Author: Trustless Labs

Image Source: Trustless Labs
There are currently two types of Rollup SDKs: ZK and OP, mainly based on Arbitrum Orbit, OP Stack, ZK Stack, and Polygon CDK. This article provides a comprehensive introduction and comparative analysis of these four solutions. Among them, due to its scalability, security flexibility, and cost advantages, Polygon CDK shows tremendous potential.
Whether it's Manta's transition from OP Stack to Polygon CDK or ZKFair's fair launch, Polygon CDK empowers projects to handle large total value locked (TVL) and ecosystems. We believe that ZK Rollup is the ultimate solution for Rollup scalability. By leveraging its advantages such as modularity, customizability, multiple data availability solutions, and low entry barriers, Polygon CDK is gradually dominating the market. Combined with the outstanding performance of the flagship project ZKFair, we believe that Polygon CDK is the most promising and optimal solution among the current ZK Rollup SDKs.
1. Overview of Rollup SDKs
From the perspective of underlying technical implementation, Rollup SDKs can be divided into two categories: one is OP-Rollup SDK that maintains security based on Optimistic Fraud Proofs, and the other relies on zero-knowledge proofs to establish on-chain trust, which is ZK-Rollup SDK. OP-R SDK was initially proposed by Optimism, introducing the concept of OP Stack. In March 2023, Arbitrum launched the Orbit solution. Subsequently, ZK-R SDK emerged, with representative solutions including ZK Stack from zkSync and Polygon's Polygon CDK.
1.1 Arbitrum Orbit
Arbitrum Orbit aims to allow modifications to the Arbitrum Nitro codebase. It has a permanent and recursive license, allowing the creation of Orbit chains that can host other chains under the same licensing conditions. Orbit chains can settle to various Arbitrum networks but do not support network switches after deployment. It supports AnyTrust and Rollup chain types to meet different security and cost requirements.
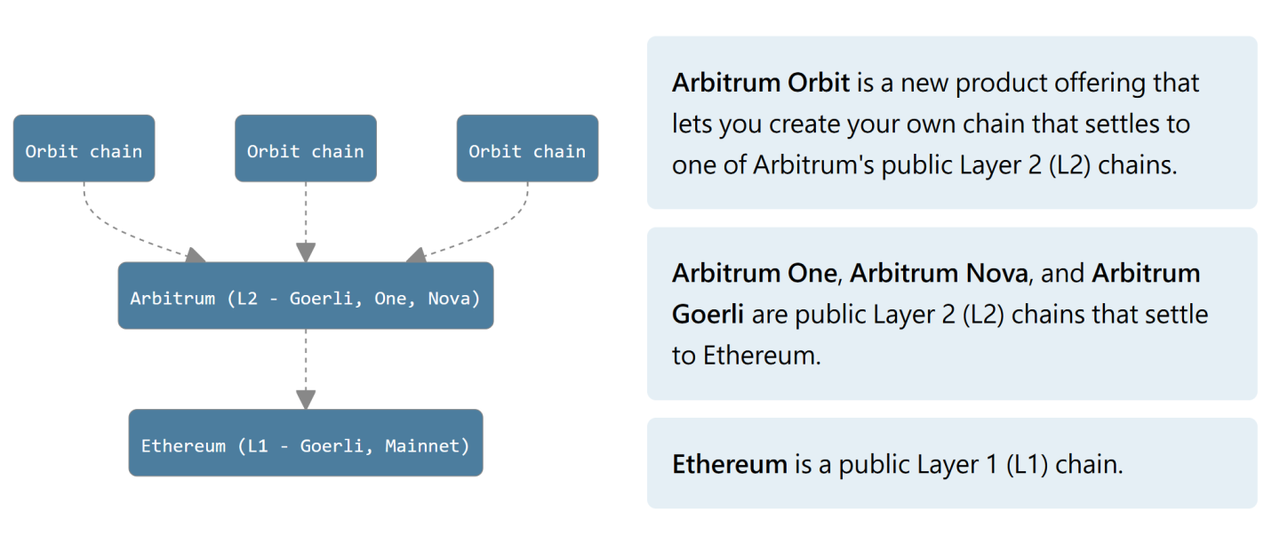
Image Source: https://koreablockchainweek.com/blogs/kbw-blog/arbitrum-101
As shown in the figure, the goal of Arbitrum Orbit is to enable developers to build second or even third-layer networks for Arbitrum. Developers can choose between Arbitrum Rollup (where all transaction data is published on the settlement layer) and AnyTrust Chain (where transaction data is maintained by a DAC data availability committee and DACerts data availability proofs are published to the settlement layer, similar to Validium). They can customize gas tokens and economic models, among other features. Meanwhile, Arbitrum is also promoting Stylus, allowing developers to build Rollup based on both EVM and WASM VM using Orbit. Arbitrum Orbit users can flexibly choose to build their third-layer networks based on Arbitrum One or Arbitrum Nova, with the settlement layer positioned on the Arbitrum second-layer network. This means that transaction fees on the third-layer network will revert to the second-layer network of the Arbitrum protocol. If building a second-layer network based on Ethereum as the settlement layer, permission authorization from Offchain Labs or Arbitrum DAO is required.
1.2 OP Stack
OP Stack consists of software components that make up the infrastructure of the Optimism mainnet. OP Stack has undergone Bedrock iterations, helping to build Optimistic Rollup networks and support the Optimism Superchain (interconnected second-layer networks). Its architecture includes an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) for execution, a single sequencer module for processing transactions, and a multi-layer network for data formatting, settlement, and governance.
After recently upgrading OP Stack to the Bedrock version, the cost of individual transactions has been reduced by over 70% through optimized transaction compression strategies. At the same time, processing multiple transactions within the same second-layer block has reduced the size of state data. The refinement of these components makes development more convenient, which is the competitive advantage of OP Stack.
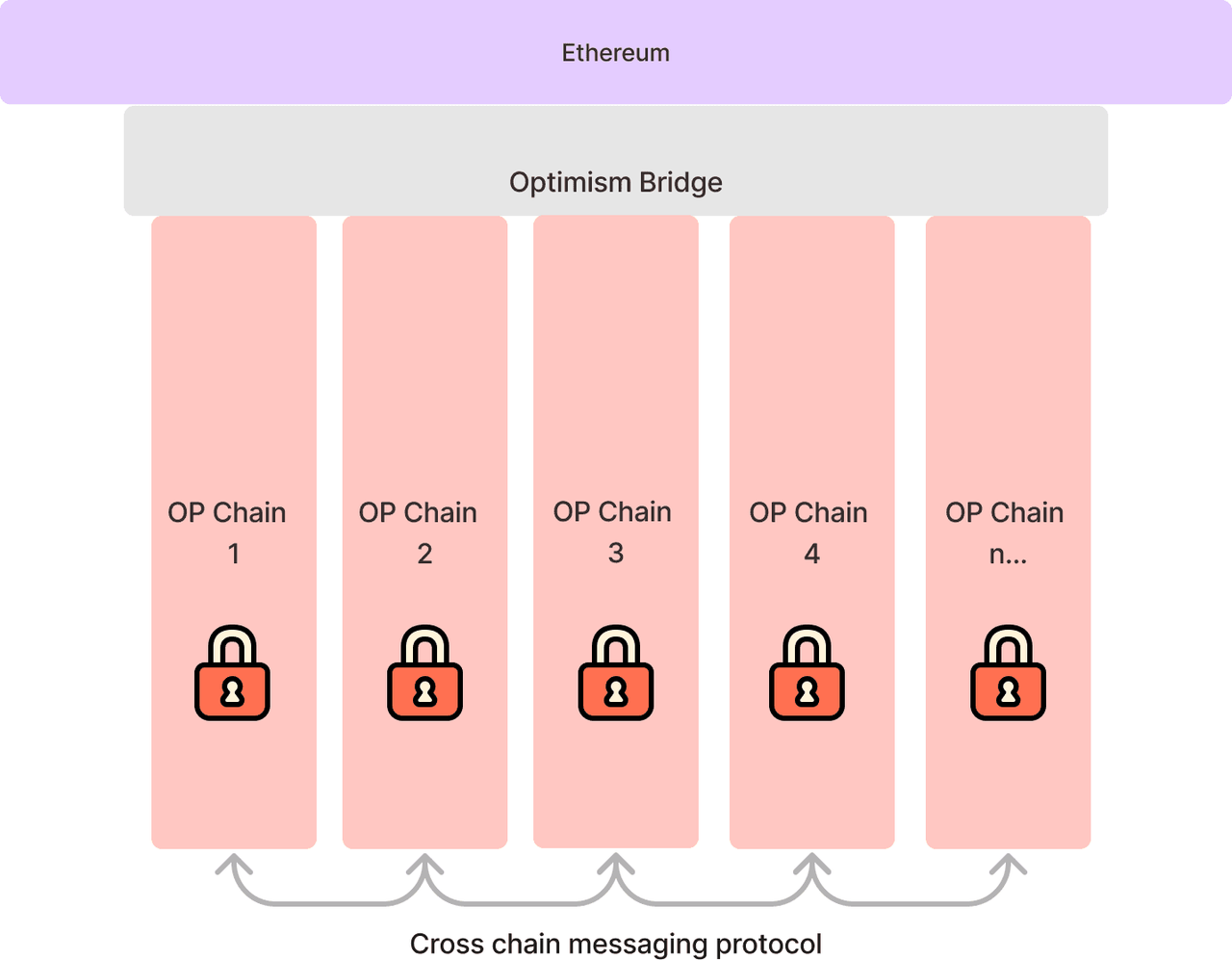
Image Source: https://docs.optimism.io/stack/explainer
In its SuperChain plan, all Rollups using OP Stack will be integrated into standardized OP chains. These chains can communicate directly through a cross-chain messaging protocol and share a common Ethereum cross-chain bridge. Additionally, transaction sequencing on these chains will be handled by the same sequencer network.
1.3 ZK Stack
ZK Stack is a modular, open-source framework designed to build custom ZK-driven second-layer and third-layer networks (Hyperchains) based on zkSync Era code. Developed under an open-source license, ZK Stack is freely available, enhancing usability and community participation. Hyperchains built using this framework seamlessly connect in a trustless network, ensuring low latency and shared liquidity to enhance interoperability. ZK Stack leverages the reliability of zkSync Era to provide a secure foundation, while its emphasis on community contributions and ownership supports decentralized ecosystems to a certain extent. The sovereign nature of this framework gives developers a degree of autonomy over their Hyperchains, helping to build a decentralized and sustainable system to some extent. In addition, ZK Stack is suitable for various use cases, including games, social networks, and enterprise applications, providing tailored solutions for specific needs. With its asynchronous connection options, ZK Stack becomes one of the tools for building decentralized blockchains that are secure, customizable, and interoperable to some extent.
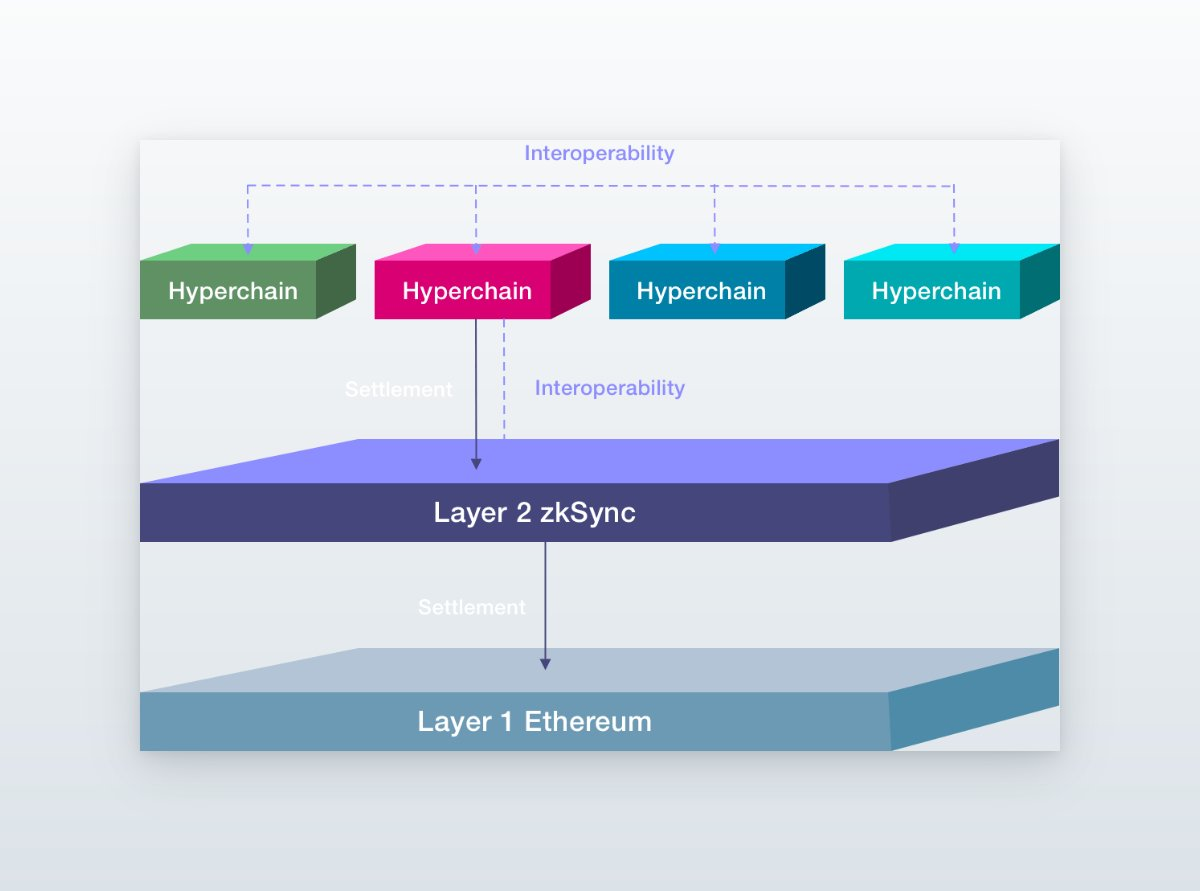
Image Source: https://x.com/zerokn0wledge_/status/1673436051199922176?s=20
zkSync Era has overcome the fragmentation of cross-network liquidity. As a pioneer, Hyperchain has led this highly scalable unified liquidity network and set an example for other networks.
However, despite the powerful features of ZK Stack, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution for all scenarios. For traditional decentralized finance (DeFi) applications or non-fungible token (NFT) projects, deploying on existing Hyperchains such as zkSync may be more efficient and provide synchronous integration with other protocols.
1.4 Polygon CDK
Polygon CDK is an open-source and modular codebase designed to simplify the complex process of building and launching ZK-driven second-layer (L2) chains on Ethereum. This toolkit allows developers to design networks according to their specific needs, providing core modularity that enhances flexibility. Using zero-knowledge proofs ensures encrypted security of transactions and near-instant finality. By deploying chains using CDK, developers can launch automatically interoperable ZK-driven L2 networks that connect to a shared ZK bridge, forming a value layer of the internet.
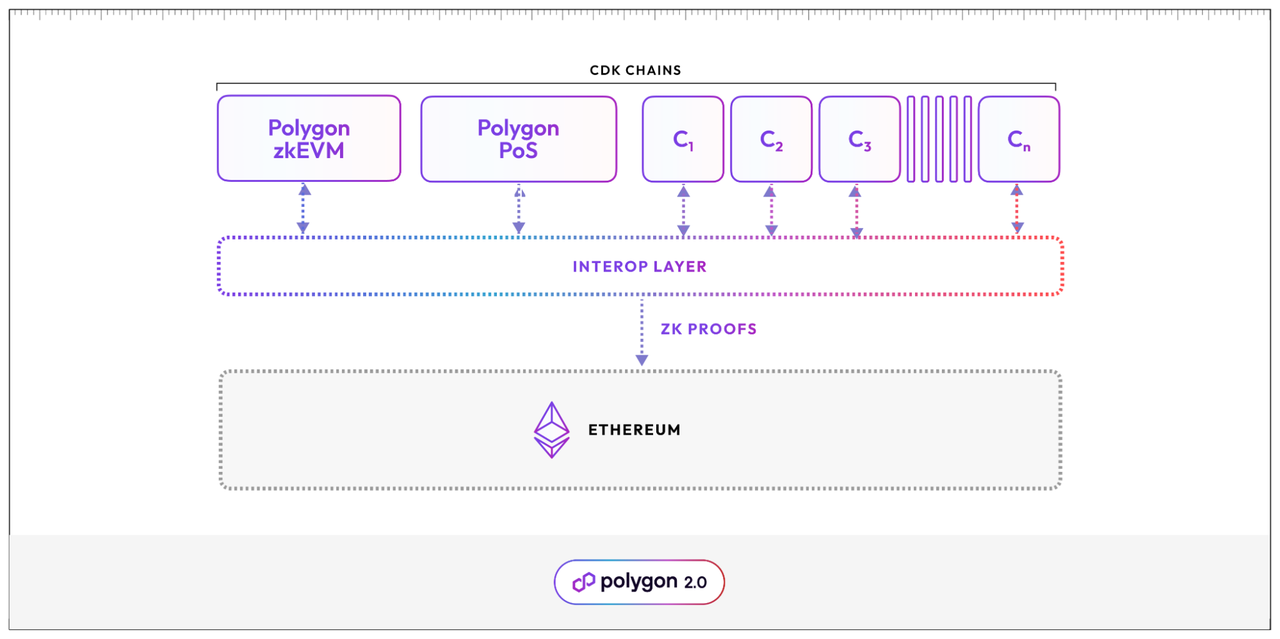
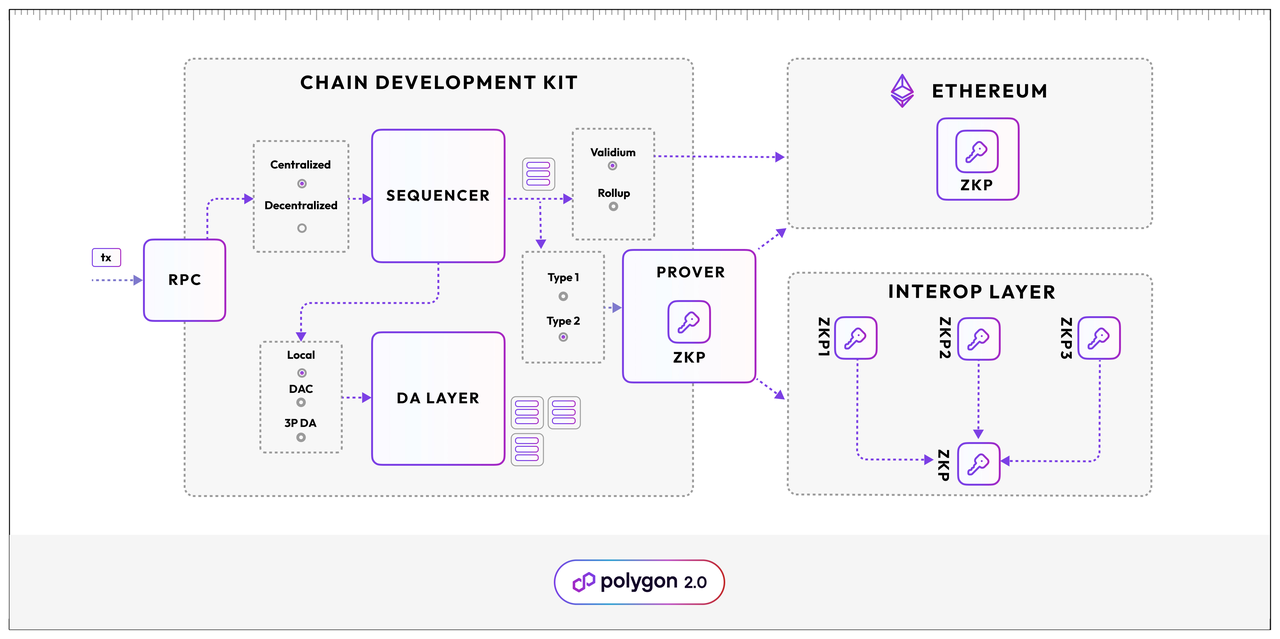
Image Source: https://polygon.technology/blog/introducing-polygon-chain-development-kit-launch-zk-l2s-on-demand-to-unlock-unified-liquidity
Developers can customize the chain's execution environment, choose zkEVM, select the "validium" mode, and choose a centralized sequencer. Customization extends to having local DAC for data availability, adjusting the timing of ZK proof submission, and specifying tokens for Gas. It is worth noting that despite these customization features, NFT Chain can seamlessly interoperate with other Polygon chains and share liquidity. The modularity of CDK ensures flexibility without sacrificing scalability or disrupting liquidity. As one of the core technological components of Polygon 2.0, the Interop Layer plays a crucial role, accepting ZK proofs, aggregating them, and publishing proofs and updated chain states to Ethereum, ensuring near-instant finality and cross-chain execution. Polygon's cutting-edge ZK technologies, such as zkEVM, ensure the future reliability of chains developed using CDK, benefiting from ongoing technological advancements. The on-chain security of CDK deployment relies on cryptography, providing a more secure, interconnected, and infinitely scalable value layer without complex incentives.
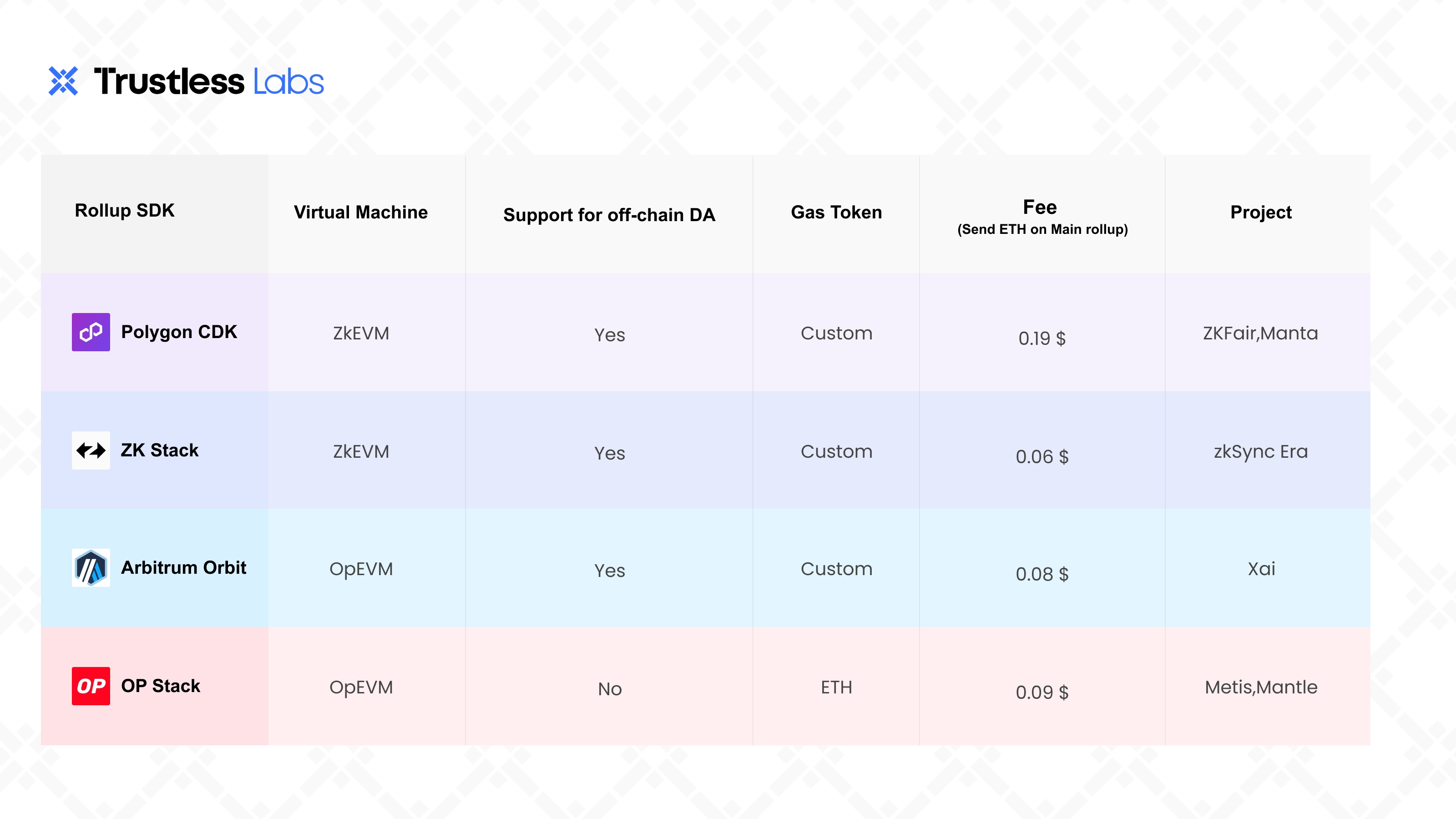
Image Source: Trustless Labs
2. In-depth Analysis of Polygon CDK: Leader in the Rollup SDK Race
2.1 Scalability and Compatibility
Using Polygon CDK, developers can directly deploy Rollups that are fully equivalent to the EVM, providing convenience for EVM developers to seamlessly migrate to the ecosystem. At the same time, Polygon CDK achieves high modularity by breaking down the components of Rollup into independent services. For example, the synchronizer is responsible for synchronizing blocks between the first and second layers, the prover generates proofs, the sequencer verifies transactions and packages blocks, and the RPC service provides external access. Rollup creators can extend specific services as needed.
With Polygon CDK, it is possible to create a zero-phase Rollup where the state root of the second layer is submitted to the first layer. Additionally, the Rollup's state can be reconstructed based on all data on the first layer. Furthermore, the contracts on the first layer will verify the validity of ZK proofs, ensuring that all state changes on the second layer are entirely legitimate.
Polygon CDK supports dedicated data availability layers and data availability committees, ensuring reliable data availability even when choosing Validium. Polygon CDK supports various parameter customizations, allowing developers to choose between zk-Rollup and Validium modes and build their own second layer. It also supports customizations such as Gas Token, gas fees, proof submission frequency, batch size, and more.
2.2 Performance and Cost
Polygon CDK achieves fast zero-knowledge proof generation through recursive STARK and Polygon Zero. With optimized hardware settings, it can achieve over 2000 TPS, far exceeding the throughput of the Ethereum mainnet. It also allows for more frequent validity proofs, enabling the first layer to quickly verify the state of the second layer and provide fast finality for the second layer.
Rollup allows for custom Gas Token and gas fee collection rules, giving developers the freedom to reduce costs for Rollup users. Additionally, the maintenance cost of Rollup depends on the size of the data submitted to the first layer, and since zkSNARK proofs are smaller, the maintenance cost is lower. According to official data, the average gas fee per transaction on Polygon Zkevm is only 0.000294 ETH.
3. Case Analysis of Polygon CDK
3.1 ZKFair
Polygon's ZK proof system, based on mathematical proofs, provides a stronger security model compared to OP Stack's fraud proofs driven by socio-economic incentives. Additionally, the modularity and sovereign framework of Polygon CDK provide unparalleled flexibility for developers, which is a feature utilized by ZKFair for its tailored blockchain solution. Meanwhile, Polygon CDK's focus on interoperability and shared liquidity is crucial for the prosperity of blockchain networks. It allows seamless integration with Ethereum and other Polygon chains, attracting a large user base and liquidity pools. While each SDK has its advantages, Polygon CDK stands out as a notable solution in the Rollup SDK field due to its modularity, advanced security, interoperability, and flexible cost-performance balance.
ZKFair chose to use Polygon CDK, which aligns with its goals of scalability, performance, and economic flexibility, which are crucial for innovative projects in blockchain technology. Leveraging the customizable parameters provided by Polygon CDK, ZKFair deployed a Rollup with stablecoin USDC as the Gas Token. Using the configurable gas fees offered by CDK, ZKFair implemented a customized gas adjustment solution, achieving fair distribution of governance tokens. This marks the successful launch of the first second-layer based on Polygon CDK, with its Total Value Locked (TVL) growing from 0 to $160 million within three days. In the first two weeks of its launch, the second layer had over 450,000 active addresses and processed over 5 million transactions.
With the modular design of Polygon CDK, ZKFair plans to migrate its Data Availability (DA) layer from Data Availability Committee (DAC) to Celestia. Integrating with Celestia's modular Data Availability (DA) layer for data expansion significantly reduces gas costs in the ZKFair ecosystem, providing a more cost-effective and user-friendly blockchain experience compared to other solutions.
3.2 Manta's Transition from OP Stack to Polygon CDK
Manta's transition from OP Stack to Polygon CDK reflects its pursuit of enhancing user experience, especially in accelerating withdrawal settlements. The zkEVM technology in Polygon CDK provides fast settlements and robust security through ZK proofs, which is significantly superior to OP Stack's Optimistic Rollup. Another important reason for Manta's transition is its integration with the broader Polygon ecosystem. This transition enables Manta to leverage the shared liquidity of the Polygon network and enhance ecosystem integration through a trustless ZK bridge.
Conclusion
This report on the exploration of various Rollup SDKs emphasizes the dynamic diversity of blockchain technology. While each SDK—Arbitrum Orbit, OP Stack, ZK Stack, and especially Polygon CDK—has made significant contributions to the blockchain ecosystem, more and more projects are choosing to use Polygon CDK to seek scalability, security, and efficiency. This preference is reflected in Manta's shift to Polygon CDK for a better user experience and ZKFair's strategic choice of Polygon CDK for its strong security and flexibility.
Polygon CDK, with its ZK technology, interoperability, and economically efficient solutions, has emerged not only as an innovative tool but also as a comprehensive solution to address modern blockchain challenges. It bridges the gap between ideal and practical, providing a platform consistent with the growing demands of the blockchain community. This positions Polygon CDK not only as an SDK but also as a catalyst for the next wave of blockchain innovation, propelling projects like ZKFair into new realms of performance and scalability. In the evolving landscape of blockchain technology, Polygon CDK stands out as a prominent path, combining efficiency, security, and accessibility, and charting a future that is not only technologically advanced but also inclusive and progressive.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




