BOB ensures security through BTC L1, the most secure L1, and uses this security to create a trustless bridge connecting BTC, ETH, and other L1 blockchains. Therefore, Hybrid L2 does not rely on third-party bridging tools for interoperability while addressing the issue of fragmented BTC multi-chain liquidity.
Written by: IOSG Ventures

Summary
BOB belongs to a brand new type of L2: Hybrid L2. BOB ensures security through BTC L1, the most secure L1, and uses this security to create a trustless bridge connecting BTC, ETH, and other L1 blockchains. Therefore, Hybrid L2 does not rely on third-party bridging tools for interoperability while addressing the issue of fragmented BTC multi-chain liquidity.
1. Introduction
BTC was created as a decentralized, transparent, and censorship-resistant payment system. A decade later, smart contract chains have driven the creation of DeFi applications and other innovative products, such as NFTs, tokenized social media and gaming, as well as DAOs and other trustless governance structures. In this context, although BTC L1 remains the core of global cryptocurrency adoption, it has lagged in innovation and developer activity.
Despite the slow development and lack of flexibility of BTC L1, it still surpasses all other cryptocurrencies combined in terms of market capitalization, trading volume, and active user count. As of October 2024, BTC has 300 million users globally, a market cap of $1 trillion, and unmatched brand recognition and dominance. However, the DeFi activity on BTC L1 is the lowest among all cryptocurrencies: Ethereum's DeFi TVL to market cap ratio is 30%, while BTC's DeFi TVL accounts for only 0.1%, a difference of 300 times.
In recent years, many have attempted to introduce smart contracts and DeFi on BTC L1 through protocol changes and forks, but these attempts have failed. BTC L1 opposes any protocol upgrades that could significantly alter its functionality or increase complexity. Therefore, BTC L1 will not possess native programmability like Ethereum for a long time to come, and ultimately BTC L2 will become the best solution for DeFi within the BTC ecosystem.
1.1 Hybrid L2
Hybrid L2 is a BTC L2 solution designed to address the main challenges of scaling DeFi on BTC L1. This type of L2 typically possesses three key attributes:
- BTC L1 Security: Utilizing OP verification and error proofing on BTC L1 through BitVM2.
- Trustless BTC Bridging: Using an improved BitVM bridging design, users can access BTC as long as BTC L1 is secure and there is at least one honest node in the network capable of executing on-chain disputes. This new security model is known as "existence is trust" (1-of-n), as it relies on minimal assumptions and offers significantly superior security compared to existing BTC multi-signature bridges.
- Trustless Ethereum Bridging: BOB uses BTC L1 security combined with the bridging design of Ethereum OP rollups for L1/L2, encoding Ethereum's L2 withdrawals as part of L1 smart contracts to ensure the correctness of L2 withdrawals. This design can be extended to most L1 chains with smart contract capabilities.
As the first Hybrid L2, BOB provides a practical trustless cross-chain interoperability solution: first, BTC L1, as the most secure decentralized network, can simultaneously protect L2 and all cross-chain bridges. On top of this, BOB further addresses the issue of fragmented cross-chain BTC liquidity – users can deposit assets across various chains using native BTC liquidity and the secure withdrawal mechanism of BTC L1 through the BOB network. Ultimately, BOB maintains the security and sustainability of BTC L1 by paying fees to BTC L1.
2. The Current State of BTC L2: A Double-Edged Sword
BTC L2 has the potential to bring innovation to BTC L1 while maintaining its core principles. It can unlock the prospects of DeFi use cases, empowering trading, lending, and staking without relying on centralized exchanges. This presents a huge opportunity to unlock BTC's trillion-dollar market. Currently, dozens of chains claim to be "BTC L2."
However, building BTC L2 is a challenging task, and previous attempts have failed to reach the level of success seen with Ethereum. We believe that launching BTC L2 successfully faces the following three major challenges:
- BTC Security and Trustless BTC Bridging: This is the key feature that distinguishes BTC L2 from all other chains. The security of BTC L1 allows users to deposit and withdraw BTC without relying on third parties. So far, almost all BTC bridges have relied on multi-signatures. BOB is the first team in history to realize this blueprint through BitVM2.
- Building a Competitive Ecosystem: L2 can only succeed if its dApp ecosystem is successful. The key to creating successful products is to provide the best developer tools and DeFi infrastructure, such as wallets, institutional custody, and oracles. This means L2 teams must keep up with the pace of development, such as ms-level transaction speeds and abstracted gas fees. If a competitive developer environment cannot be provided, BTC L1 applications will struggle to compete with Ethereum and other network competitors.
- Introducing Blue-Chip Liquidity (Cold Start Problem): In the DeFi ecosystem, introducing stablecoins, fiat on/off ramps, and bridges connecting other networks is crucial. For developers, network effects are the decisive factor for the success of new products, so developing projects on isolated chains presents significant challenges.
3. Background of BOB: Bridges, Light Clients, and BitVM
The innovation of BOB is primarily reflected in three core technological concepts: cross-chain bridging, light clients, and BitVM. These technologies together form the value proposition of BOB, so it is necessary to delve into these three aspects.
3.1 Light Clients
The "Simplified Payment Verification" (SPV) light client protocol of BTC L1 allows nodes to perform payment verification without downloading the entire blockchain data. This method only requires the light client to verify consensus finality through block headers and can validate based on selected transactions.
The light client of BTC L1 has verifiable security and can be validated by other blockchains with smart contract capabilities. For example, Threshold has been running such light clients on Ethereum for years. However, Ethereum does not have a secure light client because it needs to store and track the public keys of over a million validators, increasing system complexity.
3.2 Cross-Chain Bridges
We have demonstrated two properties of "bridging" or "wrapping" assets to different blockchains:
a) It allows both chains to operate correctly at the same time;
b) It is difficult to achieve without a trusted third party.
In practice, we can reduce reliance on third parties by allowing any network participant to take on verification responsibilities. Through so-called "light client bridges," Chain A and Chain B can verify each other's consensus protocols through their respective smart contracts. When we deposit asset a into the bridge on Chain A, the smart contract on Chain B will verify that the transaction has reached consensus on Chain A before minting the wrapped token b(a). Conversely, when we burn b(a) on Chain B, we must first verify that the transaction has reached consensus on Chain A. Due to the complexity of light clients, there are currently very few successful implementations of this design.
3.3 BitVM
BitVM is a mechanism for executing arbitration programs on BTC L1 in an OP manner. Its execution occurs off-chain, and in case of failure, it is resolved through on-chain disputes. Its two main use cases are OP aggregation on BTC L1 (similar to Arbitrum) and trustless bridging. In both cases, BitVM allows users to access BTC from L2 as long as there is at least one honest node in the network, making deposits impossible to steal.
The most commonly used version of BitVM is BitVM2. Its design summary is as follows:
- Compressing the program into a SNARK verifier and implementing it in BTC L1 scripts.
- Splitting the verifier into subprogram blocks of less than 4MB for execution in BTC L1 transactions.
- BitVM2 operators submit the program through a Taproot tree during setup and pre-sign transactions.
- Users deposit funds into BitVM2 (e.g., bridging deposits).
- When attempting to withdraw funds from BitVM2, anyone can challenge the operator.
- If challenged, the operator must reveal the results of all intermediate subprograms and show the final computation result.
- If the operator cheats, some revealed subprogram results will be incorrect, and anyone can prove the operator's cheating by executing specific subprograms.
- Cheating operators will be expelled and will no longer have access to deposits.
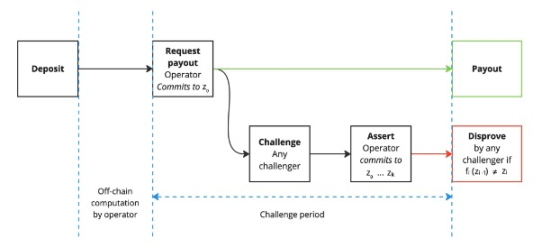
Source: bitvm.org
Our latest paper will provide a detailed overview of BitVM2.
4. BOB Hybrid L2
The innovative design of BOB's Hybrid L2 is based on the trust concept of BTC L1 as a decentralized network and its simplicity in consensus verification.
4.1 BTC L1 Security
BOB's Hybrid L2 will utilize BTC L1 for settlement and security assurance. The currently recognized ideal design for BTC L2 is based on zk-rollups: all state changes are computed off-chain and then verified and recorded on-chain through zk proofs. However, as of now, BTC L1 cannot support zk-rollups because implementing zk provers in BTC L1 scripts requires additional opcodes to avoid consensus forgery. Therefore, BOB achieves security through OP verification of BitVM2. This method generates validity proofs for each state transition and publishes them to BTC L1 along with the state differences. In conjunction with BitVM2, any network participant can initiate a challenge through the fault proof mechanism to overturn failed operations within 7 days and ensure security.
This means that through BitVM2, we can allow any node in the network to participate in the fault proof mechanism, thus raising challenges when errors are detected. This design makes security almost equivalent to BTC L1 itself: as long as there is one online and honest node in the network, fault proof can be triggered.
4.2 Trust-Minimized BTC L1 Bridging
The BitVM2 fault proof also enables BOB to create a trust-minimized BTC L1 bridge. Specifically, this is a light client bridge where BTC L1 supports BOB through a light client running in BitVM2. This bridging allows users to deposit BTC into the BOB network securely and withdraw it back to the BTC L1 network when needed. This new design relies on the "existential honesty" security model, requiring only a 1-of-n honest assumption to ensure correct operation, which is stricter than existing multi-signature bridging solutions.
In existing BTC bridges, most rely on multi-signature schemes and require a majority of signers to be honest. However, in the design of BitVM2, even if all bridging operators are dishonest, as long as there is one online participant in the network, the funds cannot be stolen. This design addresses the security vulnerabilities in multi-signature schemes and constitutes the safest BTC bridging solution in history.
4.3 Trust-Minimized Ethereum Bridging
BOB's Hybrid design also supports secure access to ETH and ERC20, similar to Optimism's design. When users wish to withdraw assets from L2 to Ethereum, they must wait for a 7-day challenge period to ensure that no fault proofs have been raised. This mechanism ensures the security of asset bridging between the Ethereum and BTC L1 networks, thereby addressing the inherent risks of cross-chain bridging.
In the design of BOB's Hybrid L2, the ETH bridge smart contract will wait for BOB to complete final confirmation on the BTC L1 network, ensuring that all proofs are correct. This functionality is part of the bridge smart contract, which can verify the BTC L1 blockchain and is implemented through the BTC L1 light client. Therefore, any user depositing ETH and ERC20 tokens into BOB can retrieve these assets back to Ethereum as long as the BTC L1 network is secure and there is one online node capable of triggering fault proof.
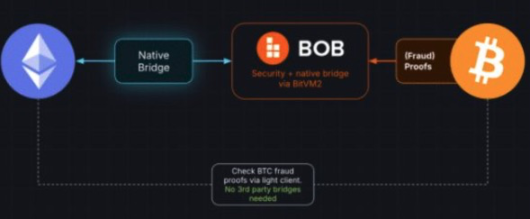
Source: BoB
5. Outlook: BOB as the Center of DeFi
The uniqueness of Hybrid L2 positions BOB at the center of the largest DeFi ecosystem in the industry. Currently, BOB is leveraging the network effects of BTC L1 and ETH and will expand to other chains in the future.
5.1 Self-Sufficiency through Ethereum
For dApps built on BOB, they can benefit from Ethereum's best infrastructure and development tools while attracting the core user base of DeFi and connecting with all exchanges and institutional players. Notably, almost all Ethereum users hold BTC, and most BTC users also engage with ETH DeFi.
5.2 Growth Driven by BTC L1
Over time, the additional security and access to BTC provided by the trust-minimized BitVM2 bridging will unlock more untapped BTC liquidity pools and allow dApps on BOB to not only catch up with their Ethereum competitors but also surpass them. This effect will be further enhanced by the global adoption of BTC L1 and its diverse user base: while ETH L2 competes for the same user base, BOB's dApps can leverage BTC's user base of over 300 million and thousands of real-world businesses.
5.3 BTC L1 as a Multi-Chain DeFi Hub
BTC L1, ETH, and stablecoins account for 90% of the market. However, just like existing banks, we believe that in the future, there will be hundreds of chains focusing on different application scenarios or geographical locations. All these chains will need secure access to BTC L1, and there will also need to be a way to exchange assets between them.
Currently, centralized exchanges play this role: they connect all chains, allowing users to access assets and exchange them for the corresponding L1. However, centralized exchanges have historically caused significant issues and will continue to do so until we fully transition to DeFi.
In contrast, BOB's mission is to position BTC L1 as the cornerstone of a secure and transparent DeFi ecosystem. As a Hybrid L2, BOB will securely bridge assets to any smart contract chain capable of verifying the BTC L1 blockchain. This means that modern L1 and L2 chains, including Solana, Tron, Sui, Aptos, Monad, Avalanche, Cosmos, Polkadot, and others, can securely deposit and withdraw assets through BOB. All of this is done through trust-minimized operations on BTC L1 without relying on third-party bridging.
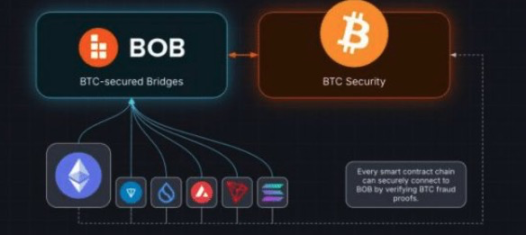
Source: BoB
Using BTC L1 as a trust anchor to create an interoperable DeFi ecosystem is the core advantage of the Hybrid L2 design. Rather than dispersing the liquidity of BTC L1 across dozens of chains, BOB will concentrate liquidity around BTC, providing a truly viable alternative to centralized exchanges and placing BTC at the center of DeFi.
6. Conclusion
BOB Hybrid L2 addresses some of the most pressing challenges in building a decentralized financial system on the foundation of BTC L1. It provides the necessary infrastructure by creating a BTC bridge that inherits the security of BTC L1 while maintaining trust minimization, enabling a broad user base to join BTC L1 without relying on centralized service providers. At the same time, BOB prevents the fragmentation of BTC liquidity through trust-minimized bridging to Ethereum and other smart contract L1 chains, offering a practical, BTC L1 security-based solution to the long-standing cross-chain interoperability issues, making BTC the core of DeFi.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




