Author: Route 2 FI
Translation: Ladyfinger, Blockbeats
Editor's Note: In the current digital age, the concept of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) is attracting increasing attention. DePIN represents not only a new network architecture concept but also provides a platform for innovation in areas such as storage, computing, artificial intelligence, and wireless networks. Through token incentive mechanisms, DePIN stimulates users to contribute to the network and provide value, while demonstrating significant advantages in resource efficiency, lowering entry barriers, and decentralization.
Recently, the rise of several projects based on the DePIN concept has shown tremendous potential and innovation in decentralized storage and computing. Projects such as Filecoin, Helium, Shadow Token, and Aethir have not only opened up new application scenarios but also provided strong case studies for the practical application and development of decentralized networks.

What is DePIN?
DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks) is a term proposed by Messari, referring to networks that aggregate and provide services or resources to users, ultimately matching the supply and demand of specific resources. This concept covers a wide range of categories, including physical infrastructure networks and digital resource networks. Under these two categories, there are multiple fields such as storage, computing, artificial intelligence, wireless networks, imaging, and map production. The DePIN protocol rewards and incentivizes users to contribute to and provide value to the entire network through a token incentive mechanism.
The DePIN protocol has several advantages:
Resource efficiency: Providers with underutilized resources can "rent out" these resources to other consumers, ensuring that idle resources are not wasted.
Lowering entry barriers: DePIN effectively reduces the barriers to accessing certain resources. For example, if one needs to use specific GPUs for tasks that are not easily obtainable on the open market, users can easily "rent" computing power from suitable providers without having to worry about purchasing components.
Decentralization: Users of the service do not have to worry about downtime faced by centralized entities.
According to data from CoinGecko, the market value of the DePIN category has witnessed a 35% growth in the field, demonstrating its strong performance and future growth potential.
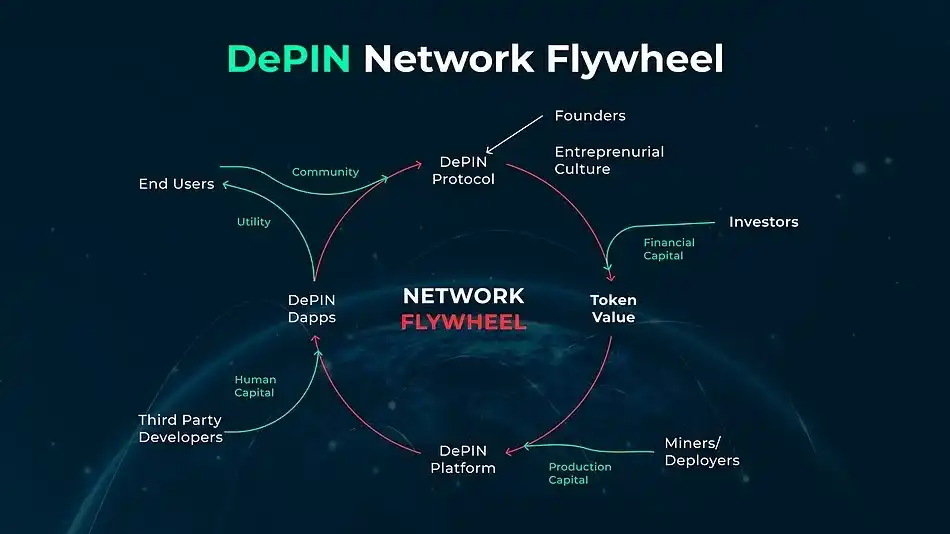
Reasons for the Need for DePIN
According to information from CoinGecko, DePIN allows facilities to grow capacity in a more flexible manner. Networks can increase resources without increasing the capacity of each resource. This provides good flexibility, and facilities built using this system can easily scale up or down according to demand. Blockchain can also control available resources and allocate them to demand.
In low-demand situations, some providers may experience lower workloads. In high-demand situations, the network can reactivate dormant resources, add more instances, and increase the capacity of the entire network without any changes. Based on available dormant resources and the allocation system of DePIN, systems like this can scale infinitely.
Similar to DeFi, DePIN is also decentralizing infrastructure systems, shifting from enterprises to individuals collectively investing resources in building facilities. This system distributes control of facilities to different providers, similar to miners in PoW networks.
DePIN is like a DAO within the industry, where everyone in the system contributes resources and has relative control based on their capabilities. In a system where every provider has equal capabilities, DePIN becomes a decentralized system or almost decentralized.
The pricing model of DePIN is different from traditional facilities. Factors affecting the pricing model include the cost of private providers operating their own facilities and other network-related factors. There may be fewer additional charges on the platform because the platform itself does not need to incur any costs to provide these facilities.
Overall, the pricing model of DePIN is expected to be cheaper, and the expected pricing will be fair, as it considers fundamental factors, without unfair price inflation typically associated with facilities operated by centralized institutions. For a people-driven system, DePIN is also more likely to consider affordability in its pricing model, unlike a business.
DePIN networks can be established with almost no cost, and providers have good flexibility in providing services. For example, providers can submit their facilities to multiple networks. Users also pay fair prices for the services they receive from the network. DePIN aims to provide a cost-effective system with the lowest possible cost to deliver the best possible services.
Anyone can contribute their resources to DePIN. On the user side, anyone can also access the services provided by DePIN. There is no price negotiation or user screening for these services. Once providers have the necessary infrastructure, they can run a provider-side account on DePIN, just as anyone can deploy liquidity pools on DEX or easily obtain loans from the money market.
Incentives are an important tool for DePIN. For providers, they provide a passive or active income opportunity based on how DePIN operates. Individuals can also primarily build income streams from DePIN. Projects like Nunet hope to reduce the number of dormant computing resources through its AI-driven computing power market. Providers can earn income from facilities that would otherwise remain idle.
DePIN Projects
Filecoin ($FIL)

Filecoin is well known as a decentralized storage layer, allowing anyone to store data in a decentralized manner (also known as the "Dropbox" of Web3). It is built on the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), incentivizing data storage providers to ensure the secure storage and retrieval of data. Filecoin provides an open market for anyone who wants to store files or earn rewards for storing other users' files. Filecoin has been actively used by users, and the current data snapshot stored on Filecoin is:
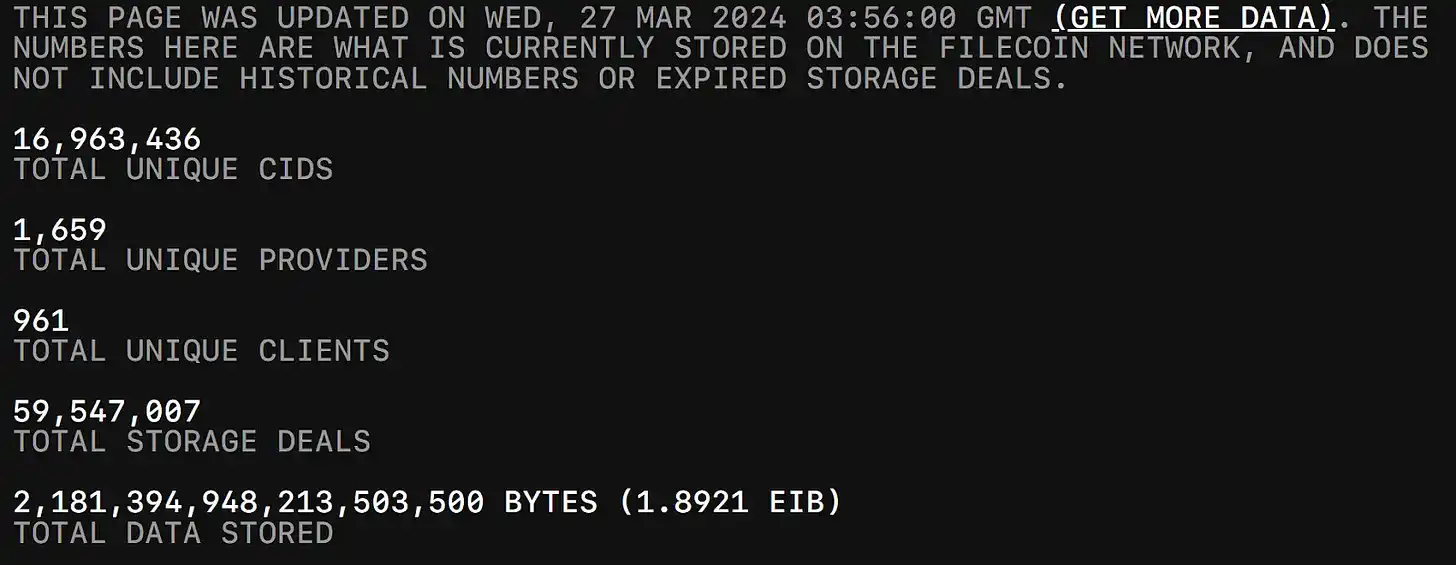
In addition, the Filecoin blockchain supports smart contracts through the introduction of the Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM) on March 14, 2023. FVM allows smart contracts to be deployed on the Filecoin network, similar to smart contracts on Ethereum. With FVM, computational logic conditions can be combined with traditional Filecoin storage and retrieval, opening up many potential use cases.
In the long-term data storage aspect, Filecoin remains a market leader. Coupled with its innovations, Filecoin continues to be a strong player in the decentralized storage field.
Helium ($HNT)

Helium is a decentralized wireless infrastructure network supported by Solana. It initially started as an Internet of Things (IoT) network, providing connectivity for IoT devices using the Low Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) protocol. It later expanded to 5G hotspots, where the Helium 5G network is powered by user-operated nodes. Node operators are compensated with tokens in exchange for providing resources to the network.
An interesting real-world application of Helium is Helium Mobile, a U.S.-based network provider that utilizes Helium nodes wherever available within range.
Shadow Token ($SHDW)

Shadow Token by GenesysGo, often referred to as the "Filecoin of Solana," is a cloud storage platform aimed at decentralizing the traditional cloud storage stack. shdwDrive achieves the core goal of shdwDrive's distributed ledger technology through DAGGER, allowing them to reduce the cost of enterprise data center storage.
Combined with DAGGER's consensus mechanism and Solana's execution environment, shdwDrive becomes a powerful cloud service platform, paving the way for a range of file storage applications.
Shadow Token has its native token - $SHDW, with a current FDV of approximately 3.785 billion USD. The upcoming catalyst for the token is the recently announced listing on Coinbase. Currently, users can only purchase this token on the Solana chain, but once listed on centralized exchanges, there will be more retail funds flowing into this token.
Following this news, the price of SHDW in USD has risen by approximately 55% in the past 24 hours, from 1.35 USD to 2.49 USD.
Aethir ($ATH)
Aethir Cloud is a newly emerging cloud computing protocol, positioning itself as a new competitor to current decentralized computing giants such as Render and Akash. Aethir is a decentralized platform that aggregates computing processing power. Aethir connects providers of this computing power with users and consumers who need to use GPU hardware for various applications such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud gaming.
Aethir Network consists of three components:
- Containers
- Checkers
- Indexers
These components are briefly described as follows:
Containers are virtual endpoints that execute and render actual workloads. Workloads from local devices are transferred to containers, providing users with a "zero-latency" experience.
Checkers can be seen as "referees" supervising containers to ensure the quality of service provided by the network.
Indexers match suitable containers based on consumer requests, aiming to deliver services in the shortest possible time.
Aethir Cloud has received support from notable investors such as Maelstrom, Mirana Ventures, and Animoca Brands. In its latest Pre-Series A funding round, Aethir raised over 9 million USD at a valuation of 150 million USD. Additionally, Aethir held a node sale event for its Checker nodes, raising over 26.8k ETH.
Grass
Grass is a Layer 2 dataset that utilizes network scraping nodes to gather artificial intelligence training data from various websites for builders to access. Due to users running the Grass application and becoming Grass nodes in anticipation of airdrops, Grass has recently gained significant attention.
The working mechanism of Grass involves devices from around the world forming a node network, with these nodes specifically capturing and processing network data. This data is then transformed into structured datasets for AI training.
The lack of transparency behind the data and algorithms powering AI applications often leads to users being unable to understand how AI models arrive at their conclusions. Grass aims to address this issue.
How does Grass solve these problems? This is where the second-layer Rollup technology becomes crucial. Through this technology, all data captured by Grass nodes is recorded and the source websites of the data are verified. This metadata is then stored in the dataset, increasing the credibility of data accuracy. Given the enormous amount of data processing required, L2 employs ZK processors for batch validation of data.
The detailed architecture of the Grass network is as follows:

Grass is currently conducting a point program for users running nodes, as well as speculative airdrops. Grass's most recent funding was on December 20th, where they raised 3.5 million USD in a seed round, led by notable investors such as Polychain Capital and Tribe Capital.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




