Author: arndxt
Translation: Saoirse, Foresight News
Editor's Note: The market is at a delicate turning point. The author believes that the strange balance of rising assets amid high interest rates is about to be broken. The author specifically points out that the open interest in alternative coins has now surpassed Bitcoin for the first time, a situation that has historically corresponded to local tops, serving as a signal of a market peak; at the same time, there is an 88% probability of a pullback following the Federal Reserve meeting, which severely skews the risk-reward ratio. Based on this, the author suggests that locking in profits or avoiding pullbacks is the best strategy at this time, and investors need to remain vigilant and adjust their investment layout in a timely manner.
The current trend is nearing its end.
Currently, our established research model shows that the market is approaching a trend reversal point. From the perspective of risk and reward, the current pattern is clearly unbalanced: after the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting, the probability of a market pullback is extremely high.
It is recommended to lock in existing profits before the final wave of the market arrives.
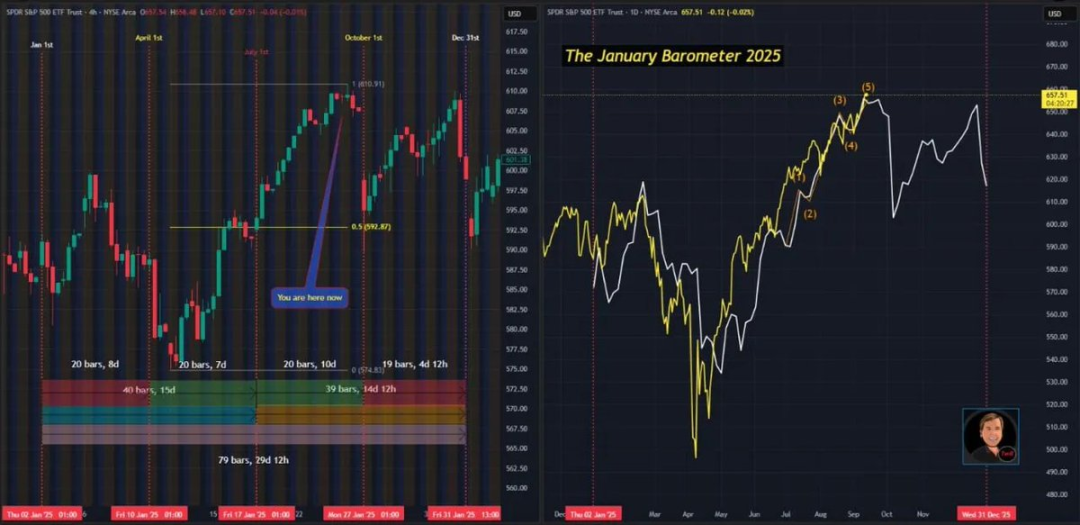
Image source: @RamboJackson5
Since December of last year, the open interest in alternative investments (cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin) has surpassed Bitcoin for the first time; historically, the last two occurrences of this phenomenon coincided with local market tops.
Today, perhaps only 1% of market participants can feel the true market frenzy. For the remaining participants, the real winners will be those investors who position themselves around "assets that can continuously attract market attention" during periods of liquidity tightening.
The core characteristics of the current market are: liquidity is showing a "selective concentration" trend, the macro environment is overall bearish, and fiat currencies are continuously depreciating. Even in such an unfavorable environment, asset prices are still rising against the trend.
The biggest difference in this cycle compared to previous ones is that: the market cycle of 2021 was driven by liquidity—credit costs were low, liquidity was abundant, and risk assets benefited comprehensively from the easing environment;
The market in 2025 is completely different: current interest rates are high, liquidity is tight, yet risk assets (Bitcoin, stocks, and even gold) are still gradually rising.
Why does this contradiction exist? The core driving force is the depreciation of fiat currency—investors are allocating assets to hedge against the risk of cash depreciation.
This trend has fundamentally changed the market rhythm: the previous "broad-based rally" risk appetite is being replaced by a structural market where "capital is concentrated on high-quality, resilient assets." The market logic has shifted from "blindly chasing all assets" to "precisely seizing opportunities, maintaining patience, and strictly adhering to discipline."
Ultimately, the depreciation of fiat currency itself is key. Today, investors allocate assets not only to pursue profit growth but also to hedge against the risk of cash depreciation.
- 2021: Liquidity expansion drives growth → Risk assets outperform;
- 2025: Fiat currency depreciation drives growth → Hard assets (gold, commodities, etc.) and quality targets perform strongly.
This shift in market logic has significantly increased the difficulty of investing—you can no longer rely on an environment of "flooding capital and abundant opportunities." However, for investors who can adapt to the new logic, this also means clearer structural opportunities.
Liquidity Reality Check
Despite numerous bullish signals in the market (Bitcoin's market cap share declining, open interest in alternative investments surpassing Bitcoin, CEX tokens rotating upward), overall liquidity remains scarce. Over the past few years, "pump-and-dump projects" driven by meme coins and tokens endorsed by celebrities have left many investors suffering from "investment post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)."
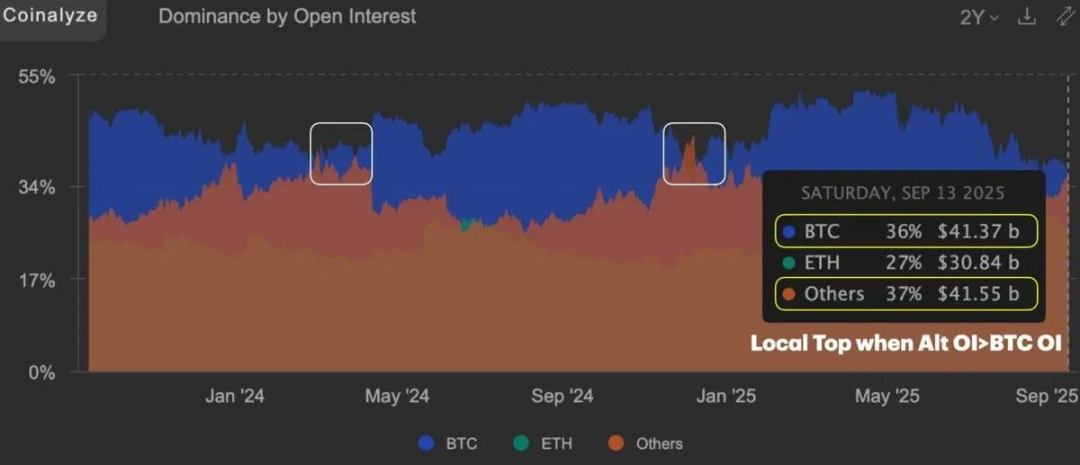
Image source: @JukovCrypto
Affected by "investment PTSD," many traders are keen to chase "newly launched hot projects" for short-term thrills, but they provide almost no sustained funding support for genuine project developers.
As a result, market liquidity is increasingly concentrating on "high market cap assets with loyal communities"—these assets can continuously attract market attention and capital inflows.
Federal Reserve and Bond Market
The bond market has already priced in expectations of a "market downturn." According to FedWatch tool data, the market estimates the probability of a 25 basis point rate cut by the Federal Reserve at about 88%, while the probability of a 50 basis point cut is only 12%. It is important to note:
- Historically, a "first rate cut of 50 basis points" is often seen as a signal of economic recession, typically leading the market into a state of "slow bleeding";
- Conversely, a "first rate cut of 25 basis points" is more often interpreted as a signal of "economic soft landing," supporting economic growth.
The current market is at a critical turning point. Considering seasonal indicators, the risk of increased market volatility after the Federal Open Market Committee meeting has gradually become apparent.
Core Conclusions
"Continuous stability" beats "short-term speculation";
"Patient positioning" beats "FOMO (fear of missing out)";
"Precise timing" beats "pursuing Alpha (excess returns)."
The following will provide a detailed analysis from the perspectives of macro event outlook, Bitcoin heat indicators, market panorama review, and core economic data interpretation, with data as of September 14, 2025.
Macro Event Outlook
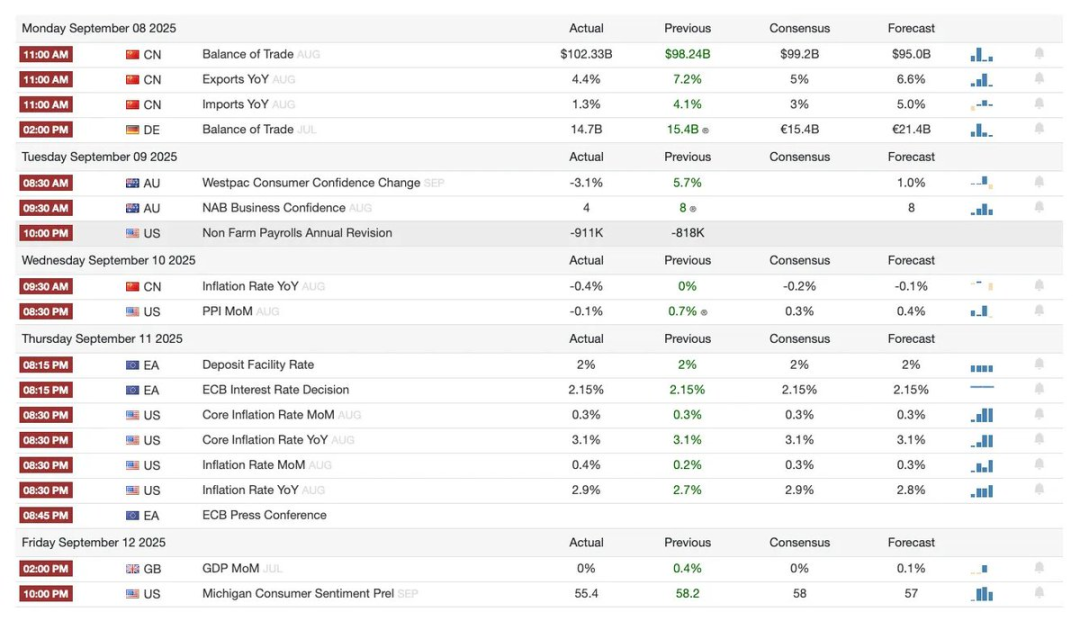
Last Week Review
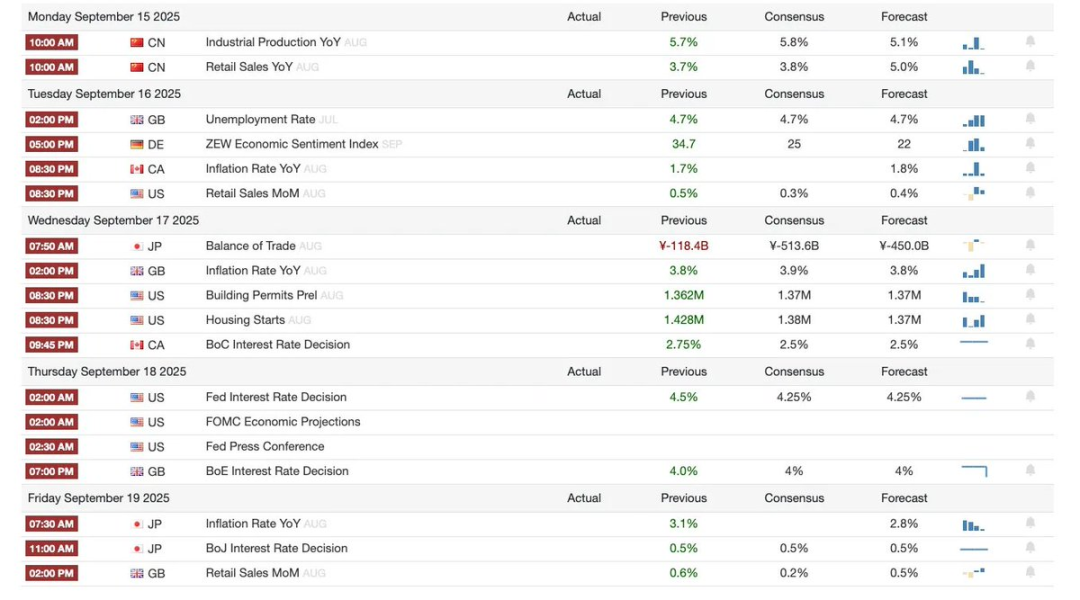
Next Week Preview

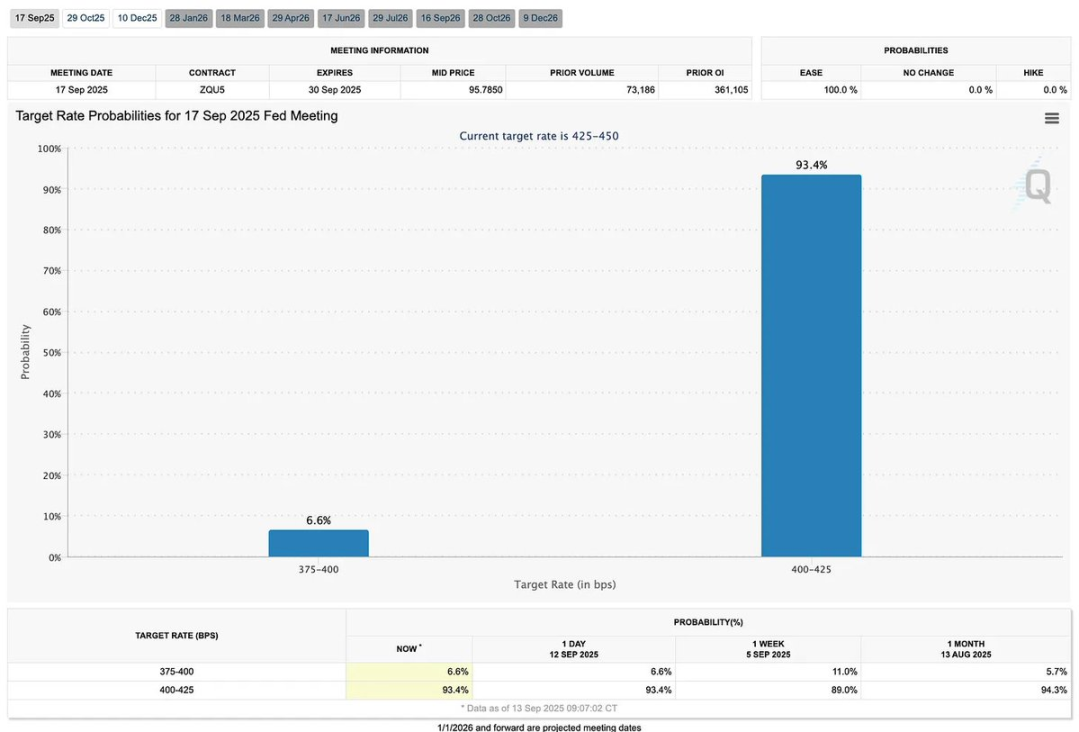
Bitcoin Heat Indicators
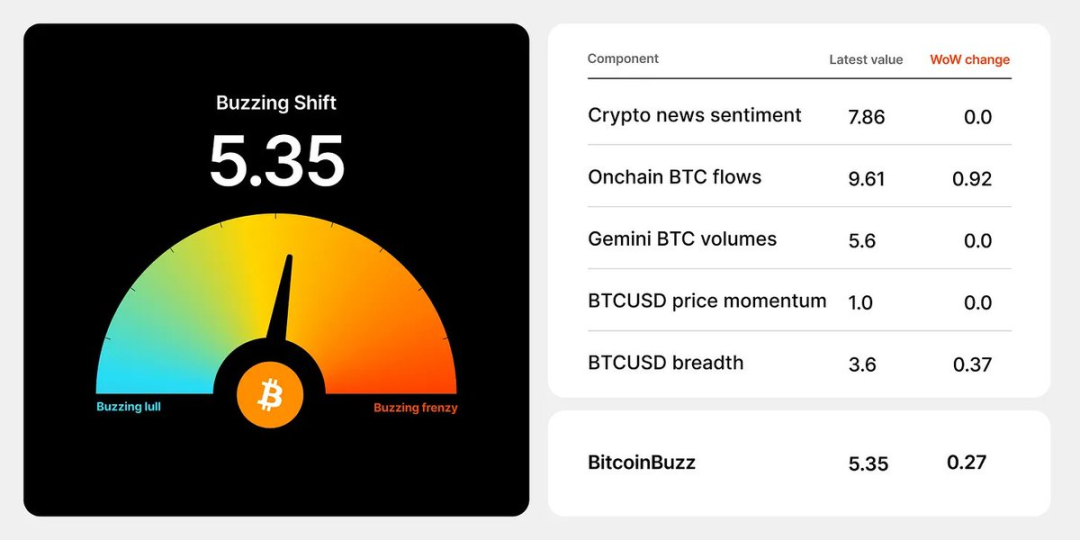
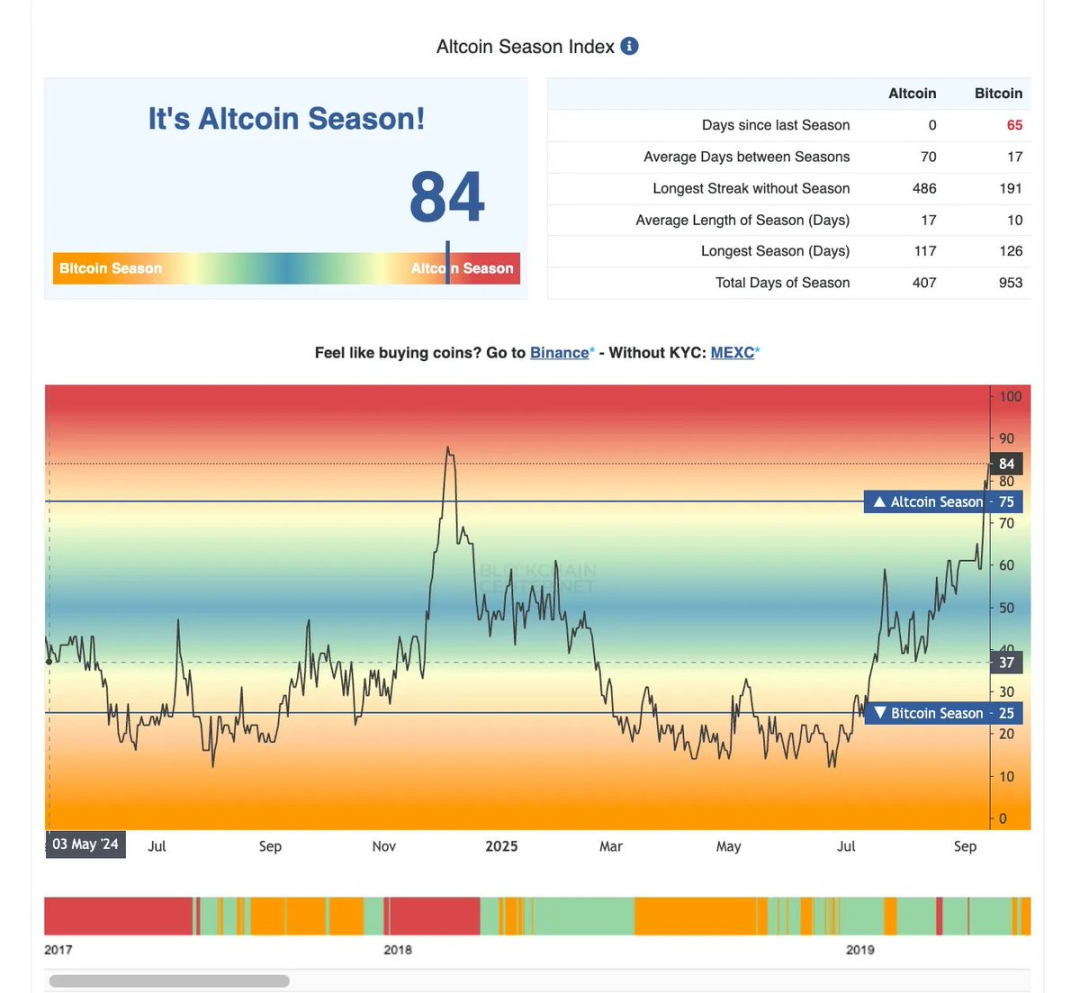
Market Panorama Review
- Dogecoin ETF milestone: The DOJE ETF, jointly launched by REX Shares and Osprey Funds, becomes the first fund in the U.S. to directly track the price of Dogecoin. This event marks a certain recognition of "meme coins" in traditional financial markets, but due to the lack of practical application scenarios for Dogecoin, its demand is expected to remain primarily retail-driven.
- Chicago Board Options Exchange (Cboe) perpetual futures plan: The proposed Bitcoin and Ethereum futures contracts could have a maximum duration of 10 years, using a daily cash settlement mechanism. If this plan receives regulatory approval, it is expected to reduce rollover costs for investors, enrich institutional investors' derivative strategies, and enhance market liquidity.
- Ant Digital asset tokenization: Ant Digital has bound $8.4 billion in renewable energy assets with AntChain, achieving "real-time production data tracking" and "automated profit distribution." This "institution-first" model highlights the application value of blockchain technology in large-scale infrastructure financing.
- Forward company's Solana treasury layout: A $1.65 billion private equity investment (PIPE) led by Galaxy and Jump Crypto has made Forward Industries one of the core holding institutions in the Solana ecosystem. This marks the first large-scale allocation of institutional funds into "cryptocurrency assets outside of Bitcoin and Ethereum," which is expected to reshape Solana's capital market narrative.
Core Economic Data Interpretation
Key Insights for Ordinary Users
- Tightening job market: Especially with a reduction in job opportunities in traditional industries, it is recommended to shift towards fields with stronger risk resilience, such as healthcare and services, through skill enhancement.
- Short-term improvement in purchasing power, but risks remain: Current wage purchasing power has improved, but inflation driven by tariffs may quickly erode this benefit, so caution is advised for large expenditures.
- Debt relief opportunities approaching: If interest rates are lowered, debt pressure may ease, but current household financial pressures are continuously rising, so it is advisable to maintain a conservative budget and prepare for debt refinancing.
- Increased investment volatility: Rate cuts may provide a short-term boost to the market, but inflation risks could lead to rapid profit reversals, necessitating vigilance against volatility risks.
Labor Market Dynamics
- New job creation continues to decline → Increased competition for positions, particularly evident in low-skill jobs;
- Significant industry differentiation: Demand remains strong in healthcare (+46,800 jobs) and hospitality (+28,000 jobs); however, hiring activity in manufacturing, construction, and business services has noticeably slowed;
- Employment growth has significantly cooled: New job creation dropped from 868,000 in Q4 2024 to 491,000 in Q1 2025 and 107,000 in Q2 2025; only 22,000 new jobs were created in August 2025, nearing a stagnation state;
- Reasons behind industry differentiation: Tariff pressures, investment uncertainty, and immigration policies limiting labor supply have led to contractions in cyclical industries (manufacturing, construction, etc.).
Wage and Labor Force Participation Rate Trends
- Year-on-year wage growth of 3.7%: Although the growth rate is lower than previous levels, it is still above the inflation rate, indicating a slight improvement in real purchasing power—this is one of the few positive signals in the current economic environment;
- Caution is needed regarding tariff inflation risks: If tariffs lead to rising commodity prices, the purchasing power gains from wage growth may quickly disappear;
- Income growth rate: Year-on-year growth of 3.7%, the lowest level since mid-2021, which alleviates the pressure of the "wage-inflation spiral," but remains above inflation, providing a net benefit to consumer purchasing power;
- Labor market structure: The labor force participation rate is slowly rising, but the unemployment rate has risen to 4.3% (the highest since 2021), with employment pressure mainly concentrated in the low-skill labor group, while high-skill, highly educated groups maintain stable employment.
Macroeconomic Impact
- Rate cut window approaching: If the Federal Reserve cuts rates as expected, financing costs for mortgages, consumer loans, and credit cards are likely to decrease;
- Rising household debt pressure: Current default rates on credit cards, auto loans, and student loans continue to climb; if you are facing debt pressure, it is advisable to plan ahead—refinancing conditions may improve later this year;
- Bond market dynamics: The yield on 10-year U.S. Treasury bonds has fallen to 4.1% (the lowest in 10 months), reflecting that the market has already priced in expectations of "economic slowdown + Federal Reserve rate cuts";
- Federal Reserve policy outlook: The futures market indicates a roughly 90% probability of a rate cut in September, with expectations of 2-3 cuts by the end of the year—despite persistent inflation, the market still bets on aggressive easing policies from the Federal Reserve;
- Financial pressure differentiation: The household sector faces dual pressures from rising credit defaults and the resumption of student loan repayments, while the corporate sector's financing environment remains loose.
Strategic Insights
- The economy is showing a "differentiated pattern": Institutions (enterprises, financial markets) enjoy a loose financing environment, while the household sector faces rising financial pressures;
- Policy is caught in a "dilemma": If the Federal Reserve cuts rates, it may exacerbate inflation; but if it does not cut rates, the pressures of slowing employment and rising debt defaults will intensify;
- Investment layout suggestions:
- Risk-resistant sectors: Healthcare, hospitality—benefiting from demographic trends and experiential consumption demand;
- High-risk sectors: Trade-sensitive industries (manufacturing, construction)—significantly affected by tariffs and labor supply bottlenecks;
- Macroeconomic environment summary: Expectations of rate cuts + slowing labor market may drive asset prices to rebound, but inflation risks will lead to "asymmetric volatility" in assets such as stocks, credit, and commodities.
Eurozone Policy Outlook
- Current inflation status: Although it has significantly retreated from the 2022 peak, it remains above target levels and exhibits "plateau" characteristics, limiting the European Central Bank's (ECB) easing space;
- Policy differentiation risks: The Federal Reserve tends toward easing due to "slowing employment," while the ECB remains cautious due to "sticky inflation"—this differentiation may exacerbate fluctuations in the euro to dollar exchange rate;
- Investor perspective:
- Interest rates: The ECB has limited room for rate cuts, and eurozone bond yields may remain relatively high;
- Stocks: The decline in service sector inflation is beneficial for corporate profits, but cost shocks from global tariffs may compress profit margins;
- Macroeconomic risks: Economic growth momentum is weak, but the ECB finds it difficult to ease, potentially leading to a "mild stagflation" scenario;
- ECB stance: Current inflation remains above the 2% target, with a low probability of a rate cut in September, and uncertainty remains regarding a potential cut in December;
- Market expectations: The futures market indicates a roughly 50% probability of a rate cut by the end of the year—while the market leans toward easing expectations, the signals released by the ECB remain cautious;
- Lagarde (ECB President) statement: Adopts a "wait-and-see strategy," inclined to maintain current rates to avoid premature easing.
Global Interconnected Impact
- Tariff spillover risks: U.S. tariffs may raise input costs through global supply chains, with ECB officials (Schnabel) identifying this as an "upside risk" for eurozone inflation;
- Transmission mechanism: Even with weak domestic demand in the eurozone, "imported inflation (high-cost imports)" may still limit the ECB's policy flexibility.
Focus on the Chinese Market
China is currently adopting a "dual-track strategy": politically, strengthening cooperation with India to respond to external shocks, and economically, injecting liquidity and guiding market expectations to alleviate economic vulnerabilities.
- Core logic: Hoping to leverage a leading position in technology to compensate for shortcomings in economic growth;
- Potential risks: If the real economy continues to stagnate, and the market relies solely on liquidity support to maintain high levels, it may lead to structural vulnerabilities beneath a facade of prosperity.
Current Status of Tariff Impact
- CICC data shows: Chinese export enterprises bear only 9% of U.S. tariff costs, far lower than the burden borne by European and Southeast Asian companies;
- Implications: U.S. importers are currently absorbing tariff costs themselves, compressing their profit margins. This model is unsustainable—ultimately, U.S. consumers will face rising prices, further exacerbating inflation risks;
- Export pressure on China: China's exports to the U.S. continue to decline, with rising factory idle rates, potentially creating underlying pressure on domestic stability; this vulnerability, while not obvious, has significant implications.
Geopolitical Landscape Restructuring
- U.S. "containment" strategy towards China encounters setbacks: The U.S. has imposed a 50% tariff on India for importing Russian oil, weakening its own "containment alliance" against China;
- China's strategic response: Quickly seizing this rift to facilitate the first trilateral talks between India and Russia in years in Beijing;
- Key insight: If China and India deepen cooperation, the U.S.-led "Quad Security Dialogue" (comprising the U.S., Japan, Australia, and India) may face risks of strategic hollowing.
The "Safety Valve" Role of Capital Markets
- Divergence between market and economy: Despite the weak fundamentals of the Chinese economy, the stock market has reached a 10-year high—this rise is not driven by corporate profits but by "liquidity injections" and "the $22 trillion shift of household savings from deposits (yielding about 1%) to the stock market";
- Attractiveness logic: With a 10-year Treasury yield of only 1.7%, stocks possess structural attractiveness in terms of "relative returns"; simultaneously, global investors are also chasing Chinese assets with technological advantages;
- Core insight: The current market optimism is a bet on "liquidity easing + technology narrative," rather than confidence in a recovery of the real economy.
Macroeconomic Risk Warning
- Bubble risk: If the real economy fails to achieve a genuine recovery, the current stock market rise may evolve into another round of "liquidity-driven bubbles";
- Increased policy dependence: If exports continue to decline and consumer demand remains weak, China may need to further intensify monetary easing and employ more capital market regulatory measures to maintain market stability.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




