Why pay attention to the Cancun upgrade?
On January 12, the U.S. SEC announced the approval of a Bitcoin spot ETF, which was eagerly anticipated and seen as a milestone with significant implications. However, the crypto market reacted indifferently to this event, and even after that, the price of Bitcoin began to decline. In the past half month, it dropped from a high of $46,000 to below $40,000, with a decrease of -13%. The inflated effect of the ETF event was burst, and a large amount of capital flowed to other public chains and project protocols with new narratives.
The game of Bitcoin ETF has temporarily come to an end, and the market's attention has shifted to the Ethereum spot ETF. The current market analysis estimates a 50% probability of approval in May this year. After experiencing the strong rise in coin prices during the previous Bitcoin ETF hype, it is essential to position in advance for the next surge of mainstream tokens, such as Ethereum.
In addition, the next upgrade of Ethereum—Cancun upgrade—is coming soon and is expected to be completed by the end of February. The primary purpose of this upgrade is to expand the Ethereum main chain, enhance the scalability, security, and usability of the Ethereum network, increase the TPS of the main chain, and reduce gas fees, which is extremely beneficial for the Ethereum L2 ecosystem and will drive the flourishing of the L2 ecosystem.
Taking into account the above two reasons, this issue will explain the Cancun upgrade and analyze the favorable projects.
What is the Cancun upgrade?
The Cancun upgrade is another upgrade to the Ethereum main chain following the Shanghai upgrade. The name "Cancun" comes from a seaside city in Mexico, which is a world-famous resort and one of the cities where the Ethereum developer conference (EthCC) is held.
The Cancun upgrade aims to address the core issue of the Ethereum blockchain network, which is the transaction fees. In an article "Make Ethereum Cypherpunk Again" published by V God in December 2023, it was stated that one of the core reasons that blockchain is limited to asset speculation is the rise in transaction fees. The high network transaction fees have caused people to shift from users of the blockchain network to speculators. In order to realize the application value of blockchain, the transaction fees of the blockchain network must be reduced by an order of magnitude. Although the emergence of L2 has already reduced the network fees compared to the Ethereum mainnet, this is still far from enough.
The Cancun upgrade is expected to provide several enhancements to the Ethereum network:
- Scalability improvement: The introduction of Proto-Danksharding is expected to increase transaction processing speed and volume, especially beneficial for establishing L2 solutions on the Ethereum main blockchain.
- Gas fee reduction: By integrating data Blob and activating EIP-4844, transactions become more cost-effective.
- Security progress: The implementation of EIP-6780 in this upgrade aims to improve network security measures, providing stronger protection for user data and investments.
- Optimized data storage: The implementation of EIP-1153 in this upgrade will bring more efficient blockchain data storage, improve operations, and reduce costs, benefiting second-layer solutions that rely on simplified data management.
- Cross-chain enhancement: EIP-4788 in this upgrade aims to improve the usability and security of cross-blockchain interactions, supporting enhanced interoperability with second-layer solutions.
The core content of the Cancun upgrade is the EIP-4844 protocol—introducing Proto-Danksharding, which is a precursor to Danksharding. This protocol may reduce L2 transaction fees by 10 to 100 times.
Danksharding is a solution that describes how L2 can separately design a data type Blob (specifically used to store transaction data submitted from L2 to L1) and separate it from Layer1's Calldata. This way, the Blob data type only needs to be accessed and verified by those in need within a certain period of time, without the need for Layer1 execution layer to execute all of it, significantly reducing the burden on Layer1.
The Proto-Danksharding introduced in the Cancun upgrade is the first step in the comprehensive expansion of Ethereum. Each Blob introduced in this phase has a size of 128 KB, and each Ethereum block is planned to contain 3-6 Blobs (0.375 MB - 0.75MB), gradually expanding to 64 in the future. In comparison, the current data size that each Ethereum block can accommodate is less than 200KB. With the introduction of Blob, the data capacity of Ethereum blocks will significantly increase. Therefore, Proto-Danksharding will lay the foundation for further complete Danksharing, introducing block proposers and builders separation, and implementing data availability sampling.
The specific content of the Cancun upgrade (completed technical improvements) includes:
- Introduction of Blob transactions: Blob is an abbreviation for Binary Large Object. Blob transactions are a new type of transaction that will be used in future sharding.
- Introduction of all execution layer logic required for future complete sharding implementation.
- Introduction of cross-verification logic between all execution and consensus layers required for future complete sharding implementation.
- Implementation of layering between beacon block verification (i.e., Ethereum Layer 2 data) and Blob data availability sampling.
- Introduction of most of the logic required for future complete sharding in beacon blocks.
Sharing of Cancun upgrade favorable projects
For this upgrade, it is directly beneficial to the entire L2 ecosystem. According to the data statistics from I2fees.info on 2023/12/11, the introduction of Blob has significantly reduced L2 transaction fees and to some extent increased throughput. It has also further promoted the development of Restake and DA track projects.
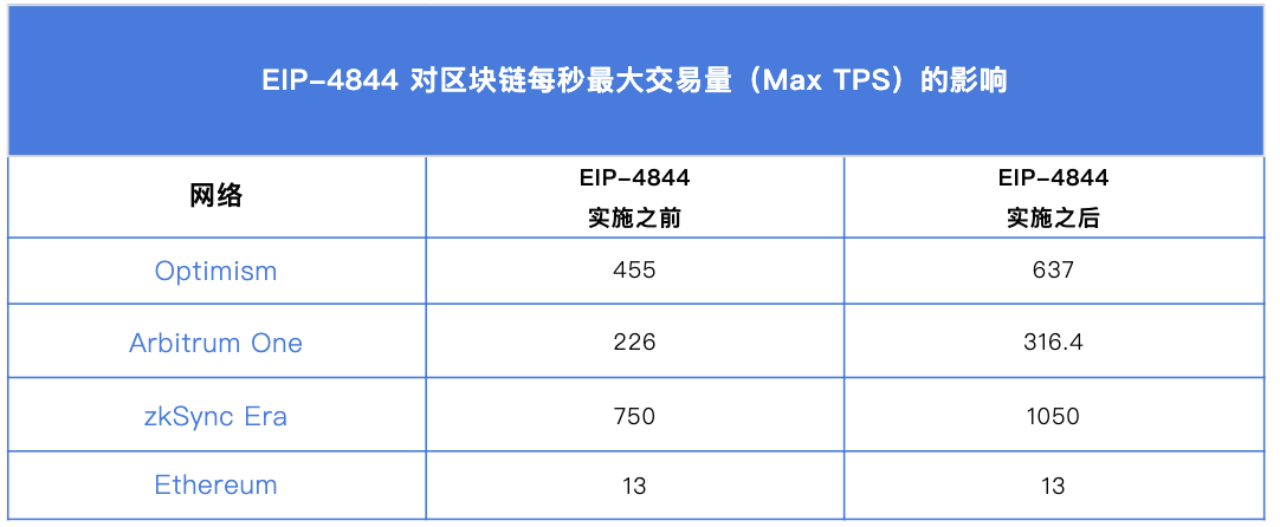
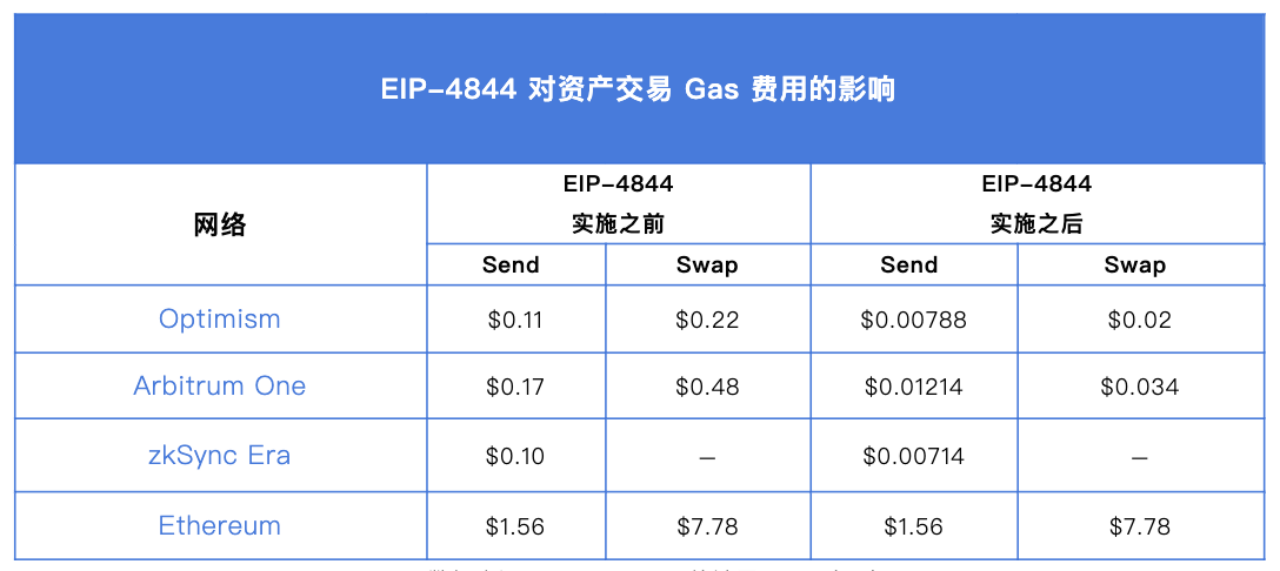
1. Arbitrum
As a leader in Ethereum L2, Arbitrum currently has the most diverse protocols of all types of L2. We believe that Arbitrum can largely benefit from this upgrade mainly for the following reasons:
- Large number of protocols: According to incomplete data statistics from DeFiLlama, the number of protocols on Arbitrum is approximately 520, far exceeding the second-ranked Optimism with 216.
- Large TVL volume: According to L2beat data, Arbitrum's current TVL is approximately 10 billion, accounting for 49.26% of Ethereum Rollup's TVL.
- Large transaction volume: According to L2beat data for the past 30 days, the network transaction volume ranking shows that Arbitrum has approximately 28 million in transaction volume, ranking second only to zkSync, which has not yet issued coins but still has a large amount of activity, and leading Optimism network by nearly three times in transaction volume.
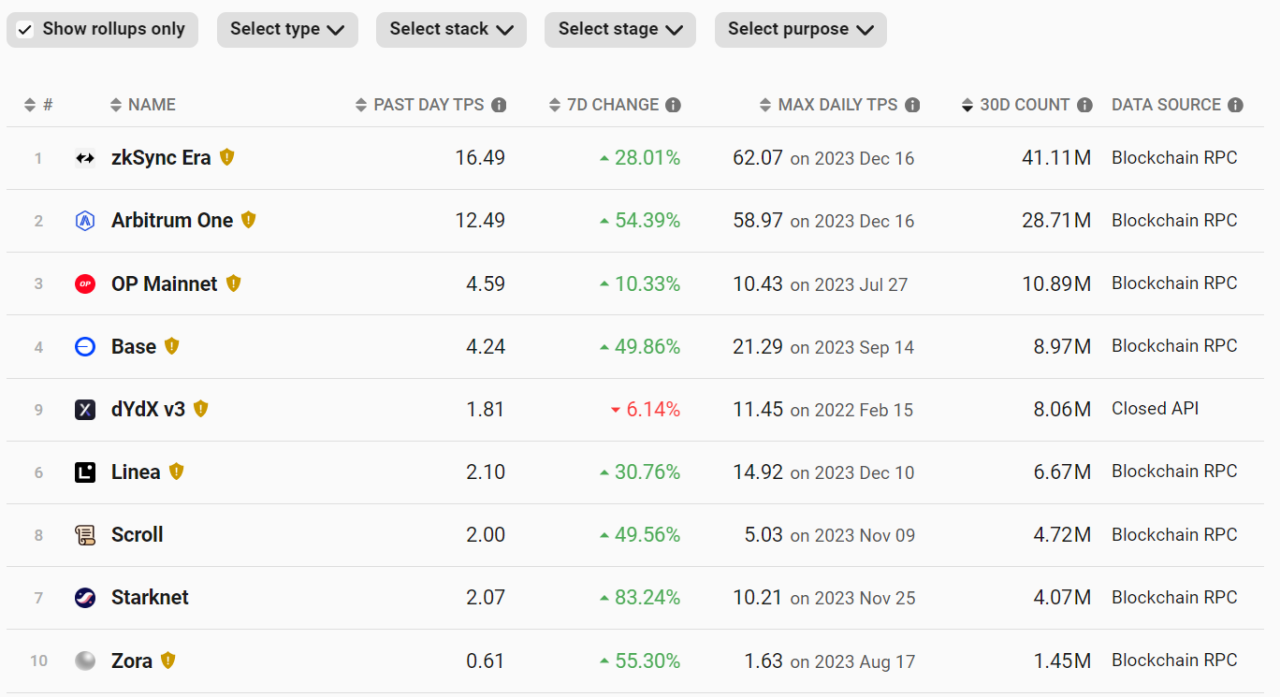
Taking into account the above three points, Arbitrum, as the leader in terms of volume, is obviously able to benefit more from the reduction in transaction fees and the optimization of TPS, which is also beneficial for the prosperity of protocols such as GMX and GNS with higher performance requirements on Arbitrum. From the perspective of network fundamentals, Arbitrum is undoubtedly one of the biggest beneficiaries of the Cancun upgrade.
2. Optimism
Different from Arbitrum, the focus of competition for Optimism is more on the Optimism Super Chain network built on OPStack. The value of Optimism depends more on the network value of Optimism Super Chain. Since the release of OP Stack, many projects such as Base, Lyra, opBNB, and Debank have built their own L2 based on OP Stack. The upgrade of OP Stack Bedrock version further optimizes transaction costs, transaction processing within blocks, and node performance, making it more attractive to build L2 based on OP Stack.
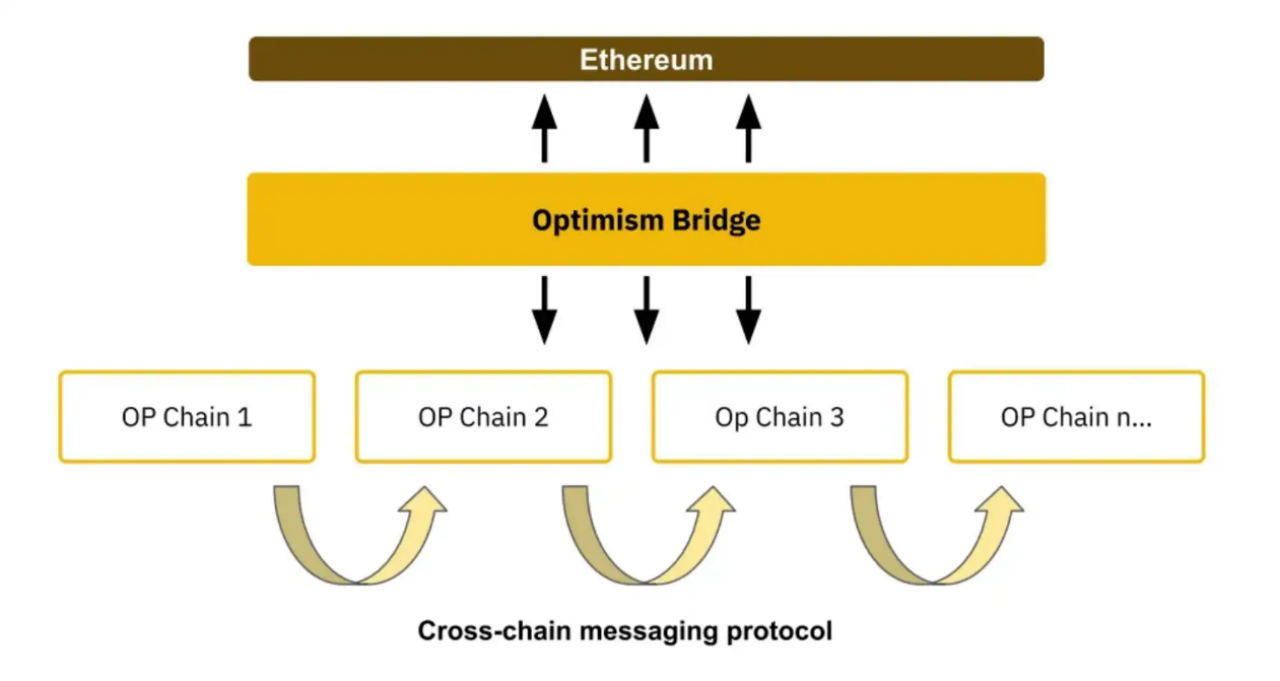
If the Cancun upgrade can benefit all L2 at the same time, then the upgrade premium enjoyed by Optimism is the combination of the network value brought by all Optimism ecosystems. If the Cancun upgrade can give birth to more new L2, then the upgrade premium enjoyed by Optimism is that more L2 chains will be built using OP Stack, and Optimism will be closer to the ultimate vision of the Optimism SuperChain super ecosystem.
3.EthStorage
EthStorage focuses on solving Ethereum's dynamic storage issues. Based on Ethereum's data availability, it provides a second-layer solution for programmable storage at a lower cost.

Due to the short-term storage of Blob data, there are issues with accessing historical data. Therefore, decentralized storage protocols will provide a new development channel, and L2 scaling solutions will also need to use data availability layers. EthStorage will significantly reduce the storage costs of a large amount of data on Ethereum, saving 100 to 1000 times the cost.
4.THORChain
THORChain is a decentralized cross-chain AMM trading protocol. The protocol aims to decentralize cryptocurrency liquidity through public nodes and ecosystem product networks, allowing individuals, products, or institutions to access local and cross-chain liquidity.
As a cross-chain bridge project, it mainly benefits from the EIP-4788 and EIP-4844 upgrades in the Cancun upgrade, with unexpected improvements in cross-chain bridge gas fees and confirmation times. Considering the influx of a large amount of funds into the BTC chain in the past six months, and the recent hype of Bitcoin ETF, these funds may flow into the Ethereum chain, so this sector may potentially gain Alpha returns.
5.Metis
Metis is an Ethereum L2 Optimistic rollup platform developed based on Optimism. By introducing powerful L2 technology, Metis provides a scalable and high-performance solution for Ethereum, offering users and developers a fast, efficient, and low-cost transaction experience.
With the emergence of more L2 due to the Cancun upgrade, the competition of decentralized sequencers may become increasingly severe. It is foreseeable that the competition of decentralized sequencers will become the core theme of L2 competition after the Cancun upgrade.

Metis may become the first Ethereum L2 to run a decentralized PoS sequencer. It has broken the centralized pattern of sequencers, allowing nodes staking at least 20,000 METIS tokens to enter the sequencer pool as sequencer operators. Sequencers in the pool will be responsible for determining the order of transactions, and at least 2/3 of sequencer signatures are required to upload data to the L1 mainnet. In addition, to further prevent sequencer misconduct, Metis also introduces the role of validators to conduct sample surveys on blocks to ensure the correct sequencing of transactions by sequencers.
6.EigenLayer
As the staking amount on Ethereum continues to increase, the demand for re-staking is becoming increasingly prominent. EigenLayer allows users to re-stake ETH, lsdETH (ETH staked in liquidity), and LP Tokens on other side chains, oracles, middleware, etc., as nodes and receive validation rewards. This allows third-party projects to enjoy the security of the Ethereum mainnet, and ETH stakers can also earn more rewards.

In addition, EigenLayer has announced to provide re-staking services for Cosmos, allowing Cosmos to gain the security of Ethereum and opening up a new world of incremental returns for Ethereum stakers.
7.Kelp DAO
Kelp DAO is a Restaking project by the multi-chain LSD project Stader Lab, belonging to the Liquid-LSD Restaking type mentioned earlier. It currently allows deposits of Lido's stETH and Stader's ETHx LST tokens, but due to the full capacity of EigenLayer LST, deposits are currently suspended.

Although Stader Lab has issued tokens, Kelp DAO has introduced a point system. As a sub-project of Stader Lab, Kelp DAO is expected to launch its own token. It is also possible to expect a synergistic effect between SD (Stader Lab's token) and Kelp DAO.
8.ether.fi
ether.fi is a product of the Liquid Native Restaking type, which has received a $5.3 million seed round investment from BitMEX founder Arthur Hayes. Different from Lido, ether.fi uses a decentralized, non-custodial method to stake ETH and provides re-staking services. As it is native ETH re-staking, it is not affected by the limit of EigenLayer LST and can still be deposited. The collateral token eETH (wrapped token weETH) is one of the few LRT collateral tokens with liquidity.

9.Celestia
Celestia uses a modular architecture to deconstruct the blockchain into data, consensus, and execution. Most blockchains still bundle consensus and execution functions on one layer, and build smart contracts on that layer. Users are bound to this execution environment, greatly limiting the potential for optimization and specialization for specific use cases.

The modular architecture of Celestia places the execution layer on its own blockchain, allowing optimization and specialization for specific use cases. Any developer building decentralized applications based on this architecture will have more complete security and scalability on the original blockchain execution layer. In the modular blockchain of Celestia, data availability sampling is achievable, allowing nodes to verify a block with a small sample, and low hardware configuration devices such as home computers and mobile phones can act as nodes.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



