The architecture of DeFi releases new financial freedoms, breaking down barriers of geography, identity, and institutions.
Written by: zacharyr0th, Aptos Labs
Translated by: Alex Liu, Foresight News
DeFi Use Cases
The traditional banking system remains the foundation of finance, but has long been plagued by systemic risks, regulatory failures, and conflicts of interest.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) provides access to financial tools without permission—featuring censorship resistance, borderless stablecoin usage, and transparent yield generation.
The future financial landscape will emerge from a pragmatic integration between traditional institutions and decentralized infrastructure.
The global financial system is built on a vast network of intermediaries, processing trillions of dollars in transactions daily. This architecture has historically supported global trade and capital flows, but has also led to bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and systemic risks.
While technology continues to advance, traditional institutions remain deeply entrenched, both operationally and politically and socially. Some institutions are seen as "too big to fail," while others quietly go bankrupt. Despite the prominence of many institutions, their histories are still marred by regulatory violations and unresolved conflicts of interest.
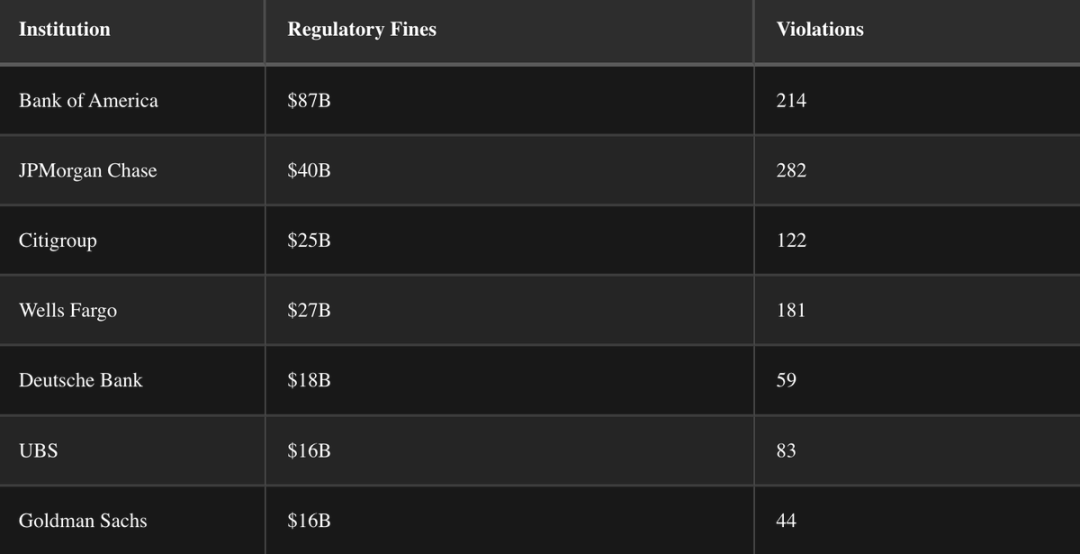
These phenomena reflect a deep-seated systemic issue—not just regulatory inadequacy, but a design flaw.
Worse still, the lines between regulators and the regulated are often blurred. Former SEC Chairman Gary Gensler worked at Goldman Sachs for 18 years before regulating Wall Street; Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell accumulated considerable wealth in investment banking before formulating monetary policy; former U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen received over $7 million in speaking fees from the financial institutions she later regulated.
Certainly, the expertise between the public and private sectors can be compatible, but this "revolving door" phenomenon is not new; it has almost become the norm.
The Mission and Operation Mechanism of Central Banks
In 1913, after a series of bank runs, the Federal Reserve was established. Designed by financiers like J.P. Morgan, the Federal Reserve is a quasi-governmental institution: theoretically accountable to Congress, but operating independently in practice.
In 1977, the Federal Reserve's dual mandate was formally established:
Maximize employment
Maintain price stability (currently interpreted as around 2% inflation rate)
Although monetary policy continues to evolve, its main tools have remained consistent: interest rate adjustments, balance sheet expansion, and open market operations.
Since 2012, the Federal Reserve has explicitly set a 2% annual inflation rate as its target, which has had widespread implications for asset values and the purchasing power of the dollar. From a long-term historical perspective, interest rates have shown a steady decline.
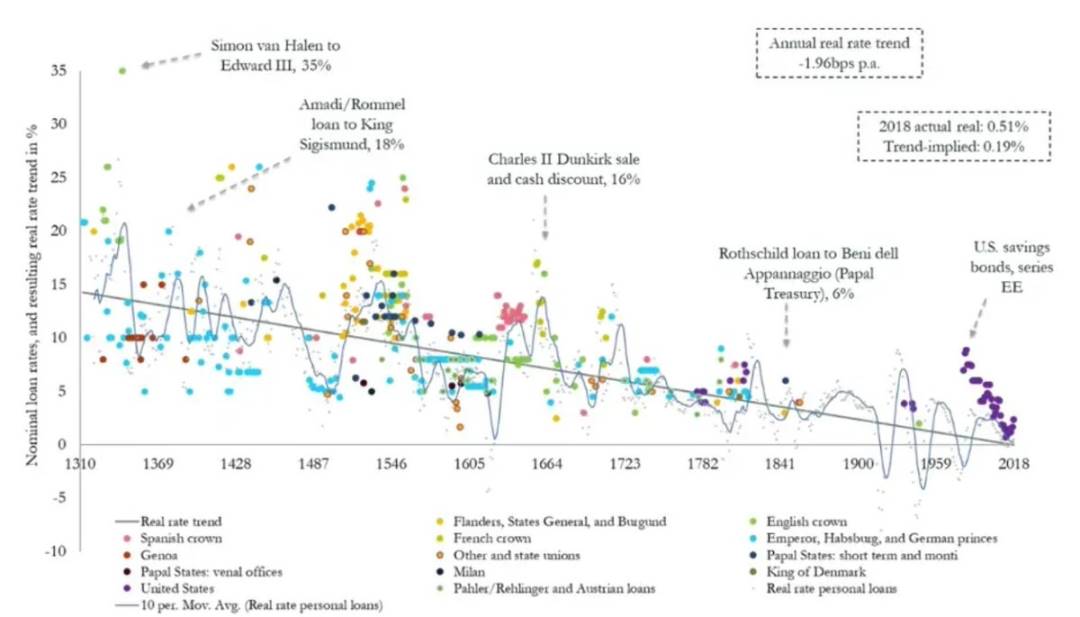
As the financial system becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, borrowing costs continue to decline.
Value and Perception
Since 2008, the correlation between the Federal Reserve's balance sheet and the S&P 500 index has increased, raising questions about the long-term effects of monetary expansion.
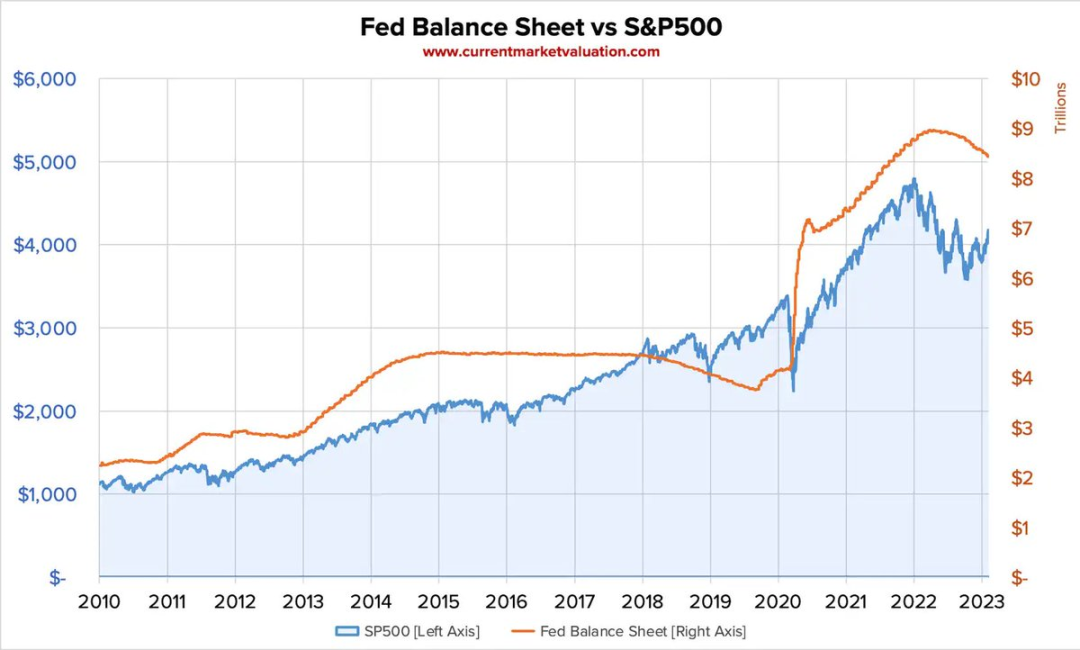
Some believe that the U.S., due to its global dominance, can "print money freely" with minimal consequences; the dollar's status as a reserve currency and global trust in U.S. institutions provide a buffer against inflation erosion. However, not all countries enjoy this privilege. In many parts of the world, especially where goods and services are not priced in dollars or euros, DeFi is not an option, but a necessity.
In developed economies, people can discuss the theoretical benefits of decentralization; but for billions in underdeveloped regions, they face real problems that traditional banks cannot or will not address: currency devaluation, capital controls, lack of banking infrastructure, and political turmoil. These require solutions outside the traditional system.
Stablecoins and Anti-Inflation
Between 2021 and 2022, Turkey experienced severe economic turmoil, with inflation rates soaring to 78.6%.
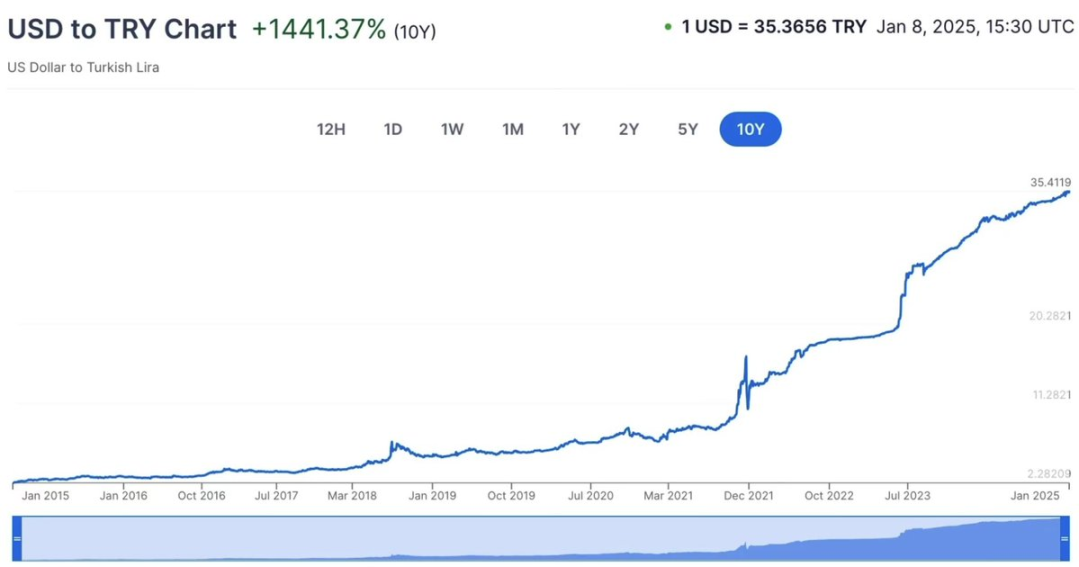
For ordinary people, local banks could not provide effective responses, but DeFi could. Through stablecoins and non-custodial wallets, individuals can avoid asset devaluation, conduct global transactions, and bypass unjust capital controls—all achieved through open-source tools accessible to anyone.
These wallets do not require bank accounts or cumbersome paperwork; access to on-chain accounts is possible with just a private key or mnemonic phrase.
Censorship Resistance
The bank accounts of many truck drivers protesting at the U.S.-Canada border were frozen by authorities, preventing them from repaying loans and purchasing necessities—despite not violating any specific laws.
In a centralized system, financial autonomy is not a given, whereas DeFi offers a different model: governed by code on open infrastructure, rather than regional policies.
Yield and Innovation
DeFi protocols redefine financial primitives: lending, trading, insurance, etc., but these innovations come with new risks.
Some protocols have collapsed, and malicious participants have been exposed, but the market naturally filters for sustainable innovations. Survivors—such as automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools—represent the best practices of DeFi: building transparent, permissionless infrastructure that allocates transaction fees to liquidity providers rather than concentrating market-making profits in the hands of a few gatekeepers.
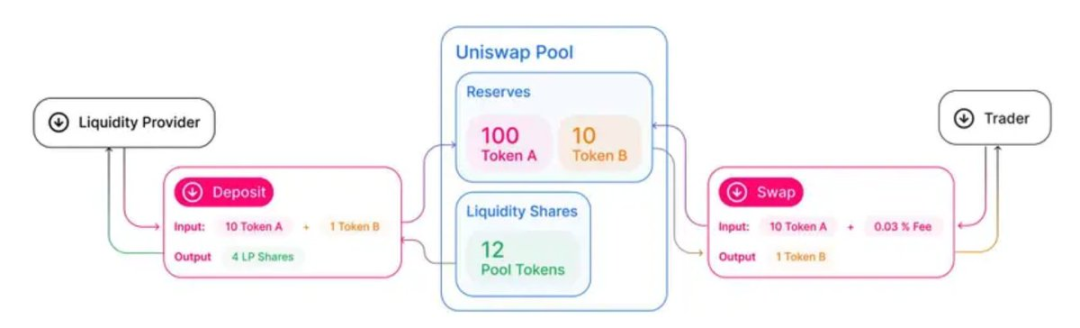
This is a starkly different model from traditional finance—where access to traditional markets, especially market-making businesses, is highly restricted and lacks transparency.
A Balanced Future
At least in the short term, the future of finance will not be entirely decentralized nor entirely centralized, but rather a hybrid form. DeFi is not a complete replacement for traditional finance, but it does fill the gaps overlooked by the traditional system: accessibility, censorship resistance, and transparency. In economies troubled by regional inflation or financial repression, DeFi is already addressing everyday issues.
In countries like the U.S., where the banking system is safer, the value proposition of DeFi also holds, but more in theory. For most people in stable economies, traditional banks still offer conveniences, consumer protections, and reliability that DeFi has not yet fully matched. Once traditional financial infrastructure upgrades to a blockchain-based settlement layer, this theory will gradually become reality.
Until then, some will pursue financial sovereignty, some entrepreneurs will build on the frontier, and some smart capital will leverage DeFi primitives for higher risk-adjusted returns—of course, accompanied by a plethora of meme coins and airdrop activities.
What Others Think?
"The goal of DeFi is not to compete with traditional finance, but to create an open, accessible financial system that complements existing infrastructure." — Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum
"DeFi protocols represent a paradigm shift in financial infrastructure, providing programmable, transparent alternatives to traditional financial services." — Dr. Fabian Schär, Professor of Distributed Ledger Technology at the University of Basel
"While DeFi platforms may offer promising technological innovations, they still need to operate within a framework that protects investors and maintains market integrity." — Former U.S. SEC Chairman Gary Gensler
Why DeFi Matters
In a world of economic volatility and institutional trust deficits, decentralized systems are gradually demonstrating their capabilities: leveraging the new properties of blockchain to enhance traditional payment and financial operations.
The architecture of DeFi—permissionless, global, and transparent—releases new financial freedoms, breaking down barriers of geography, identity, and institutions. Smart contracts automate complex processes, reduce costs, and eliminate friction, which traditional infrastructure cannot achieve.
Risks still exist, but progress is also being made.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




