- ### Background of the AI Revolution
Background of the AI Boom
With the vigorous development of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, we are entering a new era driven by data. Breakthroughs in fields such as deep learning and natural language processing have made AI applications ubiquitous. The birth of ChatGPT in 2022 ignited the AI industry, leading to a series of AI tools such as Wensheng video and automatic office, and the application of "AI+" has also been put on the agenda. The market value of the AI industry has also soared all the way, and is expected to reach 185 billion US dollars by 2030.
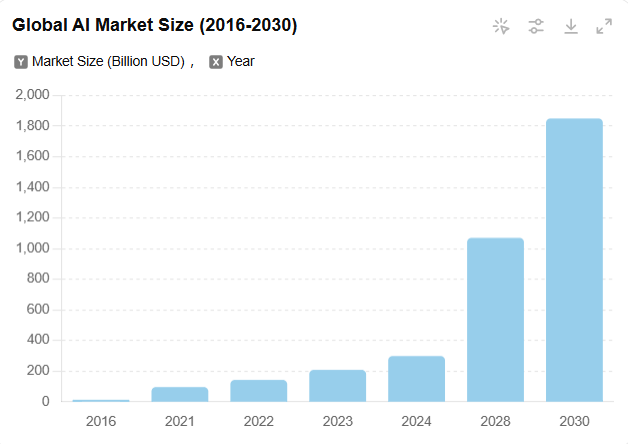
Figure 1 Changes in AI market value
Monopoly of AI by Traditional Internet Companies
Currently, the AI industry is mainly dominated by companies such as NVIDIA, Microsoft, Google, and OpenAI. Technological advancements have also brought about a series of challenges such as data centralization and uneven distribution of computing resources. At the same time, the decentralized concept of Web3 provides new possibilities for solving these problems, and in the distributed network of Web3, the current development pattern of AI will be reshaped.
Current Progress of Web3+AI
Amid the booming AI industry, a large number of high-quality Web3+AI projects have emerged. Fetch.ai creates a decentralized economy through blockchain technology, supporting autonomous agents and smart contracts for optimizing the training and application of AI models; Numerai uses blockchain technology and a community of data scientists to predict market trends and incentivize model developers through a reward mechanism; Velas builds a high-performance smart contract platform for AI and blockchain, providing faster transaction speeds and higher security. AI projects themselves contain three major elements: data, algorithms, and computing power. The current development of Web3+data and Web3+computing power is in full swing, but the Web3+algorithm direction has been at odds, ultimately leading to the formation of projects with single-direction applications. Bittensor seizes this gap by building an AI algorithm platform with a competitive and incentive mechanism through the blockchain itself, retaining the highest quality AI projects.
- ### Development Path of Bittensor
Innovative Breakthroughs
Bittensor is a decentralized incentive machine learning network and digital commodity market.
Decentralization: Bittensor operates on a distributed computing network controlled by thousands of different companies and organizations, addressing issues such as data centralization.
Fair Incentive Mechanism: The Bittensor network provides $TAO tokens to its subnets in proportion to their contributions, and the rewards provided by subnets to their miners and validators are also proportional to the node's contribution.
Machine Learning Resources: A decentralized network can provide services to every individual in need of machine learning computing resources.
Diverse Digital Commodity Market: Initially, the digital commodity market of the Bittensor network was designed specifically for the trading of machine learning models and related data. However, benefiting from the expansion of the Bittensor network and the Yuma consensus mechanism, it has become a market for trading any form of data.
Development History
Unlike many overvalued VC projects in the current market, Bittensor is a fairer, more interesting, and more meaningful geek project, and its development history does not involve the process of "from painting a rosy picture to deceiving investors" like other projects.
Concept Formation and Project Launch (2021): Bittensor was created by a group of technology enthusiasts and experts dedicated to promoting decentralized AI networks. They used the Substrate framework to build the Bittensor blockchain to ensure its flexibility and scalability.
Early Development and Technical Verification (2022): The team released the Alpha version network to verify the feasibility of decentralized AI. They introduced the Yuma consensus, emphasizing the principle of data ignorance to maintain user privacy and security.
Network Expansion and Community Building (2023): The team released the Beta version and introduced the token economic model (TAO) for incentivizing network maintenance.
Technological Innovation and Cross-Chain Compatibility (2024): The team integrated Distributed Hash Table (DHT) technology, making data storage and retrieval more efficient. At the same time, the project began to focus on the promotion and further expansion of subnets and the digital commodity market.

Figure 2 Bittensor network promotional image
In the development history of Bittensor, there has not been much involvement of traditional VCs, avoiding the risk of centralized control. By incentivizing nodes and miners with tokens, the project also ensures the vitality of the Bittensor network. Essentially, Bittensor is a GPU miner-driven AI computing power and service project.
Token Economics
The token of the Bittensor network is TAO, which, in many aspects, is similar to BTC as a representation of admiration for Bitcoin. Its total supply is 21 million tokens, with halving occurring every four years. TAO tokens were distributed through a fair launch at the start of the Bittensor network, with no pre-mining, so there are no tokens reserved for the founding team and VCs. Currently, a Bittensor network block is generated approximately every 12 seconds, rewarding 1 $TAO token per block. Approximately 7,200 TAO tokens are generated per day, and these rewards are distributed based on contributions to each subnet, and then allocated to subnet owners, validators, and miners within the subnet.
Figure 3 Bittensor community promotional image
TAO tokens can be used to purchase and obtain computing resources, data, and AI models within the Bittensor network, and they also serve as credentials for participating in community governance.
Current Status of Development
The total number of Bittensor network accounts currently exceeds 100,000, with over 80,000 non-zero accounts.
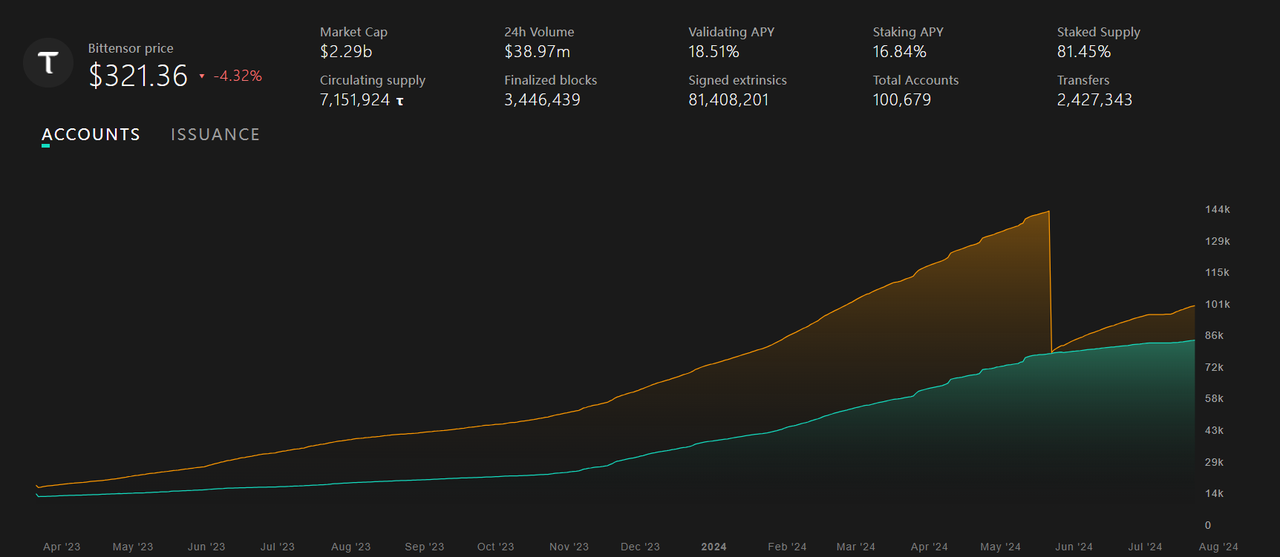
Figure 4 Changes in the number of Bittensor accounts
In the past year, TAO has surged several times, with a current market value of 22.78 billion US dollars and a coin price of 321 US dollars.
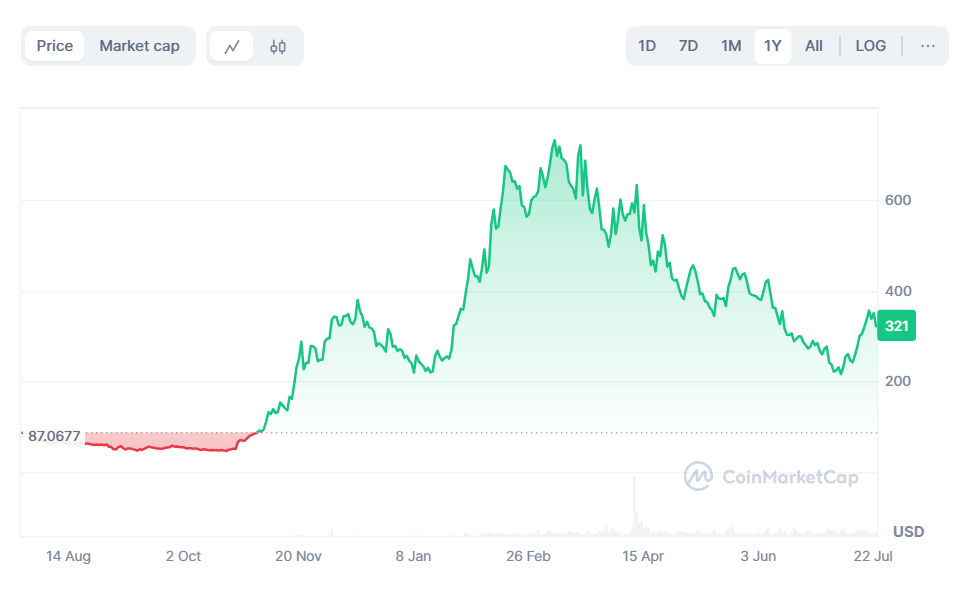
Figure 5 Changes in TAO token price
- ### Gradually Implemented Subnet Architecture
Bittensor Protocol
The Bittensor protocol is a decentralized machine learning protocol that supports the exchange of machine learning capabilities and predictions among network participants, and promotes the sharing and collaboration of machine learning models and services in a peer-to-peer manner.
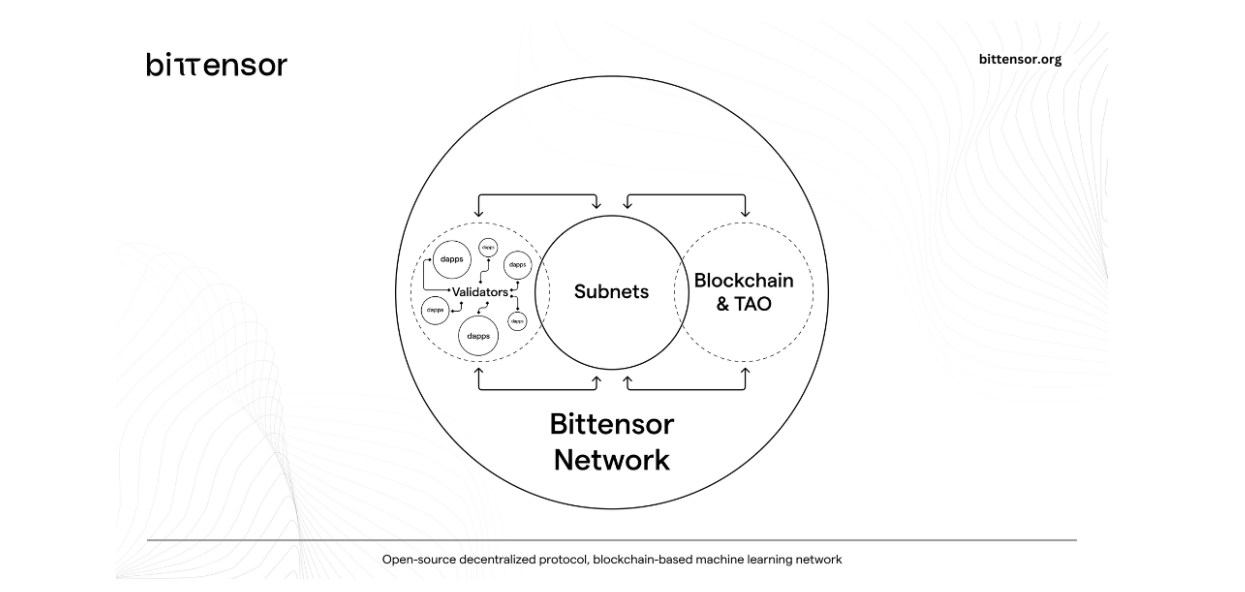
Figure 6 Bittensor protocol
Bittensor Subnet Architecture
The Bittensor protocol includes network architecture, subtensors, subnet architecture, validator nodes, and miner nodes in the subnet ecosystem. Essentially, the Bittensor network is a group of nodes participating in the protocol, running Bittensor client software on each node to interact with other nodes in the network. These nodes are managed by individual subnets, which employ a mechanism of natural selection, eliminating poorly performing subnets and expelling poorly performing validator and miner nodes within each subnet. It is evident that subnets are the most crucial component of the Bittensor network architecture.
Subnet Logic
Subnets can be seen as independently running code segments with unique user incentives and functionality, while each subnet maintains the same consensus interface as the Bittensor main network. Subnets include local subnets, testnet subnets, and mainnet subnets. Apart from the root subnet, there are currently 45 subnets, and it is expected that the number of subnets will increase from 32 to 64 between May and July 2024, with 4 new subnets added each week.
Subnet Roles and Emission
The entire Bittensor network consists of six functional roles: users, developers, miners, staking validators, subnet owners, and committees. Within subnets, there are subnet owners, miners, and staking validators.
Subnet Owners: Subnet owners are responsible for providing basic miner and validator code, can set unique incentive mechanisms, and allocate miner work incentives.
Miners: Miner nodes are encouraged to iterate server and mining code to maintain a leading position in competition with other miners within the same subnet. Miners with the lowest emissions will be replaced by new miners and will need to re-register their nodes. It is worth noting that miners can run multiple nodes in multiple subnets.
Validators: Validators earn rewards by measuring the contribution of each subnet and ensuring its correctness. They can also stake TAO tokens on validator nodes, which can earn staking rewards ranging from 0-18% (adjustable).
Subnet emission is the mechanism for distributing TAO token rewards to miners and validators in the Bittensor network. Generally, 18% of the emission rewards obtained by the subnet are allocated to subnet owners, 41% to subnet validators, and 41% to miners. A subnet contains 256 UDI slots, with 64 UID slots allocated to validators and 192 UID slots allocated to miners. Only the top 64 validators with the highest staking amount can obtain validator permission and are considered active validators within the subnet. The staking amount and performance of validators determine their status and rewards within the subnet. Miner performance is scored based on requests and evaluations from subnet validators, and poorly performing miners will be replaced by newly registered miners. Therefore, the higher the total staked tokens by validators, the higher the computing efficiency of miners, and the higher the total emission of the subnet, the higher the ranking.
Subnet Registration and Elimination
After a subnet is registered, it enters a 7-day immunity period, with the initial registration fee being 100 $TAO. The registration fee will double for subsequent registrations, and this fee will gradually decrease to 100 TAO over time. When all subnet positions are filled, registering a new subnet will remove the subnet with the lowest emission that is not in the immunity period to accommodate the new subnet. Therefore, subnets need to maximize the staking amount of validators and the efficiency of miners within the UID slots to ensure they are not removed after the immunity period.

Figure 7 Subnet Names
Benefiting from the subnet architecture of the Bittensor network, the decentralized AI data network Masa has been implemented, becoming the first dual-token reward system in the Bittensor network, attracting $18 million in funding.

Figure 8 Masa Promotion
- ### Consensus and Proof Mechanisms
The Bittensor network includes various consensus and proof mechanisms. In traditional decentralized networks, PoW (Proof of Work) is often used for miner nodes to ensure their contributions to the network and earn rewards based on their computing power and data processing quality. For validator nodes, the PoV (Proof of Validation) mechanism is generally used to ensure network security and integrity. In the Bittensor network, the innovative PoI (Proof of Intelligence) mechanism, in conjunction with the Yuma consensus, achieves validation and reward distribution.
Proof of Intelligence Mechanism
The PoI mechanism in Bittensor is an innovative validation and incentive mechanism that proves participants' contributions through the completion of intelligent computing tasks, ensuring network security, data quality, and efficient utilization of computing resources.
Miner nodes prove their work by completing intelligent computing tasks, which may include natural language processing, data analysis, and machine learning model training.
Tasks are assigned to miners by validators, and after completing the tasks, miners return the results to the validators, who then score the quality of the task completion.
Yuma Consensus
The Yuma consensus is the core consensus mechanism of the Bittensor network. After validators score the task completion, the scores are input into the Yuma consensus algorithm. In the consensus algorithm, validators with a higher staked TAO amount have a greater weight in the scoring, and the algorithm filters out results that deviate from the majority of validators. Finally, the system distributes token rewards based on the comprehensive scores.
Figure 9 Consensus Algorithm Illustration
Data Ignorance Principle: Ensures privacy and security in the data processing process, meaning nodes can complete computations and validations without needing to know the specific content of the processed data.
Performance-Based Rewards: Allocates rewards based on the performance and contribution of nodes, ensuring efficient and high-quality computing resources and data processing.
MOE Mechanism Collaboration
Bittensor introduces the MOE mechanism into the network, integrating multiple expert-level sub-models within a model architecture. Each expert model has relative advantages when addressing specific domain problems. Therefore, when new data is introduced into the entire model architecture, different sub-models can collaborate to achieve better operational results than a single model.
In conjunction with the Yuma consensus mechanism, validators can also score expert models and rank their capabilities, and allocate token rewards, thereby incentivizing model optimization and improvement.
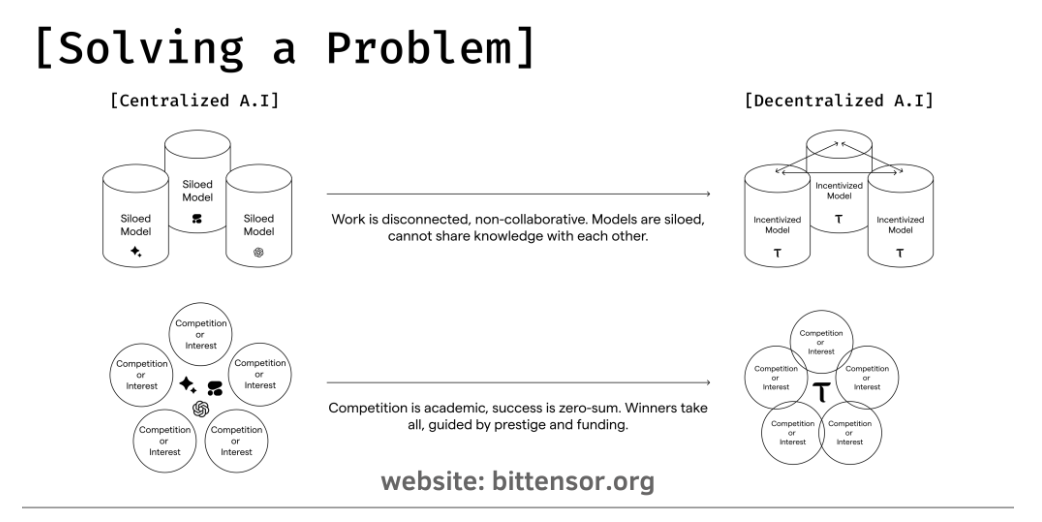
Figure 10 Problem-Solving Approach
- ### Subnet Projects
As of the time of writing, the number of registered Bittensor subnets has reached 45, with 40 of them named. When the number of subnets was limited in the past, there was intense competition for subnet registration, and the registration fee once reached as high as one million US dollars. Currently, Bittensor is gradually opening up more subnet registration slots. Newly registered subnets may not match the stability and model effectiveness of longer-running subnets. However, due to the subnet elimination mechanism introduced by Bittensor, in the long run, it is a process of natural selection, where subnets with poor model performance and insufficient capabilities will struggle to survive.
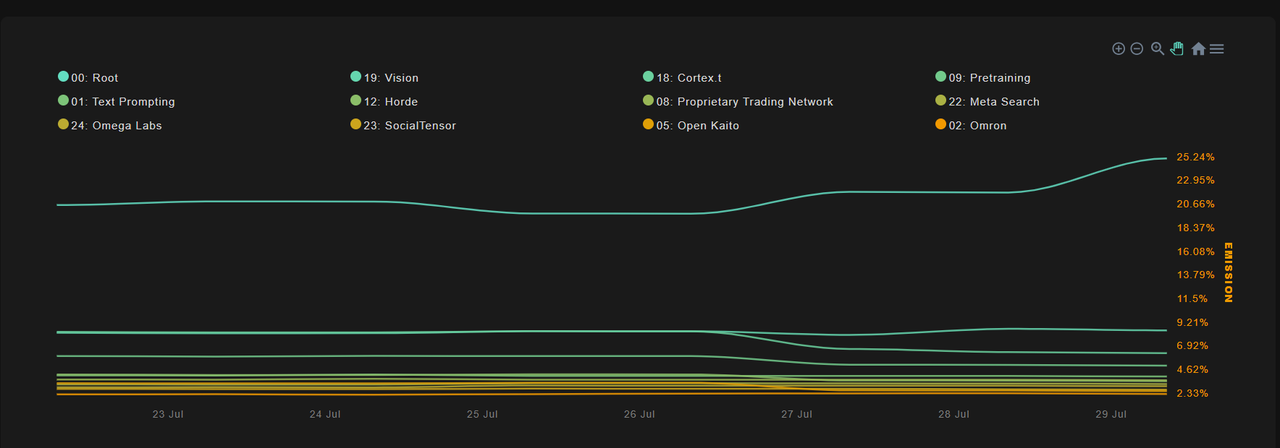
Figure 11 Bittensor Subnet Project Details
Excluding the root subnet, subnets 19, 18, and 1 have received significant attention, with emission proportions of 8.72%, 6.47%, and 4.16% respectively.
- Subnet 19
Subnet 19, named Vision, was registered on December 18, 2023. Vision focuses on decentralized image generation and inference, providing access to the best open-source LLM, image generation models (including models trained on the subnet 19 dataset), and other miscellaneous models such as embedding models.
Currently, the registration fee for the Vision subnet slots is 3.7 TAO, with a total node income of approximately 627.84 TAO in the past 24 hours and a node value recovery of 64.79 TAO in the past 24 hours. If newly registered nodes can reach the average level, the daily income can reach 2.472 TAO, approximately $866.
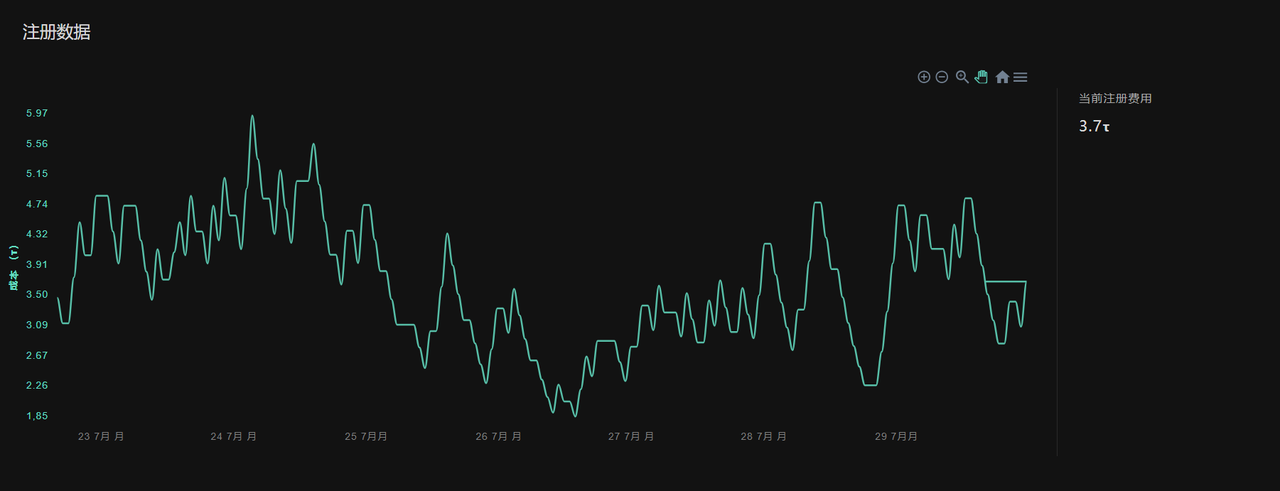
Figure 12 Vision Subnet Registration Fee Data
The total value of recovered nodes in the Vision subnet is approximately 19200 TAO.
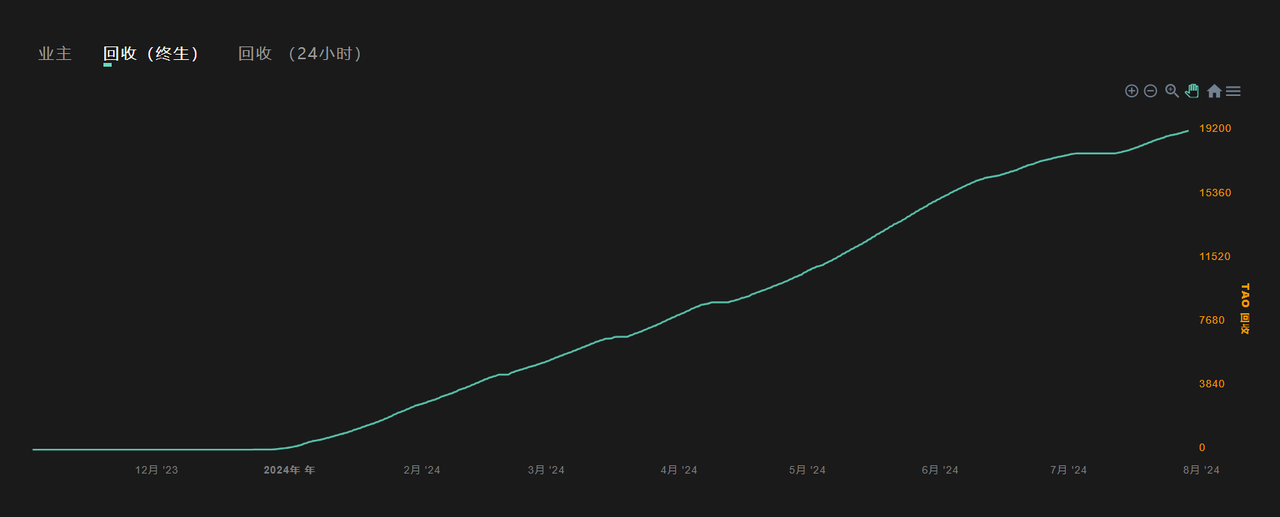
Figure 13 Vision Subnet Recovery Fee
- Subnet 18
Subnet 18, named Cortex.t, developed by Corcel, is dedicated to building an advanced AI platform, providing reliable, high-quality text and image responses to users through APIs.
Currently, the registration fee for Cortex.t subnet slots is 3.34 TAO, with a total node income of approximately 457.2 TAO in the past 24 hours and a node value recovery of 106.32 TAO in the past 24 hours. If newly registered nodes can reach the average level, the daily income can reach 1.76 TAO, approximately $553.64.
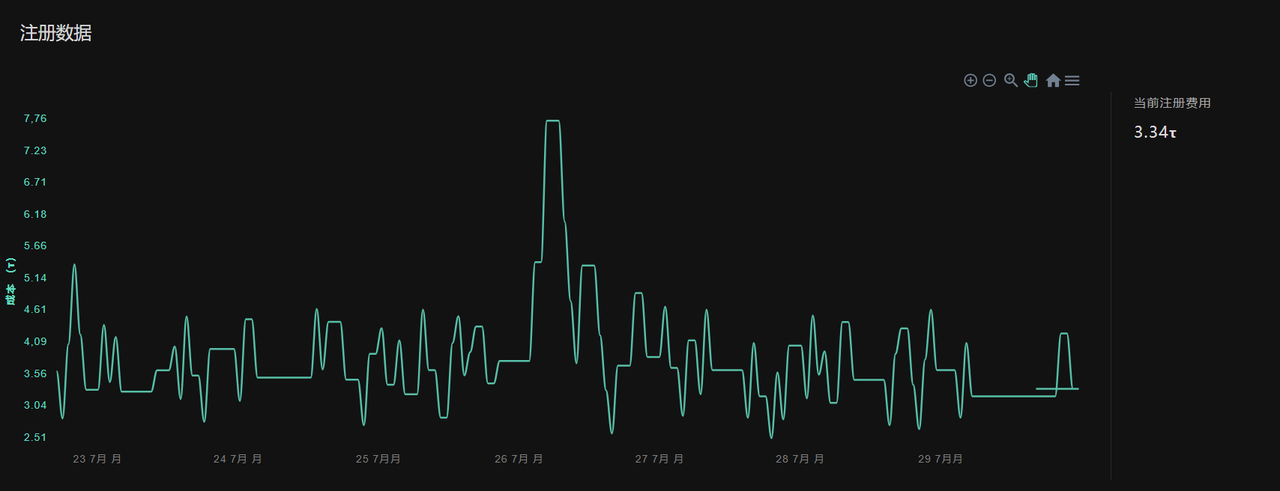
Figure 14 Cortex.t Subnet Registration Fee Data
The total value of recovered nodes in the Cortex.t subnet is approximately 27134 TAO.
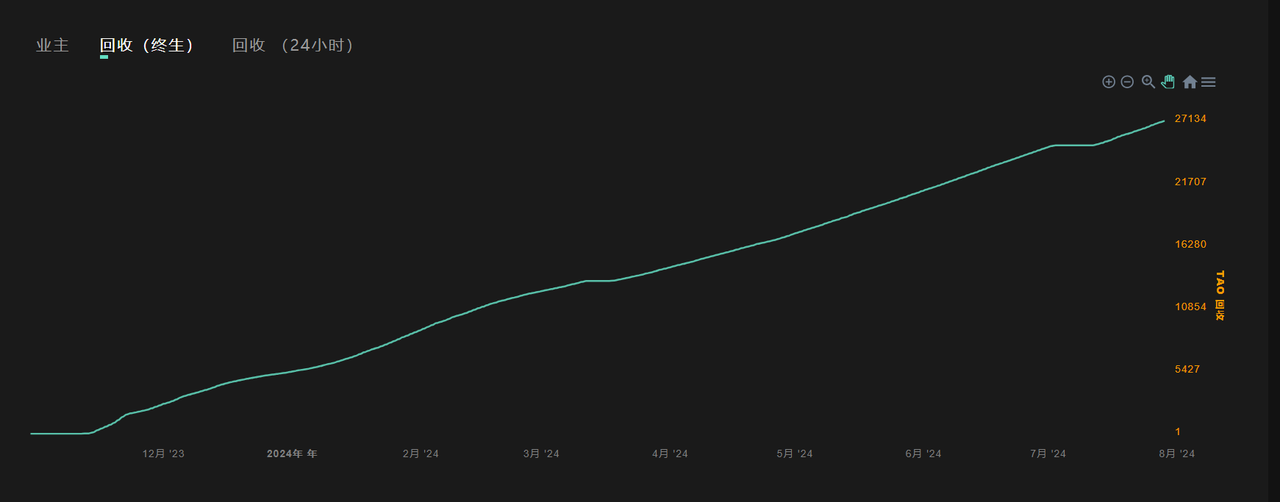
Figure 15 Cortex.t Subnet Recovery Fee
- Subnet 1
Subnet 1, developed by the Opentensor Foundation, is a decentralized subnet specifically for text generation. As the first project of the Bittensor subnets, it has been heavily criticized. In March of this year, Eric Wall, founder of Taproot Wizards, referred to Bittensor's TAO token as a meme coin in the AI field and pointed out that subnet 1 allowed hundreds of nodes to produce similar results through AI when answering text-based questions, which did not improve the effectiveness of solving real-world problems.
- Others
In terms of model categories, subnets 19, 18, and 1 all belong to the generation model category. In addition, there are also large data processing models, trading AI models, etc., such as subnet 22 Meta Search, which provides market sentiment analysis through Twitter data, and subnet 2 Omron, which learns and continuously optimizes staking strategies using deep neural networks.
In terms of income risk, if the slot can be successfully operated for several weeks, the income is obviously very substantial. However, if newly registered nodes cannot use high-performance graphics cards and optimize local algorithms, it will be difficult to survive in competition with other nodes.
Future Development
From the perspective of popularity, the popularity of the AI concept itself is not inferior to the Web3 concept, and even a considerable amount of hot money that would have originally flowed into the Web3 industry has been attracted to the AI industry. Therefore, Web3+AI will be the market focus for a long time in the future.
From the perspective of project architecture, Bittensor is not a traditional VC project. Since its launch, the project has increased by tens of times and is supported by both technology and the market.
From the perspective of technological innovation, Bittensor breaks the previous situation where Web3+AI projects operated independently. Its innovative subnet architecture can also reduce the difficulty for many teams with AI technical capabilities to migrate to decentralized networks and quickly obtain income. Due to the competitive elimination mechanism, subnet projects must continuously optimize models and increase staking amounts to prevent being replaced by new subnets.
From a risk perspective, as Bittensor increases the number of subnet slots, it will inevitably lower the difficulty of subnet registration, increasing the possibility of mixed projects taking advantage of the situation. At the same time, as the number of subnets increases, the TAO tokens obtained by originally registered subnets will gradually decrease. If the TAO token price does not rise with the increase in the number of subnets, the income is likely to fall short of expectations.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




