Despite the market downturn, practical applications such as tickets and product certificates have emerged in the South Korean NFT market.
Author: Tiger Research Reports
Translation: Deep Tide TechFlow
Key Points Summary
Since 2021, various projects have emerged in the domestic NFT market, including NFT platforms and communities led by major companies. However, since 2022, the market has been unstable.
Due to excessive localization, lack of practical utility, and regulatory challenges, the market's decline has even exceeded the global market.
Despite the market downturn, practical applications such as tickets and product certificates have emerged in the South Korean NFT market. This indicates that NFTs may develop into a technology with practical value, rather than just a speculative tool, making its future development worth paying attention to.
1. Introduction
The NFT market in South Korea has experienced rapid growth since 2021, in sync with global trends, especially the popularity of blue-chip NFTs such as Cryptopunk and BAYC. This growth has been driven by the rapid development of multiple projects on Klaytn (a domestic blockchain network). Well-known projects such as Metakongz and Sunmiya Club have attracted global investors' attention and have seen a large number of transactions on the leading global NFT market OpenSea. In addition, the launch of domestic NFT markets has injected vitality into the South Korean NFT industry.
However, with the major shocks such as the collapse of Terra Luna in May 2022 and the FTX incident in November of the same year, the market environment began to change, leading to the so-called "crypto winter." As a result, the NFT market experienced a decline, with many projects facing difficulties and even prematurely ceasing operations. Nevertheless, some companies continue to persevere, operating or launching new projects.
In this report, we comprehensively analyze the current status of the South Korean NFT market, focusing on projects that have closed due to the market downturn and those that continue to operate successfully in adversity. By comparing and analyzing the strategies of these projects, we aim to identify the key trends shaping the South Korean NFT market and provide insights into its future development direction.
2. Overview of the South Korean NFT Market in 2024
The South Korean NFT market experienced rapid growth in early 2022. With large enterprises in the finance, retail, and telecommunications industries actively entering the NFT field, the market was quickly dominated by these major corporations.
2.1. NFT Platforms
Content outside of Feishu documents cannot be displayed at the moment
During this period, there was fierce competition among NFT platforms, each vying for domestic users by providing localized services and offering one-stop solutions from NFT creation to trading. This strategy aimed to quickly attract a stable customer base from mature enterprises by providing a convenient user experience. In addition, these companies leveraged their rich experience and resources in platform-related services such as trading, sales, and settlement to quickly establish comprehensive markets and various related functions.
Source: Left image is Pala, right image is KT Mincl
In 2023, there was a significant change in the market situation. Many companies began to close their NFT platform services for various reasons. Due to their excessive focus on the domestic market, their user base was relatively limited, making it difficult to compete with global platforms such as OpenSea, Magic Eden, and Blur. Furthermore, the lack of attractive NFT projects that could sustain stable trading volumes also weakened their market position. Finally, the overall downturn of the NFT market led to a decrease in demand, which may have been a decisive factor in the closure of these platforms.
2.2. NFT Projects
Content outside of Feishu documents cannot be displayed at the moment
NFT projects continue to emerge from large enterprises to community-driven entities. Companies launch NFT projects by utilizing existing intellectual property (IP) or developing new character IPs, aiming to provide customers with a richer brand experience and enhance customer loyalty through unique benefits. Notable examples include the Belly Bear NFT from Lotte Home Shopping and the Puuvilla NFT project from Shinsegae Department Store, which issued 9,500 and 10,000 NFTs, respectively. Both projects combined membership benefits and quickly sold out, becoming early successful examples in the South Korean NFT market.
Most of these projects rely on a simple membership-based business model, primarily generating profits through secondary market transactions. However, with the downturn of the NFT market, these projects have struggled to maintain sustainable income, leading many projects to discontinue their community channels or shut down completely. Even NFT projects leveraging the brand value of large companies face challenges in maintaining an active community. Despite initial success, these projects have failed to provide long-term value and practical utility, ultimately hindering their continued development and user participation.
3. Continued Downturn of the NFT Market
Against the backdrop of a prolonged downturn in the global cryptocurrency market, the South Korean NFT market is experiencing a more pronounced decline. This steeper downward trend is mainly attributed to three reasons: 1) excessive localization of the South Korean NFT market, 2) a high number of NFT projects lacking proven practical value, and 3) increasing regulatory barriers related to cryptocurrencies.
3.1. Excessive Localization of the South Korean NFT Market
South Korea's preference for localized social media platforms and communities has led to an excessive localization of its NFT market. When trends such as NFTs become popular domestically, they often form closed communities, limiting the participation of global users. Furthermore, the increasing number of NFT platforms designed for Korean speakers exacerbates this isolation, as users tend to prefer native language platforms for convenience. This closed environment hinders the integration of the South Korean NFT market with the global ecosystem.
This description of the South Korean market contrasts sharply with the global NFT ecosystem. In the global market, NFT projects primarily operate through English community channels and markets. Platforms such as Reddit, X (formerly Twitter), OpenSea, and Warpcast are the main venues for discussing and promoting NFT projects, all using English as the communication language. This language barrier presents a significant obstacle for South Korean local NFT projects that aim to expand into the international market.
3.2. Unproven Value of NFTs

Source: Left) SeoulArtistNFT, Right) BlueberryNFT
The South Korean NFT market, similar to global trends, initially attracted attention through collectible NFTs. Many NFTs related to well-known Korean artists and sports stars were launched, with some achieving high transaction volumes based on the creators' fame. However, these NFTs, primarily considered collectibles or speculative assets, have struggled to sustain long-term interest and have gradually been marginalized in the market.
Following this initial stage, the market saw the emergence of a second wave, namely the introduction of membership-based NFTs, mainly supported by large companies. Although the initial issuance prices of these NFTs surged, subsequent trading volumes and prices sharply declined, with little sign of recovery.
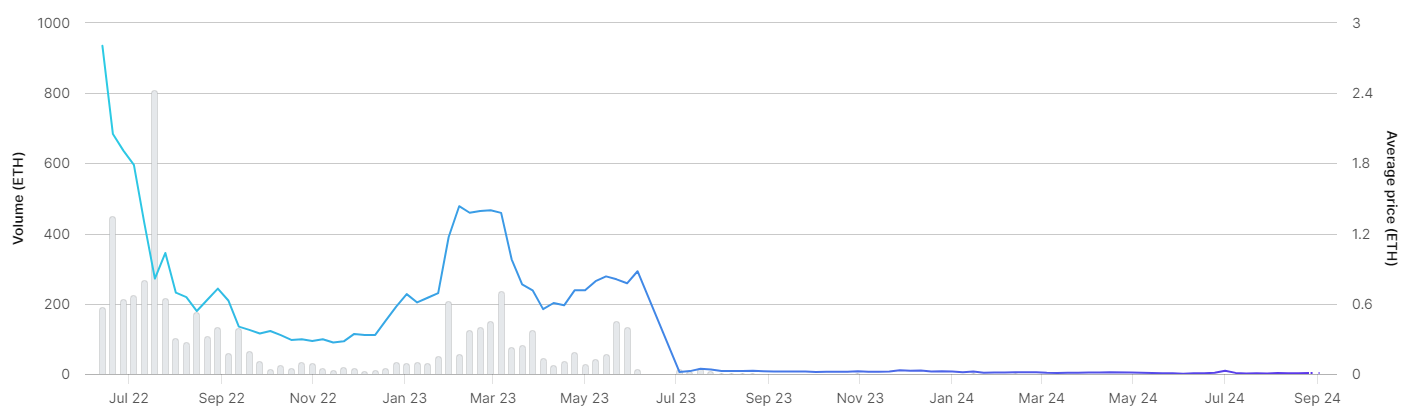
MetaKongz NFT sales trend, Source: Opensea
The emergence of this phenomenon is due to the ongoing questioning of the intrinsic value of NFTs. While the development of digital technology has made the concept of "digital collectibles" popular and sparked a speculative frenzy, this frenzy has gradually subsided. Simply owning digital images has failed to sustain public interest and recognition. Similarly, membership-based NFTs initially provided holders with benefits such as discounts and exclusive events, but they have struggled to create lasting value. This is mainly because these NFTs have failed to meet people's expectations and lack practical utility, making it difficult for them to achieve sustainable development in the market.
3.3. High Thresholds Imposed by Regulations
Another major challenge facing the domestic NFT market is the increasing regulatory barriers. The "Virtual Asset User Protection Act," which came into effect in July, and the subsequent release of NFT guidelines have made the operation of NFT-related businesses more complex. According to the guidelines, NFTs may be classified as virtual assets if they meet any of the following conditions:
- When a large number or series of similar or identical NFTs are issued
- When NFTs can be divided
- When NFTs can be used as a method of direct or indirect payment for certain goods or services
- When NFTs can be used as a means of exchanging virtual assets between unspecified individuals or as a payment method for goods or services related to other virtual assets.
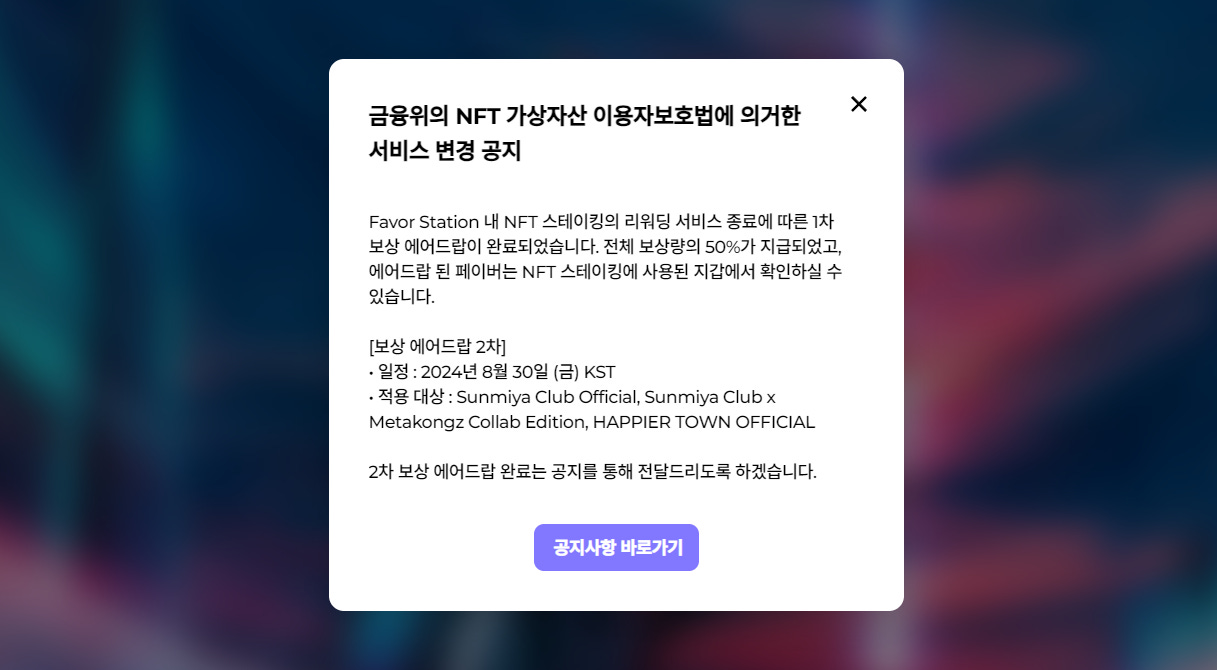
Sunmiya Club will terminate its NFT staking reward service after the "Virtual Asset User Protection Act" comes into effect, Source: sunmiya.club
Classifying NFTs as virtual assets poses a significant challenge for businesses. In South Korea, operating virtual asset-related businesses requires obtaining a Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) license. After obtaining this license, companies also need to undergo Information Security Management System (ISMS) certification, a process that is both expensive and time-consuming. This presents a major obstacle for companies or project teams with limited financial and human resources, making it difficult for them to enter the NFT field. Additionally, this raises the barrier to entry for startup companies in innovative NFT applications.
In anticipation of the implementation of the "Virtual Asset User Protection Act," several existing services have chosen to reduce or close operations to avoid strict regulatory requirements. Many NFT-related companies may shift their business focus or completely exit the market.
4. How Will the South Korean NFT Market Develop in the Future?
Source: Hyundai Card
Despite the domestic NFT market being in a downturn, there are still many successful applications of NFTs. One typical example is the introduction of NFT-based concert tickets by Hyundai Card, aimed at preventing counterfeiting and black market trading. This demonstrates how NFT technology can create practical value in existing industries. Hyundai Card's initiative is not just about adopting new technology but addressing real-world issues, showcasing the practical benefits of NFTs. As NFT technology continues to evolve, it may address everyday inconveniences and enhance public service experiences.
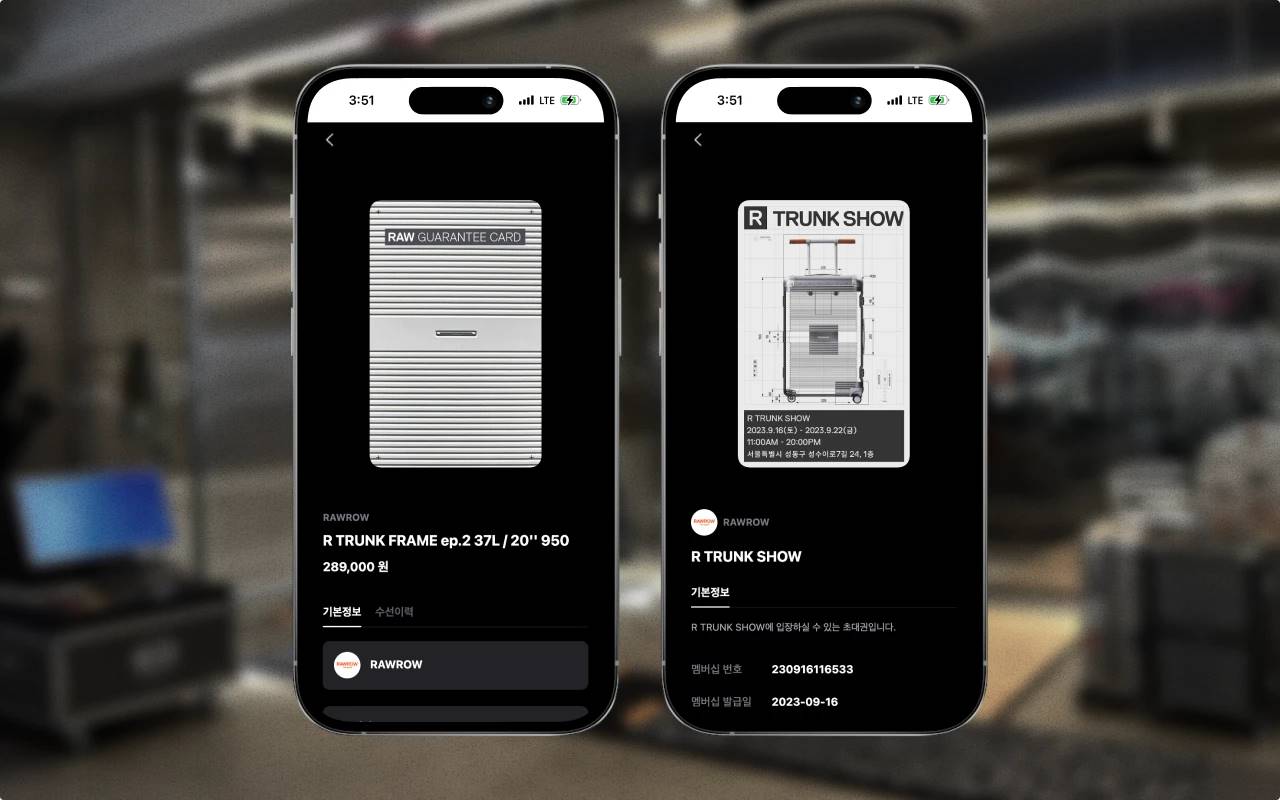
Source: Vircle
NFT technology is also being applied in areas such as product verification and customer relationship management (CRM). A typical example is Vircle, which provides NFT-based product warranty services. The company is expanding its business through collaborations with fashion and electronics brands, as verification and after-sales services are crucial in these fields.
NFT digital warranties offer several advantages, including solving the problem of lost paper warranties and enabling customers to conveniently activate and access after-sales services through mobile devices. For businesses, this data can be used for more efficient customer relationship management. Additionally, digital warranties can serve as a membership system, integrating customer information from various channels into a unified system. These examples demonstrate the potential of NFT technology to bring tangible benefits to businesses and customers.
5. Conclusion
The South Korean NFT market continues to face many challenges in its recovery process. In addition to the factors mentioned earlier, negative events related to NFTs have also exacerbated public skepticism. Scandals involving Korean internet celebrities and multiple projects being involved in "fundraising" scams have severely damaged public trust. Furthermore, many people still perceive NFTs primarily as speculative tools, which remains a significant obstacle to market development.
To improve this situation, it is essential to accumulate successful cases that demonstrate the creation of practical value through NFT technology. A positive shift in public perception is crucial to achieving this goal. This challenge is not limited to the NFT industry; most Web3 projects face similar issues when seeking broader acceptance and understanding.
South Korea has advantages in some areas where NFTs can be effectively applied, such as gaming, webcomics, and K-pop. Despite the challenges the market currently faces due to localization and unclear regulations, new attempts at NFTs within the existing framework are gradually unfolding, bringing promising developments. With an increasing number of successful cases and the continuous improvement of NFT-related technology and expertise, coupled with increased investment from the government and businesses, South Korea is poised to introduce innovations that lead the global NFT market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




