This article will delve into the development and challenges of ZKML technology, using the cases of Worldcoin and Vanna as examples, to promote the widespread application and prosperity of this technology in the blockchain field.

With the rapid development of blockchain technology, data privacy and security have become core issues. Zero-knowledge machine learning (ZKML), as an emerging technology, effectively combines the security of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) and the intelligence of machine learning (ML), bringing unprecedented opportunities to the Web3 world.
Currently, ZKML technology is widely used in the blockchain field, mainly in the following areas:
- Hardware acceleration: Projects such as Cysic and Ulvetanna use hardware acceleration to improve the efficiency of on-chain computation due to the computational complexity of ZK proofs.
- On-chain data processing: Projects like Axiom and Herodotus focus on transforming on-chain data into formats suitable for ML training and ensuring that ML output results can be easily accessed from the chain.
- Circuitization of computation: To enable ML computation to be processed by the ZK of the blockchain, projects like Modulus Labs and Jason Morton transform the ML computation mode into circuit form.
- ZK proof of results: To address the trust issue of ML models, projects like RISC Zero and Axiom use ZK-SNARKs-based proofs to verify the authenticity of the models.
ZKML is currently developing rapidly and can help in the construction of decentralized identity (DID) for Web3. Previously, identity management modes such as private keys and mnemonic phrases resulted in a poor user experience for Web3. True DID construction can be completed through ZKML for the identification of Web3 subjects' biological information, while ensuring the privacy of user biological information. Worldcoin is using ZKML to implement zero-knowledge DID verification based on iris scanning.
This article will delve into the development and challenges of ZKML technology using the cases of Worldcoin and Vanna as examples, to promote the widespread application and prosperity of this technology in the blockchain field.
1. Worldcoin Case Study: The Application of ZKML in Identity Verification and Privacy Protection
- DApp Integration with Worldcoin
Worldcoin ID can be used for identity authentication. Worldcoin provides an IDKit SDK for identity authentication using the World App, with the specific process as follows:
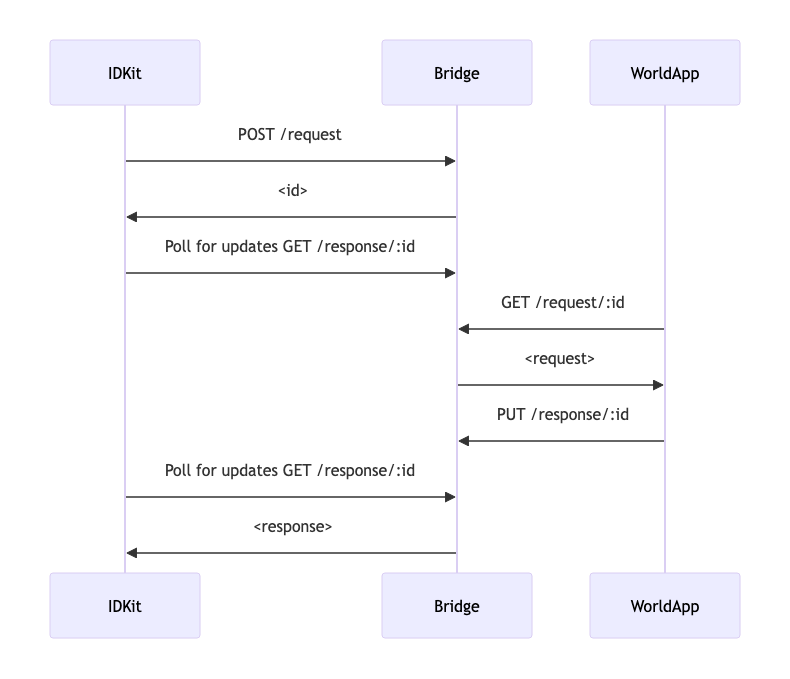
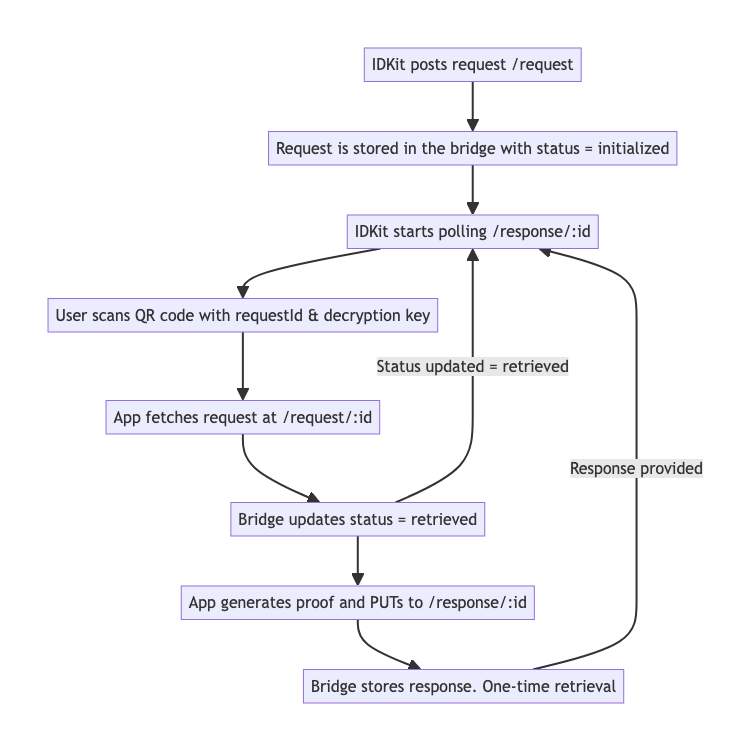
After processing the above process, the user's biological information is used as a login credential, ultimately generating a proof for identity verification in the Worldcoin App.
Application of ZKML in Worldcoin
- ML Application in Worldcoin
By running the IrisCode model on self-hosted biometric data (user terminal), it verifies whether the user has locally created a valid and unique WorldID, and calls the _addMember(uint256 groupId, uint256 identityCommitment) function on the WorldID Semaphore identity group with a valid identity commitment to publicly authorize without permission.
- ZK Application in Worldcoin
Registration Process
During the registration process in Worldcoin, users generate a WorldID through iris scanning and call the _addMember function on the Semaphore identity group with a valid identity commitment to achieve public authorization without permission.
Signup Sequencer: The registration sequencer sorts the data (identity) submitted in batches to the Ethereum smart contract.
Semaphore MTB: SMTB is a service for batch processing Merkle tree updates. It accepts Merkle tree updates and merges them into a single update. This is very useful for reducing the number of transactions that need to be submitted to the blockchain. By generating SNARK, the correctness of batch Merkle tree updates can be ensured.
Tx Sitter: Signs the transaction and sends it to the blockchain.
The proof input consists of an external nullifier (public 32-byte value that scopes the uniqueness of verifications) and a secret identity nullifier, from which the nullifier hash is calculated for user identity recognition.
Login Process
During the login process, the user's submitted identity nullifier is transformed into a proof, similar to zkrollup. After the user submits the identity nullifier, multiple Merkle state updates are aggregated and published to the blockchain.
Summary
Worldcoin's technical implementation involves multiple aspects, including the local running of the IrisCode model, the generation of external nullifiers, batch processing by Semaphore MTB, and transaction processing by Tx Sitter. Because the process of converting the iris to World ID using the IrisCode model occurs on the user terminal, this part is not run by external nodes to protect user privacy. The combination of these technologies allows Worldcoin to protect user privacy while achieving efficient and secure identity verification.
The Worldcoin case demonstrates the potential and effectiveness of ZKML technology in practical applications. By combining zero-knowledge proofs and machine learning, Worldcoin not only enhances the security of identity verification but also provides strong support for user privacy protection.
This case provides valuable reference and inspiration for other blockchain projects.
2. Vanna Network and ZKML: Intelligent Reasoning and Verification in Blockchain
Overview of Vanna Network
Vanna Network is an innovative blockchain platform that focuses on providing efficient zero-knowledge proof generation and verification services. It combines the transparency and immutability of blockchain with the privacy protection features of zero-knowledge proofs, providing users with a secure and reliable data processing environment.
Functions of Vanna Network
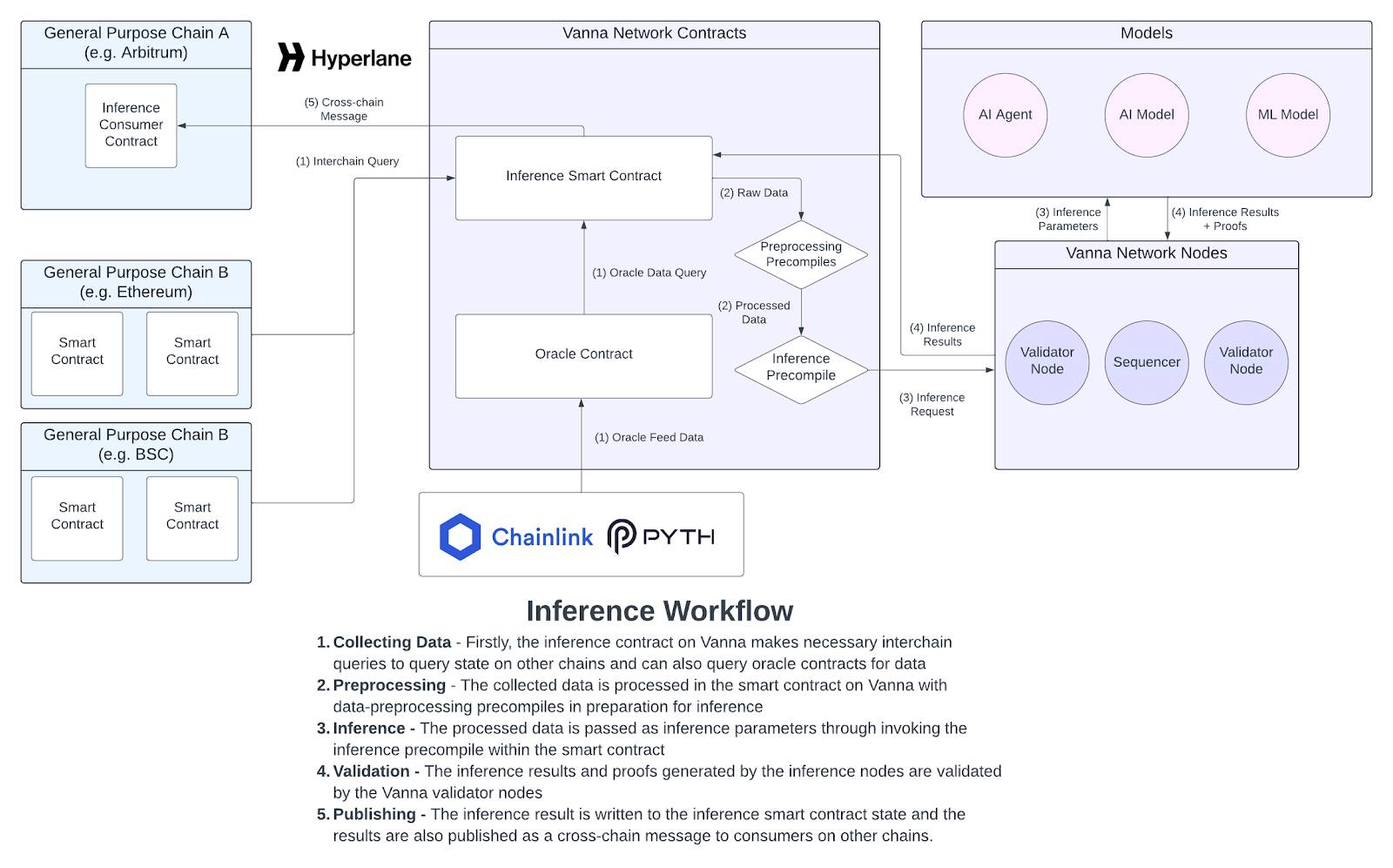
- Data Query: Access Oracle feed data or on-chain status by querying smart contracts across chains.
- Preprocessing: Use Vanna's built-in pre-compiler to preprocess the raw data of the query to prepare for reasoning.
- Reasoning Execution: Run reasoning seamlessly and scalably at any encryption security level suitable for your use case.
- Reasoning Verification: All encrypted proofs ensuring reasoning are verified by validator nodes on the Vanna network.
- Publishing and Tracing: Reasoning results can be cross-chain messaged to any on-chain contract and published to the data availability layer.
Vanna Network Features
- Parallel Reasoning Pre-execution
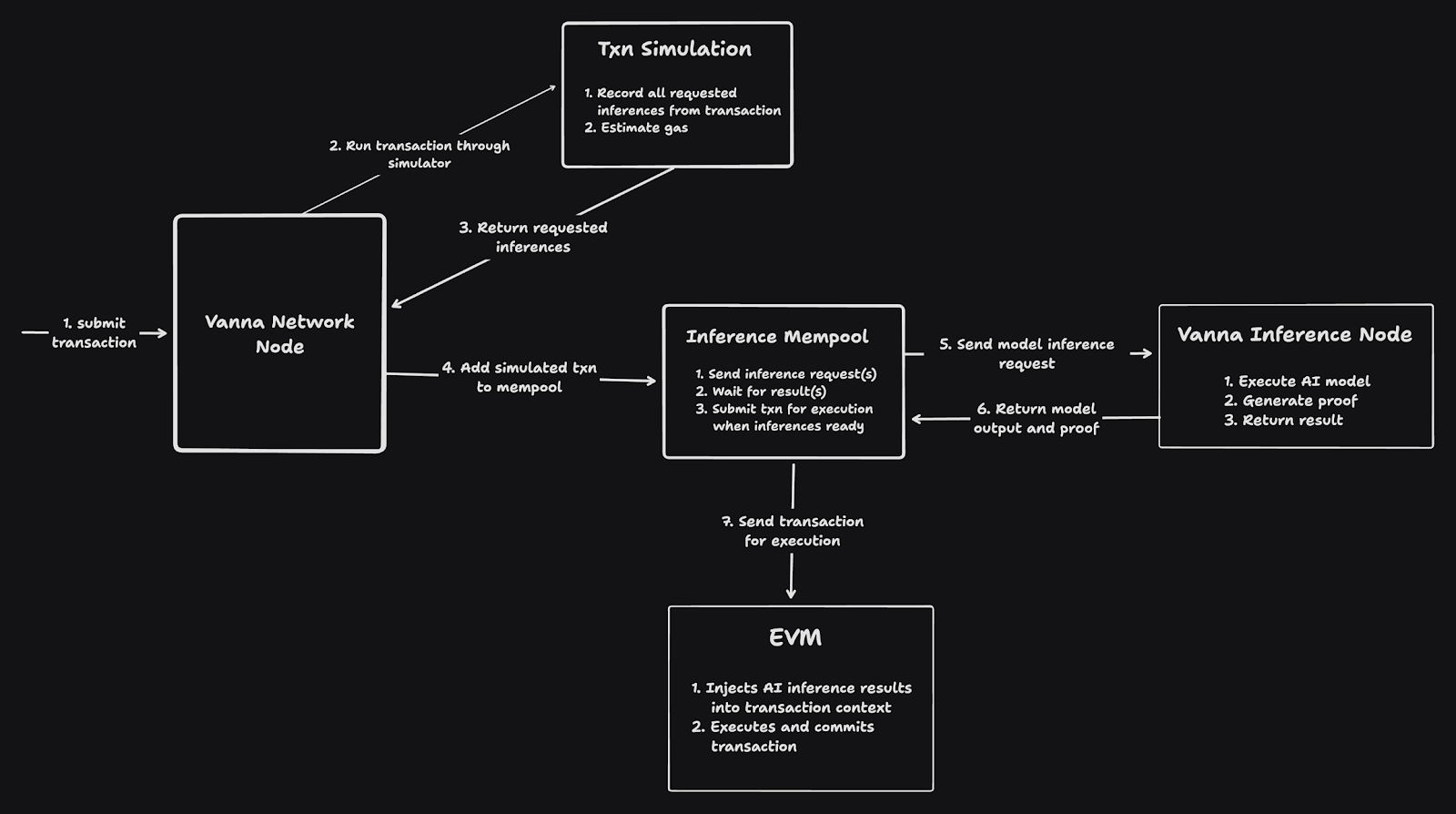
Divided into three stages:
Stage 1: Simulation
Vanna runs each transaction through a simulator to determine which reasoning requests the transaction will issue. No execution takes place here.
Stage 2: Reasoning Memory Pool
Transactions and their reasoning requests are added to the reasoning memory pool, which sends the requests to Vanna reasoning nodes. Reasoning and proof are executed here.
Stage 3: EVM Execution
The reasoning results are injected into the EVM so that transactions can directly read them, just like reading any other variable. The transaction is then executed and submitted to the blockchain.
- Verification-Computation Separation
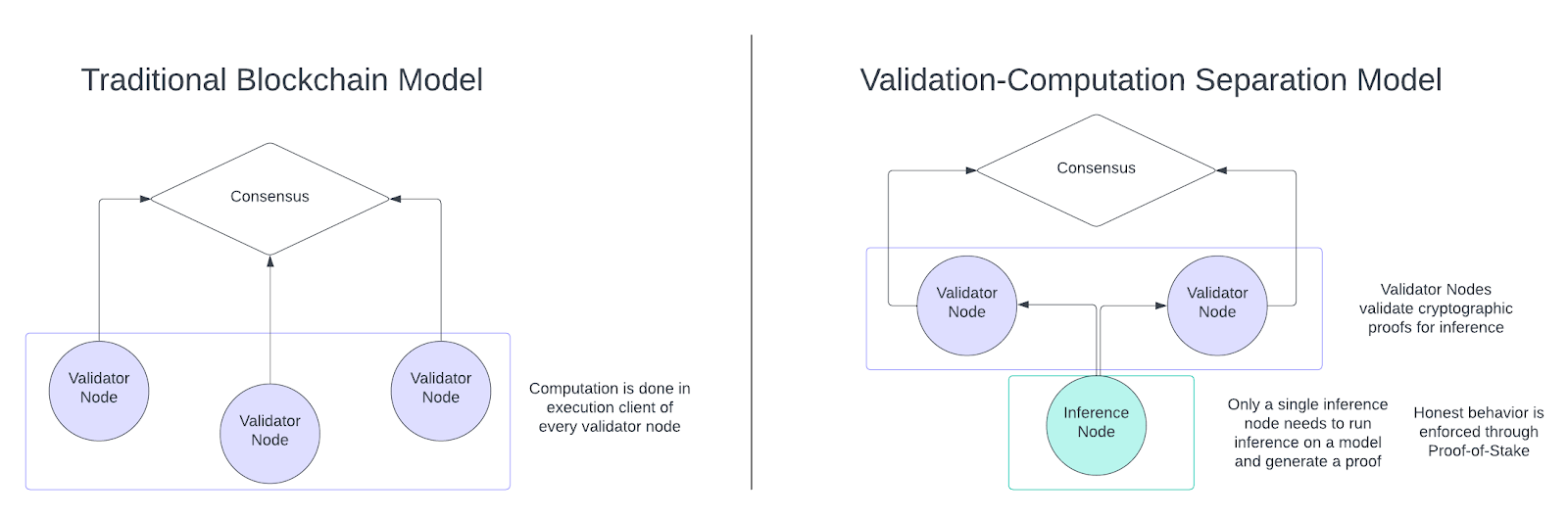
Vanna Network uses two types of nodes, namely validator nodes and reasoning nodes, and forks network verification and reasoning computation to these two types of nodes respectively.
Validator Nodes: Rollup nodes independently verify transactions and the state of the Vanna network. Rollup nodes on the Vanna network also participate in verifying the encrypted proofs generated by reasoning nodes.
Reasoning Nodes: Reasoning nodes do not verify transactions and blocks on the network, but focus only on computing AI/ML reasoning and generating encrypted proofs for reasoning.
- Staking and Penalties
Vanna Network provides cryptographic economic security in the form of application-layer staking contracts. When reasoning nodes come online to participate in protecting the network, they must deposit Vanna tokens in a staking contract. The staking contract enforces the behavior of reasoning nodes, with reduction conditions including but not limited to:
- zkML - generating invalid proofs that cannot be verified cryptographically
- opML - successfully challenging reasoning generated by nodes
- zkFP - successfully challenging reasoning generated by nodes, or failing to generate a ZK SNARK proof for that reasoning
Summary
Through its unique design and features, Vanna Network demonstrates the potential application of ZKML in the blockchain. Its parallel reasoning pre-execution, verification-computation separation, and staking and penalty mechanisms showcase the potential of ZKML in the blockchain.
- Development Sword of ZKML EZKL: Simplifying the Generation and Verification of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Overview of EZKL
EZKL takes a high-level description of a program and sets up a zero-knowledge prover and verifier. It focuses on programs represented as computation graphs in pytorch AI/ML models and other formats. Once set up, the prover can prove the following statements:
- "I ran this public neural network with some private data, and it produced this output."
- "I ran my private neural network with some public data, and it produced this output."
- "I correctly ran this public neural network on some public data, and it produced this output."
Workflow of EZKL
The workflow of EZKL is as follows:
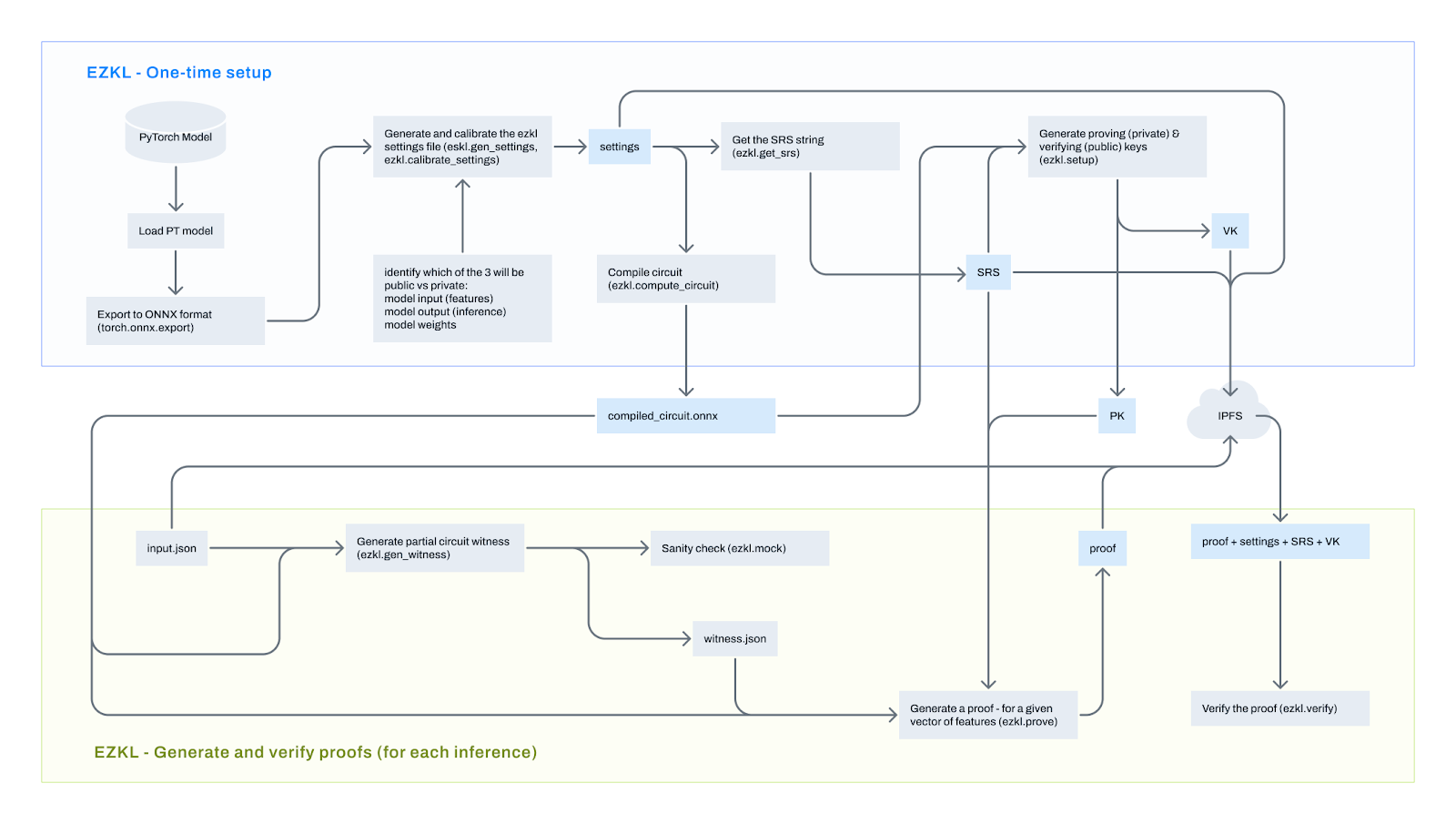
- Define the neural network model: Define a simple neural network.
- Model training: Generate input data and obtain output through the model.
- Model export: Export the model in ONNX format.
- Generate zero-knowledge proof setup: Generate setup files.
- Compile circuit: Compile the model to generate circuit files.
- Generate zero-knowledge proof: Generate SRS, witness files, proof keys, and verification keys.
- Verify zero-knowledge proof: Generate and locally verify the zero-knowledge proof or create Solidity code and ABI files for an EVM verifier, deploy the contract, and verify the proof on-chain.
- Challenges and Prospects of ZKML
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, zero-knowledge machine learning (ZKML) is gradually becoming a key force in improving application privacy and security. It not only heralds the emergence of innovative applications such as smart contract privacy protection and enhanced security in decentralized finance (DeFi), but also has the potential to become an indispensable part of blockchain technology, providing a solid technical foundation for building a more secure and privacy-focused digital world.
Challenges
Despite the enormous potential of ZKML, it also faces some challenges in its application:
- Technical complexity: The implementation of ZKML requires deep mathematical and cryptographic knowledge, which undoubtedly increases the difficulty of development and maintenance, requiring developers to have higher professional skills.
- Performance bottlenecks: The process of generating and verifying zero-knowledge proofs is computationally intensive and may affect the system's response time and processing capabilities. To address this issue, projects like Lumoz provide a modular compute layer to improve performance.
- User acceptance: Although ZKML provides powerful privacy protection features, users may be hesitant due to their lack of understanding of its complexity and security.
- Regulatory challenges: The development of privacy protection technologies requires regulatory agencies to update relevant regulations to adapt to the changes and challenges brought about by new technologies.
Prospects
Despite the challenges, the deep integration of ZKML technology with the future development of blockchain is full of hope:
- Technological progress: With further research and technological maturity, the implementation of ZKML will become more efficient and user-friendly.
- User education: Through education and outreach, understanding of the complexity and security of ZKML technology can be increased, leading to greater acceptance.
- Regulatory adaptation: Regulatory adaptation and innovation will provide legal and policy support for the development of ZKML technology.
- Application innovation: The continuous advancement of ZKML technology will inspire the emergence of more innovative applications, driving the wider application of blockchain technology.
- Conclusion
The development of ZKML technology is a major step in the blockchain field, heralding the arrival of a new era of data privacy and security. Faced with technical complexity, performance bottlenecks, and regulatory challenges, we should remain optimistic and believe that as technology advances and user acceptance increases, ZKML will play a more important role in the blockchain field, driving wider application and innovation.
Reference Material
- Worldcoin Docs
- Introduction to zero-knowledge proofs, Semaphore, and their application in World ID
- In-depth analysis of ZKML: technical principles, application scenarios, advantages, and challenges
- Is Worldcoin on the right path by using iris scanning for identity verification?
- A Gentle Introduction to ZKML
- a16z Crypto Investor: Zero-Knowledge (ZK) technology is severely underestimated
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




