Robots need encryption, a key operational guarantee for a world without humans.
Author: Krix
Translation: Deep Tide TechFlow
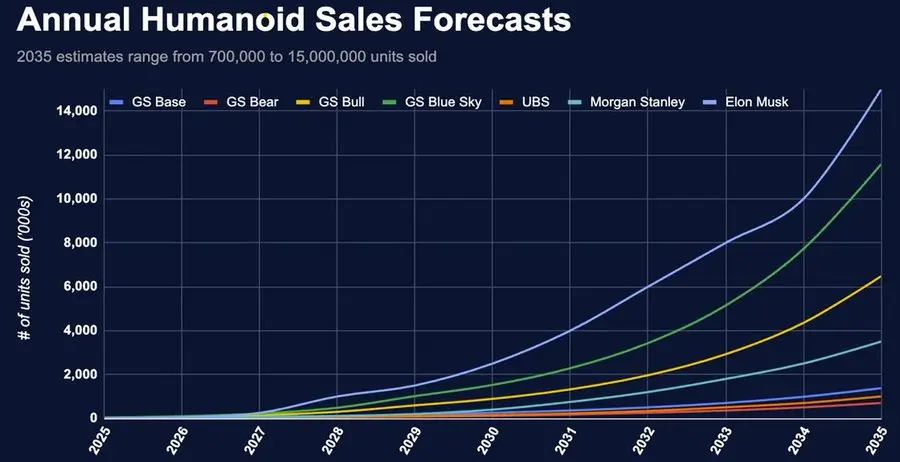
Morgan Stanley predicts that by 2050, the number of humanoid robots (Note: robots that resemble humans and can act like humans) could reach nearly 1 billion, and Elon Musk has stated that by 2040, the number of humanoid robots will exceed that of humans. The discussions about how the world will operate in the coming decades are both exciting and genuinely concerning.
With increased production efficiency, reduced costs, and advancements in materials and technology, many thought leaders believe we are on the brink of a robotic era. It is expected that by 2029, this will drive the robotics market size to $73 billion.
Clearly, most of the growth will come from private equity. However, as the regulatory environment in the crypto space becomes clearer, more and more startups will turn to blockchain to raise funds efficiently and quickly through token sales.
At this stage, the total valuation of the robotics industry in the crypto space is approximately 250 million dollars. This is just a drop in the bucket.
The purpose of this article is to provide a clearer overview of the existing subfields and introduce some of the most promising projects.
Why Robotics Needs Encryption
Before delving into the value propositions of these projects, it is essential to clarify the key connections between these seemingly distant fields.
- Collaboration Layer
In a world where a swarm of robots works collaboratively (e.g., delivery drones or factory robots), a collaboration layer is needed to enable these independent machines to cooperate beyond the limitations of their operating systems.
- Financial Layer
Traditional payment systems cannot meet the demands of large-scale microtransactions due to issues of fees and delays. The low-cost, instant blockchain transactions in the crypto space enable a seamless machine-to-machine (M2M) economy, which is crucial for a future where billions of robots operate without human supervision.
- Decentralized Ownership and Leasing Models
The high cost of robotic hardware (e.g., an Optimus robot costs between $20,000 and $30,000) limits its widespread adoption.
The crypto space can enable fractional ownership through NFTs or tokenization, allowing individuals to invest in or lease a fleet of robots.
One can envision a market that transforms this concept into "Robot-as-a-Service" assets, making it easier for small businesses and consumers to access robots.
- Data Security and Verifiability
Robotic technology relies on vast datasets for AI training, but centralized data storage poses risks of leaks or manipulation.
Blockchain provides immutable and verifiable data records, ensuring that the data generated by robots (e.g., sensor inputs) is secure and tamper-proof.
This is crucial for regulatory compliance and trust in applications such as healthcare or elder care robots.
- Funding and Community Alignment
Developing advanced robotic technology requires significant funding, but traditional venture capital models progress slowly and have a high equity investment ratio. Crypto space launch platforms and token sales offer a fast, community-driven funding method that balances incentives between developers and users.
With the advantages listed above, it becomes clearer what areas need attention.
Now, let's get to the main topic.
Openmind
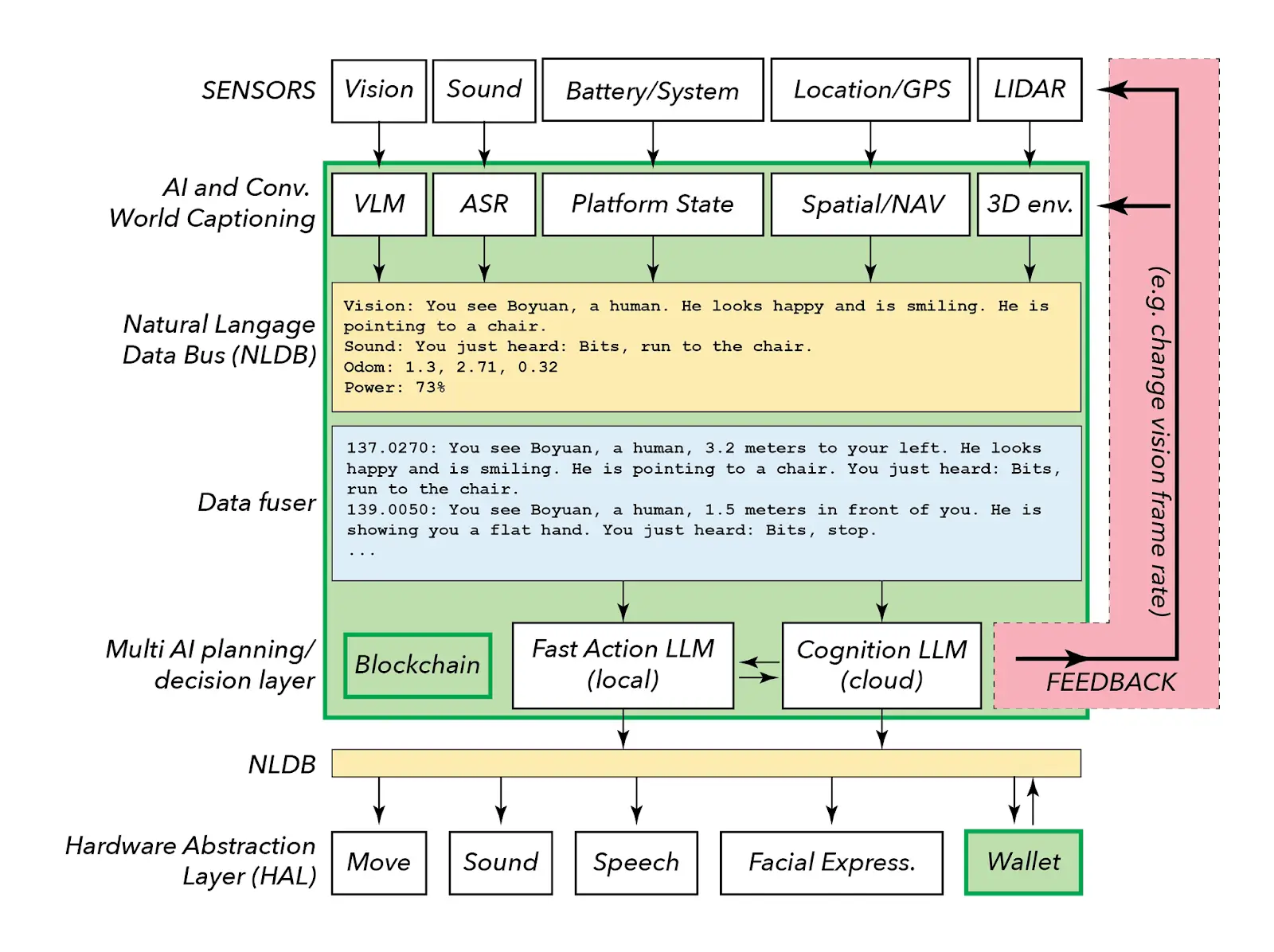
Recently, OpenMind secured 20 million dollars in investment from industry leaders like Pantera Capital and has become one of the leaders in the field with its interoperability layer FABRIC (a digital nervous system for intelligent machines worldwide).
Fabric provides core primitives for identity, location, verification, and settlement, transforming individual robot collections into a unified collaborative ecosystem.
Fabric achieves multi-agent collaboration and real-time decision-making through the following four key features:
Verifiable Machine Identity: Each machine receives an independent and cryptographically secure identity (ERC-7777), enabling trustless verification, preventing fraud, and ensuring the integrity of communication.
Location Proof: A decentralized and tamper-proof GPS system that allows machines to prove their physical location, which is crucial for collaboration and shared mapping.
Task Verification: A standardized protocol for verifying task completion using cryptographic signatures of sensor data or digital proofs, while triggering automatic payments.
Stablecoin Settlement: A built-in payment layer that uses stablecoins for frictionless, real-time settlements without worrying about volatility or reliance on traditional financial systems.
FABRIC provides seamless connectivity for the future workforce, while OM1 is an open-source AI-native operating system that allows developers to configure and deploy agents in digital and physical environments.
This means you can create an AI character that can run on cloud or physical robotic hardware (e.g., Quadrupeds, TurtleBot 4, and Humanoids).
Notably, the project recently launched the OpenMind App, dubbed the "Uber of the robot world." Yes, the app also involves a points system.
Original tweet link: Click here
Auki
Auki is another heavyweight that has been deeply involved in this field for over 5 years. Focusing on spatial computing, Auki addresses the challenge of AI exhibiting intelligence in the real world through its technology called Posemesh.
Posemesh is built on a DePIN network that can securely and privately share spatial data and computing power of digital devices. This enables robots to collectively understand the physical world and interact better with each other.
You do not need to share camera information with centralized entities; instead, you can privately exchange spatial data with other peers in the domain you are accessing or in your area.
On Auki, devices can contribute or request sensor data, processing power, storage, networking, and monitoring services.
The reputation and reward system based on Base L2 ensures security through cryptography and provides an economic foundation for resource allocation and operation within the DePIN network.
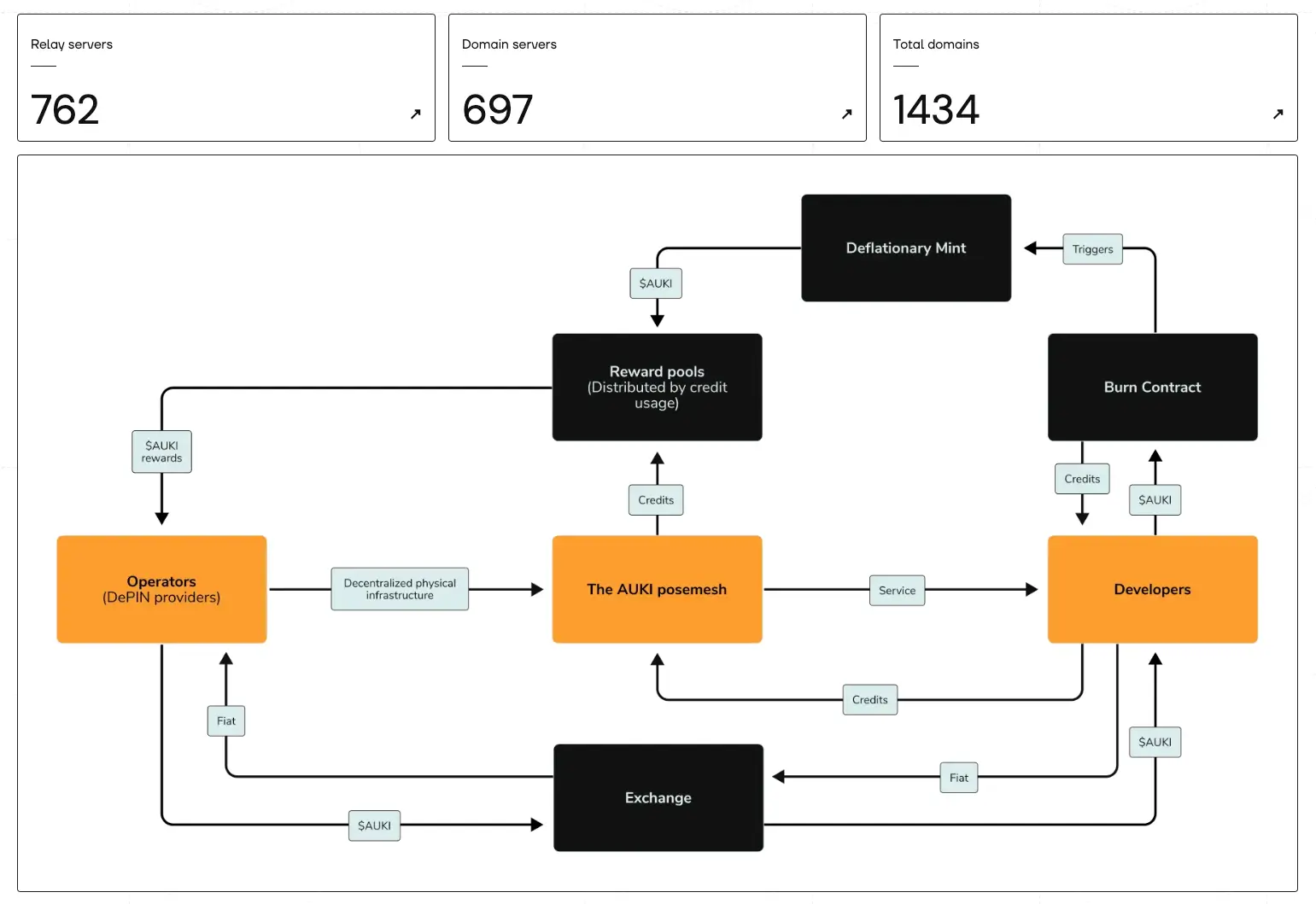
The token symbol is $AUKI.
Note: For a deeper understanding of the development history and future direction, it is recommended to read their thought-provoking seven-part introduction article.
Codec
Continuing the exploration of the field of robotic collaboration, Codec is a Solana-based project that addresses the fundamental limitations of traditional automation in current distributed computing environments.
Codec applies the concept of AI automation workflows to the robotics field, providing a unified platform that operates across cloud, edge, desktop, and robotic hardware.
Interestingly, its collaboration layer is also called Fabric, sharing the same name as OpenMind's product, and the concepts are similar (though the technical details differ).
Fabric is built on a three-layer architecture: machine layer, system layer, and intelligence layer.

Through Fabric and the Operator Kit, a unified Python framework for creating, training, and deploying intelligent operators, along with the supporting VLA model, Codec enables digital or physical agents to perform complex tasks that rely on visual or other sensor inputs.
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the CodecFlow technology stack, the team released RoboMove, a simulated robot capable of executing actions based on human input.
Original tweet link: Click here
The token symbol is $CODEC.
RoboStack
While projects like OpenMind, Auki, and Codec bring robots closer to the real world, purchasing expensive hardware and tools at an early stage is clearly too extravagant for most startups and organizations. Therefore, a realistic environment testing platform (more like in the cloud) may be the key to accelerating grassroots robotic development.
At the core of RoboStack is the RCP (Robot Context Protocol), a standardized communication layer for connecting robots, AI agents, and human users, forming a unified ecosystem.
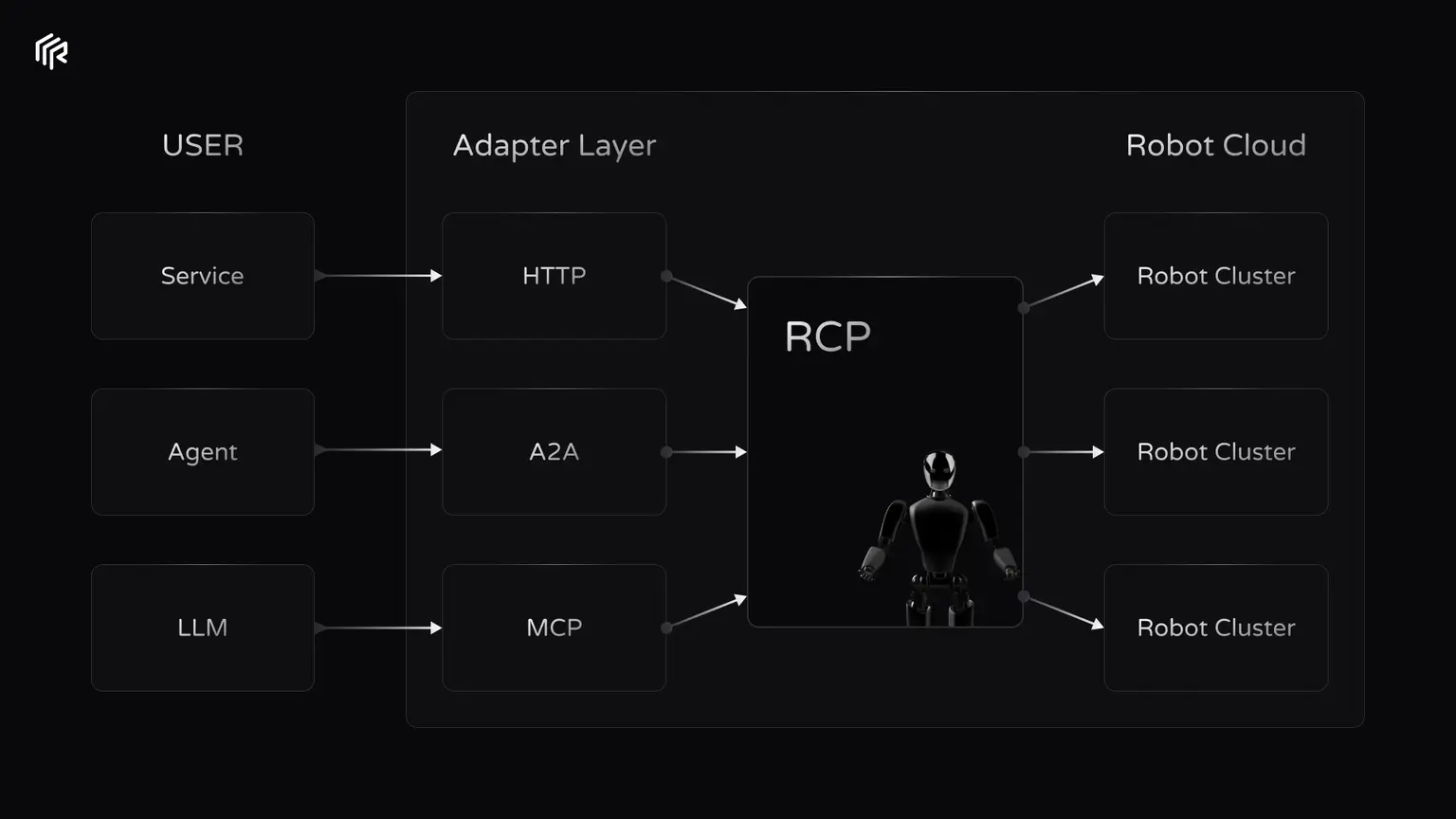
In the cloud, users can simulate and reproduce various conditions, including extreme or hard-to-reach environments.
The platform allows you to fully customize robot settings, sensor configurations, and environmental factors.
Once workflows are defined, the system automatically runs in the cloud, collecting and storing all generated data for AI training, analysis, or research purposes.
Original tweet link: Click here
The token symbol is $ROBOT.
Let’s take a step back from the complex operations of machine collaboration and focus on another key issue: how robots can translate the power of AI into real-world capabilities. Hint: understanding a concept does not mean it can be easily replicated.
Original tweet link: Click here
Silencio
You see, while ChatGPT may know the commands to generate sound, truly understanding sound is much more complex, as it relies on context such as tone, pitch, rhythm, and environment.
The same sound can have completely different meanings in a song, a warning signal, or everyday conversation, and without a large number of real-world examples, it is difficult to capture these nuances.
Silencio addresses this challenge through its DePIN network, collecting and processing real-world audio data points, enabling robots to achieve advanced auditory perception and environmental awareness.
By providing diverse audio datasets, including environmental sounds, multilingual speech, and non-verbal cues (like laughter or footsteps), Silencio trains AI models to enhance robots' sound classification, speech recognition, and contextual understanding capabilities, overcoming the interpretive limitations of complex acoustic environments.
Its flagship mobile application has collected over 40 billion data points from 1.1 million contributors across more than 180 countries.
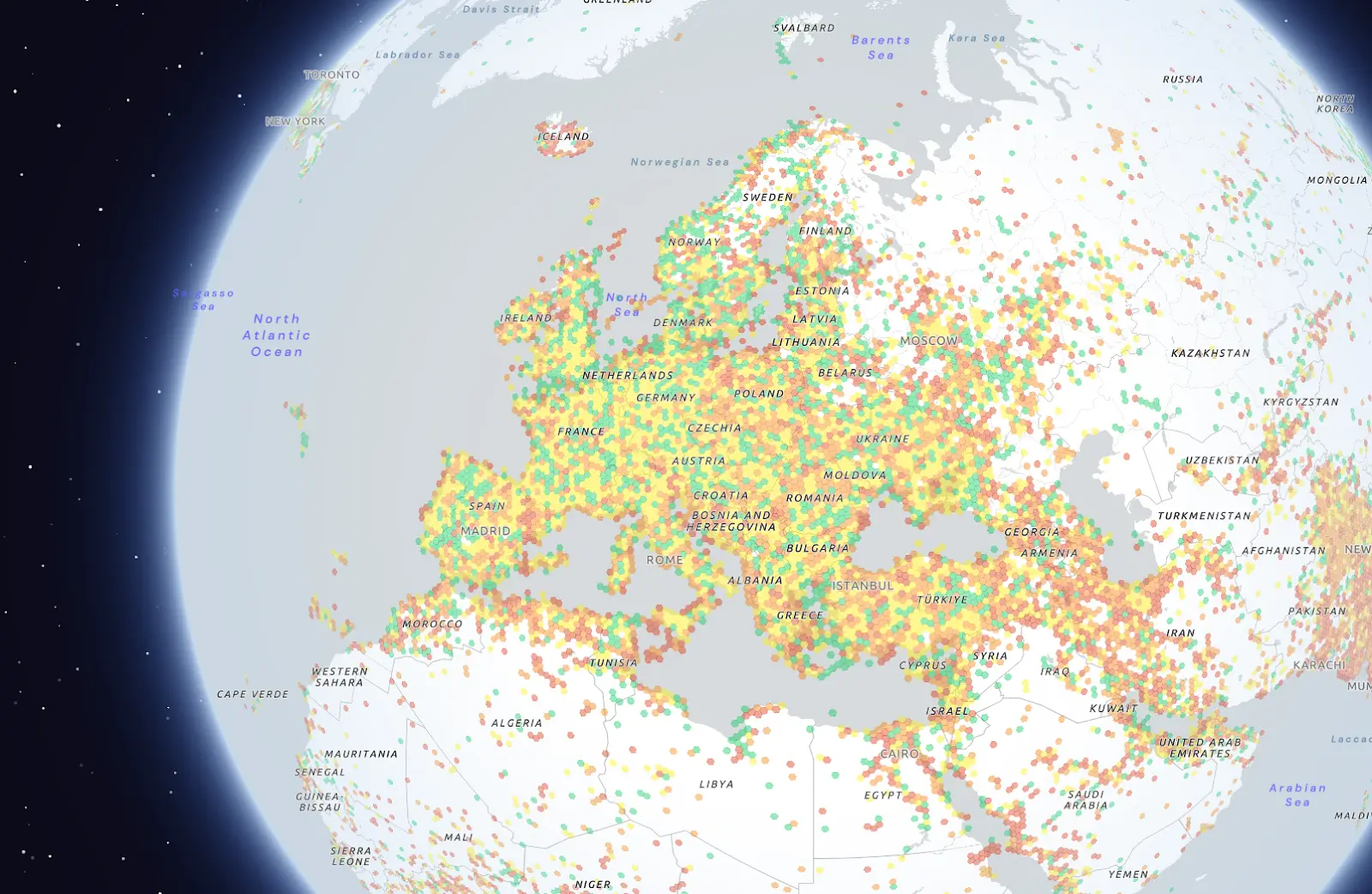
The token symbol is $SLC.
Over the Reality
While Silencio focuses on capturing audio, Over the Reality focuses on capturing visual effects, which are more important for robots operating in real life.
Although equipping robots with LiDAR and cameras seems straightforward, these sensors are insufficient for a comprehensive understanding of complex dynamic environments without 3D visual mapping. 3D visual mapping is crucial as it integrates data from multiple sensors to create a detailed volumetric representation of the surrounding environment.
It can capture depth, spatial relationships, and object orientation, allowing robots to navigate precisely in cluttered spaces like warehouses or disaster areas.
In short: the more data points, the more powerful the robot's capabilities.
Similar to Silencio, Over the Reality is built on a DePIN network, incentivizing a global mapping community to scan high-traffic areas using standard smartphones and 360-degree cameras, rewarding them with OVR tokens.
OVRMaps has mapped over 150,000 locations and has more than 70 million images, covering an area of over 44 million square meters.
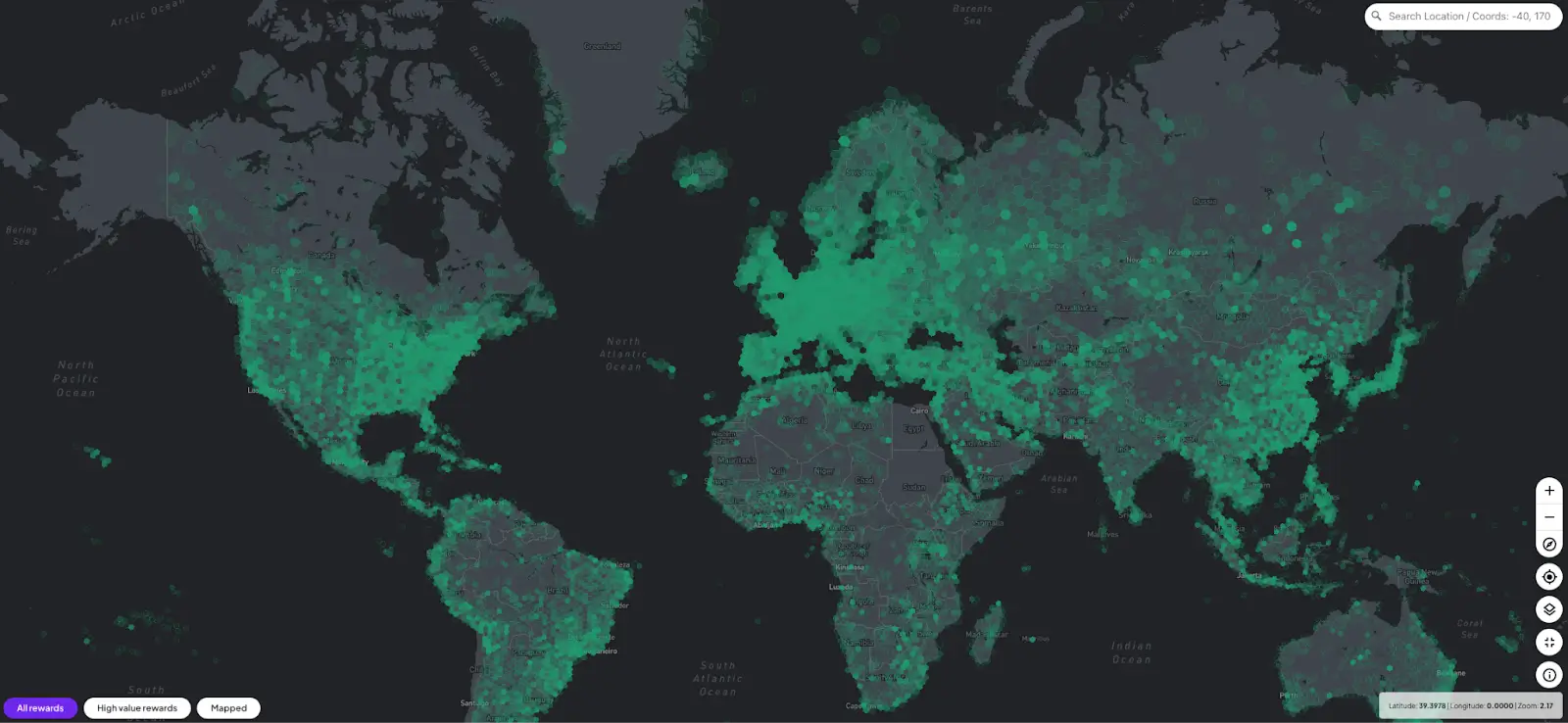
The token symbol is $OVR.
Projects Worth Noting
SHOW ROBOTICS: Developing robots with embodied artificial intelligence, combining advanced AI with robotics technology, focusing on entertainment and practical applications to create machines that can learn and perform real tasks.
HomebrewRobotics: Building a marketplace for robot models, enabling everyone to use robot models by providing pre-built software and other AI-driven programming tools.
Peaq: Not elaborated here due to its high profile.
Conclusion
While the robotics field is both novel and exciting for many, finding truly high-quality projects in this space remains challenging.
The core takeaway of this article is: rather than betting on the latest projects that may just be cash grabs, focus on mature players that have been deeply involved before the hype began and choose to invest in them.
Currently, the total market capitalization of all robotics projects is still below $300 million, making the screening task relatively straightforward.
Of course, some of the projects mentioned in this article are also newer, but through careful screening (referred to as "spider sense"), dozens of projects have been omitted to ensure the quality of the projects mentioned. While a couple of noteworthy projects may have been missed due to time constraints, the projects mentioned above should provide a clear direction for everyone in this field.
Stay curious!
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




