The requirement for tax reporting stipulates that form 8300 must be completed, which is the "Report of Cash Payments Over $10,000 Received in a Trade or Business" and the specified information must be reported within 15 days of receiving the cash.
Authored by: TaxDAO
The "Infrastructure Investment and Employment Act" amended Section 6050I of the Internal Revenue Code to add digital assets to the list of assets included in the cash definition in Section 6050I(d). According to Section 6050I(a), any person (recipient) engaged in a trade or business who receives more than $10,000 in cash in a single transaction (or two or more related transactions) must submit a report detailing the receipt of the cash. The requirement for tax reporting stipulates that form 8300 must be completed, which is the "Report of Cash Payments Over $10,000 Received in a Trade or Business," and the specified information must be reported within 15 days of receiving the cash. Currently, the announcement published by the IRS indicates that cryptocurrency transactions do not currently require the filing of form 8300.
1. Filing Form 8300
Federal law requires an individual to report cash transactions over $10,000 by submitting Form 8300. The information on the form can help law enforcement combat money laundering, tax evasion, drug trafficking, terrorist financing, and other criminal activities. According to the law, "person" refers to individuals, corporations, partnerships, associations, trusts, or estates. Tax-exempt organizations also fall within the definition of "person" and may be required to report certain transactions. Starting from January 1, 2024, if a business needs to submit certain other tax-related forms electronically, they must also submit Form 8300 electronically. Beginning with the 2024 calendar year, if they need to submit at least 10 other types of tax-related forms in addition to Form 8300, they must submit Form 8300 electronically for that specific calendar year. The number of Form 8300 submissions does not affect the threshold requirements for tax-related forms.
1.1 Specific Details of Filing Form 8300
1.1.1 Identity of the Recipient of Cash
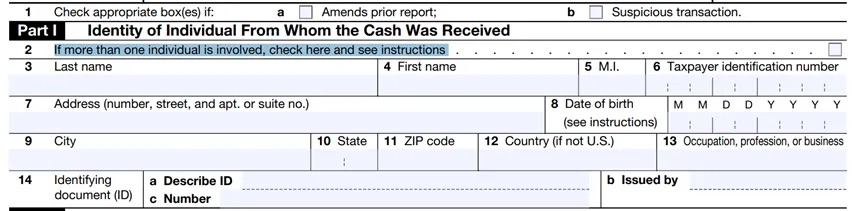
If the transaction is reported by two or more persons, the second item needs to be checked. Regarding the eighth item about the date of birth, if the individual's date of birth is July 6, 1960, enter 07/06/1960. For the thirteenth item about occupation and industry, the nature of the occupation, profession, or business must be clearly described, such as "plumber," "lawyer," or "car dealer." General or non-descriptive terms such as "businessman" or "sole proprietor" should not be used. If retired or unemployed, enter the previous occupation, such as "retired lawyer" or "unemployed roofer." For electronic filers, this entry is limited to 25 characters. The fourteenth item is for verifying the individual's name and address who received the cash by checking documents such as a driver's license, passport, alien registration card, or other official documents.
1.1.2 Person Representing the Transaction
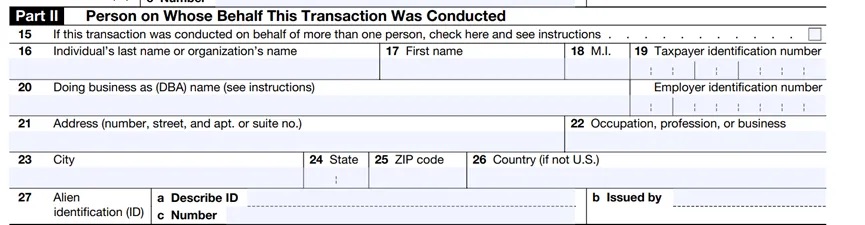
If the transaction is conducted on behalf of multiple persons, the box needs to be checked, and the second part needs to be completed for any of the persons. If there are three or more additional persons, the filer should complete and attach a copy of the second part for each additional person, and electronic filers can add additional entries for the second part (up to 99). For items sixteen to nineteen, if the person representing the transaction is an individual, complete items 16, 17, and 18. Enter their TIN in item 19. If the individual is a sole proprietor and has an EIN, both the SSN and EIN must be entered in item 19. For item twenty, if the sole proprietor or organization listed in items 16 to 18 conducts business under a name other than that listed in item 16, it must be entered in item twenty.
1.1.3 Transaction Description and Payment Method

For item twenty-eight, enter the date cash was received, in the format 01/01/2022. If cash was received in multiple payments, enter the date of the payment that resulted in a total amount exceeding $10,000. For item twenty-nine, the total amount of cash received, the total amount of cash received on the day when the cash amount exceeded $10,000 within 12 months. For item thirty, if the amount shown in item 29 was received in multiple payments, check this box. For item thirty-one, if different from the amount shown in item 29, enter the total price of property, services, cash exchanges, etc. For item thirty-two, enter the amount of each form of cash received. For item thirty-three, check the appropriate box to describe the type of transaction.
1.1.4 Business Receiving Cash
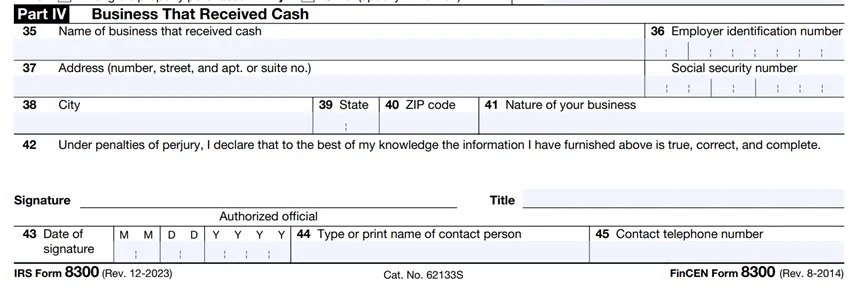
For item thirty-five, enter the name of the business receiving the cash. For item thirty-six, enter the employer identification number, if it is a sole proprietorship, enter the SSN. If the business has an EIN, it must be provided. All other business entities must enter the EIN. For item forty-two, sign the individual signature authorized by the business receiving the cash.
1.2 Reporting Time for Form 8300
An individual must submit Form 8300 within 15 days of receiving the cash. If the individual receives multiple payments for a single transaction or two or more related transactions, and the total amount exceeds $10,000, Form 8300 must be submitted. Each time the total payment exceeds $10,000, another Form 8300 must be submitted.
1.3 Recordkeeping for Form 8300
Businesses must retain a copy of each Form 8300 they submit, along with all supporting documents and required statements sent to customers, for a period of five years from the date of submission.
If a business submits electronically, they will receive an email confirmation that the form has been submitted, but the email confirmation from electronic submission does not meet the recordkeeping requirement. When using electronic submission, the filer must save or print a copy of the form before the final submission. The confirmation number should be associated with the saved copy.
2. Risks of Not Filing Form 8300
Although most cash transactions are legal, Form 8300 can help track tax evasion, profits from drug trafficking, terrorist financing, and other illegal funds. Failure to file Form 8300 as required or will face significant penalties. Businesses may be subject to civil and criminal penalties for non-compliance with the law.
2.1 Penalties for Minor Errors
If the error involves an amount not exceeding $100, the filer does not need to correct the information return or recipient statement to avoid penalties for failing to file correct information returns or correct recipient statements.
2.2 Civil Penalties
The following civil penalties apply to information returns required to be filed within a specified calendar year.
For failure due to negligence to timely file, provide all required information, or provide correct information, the penalty for each information return is $310, with an annual maximum of $3,783,000.
For individuals with an average annual gross receipt not exceeding $5,000,000, the maximum limit is $1,261,000. The penalty applies to each information return.
If any failure to file is corrected within 30 days after the specified filing date, the penalty will be reduced to $60 instead of $310, and the annual maximum amount will not exceed $630,500. For individuals with an average annual gross receipt not exceeding $5,000,000, the maximum penalty limit is $220,500.
The penalty for willfully disregarding the requirement to timely submit necessary or correct information is: (1) $31,520 or (2) the amount of cash received in the transaction, not exceeding $126,000 (without calendar year limitation), whichever is higher.
The penalty for negligently failing to timely, completely, and correctly provide notice to the persons identified on Form 8300 is $310 per statement, with an annual maximum of $3,783,000. For individuals with an average annual gross income not exceeding $5,000,000, the maximum limit is $1,261,000.
If any failure to provide as described in the prescribed provisions is corrected within 30 days, the penalty is $60 instead of $310, with a maximum of $630,500. For individuals with an average annual gross income not exceeding $5,000,000, the maximum penalty limit is $220,500.
If any errors described in paragraph (a)(2) are corrected after the 30th day described in paragraph (1) but on or before August 1 of the calendar year in which the correction is made, the penalty is $120 instead of $310, with a maximum of $1,891,500. For individuals with an average annual gross income not exceeding $5,000,000, the maximum penalty limit is $630,500.
Willfully disregarding the requirement to provide timely, correct, and complete notice will result in a penalty of $570 per occurrence, or 10% of the total amount that should have been reported correctly (without calendar year limitation).
2.3 Criminal Penalties
Any person required to submit Form 8300 who willfully fails to file, fails to timely file, or fails to include complete and correct information will be subject to criminal sanctions as a felony. Sanctions include a maximum fine of $25,000 (or $100,000 for corporations) and/or up to five years in prison, as well as prosecution costs.
Any person who willfully submits false Form 8300 regarding material matters may be subject to a maximum fine of $100,000 (or $500,000 for corporations) and/or up to three years in prison, plus prosecution costs.
Penalties for failure to report may also apply to anyone attempting to interfere with or prevent a seller (or business) from submitting the correct Form 8300, including the payer. This includes attempting to structure transactions in a way that involves breaking down large cash transactions into smaller ones to conceal the true amount of cash involved in the transaction.
3. How to Report Cryptocurrency Assets on Form 8300?
In a recent IRS announcement, although cryptocurrency transactions are not currently required to be reported on Form 8300, as "digital assets" are widely used as a means of payment, we anticipate that the IRS may require reporting of such transactions in the future. Here is a more in-depth analysis of this situation:
Definition of the nature of the transaction: We predict that only transactions using cryptocurrency as a means of payment in normal trade or business activities will require reporting on Form 8300. This means that if cryptocurrency is obtained through mining activities, such acquisition methods do not fall within the category of transactions that must be reported.
Determination of the value of cryptocurrency assets: How to accurately determine whether the value of cryptocurrency exceeds $10,000? For cryptocurrencies with fair market value and traded on exchanges, although prices may vary between different exchanges, their value can be relatively easily determined by referencing the trading prices of the target exchange. However, for NFTs and other digital assets with potentially more subjective value and less clear market pricing, the ambiguity of value confirmation is very strong. Therefore, we anticipate that NFTs may also not be included in the category of transactions that must be reported.
Considering the uncertainty of the regulatory environment, although it is currently unclear how specific reporting requirements will change, investors should remain vigilant about future reporting obligations and be prepared to adapt to new reporting requirements. As the compliance of cryptocurrency assets and updates to tax and regulatory strategies will play a crucial role in ensuring the stability of the cryptocurrency market and investor confidence.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




