Building a vision of a secure and user-friendly decentralized network relies on the development of key infrastructure. This vision is supported by a shared economic framework and has garnered the support of millions. Layer 2 scaling solutions play a crucial role in building this foundation and enhancing Ethereum's capabilities. These projects collaborate to form a powerful ecosystem, driving Ethereum to fully realize its potential.
This article will delve into the innovations, narratives, challenges, and their transformative impact on Ethereum's widespread adoption. Our analysis will be based on data from Footprint Analytics' Layer 2 research page, providing valuable insights for this evolving ecosystem.
Why Do We Need Layer 2?
For a long time, blockchain technology has been appreciated for its decentralization, security, and scalability. However, the "blockchain trilemma" suggests that achieving all three within a simple architecture is highly challenging. Ethereum currently processes over 1 million transactions per day, but due to increasing demand, it often faces issues of network congestion and high transaction fees. To address this issue, Layer 2 networks have emerged as an innovative solution.
The primary goal of Layer 2 is to increase transaction throughput by achieving higher transactions per second (TPS) while maintaining decentralization and security. These Layer 2 solutions aggregate multiple off-chain transactions into a single Layer 1 transaction. As a result, transaction fees are significantly reduced, making Ethereum more user-friendly and inclusive to a wider audience.
Types of Layer 2
Currently, there are mainly 3 types of Layer 2: Rollups, State channels, and Plasma.
Rollups
As a Layer 2 solution, Rollups aggregate multiple transactions into a single transaction on Layer 1, saving user costs by distributing transaction fees among participants within the Rollup. Rollups mainly come in two types: Optimistic Rollups and Zero-knowledge Rollups (ZK-Rollups). Optimistic Rollups use fraud proofs to ensure the validity of off-chain transactions, while ZK-Rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to enhance privacy and security.
Examples of Optimistic Rollups include Arbitrum (Arbitrum One), Optimism (OP Mainnet), and Base.
Arbitrum was launched by the Offchain Labs team in August 2021 and has since become a leader in the industry, occupying over 50% of the market share. Through the Nitro upgrade, Arbitrum achieved full EVM compatibility, allowing smart contracts to seamlessly migrate from Ethereum to Layer 2 with minimal or no modifications.

Optimism is the second-largest Ethereum Layer 2 solution, soft-launched in January 2021 and fully opened to the public in December of the same year. Optimism adopts an EVM-equivalent architecture, providing a seamless scaling solution for Ethereum applications.
Base, built in collaboration with Optimism, went live on the mainnet in July 2023. In just a few months, it has achieved tremendous success, securing the third-largest share in the Layer 2 market. Incubated by Coinbase, Base leverages Coinbase's expertise in building crypto products.
On the other hand, applications of ZK-Rollup include zkSync Era, Starknet, Linea, and Polygon zkEVM.
zkSync Era is the world's first zkEVM blockchain, released to all users on the mainnet in March 2023 and quickly capturing the fourth market share in the Layer 2 market. In terms of user activity (including TPS and transaction volume), zkSync Era has become the dominant Rollup solution.
- Starknet went live on the mainnet in November 2021. It utilizes the STARK cryptographic proof system, achieving security, low cost, and high performance. Starknet uses Cairo as the development language and is not compatible with EVM. Efforts are currently underway to achieve compatibility between Solidity and Cairo through a translator called Warp.
- Linea, a Layer 2 solution under ConsenSys, went live on the mainnet in July 2023. It provides EVM compatibility, allowing developers to easily migrate and build applications on its network.
- Polygon zkEVM was publicly launched in March 2023 with the goal of EVM equivalence. Polygon (formerly Matic) is a blockchain platform that offers diverse blockchain solutions, and Polygon zkEVM is one of its products.
State channels
State channels are a mechanism that allows participants to conduct rapid and unrestricted off-chain transactions and settle the final results on Ethereum. This method can reduce network congestion, costs, and transaction delays.
Raiden Network is a off-chain scaling solution focused on researching state channels technology, defining protocols, and developing reference applications. It achieves near real-time, low-cost, and scalable payment functionality, compatible with ERC20 tokens on Ethereum. The network aims to improve scalability and usability while maintaining compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem.
Plasma
Plasma chains are independent blockchains linked to the Ethereum main chain through anchoring, utilizing fraud proofs (similar to Optimistic Rollups) to resolve disputes.
OMG Network utilizes the Layer 2 Plasma architecture to provide strong security guarantees and high throughput. It offers a scalable solution for third-party developers looking to build decentralized payment applications on Ethereum.
Data Insights
A consensus is forming: Ethereum's widespread adoption is only a matter of time. So, how is its progress?
Similar to the diffusion of other technologies, Ethereum's adoption trajectory can be described by the classic bell curve. It starts with a small group of innovators rapidly adopting the technology, followed by the involvement of early adopters. As Ethereum continues to evolve and mature, it gradually expands its coverage, attracting the majority of both early and late adopters, eventually entering the phase of widespread adoption. Ultimately, in the final stage of adoption, the technology reaches the remaining population, known as the "laggards."
Let's explore the impact of Layer 2 on Ethereum's widespread adoption from the following perspectives:
Total Value Locked (TVL)
Total Value Locked (TVL) is considered a leading indicator of adoption.
As of the end of October 2023, Arbitrum leads by a wide margin with a TVL of $60.04 billion and a market share of 61.03%, solidifying its position as the market leader. Optimism closely follows with a TVL of $25.98 billion and a market share of 26.41%, demonstrating its widespread adoption and user participation.
Other chains make up the second tier but lag significantly behind, with less than 5% market share. The newly launched Base, which went live on the mainnet on July 13, 2023, holds the third position with a TVL of $4.63 billion. zkSync Era ranks fourth with a locked value of $4.51 billion, while Starknet ranks fifth with a TVL of $1.35 billion.
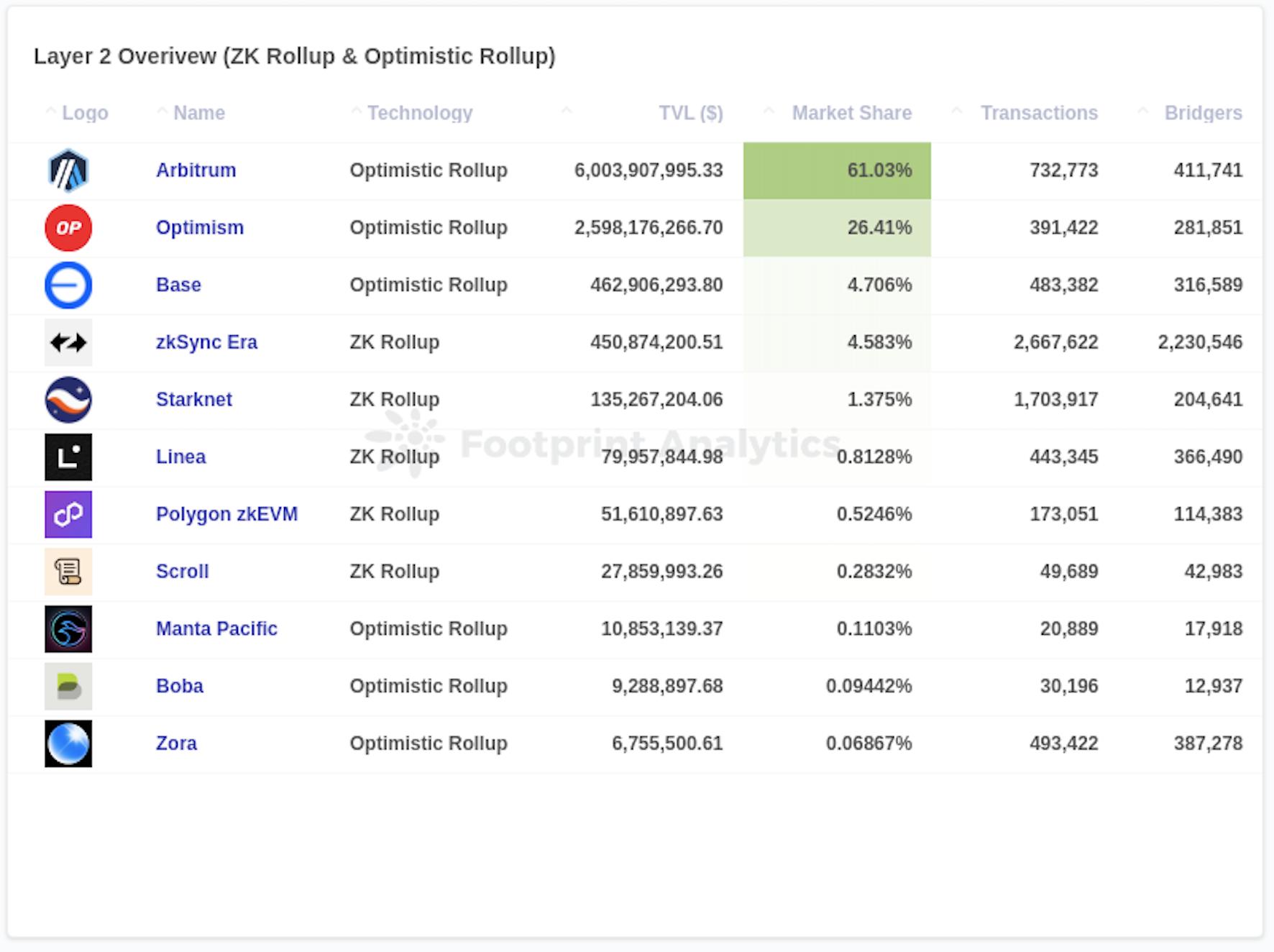
Source: Layer 2 Overview
Number of Users and Transaction Volume
User activity, such as the number of unique users (bridgers) interacting with Ethereum and transaction volume, is a key metric for measuring adoption.
Among various Layer 2 solutions, zkSync Era leads by a wide margin, accumulating 2.67 million unique users, accounting for 37.10% of all Rollups, and facilitating 2.23 million transactions, representing 50.84% of Rollup activity. zkSync Era initially attracted a large number of users through its airdrop activity and has since maintained its leading position. In terms of transaction volume, Starknet closely follows with 1.7 million transactions, accounting for 23.70% of Rollup activity.
Base and Linea, launched on the mainnet in July 2023, have gained widespread popularity in the market. They have surpassed Optimism and Polygon zkEVM in both user participation and transaction volume.
Transaction Throughput
Transaction throughput is one of the primary scalability challenges frequently discussed in the blockchain community.
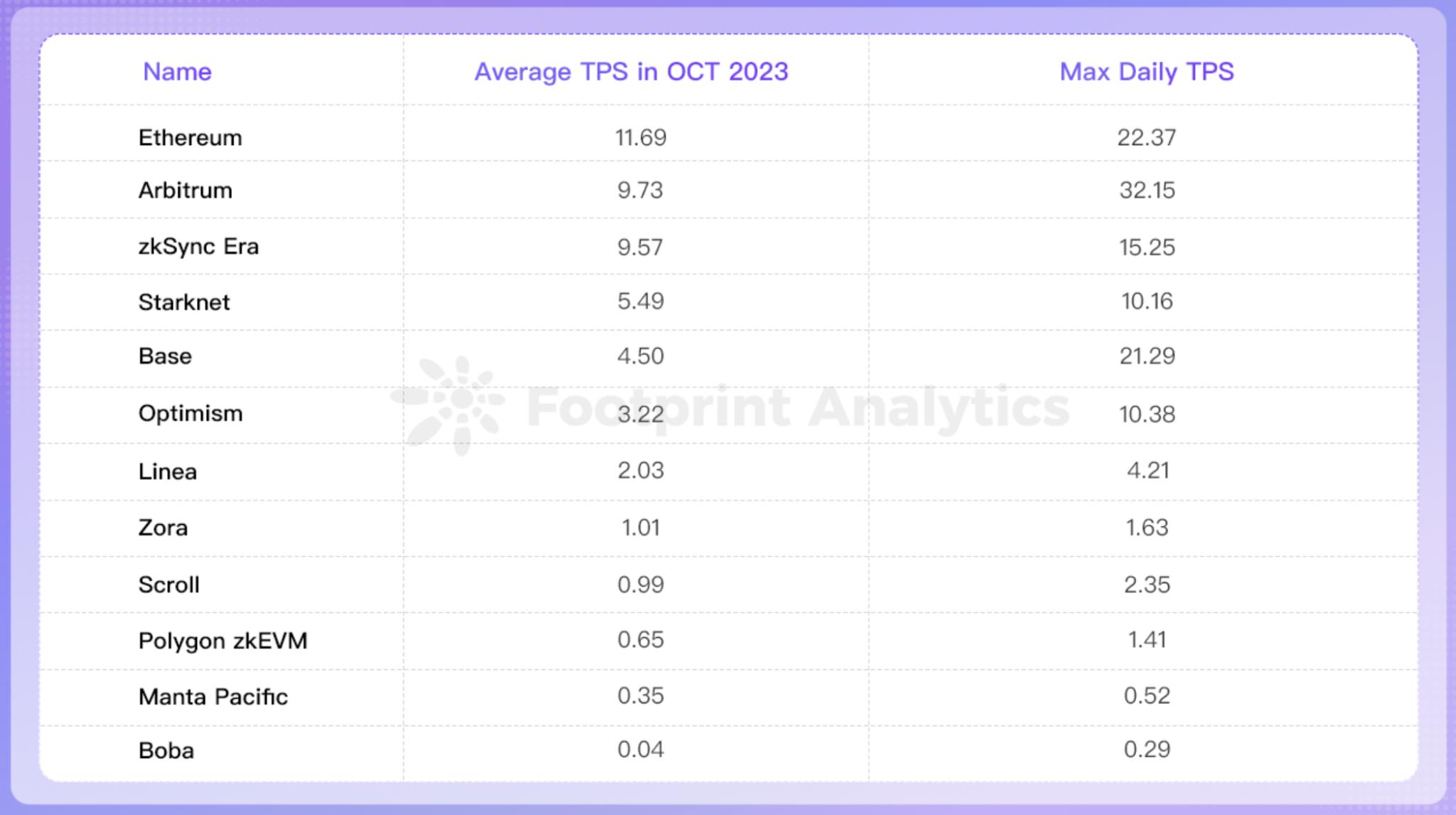
Currently, Ethereum's mainnet processing capacity is approximately 15 transactions per second (TPS). In comparison, Visa has the capacity to process about 24,000 TPS, and Mastercard can handle 5,000 TPS.
Layer 2 is narrowing this gap. In October, the average TPS of well-known Rollup solutions such as Arbitrum and zkSync Era is approximately 9.5 to 10, making them the most performance-close Rollups to Ethereum. Rollups collectively make significant contributions to scalability, with the total transaction throughput in October exceeding that of the Ethereum mainnet by 321%, resulting in a scalability factor of 4.21.
While Rollup technology helps improve scalability, none of the Rollups currently surpass Ethereum in terms of throughput. Attracting and retaining users is challenging for both Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks in a bear market. Establishing a thriving Layer 2 ecosystem requires not only robust solutions but also high-traffic applications. Additionally, the lack of seamless interaction between multiple Layer 2s and between Layer 1 and Layer 2 affects user experience, resulting in the need to switch wallets and incurring liquidity costs.
Costs
Layer 2 plays a crucial role in reducing Ethereum network fees. By aggregating multiple off-chain transactions into a single Layer 1 transaction, transaction fees on Ethereum are significantly reduced.
According to Footprint Analytics data, the average transaction fees for Rollups in October 2023 range from 3% to 10% of Ethereum's fees.
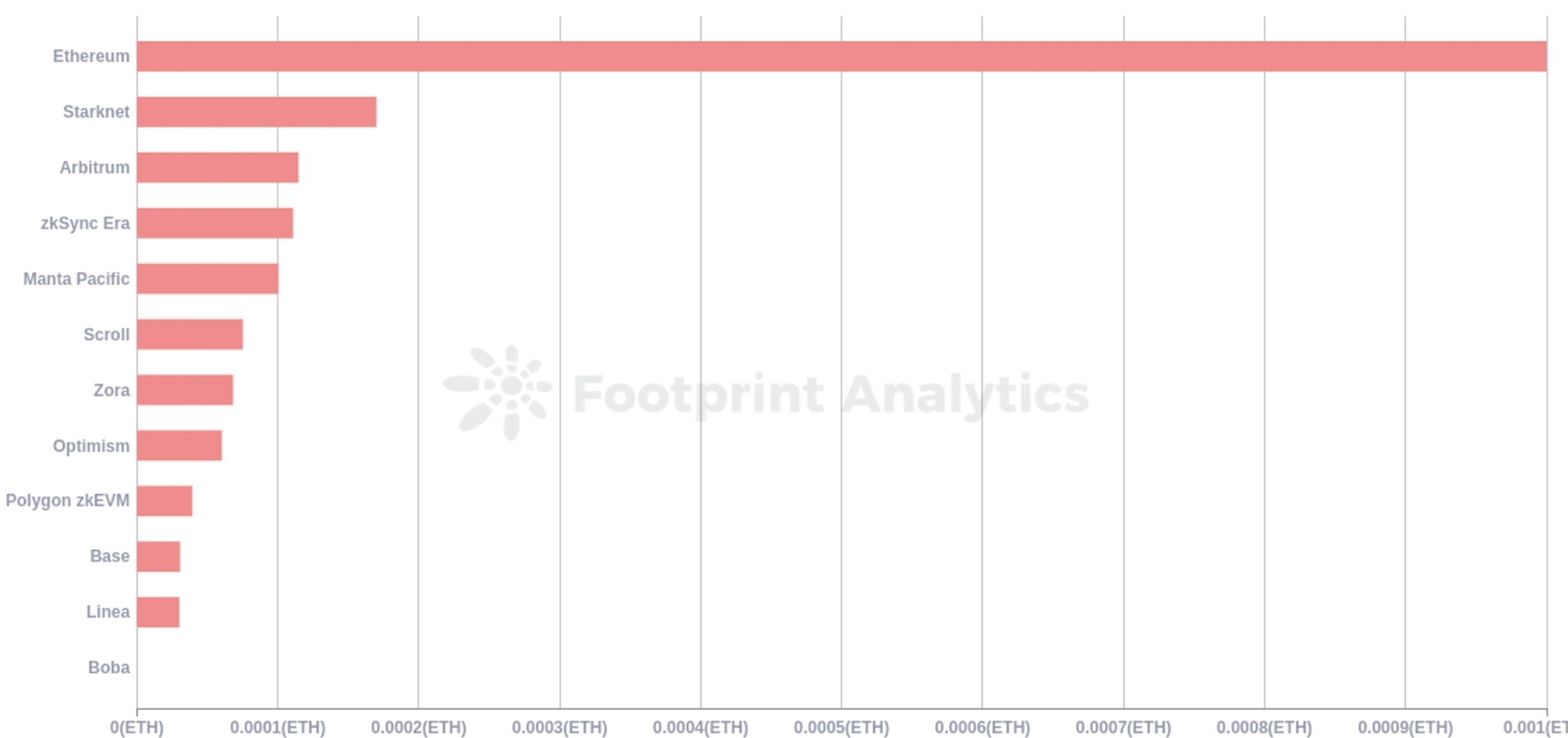
Source: Average Gas Fee
These numbers indicate that Layer 2 is becoming increasingly popular and adopted, highlighting its potential in alleviating Ethereum congestion and improving scalability.
Innovations in Layer 2
In the ever-changing field of blockchain technology, leading Layer 2 solutions such as Optimism, zkSync, and Arbitrum actively pursue innovative approaches to address persistent challenges and maintain a focus on interoperability. These prominent participants maintain rapid innovation in both technology and applications, striving to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Superchain, proposed by the Optimism ecosystem, is a network composed of multiple networks that share a public codebase called OP Stack. The framework aims to establish an interoperable environment where various Layer 2 networks can communicate and transact with each other, similar to how the internet enables communication between devices. By providing horizontal scalability, Superchain addresses challenges associated with traditional multi-chain architectures. These challenges include different security architectures among parallel chains, potential increased system risks with the addition of more chains, and the cost of establishing new nodes for each additional chain.
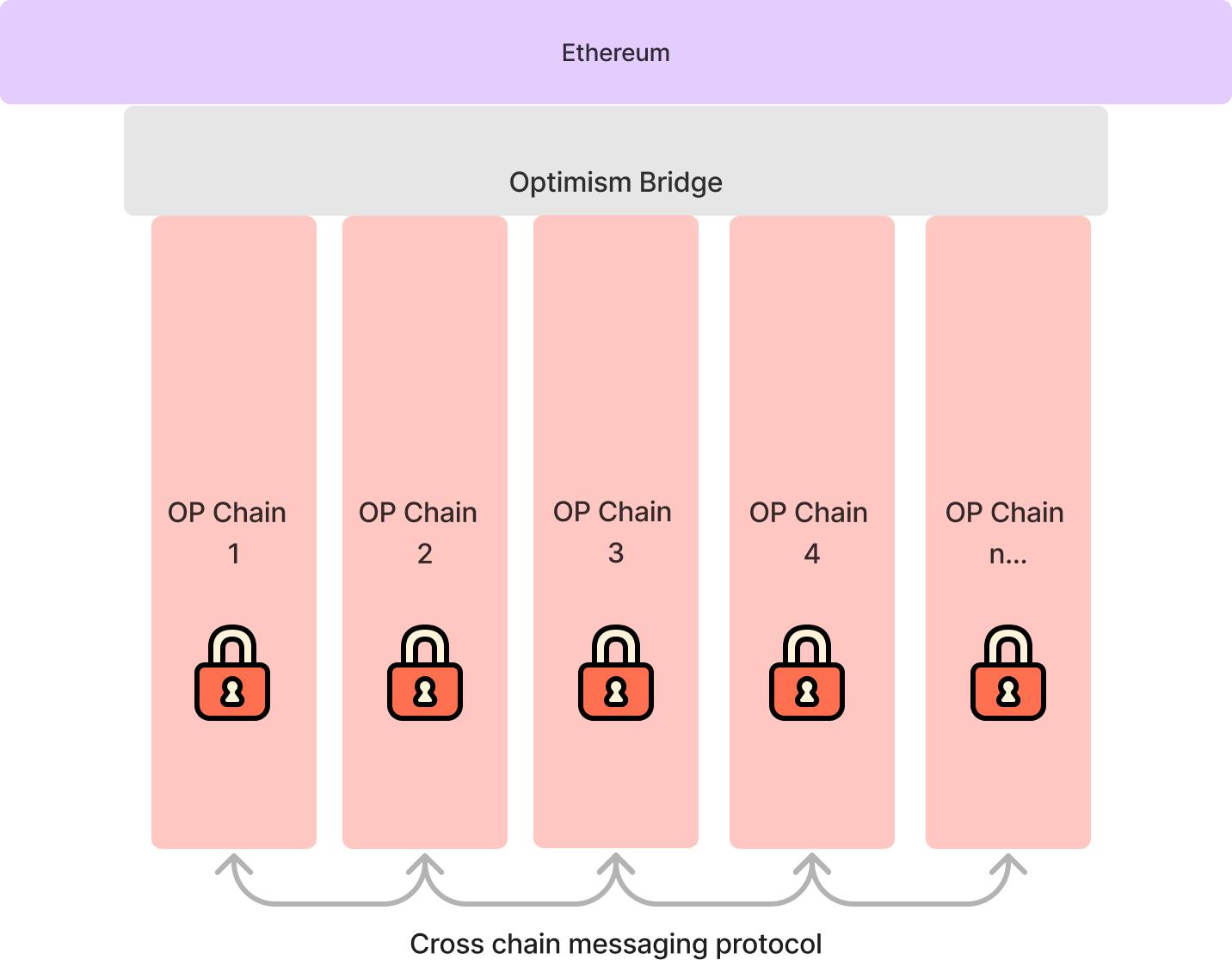
Source: Superchain - OP Stack DocsIn June 2023, zkSync launched Hyperchains, a new type of network that runs as a fractal instance of zkEVM. These Hyperchains share settlement parallelism with Layer 1 and can flexibly operate as a Layer 2 network alongside zkSync Era or as a Layer 3 Validium. Hyperchains in the zkSync ecosystem can be developed and deployed by anyone without permission. To ensure trust and seamless interoperability, each Hyperchain must be powered by the same zkEVM engine on the ZK Stack. GRVT is the first Hyperchain in the zkSync ecosystem, serving as a hybrid cryptocurrency exchange that combines the advantages of centralized and decentralized exchanges. Its alpha version is expected to be released in November 2023, followed by the mainnet version in the first quarter of 2024. 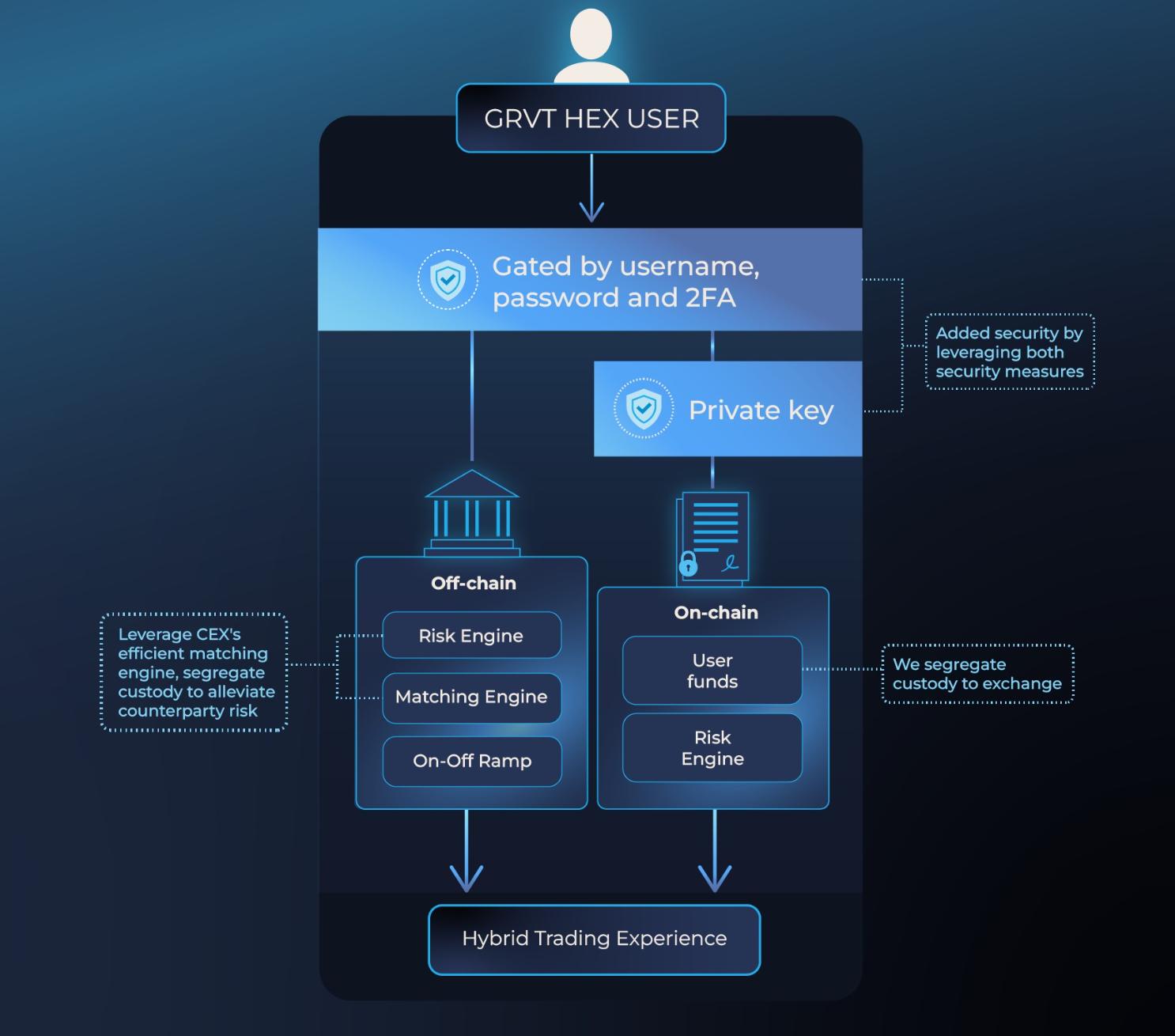 Source: [Architecture - GRVT](https://docs.grvt.io/introduction/architecture-overview) Arbitrum Stylus, launched by Arbitrum in August 2023, allows the development of smart contracts using multiple programming languages such as Rust, C, and C++ on its Layer 2 network. In addition to Solidity, developers can now write smart contracts using WebAssembly (WASM)-compatible languages. WASM can run code in languages like Rust and C++ on the network, and with Arbitrum Stylus, this code can also run on the blockchain. Stylus introduces a second equally interoperable virtual machine with the EVM, providing a new approach to writing smart contracts. ### Layer 2 Narratives Since 2022, Layer 2 has become an important narrative in the cryptocurrency space. Narratives in the Layer 2 field have played a crucial role in shaping public awareness and influencing market trends, providing insights into the future of Layer 2 and Ethereum as a whole. - Full-chain games: These games use blockchain to replace centralized game servers, putting all aspects of the game on the chain, including assets, logic, state, and storage. Starknet and COMBO (currently running on the testnet) have positioned themselves as important supporters of full-chain games within the public chain domain. - Modular blockchains: Initially, blockchains adopted a monolithic design, with a single blockchain handling all tasks. However, the concept of modular blockchains has emerged, focusing on specific functions rather than attempting to cover all functions. Celestia is the first modular blockchain network. It is ready and announced its airdrop and launch plans in October 2023.  - Zero Gas fees: Gas fees have been a major obstacle to Ethereum's widespread adoption. To address this pain point, GasZero (currently running on the testnet) has emerged as a Layer 2 network that provides a unique solution: no Gas fees for trusted end users. On GasZero, users can interact with decentralized networks and smart contracts without pre-storing any tokens in their wallets. - Layer 3: The concept of Layer 3 in the blockchain industry currently does not have a widely accepted definition. Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin believes it is too early to define it clearly, as the architecture of the multi-Rollups ecosystem is still evolving, and most discussions remain theoretical. However, Vitalik shared three possible future roles for Layer 3: - Layer 2 for scaling, Layer 3 for custom features such as privacy protection. - Layer 2 for general scaling, Layer 3 for custom scaling. - Layer 2 for trustless scaling (Rollups), Layer 3 for weakly trusted scaling (Validiums). ### Challenges for Layer 2 As an alternative to the congested Ethereum network, economically efficient Layer 2 networks are gaining increasing attention. While cautiously expanding certain capabilities, maintaining a robust base layer is crucial. The Ethereum community encourages the development of technology and applications, but maintaining a delicate balance between user-friendliness and the benefits of decentralization is essential, as emphasized by Vitalik Buterin at the Ethereum Hong Kong Hackathon event in October 2023. According to Vitalik's perspective, Layer 2 faces four key challenges: - Security and decentralization of proof systems: Validity (zero-knowledge) proofs and fraud proofs are used to prove the legitimacy of transactions without processing them on the Ethereum chain. However, validity proofs face centralization issues due to their reliance on specific hardware. - Decentralization of sequencers: These sequencers verify, order, and compress transactions, then transmit them to Layer 1. However, this centralized setup has been criticized for its potential to become a single point of failure, audit vulnerabilities, or be easily shut down by authorities. - Cross-Layer 2 wallets: They make seamless interaction between multiple Layer 2 solutions possible without switching wallets. - Data availability: It refers to the availability of on-chain data, storing complete copies of blockchain data to validate transactions. It is worth noting that solutions like Validiums and Optimiums are often not classified as Layer 2 because they do not publish data on Layer 1. Instead, they introduce additional trust assumptions above Layer 1. Additionally, as mentioned earlier, currently no Layer 2 network can surpass Ethereum in terms of throughput. Developing the Layer 2 ecosystem is a top priority. - Ecosystem and applications: Currently, most applications in the Layer 2 network ecosystem are DeFi applications. To expand its ecosystem and attract more users, Layer 2 needs to introduce more types of mainstream dApps. ### Conclusion In conclusion, by effectively addressing the scalability and cost challenges hindering Ethereum's development, Layer 2 networks are driving Ethereum towards widespread adoption. These networks provide innovative solutions, increase transaction throughput, reduce costs, and make Ethereum more accessible and inclusive to a wider audience. Furthermore, in response to scalability challenges, opBNB has emerged as a response to BNB Chain. In September 2023, opBNB successfully completed its mainnet launch. Indeed, in the face of these challenges, the measures and future development directions of other public chains are equally anticipated. The focus remains on ecosystem development and user attraction. Infinite possibilities lie ahead, and each public chain will embark on its unique path to scalability and widespread adoption.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




