Original Source: Tech New Knowledge

Image Source: Generated by Wujie AI
Large models are like beacons, reigniting the competition among various business segments under the big tech companies.
From Alibaba's decision to integrate all products into the Tongyi Qianwen large model, to Baidu's complete reshaping of its product line using Wenxin Yiyuan, and Tencent's recent disclosure that over 180 business areas have been closely integrated with the Hunyuan large model - this marks the comprehensive popularization of AI transformation applications.
BAT has coincidentally sparked a frenzy of self-AI evolution. With new energy injected into the business landscape, the wheel of competition in the same field is bound to spin rapidly once again.
Map products, as the gateway to internet traffic in the golden age of the internet, are also the cornerstone of many B-end businesses. The big tech companies have been entangled in this battlefield, and the rise of AI large model technology has brought about a profound transformation.
At a recent Baidu World Conference, Robin Li firmly believed that the era of native AI is imminent. Among the six major AI applications he showcased, the large model transformation of Baidu Maps not only involves the "AI guide" for consumers, but also extends to the lane-level navigation for businesses.
As the giants in the map industry, Tencent Maps and Alibaba's AutoNavi naturally have their own strategies to deal with this, but their routes are different. After all, in addition to the differences in the degree of attention paid by the major companies to this business, BAT has long marked their own territories and positioning in the map field.
Accelerating Differentiation of BAT Maps
With the deep adjustments, strategic positioning, and unique DNA of the big companies in the map business in recent years, the connotation of maps has long surpassed its initial simple definition. AutoNavi has long declared "more than just a map."
Many people consider the "tearing each other apart" incident between AutoNavi and Baidu as a point of differentiation. At that time, the fledgling Tencent Maps had just begun to explore LBS scenarios.
In 2016, then-president of AutoNavi, Yu Yongfu, announced that the daily active data of the AutoNavi Maps mobile client had surpassed that of Baidu Maps, making it the number one mobile map application in the industry. Baidu Maps responded, and the two argued for a long time thereafter.
According to the QuestMobile "2022 China Mobile Internet Strength List Report" for the first half of 2022, as of June 2022, AutoNavi Maps has accumulated 680 million MAU, compared to Baidu Maps' 480 million MAU.
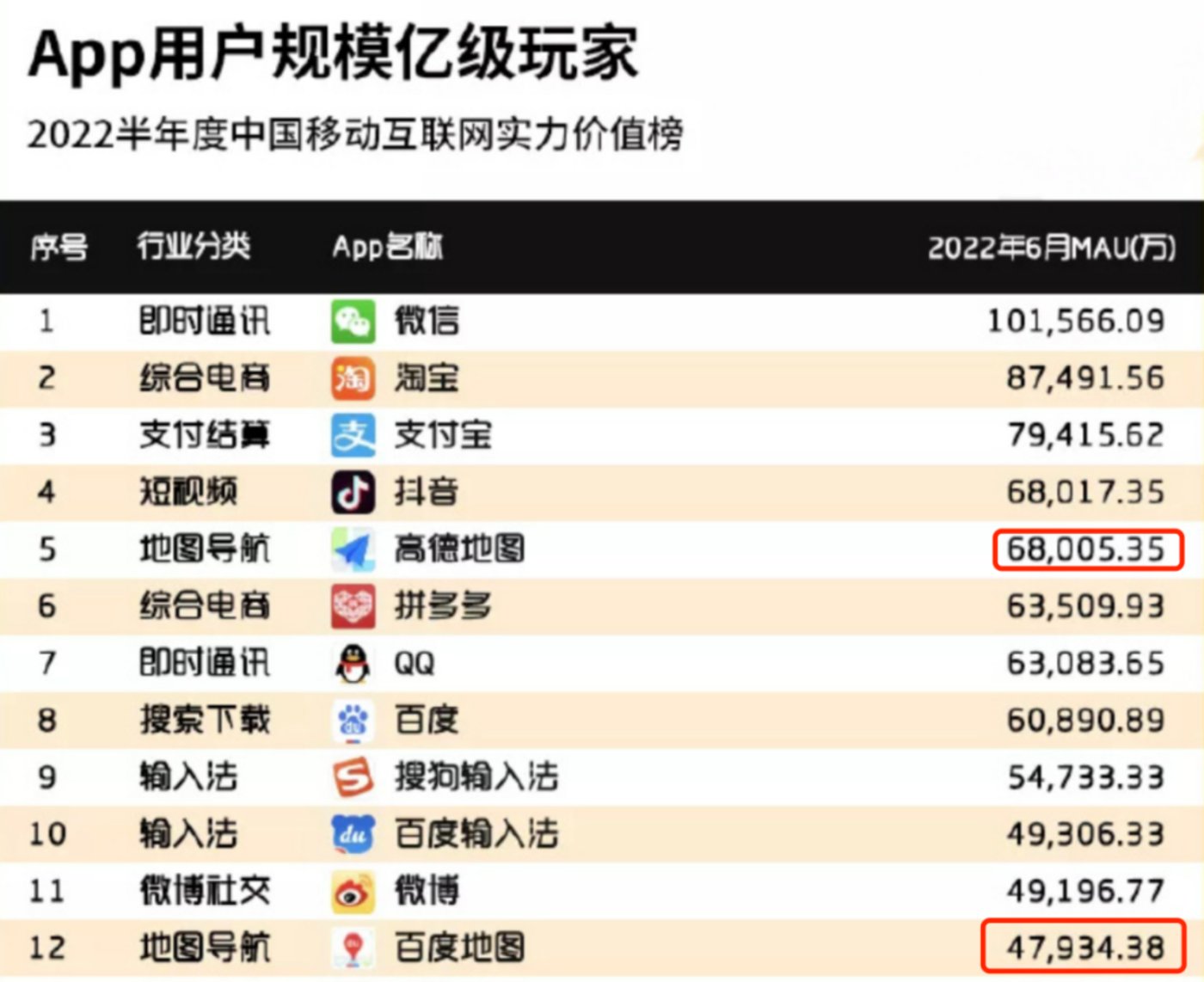
This user-side confrontation ultimately comes down to strategic choices.
Baidu Maps in the Baidu mobile ecosystem is even comparable to WeChat in Tencent. Burdened with too many tasks, its steps are not light. In the early days, in an offline market, relying on support from big companies, it vigorously promoted O2O and commercialization, which made it slightly less prominent in the competition.
When Yu Yongfu took the helm of AutoNavi, he decisively abandoned the O2O business and focused on travel and location services, undoubtedly a "retreat for advancement" victory.
Just as the heat of user competition gradually cooled, the coordinated strategic steps of the major companies made the differentiation of map business even more apparent. The adjustment of organizational structure best reflects the group's changes in positioning for the map business.
Tencent Maps, the "third oldest" in the game, was the first to act. On September 30, 2018, Tencent made its third major organizational restructuring, reducing the number of major business groups from seven to six. The newly formed CSIG (Cloud and Smart Industries Group) showed its edge, and the original Tencent Maps under MIG was split and integrated into CSIG led by Tang Daosheng. This meant that Tencent Maps' LBS strategy shifted to serve the B-end and G-end markets more.
By July 25, 2022, Tencent once again adjusted the CSIG structure, establishing the Map Product Department and the Digital Twin Product Department. The Map Product Department focuses on C-end maps and travel services, while the Digital Twin Product Department builds digital foundations and applications for the B-end.
A series of combinations has made Tencent Maps' roadmap gradually clear - focusing on smart travel and B-end digital services.
Following closely is Baidu Maps.
In May 2022, Baidu directly incorporated its map business into the IDG (Intelligent Driving) business group to form a panoramic "car-road-travel map." This seems to imply that as early as the establishment of IDG in 2017, the direction of Baidu Maps had quietly changed.
Although Baidu Maps was once a key player in local life, mobile navigation, and car networking, with Baidu's exit from the local life market and the continuous flow of mobile navigation market share to AutoNavi, Baidu Maps now focuses more on the commercial exploration of the B-end market.
As for AutoNavi Maps, after contending with Baidu Maps and Didi, it has gradually reshaped its core position within the Alibaba Group.
In July 2021, Alibaba integrated the three major geographical location businesses of AutoNavi, Local Life, and Fliggy into the Life Services division, under the full control of Yu Yongfu. Since then, AutoNavi has explicitly adopted "life services" as its new strategy, upgrading to an "open service platform for a good life out of the door."
On March 22, 2022, AutoNavi and Alibaba's Local Life announced the merger of the word-of-mouth in-store business, marking AutoNavi's gradual transformation into an important role within the group.
After years of tempering, the three map giants have each outlined unique strategic blueprints.
Gathering Under the Wave of AI Large Models
The strategic focus of the three major map manufacturers varies, and the trajectory of AI large model transformation also differs.
In the realm of AI, Baidu has been moving steadily. At the Baidu World Conference, the 18-year-old navigation product, Baidu Maps, underwent another iteration in the wave of large models.
Robin Li explained in detail that Baidu Maps underwent a comprehensive reshaping in the two major directions of "new interaction" and "new navigation," and introduced the "AI guide" function for the first time. Users can initiate dialogue with the map using natural language, accessing various hidden functions and services, enhancing travel and decision-making efficiency.
As mentioned earlier, the B-end has become the core focus of Baidu Maps. Therefore, it can be seen that Baidu Maps has developed and implemented the industry's first map-generated large model, significantly reducing map production costs by 95% using a new strategy of end-to-end lane network. This innovation greatly improves the overall efficiency of map production.
The expensive cost of high-precision maps has become a major obstacle to widespread deployment by car manufacturers. In fact, many car manufacturers' true goal in choosing the "mapless" route is to implement intelligent driving functions on a large scale. A 95% cost reduction means that Baidu's lane-level maps have the potential for nationwide promotion.
In addition, Baidu Maps has also launched a logistics large model beta version, focusing on logistics address resolution and dispatch decision-making using large model technology combined with logistics characteristics.
Evidently, Baidu Maps is cleverly using AI large models to deeply innovate its product capabilities for both the B-end and C-end.
AutoNavi has also not been sitting idly. In April of this year, Zhang Yong clearly stated at the Alibaba Cloud Summit that all products under Alibaba, such as Tmall, DingTalk, AutoNavi Maps, Taobao, Youku, and Hema, will be integrated into the "Tongyi Qianwen" large model to achieve comprehensive innovation.
On September 20, AutoNavi belatedly launched the Safe Travel large model, integrating map, location, navigation data, and intelligent decision-making systems to help ride-hailing platforms identify risks, provide real-time warnings and protection, improve safety management, and reduce risks.
It is reported that over 100 ride-hailing platforms have connected to this model, providing over 10 million road safety warnings daily, and reducing driver speeding rates by 18.4%. The driving behavior profile generated by this model enables ride-hailing platforms to organize over 1,000 driver training sessions per month, effectively promoting behavior improvement.
From the perspective of public market dynamics, AutoNavi's large model reform mainly focuses on the C-end travel business, with no apparent action in other areas of the life services division. This may be closely linked to its strategic direction. Previously, Yu Yongfu revealed that this year, AutoNavi's key project is the "integrated travel service platform."
On the other hand, after Alibaba's "1+6+N" organizational restructuring, whether the large model can be deeply integrated into various business segments remains unknown. This may also be the reason why AutoNavi's actions in the large model field are slightly less competitive.
Tencent Maps' strategy is in contrast to AutoNavi's. Although the V10.0 version of Tencent Maps and the MAX version of AutoNavi were released simultaneously, and both have put in a lot of effort in the 3D visualization of buildings, the former's main focus in large models is the transformation of the smart travel field.
At the 2023 Tencent Global Digital Ecology Conference, Tencent showcased its insights into the intelligent transformation of the transportation and automotive industries. Tencent plans to further strengthen its AI capabilities and support various industries in creating specific intelligent applications through its industry large models. Tencent also plans to further improve the combination of its map and digital twin technology in the transportation and travel fields.
Restructuring of the Business Ecosystem and Opportunities
Guojin Securities pointed out that with the arrival of the AI era, there is a significant shift in the internet traffic landscape, and maps have the potential to become important traffic entry points.
Research shows that with the advent of the large model era, the way users handle tasks may undergo a transformation. Thanks to AI's deeper and more precise grasp of user needs, we will further improve efficiency and reduce friction on the basis of the internet era.
Using Plugin as an example, AI as an entry point can deeply interpret user needs, automatically break down tasks, and call relevant apps to meet those needs. It is worth noting that some tasks may no longer depend on other apps and can be completed solely through the AI entry point.
With the formation of AI entry points, the value chain of mobile internet is expected to be reconfigured. An ecosystem centralized around AI entry points may gradually stabilize and bring substantial profits to enterprises. Specifically, companies with large models and major traffic entry points will have significant competitive advantages, making it easy to integrate various apps in other fields and build and consolidate their unique ecosystems, thereby taking a leading position in the era of large models.
So, will map products be integrated or become the main traffic entry point? The evolution of traffic entry points in the internet era can be viewed from the perspectives of user connectivity and search efficiency.
Guojin Securities analysis points out that apps that strike a balance between user connectivity and search efficiency are more likely to be integrated into other products or platforms.
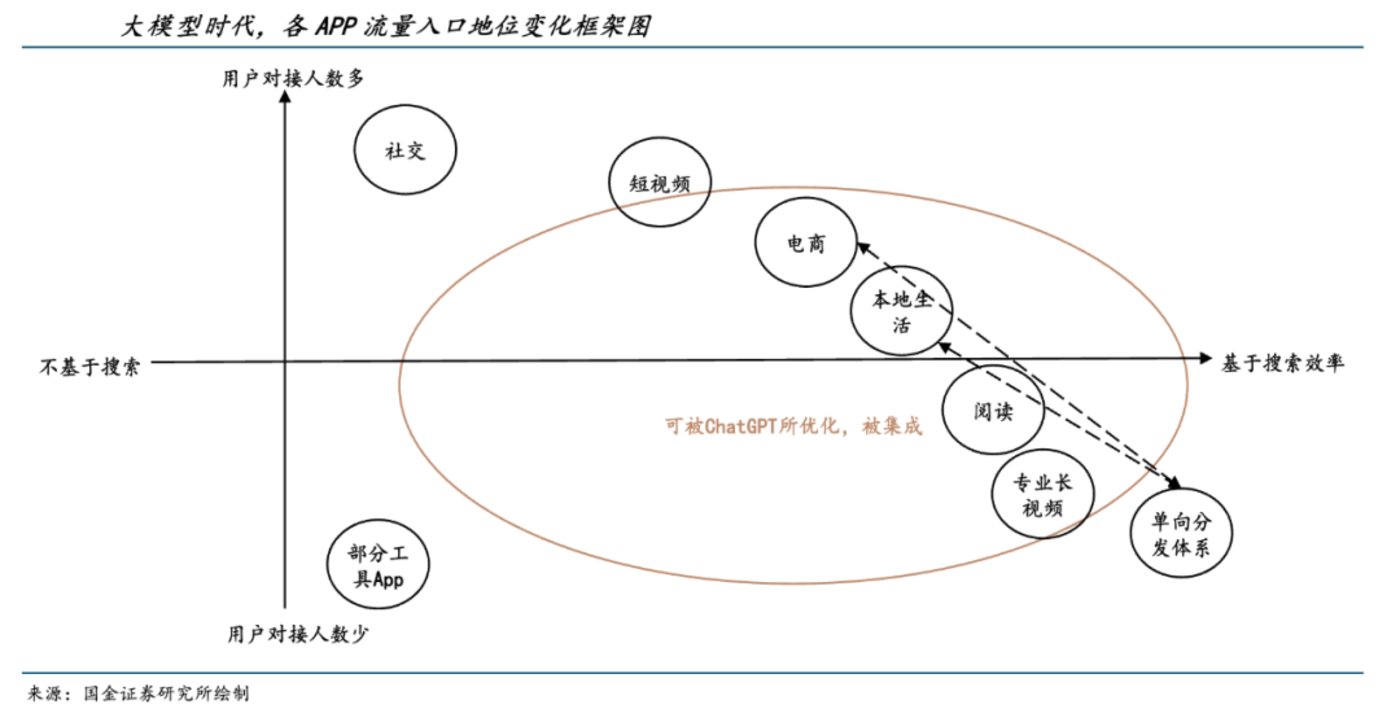
Based on this analysis framework, social and map apps are unlikely to be integrated into other systems, but are expected to become the main traffic entry points in the era of large models.
Following this logic, under the impetus of large models, applications can not only handle more complex tasks but also provide precise personalized services.
Take maps, for example. They can not only provide accurate navigation but also update real-time traffic information and even predict future traffic trends. Combined with user behavior analysis, map applications will create a "one-stop" experience for users in areas such as dining, entertainment, and shopping, further increasing user stickiness and traffic.
This transformation means that maps, with the assistance of AI, are no longer just navigation tools but the core of the entire ecosystem. Maps that integrate functions such as ride-hailing, local life, and tourism have become almost like a "Swiss Army knife" for user travel. This one-stop operation not only benefits users but also presents map manufacturers with enormous commercial potential.
Specifically, as map applications become more intelligent and comprehensive, the traditional advertising model is transitioning to a commission-based model. Whether it's dining, ride-hailing, or tourism, maps can provide direct user traffic to businesses, thereby earning substantial commissions. Combining advertising and commissions, the commercial space of map applications is set to explode.
Guojin Securities analysis indicates that after becoming the main traffic entry point, the profit model of map applications will be dominated by commissions and advertising through the integration of other travel apps.
Considering that the commission market size in the travel industry exceeds 200 billion, combined with the fact that nearly 50% of Meituan's in-store and travel business advertising revenue, it is estimated that the advertising contribution from businesses may be equivalent to the commission scale. This means that, combined with commissions and advertising, the total value of the travel-related market reaches about 400 billion. In the era of large models, map application manufacturers have the potential to further tap into this value chain.
Furthermore, the above discussion mainly focuses on consumer life scenes for the C-end, while the large model commercial areas for the B-end and G-end have not been factored in.
For AutoNavi Maps, which has integrated Fliggy and local life, it seems to have seized the opportunity of this era. As for Baidu Maps and Tencent Maps, despite their main strategies shifting, they still retain vitality in the C-end market, creating possibilities for future comebacks.
Final Thoughts
As an important tool for people's travel, consumption, and life, map products are undergoing a profound transformation driven by AI. In this new war, only enterprises with strong AI capabilities, traffic, and ecosystem strategies can stand at the forefront, while those immersed in the past are likely to be eliminated.
Now, the three giants of BAT are already at the forefront of this war. For them, this is an era of both opportunity and challenge, and the winners will gain a future market worth billions.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




