Current Status of Consensus Algorithms
Consensus algorithms are a critical component of today's distributed systems. By providing a trustless consensus mechanism, they ensure the security and stability of the network. However, most blockchain consensus algorithms face challenges in power distribution in practice, leading to the concentration of power in a few entities, which violates the principle of decentralization.
Therefore, when evaluating consensus algorithms, we should focus on their power distribution mechanisms to ensure fairness and decentralization. Additionally, security and resistance to attacks are crucial for the successful implementation of consensus algorithms. Despite the goal of ensuring network security, there are often vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit to compromise the network's security. Lastly, economic incentives and consensus mechanisms also play an important role in the success of consensus algorithms. Factors such as user participation, incentive mechanisms, and economic models have a significant impact on the effectiveness of consensus algorithms.
This Bing Ventures research article will focus on the power distribution and security of consensus algorithms, providing readers with deeper insights. By delving into these issues, we can provide more comprehensive solutions for the improvement and optimization of consensus algorithms, thereby promoting the development of network security and decentralization.
Current State of Consensus Algorithms
First, a major issue in the current state of consensus algorithms is the tendency towards centralization. Despite the goal of achieving decentralized systems, certain algorithms exhibit a tendency towards centralization. This is mainly reflected in certain consensus algorithms relying on specific sets of validating nodes, leading to increased power concentration and system vulnerability. To address this issue, we need to explore more decentralized consensus algorithm designs, such as introducing multiple independent sets of validating nodes or adopting mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake to ensure the practical realization of decentralization principles.
Secondly, performance limitations are another key issue for consensus algorithms. Some consensus algorithms may face challenges such as low throughput and high latency, limiting the system's scalability and practical application capabilities. To meet real-world demands, we need to continuously optimize consensus algorithms to improve their performance and efficiency. For example, by introducing parallel computing, optimizing network communication, and improving block confirmation mechanisms, we can enhance the overall performance of consensus algorithms and further drive the widespread application of blockchain systems.
Energy consumption is an important issue facing current consensus algorithms. Some consensus algorithms, especially those based on Proof-of-Work, have very high energy requirements. This not only increases the operating costs of the system but also has a negative impact on the environment. Therefore, designing and adopting more energy-efficient consensus algorithms is a significant concern.
Security and resistance to attacks are indispensable focus points for consensus algorithms. Consensus algorithms need to have strong security to protect the system from various malicious attacks and manipulations. However, some consensus algorithms may have security vulnerabilities, making the system susceptible to issues such as Byzantine faults and double-spending attacks. To provide more reliable and secure solutions, the design of consensus algorithms needs to fully consider various potential attacks and introduce corresponding defense mechanisms, such as Byzantine fault-tolerant algorithms, key management, and multi-signature schemes.
The scalability of consensus algorithms is also an important issue that urgently needs to be addressed. As the scale of blockchain and distributed systems continues to expand, consensus algorithms need to be able to handle the increasing transaction volume and user base. Some algorithms may experience performance degradation in large-scale networks, limiting the system's development and application scope. Therefore, achieving highly scalable consensus algorithms is an urgent task. By introducing strategies such as sharding, asynchronous communication, and parallel processing, we can improve the performance and throughput of consensus algorithms in large-scale networks, thereby driving further development of blockchain technology.
The choice of consensus algorithms may lead to community divergence, posing challenges for standardization and interoperability. Different blockchain projects and teams may choose different consensus algorithms, potentially leading to issues with interconnection between different systems. To achieve interoperability between different blockchain networks, it is necessary to strengthen the standardization of consensus algorithms, promote collaboration and consensus among all parties. Advancing the standardization of consensus algorithms will help build a more open and collaborative blockchain ecosystem.
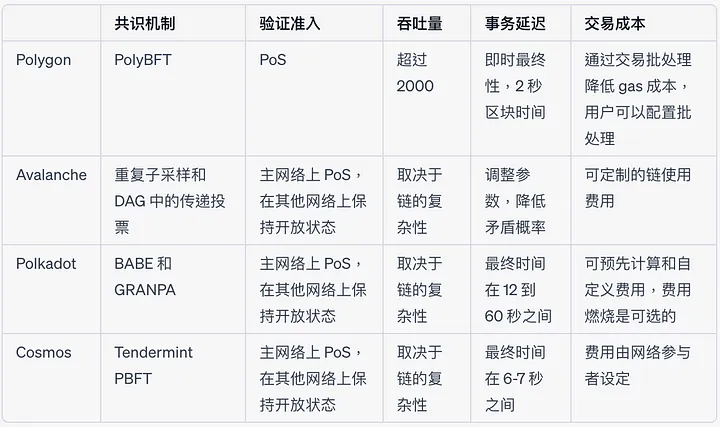
Source: Bing Ventures
Advantages of Tendermint Consensus Mechanism
The Tendermint consensus mechanism has demonstrated its unique characteristics and advantages in the blockchain field. Firstly, Tendermint adopts a deterministic consensus mechanism, selecting block proposers through weighted round-robin, which ensures fair and balanced participation of nodes. The proportion of stake determines the opportunity to become a leader, thereby ensuring fairness and effectiveness in the consensus process.
Secondly, Tendermint consensus exhibits excellent security and resistance to attacks. As a Byzantine fault-tolerant algorithm, it can tolerate nodes violating the protocol in various ways, including intentional malicious operations. Through Byzantine fault-tolerant protocols and pre-commitment mechanisms, Tendermint can ensure that over 2/3 of the validating nodes pre-commit to the same block in the same round, thereby ensuring block submission and consensus security. Additionally, assuming that less than 1/3 of the validating nodes are Byzantine nodes, Tendermint can avoid forks in the presence of asynchrony, further enhancing system security.
Furthermore, Tendermint consensus also features a robust economic incentive mechanism. Similar to many other PoS-based protocols, validating nodes must stake a certain amount of tokens as an economic incentive, and improper behavior will result in loss of the stake. This economic incentive mechanism is crucial for maintaining the correct behavior of nodes, as the potential penalties far exceed any gains from correct behavior. This mechanism ensures the fairness and effectiveness of the consensus process while preventing potential attacks and malicious behavior.
However, the Tendermint consensus mechanism also faces some challenges and limitations. Since the selection of block proposers is deterministic, attackers can disrupt the operation of the entire chain by conducting distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on validating nodes. To mitigate the impact of such attacks, a Sentry Node Architecture (SNA) can be adopted to conceal the IP addresses of validating nodes and provide a list of easily scalable public IP addresses, thereby enhancing network security and robustness.
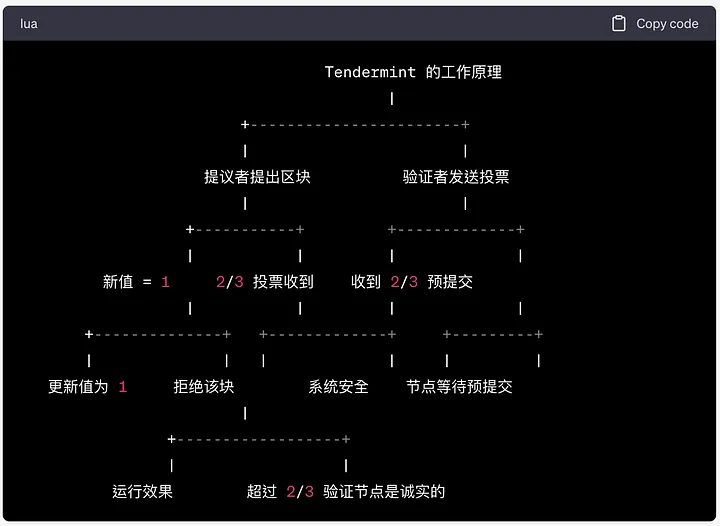
Tendermint Consensus Principle, Source: Bing Ventures
Future Optimization of Consensus
In terms of optimizing consensus mechanisms, there are several promising projects worth noting. One of them is Ethermint developed by EvmosOrg, which makes Tendermint compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), thereby improving transaction confirmation speed. This optimization is expected to be more widely adopted in the future, enabling Ethereum-based applications to achieve higher performance and throughput.
Another noteworthy project is zkMint being developed by PolymerDAO, which is a Tendermint consensus engine friendly to zero-knowledge proofs (ZK). By introducing ZK technology, consensus efficiency and security can be enhanced, achieving a higher level of privacy and data protection. As ZK technology continues to develop and mature, the application potential of this consensus engine will gradually become apparent.
Additionally, Typhon consensus being developed by Anoma addresses block proposal bottlenecks and improves transaction processing speed through parallel processing. This parallel processing approach is expected to be adopted by more consensus algorithms in the future to cope with the increasing transaction load and enhance system scalability.
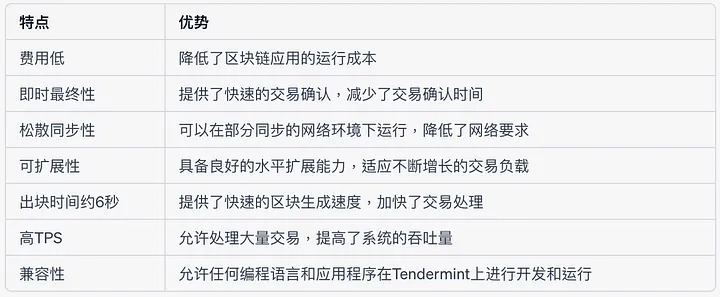
However, consensus optimization still faces some challenges. For example, in Evmos, the BFT consensus mechanism of Tendermint Core is adopted, which does not have the concept of pending state, thus achieving fast transaction confirmation. However, this can lead to Ethereum Web3 compatibility query issues, as these queries may enter a pending state. To maintain Ethereum compatibility while providing fast query functionality, future development needs to address query order and consistency issues.
Another challenge is in Ethereum, where blocks are generated by block validators in a FIFO manner and select transactions included in the local memory pool. However, on Evmos, transactions cannot be sorted or selected from the memory pool of Tendermint nodes. This may result in inconsistent transaction order seen by different nodes, leading to bandwidth latency and network synchronization issues. To improve system availability and consistency, the issue of block sorting needs to be addressed.
Additionally, after Tendermint version 0.35b, transaction priority (tx priority) was introduced, allowing specific transactions to enter the block with priority. However, high-weighted nodes propose blocks more frequently, which may lead to the emergence of the Miner Extractable Value (MEV) problem. To ensure fairness and effectiveness of transactions, further research and improvement of the consensus mechanism are needed to address the MEV problem in future development.
Tendermint consensus has tremendous potential to drive the development of blockchain and distributed systems by optimizing transaction confirmation speed and introducing zero-knowledge proof technology to enhance efficiency and security. However, to realize this potential, challenges such as query order and consistency, block sorting and selection consistency, and the MEV problem need to be addressed. By addressing these issues, Tendermint consensus will be able to provide users with a better experience and more efficient transaction processing capabilities, driving the widespread application and development of blockchain technology.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




