1. Introduction
Since the release of the Bitcoin white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, Bitcoin has been hailed as "digital gold" and has maintained an unshakable position in the field of cryptocurrency. Its decentralization, scarcity, and security have enhanced its attractiveness as a long-term store of value.
In contrast, since its launch in 2015, Ethereum has rapidly become another important pillar in the blockchain industry, thanks to its powerful smart contract platform and flexible development environment. The smart contract functionality of Ethereum provides unlimited possibilities for the development of decentralized applications (dApps), leading to significant achievements in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFT) fields.
Despite Bitcoin's important position in the crypto world, compared to Ethereum, the Bitcoin ecosystem still faces some unique challenges:
Lack of smart contract platform: The Bitcoin ecosystem lacks a powerful smart contract platform, limiting the development of complex dApps and DeFi.
Underutilization of assets: For many Bitcoin holders, a major challenge is that their assets are not fully utilized, leading to missed opportunities to profit from emerging industries such as DeFi and NFTs.
Fragmentation of BTC across various blockchain networks: Bitcoin is dispersed across multiple independent blockchain networks and layer-two solutions, which may lack effective interoperability and compatibility, thereby limiting the application and liquidity of Bitcoin.
Although Bitcoin's original design is relatively simple, its community and developers continue to drive technological innovation to enhance its functionality and usability. Among these, the SegWit update addresses transaction malleability issues and increases block capacity by separating transaction information and signature data; the Taproot update introduces Schnorr signature technology, enhancing transaction privacy and efficiency, laying the foundation for the development of on-chain smart contracts; and the BRC-20 standard enables the Bitcoin network to support the creation and trading of tokenized assets, expanding its use cases and enhancing its competitiveness in decentralized finance and other blockchain applications, providing potential and foundation for Bitcoin's financial applications.
Entrepreneurs have not rested on their laurels, continuously exploring new solutions and applications. With technological advancements, the liquidity of Bitcoin is gradually improving. GeekCartel aims to lead everyone to understand the development and technical principles of these Bitcoin liquidity solutions, and to observe the latest developments from a more comprehensive perspective, helping users better utilize Bitcoin assets and explore more application scenarios. Note: This article does not constitute investment advice.
2. Exploring Bitcoin Liquidity: A New Path to Enhancing Applications and Value
Babylon: Bringing Bitcoin Security into the PoS Ecosystem
Technical Implementation:
Babylon is a Layer 1 PoS chain developed based on the Cosmos SDK. Babylon has proposed a Bitcoin staking protocol, designed as a modular plugin for many different PoS consensus algorithms, providing a primitive for restaking.
Babylon is able to transfer the security of Bitcoin to many PoS chains (such as Cosmos, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Polygon, and other blockchain ecosystems with strong interoperability), creating a more powerful and unified ecosystem.
Babylon achieves Bitcoin security sharing through the Bitcoin timestamp protocol and the Bitcoin staking protocol.
Bitcoin timestamp protocol: Babylon enhances the security of the PoS protocol by sending the hash value and validator signature of PoS blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain, using Bitcoin's timestamp technology. This process includes several key steps:
Checkpointing: At the end of each epoch, honest validators sign the hash value of the last PoS block of that period and submit this hash value and their signature as a checkpoint to the Bitcoin network. Due to the immutability and time-sequencing properties of the Bitcoin blockchain, these checkpoints provide an immutable proof of time.
Slashing: If a validator's behavior is deemed malicious (e.g., signing conflicting blocks), their staked funds will be reduced. The checkpoints on the Bitcoin blockchain provide temporal evidence to support this slashing behavior, proving that malicious behavior did indeed occur before a specific time.
The Bitcoin timestamp protocol can also address PoS long-range attacks. A long-range attack refers to the possibility of a validator in a PoS chain unstaking and going back to a historical block where they were still a validator, initiating a fork of the chain. This problem is inherent in PoS systems and cannot be completely resolved solely by improving the consensus mechanism of the PoS chain itself, and both Ethereum and Cosmos face this challenge.
By introducing Bitcoin timestamps, the on-chain data of the PoS chain will be stored on the Bitcoin chain in the form of timestamps, even if someone tries to create a fork of a PoS chain, the corresponding Bitcoin timestamp will definitely be later than the original chain, rendering the long-range attack ineffective.
Bitcoin staking protocol: This protocol allows Bitcoin holders to stake their idle Bitcoin to enhance the security of PoS chains and earn rewards in the process.
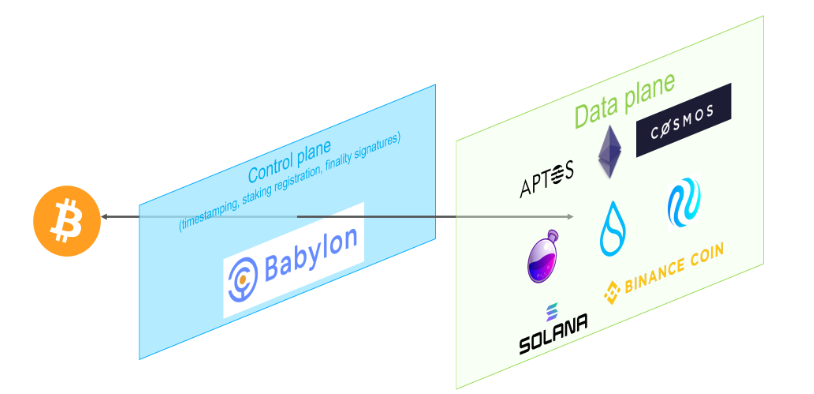
The core infrastructure of the Bitcoin staking protocol is the Control Plane between Bitcoin and PoS chains, as shown in the following figure.
1. Introduction
Since the release of the Bitcoin white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, Bitcoin has been hailed as "digital gold" and has maintained an unshakable position in the field of cryptocurrency. Its decentralization, scarcity, and security have enhanced its attractiveness as a long-term store of value.
In contrast, since its launch in 2015, Ethereum has rapidly become another important pillar in the blockchain industry, thanks to its powerful smart contract platform and flexible development environment. The smart contract functionality of Ethereum provides unlimited possibilities for the development of decentralized applications (dApps), leading to significant achievements in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFT) fields.
Despite Bitcoin's important position in the crypto world, compared to Ethereum, the Bitcoin ecosystem still faces some unique challenges:
Lack of smart contract platform: The Bitcoin ecosystem lacks a powerful smart contract platform, limiting the development of complex dApps and DeFi.
Underutilization of assets: For many Bitcoin holders, a major challenge is that their assets are not fully utilized, leading to missed opportunities to profit from emerging industries such as DeFi and NFTs.
Fragmentation of BTC across various blockchain networks: Bitcoin is dispersed across multiple independent blockchain networks and layer-two solutions, which may lack effective interoperability and compatibility, thereby limiting the application and liquidity of Bitcoin.
Although Bitcoin's original design is relatively simple, its community and developers continue to drive technological innovation to enhance its functionality and usability. Among these, the SegWit update addresses transaction malleability issues and increases block capacity by separating transaction information and signature data; the Taproot update introduces Schnorr signature technology, enhancing transaction privacy and efficiency, laying the foundation for the development of on-chain smart contracts; and the BRC-20 standard enables the Bitcoin network to support the creation and trading of tokenized assets, expanding its use cases and enhancing its competitiveness in decentralized finance and other blockchain applications, providing potential and foundation for Bitcoin's financial applications.
Entrepreneurs have not rested on their laurels, continuously exploring new solutions and applications. With technological advancements, the liquidity of Bitcoin is gradually improving. GeekCartel aims to lead everyone to understand the development and technical principles of these Bitcoin liquidity solutions, and to observe the latest developments from a more comprehensive perspective, helping users better utilize Bitcoin assets and explore more application scenarios. Note: This article does not constitute investment advice.
2. Exploring Bitcoin Liquidity: A New Path to Enhancing Applications and Value
Babylon: Bringing Bitcoin Security into the PoS Ecosystem
Technical Implementation:
Babylon is a Layer 1 PoS chain developed based on the Cosmos SDK. Babylon has proposed a Bitcoin staking protocol, designed as a modular plugin for many different PoS consensus algorithms, providing a primitive for restaking.
Babylon is able to transfer the security of Bitcoin to many PoS chains (such as Cosmos, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Polygon, and other blockchain ecosystems with strong interoperability), creating a more powerful and unified ecosystem.
Babylon achieves Bitcoin security sharing through the Bitcoin timestamp protocol and the Bitcoin staking protocol.
Bitcoin timestamp protocol: Babylon enhances the security of the PoS protocol by sending the hash value and validator signature of PoS blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain, using Bitcoin's timestamp technology. This process includes several key steps:
Checkpointing: At the end of each epoch, honest validators sign the hash value of the last PoS block of that period and submit this hash value and their signature as a checkpoint to the Bitcoin network. Due to the immutability and time-sequencing properties of the Bitcoin blockchain, these checkpoints provide an immutable proof of time.
Slashing: If a validator's behavior is deemed malicious (e.g., signing conflicting blocks), their staked funds will be reduced. The checkpoints on the Bitcoin blockchain provide temporal evidence to support this slashing behavior, proving that malicious behavior did indeed occur before a specific time.
The Bitcoin timestamp protocol can also address PoS long-range attacks. A long-range attack refers to the possibility of a validator in a PoS chain unstaking and going back to a historical block where they were still a validator, initiating a fork of the chain. This problem is inherent in PoS systems and cannot be completely resolved solely by improving the consensus mechanism of the PoS chain itself, and both Ethereum and Cosmos face this challenge.
By introducing Bitcoin timestamps, the on-chain data of the PoS chain will be stored on the Bitcoin chain in the form of timestamps, even if someone tries to create a fork of a PoS chain, the corresponding Bitcoin timestamp will definitely be later than the original chain, rendering the long-range attack ineffective.
Bitcoin staking protocol: This protocol allows Bitcoin holders to stake their idle Bitcoin to enhance the security of PoS chains and earn rewards in the process.
The core infrastructure of the Bitcoin staking protocol is the Control Plane between Bitcoin and PoS chains, as shown in the following figure.

Figure 1: System architecture with Control Plane and Data Plane. Image source: Bitcoin Staking Protocol Whitepaper
The Control Plane is implemented in the form of a chain to ensure that it is decentralized, secure, censorship-resistant, and scalable. The Data Plane represents the PoS chain, and this control plane is responsible for various key functions, including:
- Providing Bitcoin timestamp services for PoS chains to synchronize with the Bitcoin network.
- Acting as a marketplace, matching Bitcoin stakes with PoS chains, and tracking staking and validation information, such as EOTS key registration and refresh.
- Recording the finality signatures of PoS chains.
Babylon uses advanced cryptographic technologies, such as One-Time Signature (EOTS), to convert slashable PoS attacks into Bitcoin UTXOs that can be used for burning.
EOTS is a special digital signature scheme, and signing different blocks at the same height would lead to key exposure. The Bitcoin network uses the UTXO model to track transactions and account balances. Each UTXO represents a certain amount of Bitcoin at a specific address in the Bitcoin network, which can be spent by the holder of the private key for that address.
When PoS validators stake Bitcoin to participate in the consensus process of the network, their staking behavior is locked in specific UTXOs. By using EOTS, it ensures that if a validator violates the protocol (such as signing two different blocks at the same height), their private key will be exposed. Once the private key is exposed, it can sign a transaction that sends the originally staked Bitcoin to a burn address. This way, the offending validator will be economically penalized for their dishonest behavior.
In summary, Babylon is a Layer 1 blockchain that, through the Bitcoin timestamp and Bitcoin staking protocols, transfers the security of Bitcoin to many PoS chains, enhancing the security of these chains and providing profit opportunities for Bitcoin holders. Its unique staking scheme allows Bitcoin holders to stake BTC without the need for bridging. However, as staked BTC is locked in smart contracts, these BTC will appear as unspent outputs (UTXOs) on the Bitcoin chain, and with an increase in staking, it may lead to a decrease in transaction processing speed and an increase in transaction fees on the Bitcoin chain, which is one of the main challenges faced by Babylon.
Project Progress:
Babylon is currently in the testnet phase and has announced collaborations with a series of projects at the forefront of the Bitcoin revolution, including Ankr, Lorenzo Protocol, B² Network, Nubit, Yala, Nomic, Automata, Glacier, and Solv.
According to official data, Babylon has integrated with 50 Cosmos chains through the IBC protocol, covering areas such as DeFi, gaming, and infrastructure.
Investment Information:
On December 6, 2023, Babylon secured a Series A funding of $18 million led by Polychain Capital and Hack VC, with other participating institutions including Framework Venture, Breyer Capital, Symbolic, and GeekCartel.
In February 2024, Binance Labs announced an investment in Babylon, with the investment amount undisclosed.
On May 30, 2024, Babylon announced the completion of a new funding round, raising $70 million, led by Paradigm.

Figure 2: Latest funding status of Babylon. Image source: Official Twitter
BounceBit: The Fusion of DeFi and CeFi
Technical Implementation:
BounceBit Chain is a PoS Layer 1 secured by validators staking BTC and its native token—a dual-token system (native tokens BB and BTC) that leverages the security of native Bitcoin, with full EVM compatibility.
Validators stake BB or BBTC to record and validate transactions on the network, earning transaction fees as staking rewards, with no minimum token holding requirement. This dual-token system not only expands the stakeholder base but also adds additional flexibility and security layers to the network's consensus mechanism.
BounceBit also supports interoperability with EVM-compatible chains, identifying and merging equity assets such as BTCB on the BNB chain and ERC20 token WBTC. This diversifies the use cases of BTC and enhances user participation.
BounceBit introduces a unique feature—parallel yield generation from CeFi and DeFi. Users can stake BTC and mine on-chain using Liquidity Staking Derivatives (LSD) while earning original CeFi yields, a process known as Restaking Bitcoin. The ecosystem offers three types of returns for Bitcoin holders: CeFi yields, node operation rewards for staking BTC on the BounceBit chain, and opportunity yields from participating in on-chain applications and Bounce Launchpad.
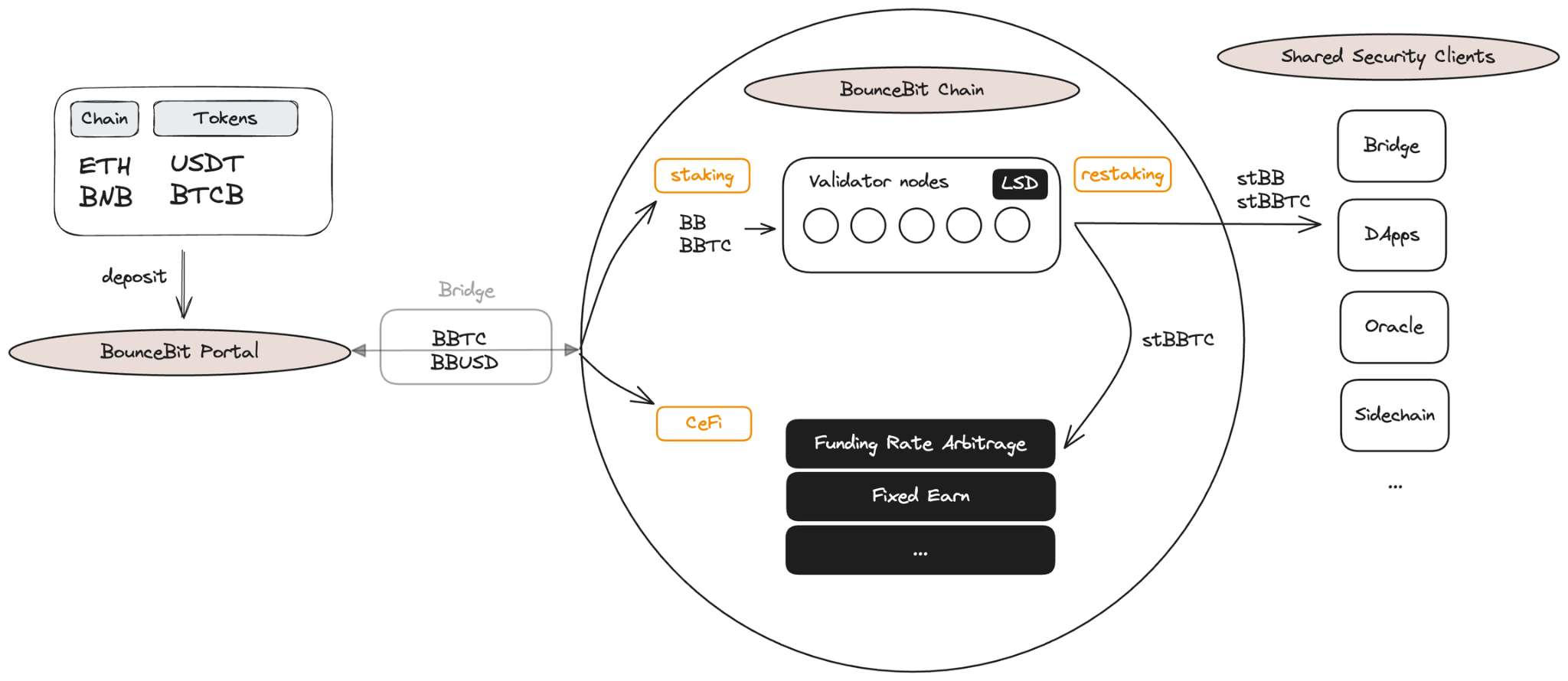
Figure 3: User flow. Image source: BounceBit Docs
As shown in Figure 3, users deposit various tokens into the BounceBit Portal to convert them into LCT (BBTC or BBUSD). These LCTs (Liquid Custody Tokens) can be bridged to the BounceBit chain for CeFi yields, and BB or BBTC can be staked in validator nodes to receive stBB or stBBTC as LSD, which can be restaked to enhance network security.
BounceBit introduces the concept of "Liquid Custody," theoretically ensuring the safe storage of assets, maintaining the liquidity of collateralized assets, and providing more opportunities to earn returns. In the above process, when users deposit assets into BounceBit, they receive an LCT—BB or BBTC, representing their assets securely held in custody while being bridgeable to BounceBit for use in supported scenarios to earn additional returns.
BounceBit allows staking validators to participate in network security and consensus mechanisms, helping to ensure network stability and security.
Shared security and consensus: Inspired by the shared security model of Restaking, BounceBit's BTC bridge implements a system where validators collectively maintain and protect the cross-chain bridge. This collaborative approach allocates security responsibilities, enhancing the reliability of cross-chain transactions.
Over 50% approval for transactions: To validate and execute any cross-chain transaction, over 50% of validators' approval is required. This consensus mechanism ensures that every transaction undergoes thorough scrutiny and approval by the entire network of validators, adding an extra layer of security and trust to the bridging process.
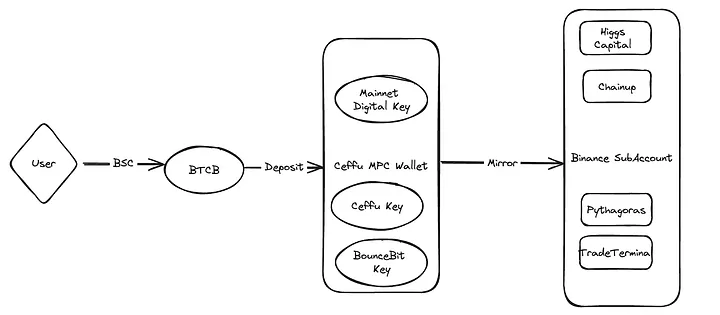
Figure 4: CeFi integration process. Image source: BounceBit Medium
Through its innovative CeFi + DeFi framework, BounceBit empowers BTC holders to earn returns across multiple networks. Unlike many protocols that emphasize decentralization, when Bitcoin is stored in a multi-signature wallet, it cannot generate returns (decentralized protocols typically incorporate complex yield-generating mechanisms that require assets to run in smart contracts, and Bitcoin's smart contract capabilities are limited). BounceBit addresses this issue by integrating the CeFi model, utilizing Mainnet Digital's custody services and Ceffu's MirrorX technology, allowing BTC to be active on-chain and traded on CEX sub-accounts with credit.
As shown in Figure 4, users interact with BSC (BNB Smart Chain) and deposit BTCB into Ceffu's Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallet. In MPC, a given number of participants each hold private data. Participants can collectively compute the value of a public function on this private data while keeping their data confidential. This wallet uses multiple keys to secure transactions, including Mainnet Digital keys, Ceffu keys, and BounceBit keys. Finally, it maps to a Binance sub-account, with components (Higgs Capital, Chainup, Pythagoras, TradeTerminal) supporting different sub-account needs.
In summary, BounceBit is a PoS Layer 1 network that supports restaking of Bitcoin, integrating CeFi and DeFi models, providing auctions, DEX, and other financial services, allowing Bitcoin holders to earn returns across multiple networks. It is fully EVM-compatible, supports interoperability with other EVM chains, and securely transfers and maps BTC through its bridging system. However, this combined CeFi and DeFi approach may face security challenges, especially in the security mechanisms of cross-chain bridges and the management of multi-signature wallets, requiring a high level of security and stability to ensure the safety of funds and transactions.
Project Progress:
According to the latest report from the official source, the Mainnet launch on May 13th has already reached a TVL of 882 million on-chain, with nearly 400,000 early contributors. As of the time of writing, according to official data, the total supply of BBTC tokens bridged through BounceBit is 1,482, with 155,583 users holding BBTC, and a staking amount (LSD) of 5,099 BBTC.
BounceBit recently announced partnerships with Ethena, allowing users to participate in BounceBit and Ethena activities by staking $BBUSD. It also partnered with Nubit to enhance data integrity and data capacity. Additionally, the official source has also partnered with LayerZero Labs, USDX, zkLink Nova, Pell Network, and Free.
Investment Information:
In February of this year, BounceBit raised $6 million in a seed round, led by Breyer Capital and Blockchain Capital. In March and April, it received strategic investments from OKX Ventures and Binance Labs, respectively.

Figure 5: Investment institutions supporting BounceBit. Image source: BounceBit Official Website
Solv: Unleashing the Power of SolvBTC, Opening the Door to BTCFi
Technical Implementation:
Solv Protocol has launched SolvBTC, a pioneering full-chain yield-bearing Bitcoin asset. Developed within a secure asset management framework, SolvBTC unlocks new possibilities and opportunities for Bitcoin holders while creating an efficient BTCFi ecosystem.
Solv, as a unified liquidity gateway, integrates various liquidity resources and investment opportunities into one platform. Users can find and manage their investments on the Solv Protocol without needing to access multiple different platforms or protocols. By converting idle base assets into interest-bearing assets and promoting cross-protocol, cross-ecosystem Lego combinations, Solv stimulates the liquidity vitality of the entire network, creating an efficient liquidity allocation layer.
Taking SolvBTC as an example, as shown in Figure 6, users can tokenize staking, restaking, and DeFi trading yields of BTC and BTC-related assets (such as wBTC, BTBC, MBTC, etc.) through application-layer DeFi protocols (such as DEX-decentralized exchanges, stablecoins, lending, etc.). Merlin, Stacks, Botanix, Bitlayer, these are infrastructure platforms and chains that support the operation of SolvBTC. They provide the necessary technical support and ecosystem connections for SolvBTC to operate smoothly across multiple blockchains and protocols.
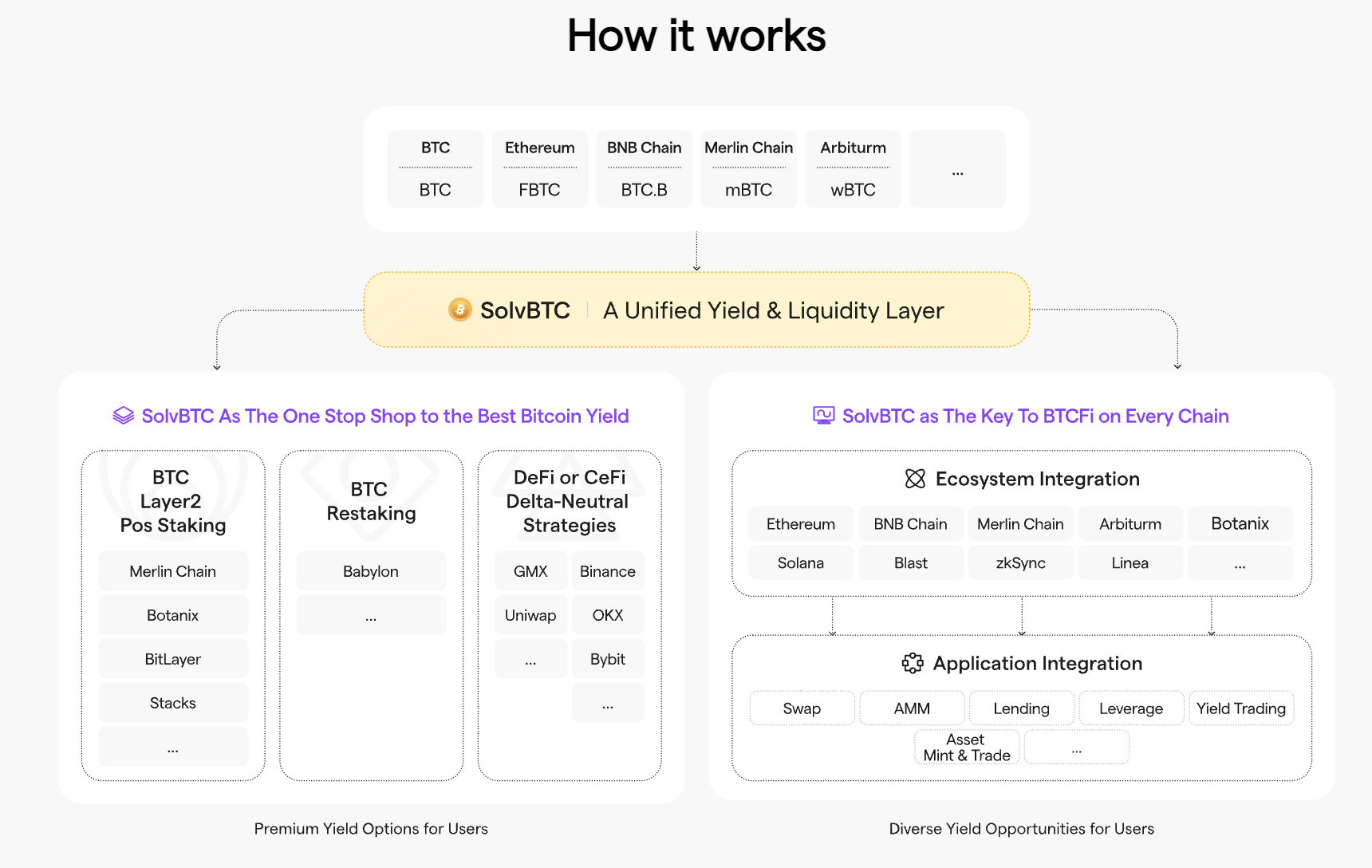
Figure 6: Solv architecture. Image source: Official Medium
In addition, SolvBTC is fully integrated with DeFi and CeFi projects in various ecosystems, allowing users to explore new growth paths and maximize their earning potential. This integration brings Bitcoin liquidity into various DeFi protocols to promote the prosperity of BTCFi. SolvBTC has also become the unified liquidity gateway for BTCFi.
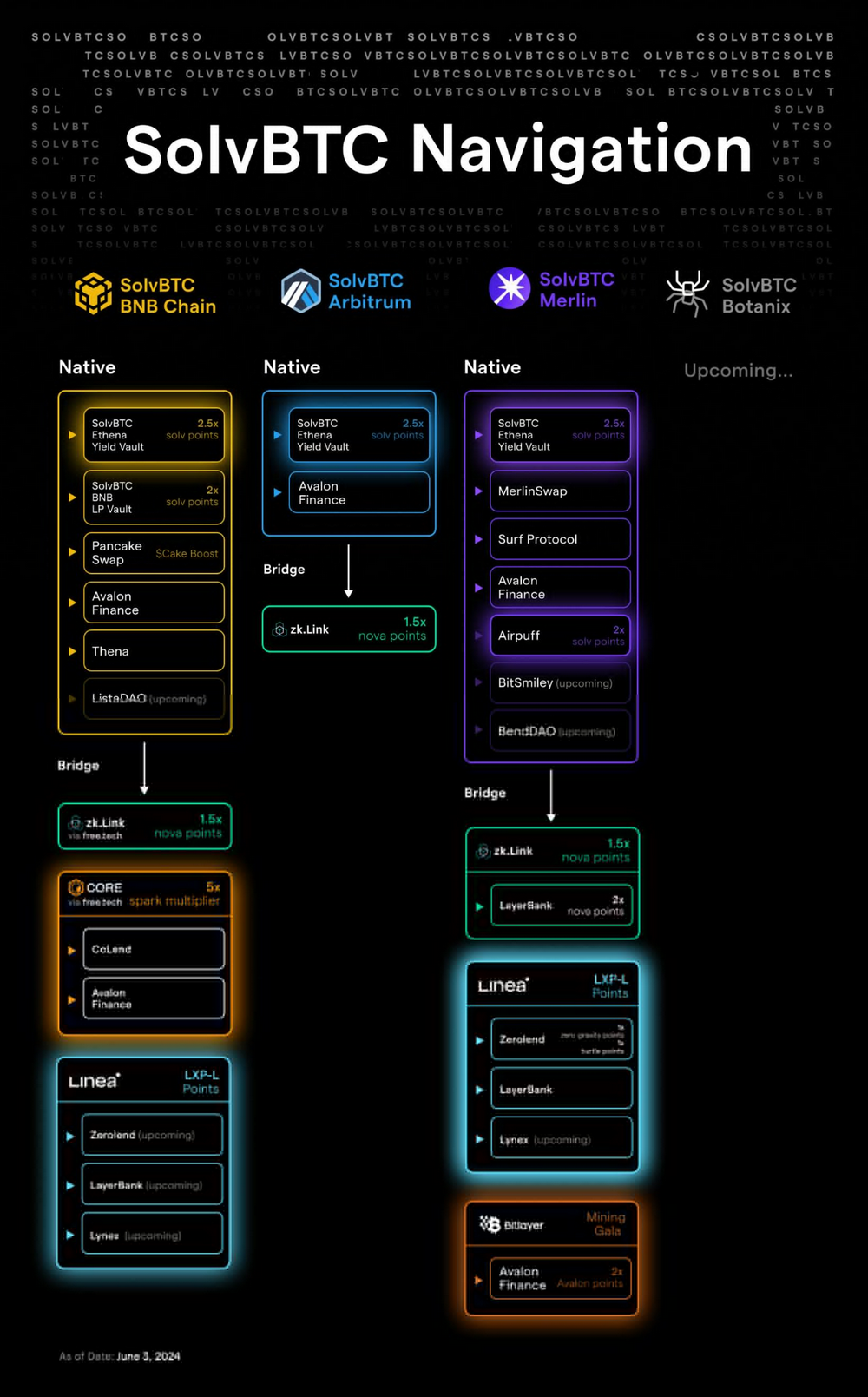
Figure 7: SolvBTC Navigation Map. Image source: Official Twitter
Solv has implemented a decentralized asset management architecture, which includes the built-in Solv Guard and Oracle. By utilizing smart contracts, Solv has established a trustless process standard prioritizing asset security to provide users with high-quality income sources.
Solv Guard is a system customized with unique operational mechanisms and specific permission scopes based on the trading strategies of each Vault. It defines rules regarding the destination of transfers and operations with DeFi protocols, allowing only secure wallet multi-signatures to operate within specified scopes.
Smart contract upgrades require joint control through multi-signature addresses and a time-lock mechanism with reputable partners. Additionally, if the strategy involves operations on centralized exchanges, Solv will collaborate with on-chain custody institutions such as Ceffu and Copper to ensure the security of off-exchange fund settlements.
By granting governance rights based on the use of secure wallet multi-signatures, Solv separates governance rights from user permissions. This separation allows for future configuration of parameters and contract upgrades by changing the governance structure.
Trading Strategy Vault: Stores funds, provides liquidity, and executes fund allocation. Its core design philosophy is to ensure operational efficiency of funds while eliminating counterparty risk (counterparty risk refers to the risk that the other party will not fulfill its financial obligations during a trade; here, trades are automatically executed by smart contracts, reducing reliance on a single intermediary or counterparty, thus reducing counterparty risk).
In this Vault, investment and repayment operations are achieved through maintaining a Delta-neutral strategy (Delta-Neutral Strategies) in the investment portfolio.
The Vault uses Solv Guard to maintain and real-time price oracles to ensure the security of operations and decisions based on current market data.
In summary, Solv has introduced SolvBTC, a pioneering full-chain yield-bearing Bitcoin asset designed to provide new opportunities and possibilities for Bitcoin holders while creating an efficient BTCFi ecosystem. SolvBTC integrates various liquidity resources and investment opportunities into a unified platform, allowing users to easily find and manage investments on the Solv Protocol. The Solv architecture includes decentralized asset management mechanisms such as Solv Guard and oracles, and collaborates with multiple infrastructure providers to ensure asset security and efficient system operation. In addition to SolvBTC, the official source also offers various assets and investment strategies. Despite using security measures such as multi-signatures, the smart contract itself still carries the risk of vulnerabilities or attacks, which could lead to asset loss or theft. Therefore, Solv actively collaborates with reputable audit firms to minimize this risk.
Project Progress:
SolvBTC has already supported Bitcoin assets on BNB Chain, Merlin, Arbitrum, and the Bitcoin mainnet, and is soon to support the Ethereum mainnet. The official announcement includes collaborations with the Ethena team to integrate robust strategy yields into SolvBTC.ena, as well as collaborations with Babylon and BotanixLabs. On June 6th, Binance Web3 launched the Solv staking reward activity, allowing users to earn rewards by staking BTCB to exchange for SolvBTC.
As of the time of writing, Solv has achieved a TVL of over $1.2 billion, providing high-quality income to over 100,000 users; with 17,490 BTC already staked on Solv.
Investment Information:
Solv has received investments from Binance Labs, Blockchain Capital, and Mirana among others.

Figure 8: Investment institutions supporting Solv. Image source: Official Documentation
Lorenzo: Bitcoin Liquidity Finance Layer
Technical Implementation:
Lorenzo provides Bitcoin holders with an efficient market to easily find the best investment opportunities.
Lorenzo incentivizes users to stake and provide income by tokenizing staked Bitcoin into Liquid Principal Tokens (LPTs) and Yield Accruing Tokens (YATs). Additionally, Lorenzo provides trading infrastructure for LPT and YAT, ensuring users can conveniently manage and exchange their tokens to maximize their investment returns.
Liquid Principal Tokens (LPTs): LPTs represent the staked Bitcoin principal tokens. Taking Babylon as an example in Figure 9, for instance, Babylon-Lorenzo-01 is a Bitcoin Liquidity Restaking Plan (BLRP). When users stake Bitcoin as collateral in Babylon-Lorenzo-01, they receive stBTC in a 1:1 exchange as LPTs, which they can buy, sell, or manage on the Lorenzo platform, thereby increasing the liquidity and operability of the staked Bitcoin.
Yield Accruing Tokens (YATs): YATs represent the tokens accumulating yields from restaking transactions. Using Babylon-Lorenzo-01 as an example again, YATs will accrue yields from Babylon and Lorenzo upon maturity, and can also be bought, sold, or managed on the Lorenzo platform, allowing users to realize or reinvest their yields.
Before the emergence of Babylon, BTC assets were distributed across various public chains. However, Babylon's emergence concentrates these BTC assets for staking and releases stBTC as a liquidity staking token into various ecosystems. The support for stBTC in various ecosystems will impact the new distribution pattern of BTC. Lorenzo will become the traffic distribution entry for BTC, with stBTC serving as the liquidity layer, and YATs fulfilling the financial aspect, similar to building an interest rate market like Pendle, providing investment returns for users.
BLRP is a plan on the Lorenzo platform for obtaining Bitcoin liquidity. Through BLRP, project teams can utilize staked Bitcoin liquidity, and stakers will subsequently receive reward yields. The creator of each BLRP needs to clearly specify how the staked Bitcoin liquidity will be used, the rules for issuing Bitcoin restaking tokens, and how stakers will receive rewards.
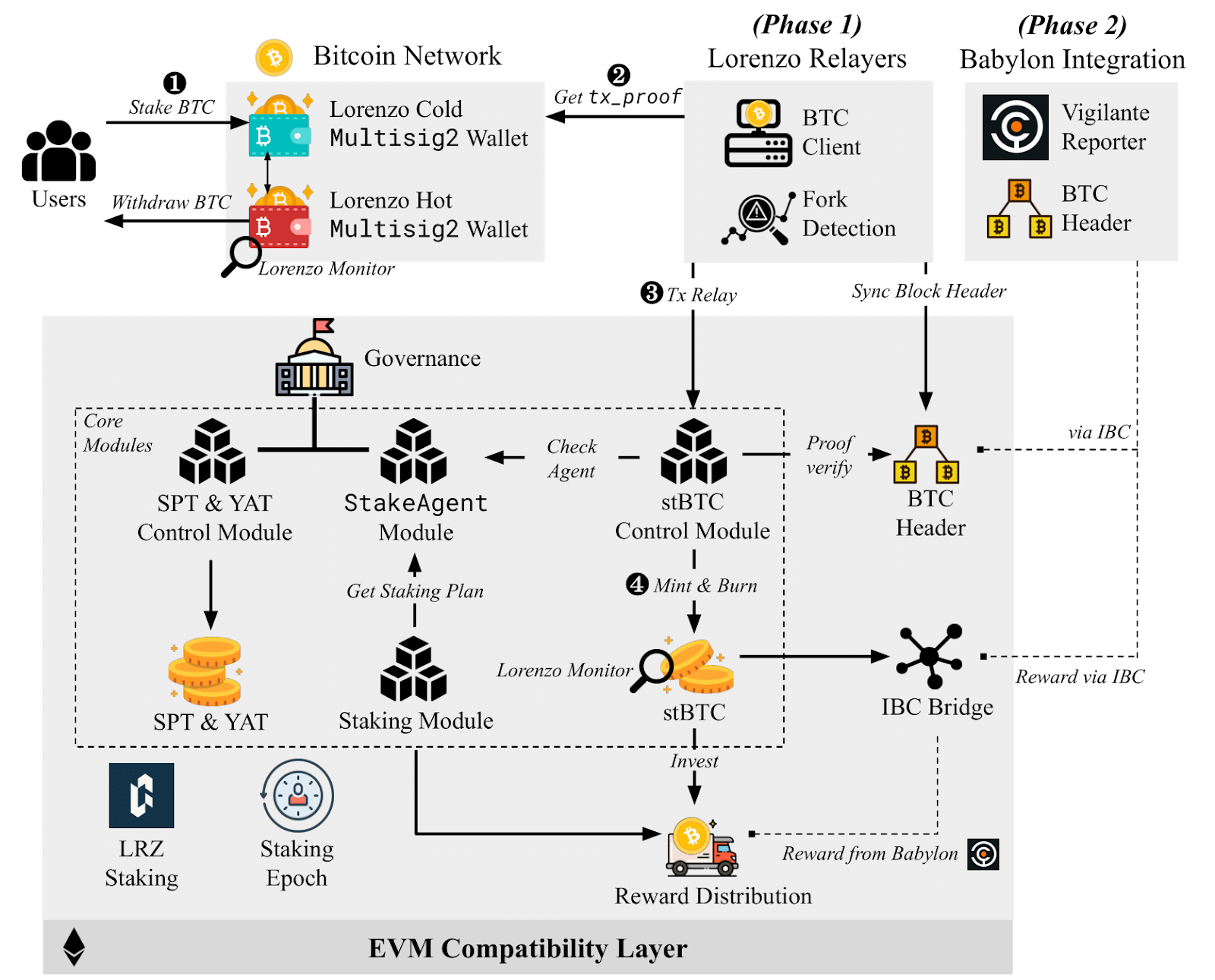
Figure 9: Architecture of the Lorenzo Protocol. Image source: Official Documentation
According to Figure 9, we can see that the main settings in the Lorenzo protocol architecture are as follows:
User Staking and Withdrawal of Bitcoin
Staking BTC: Users stake Bitcoin in Lorenzo's multi-signature cold wallet.
Withdrawal of BTC: Users can withdraw their Bitcoin through Lorenzo's multi-signature hot wallet.
Lorenzo Relayers
Obtaining Transaction Proofs: Lorenzo Relayers obtain transaction proofs (tx_proof) from the Bitcoin network.
Fork Detection: Relayers are also responsible for detecting forks in the Bitcoin blockchain to ensure data consistency and reliability.
stBTC Control Module
Responsible for minting and burning stBTC, and performing proof verification.
Core Modules
Staking Agent Module: Manages staking plans and checks agents.
stBTC Control Module: Responsible for minting and burning stBTC, and performing proof verification.
SPT & YAT Control Module: Manages and controls the issuance and trading of LPTs and YATs.
Staking Module: Obtains and manages staking plans, coordinates staking operations.
When a user stakes Bitcoin in a target on the Lorenzo platform (such as a specific investment plan or project), the staking agent needs to complete the following process:
Complete restaking: The staking agent needs to promptly stake the user's Bitcoin in the specified project.
Upload restaking proof: The staking agent needs to upload proof of the restaking operation to the Lorenzo platform to ensure transparency and trustworthiness of the transaction.
Token issuance: According to the target's defined rules, the staking agent issues LPTs and YATs for each restaking transaction on the Lorenzo platform.
Token transfer: The staking agent transfers the generated LPTs and YATs to the staking user's address, allowing the user to manage and trade these tokens.
Lorenzo not only acts as a staking agent to handle users' Bitcoin staking, but also supervises the actions of other staking agents. If a staking agent engages in any misconduct, Lorenzo will intervene and take measures to ensure compliance with regulations.
From the above content, we can see that Lorenzo has designed some functions as a modular architecture to achieve scalability. According to official information, Lorenzo supports Babylon, and through the IBC bridge and proof verification mechanism, Lorenzo brings Bitcoin liquidity into multiple blockchain ecosystems (and will integrate with other chains in the future), enhancing the flexibility and use cases of Bitcoin staking. Lorenzo is also compatible with EVM, enabling it to run Ethereum smart contracts, providing trading infrastructure for LPT and YAT (such as providing trading pairs, lending protocols, and different structures of Bitcoin yield products), promoting diversified DeFi application development. As an innovative market for Bitcoin LPT and YAT, if Lorenzo encounters insufficient liquidity or significant market fluctuations, it needs to strive to increase platform user participation and trading volume to enhance overall market liquidity.
Project Progress:
The Lorenzo betanet was launched on May 26th, allowing users to try using Lorenzo to bridge stBTC to the Bitlayer ecosystem.
According to official information, the cooperation and integration projects announced in the first quarter include: Babylon, Cosmos Hub, BounceBit, Flash Protocol, Nubit; and recently partnered with Bitlayer, Portal Finance, enzo, BitSmiley, and others.
Yala: Implementing a Bitcoin-native DeFi protocol for multi-chain stablecoins
Technical Implementation:
The innovation of Yala lies in bringing Bitcoin liquidity to various ecosystems, allowing BTC users to earn yields through stablecoins. The protocol aims to leverage the inherent security and liquidity of Bitcoin. Using Yala's modular infrastructure, it provides lending protocols, allowing users to borrow stablecoins ($YU) by depositing BTC or UTXO assets as overcollateralization. Users can generate yields using $YU stablecoins across various DeFi protocols in the ecosystem. The Yala Finance system includes Vaults, liquidation algorithms, automatic stabilizers, insurance modules, and other basic components, providing a comprehensive DeFi ecosystem for BTC assets. 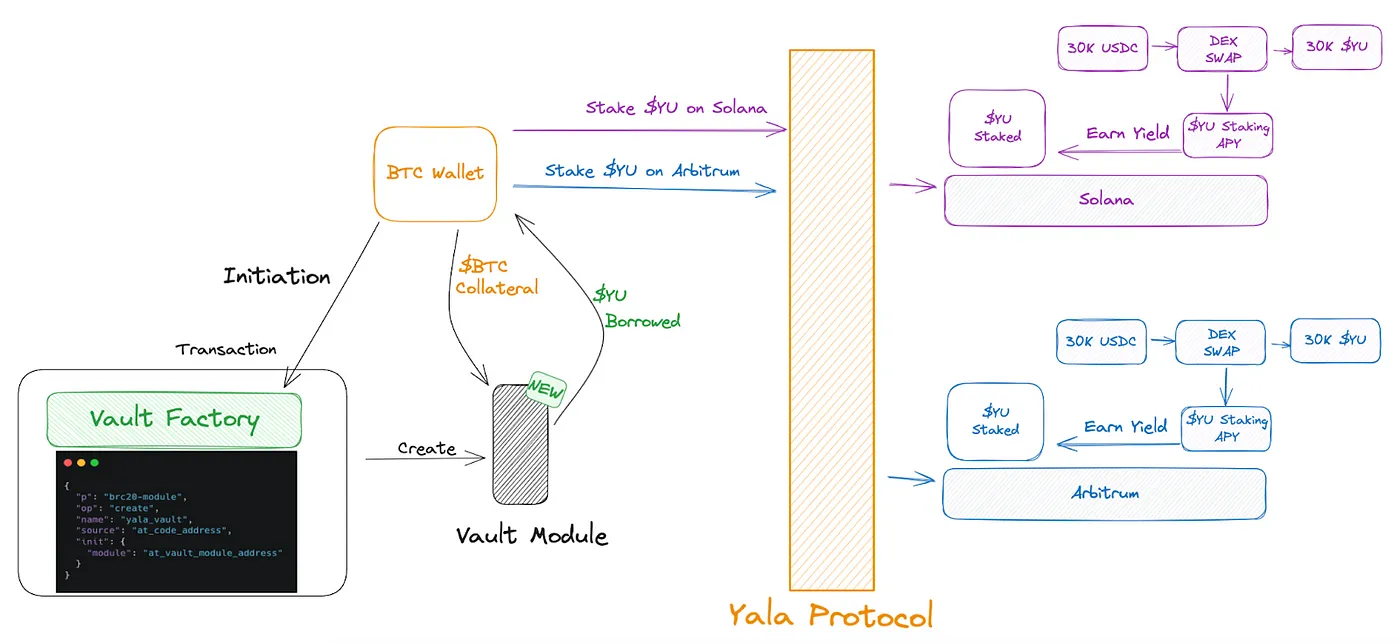
Figure 10: $YU across different ecosystems. Image source: Yala Medium
As shown in Figure 10, Yala makes investments more flexible and active by using a combination of different DeFi protocols and multiple blockchains (Solana, Arbitrum, and BTC L2, such as Botanix). Users can choose to diversify their investments across various activities such as staking, liquidity mining, and borrowing, spanning different ecosystems. This user-centric approach allows leveraging the unique advantages of each activity and blockchain to help users build diversified and robust investment portfolios.
The Yala architecture includes the application layer, consensus and data availability (DA) layer, execution layer, and settlement layer. Based on this design, developers can use Yala's SDK to implement custom modules for developing BTC ecosystem applications.
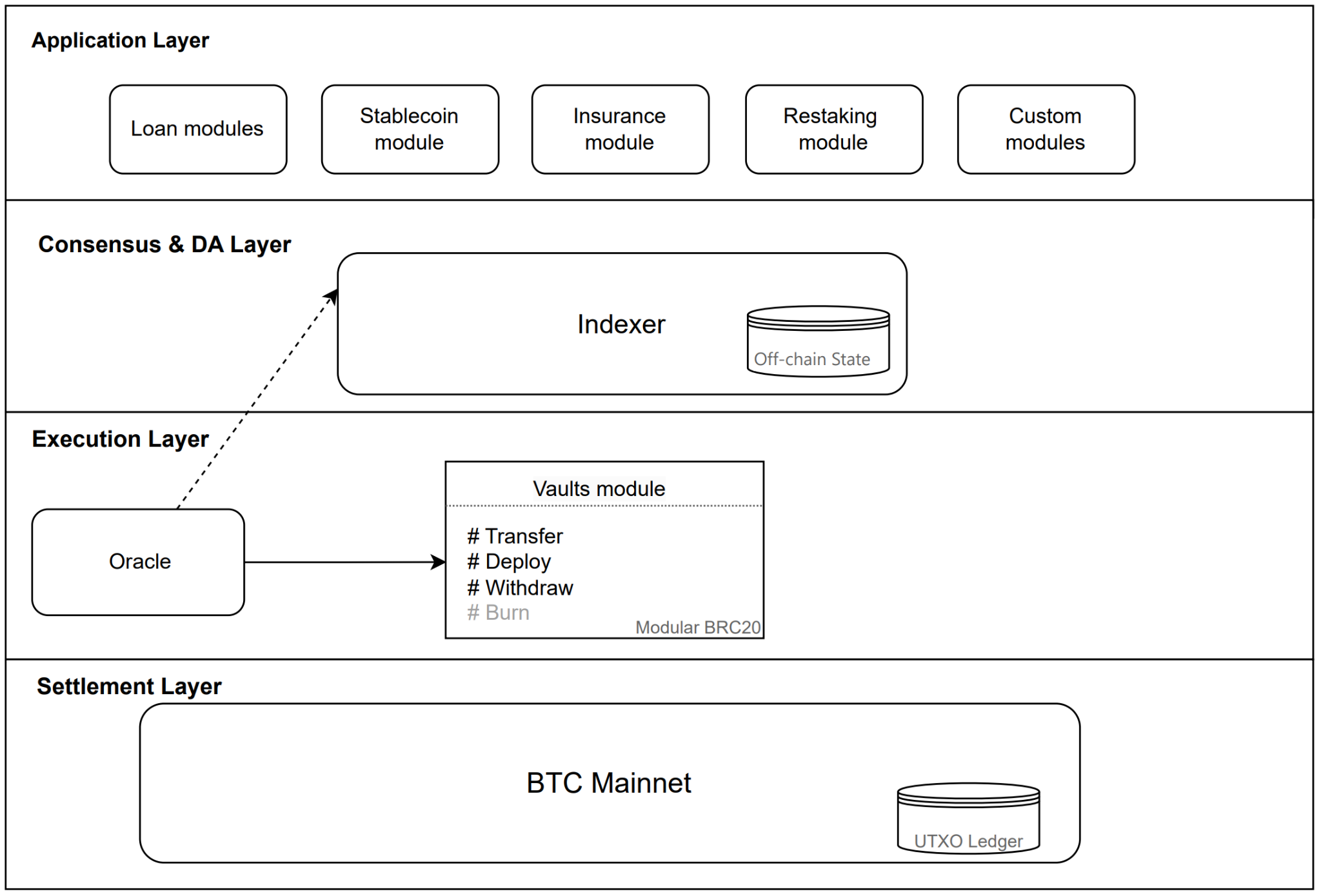
Figure 11: Modular architecture of Yala. Image source: Official Documentation
Application Layer: The application layer is where applications run, and the modules on it define the logic of state changes. Modules can be smart contracts on purpose-built blockchain virtual machines, such as smart contracts on EVM, or Tapscript in Inscrption Assets. Through this module, the native stablecoin of Yala can generate additional yields across various DeFi protocols and blockchains in different ecosystems. The Yala application layer includes lending modules, restaking modules, insurance modules, stablecoin modules, and custom modules.
The stablecoin module forms the foundation of the Yala financial system, and the stablecoin is multi-chain and native on each target chain. For example, since BRC-20 tokens cannot be minted directly, the system maintains a stablecoin reserve pool, namely the stablecoin module. Users simulate the traditional stablecoin minting/burning process by transferring and extracting inscriptions to the stablecoin issuance module (in the initial stage, the Yala Foundation, as a community-supervised central entity, is responsible for ensuring the stability of $YU; the governance foundation will transition into a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) to ensure sustainable development and broader community participation).
Consensus and Data Availability Layer: In the Yala system, DeFi transactions occur on the target chain, and data is updated and agreed upon by Indexer nodes to reflect the final state changes through UTXO transactions on the Bitcoin main chain, ensuring data security and consistency.
Data availability refers to the ability of data stored in the blockchain network to be effectively accessed and utilized by all participating nodes. Unlike data availability in other blockchains, BTC assets use the UTXO format, which involves two state changes (input and output), and BTC has a longer block interval, approximately 10 minutes.
In Yala, data availability is implemented by focusing on off-chain state changes in the witness script format, maintained by the Indexer. The Indexer captures global state and balances in the form of witness scripts, which are an extension script introduced in Segregated Witness (SegWit) to improve the efficiency and security of Bitcoin transactions by separating signature data from transaction data. The off-chain state changes are eventually reflected in on-chain UTXO transfer transactions, and BTC's consensus mechanism and security validate these on-chain UTXO transactions, indirectly ensuring the reliability and consistency of off-chain state changes. Additionally, Yala collaborates with the DA provider Nubit, which provides state validation for the Bitcoin indexer. Based on this design, Yala's challenge is to achieve the trustworthiness of the Indexer and the secure real-time update of off-chain states. In response, Yala has proposed some future development directions and solutions:
Achieving Trustworthiness of the Indexer:
Data Availability Sampling: In the DA layer, direct use of Data Availability Sampling (DAS) to reduce verification costs; validators only need to randomly download a portion of data blocks to verify the availability of all data. Erasure coding and KZG polynomial commitments will also be used to implement DAS in the Yala DA layer.
Content Verification: The DA layer of Yala needs to verify content including transaction data, the Merkle tree of transaction data, and commitments. Transaction data will be directly verified by the Indexer, and the Indexer will also generate the Merkle tree. Currently, commitments can also be generated by the Indexer, and there may be consideration for adding dedicated validators in the future. Verified content will be stored in a distributed manner and made public for a period of time (similar to blob storage time on ETH, set to one month), during which anyone can verify the verified content.
Utilizing Nubit's DA Layer Solution: Nubit is a Bitcoin-native data availability layer with instant finality. Yala is collaborating with the data availability (DA) layer Nubit to build the Indexer. With the data availability layer of Nubit, Yala's Indexer can provide deeper and more reliable verification of Inscription Assets events.
Execution Layer:
The execution layer includes BTC Vaults and Oracle modules.
Oracle Module: Lending protocols require real-time access to the market price of collateral assets to determine when to trigger conditional execution. The Yala Foundation is responsible for maintaining the Oracle module and Oracle Security Module (OSM). The Oracle module retrieves price inputs from off-chain sources. Off-chain Oracle nodes retrieve the required data through off-chain data APIs, format it, and return it to the Oracle module. To prevent attackers from attempting to control the majority of Oracles, the Yala protocol uses OSM to receive price inputs instead of directly from the Oracle. OSM serves as a defense layer between the Oracle and the protocol, with a 30-minute delay in publishing prices to enable emergency defense in case of Oracle compromise. The Yala Foundation is responsible for deciding the duration of emergency Oracle and price delay.
BTC DeFi Module: All DeFi transaction operations in Yala are guided by the Indexer (consensus layer) and state changes are based on price information from the Oracle.
Yala innovatively designed a modular architecture to implement a Bitcoin-native DeFi protocol. Yala's stablecoin is multi-chain and native on the target chain, allowing users to earn additional yields through $YU across various DeFi protocols in multiple ecosystems. Additionally, the Indexer in the consensus layer maintains off-chain transaction states and reflects them onto the chain's UTXO, leveraging Bitcoin's consensus mechanism to validate transactions. However, the trustworthiness of Yala's Indexer and the secure real-time update of off-chain data still pose challenges, and Yala is actively exploring specific advancement solutions. Currently, leveraging the information verification of Polyhedra’s zkbridge helps Yala achieve multi-chain verification functionality in the Bitcoin and EVM ecosystems to ensure the security of DeFi. Additionally, utilizing Nubit DA helps verify inscription information in the Bitcoin ecosystem. The Yala team is actively exploring and passionately pursuing the development of this innovative project from zero to one, aiming for further improvement and optimization of the system in the future.
Project Progress:
Yala officially announced partnerships with Alchemy Pay, Avail, Babylon, Botanix, Map protocol, Nubit, Polyhedra, and Stacks.
According to official information, the development team is currently continuing to improve Yala's infrastructure.
III. Project Comparison
This article has outlined several Bitcoin liquidity-related projects, including Babylon, BounceBit, Solv, Lorenzo, and Yala, with the aim of providing a better understanding of these projects. Next, we will conduct a comparative analysis of these projects to provide a more objective perspective.
Name
Babylon
BounceBit
Solv
Lorenzo
Yala
Core Project
Bringing Bitcoin Security to PoS Chains
Combining CeFi and DeFi to Activate Bitcoin Liquidity
Bringing Bitcoin liquidity into various DeFi protocols through SolvBTC
Providing a trading market for Bitcoin's LPTs and YATs; optimizing user returns
Realizing a Bitcoin-native DeFi protocol for multi-chain stablecoins
Technical Implementation
Sharing Bitcoin security through the Bitcoin timestamp protocol and Bitcoin staking protocol
Validators jointly maintain cross-chain bridges, Mainnet Digital's custody services, supplemented by Ceffu's MirrorX technology
Integrating various liquidity resources and investment opportunities into one platform
Executing investment strategies through the Vaut trading strategy
Modular design, SPT & YAT control module managing and controlling the issuance and trading of LPTs and YATs; collateral agent supervision mechanism
Modular design, minting multi-chain native stablecoins through the stablecoin module, supporting multiple DeFi protocols
Supported Chains
Bitcoin, Cosmos, Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, Polygon, etc.; EVM compatible
Bitcoin, BNB Chain, Ethereum, etc.; EVM compatible
Bitcoin, Merlin, Arbitrum, BNB Chain, etc.; EVM compatible
Bitcoin, Babylon, BitLayer, with future support for other chains; EVM compatible
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, Arbitrum, etc.; EVM compatible
Security Mechanisms
Based on Bitcoin timestamp checkpoints and penalty mechanisms; one-time extraction signature for PoS attack (EOTS)
Validators approve (>50%) cross-chain transactions; Ceffu multi-signature wallet
Safe Guardian transaction rules, multi-signature, and time lock control smart contract upgrades
Multi-signature wallet, proof verification, fork detection; collateral agent supervision mechanism
Achieving consensus and data availability through the Indexer (off-chain) and on-chain verification through UTXO
From the table, it can be seen that although each project has different focuses, they are all committed to promoting Bitcoin liquidity. Through their unique technical solutions, users can maximize the economic value of their Bitcoin. This not only helps users earn returns through different methods but also significantly enhances the liquidity and application breadth of Bitcoin as a digital asset.
IV. Conclusion and Outlook
More and more projects aimed at improving Bitcoin liquidity efficiency are emerging, not only enhancing Bitcoin's liquidity but also expanding its application in the decentralized finance technology field. These projects greatly promote the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem by providing innovative solutions and convenient trading functions.
The approval of Bitcoin ETF this year is also an important milestone in the cryptocurrency field. The approval of ETF not only showcases Bitcoin's potential to investors outside the crypto community but also enables compliant funds to enter this market more conveniently and securely. This has profound implications for Bitcoin and the entire cryptocurrency market.
As products related to Bitcoin liquidity are directly linked to funds, each project needs to ensure the security of its protocols or smart contracts, especially when dealing with cross-chain operations and complex financial products, as any small vulnerability could lead to significant fund losses. Due to differences between different blockchains, especially the lack of a comprehensive smart contract system on Bitcoin, integration and interoperability pose a major challenge. Developers need to have extensive knowledge and adaptability to effectively exchange data and assets between different blockchains. Despite facing many challenges, with technological advancements and market adaptation, GeekCartel believes in an optimistic future for the Bitcoin ecosystem, expecting to bring more diverse and secure decentralized financial products and services.
Source: https://medium.com/@GeekCartel
References
Images:
https://docs.babylonchain.io/assets/files/btc_staking_litepaper-32bfea0c243773f0bfac63e148387aef.pdf
https://docs.bouncebit.io/cedefi/bouncebit-cefi-+-defi/infrastructure
https://medium.com/@bouncebit/explaining-bouncebits-philosophy-77b4682cf111
https://docs.yala.org/yala-a-bitcoin-based-asset-protocol/yala-architecture
Text:
https://lorenzo-protocol.notion.site/56688385995649bfa7ea87bdbcc4ebf4
https://www.investopedia.com/bitcoin-taproot-upgrade-5210039
https://www.coinbase.com/en-sg/learn/crypto-glossary/what-are-brc-20-tokens
https://docs.babylonchain.io/assets/files/btcstakinglitepaper-32bfea0c243773f0bfac63e148387aef.pdf
https://docs.babylonchain.io/assets/files/btcstakinglitepaper-32bfea0c243773f0bfac63e148387aef.pdf
https://academy.binance.com/en/glossary/unspent-transaction-output-utxo
https://medium.com/@bouncebit/introducing-liquid-custody-on-bouncebit-78e5923f7687
https://www.ceffu.com/blog/what-is-multi-party-computation-technology
https://www.theblock.co/post/279603/bitcoin-restaking-protocol-bouncebit-funding-tvl
https://docs.lorenzo-protocol.xyz/introduction/bitcoin-liquidity-finance
https://docs.lorenzo-protocol.xyz/introduction/bitcoin-restaking-token-issuance-and-settlement
https://news.bitcoin.com/building-on-bitcoin-how-yala-is-transforming-btcs-potential-into-a-reality
https://academy.binance.com/en/glossary/unspent-transaction-output-utxo
https://medium.com/yalabtc/a-deep-dive-into-yalas-collateral-and-insurance-strategies-962da37dd9c1
Acknowledgments
There is still much research and work to be done in this emerging infrastructure paradigm, and there are many areas not covered in this article. If you are interested in any related research topics, please contact Chloe.
Many thanks to Severus and Jiayi for their insightful comments and feedback on this article.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




