Source/Author: Shaunda
Translation: BitpushNewsYanan
Abstract
This article explores the investment value of decentralized perpetual protocols. In the cryptocurrency market, futures trading is usually more popular and has a larger trading volume than spot trading. However, the situation has changed—on-chain spot trading volume has surpassed futures trading volume.

This change is mainly attributed to blockchain technology, especially the gradual resolution of throughput limitations at the L1 level. In the past, these limitations made on-chain order trading less feasible. But thanks to the latest advancements in L1 scaling, we are now able to build more flexible and efficient decentralized perpetual protocols.
These emerging protocols provide a more convenient and secure platform for cryptocurrency trading. Compared to traditional centralized exchanges, decentralized exchanges demonstrate higher transparency and fairness while ensuring the security of user assets.
This article also provides a detailed introduction to several leading decentralized perpetual exchanges, such as Hyperliquid, IntentX, and Vertex. These exchanges each adopt unique technical architectures aimed at providing a higher quality trading experience and service. Through in-depth analysis of these exchanges, we can better understand the practical applications and development trends of decentralized perpetual protocols.
Looking ahead, decentralized perpetual protocols will continue to experience innovation and development. By implementing incentive programs, adopting long-tail asset strategies, and enhancing user experience, these protocols are expected to further expand market share and meet evolving user demands. The conclusions of this article provide valuable insights for investors and market participants, helping them better grasp the future direction of decentralized perpetual protocols.
Perpetual Futures
Perpetual futures are a type of derivative contract that allows traders to speculate on the future price of assets without a set expiration date. These contracts are Delta-One products, meaning that for every change in the underlying asset, the derivative price will also change by the same amount.
Although BTC-USD perpetual trading should always follow the price of BTC, there is actually a slight imbalance between long and short demands, resulting in perpetual premiums. A high premium indicates dominance by long traders, driving the perpetual price above the spot price; a discount indicates a greater number of short positions, leading to market imbalance.
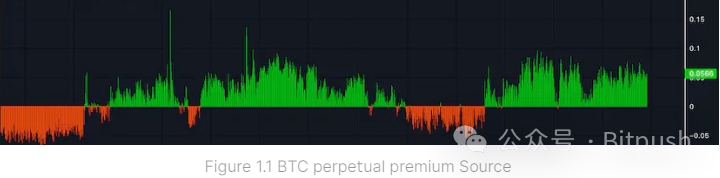
To balance the contract price with the spot price, exchanges introduce a floating funding rate adjusted every 8 hours based on the perpetual premium. When the contract is at a premium, longs pay fees to shorts; when at a discount, shorts pay fees to longs. The funding rate is not only a trading cost but also an indicator of market sentiment: a high long funding rate indicates strong bullish sentiment, while the rate may turn negative during market downturns. Therefore, traders may need to pay or receive funding fees based on market conditions.
Perpetual futures settle in cash, and opening leveraged perpetual positions requires cash collateral. Traders can use isolated margin or cross margin as collateral. Isolated margin is a specific amount of capital provided by traders for leveraged positions, while cross margin uses the entire account as collateral for all positions.
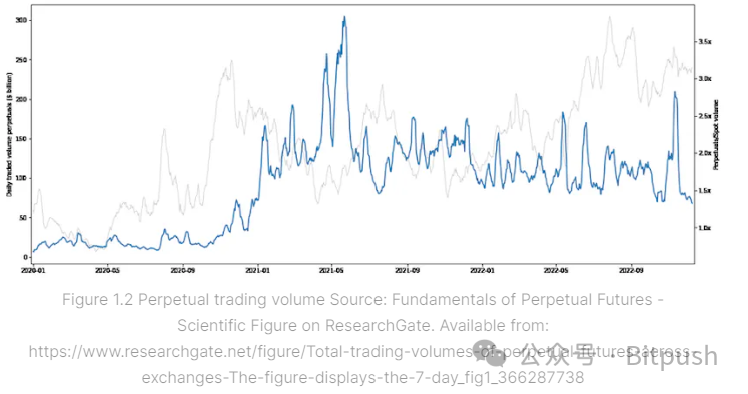
Leveraged trading is extremely popular in the cryptocurrency field, with average trading volumes in 2022 reaching 2-3.5 times that of spot trading.
Traders use collateral to open futures contracts and can hold them long-term as long as they maintain the minimum margin and pay the funding rate. If the position's loss exceeds the collateral, it triggers liquidation and automatic closure.
For example, a trader uses $1000 as collateral to borrow a $10,000 BTC-USD coin-based margin position, i.e., 10x leverage. They need to pay the funding rate based on the $10,000 nominal position.
Outcome A: BTC price rises by 10% - the trader's position value is $11,000, resulting in a 100% profit or loss on their collateral.
Outcome B: BTC price drops by 10% - the trader's position value is $9000, leading to liquidation and a -100% profit or loss.
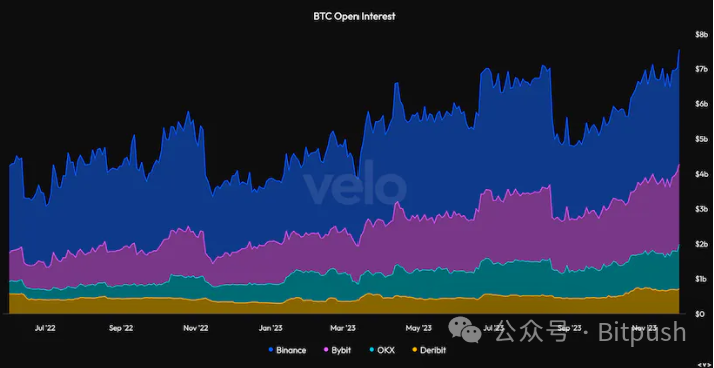
Open interest refers to the total number of outstanding derivative contracts, such as options or futures, representing the current market's leverage scale. In 2021, Bitcoin's (BTC) total open interest reached a peak of $20 billion, indicating that $20 billion in assets were borrowed for leveraged Bitcoin positions.
Open interest is an important indicator of market participants' interest in a specific asset, especially in derivative markets. High open interest usually means more traders are participating in the market and are willing to take risks for higher returns. However, open interest can also be seen as an indicator of potential market volatility, as high open interest may imply that more contracts will need to be closed in the future, which could lead to price fluctuations.
Centralized Exchanges
Traditionally, trading of derivative contracts mainly occurs on centralized exchanges, which act as intermediaries for buyers and sellers, providing liquidity for various tokens and executing trades on behalf of users. These exchanges are popular among users due to their user-friendly interfaces and convenient features, such as easy trading between fiat and cryptocurrencies.
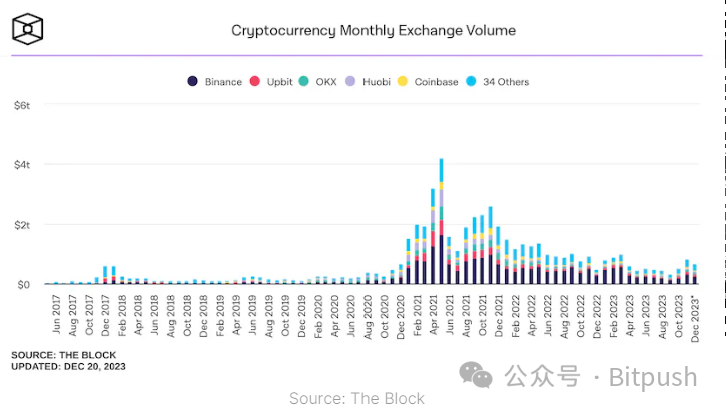
Key participants in this field include Binance, Coinbase, Upbit, OKX, and Kraken. In 2023, their average monthly trading volume exceeded $500 billion.
Compared to decentralized exchanges and wallets, users prefer centralized exchanges for the following reasons:
User experience and interface: Binance and other centralized exchanges have simple and user-friendly interfaces, providing tutorials, user support, and intuitive trading designs.
Fiat and cryptocurrency trading: Centralized exchanges support convenient trading between debit cards, bank transfers, and other methods, making them the preferred platform for investors to buy and sell cryptocurrencies.
Leverage trading: They offer leverage of up to 100x and over 400 cryptocurrency trading pairs.
However, centralized accounts have the following drawbacks:
"Not your keys, not your crypto": After FTX's bankruptcy, traders began to realize the related risks of keeping funds on exchanges. Funds held by exchanges are often used to earn additional income while exposing user funds to risks.
Strict KYC regulations: Due to strict regulations, centralized exchanges must comply with international and domestic laws. This means strict Know Your Customer (KYC) verification for all customers. Centralized exchanges face increasingly strict regulations, leading to Binance's exit from the markets of Germany, the Netherlands, the UK, and India in 2023.
Decentralized Spot Exchanges (Uniswap)
In 2020, a significant breakthrough was achieved in the cryptocurrency field with the launch of decentralized exchanges on Ethereum, allowing users to trustfully exchange ERC20 tokens. This exchange utilizes liquidity pool technology, where users pair two ERC20 tokens, and the tokens in the pool remain equivalent. The price is determined by automated market makers, eliminating the reliance on centralized market makers.
Order Book Model (Centralized Exchanges)
Consists of a centralized database where different buyers and sellers submit their trades. The limit orders of these trades form the buy orders (buyers) and sell orders (sellers) on both sides of the order book. Order book exchanges require users to place orders and wait for execution. Market makers are typically institutional funds.
Automated Market Makers (Decentralized Exchanges)
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) operate differently from order book models as they do not rely on third-party buy and sell requests. Instead, they use liquidity pools and algorithms to set prices based on token supply ratios. Liquidity providers inject tokens into the pool to create liquidity and receive trading fee rewards based on their contributions.
Uniswap's liquidity pools use the constant product formula to determine asset prices. The constant product function ensures that trades do not change the product of the reserve balances of a token pair. This mechanism provides decentralized exchanges with an efficient, transparent, and trustless price discovery mechanism.
The applicable formula is x*y = k, where x represents the quantity of token A in the liquidity pool, y represents the quantity of token B in the liquidity pool, and k is a constant.
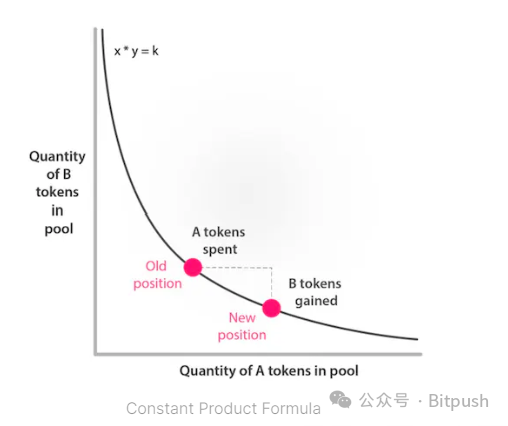
When one token is withdrawn from the pool, the price of the other token gradually increases, achieving automated market making and ensuring constant liquidity regardless of the presence of counterparties.
Trading fees are directly paid to liquidity providers, and they also benefit from incentive programs of decentralized exchanges, which distribute native tokens to liquidity miners. Fee distribution is based on the proportion of liquidity providers' total LP shares.
This sparked the famous DeFi summer boom; during this period, the total locked value on all EVM-compatible chains increased from $590 million in January 2020 to $150 billion in January 2022. At its peak, decentralized exchange spot trading volume accounted for 20% of all cryptocurrency spot trading volume, and the market value of the industry leader Uniswap reached $21 billion.
However, DeFi has a problem. Ethereum's gas fees are too high for users. For a typical Uniswap trade, users need to pay over $30 in gas fees. The trading process roughly involves:
Transferring cryptocurrency from centralized exchanges (such as Binance, Coinbase) to Metamask;
Granting permission for Uniswap to use ETH (base token) → exchanging the base token for the desired token → granting permission for Uniswap to use the desired token → exchanging back to ETH;
Each of these steps requires additional gas fees. Users can only purchase ERC20 tokens on Ethereum. If a user wants to buy BTC, they need to purchase wrapped BTC (WBTC), which adds additional risk.
The exchange fee paid to LP is 30 basis points. The new v3 update created liquidity tiers ranging from 5 basis points to 100 basis points. Additionally, Uniswap added a 15 basis point front-end fee.
At the time, the problems of decentralized exchanges can be summarized as follows:
Dispersed liquidity: Each exchange has unique liquidity pairs, leading to fragmented liquidity on the same blockchain. Additionally, liquidity is fragmented between different blockchains (such as ETH, ARB, AVAX). However, currently only ERC20 tokens can join liquidity pools, which limits flexibility to some extent.
High fees: High swap fees, high Ethereum gas fees, and the need for multiple authorizations.
High slippage: Impermanent loss due to low liquidity and low market value in liquidity pools caused by dispersion.
Despite this, DeFi remains a groundbreaking innovation in the cryptocurrency field, achieving trustless asset swaps.
Decentralized Perpetual Exchanges (GMX, DYDX)
Early tools of decentralized finance were mainly limited to spot exchanges due to the high fees and limited transaction speed of Ethereum (15 TPS). This made it difficult to implement order book exchanges. However, with the introduction of layer 2 networks and the improvement of alternative infrastructure at the L1 level, this situation has changed.
GMX (GLP-based Perpetual Contracts)
In 2021, GMX innovated the Uniswap spot exchange model. Unlike traditional spot exchanges, GMX users do not directly buy and sell tokens. They deposit collateral and hold long or short positions. Profits from short positions are paid in USDC, while profits from long positions are paid in the other token of the trading pair.
GMX collaborates with the GLP pool. Liquidity providers provide liquidity to the GLP pool by locking any index asset in the pool. In return, the protocol mints GLP tokens representing the equity of liquidity providers. The protocol then automatically stakes the newly minted GLP tokens. Traders use the GLP pool as counterparties. They pay USDC collateral to borrow assets from the GLP pool and receive their upward profits.
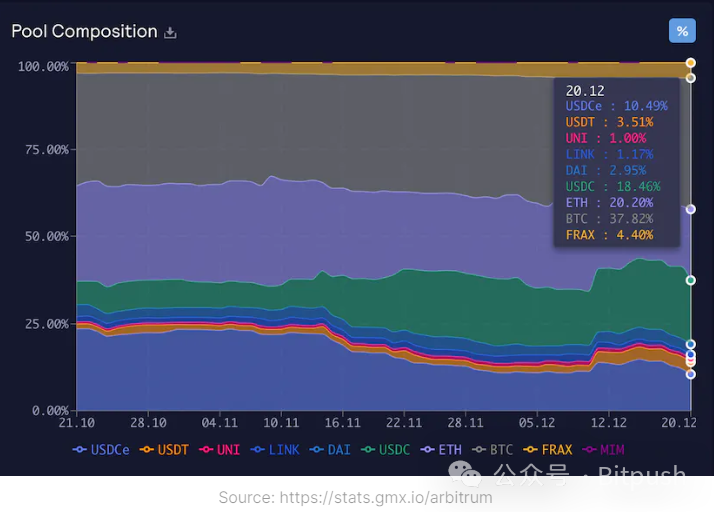
For example, a trader pays $10,000 as collateral to borrow $100,000 worth of BTC at 10x leverage from the GLP pool. If the price of Bitcoin doubles, they can earn the upward profits originally belonging to the GLP pool (i.e., earn $100,000 and repay the loan with $100,000 worth of BTC). However, if the trade fails, they will lose the collateral and need to return the borrowed assets. It's worth noting that the average annual return rate of the GLP pool in recent years has reached 20%.
The fees involved are as follows:
Position fees: 10 basis points for borrowing and closing positions.
Borrowing fees: These are dynamic fees calculated based on utilization and the chosen profitable underlying asset. The calculation formula is: (borrowed asset)/(total assets in the pool)*0.01.
Swaps: The swap fee is not fixed but is calculated based on whether the swap operation optimizes the asset weight distribution in the GMX liquidity provider (GLP) pool. If the swap brings the asset weight closer to or deviates from the target allocation, the swap fee will be adjusted accordingly.
Pros/cons are as follows:
GMX introduces a new way of on-chain leverage by introducing the GLP model. As traders can access the vast GLP liquidity, the GLP pool supports high leverage trading of up to 50x. However, this mechanism also has significant limitations: only assets in the GLP pool can be traded, greatly limiting the number of trading markets for GMX. Currently, GMX only offers 9 perpetual markets, including BTC, ETH, SOL, ARB, LINK, XRP, DOGE, UNI, and LTC.
DYDX (Order Book-based Perpetual Contracts)
DYDX adopts a unique on-chain/off-chain order book model to address latency and cost issues. In this model, the order book is not directly stored on the blockchain but is hosted by validators in their memory, enabling off-chain operations. When users submit orders, including details such as price, volume, expiration date, and order type (buy or sell), they are recorded in the off-chain order book. Once a matching order appears, the smart contract verifies the availability of trading funds and executes the trade after confirming its accuracy. It's worth noting that while trading activity mainly occurs off-chain, the final trade settlement still occurs on the blockchain. This off-chain order book model not only significantly reduces gas fees but also greatly improves transaction speed.
To incentivize market makers, dYdX has established a liquidity provider reward program. The program determines the contribution of market makers to platform liquidity by comprehensively evaluating their trading volume, bid-ask depth, and spread with the mid-market price, and rewards them accordingly in the form of $ethDYDX tokens, aiming to encourage more market makers to provide liquidity to the platform, thereby promoting market stability and development.
Recently, dYdX migrated from the Ethereum layer 2 network to its independent blockchain, the dYdX chain. This migration is part of the dYdXv4 upgrade, aiming to better support the platform's order book functionality by increasing throughput. The dYdX chain is built using the Cosmos SDK and Tendermint proof-of-stake consensus protocol, capable of processing up to 2000 transactions per second. The migration to an independent chain has various impacts:
Fully Decentralized: The dYdX chain is a completely independent, open-source blockchain software, which means it does not rely on any external blockchain or system.
Community Control: The v4 upgrade enables the exchange to achieve full decentralization and community governance. Changes to the tech stack are decided through community governance voting by the dYdX Foundation.
Fee Sharing: In the early days as a layer 2 network, dYdX did not share the fees charged between market makers and traders with users. However, with dYdX's migration to its independent blockchain, a new mechanism has been implemented—trading fees will now be shared among users staking on the dYdX chain.
Current Overview of Decentralized Perpetual Contracts Field
Since 2021, Ethereum's scalability on L2 and Layer 1 platforms has been significantly enhanced, greatly driving the development of derivative infrastructure. In this field, not only has trading volume repeatedly reached new highs, but the number of participants has also experienced rapid growth. As of December, on-chain derivative trading volume has reached an astonishing $114 billion, a significant increase from $84 billion in November.
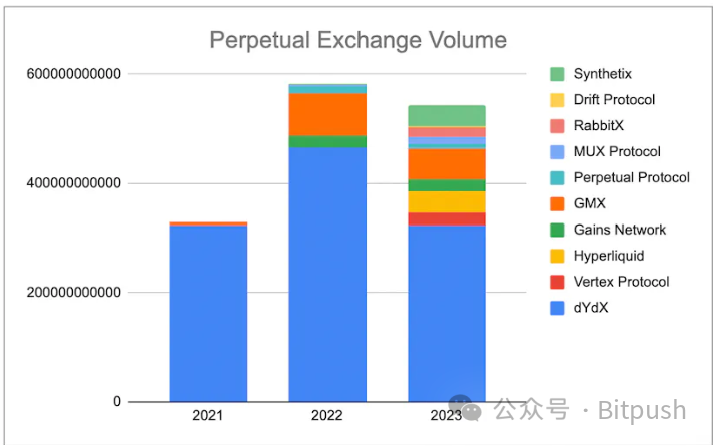
Current decentralized derivative exchanges can mainly be distinguished based on their architectural designs:
Synthetic Assets and Asset Compositions Based on Oracles: Oracle-based protocols use liquidity pools as counterparties for trading. In synthetic liquidity, a single asset serves as the basis for all trading markets. By using oracles, liquidity providers (LPs) can become counterparties in these markets. In the asset composition model, multiple assets are used as counterparties.
Virtual Automated Market Makers (vAMMs): vAMMs drive independent price discovery mechanisms decoupled from the underlying spot prices by providing decoupled market structures. This mechanism may lead to differences between futures prices and asset spot prices, creating opportunities for arbitrage traders. However, it should be noted that due to insufficient deep liquidity, investors may encounter unexpected or unfavorable price fluctuations when opening or closing positions.
Spot AMMs: Spot AMMs can be integrated into other spot AMMs or DEX (decentralized exchange) aggregators, enabling trading on platforms such as Uniswap and Curve. The price discovery mechanism is closely related to the number of integrated venues and the liquidity within these venues. For spot AMMs, the primary role of oracles is to ensure the execution of the most favorable prices for buyers and sellers, i.e., by collecting price information from various exchanges and selecting the most advantageous price for traders.
Order Book: The order book mechanism has driven the development of peer-to-peer trading, where buyers' bids and sellers' asks interact to collectively build a market environment for price discovery and trade execution. Under this protocol, traders can freely choose any price for trading, completely eliminating the reliance on oracles in such setups.
Hybrid Models: AMM + Order Book: Hybrid models combine order books and AMMs to ensure continuous liquidity. For example, Drift v2 uses three different liquidity mechanisms: instant (JIT) Dutch auctions, limit order books, and constant product AMM. Vertex uses a price/time priority algorithm, so orders will be executed based on the best price, whether priced by AMM or market maker. Similarly, Vertex also adopts a hybrid model, using a price/time priority algorithm to determine the order execution sequence. This design ensures fairness and efficiency in trading, providing traders with a better trading experience.
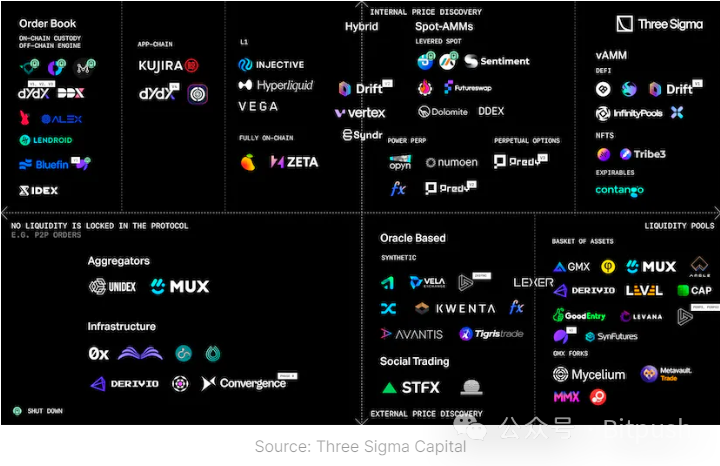
The following are the leaders in the current decentralized derivative field and their architectural choices:
Hyper Liquid (L1 Order Book, Fully On-Chain)
Hyperliquid L1 is a blockchain customized for high-performance decentralized derivative exchanges, using an optimized Tendermint consensus mechanism to achieve fast end-to-end response in 0.2 seconds and process up to 20,000 order placement, cancellation, and settlement operations per second. The system is built on the Rust language and ABCI server and secured through proof of stake, ensuring safety. Compared to Tendermint's default limit of 1,000 transactions per second, Hyperliquid L1's performance has been significantly improved.
Hyperliquid adopts a fully on-chain order book model, ensuring transparency and traceability of all trading activities. Additionally, Hyperliquid has established a treasury (HLPS), an innovative mechanism aimed at democratizing market making. Through the treasury, users can deposit their market-making strategies and earn profits from them.
Hyperliquid has not yet issued tokens, but they have announced a points activity as a prelude to an upcoming airdrop. According to this activity, Hyperliquid plans to distribute 1,000,000 points to its users weekly over a six-month period. The first points distribution was successfully conducted on November 9th. These points are intended to reward users who have made positive contributions to the success of the Hyperliquid protocol, thereby incentivizing community participation and further protocol development.
Unique features of Hyper Liquid include:
Custom L1 Uniswap Perpetual Contracts: Hyperliquid has introduced unique L1 Uniswap perpetual contracts that operate independently from other markets, using Uniswap v2/v3 oracles to determine prices. This eliminates the need for centralized exchanges in price discovery. Additionally, these contracts support tokenless futures trading, simplifying the trading process.
Index Perpetual Contracts: Index contracts on Hyperliquid L1 take a different approach, not relying on spot asset prices but closely tracking a specific formula defining its underlying index. For index perpetual contracts, their operation mechanism does not track a series of centralized exchange (CEX) median prices. Instead, it relies on validators regularly submitting the calculated results of the index formula to Hyperliquid L1. These submitted values are then processed by the system, taking the median as the basis for calculating the funding rate, replacing the traditional spot oracle formula. For example, NFTI-USD (representing the blue-chip NFT index) and FRIEND-USD (representing Hyperps' Friend tech stock index) operate in this manner, providing investors with formula-based derivative trading opportunities different from traditional spot markets.
Treasury: The treasury feature is a major innovation of Hyperliquid, allowing users to create their own treasuries and become treasury leaders. Other users can choose to deposit funds into these treasuries and automatically replicate the trading strategies of treasury leaders. In return, treasury leaders will receive 10% of the profits earned.
Aevo (formerly RibbonFinance) - On-Chain/Off-Chain Order Book
Aevo is a high-performance decentralized derivative exchange focused on options trading. The exchange operates on a custom EVM roll-up connected to Ethereum. Aevo runs an off-chain order book, with settlement conducted on-chain. This means that once orders match, trades are executed and settled through smart contracts. Aevo is known for its options contracts, currently holding a 77% market share, while also offering over-the-counter (OTC) and structured options trading. Investors in Aevo include Paradigm, Dragonfly Capital, Ethereal Ventures, Coinbase Ventures, Nascent, Robot Ventures, Scalar Capital, and Alliance.
Aevo adopts a voting custody token economic system, allowing users to lock Aevo to gain voting rights and rewards. After staking Aevo for 3 months, it becomes sAEVO, a non-transferable version of AEVO, granting users double voting rights, commission discounts, and priority access to new products. According to proposal RGP-33, Aevo's voting has decided to rename from RBN and upgrade to $Aevo, with plans for a 1:1 token swap in January 2024.
Aevo's unique features include:
aeUSD: aeUSD is an innovative financial tool on the Aevo Layer 2 platform, structured as an ERC-4626 asset. It is a hybrid asset composed of 5% USDC and 95% sDAI. This asset serves as collateral on the Aevo exchange, fully whitelisted by the exchange, and has a 100% collateral ratio. This means users can fully collateralize their positions with aeUSD. Investors, including individual users, market makers, and various financial strategies, can earn a competitive 4.75% annualized yield (APY) on exchange margin using aeUSD.
Options: Aevo options provide a powerful margin system and a wide range of tradable instruments, covering daily, weekly, monthly, and quarterly options to meet the trading needs of different investors. The platform uses European option settlement, meaning options can only be settled on the expiration date, providing investors with a more standardized and stable trading environment.
Treasury: Aevo has a treasury where users can run automated strategies and earn profits. Although Aevo's treasury is currently in the early access stage, they previously had two active treasuries: Theta Treasury and Ribbon Earn Treasury. The Theta Treasury runs an automated European option selling strategy, periodically earning profits by writing out-of-the-money options and collecting premiums. When users deposit assets into the Theta Treasury, the treasury mints and holds the user's shares. Then, the treasury writes out-of-the-money call options on all deposits weekly. If the options expire out-of-the-money, the treasury reinvests the profits back into the strategy, effectively compounding for depositors over time. The Ribbon Earn Treasury is described as an all-weather yield product, providing principal protection and combining lending and exotic options to enhance returns by exposing to short-term market volatility.
IntentX (RFQ Exchange)
IntentX is a next-generation over-the-counter (OTC) derivative exchange offering perpetual futures trading. It operates on an intent-based architecture, different from traditional order book or automated market maker (AMM) models. IntentX allows traders to express their trading intent rather than execute orders with committed capital. These intents are then executed by external solvers (market makers) that can access liquidity from centralized exchanges (CEXs), ensuring competitive quotes and minimal slippage. The platform is built on Base and leverages cutting-edge technologies, including LayerZero (a cross-chain communication protocol), account abstraction, and request for quote (RFQ) architecture.
IntentX's unique features include:
LayerZero Full-Chain Functionality: With the advanced cross-chain communication protocol LayerZero, IntentX achieves seamless cross-chain scalability and expansion capabilities, making it easy to deploy across the entire decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem without worrying about technical challenges or liquidity bottlenecks.
Competitive Advantages: IntentX offers over 180 tradable cryptocurrency pairs with deep liquidity, leverages up to 60x on perpetual futures, provides "trade to mine" incentives for xINTX rewards, and offers cross-margin accounts for efficient margin management.
Token Economic Structure: 100% of the revenue is shared with XINT holders.
Vertex Protocol (Hybrid AMM Order Book Exchange)
Vertex Protocol aims to improve capital efficiency, reduce user costs, and enhance overall user experience through innovative hybrid order book-AMM design. This design combines the order book model of centralized exchanges (CEXs) with the automated market maker (AMM) architecture. In the Vertex model, the aggregated liquidity of AMMs complements the buy and sell orders on the order book, and smart contracts provide liquidity to the market. This unique design allows Vertex to achieve low-latency trading and efficient liquidity utilization across a wide range of DeFi assets.
Vertex Protocol's unique features include:
Integrated Hybrid Model: Vertex Protocol successfully integrates the order book model of centralized exchanges (CEXs) with the AMM architecture, playing a crucial role in the prosperity of decentralized exchanges (DEXs). This hybrid design aims to provide users with excellent price matching, trade execution, and opportunity capture experiences.
Vertical Integration: As a vertically integrated decentralized exchange (DEX), Vertex Protocol offers comprehensive services including spot trading, perpetual contracts, and money markets. This one-stop service eliminates the hassle of switching between different platforms or applications, significantly improving trading convenience and efficiency. With its innovative hybrid architecture and vertical integration features, Vertex Protocol is committed to providing DeFi users with a more efficient and convenient trading experience while maintaining the core advantages of decentralized exchanges.
Injective (Infrastructure & Decentralized Exchange)
Injective is a layer one protocol dedicated to providing the necessary infrastructure for building decentralized exchanges. Its outstanding block time processing capacity (processing over 10,000 transactions per second) and plug-and-play modular design enable developers to easily create order book-based decentralized exchanges. It's worth noting that all decentralized exchanges built on the Injective protocol share the same on-chain order book. This feature not only ensures efficient liquidity utilization within the entire ecosystem but also allows users to seamlessly switch and share their user base across different exchanges. The native perpetual exchange of the Injective protocol is Helix Exchange.
Injective's unique features include:
Shared Liquidity: Injective L1 provides infrastructure for decentralized perpetual exchanges, including shared liquidity. Each exchange on Injective shares the same liquidity provided by Injective's market makers.
Spot Exchange with IBC Bridge: The Injective exchange built using the Cosmos SDK enables cross-chain interaction and interoperability through the IBC bridge, allowing assets to freely move between different blockchains, enriching the platform's trading options. Users can easily purchase native SOL and transfer it directly to the Phantom wallet.
Trading Bots: The grid trading bot of Helix Exchange provides automated strategies, executing buy and sell operations automatically within preset price ranges, capturing market movements without the need for continuous monitoring by traders.
Rage Trade (Aggregator)
Rage Trade is a multi-chain perpetual aggregator compatible with various chains such as EVM L2, L1, AppChains, and Cosmos, creating a decentralized derivative trading environment. It allows users to inject liquidity for perpetual trading using LP tokens from other protocols, simplifying the trading process and enabling users to choose the optimal path for leveraged trading. Additionally, Rage Trade provides cross-chain access and comparison of perpetual contract prices across different exchanges, allowing users to execute trades at the best prices, significantly improving trading efficiency and returns.
Infinity Pools (VAMM)
Infinity Pools is an innovative decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that revolutionizes leveraged trading. It allows unrestricted leveraged trading of any asset, eliminating liquidation risk, counterparty risk, and reliance on oracles. The protocol operates simply: liquidity providers (LPs) of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) deposit LP tokens into the protocol, which are then aggregated and borrowed by traders seeking leverage. For example, an ETH-USD Univ3 LP can provide tight liquidity within a specific range, which traders can borrow using the LP, pledging the corresponding collateral ETH.
The characteristics include: infinite leverage, achieving nearly infinite leverage levels through pre-secured liquidation liquidity; infinite assets, leveraging existing DEXs, allowing safe leveraged trading of any asset without permission; oracle-independent, prices directly linked to borrowed LP positions; no liquidation risk, avoiding traditional liquidation methods due to the absence of cash loans.
The protocol does not require liquidation bots or oracles, thus it can independently expand to any asset market, limited only by existing liquidity. InfinityPools also improves the earnings model for LPs: in addition to earning exchange fees within the capital range, they can also continue to profit from lending to traders.
Protocol Comparison
Fees
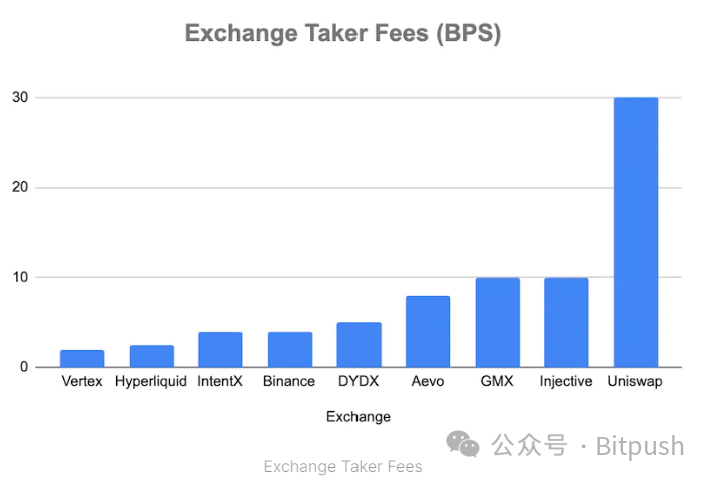
Decentralized exchanges are now competing with giants like Binance in terms of fees, offering low maker fees. Compared to leading decentralized spot exchanges, decentralized perpetual exchanges have more affordable fees, far lower than Uniswap's default fees.
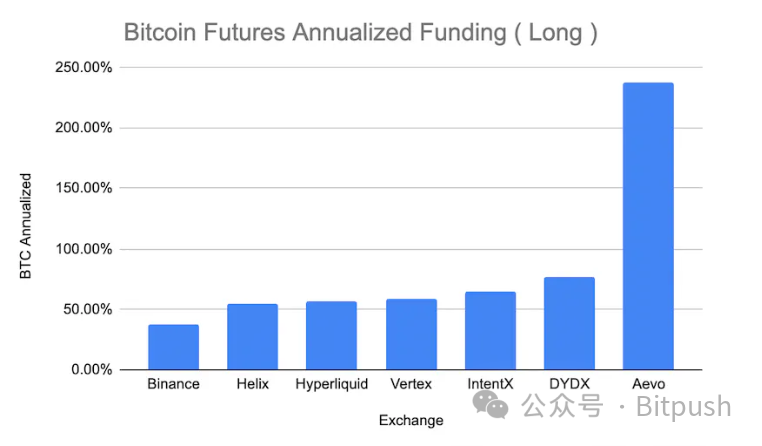
Although Binance leads in annualized funding rates, decentralized derivative exchanges still demonstrate strong competitiveness, with future costs expected to be further reduced through market innovation. With its unique VAMM design, InfinityPools brings innovation to the DeFi field, providing more choices and opportunities for both sides of the trade.
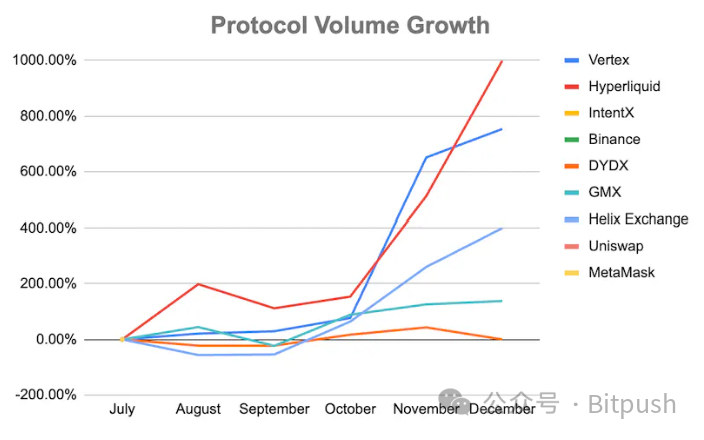
Protocol Growth
The following is a comparison of the growth in protocol trading volume. Most protocols have experienced rapid growth, with an average trading volume increase of 400% since July. Among them, Hyperliquid and Vertex lead in growth, while GMX lags behind due to limited fees and trading pairs.
- Overall surge in derivative trading volume: Derivative trading volume has rapidly increased, with an average growth rate of 400%.
- Impact of token incentives: Both Vertex and Hyperliquid have seen a surge in trading volume. Vertex's monthly trading volume increased from 17.8 billion in July to 125 billion in December, a 753% increase, while Hyperliquid increased from 646 million to 7.1 billion within the same time frame. VRTX and HyperLiquid both subsidized trading volume through token incentives.
- DYDX & GMX facing competition: Compared to their competitors, giants GMX and DYDX have experienced slower growth. While they hold a dominant position as pioneers, newcomers can deploy aggressive strategies to attract new users.
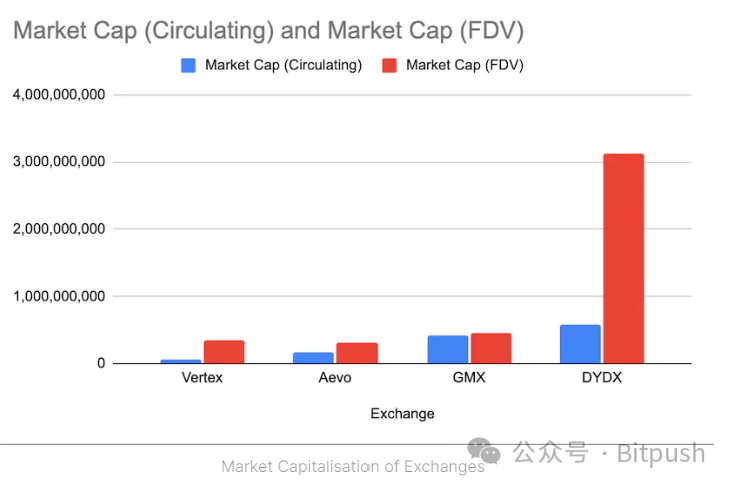
Market Cap
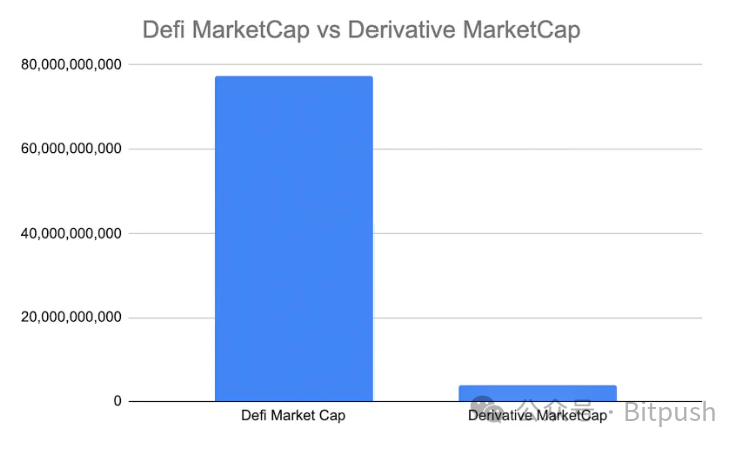
The total market value of the derivatives field has reached $3.8 billion, with SNX, DYDX, and GMX ranking in the top three. It is worth noting that many exchanges have not yet issued tokens. Although the trading volume of decentralized derivatives is comparable to decentralized exchanges, its market value is only one-fourth of the latter.
In the context of decentralized finance, derivatives are still in the early stages, accounting for only 4.7% of the total market share.
Future Outlook
This section focuses on the key factors and plans that will play a crucial role in achieving widespread adoption of financial derivatives in 2024, helping readers better understand market trends and future development directions.
Market Expansion
In 2020, Uniswap introduced a major innovation: permissionless listing of any ERC-20 pair. Compared to centralized exchanges limited by liquidity, regulations, and reviews, Uniswap can create liquidity pairs within seconds. In September 2020 alone, Uniswap witnessed 300,000 mintings, injecting a large amount of liquidity into the pools, mainly focused on permissionless small pools. Its advantage lies in the ability to trade any asset, regardless of market cap, liquidity, or regulatory status.
Decentralized perpetual exchanges are developing in this direction. Market leader DYDX plans to create a decentralized, permissionless perpetual protocol where any asset with price feeds can be listed. In the future, carbon credits, prediction markets, and indices will all be traded on DYDX. Meanwhile, InfinityPools, launched in 2024, will allow leveraged trading of any Uniswap v3 token, just as Uniswap allows spot trading of any asset, opening the door to futures trading pairs.
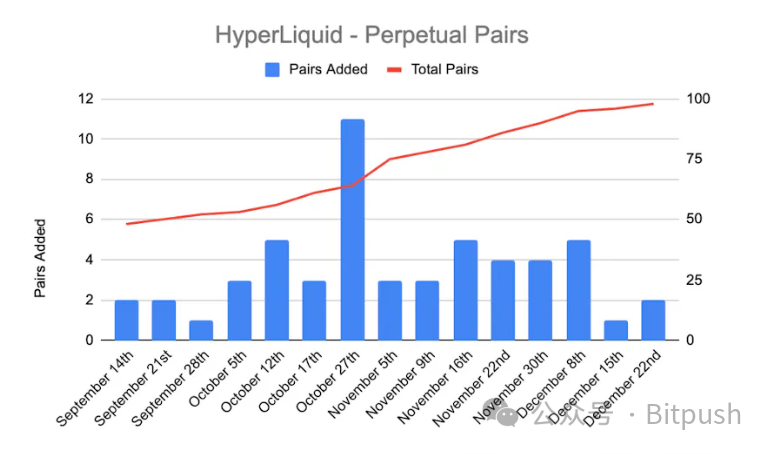
Previously, most decentralized exchanges focused on infrastructure development, creating L1s capable of high throughput and low latency. Now that the foundation is solid, teams are shifting focus to creating trading pairs and expanding growth. Since September, Hyper Liquid has been adding an average of 4 new trading pairs per week.
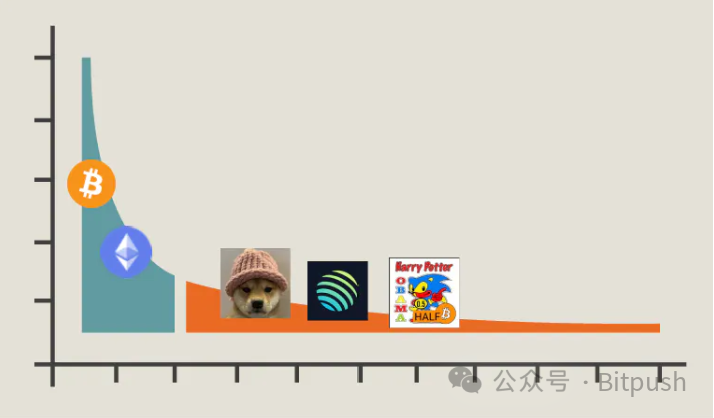
Another significant difference lies in the different focuses of each protocol. While Binance leads in high market cap assets, its strict regulations present significant growth opportunities for perpetual protocols. On Hyperliquid, 53% of retail trades come from "other" tokens, i.e., non-mainstream coins such as BTC, ETH, ARB, AVAX, etc. This long-tail strategy targeting retail demand provides a large number of trading pairs and may be a key driver of trading volume. Hyperliquid and Aevo have launched long-tail products, such as pre-sale perpetual contracts for BLAST and JUP, and listed some retail assets not listed on Binance, such as HPOS, SHIA, UNIBOT, etc. Meanwhile, Hyperliquid is also active in Memecoins, listing 8 perpetual contracts, compared to Binance's 9. These exchanges also enhance their competitiveness through unique structured protocols, such as replicated trading treasuries and pre-sale products.
Simplified User Experience
Decentralized perpetual exchanges are committed to optimizing the user experience to be more similar to centralized exchanges in terms of convenience. Compared to other decentralized exchanges, decentralized perpetual exchanges have made significant progress in native charts, zero gas fee transactions, and MEV protection. Their greatest advantage lies in bypassing the cumbersome KYC process, allowing users to complete registration in seconds without waiting for days for approval.
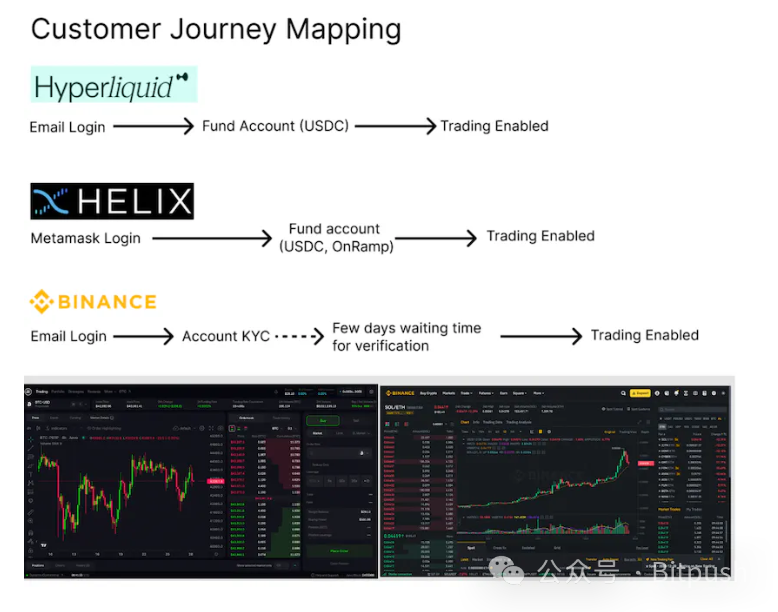
Exchanges will benefit from multiple improvements, especially the native on-ramp and off-ramp feature, allowing users to directly deposit funds into their accounts without relying on centralized exchanges. Meanwhile, spot exchanges with IBC bridge support allow users to purchase and hold tokens across blockchains, further enhancing trading flexibility and convenience.
Incentive Programs and Community Governance
The decentralized perpetual protocols aim to provide fees comparable to centralized finance and further reduce trading costs through token incentives. This strategy is similar to the liquidity mining model in 2020, which brought significant capital inflows to decentralized exchanges.
For example, Hyperliquid has launched a 6-month points program. Similarly, Intent X and Vertex have allocated 26% and 44% of tokens to traders as earnings, respectively. On the dYdX chain, there are 50,000 $DYDX available for traders to earn daily.
These incentive measures are designed to attract users and liquidity providers to provide trading volume and liquidity. The unique token economic model increases user stickiness through revenue sharing and staking mechanisms, such as IntentX paying all fees to INTENTX holders, and Vertex and GMX paying 50% and 30% of fees to stakers, respectively. In addition, tokens for decentralized perpetual contracts also have potential for appreciation.
Conclusion
Since July 2023, decentralized derivative trading volume has surged by 400%, but it only accounts for 2% of total cryptocurrency futures trading volume, showing its enormous potential. Although futures trading typically exceeds spot trading by 2-3.5 times, the monthly trading volume of decentralized derivatives is comparable to on-chain decentralized exchanges (DEX) for spot trading. Perpetual exchanges have long been plagued by high fees and latency issues, but recent infrastructure and protocol innovations have enabled them to compete with centralized giants. Currently, General Liquidity Pools (GLP), synthetic assets, and order book model exchanges have performed well. The order book model excels in composability and low latency, with successful applications by DYDX and Hyperliquid. In addition, decentralized perpetual protocols are expanding the market through strategies such as incentives and fee discounts. Unrestricted by regulations, flexible token listings without the need for KYC, and the potential for community governance and token appreciation effects are expected to drive continued prosperity in the decentralized derivatives market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




