with the development of technology, such as Layer 2 technology continuously evolving and improving, solutions like Rollups will become more mature, significantly enhancing Bitcoin's transaction processing capabilities.
With the emergence of reliable cross-chain bridges, more secure and efficient asset transfers and interactions between Bitcoin and other blockchain networks will also be possible, allowing Bitcoin to participate more broadly in DeFi applications across different chains.
Moreover, with solutions like RSK, AVM, and BitVM, Bitcoin's smart contract functionality will be enhanced, enabling it to support more complex financial business logic and applications.
All these technological advancements will provide stronger technical support for decentralized financial services within the Bitcoin ecosystem, enabling more flexible staking, lending, derivatives trading, and other financial products.
As DeFi revives, we may see BTCFi's connection to real finance becoming closer, with the application of stablecoins in the BTCFi ecosystem continuously expanding, providing more efficient and low-cost solutions for cross-border payments and international trade. For instance, the USDi stablecoin supported by RGB++, with its 1:1 peg to the US dollar and AML/KYC compliance requirements, makes it an important tool in the international payment field, expected to be widely adopted in global cross-border e-commerce and international settlement scenarios in the future, promoting the widespread use of Bitcoin in the global financial system.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



