Table of Contents
1. BTC Programming Potential to Be Developed
- Bitcoin: Recognized Value Storage Consensus
- BTC Takes the Path of Security > Flexibility
2. Programmable Bitcoin
- Self value store - Building an Economic Ecosystem for Diversified BTC Assets
- Ordinals - Empowering the NFT Ecosystem
- RGB++ - Supporting Multi-asset Issuance and Contract Establishment
- DLC Technical Route Project - Efficiently Maintaining Asset Security Circulation
- Vertical Scaling - Ensuring Mainnet Security through BTC Programming/Validation
- BitVM - Programming on BTC
- ZK rollup - Validating ZKP on BTC Mainnet
- Horizontal Eco-Expansion - Babylon as BTC's EigenLayer to Enhance Capital Efficiency
- Technical Highlights
- Economic Reuse
3. Summary
1. BTC Programming Potential to Be Developed
Bitcoin: Recognized Value Storage Consensus
BTC has a large market value and stable data: The current market value of Bitcoin has reached $137.2 billion and has shown stable transaction and activity indicators. As of April 1, 2024, the monthly trading volume of BTC ranged from $10 billion to $15 billion, and the active addresses remained stable at 30 million.
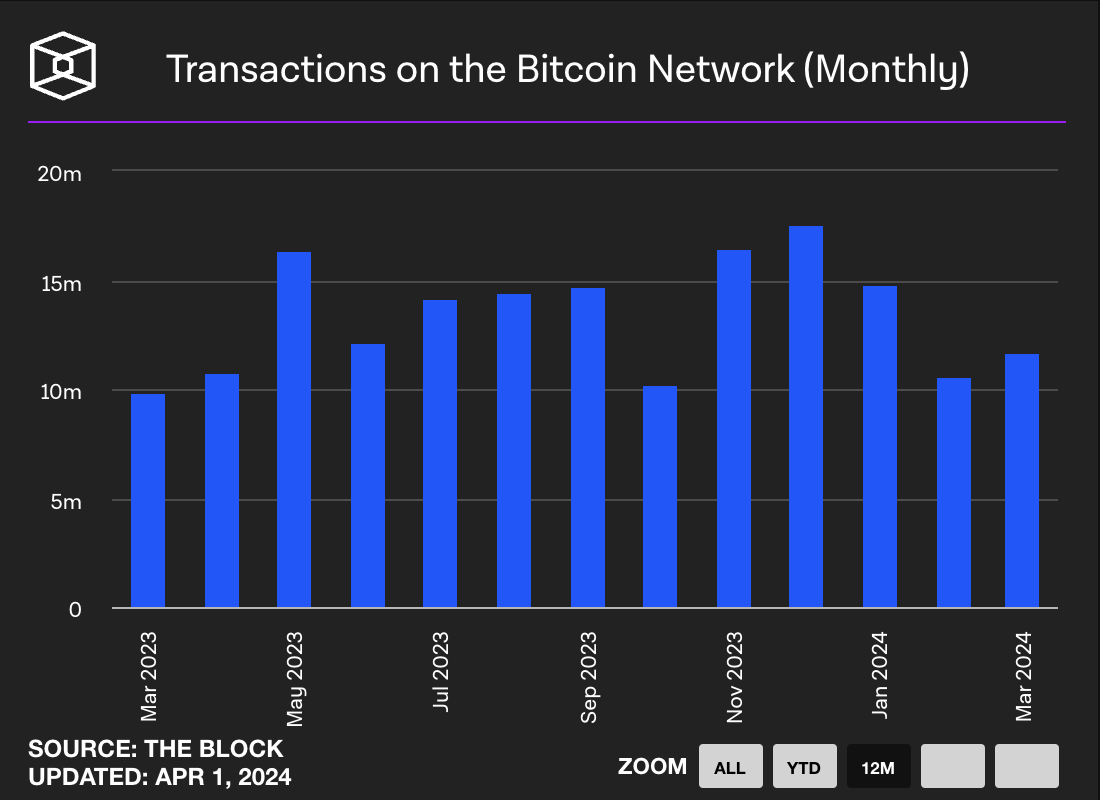
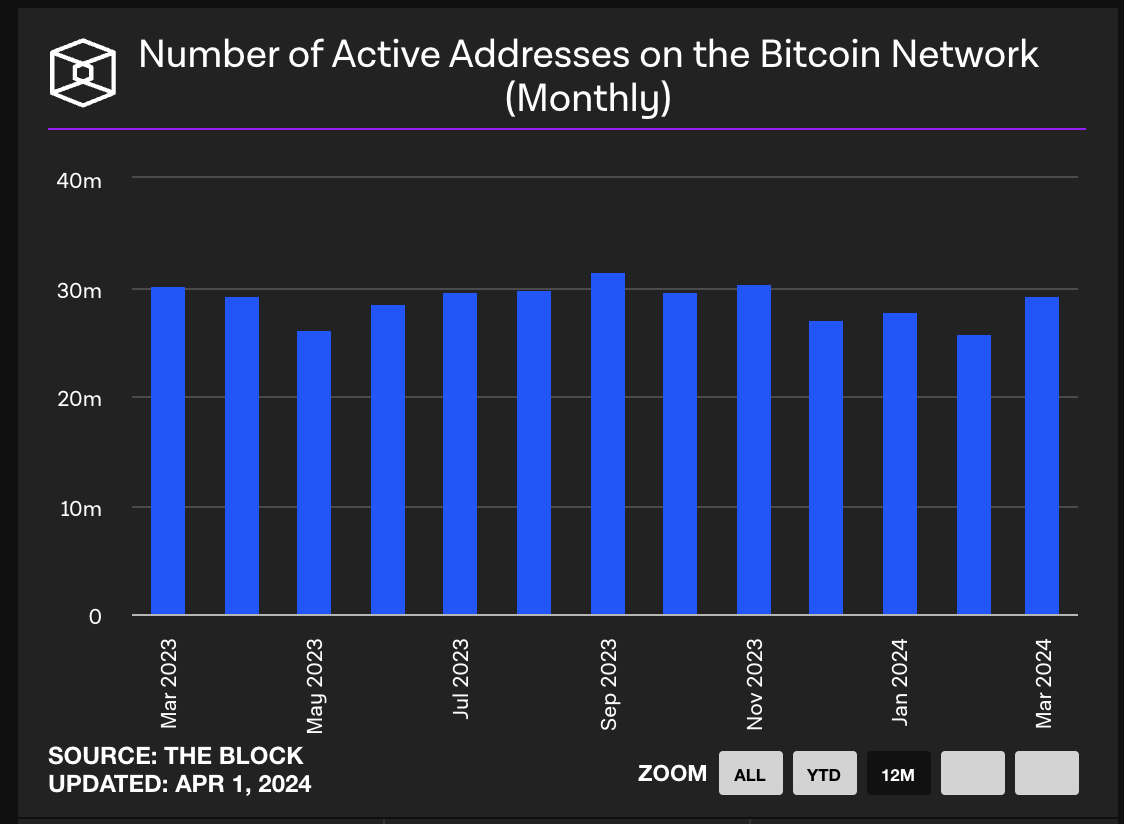
Source: The Block - On-chain Metrics - Bitcoin
In addition, according to CoinGecko's data, Bitcoin's share in the cryptocurrency market has been stable at around 50%.
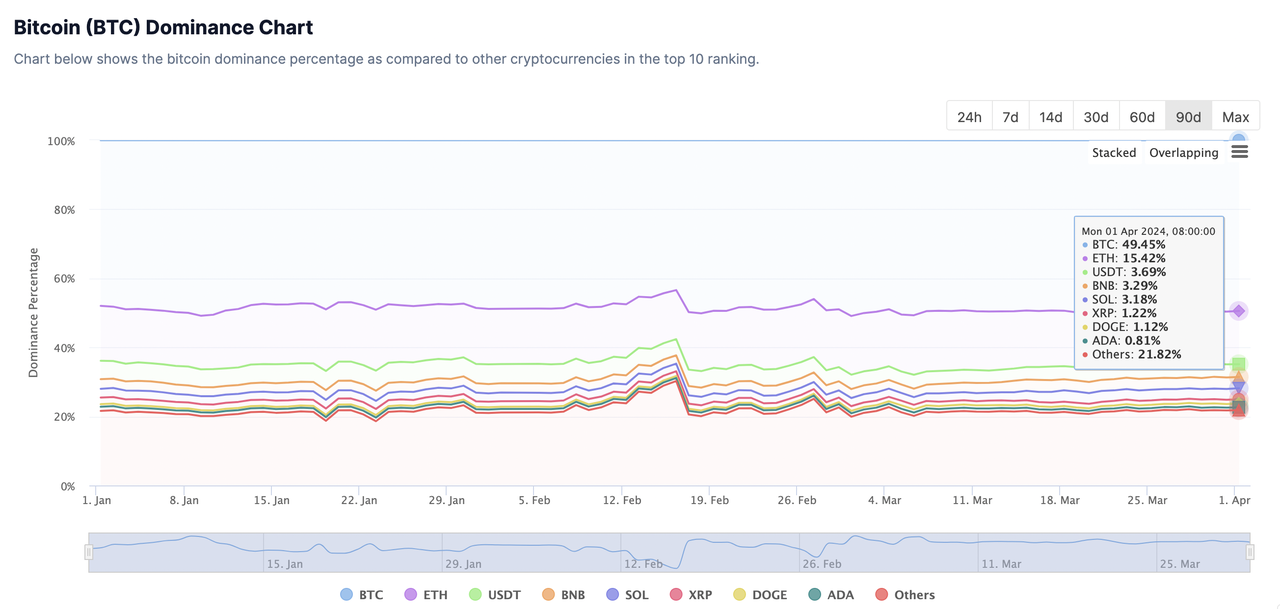
Source: CoinGecko - Global Charts
Bull market + sustained halving benefits BTC price: It is worth noting that the reserves of Bitcoin in exchanges have been continuously decreasing, implying that a large amount of Bitcoin may be held in individual custodial wallets on the chain. Generally, the decrease of Bitcoin in exchanges is interpreted as a bullish signal by the market. The total market value of the crypto market is currently $26 trillion, approaching the peak market value of the 2021 DeFi bull market (approximately $30 trillion), and it is still trending upwards, indicating the possibility of another bull market ahead.
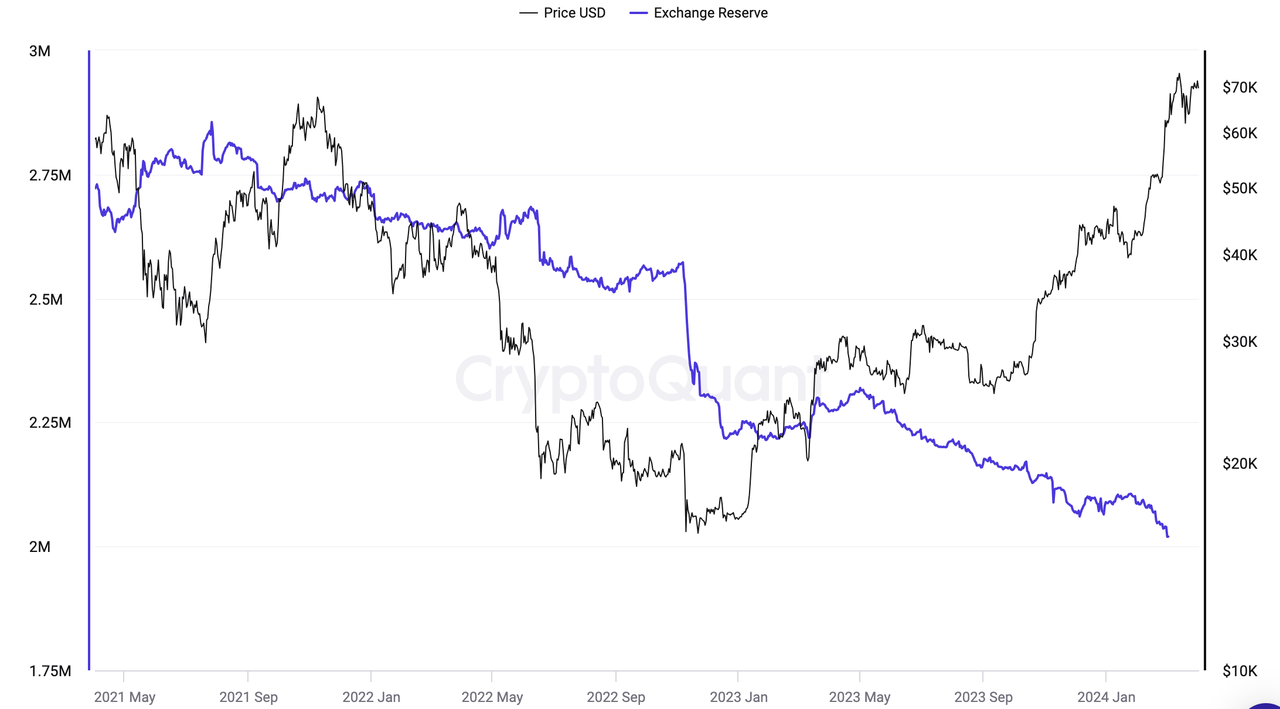
Source: CryptoQuant - Bitcoin Halving
The market has reacted positively to the upcoming Bitcoin halving event on April 20, 2024, which is expected to reduce the production of new Bitcoin, further driving up its price due to exacerbating the supply-demand imbalance.

Source: Watcher Guru - Bitcoin Halving
From the miners' perspective, the halving event means that the cost of mining each Bitcoin will increase, which is generally considered as a lower limit for the price of Bitcoin. The current estimated production cost of Bitcoin is between $18,000 and $21,000. According to CoinShares' analysis, the average cost after halving will rise to approximately $38,000.
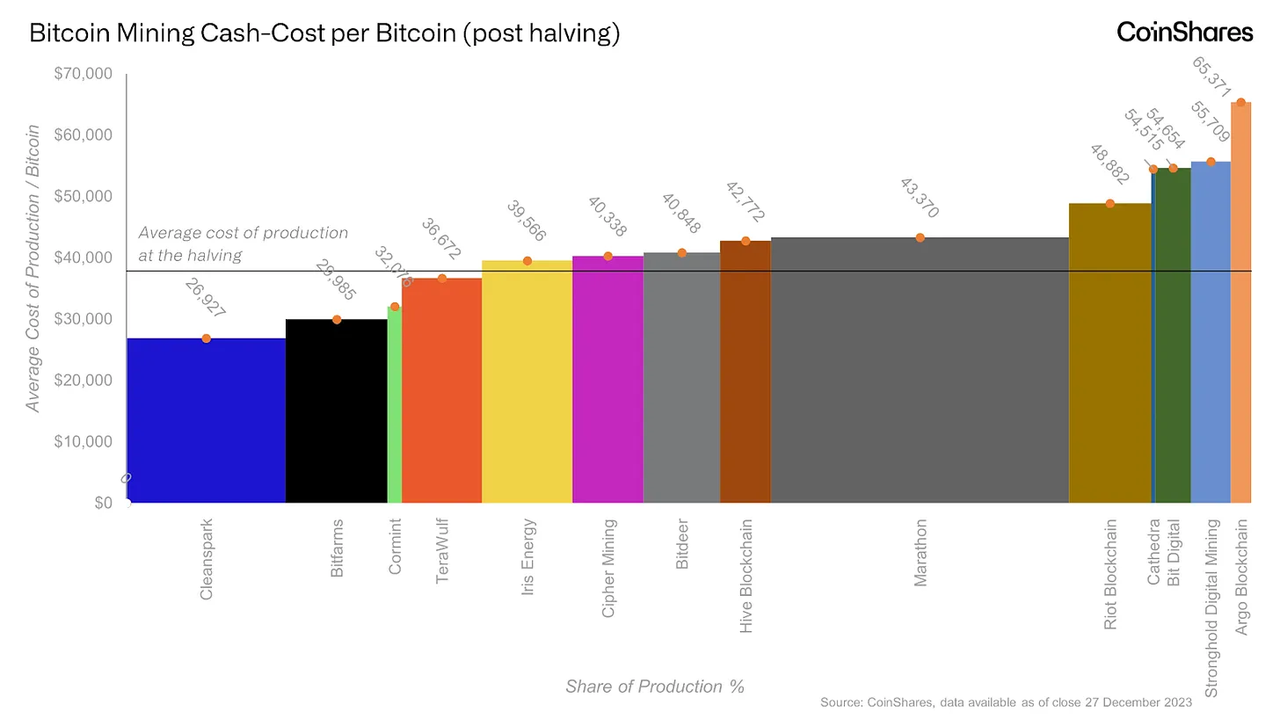
Source: Blockcrunch - Exploring the Frontier of Bitcoin
BTC Spot ETF: The emergence of Bitcoin spot ETFs has made Bitcoin's volatility more similar to traditional financial markets and has gained support from financial institutions including Blackrock, which is widely seen as a further recognition of Bitcoin. Based on this, it can be expected that more new capital, which previously held a reserved attitude towards the crypto market, will flow in.
BTC Takes the Path of Security > Flexibility
The reason Bitcoin is classified as a value storage tool is its lack of programmability, stemming from its non-Turing complete script language and the core development team's restrictions on its executable operation types:
1) Initial stage and scaling disputes: Satoshi Nakamoto set the initial block capacity limit of Bitcoin to 1MB, and if there is a need for scaling later, the block height can be set to automatically upgrade the block capacity in the code. However, after Satoshi Nakamoto's retreat, there were internal disputes within the Core development team about whether to scale, mainly concerned about the impact of scaling on decentralization and system risks.
2) Key technical disputes and community choices: To balance security and scalability, the BTC community introduced Segregated Witness (SegWit) and the Lightning Network in 2015, emphasizing security. However, the community had disagreements, leading to the 2017 hard fork of BTC, resulting in Bitcoin Cash (BCH), and further splitting into BSV.
3) Two technical upgrades to the Bitcoin protocol in 2017 and 2021: Segregated Witness (expanding to a theoretical 4MB through "segregating" signature data) and Taproot (introducing Schnorr signatures to optimize transaction privacy, efficiency, and security). However, compared to the capacity of other chains like Ethereum (charged in gas, from a limit of 5,000 Gas in 2015 to the current target limit of 15 million);
BTC chooses to sacrifice scalability in the impossible triangle of Scalability, Decentralization, and Security: This results in its inherent characteristics only allowing the recording of transfer transactions on blocks, with almost no ability to store other content. Because the Bitcoin network does not support smart contracts, it is also unable to issue NFTs through contracts. Coupled with low transaction throughput, slow speed, and high fees, its scalability is greatly limited.
BTC, as a value store, cannot generate income as collateral like gold and is mostly idle. Sending Bitcoin to the Ethereum virtual machine chain to replicate DeFi lending also requires additional trust assumptions (the need for a trusted exchange environment): This introduces a reliance on a centralized entity or a group of multi-signature validators, which has lower security. The market value of the most popular bridged token WBTC is only 10 billion US dollars, which is less than 1% of the total market value of Bitcoin.
2. Programmable Bitcoin
In the process of developing the Bitcoin ecosystem, there are mainly two dilemmas, namely the low scalability of the Bitcoin network (requiring better scaling solutions) and the limited applications in the Bitcoin ecosystem (requiring popular applications). Around these two dilemmas, the current construction of the Bitcoin ecosystem mainly focuses on programmable BTC, with three core projects:
1) Ordinals, RGB, and DLC protocols endow BTC with NFT and FT ecosystems while expanding its own value storage;
2) BitVM and ZK rollup calculations are executed off-chain and verified on the Bitcoin chain, realizing a modular and inheritable Rollup ecosystem that expands capacity vertically while using the Bitcoin mainnet to ensure its new value storage;
3) Babylon utilizes Bitcoin's native security to facilitate the establishment of a new economic model, i.e., a PoS chain strengthens its security through Bitcoin, and Bitcoin holders earn profits by supporting the security of the PoS chain, forming a horizontal capital efficiency improvement.
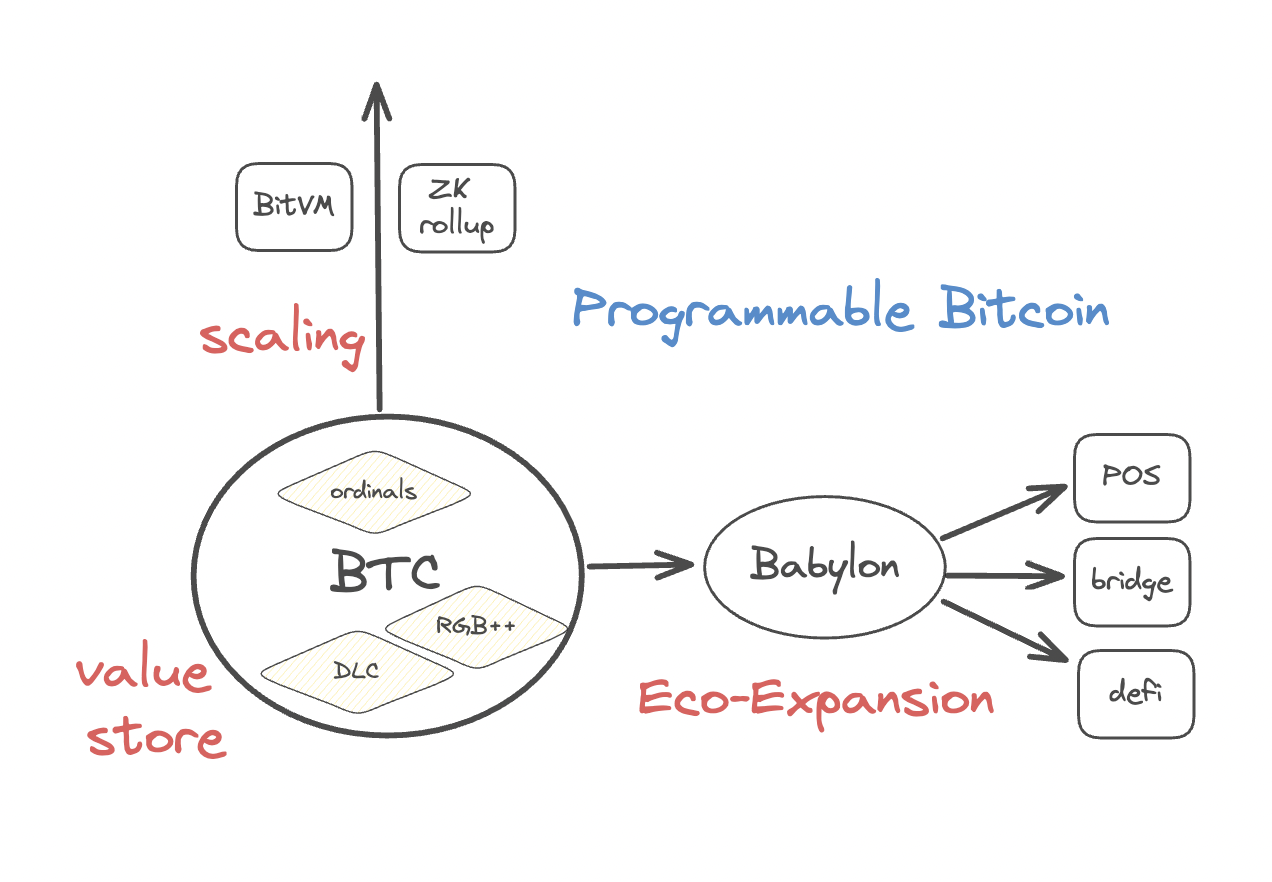
Self value store - Building an Economic Ecosystem for Diversified BTC Assets
ETF funds inject new blood into BTC, but Ordinals also attracts a lot of developers' attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Ordinals and BRC-20 Tokens "inscribe" data into the Bitcoin ledger; RGB extends the Bitcoin protocol to create and exchange different types of digital assets. The newly launched RGB++ further expands the possibilities of smart contracts and asset diversity by building a public chain, enabling off-chain verification, complex contracts, and mechanisms. The DLC technical route project provides a trustless decentralized bridge for DeFi on BTC and Ethereum by improving oracle security, allowing assets to circulate safely and quickly within the large BTC ecosystem.
Ordinals - Empowering the NFT Ecosystem
- Protocol Overview
What is Ordinals: Ordinals is an emerging Bitcoin blockchain protocol proposed by Bitcoin core contributor Casey Rodarmor in January 2023. The protocol aims to give the smallest unit of Bitcoin—satoshi (sats)—unique identifiers and attributes, transforming them into unique non-fungible tokens (NFTs). By embedding diverse data (images, text, videos, etc.) into satoshis, known as inscriptions, the Ordinals protocol enables the creation and trading of Bitcoin NFTs.
Core Features and Value: The technical innovation lies in Ordinals' inscription process, which gives each satoshi uniqueness, similar to creating artwork on paper currency. This process not only increases the utility of Bitcoin but also allows users to directly create and trade digital assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. The permanent value lies in the fact that since Ordinals is based on Bitcoin's satoshis, its underlying value is linked to Bitcoin itself and theoretically will not go to zero. Ordinals NFTs are permanently stored on the Bitcoin blockchain, becoming an inseparable part of it.
- Technical Details
Components of the Ordinals Protocol: 1) Ordinal theory allocates unique identifiers to 21 trillion satoshis, achieving non-fungibility; 2) The inscription process associates specific content with specific satoshis through UTXO, enhancing Bitcoin's scalability and security.
BRC-20 and Ordinals NFT: BRC-20 tokens are Bitcoin token standards based on Ordinals inscriptions, supporting token creation, minting, and transfer. Ordinals NFTs use the Ordinals protocol to create unique digital assets, making them different from traditional NFTs in terms of technology and design.
- Advantages, Disadvantages, and Challenges
Unique Advantages: 1) Security based on Bitcoin, making BRC-20 tokens highly secure; 2) Fair distribution, meaning all users with valid Bitcoin wallets have the opportunity to participate fairly in token issuance.
Challenges and Issues: 1) Network congestion: Widespread adoption may lead to Bitcoin network congestion; 2) Centralization risk: Potential malicious behavior due to reliance on third-party indexing tools; 3) Fee fluctuations: Sharp fluctuations in network usage fees may increase user costs.
RGB++ - Supporting Multi-asset Issuance and Contract Establishment
- Introduction to RGB and Approach
Introduction: The RGB protocol is a technology developed by the LNP/BP Standards Association, aimed at expanding Bitcoin's functionality to support smart contracts, NFTs, and token (FT) issuance, while enhancing privacy and scalability.
- Technical Approach
1) Client-side validation mode: RGB operates through client-side validation, storing smart contract data off-chain, with contract logic verification performed by clients (such as user wallets). This not only reduces reliance on Bitcoin full nodes and enhances the system's decentralization but also significantly improves network scalability.
2) Single-Use Seals: RGB uses Bitcoin's UTXO as a single-use seal, ensuring the uniqueness and tamper resistance of each contract state. Each state change (e.g., token transfer) requires spending the corresponding UTXO, using Bitcoin's network immutability to safeguard data security.
- RGB++
Introduction: Drawing on the RGB approach, RGB++ adds an existing independent blockchain (CKB) to implement BTC smart contracts.
1) RGB Approach: Single-use seals place important data of RGB transactions into UTXOs on the BTC chain, while client-side validation moves the transaction execution and verification process to off-chain clients. This ensures security with BTC and improves scalability.
2) CKB Blockchain Approach: The core lies in its Cell model and Open Transaction mechanism.
Cell model: An extension of Bitcoin's UTXO model, maintaining the transaction processing characteristics of UTXO while introducing more complex data and state management capabilities. It includes Capacity, representing the amount of resources held by the Cell, equivalent to the balance in the UTXO model, and Data indicating the storage of smart contract states or other arbitrary data.
Open Transaction mechanism: A mechanism that allows multiple parties to construct and aggregate transactions at different times.
3) RGB++ Approach: RGB++'s single-use seal is similar to RGB, using the BTC mainnet to store important data, while client-side validation is replaced by the CKB chain to serve as a public database and off-chain settlement layer. Essentially, RGB++ is a BTC sidechain (CKB) transforming into BTC's L2.
Technical Details: CKB acts as a public database for RGB assets and an off-chain settlement layer to replace RGB clients. Subsequently, it will improve performance through UTXO Stack (one-click UTXO chain) for capacity expansion. It combines two key points of the RGB protocol with the architecture of CKB: UTXOs acting as RGB containers can be mapped to Cells in CKB through the lock in Cell for implementation.
2) The off-chain client-side validation for verification can be transformed into on-chain public validation of CKB, and the verified data and state can correspond to the data and type in the Cell.
Applications:
1) Achieving off-chain validation: Using the high programmability of CKB cells, it is possible to associate several CKB transactions with a single Bitcoin RGB++ transaction. This mechanism allows for the use of CKB's high-performance characteristics to expand the processing speed of the slower and lower-throughput Bitcoin chain. By further developing "transaction folding" technology, theoretically, not all state changes need to be synchronized on Bitcoin, essentially introducing off-chain validation mechanisms on CKB.
2) Implementation of complex contracts: Non-custodial contracts refer to the ability for anyone to modify the state without the need for specific digitally signed providers, under specific contract conditions. This type of contract provides the possibility for more complex contract mechanisms such as automated market makers (AMMs). It can also introduce CKB's grid AMM design to achieve a UTXO-based market maker model.
3) Large-scale airdrops: The unique bilateral communication requirement in RGB protocol transfers brings the advantage of avoiding fraudulent tokens, but it also increases the user's threshold and product complexity. RGB++ utilizes its existing advantages to handle interactive behavior in the CKB environment, implementing a non-interactive transfer mode through a simplified send-receive two-step process.
DLC Technical Route Project - Efficiently Maintaining Asset Security and Circulation
- DLC Prudent Log Contract
Background - Placing bets in BTC, if using a multi-signature wallet, there may be malicious behavior: For example, if both parties use a 2-of-3 multi-signature scheme (requiring two signatures to withdraw funds, with a third party as a custodial agent), there is a high requirement for trust in the third party, as the third party can collude with either party to falsify the outcome.
Prudent Log - Improvement plan for DLC (Discreet Log Contract): DLC allows two participants to place bets by sending transactions off-chain, and the transactions sent require the oracle's signature to be redeemed. The main technical logic is to keep most of the contract and activities off-chain using technology similar to the Lightning Network. Participants reach a contract with the oracle without the oracle needing to know the existence of the participants or the specific content of the contract. After obtaining the result, the oracle confirms the contract by publishing a signature, and participants can use these signatures to construct valid transactions to obtain the corresponding funds.
1) Participants need to create funding transactions, locking funds in a multi-signature output.
2) Participants create and sign multiple contract execution transactions (CET), allocating corresponding funds for each possible result of the contract.
3) After the oracle publishes the result and provides a signature, participants can broadcast the correct CET to settle the contract.
In the future, adding multiple oracles can further increase security: To address collusion issues, users can and should also add multiple DLC oracles, thereby increasing the cost of bribing the oracles. Through Schnorr key aggregation, contract participants can add the public keys of two oracles that sign the same result, obtaining the aggregate public key for that result. The private key behind this aggregate public key is the sum of the signatures of these two oracles.
- Derivative Projects
DLC.Link: An improved and implemented prudent log contract technology invented by Tadge Dryja, co-founder of the Lightning Network, at MIT, providing a trustless decentralized bridge for DeFi on BTC and Ethereum.
The product has three main components. The primary focus is on the user-facing DlcBTC asset, followed by DeFi-related applications derived from the Dlc technology for B2B and developer tools for application integration:
1) DlcBTC is a non-custodial protocol that allows Bitcoin holders to participate in DeFi protocols while retaining ownership of their assets. Related components include a wallet (handling receipt of signatures, constructing and signing conditional execution transactions (CET)), a DLC authentication cluster (monitoring smart chain events to create or close DLCs), and NFTs (various types of collateral).
Workflow: 1) Users lock Bitcoin using the functionality of the DLC.Link protocol (using the DLC mechanism on the Bitcoin blockchain as a secure lockbox for recording transaction protocols), generating an equivalent amount of dlcBTC tokens; 2) The private keys of the multi-signature UTXO are distributed between users and decentralized verification nodes (composed of trusted nodes, monitoring blockchain events and supporting cross-chain communication) to enhance security. 3) The generated dlcBTC tokens can be used on various DeFi platforms (Curve, AAVE).
2) Platform: Provides developer tools such as Solidity and Clarity contracts, proof networks, and wallet SDKs.
3) DeFi-related applications: Supports credit and ordinals transactions, custody, lending, and other DeFi protocols; Bitcoin hash value derivatives; cross-chain protocols; integrates the Lightning Network (such as currency pegging, derivative trading).
Technically, DLC.Link further optimizes security, decentralization, scalability, and usability based on DLC:
1) Conditional payments based on off-chain data are implemented using PTLC (time lock) and Schnorr signatures, shifting the interaction from individual to protocol + self-packaging mechanism, reducing reliance on oracles and improving security.
2) Decentralization is ensured through operating independent third-party nodes, consensus signatures, and penalty mechanisms.
3) User operations are simplified and support for various DeFi applications is provided through integration with Bitcoin wallets and smart contracts.
4) Usability is increased through PSBT integration and the establishment of a storage platform.
Suredbits: A B2B development team that helps build prudent log contract specifications. It primarily assists users and businesses in developing customized financial engineering solutions for handling Bitcoin-related issues. Members are early and core developers of DLC.
Crypto Garage: A regulated blockchain-based crypto asset financial service company serving B2B clients. It helps B2B clients solve problems in the crypto and digital asset economy and develop future financial systems. It is an early and core developer of DLC, currently without publicly available consumer products. It launched a demo combining DLC with the Lightning Network at the end of 2022.
GitHub Repository - NDLC: A work-in-progress DLC implementation created in C#, which can be used with BTCPayServer. It optimizes the adapter signature part based on DLC, simplifying the protocol to a certain extent and improving privacy.
Vertical Scaling - Achieving Mainnet Security Support through BTC Programming/Validation Forms
The Ordinals and BRC-20 tokens recorded in the Bitcoin ledger have played an important role in driving the NFT ecosystem within Bitcoin, and protocols like RGB++ can create more assets. This has sparked a core discussion: whether it is possible to achieve a self-sufficient, fully Bitcoin Layer 1 (L1)-supported, trustless Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) mode on the Bitcoin network that does not rely on external social consensus layers and is completely supported by Bitcoin's first-layer security mechanisms?
Currently, sidechain technologies that use Bitcoin as security (such as the Lightning Network, RSK, Liquid, etc.) are seen as the only way to achieve an EVM-compatible environment. However, the security of these sidechains depends on external coordinators (off-chain trusted entities, trusted multi-signature wallets, or miners), still requiring a trust assumption. Therefore, BitVM & ZK rollup will become a better solution.
Project
Lightning Network
Stacks
Rootstock
Liquid
Technical Solutions
Specific channel payments off-chain and final settlement on the Bitcoin main chain
Sidechain, using a new PoX consensus to bind information in the Stacks chain with information on the Bitcoin network
Merged mining with BTC + multi-signature address to manage sidechain funds
Multi-signature address to manage sidechain funds
Consensus Mechanism
/
POX (burning tokens for mining)
POW (merged mining with BTC)
Strong federation
TPS
Millions
~19 (between BTC and ETH)
10-20
7-10
finality
near-instant
10 mins
12 blocks(~6mins)
2 blocks(~2mins)
Security
Multi-signature and Hash Time Lock (HTLC) ensure asset security after channel closure
PoX (Proof-of-Transfer) mining mechanism + Verifiable Random Function (VRF) + all transactions and information traceable on Bitcoin
Merged mining for security + trust multi-signature wallet miners
Trust multi-signature wallet miners
BitVM - Programming on BTC
- Overview
The whitepaper "BitVM: Computing Anything on Bitcoin" by ZeroSync project leader Robin Linus proposes BitVM, a Bitcoin Virtual Machine, offering an innovative solution to achieve Turing-complete Bitcoin contracts without changing the Bitcoin network consensus. This solution allows for the verification of any computable function on the Bitcoin network, enabling developers to run complex contracts without altering the fundamental rules of Bitcoin.
- Components and Operation Mechanism
Components - Prover and Verifier: BitVM introduces the roles of prover and verifier, where the former generates a proof based on system input without revealing the input itself. This separation ensures the accuracy of the computation results while protecting the privacy of the data involved.
Operation Mechanism - Off-chain computation and on-chain verification: By moving most of the computation process off-chain, BitVM maintains the Bitcoin consensus rules unchanged and increases flexibility. The controversial aspect of on-chain proofs, especially in the form of fraud proofs, ensures security. BitVM executes contracts through Taproot addresses or Taptree, representing a complex method of combining program instructions into a binary circuit-like structure, enabling comprehensive contract execution.
Approach to achieving Turing completeness - Logic gates and hash locks: BitVM uses opcodes and hash locks to build logic gates, solving various computational problems through simple digital logic circuit basic units (AND, NOT, OR gates). By organizing these gates into a Tapleaf tree and binding them with hash locks, BitVM ensures the integrity of the computation steps, effectively preventing dishonest claims about the computation results.
- Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of BitVM:
1) Consensus compatibility: BitVM provides additional programming capabilities for Bitcoin without the need for new opcodes or soft forks.
2) Ability for complex contracts: It can create contracts for financial transactions and build more complex DApps.
3) Efficiency: By moving most of the computation work off-chain, BitVM significantly reduces the data storage requirements on the blockchain, improving overall network efficiency.
4) Strong fraud protection: Fraud proof systems and challenge-response protocols ensure the integrity and transparency of transactions.
Limitations of BitVM:
1) Limited to bilateral contracts: The current design is only suitable for two-party setups, lacking the ability to handle multi-party transactions or contracts.
2) High computational complexity: The required off-chain data storage and computation are very large, currently only feasible in theory.
3) Limitations of the BTC logic framework: BitVM operations are within the logic framework of Bitcoin, limiting the execution capability of complex contracts.
Application - B^2 Network
Introduction: Combining BTC rollup with ZKP, achieving stronger usability and higher legitimacy on BTC layer 2 by writing storage and ZKP processes into BTC inscription; BSquaredNetwork is using BitVM to build a rollup with diverse proof mechanisms and a virtual machine, while the rollup on Bitcoin utilizes modular technology stacks, greatly improving scalability and efficiency.
Technology:
1) Execution Layer: B^2's sequencer is responsible for generating new Layer 2 blocks and aggregating multiple blocks into data batches. The data batch is sent to the aggregator and validator nodes in the B^Hub network.
2) DA Layer: B^2 Network sets up a DA layer called B^2 Hub under the Bitcoin chain, which draws on the ideas of Celestia, introducing data sampling and erasure codes to ensure that new data can be quickly distributed to a large number of external nodes and to avoid data withholding. Additionally, the committer in the B^2 Hub network uploads the storage index and data hash of the DA data to the Bitcoin chain for anyone to read.
Aggregator: Sends the data batch to prover nodes, which then generate corresponding zero-knowledge proofs. The ZK proofs are subsequently sent to the B^2 DA and validator network (B^2Hub).
B^2Hub Nodes: Verify the ZK proofs sent by the aggregator and their correspondence with the batches sent by the sequencer. If they correspond, the batch's data hash and storage index, once verified, are sent to the Bitcoin chain by a designated B^Hub node (committer).
Storage Layer: To relieve the pressure on DA layer nodes, historical data in the B^2 Hub is not permanently stored. Therefore, B^2 attempts to establish a storage network, using a storage incentive similar to Arweave's, to stimulate more nodes to store a more complete historical data set and receive storage incentives.
3) Consensus Layer: B^Hub nodes publicly disclose the entire calculation process of verifying the ZK proof, sending the commitment of the calculation process to the Bitcoin chain, allowing anyone to challenge it. If the challenge is successful, the B^Hub node that published the commitment will be economically penalized (its UTXO on the Bitcoin chain will be unlocked and transferred to the challenger).
State Verification: B^2 adopts a hybrid verification approach, verifying ZK proofs off-chain and challenging the ZK proof verification trace on-chain using the BitVM approach. As long as a single challenger node detects an error and initiates a challenge, the B^2 network is secure, aligning with the trust model of fraud proof protocols. However, due to the use of ZK, this state verification is actually hybrid in nature.
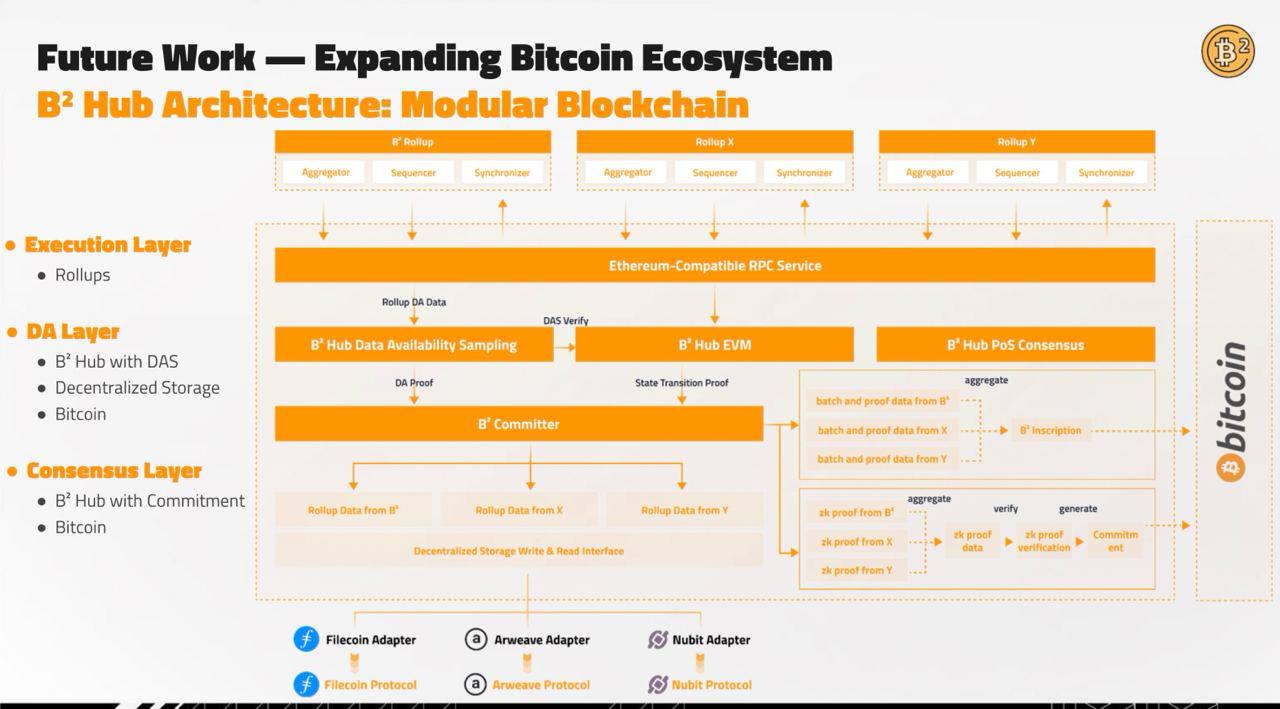
The advantage of B^2 is not simply writing data to the Bitcoin network, but it requires confirmation on the Bitcoin network to consider rollup transactions final, making it a more legitimate layer 2 compared to current market solutions. In the future, an EVM-compatible B^2 Hub can become a chain-agnostic validation layer and DA layer for multiple Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions.
ZK Rollup - Verifying ZKP on the BTC Mainnet
Citrea
Introduction: An execution layer based on Bitcoin that verifies transactions using ZK proofs, also a general L2 verification within Bitcoin.
Technical Solution:
1) Transaction Batching: Citrea collects thousands of transaction requests, which are first batched before being processed.
2) Processing transactions in zkVM and generating ZKP: The aggregated transactions are processed in a zero-knowledge virtual machine (zkVM). Once processing is complete, zkVM generates a succinct proof of validity.
3) Inscribing the proof of validity on the Bitcoin blockchain: This proof of validity is then inscribed on the Bitcoin blockchain. This step is the core of Citrea's technology, as it achieves the possibility of locally verifying transactions within the Bitcoin blockchain without modifying the Bitcoin consensus mechanism.
4) Native ZK Proof Verification: Citrea has built a native ZK proof verifier on Bitcoin's Layer 1 (L1), which is a smart contract specifically designed to verify the validity proofs inscribed on the Bitcoin blockchain. This approach differs from traditional monolithic sidechains, creating a modular world for the Bitcoin network through sharding, while maintaining settlement and data availability on-chain.
5) Creating Fee Income for Miners & Allowing Developers to Build Applications: Through this data availability mechanism, Citrea not only provides a stable source of fee income for Bitcoin miners but also extends the functionality of BTC in a trusted manner through validity proofs, surpassing the native limitations of Bitcoin. Additionally, developers can build applications in Citrea's EVM-equivalent execution environment.
chainway
Introduction: The technology provider for Citrea, part of the same team; provides a ZK-Rollup solution, with ZK-Rollup as the execution layer and Sovereign as the DA layer, anchoring Sovereign's proof information to the Bitcoin network.
Technical Solution: Uses Bitcoin as its DA. The sequencer must ensure that user transactions are published to Bitcoin via ZKP and provided to the prover for proof. The security assumption is that the sequencer cannot generate proof if it behaves maliciously and fails to meet the ZK circuit constraints.
Horizontal Eco-Expansion - Babylon as BTC's EigenLayer to Enhance Capital Efficiency
Current second-layer expansion solutions are diverse, but asset and security alone cannot form a complete economic circulation. Therefore, solutions like Babylon are needed to enhance capital efficiency in the Bitcoin ecosystem and create a value flywheel. In simple terms, Babylon is Bitcoin's EigenLayer (re-mortgaging protocol, allowing Ethereum stakers to provide verification services to POS chains, bridges, and sequencers and earn rewards).
Technical Highlights
1) Remote Staking: No need to move Bitcoin from the original chain to the PoS chain for staking, allowing Bitcoin to participate in PoS chain security without being actually transferred.
2) Innovative Use of Bitcoin Script: UTXO transactions that simulate smart contract behavior using Bitcoin Script, implementing complex staking and unstaking contract mechanisms.
3) Accountable Assertions: Utilizes Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS), allowing the extraction of private keys when a faulty validator signs two conflicting messages, then using the private key to execute a burn transaction on the Bitcoin chain, implementing a penalty mechanism for staked Bitcoin.
4) Finality Gadget: Enhances security beyond the basic consensus protocol by adding extra signature rounds, ensuring that if a security violation occurs, the private keys of the offending stakers will be publicly disclosed, leading to the destruction of their Bitcoin as a penalty.
5) Bitcoin Covenant Emulation and Quick Unstaking: Specific script mechanisms on the Bitcoin chain can lock Bitcoin, allowing these funds to be unlocked after a certain time or in case of a violation. This increases the liquidity of stakers while ensuring security.
Economic Reuse
By staking Bitcoin, users can provide verification services for PoS chains, DA layers, oracles, AVS, and more. This has sparked a new paradigm, allowing Bitcoin to generate substantial returns without giving up custody. Applications include:
- Polygon, B^2 - PoS Chain Security
Introduction: Babylon can provide security enhancement for any PoS chain in the market, especially crucial during the launch phase or for chains with a smaller market value. For example, the recent collaboration between B^2 and Babylon (where both the Hub and Rollup layers use Babylon's BTC staking and support BTC LSD and BTC Restaking).
Technical Integration similar to the Celestia modular DA layer + Eigenlayer shared security layer: Using B^2 as an example.
1) The dual asset staking mechanism avoids network control by a few nodes through large purchases of B^2 tokens.
2) B^2 Hub has Epoch consensus and CheckPoint, where validator nodes need to govern all on-chain activities during each Epoch, and the final confirmation of each POS second-layer chain block must wait for at least two BTC mainnet block timestamps.
3) Utilizes BTC timestamps to prevent "long-range attacks," making it very difficult for malicious nodes on the POS chain to attempt a long-range attack, as they would need to control the longest chain on both the POS chain and the BTC network.
Economically beneficial for mutual ecological connectivity: Users staking BTC with B^2 Hub's Validator can receive token rewards from B^2, and when Babylon's staking mainnet goes live, they can also enjoy re-staking rewards from the Babylon ecosystem. Staking BTC can yield stBTC and double rewards in both the B^2 Hub staking contract and the Babylon staking contract.
- Ankr Staking - Activating Idle Bitcoin Assets
Introduction: Ankr is a Web 3.0 infrastructure provider, offering a globally distributed node network for multi-chain access across over 40 blockchains. Ankr provides distributed blockchain infrastructure for one-click node deployment and management, as well as instant API access to major blockchains and DeFi protocols for developers.
Project Integration: Ankr is launching a new BTC staking protocol with Babylon, extending Bitcoin's security to all participating PoS chains. Ankr will create liquidity staking tokens (LST) for Bitcoin staked through Babylon, which will be issued on PoS chains using the BTC staking protocol.
- Nubit - Building a DA Layer Using Verification Services
Introduction: Nubit, a native data availability layer for Bitcoin, aims to reduce Bitcoin transaction costs. The product uses its proprietary BRC-1310 standard to achieve minimal trust requirements for Bitcoin transactions, increased data throughput, reduced storage costs, and finer data access.
Technical approach similar to Ethereum's 4844 solution to BTC: PBFT for consensus (consistent even under malicious nodes) + signature aggregation based on zk-SNARKs (reducing communication overhead, increasing scalability); RS + KZG + DAS (4844 solution, reducing communication costs while supporting network and node expansion, ensuring block data integrity and encoding correctness); inheriting BTC security by recording checkpoints (timestamps) on the BTC chain (Babylon solution); fee payment and validator reward distribution through trustless bridging based on PCN; modular indexer design for reading BTC state.
The innovative part adapts existing architectures to optimize the technical solution: Optimizes traditional PCN security and efficiency using VDF and variant HTLC; improves communication efficiency of the PBFT algorithm with zk-SNARKs signature aggregation; accelerates cost reduction through DAS and block dispersion technology; implements decentralized and user-verifiable execution layer using the modular indexer with Verkle trees.
The product is a DA layer combining multiple mature architectures, with various security assumptions: Validators use the PBFT algorithm to ensure block proposal and validation; trustless bridging acts as an intermediary, collecting user storage fees and distributing rewards to validators through PCN; full storage nodes store block data long-term to ensure data integrity; light clients use DAS to verify data integrity and availability. Security assumptions include:
1) DAS: Ensures that even light clients without storing all data can verify data accessibility and integrity.
2) 1-to-N full node security model: Significantly reduces withdrawal time using Bitcoin timestamps, allowing data recovery even in the event of a Nubit network collapse.
3) Trustless Bridging: Utilizing the Lightning Network to process transaction fees, minimizing reliance on third parties, and ensuring fund security.
Portal Finance - Seamless Cross-Chain Collaboration between Bitcoin and PoS Chains
Introduction: With the tools in the Portal ecosystem, users and autonomous agents ("AIGENT") can participate in cross-blockchain economic activities quickly, with low transaction fees and securely. The product includes DEX, AIGENT, Swap SDK, Portal Wallet, and payment channels.
Technical Applications:
1) Application of Babylon's Timestamp Protocol
Timestamp Synchronization: Babylon achieves the synchronization of timestamp events from different blockchains to Bitcoin by using Bitcoin's timestamp protocol. This application allows Portal's validator network—a decentralized exchange notary mechanism—to supervise and authenticate all transaction exchanges within the Portal DEX network while not holding any funds. This timestamp synchronization mechanism provides an additional layer of security for Portal DEX operations, enhancing the security and transparency of cross-chain transactions by leveraging Bitcoin's immutability.
Liquidity Provider and Staker Reward Distribution: Utilizing Bitcoin's security features for reward distribution in PoS networks is an innovative application. Through this method, Portal can incentivize network participants to provide liquidity and stake while ensuring security.
2) Shortening Unstaking Time: Traditional PoS chains require a long "trust period" for staking, typically taking two to three weeks. Babylon's timestamp protocol significantly speeds up the confirmation time for unstaking requests, reducing the waiting time to approximately one day. This improvement significantly enhances the efficiency and user experience of Portal validators, allowing participants to reclaim or redeploy their capital more quickly.
3. Conclusion
From Bitcoin's niche digital currency birth in 2009 to the launch of Bitcoin spot ETF in 2023, it marks a significant milestone in its becoming a mainstream asset class. Currently, BTC's market value and data stability, combined with the bull market and BTC halving leading to new price highs, along with the new trust cornerstone of spot ETF, indicate tremendous future potential.
Addressing the two dilemmas of the Bitcoin ecosystem (low network scalability and few ecological applications), the current stage of Bitcoin ecosystem development mainly focuses on programmable BTC. Three core projects empower BTC with diverse tokens (NFT, FT) while expanding its own value storage, ensuring new value storage with the BTC mainnet, and establishing an economic model where both holders and PoS chains can profit (Babylon).
1) Value Storage: Ordinals enables NFTs on BTC by giving the smallest unit, satoshi, a unique identifier and attributes; RGB protocol supports smart contracts and multi-tokens, and RGB++ combines this with an independent blockchain, CKB, to further expand BTC's smart contract solutions; DLC maintains asset circulation and cross-chain on BTC by binding multi-signatures with oracles.
2) Vertical Expansion: bitVM implements a Turing-complete contract solution to run complex contracts on BTC. Additionally, B^2 Network will use BitVM to build a Rollup with diverse proof mechanisms and virtual machines to enhance the legitimacy of layer 2; Citrea and chainway both achieve BTC verification by anchoring ZK proofs to the mainnet.
3) Horizontal Capital Efficiency Enhancement: Babylon, as Bitcoin's EigenLayer, allows users to provide verification services for PoS chains, DA layers, oracles, AVS, etc., by staking Bitcoin. B^2's collaboration with Babylon is similar to Celestia's modular DA + Eigenlayer shared security layer, providing security for PoS chains. Ankr provides cross-chain node networks and instant API access, promoting the activation of BTC assets. Nubit reduces Bitcoin transaction costs using the BRC-1310 standard and builds a DA layer using verification services. Portal Finance supports cross-chain economic activities through its ecosystem tools, reducing transaction fees and enhancing security.
In the future, Bitcoin will continue to focus on two aspects: vertical expansion will solve programmability issues through second-layer solutions capable of processing a large number of transactions rapidly; horizontal expansion will enhance capital efficiency by using Babylon and other relay protocols as reliable collateral in a wide range of applications. The integration of new applications on Bitcoin will seamlessly merge with the EVM stack, opening up endless possibilities.
References
OKX Ventures: Exploring the BTC Ecosystem https://www.chaincatcher.com/article/2110638
Polygon Ventures: Research analysis of the current bull market BTC ecosystem https://medium.com/alliancedao/the-bitcoin-l2-opportunity-9d90517da6f8
Panoramic analysis of the BTC ecosystem: Reshaping history or opening the next bull market? https://www.chaincatcher.com/article/2113734
Is RGB++ an upgrade from RGB? Is the token $CKB worth buying? https://twitter.com/zaoanyingwen/status/1761941477578731810
From RGB to RGB++: How CKB empowers the Bitcoin ecosystem asset protocol https://www.theblockbeats.info/news/50913
RGB++: Adding bricks to the orthodox Bitcoin L2 https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/53485
How do you view the latest collaboration between @BSquaredNetwork and @babylon_chain? https://twitter.com/tmel0211/status/1772851898556821817
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



