Speculative changes that once seemed distant are now being realized with a clear direction.
Written by: Heechang
Translated by: Block unicorn
Key Points
Until 2025, many on-chain assets were merely concepts. Now, they are developing in a clear direction and gradually becoming a reality. Structural changes are occurring simultaneously across three dimensions: the form, meaning, and use of currency.
First Transformation: The form of currency is diversifying. Stablecoins, tokenized bank deposits, and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) will coexist in different roles. Fiat currency on-chain and off-chain channels, payment infrastructure, and IT platforms are rapidly adopting stablecoins to expand the post-issuance business landscape and usage ecosystem at a faster pace.
Second Transformation: The concept of currency is broadening. Tokenization is transforming not only physical and financial assets but also intangible elements like attention and predictions into assets. This breaks down the boundaries between currency and assets, redefining both and moving towards a world where "everything we own" becomes a unit of liquid value.
Third Transformation: The use of currency is expanding. Centralized exchanges are moving beyond mere trading venues to build a full-stack financial ecosystem that encompasses derivatives, risk-weighted assets (RWAs), on-chain debit/credit cards, on-chain decentralized finance (DeFi), and even their own networks. As a result, the use cases of blockchain in the real world are increasingly diversifying around the central hub of exchanges.
All finance will ultimately run on the blockchain.
This was my original intention for entering the blockchain industry. Even in the face of crises like the collapse of Terra, I cannot imagine an ideal financial system—a system that is efficient, transparent, and programmable—being realized without blockchain at its core. I personally believe that the most advanced financial infrastructure can only be built on-chain, and over time, existing systems will inevitably converge towards this structure.
The year 2025 will be a year when this transformation moves towards reality. With the improvement of regulations, financial institutions, fintech companies, and governments are no longer entangled in whether to adopt blockchain. Today, the question has completely shifted from "when to adopt" to "how to participate."
Speculative changes that once seemed distant are now being realized with a clear direction. The essence of currency—its form, its concept, its use cases—is simultaneously undergoing structural transformations across three dimensions.
Now, let’s explore how these transformations are unfolding and examine the key forces driving this change.
1. First Transformation: Stablecoins Bring Diversification to the Form of Currency
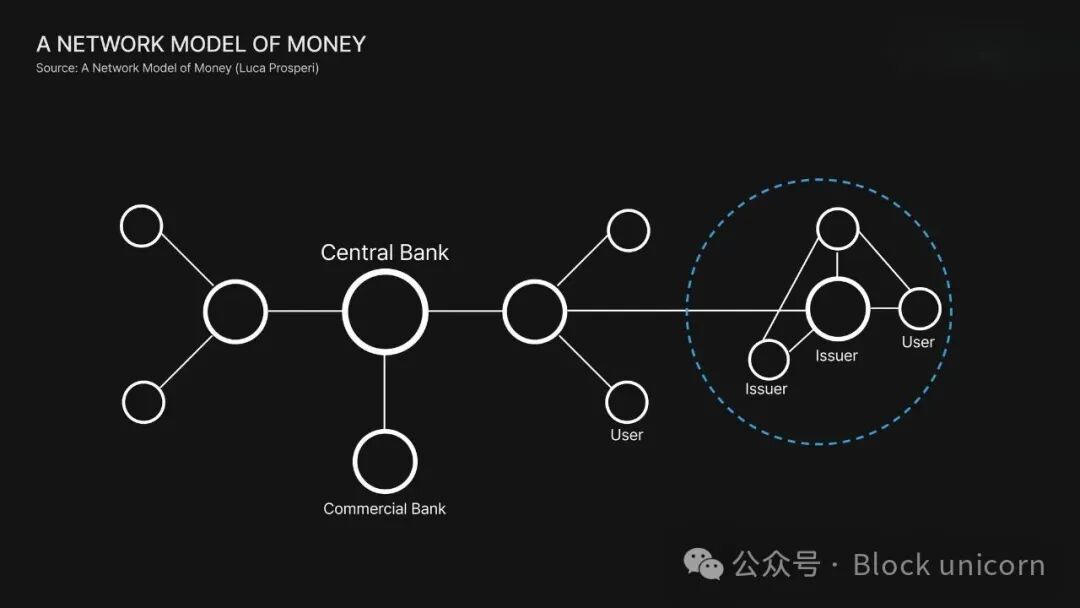
Source: "Currency Network Model" — Luca Prosperi
At its core, currency is the asset benchmark we use to measure value. When we purchase or exchange goods, we price them in our national fiat currency. Historically, only two institutions have issued and operated such currency: central banks and commercial banks. Central banks are responsible for managing the total amount and stability of currency, while commercial banks operate the flow of funds between institutions and retail.
Stablecoins add a whole new layer to this. They enable any company to create its own form of currency and build financial infrastructure around it, creating particularly powerful synergies with digital platforms. This does not mean that stablecoins will replace central banks or commercial banks. On the contrary, just as PayPal and Stripe have reshaped payment methods, and Robinhood has changed how people invest, save, and consume, stablecoins introduce a new type of currency designed specifically for the digital world.
Three major trends emerged in 2025.
Stablecoins, Tokenized Bank Deposits, and CBDCs Will Coexist Long-Term
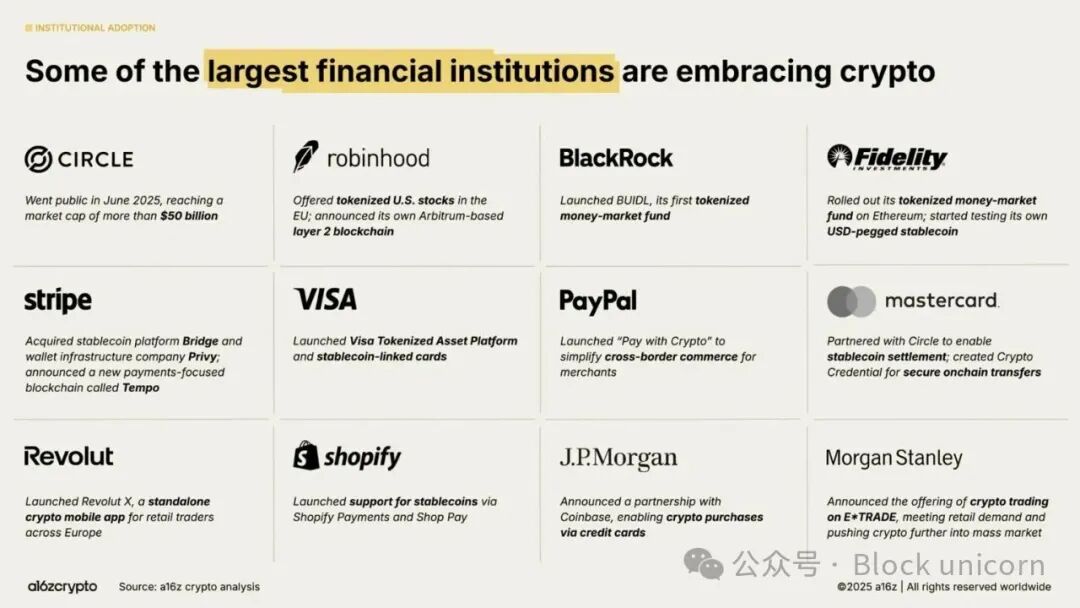
Source: "2025 Cryptocurrency Status: A Year of Mainstreaming Cryptocurrency" - a16z crypto
In the United States, the first comprehensive federal stablecoin legislation—the "GENIUS Act"—was passed by both houses of Congress and signed into law on July 18. This act introduces a licensing system for banks and stablecoin issuers and mandates that reserves must be held in cash or short-term government bonds at a 1:1 ratio.
Hong Kong has acted even more swiftly. The Legislative Council passed the "Stablecoin Ordinance" in May 2025, officially making stablecoin issuance a regulated and licensed activity starting August 1, with approval expected by early 2026.
Japan clarified the issuance qualifications for stablecoins based on amendments to the "Payment Services Act" in 2023 and initiated its first large-scale issuance in the second half of 2025. JPYC issued a stablecoin backed by yen, with reserves fully held in domestic deposits and government bonds, and fully redeemable for yen. Japan's framework strictly limits issuers to licensed financial institutions and allows for the use of trust structures to enhance the segregation of investor assets.
Among commercial banks, JPMorgan Chase continues to expand deposit tokenization and real-time settlement through its private blockchain network Kinexys. JPM Coin allows corporate clients to convert dollars in their JPMorgan accounts into on-chain tokens, which can be used for instant transfers or large settlements between global subsidiaries.
I believe that stablecoins are not here to replace the existing currency system; rather, they will coexist with central bank currencies, bank deposits, and new digital assets—each playing different roles. Let’s review these roles.
Central banks play the role of controllers. They issue fiat currencies like the dollar, manage the money supply, and provide ultimate backing during financial stress.
Commercial banks act as coordinators. Under the supervision of central banks, they operate deposit accounts, provide credit, and facilitate the flow of funds between depositors and borrowers. In short: if central banks issue dollars, commercial banks create deposit forms like "JPMorganUSD."
Stablecoins serve as catalysts. Backed by cash or short-term sovereign debt, stablecoins are not intended to replace central banks or commercial banks. Instead, they can help businesses build a digital-first financial ecosystem and enable funds to circulate faster and more widely across various services.
Ultimately, the future is not about replacement but coexistence. Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) will reinforce monetary sovereignty and macro-level stability. Tokenized deposits will maintain a regulated financial intermediation system. Stablecoins will fill the gaps left by the slower speeds of central banks and commercial banks while meeting the speed, programmability, and interoperability required by the digital economy.
Each form of currency will play a complementary role in an increasingly on-chain financial system.
Companies Controlling the "Next Layer" of Stablecoin Issuance Will Rise Rapidly
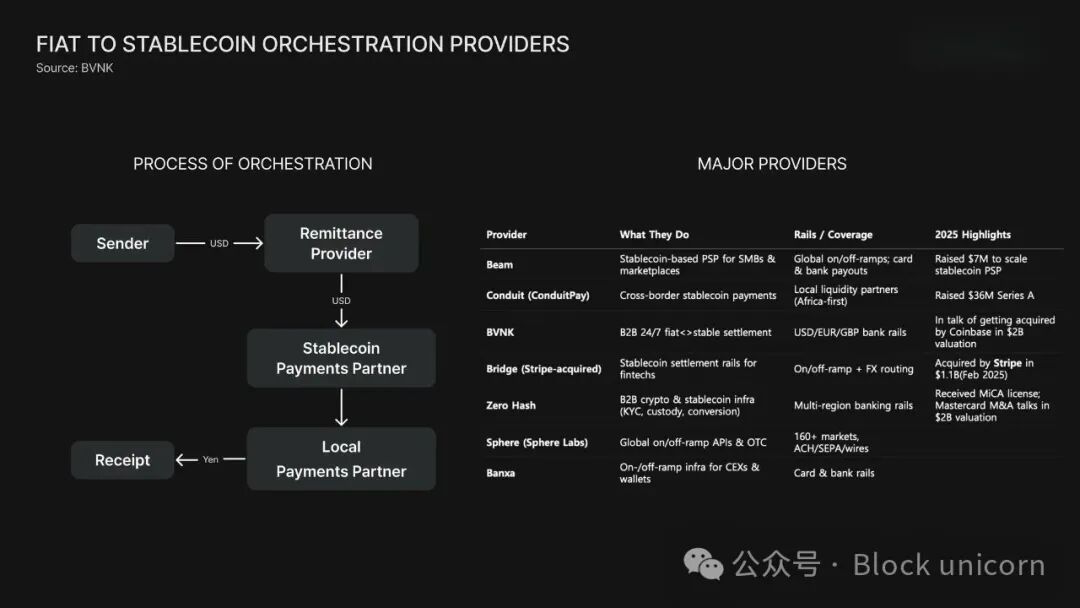
For stablecoins to be truly utilized, issuance is a primary requirement. However, to make stablecoins functional in daily life or business operations, a key step is needed: converting stablecoins to local currency and vice versa. In 2025, a large number of companies began integrating the infrastructure needed for these on-chain and off-chain payment processes.
Yellowcard, the largest cryptocurrency payment gateway in Africa, has become a regional hub capable of connecting stablecoins with local currencies while fully complying with regulatory requirements in various countries. Bridge, acquired by Stripe for $1.1 billion, also plays a similar role. Companies like Zero Hash and BVNK—reportedly being considered for acquisition by Mastercard and Coinbase for around $2 billion—now provide backend infrastructure for businesses, exchanges, and fintech platforms, enabling the large-scale practical application of stablecoins.
These services provide secure payment settlements and anti-money laundering/know your customer (AML/KYC) workflows, allowing businesses to accept stablecoins and convert them into local currency without circumventing domestic payment regulations. This architecture indicates that stablecoins are deeply integrating into the existing financial system rather than existing outside of it.
Large exchanges like Binance, Bybit, and OKX are also expanding their payment gateway functionalities, some developing them in-house while others outsource fiat channels to specialized partners. Payment companies like Banxa, Mercuryo, and OpenPayd play a core role in this ecosystem, providing fiat payment channels that seamlessly integrate with stablecoin trading processes.
All of this points to a clear transformation: the definition of stablecoins is no longer limited to their issuance but increasingly empowers individuals and businesses to use them more effectively.
IT Platforms Will Begin to Fully Embrace Stablecoins
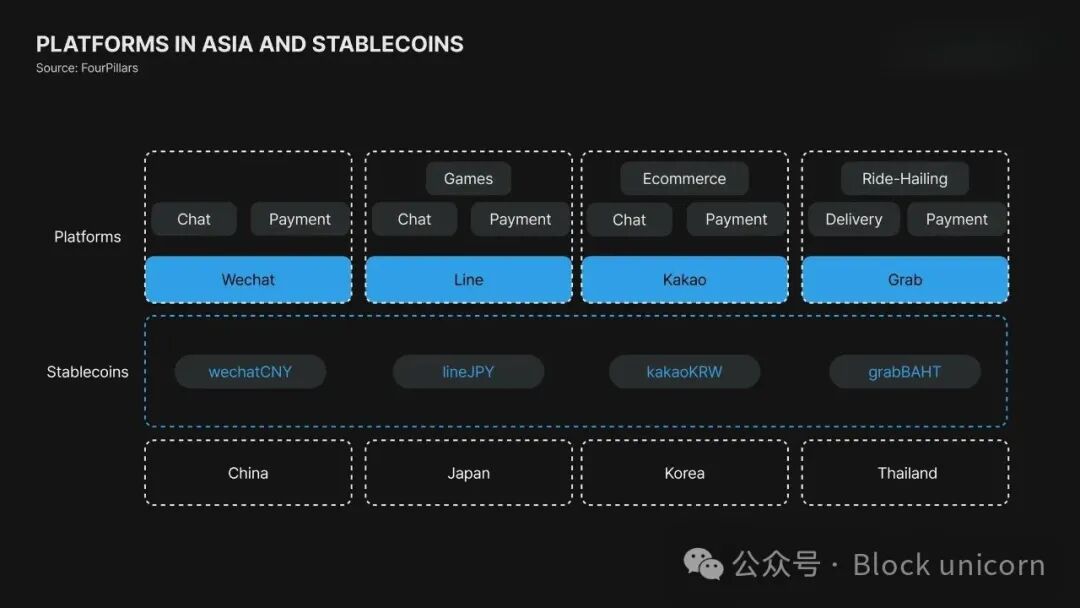
IT platforms, which are central to everyday consumer activities and business operations, are becoming the most powerful hub for expanding stablecoin applications. Asia's "super apps" integrate instant messaging, shopping, payments, and financial services, and their (non-cryptocurrency) digital wallets have created significant user engagement and transaction volume. By internally integrating stablecoins, these platforms can build their own native financial ecosystems and significantly enhance user participation.
By 2025, both PayPal and Cloudflare have launched stablecoin-related initiatives aimed at making them mainstream payment and internet infrastructure.
PayPal has integrated PYUSD into remittances, business, and e-commerce settlements, and recently invested in Stable. Stable is a Layer 1 blockchain optimized for payments based on USDT, further streamlining PayPal's global payment infrastructure.
Cloudflare launched Net Dollar, a stablecoin designed to allow AI agents to autonomously settle API fees and cloud usage fees, effectively embedding programmable currency into internet services.
This marks a broader transformation: stablecoins are becoming the foundational currency unit of the platform economy. Whether a platform issues its own stablecoin or collaborates with external issuers like Circle and Tether, stablecoins are beginning to serve as the standard currency within these digital ecosystems.
2. Second Transformation: Tokenization Expands the Concept of Currency
Through tokenization, asset ownership is transferred to the blockchain. In the past, ownership was recorded in paper documents, bank accounts, or centralized databases.
On-chain, ownership can be divided into several shares, which can be transferred under specific conditions, automatically distributed as income, or deposited and traded through smart contracts.
This structure greatly expands the accessibility of assets. Historically, markets for assets such as stocks, bonds, or private credit were only open to institutions or high-net-worth individuals. However, once tokenized, the same asset can be divided into thousandths of a share and traded in real-time. Individuals can now participate through share ownership, opening up entirely new modes of investment and consumption.
Ultimately, tokenization expands the very definition of currency itself.
What we traditionally refer to as "currency"—a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account—is no longer limited to fiat currency. An increasing number of assets can themselves perform currency functions. Government bonds, money market funds, investment funds, real estate, and even corporate equity are all becoming programmable forms of currency that can be programmed and utilized.
The Tokenized Asset Market Will Accelerate Growth
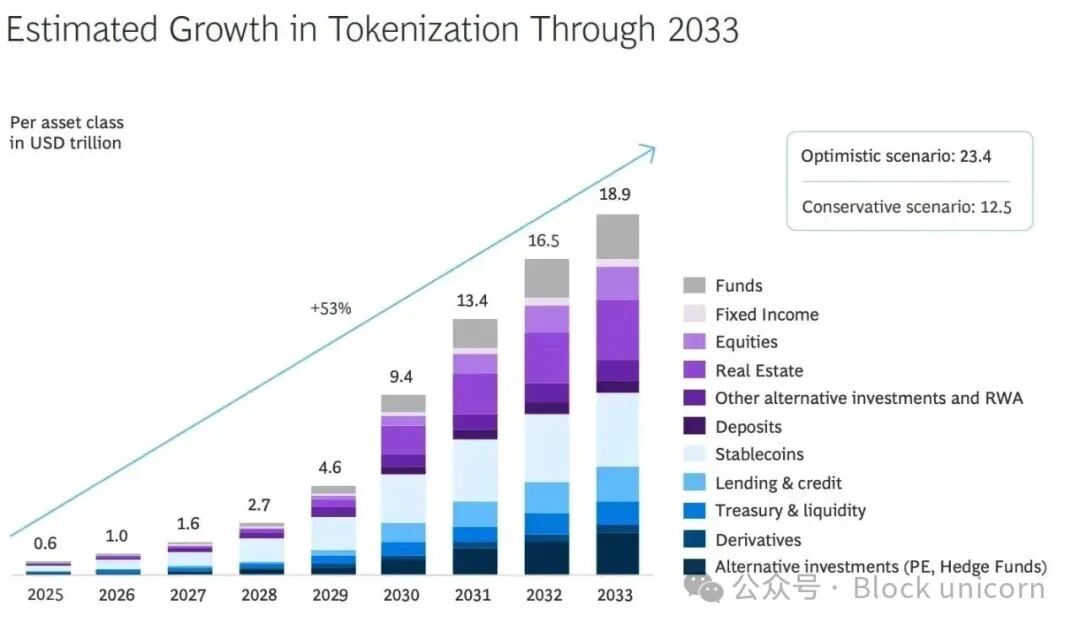
Source: RWA News: Ripple and BCG report that by 2033, the scale of tokenized real-world assets could reach $18.9 trillion.
Just five years ago, the stablecoin market was only $20 billion. Today, it has surpassed $300 billion, while the market for tokenized real-world assets (RWA) has grown from $13 million to $3.47 billion. Digital dollars, tokenized government bonds, and tokenized money market funds have become tangible investment and settlement tools for both institutional and individual investors.
At the core of this trend are global financial institutions. BlackRock provides on-chain exposure to U.S. government bonds through its tokenized money market fund BUIDL. Apollo has tokenized private credit funds, opening new liquidity channels for traditionally illiquid assets. Securitize, which provides infrastructure for these products, can now tokenize funds, equity, and alternative assets, and is even seeking to go public in the U.S. Tokenization has far surpassed the realm of blockchain startups, extending to global financial giants.
According to a joint report by Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and Ripple, the tokenized market is expected to grow 30-fold in the next eight years, reaching approximately $18.9 trillion by 2033.
The direction of development is clear: tokenized assets are becoming one of the fastest-growing areas in the global financial system.
Even Intangible Assets Will Be Tokenized

Source: Kalshi founders Tarek Mansour and Luana Lopes Lara discuss how to turn events into assets.
This year, Kaito introduced a new concept. Kaito uses a unit called "yap" to measure and quantify the extent to which a topic is mentioned or promoted on Twitter, thereby introducing the concept of the attention economy. In short, public attention is transformed into a measurable unit of value.
Prediction markets have also gained significant attention. Strictly speaking, prediction markets are not the same as tokenization, but they are conceptually similar in that they both transform non-financial information or future events into tradable assets.
Tokenization converts tangible assets or financial products such as government bonds, real estate, and funds into on-chain tokens. Prediction markets, on the other hand, convert future possibilities, such as "Will a certain candidate win the election?" into tradable contracts.
In other words, tokenization grants ownership of existing assets, while prediction markets assign value to a certain probability.
Platforms like Polymarket and Kalshi issue each event as "yes/no" tokens. After the event concludes, the winning side receives a settlement amount of $1. Unlike tokenized assets that use collateral or legal trust structures for redemption, prediction markets use oracles and verified data for settlement, relying on the "truth of the outcome."
However, both systems adhere to a core principle: they transform originally non-tradable underlying assets into market-native assets with price and liquidity.
Ultimately, prediction markets represent the tokenization of beliefs and information, shifting the focus from "What do you own?" to "What do you believe, and how do you value it?"—thus expanding the category of assets in the blockchain world.

Source: X User — Crypto_Dep
Tokenization Will Completely Change Our Understanding of Currency
The essence of tokenization is not merely transferring assets to the blockchain but changing the way assets operate. Traditionally, "currency" (like the dollar or euro) and "assets" (like bonds, stocks, or real estate) were viewed as two separate domains. Tokenization merges these two domains into a unified system.
Government bonds, venture capital funds, and even real estate can now be represented as programmable, interoperable tokens that can be transferred instantly and directly integrated into various services. Once tokenized, assets can be used, stored, and priced in real-time. This breaks down the boundaries between what we own and what we can use, erasing the distinctions that previously separated financial products from liquidity.
Our traditional financial thinking is linear: we earn money → save money → invest → consume. Tokenization breaks the distinction between "currency" and "assets." Everything we own becomes a fluid expression of value.
3. Third Transformation: The Rise of Centralized Exchanges (CEX) and the Expanding Uses of Currency
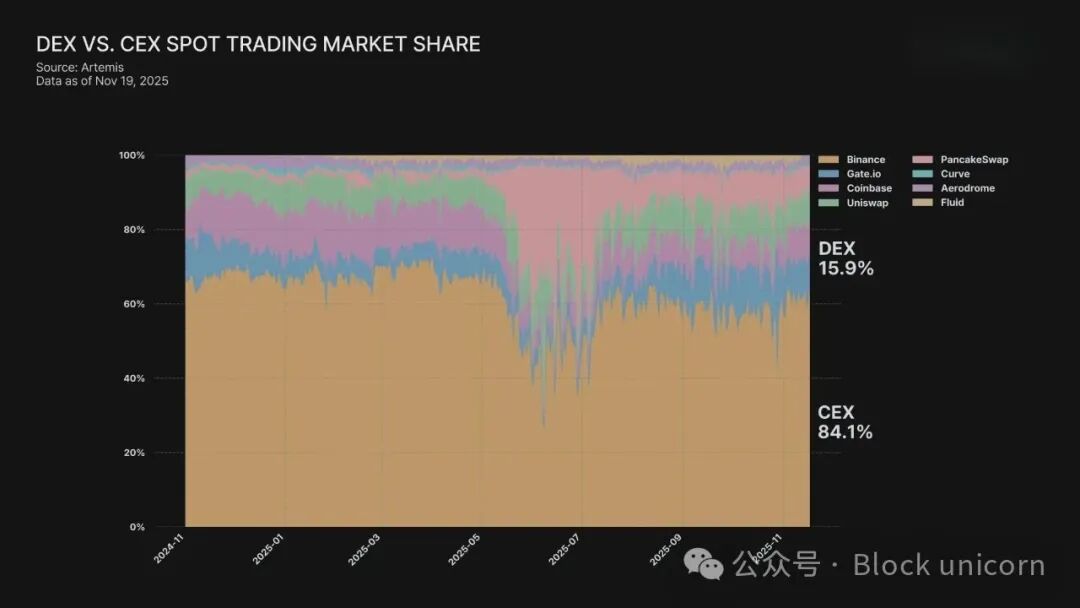
Source: Gate Research: "The Ecosystem Landscape and Integration Trends of Centralized and Decentralized Exchanges"
"How much has it gone up?"
For a long time, this simple question has been the driving force of the cryptocurrency market. News of Bitcoin rising 1000%, Ethereum soaring, or new tokens skyrocketing always captures public attention. Price volatility has become the focal point of market interest, and trading has become central to everything.
Centralized exchanges are at the heart of these trading activities.
Binance, founded in 2017, now has a daily trading volume of about $100 billion, making it one of the most liquid exchanges in the global financial market. Bybit (2018) and OKX (2017) follow closely, while exchanges like Upbit and Coinbase have become major gateways for cryptocurrencies in their respective markets.
Although decentralized exchanges have developed rapidly, the vast majority of trading volume still occurs off-chain, within centralized platforms.
In regions like South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan, regulatory restrictions and user awareness have limited on-chain activities to only a portion of users. Transitioning users from centralized exchanges to decentralized ecosystems requires not only technological changes but also a psychological shift—this transition is by no means easy.
Centralized exchanges remain the primary entry point for most users to access cryptocurrencies, shaping the flow, trading, and circulation of funds in the digital economy.
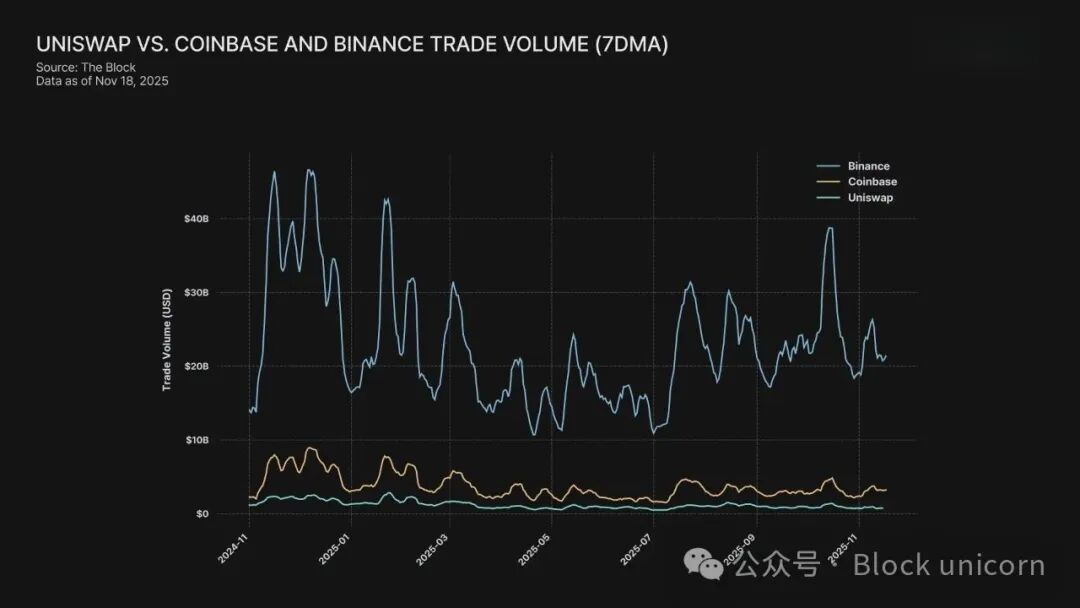
Source: Comparison of trading volumes between Uniswap and Coinbase and Binance (7-day moving average)
These platforms are no longer just cryptocurrency exchanges—they are evolving into comprehensive digital asset financial ecosystems.
The services offered by exchanges today go far beyond simple spot trading. They now provide perpetual contracts, options, and various structured derivatives, and have recently even supported the trading of tokenized stocks and risk-weighted assets (RWAs).
For example, Bybit has integrated tokenized stocks through xStocks, enabling 24/7 trading of tokenized stocks; Binance has expanded its business through derivatives and Launchpad, becoming a platform that encompasses the entire token economy.
Exchanges are also building a complete financial stack, integrating trading → deposits → lending → consumption.
As centralized exchanges transition to comprehensive financial infrastructures, it is essential to examine the strategies they are deploying and how they are preparing for the next phase of on-chain finance. Let’s delve into these strategies.
Exchange Services Will Continue to Expand
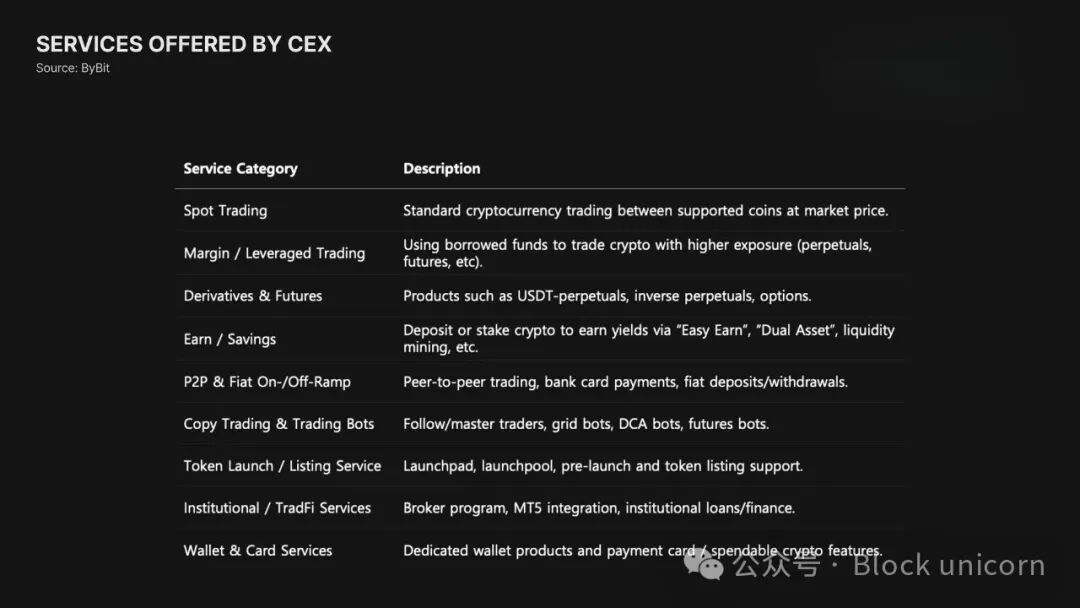
Exchanges are evolving from mere trading venues into "financial super apps."
In the past, users could only trade tokens that had already been listed. Now, with the launch of presale platforms, users can even trade before the token generation event (TGE). This allows users to directly participate in early projects with high growth potential, akin to participating in pre-IPO financing opportunities on-chain.
Launchpad platforms are also rapidly developing, becoming a way for new projects to distribute tokens before listing on exchanges. Binance, Bybit, and OKX all operate their own Launchpad platforms, attracting millions of participants and becoming key drivers for user acquisition. In this model, users are no longer just traders but become early stakeholders in the projects.
Exchanges are also continuously expanding their scope of business, shifting from cryptocurrencies to tokenized real-world assets (RWAs).
Bybit's xStock is a prime example: users can trade tokenized global stocks and ETFs around the clock, marking the rise of the trend of "decentralized access to traditional assets." The demand for on-chain investments in real-world assets is steadily increasing.
Coinbase has launched Bitcoin-based lending services through integration with the lending protocol Morpho; Robinhood is experimenting with prediction markets, further integrating new financial foundational functions directly into its platform.
In addition to trading, exchanges are building a complete service system aimed at maximizing the utility of customer assets, covering various aspects such as yield, credit, and consumption.
Yield products like staking and yield vaults provide substantial returns on assets held by exchanges. In terms of consumption, products like the Bybit Card and Coinbase Card directly connect cryptocurrency balances to everyday real-world payments.
In other words, exchanges are no longer mere intermediaries for buying and selling tokens.
They are becoming integrated on-chain financial platforms where saving, investing, lending, and consumption all occur within the same ecosystem.
Mature On-Chain Services Will Be Integrated into Exchanges
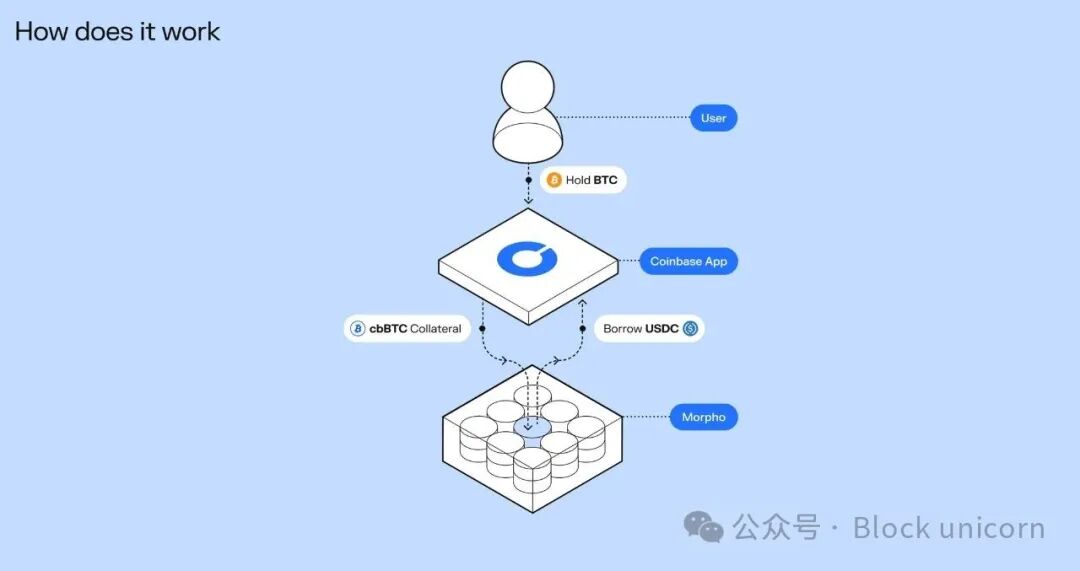
Source: Bitcoin lending from Morpho
Exchanges are no longer confined to their closed ecosystems but are expanding user functionalities by directly integrating on-chain financial services.
A typical example is Bybit integrating Ethena's USDe into its trading pairs and yield products. This allows users to add a yield-generating synthetic dollar, created and managed entirely on-chain, to their portfolios. This indicates that exchanges are increasingly viewing decentralized protocols as modular service components rather than external partners, embedding them directly into their platforms.
Coinbase has further propelled this trend. By connecting the main exchange application with the Base application, Coinbase now supports DEX trading and provides access to millions of on-chain assets. The boundary between centralized exchanges and decentralized exchanges is becoming increasingly blurred.
Users can access on-chain liquidity directly while maintaining a familiar centralized exchange interface, driving exchanges towards a hybrid CEX/DeFi model.
Coinbase has also directly integrated Morpho's lending infrastructure into its exchange application. Users can deposit Bitcoin and borrow USDC using Bitcoin as collateral, all supported by the underlying on-chain treasury. Since its launch in January, Coinbase's Morpho-based treasury has grown rapidly, with deposits reaching $1.48 billion and loans totaling $840 million.
These developments point to a grander direction:
Exchanges will increasingly support battle-tested on-chain services within their applications. This provides users with higher yield opportunities and greater asset utility while allowing exchanges to expand services without assuming protocol risks.
In fact, on-chain services are being integrated into the back end of centralized exchanges, and the user experience is gradually and seamlessly migrating on-chain.
Exchanges Will Build Their Own Ecosystems

Exchanges are no longer solely reliant on external blockchains. They are increasingly building their own or closely collaborating with blockchains that support their vertically integrated ecosystems.
A typical example is Binance's BNB Chain.
BNB was initially just a simple trading fee discount token, but it has now evolved into a fully independent ecosystem that hosts hundreds of projects, covering decentralized exchanges (DEX), NFT markets, RWAs, and more. Binance leverages this architecture to seamlessly migrate exchange users to its own on-chain services, thereby expanding the utility and demand for the BNB token.
Bybit has also adopted a similar strategy through Mantle. Bybit builds trading incentive mechanisms centered around the MNT token, guiding users through liquidity incentives and ecosystem collaborations.
Coinbase, with tens of millions of users, utilizes Base to provide on-chain services to its exchange customers. Base has become home to popular applications like Morpho and Aerodrome, showcasing how a blockchain operated by a centralized exchange (CEX) can evolve into a vibrant on-chain environment.
In the U.S., Robinhood is preparing to launch its own Layer 2 blockchain, aimed at directly handling tokenized stock, options, and cryptocurrency trading on-chain, effectively merging its traditional brokerage infrastructure with a blockchain settlement system.
Vertical integration allows them to control trading, liquidity, user traffic, and settlement on a unified platform, creating a tightly-knit ecosystem for end-to-end circulation of digital assets.
4. Understanding Change is More Important than Feeling Change
It has been less than a decade since Ethereum was born. Just five years ago, the stablecoin market was only worth a few billion dollars, and the tokenization market was virtually ignored. Today, both have developed into markets worth hundreds of billions of dollars, becoming new cornerstones of global financial infrastructure.
The pace of future transformations will be faster, and the impacts will be more diverse. Of course, on-chain services are not perfect at present, and challenges regarding security, usability, and regulation still exist. However, without understanding the current environment, one cannot grasp the next wave of opportunities. Transformation is not slowly arriving in the distant future; it is accelerating from the subtle changes that have already begun.
The elements of blockchain are no longer described using technical terms like "decentralization," but are expressed in financial language—yield products, cross-border remittances, payments. Only when more people learn to interpret and understand the world using on-chain language can they truly comprehend the transformations reshaping the financial landscape.
This year marks the beginning of this shift. I hope more people can move beyond merely "feeling" this change and start to truly understand and prepare for what lies ahead.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




