Introduction
Recently, Guatian has frequently received inquiries from project parties, asking which public chain should be deployed, the performance differences of various public chains, the ecological layout, and platform traffic, and how they will affect the project in the short and long term. Coincidentally, this year has seen the issuance of several popular public chain projects, including Arbitrium, Sui, and the yet-to-be-released zkSync, and there is a strong demand for popularizing and analyzing the basic knowledge of public chains. Therefore, we have specifically formed a public chain research group to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the highly active public chains in the market from the perspective of GameFi projects and users.
The initial plan is to write four in-depth research articles, with the main content distributed as follows:
- The first article will cover the development history of Ethereum, blockchain gaming ecology, existing issues, and further extend to the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade roadmap.
- The second article will delve into the Optimistic Rollup track, analyzing the basic technical roadmap of the OP series and the differences in technology, market, and support for blockchain gaming among representative projects such as Arbitrium, Optimism, and opBNB.
- The third article will focus on analyzing the technology of the zk Rollup track and related information about representative projects such as zkSync, StarkNet, Polygon zkEVM, Linea, and Scroll.
- The fourth article will analyze other popular Layer1 public chains, such as Solana, Aptos, Sui, Near, and Avalanche, focusing on their technical features, blockchain gaming ecology, and technical support.
We believe that through the systematic analysis above, both project parties and users will have a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the mainstream public chains in the current market. This will also provide a more solid theoretical basis for decisions related to project deployment and investment based on different public chains.
Preface
In the digital age, Ethereum shines as a bright star at the top of the blockchain world. Since its inception, Ethereum has been a pioneer in blockchain and smart contract technology, constantly creating new historical chapters. As the pioneer of blockchain gaming, Ethereum has been leading the development of the GameFi track. Guatian will lead you through the development and upgrade roadmap of Ethereum, exploring how this ecosystem has evolved from an initial project to the most important global public chain ecosystem.
I. The Origin and Development History of Ethereum
From its first day, Ethereum has been an exciting story filled with challenges, innovation, and struggle.
At the end of 2013, Vitalik Buterin released the Ethereum whitepaper, which not only inherited some of Bitcoin's design concepts but also opened a new chapter in the development of blockchain. Subsequently, in 2014, Ethereum launched its ICO and raised approximately $18 million worth of Bitcoin in just 42 days, shocking the entire blockchain community.
On July 30, 2015, Ethereum successfully released its first version, Frontier, and by the end of the year proposed a standard with far-reaching industry impact - ERC20.
However, the year 2016 soon became the most turbulent year for Ethereum. In March 2016, Ethereum launched the Homestead upgrade, a major network upgrade aimed at improving the stability and security of Ethereum, marking its entry into a more mature stage. Homestead upgrade improved Ethereum's virtual machine, smart contract development tools, and network protocols, attracting more developers and enterprises to participate. However, the good times did not last long. Between May and June 2016, the Ethereum community experienced a major crisis known as The DAO incident. The DAO was a decentralized autonomous organization with a vulnerability in its smart contract, allowing attackers to steal a large amount of Ether. This event led to community divisions, with one side advocating for a hard fork to recover the stolen Ether, while the other side insisted on not modifying the blockchain's principles. Ultimately, a hard fork occurred, splitting Ethereum into two different blockchains: Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC). Ethereum Classic adhered to the principle of non-interference with the code and continued to maintain the original Ethereum genesis block.
If 2016 marked Ethereum's evolution from an initial project to a more mature and complex blockchain platform, then 2017 was truly a prosperous moment for Ethereum. In early 2017, the Ethereum Enterprise Alliance (EEA) was established to promote the application of Ethereum blockchain in the enterprise sector. The alliance attracted numerous well-known companies, including Microsoft, IBM, and Intel, to jointly research and develop Ethereum technology.
In October 2017, Ethereum completed the first phase of the Metropolis upgrade, known as "Metropolis Byzantium." This upgrade introduced a series of improvements, including better privacy protection, enhanced smart contract security, and reduced transaction costs. Metropolis Byzantium further strengthened Ethereum's functionality, paving the way for future development.
Accompanying the mainnet upgrade, the Initial Coin Offering (ICO) frenzy swept through the entire blockchain world. In 2017, Ethereum's smart contract platform became the preferred choice for many new projects, with many new cryptocurrencies and blockchain projects raising funds through ICOs. This frenzy led to a rapid increase in the price of Ethereum and attracted a large number of investors and developers. Ethereum's price rose from a few dollars at the beginning of 2017 to several hundred dollars by the end of the year. This drew global attention, rightfully propelling Ethereum to the second-largest market value cryptocurrency in the cryptocurrency market. However, the downside of the frenzy, due to the surge in transactions and smart contracts, led to increasingly severe transaction congestion and high gas fees on the Ethereum network. This prompted the Ethereum community to begin focusing on network scalability and performance improvements, laying the groundwork for subsequent continuous upgrades of Ethereum.
By 2018, Ethereum faced serious challenges. In early 2018, Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies experienced a massive price collapse, leading to a sharp decline in the price of Ethereum. This triggered market volatility and investor concerns, reflecting the instability of the cryptocurrency market. Despite the cryptocurrency winter, Ethereum's upgrade did not stop. The development of Ethereum 2.0 made important progress in 2018, confirming the overall roadmap to switch from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) to improve scalability and energy efficiency. Meanwhile, due to the increase in transaction volume, the Ethereum network continued to face congestion and high transaction fees in 2018. This led to more attention on network performance and scalability, sparking many discussions on solving these issues.
In 2018, regulatory agencies worldwide began to take stricter regulatory measures against cryptocurrencies and ICOs. This led to investigations and sanctions against some ICO projects, and the cryptocurrency industry began to focus on legal compliance issues. Despite market fluctuations, 2018 witnessed the rise of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. DeFi projects rapidly developed on Ethereum, including decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and stablecoins, bringing decentralized innovation to the Ethereum ecosystem.
2019 was a year of innovation for Ethereum. The Ethereum 2.0 project made significant progress in 2019, including the release of the Beacon Chain, marking Ethereum's gradual transition to a more scalable and energy-efficient network. 2019 also saw the explosion of the DeFi ecosystem. Numerous DeFi projects emerged on Ethereum, including lending platforms, decentralized exchanges, and stablecoins. These projects attracted billions of dollars in funds, bringing decentralized innovation to the financial sector.
The Rise of Blockchain Games on Ethereum
With the rise of DeFi, regulatory agencies began to focus on the compliance of Ethereum and other blockchain projects. This led to some projects being required to take measures to comply with laws and regulations, sparking discussions about the balance between decentralization and compliance. Stablecoins on Ethereum, such as USDT, DAI, and USDC, have become important assets in the crypto world, providing stability and liquidity for crypto transactions. 2019 also witnessed the rise of blockchain games, with some games on Ethereum starting to attract a large number of users. These games typically use Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) to give players true ownership and interoperability.

From its inception to maturity and reaching its peak, Ethereum has undergone continuous changes and challenges, fully demonstrating its enormous potential as a smart contract platform. From the initial Homestead upgrade to the hard fork, from the frenzy of ICOs to increased regulation, and the initial rise of DeFi and blockchain games, the Ethereum community has continuously pushed for technological progress, creating endless possibilities for the future of blockchain. Below, we will further elaborate on the development history of blockchain games on Ethereum.
II. The Rise of Blockchain Games on Ethereum
To trace the development history of blockchain games, the first thing to consider is the Ethereum ecosystem. From 2017 to the present, Ethereum has seen a flourishing of blockchain games, with several phenomenal games emerging. We have selected several representative projects to discuss their development history and existing issues.
When it comes to the pioneer of blockchain games, most people would consider CryptoKitties from 2017. Although strictly speaking, it was not the first blockchain game, it was the first game to become popular on Ethereum and be widely known as a phenomenal game. It is a game based on collecting and breeding digital cats, and it was the first project to combine ERC-721, becoming the earliest NFT project. Each digital cat is a unique NFT. The adoption, breeding, and trading of these cats ignited FOMO in the crypto community, with some crypto cats fetching prices as high as millions, astonishing many ordinary players. The success of CryptoKitties sparked a strong interest in NFTs among players and project parties. Due to the game's popularity, transaction congestion and high fees became the norm, exposing scalability issues in the Ethereum network.

In 2018, Gods Unchained entered the spotlight. It is a card game similar to "Hearthstone" on Ethereum, where players can collect, trade, and battle with cards of different attributes. The game uses NFTs on Ethereum to ensure the security of the cards, marking a period of deep integration between blockchain games and card games, ushering in the era of "Fi" for everything. However, due to limitations in the Ethereum network, the game still faced transaction delays and high fees during peak periods.
The project that truly reached its peak in the previous wave of blockchain games is Axie Infinity. Axie is a collect-and-battle game based on Ethereum, where players can earn tokens by collecting, breeding, and trading virtual creatures called Axies. When it was launched in 2018, it remained relatively unnoticed due to the bear market, until a surge in the bull market in 2021 led to its rapid rise. This significantly increased the game's playability and player enthusiasm, sparking a new wave of "Play-to-Earn (P2E)" blockchain games and giving rise to numerous game guilds and gold farming studios. During its peak, Axie generated over $300 million in revenue in a month, surpassing "Honor of Kings" to become the world's most profitable game. The rise of the P2E model also marked the true arrival of the GameFi era, driving the development and trading of game assets based on blockchain technology through the DeFi+NFT model. In addition to Axie Infinity, a batch of similar games with the same model emerged in the market, such as Alien Worlds, Cryptoblades, Sorare, and Zed Run. However, due to congestion and high transaction fees on the Ethereum network, the high entry barriers and transaction costs have limited the participation of many players.

Another major branch of blockchain games is the so-called "metaverse" faction, represented by Sandbox and Decentraland, which are metaverse games with land sales as the main economic model. Taking Decentraland as an example, it is a virtual trading platform based on Ethereum, where users can buy, collect, and trade virtual land and assets in the game. Decentraland uses NFTs to ensure true ownership of virtual assets. However, the game's lack of optimization, poor user experience, and performance limitations of the Ethereum network have hindered the game's further development. In the graph below, it can be seen that the transaction volume and quantity of Decentraland land peaked at the end of 2021 (approximately $34 million) and has since declined, now accounting for less than 1% of the peak period.

1. Some Pioneering Aspects of Blockchain Games on Ethereum:
Ownership and Scarcity: Blockchain technology has given virtual assets in games true ownership and scarcity. Players can truly own and control their game assets, and the supply of these assets is limited, giving them higher value and tradability.
Economic Ecosystem: Blockchain games on Ethereum have created a real economic ecosystem for players. Players can earn returns on virtual assets through their efforts and investments in the game, and trade, sell, or rent them to other players. This economic model provides players with the opportunity to earn real value and provides greater motivation for game development.
2. Challenges Faced by Blockchain Games on Ethereum:
The biggest issue with Ethereum is its scalability, as its architecture limitations lead to insufficient scalability and slow transaction speeds. The limited throughput also results in high gas fees, especially during NFT and token sales, leading to gas wars that can paralyze the network and instantly drive transaction fees to extremely high levels, greatly affecting user experience.

III. Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade
In late April 2020, Ethereum launched the ETH2.0 testnet, and after six months of testing, it officially launched its 2.0 mainnet in December, marking the arrival of the Ethereum 2.0 era. Ethereum 2.0 is a major upgrade to the 1.0 mainnet, aimed at improving Ethereum's performance, scalability, security, and sustainability to accelerate its use and application.
Why Upgrade to 2.0
- Ethereum's high fees and congestion issues
In the previous text, we also mentioned that in transactions related to blockchain games, Ethereum has been criticized for high gas fees, slow confirmation speeds, and low efficiency. Although some teams have optimized transaction efficiency and reduced fees to some extent by developing external applications (such as Flashbots), it is still inadequate in the face of continuously increasing transaction demand. To fundamentally improve this issue, it is necessary to enter from within the Ethereum public chain and upgrade its underlying architecture to achieve a substantial performance leap for the network.
- The Rise of Competing Public Chains
Although Ethereum still holds an absolute leadership position in the current public chain market, newcomers continue to join, especially those that continuously surpass and innovate in terms of performance and architecture, to some extent shaking Ethereum's market share. Below are performance and data comparisons of several major public chains before 2020 (before the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade). Ethereum does not have an advantage in various data metrics (TPS, transaction fees, block efficiency, etc.). If development continues unchecked, it is foreseeable that Ethereum will be easily surpassed in market share and market value in the near future.
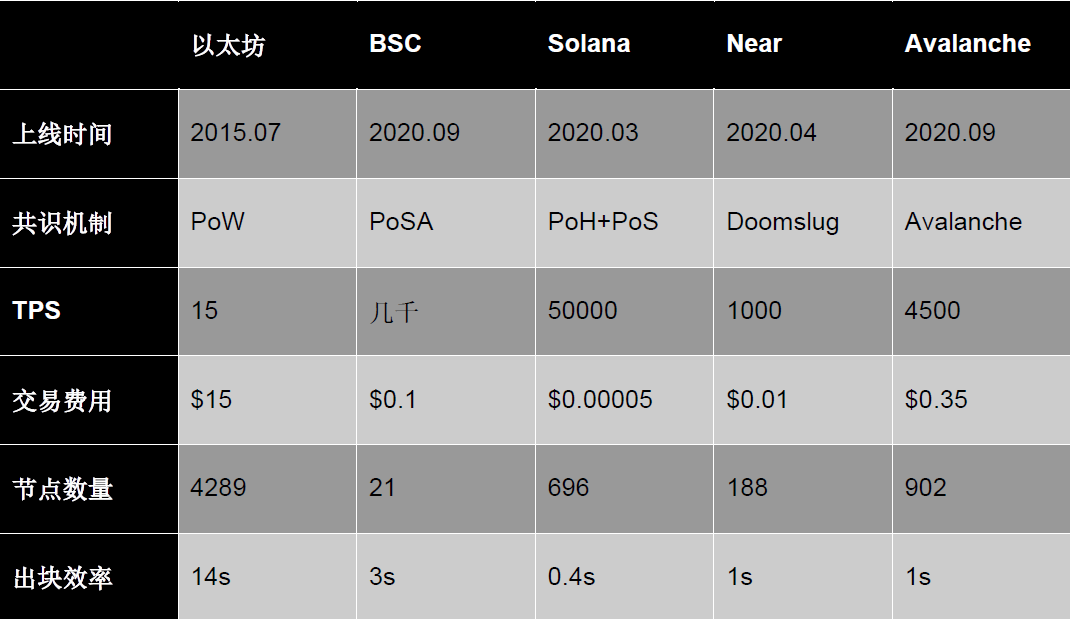
Public chains represented by BSC and Solana, which can be compatible with Ethereum EVM and have a large ecosystem, as well as support from major players such as Binance and FTX, naturally have user dividends and financial advantages, enabling them to grow rapidly and divert traffic from Ethereum. The congestion and high fees of Ethereum itself have given these public chains excellent development opportunities. All of these are forcing Ethereum to upgrade as soon as possible to continue to maintain its position as the king of public chains.
- New User Demands for Public Chain Security and Privacy
Since its inception, Ethereum has seen a thousand-fold increase in transactions, from daily volumes of thousands to a stable level in the millions. The rapid growth has brought a large influx of funds into the cryptocurrency field, along with more high-quality applications and a large number of users. At the same time, user demands for security and privacy protection in blockchain technology are constantly increasing.
In financial applications, users have a strong demand for address privacy, and the excessive transparency of the blockchain world is clearly a significant constraint on its development. How to achieve privacy protection while ensuring security is also one of the important issues that Ethereum needs to address for its future development.
Upgrade Main Content
You may have heard of the blockchain trilemma, which refers to decentralization, security, and scalability. The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade addresses these three aspects with specific solutions, thereby constructing the main content of this upgrade.
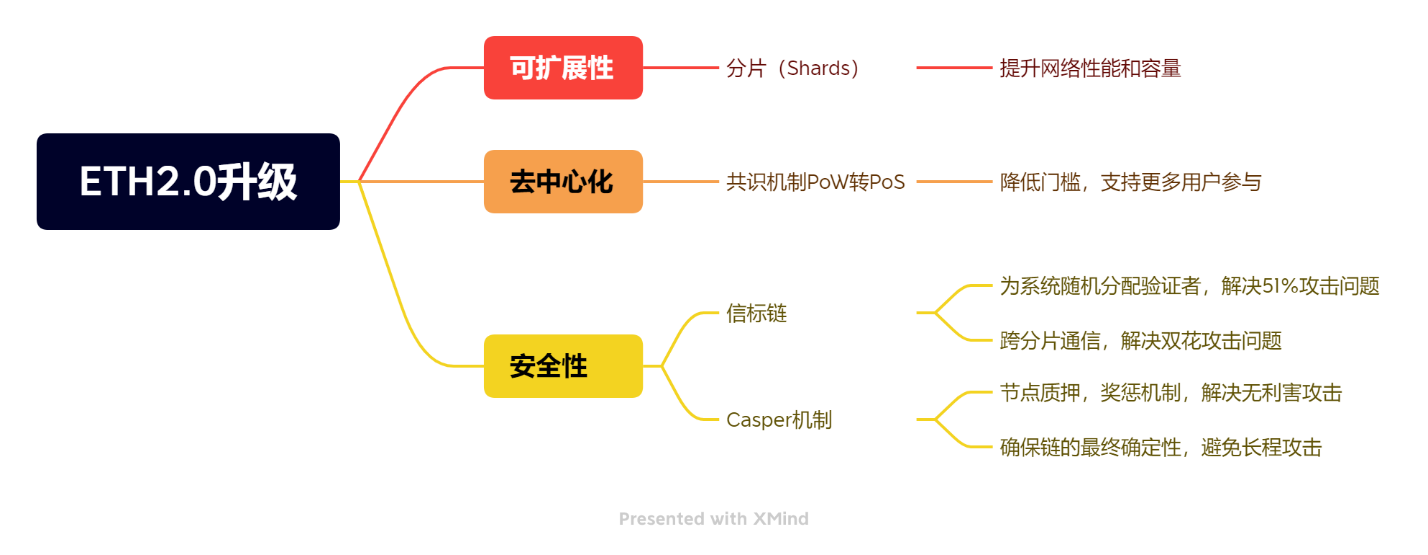
1. Shard Chains - Solving Scalability Issues
Shard chains are a mechanism that can significantly improve Ethereum's transaction efficiency and scalability. In Ethereum's latest sharding solution (Sharding 2.0), all network resources will be divided into different shards, each of which can be understood as a new chain connected to the beacon chain (hub chain). As a result, each node does not need to process all transactions, only needs to run a shard, and only needs to store a small amount of data, greatly improving work efficiency and largely alleviating Ethereum's scalability issues.
The Sharding 2.0 solution is tailored for the Rollup solution (which we will further explain in subsequent articles, along with Layer2 projects), and the Rollup solution is an extension of the sharding solution. Through Rollups, all exchange processes and executions are carried out off-chain, and the Ethereum main chain only stores transaction data. The implementation of a hybrid of data sharding and Rollups theoretically allows Ethereum to process over 100,000 transactions per second, making Rollups currently considered the most ideal scaling solution.
2. Proof of Stake (PoS) - Solving Decentralization Issues
Another important upgrade in Ethereum 2.0 is the introduction of the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Previously, Ethereum operated based on Proof of Work (PoW), which required a significant amount of computing power and energy consumption. The transition from PoW to PoS will reduce Ethereum's energy consumption by over 99%.
In Ethereum 1.0's PoW consensus mechanism, miners process and package transactions to earn ETH. In the PoS mechanism of ETH2.0, users only need to stake ETH to become validators on the network and obtain proof of stake representing shares. Under the PoW mechanism, becoming a validator requires purchasing expensive mining machines and generating sufficient computing power to be competitive. In the PoS mechanism, the entry barrier for validators can be effectively reduced. Any user who stakes 32 ETH has the opportunity to become a member of the validator committee, selected by the beacon chain's random algorithm to propose new blocks and validate new blocks, ultimately completing the block generation process through collaboration. The reduction in entry barriers allows more nodes to participate in validation, making the entire network more decentralized.
3. Beacon Chain and Casper Mechanism - Solving Security Issues
The introduction of sharding and the PoS consensus mechanism solves scalability and decentralization issues but also brings new security challenges. For example, sharding leads to 51% attack issues, double-spending attacks between shards, and PoS consensus mechanism-related issues such as nothing-at-stake attacks, long-range attacks, and simple attacks. Ethereum uses the beacon chain and the Casper consensus mechanism to bridge these two types of risks and address security issues.
To address the 51% attack issue, the beacon chain provides randomness, making each validator unpredictable and reshuffling all validators after each validation task, selecting a new validator committee to avoid collusion among validators, thereby enhancing security. Additionally, the beacon chain facilitates cross-shard communication, recording the state and information of all shards to prevent double-spending issues.
Casper is the core consensus protocol of Ethereum 2.0, responsible for managing system nodes and implementing rewards and penalties for validators. Validators need to stake and apply to become nodes on the beacon chain to run the protocol. If a validator fails to complete the assigned tasks, there is a risk of losing staked tokens or even being kicked out of the node pool, unable to continue participating in validation work. This forces validators to act honestly and comply with consensus rules through a system of rewards and penalties, largely addressing the nothing-at-stake attack issue in PoS.
Long-range attacks refer to creating a chain longer than the original main chain from the genesis block and tampering with transaction history to replace the original main chain. Simple attacks refer to creating as many blocks as possible in a unit of time within a forked chain to surpass the length of the original main chain, forming an attack. After the upgrade, Ethereum will set the first slot block of each Epoch as a checkpoint and achieve the final determinism of the chain through voting, making the blocks determined and unchangeable, thus avoiding these risks.
Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade Roadmap
Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, has outlined the future Ethereum 2.0 upgrade roadmap with six concise stages: The Merge, The Surge, The Scourge, The Verge, The Purge, and The Splurge. Each stage focuses on a specific theme and upgrade functionality.
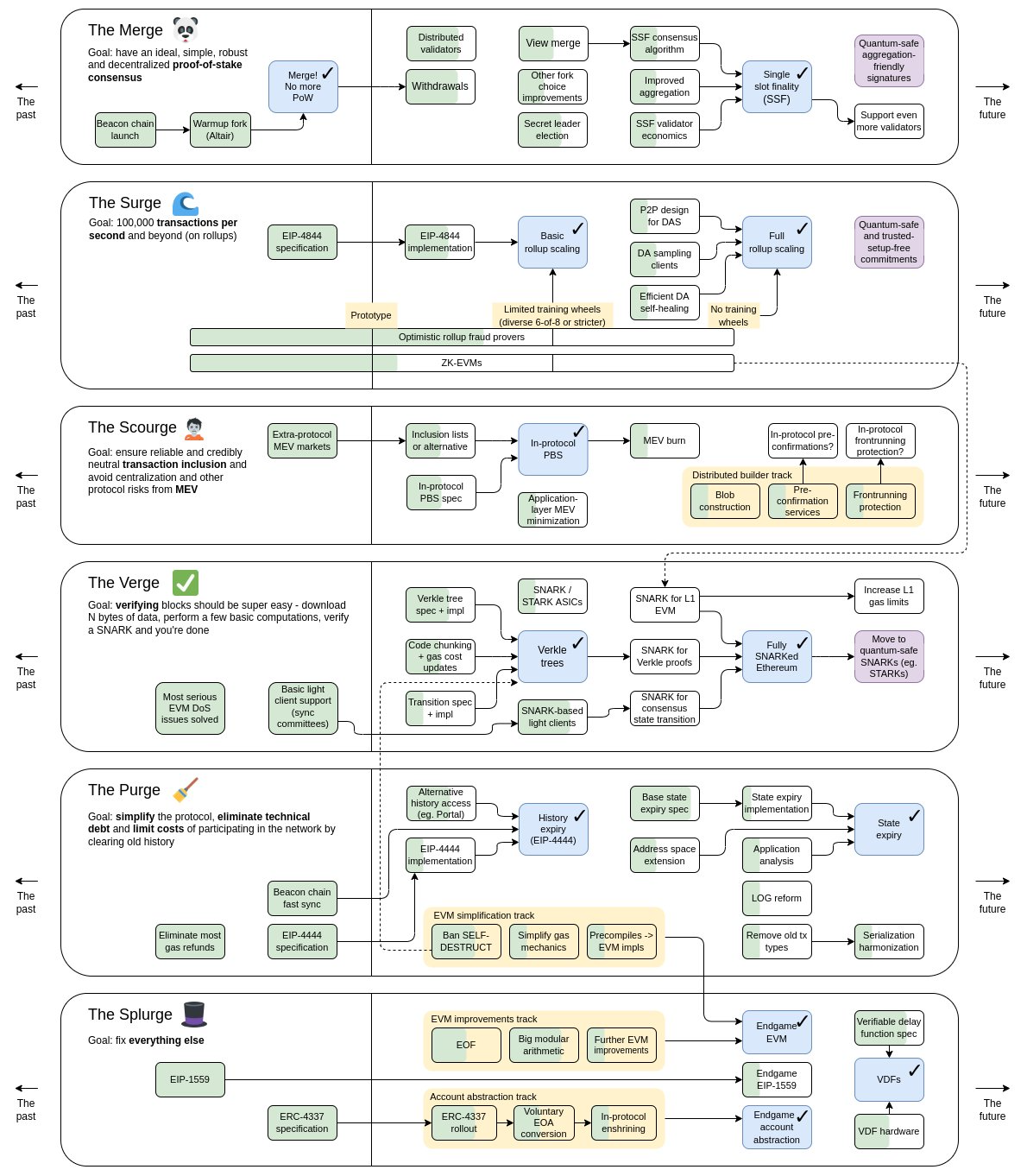
1. The Merge
The Merge
The Merge marks Ethereum's transition to a PoS system, a significant step towards realizing Ethereum's vision of a highly decentralized, scalable, secure, and sustainable network. The Merge unfolds through two key upgrades: Bellatrix and Paris (proposals EIP-3675 and EIP-4399), merging Ethereum's original execution layer with its newly established PoS consensus layer (Beacon chain), completed in October 2022.
The Merge brings about some significant changes, with the most important being that full nodes now need to run both the execution layer and the consensus layer client simultaneously. Before The Merge, a single client could handle all tasks related to transactions and blocks, but after The Merge, the execution layer and consensus layer clients each maintain peer-to-peer networks. The consensus layer client handles block propagation, proofs, and penalties, while the execution layer client continues to manage transaction execution and state maintenance.
One of the important upgrade contents of The Merge is Single Slot Finality (SSF). SSF aims to shorten Ethereum's block finality time to a single slot, instead of the current 64 to 95 slots (approximately 15 minutes). To achieve SSF, three key challenges must be addressed: developing precise consensus algorithms, optimizing the signature aggregation process, and determining the best economic approach for validator participation. While solutions to these challenges have been proposed, their implementation will take some time. Those interested can follow Vitalik's articles, which explore these issues.
Secret Leader Election is a mechanism that establishes a secret election proposer, achieving unpredictability, fairness, and uniqueness in proposer elections through random numbers and shuffling, reducing the likelihood of attacks.
The Surge
The Surge is another important aspect of Ethereum's upgrade, aimed at addressing the long-standing scalability issue that has plagued blockchain technology since its inception, ultimately achieving performance levels close to 100,000 TPS, approaching the speed of traditional electronic payments (e.g., Visa). This upgrade is achieved through Danksharding ("DS"), i.e., sharding.
Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844) is the first step of Danksharding, an important step in Deneb-Cancun (Cancun upgrade), and a crucial step for Ethereum to implement sharding, completing the scaling roadmap, significantly reducing the transaction and operational costs of Layer2 Rollups. By directly including each shard block in the beacon chain, shard blocks no longer contain executed transactions but only contain large data. Specific transaction tasks will be handled by the Layer2 rollup protocol.
After the original transaction data is submitted to the Layer1 mainnet, two different rollup routes have emerged based on different solutions, namely Optimistic rollups and ZK rollups.
1) Optimistic rollups
Optimistic rollups are based on fraud proofs or challenge proofs, taking an optimistic approach to the validity of data. If no one challenges the data and submits a fraud proof within a specified time (e.g., a week), the data is considered truthful and accurate.
However, when someone challenges and identifies fraudulent behavior in a transaction, Optimistic rollups require the implementation of a set of EVM logic in L1 smart contracts to simulate the execution of the transaction, thereby verifying the data's legitimacy and penalizing the fraudster while rewarding the challenger. Unlike Optimistic rollups, Arbitrium takes a different approach. It does not implement a set of EVM logic but instead allows challengers to interact with the contract in multiple rounds, narrowing down the range of problematic instructions. Finally, the problematic instructions are verified.
2) ZK rollups
ZK rollups are based on zero-knowledge proof technology, where L1 outsources the computation process of transactions to L2, while L1 can verify whether L2 has correctly executed the transaction. This is the charm of zero-knowledge proofs. Additionally, because the execution of transactions in L2 has already verified the transaction signature, i.e., the zero-knowledge proof part already includes signature verification, transactions submitted to L1 can exclude signatures, further saving data space. The legitimacy of transactions can be immediately confirmed, and with smaller data, ZK rollups are considered to be more in line with the future direction of L2. However, the challenge lies in how to design a universal circuit system, zkEVM, to be compatible with all applications.
The Scourge
The Scourge includes a series of upgrades aimed at mitigating the centralization of MEV while maintaining fair and transparent transaction inclusion. MEV is a metric for additional income that miners or validators can earn beyond block rewards and transaction fees, achieved by strategically including, excluding, or reordering transactions within a block. A regular validator running standard client software has no MEV value capture capability, while large validators use modified and optimized software to capture MEV value, leading to unfairness and a trend towards network centralization.
The proposed solution to address these issues is Proposer-Builder Separation (PBS), where proposers are still the protagonists in block creation, but block construction and execution are handed over to builders. In a well-functioning market, competitive builders will bid to extract the full value of MEV from blocks, enabling decentralized validator sets to receive most of the MEV rewards. Therefore, PBS effectively counteracts the centralizing force of MEV.
Another feature of PBS is the increased cost of censorship. The spirit of blockchain has always been incompatible with centralized censorship, and in the PBS scheme, block builders will add as many transactions as possible because of price competition among builders. If a builder wants to exclude a transaction under review, their potential bid may be completely lower than their competitors, making it impossible to win the auction. To win the auction and exclude the reviewed transaction, they need to invest more, thus increasing the cost of censorship.
The Verge
The Verge aims to achieve an extremely simple block verification method, requiring minimal data download and basic computation to complete verification. To achieve this goal, the existing Merkle Patricia Trie (MPT) needs to be upgraded to Verkle Trie.
Currently, Ethereum manages state data through MPT. To confirm the correctness of results, the entire MPT proof is required, followed by a series of hash verifications. Each full node in the current Ethereum network maintains a complete state tree, enabling independent transaction and state verification but making the entire verification process highly inefficient and cumbersome. Verkle Trie proofs do not require the involvement of sibling nodes, and the tree's width can be large with shallow depth, significantly improving proof efficiency, expected to increase by 5-10 times.
The Purge
The Purge represents a cleansing, aiming to achieve a simpler protocol and lighter-weight nodes by relieving the burden of historical data storage. In the Ethereum 1.0 era, each node needed to retain the entire history of blocks, but after the 2.0 upgrade, block validation introduced finality and checkpoints, and beacon chain data synchronization no longer needs to start from the genesis block, greatly improving data synchronization speed. With the introduction of EIP-4444, clients will no longer save historical data from a year ago, and expired data will be archived, with specific read and write rules for accessing archived data.
The Splurge
The Splurge
The term "The Splurge" signifies a moment of brilliance. This series includes upgrades in various categories, including account abstraction, multi-dimensional EIP-1559, and verifiable delay functions. Account abstraction will significantly lower the barrier to wallet usage. It abstracts all accounts into one type of account, the contract account. Wallets can be upgraded to contract wallets, creating a smart contract for each user to manage their assets and on-chain interactions. Contract wallets can define more business logic, such as security limits, multi-signature, and gas fee delegation. In the future, there will also be corresponding wallet templates for users to choose from, making it more convenient to configure contract wallets.
Subsequent Impact and Prospects
The impact of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade on the market is positive. Firstly, the upgrade will improve Ethereum's transaction performance and scalability. By introducing sharding technology and improved consensus mechanisms, network throughput and transaction confirmation speed will be significantly increased, greatly enhancing the availability and competitiveness of the Ethereum network, attracting more developers and enterprises to join the Ethereum ecosystem. Secondly, Ethereum 2.0 will also enhance security and stability. By introducing the beacon chain and Casper mechanism, as well as token staking, reducing reliance on energy, while enhancing network security and overall stability. Furthermore, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade will bring more innovation and functionality. By adjusting revenue distribution, reducing node burdens, lowering node thresholds, and introducing sharding technology, Ethereum will be able to support more complex smart contracts and decentralized applications. In addition, with the integration of Layer 2 solutions, Ethereum will be able to handle more transaction data and better meet market demands. This will provide developers and enterprises with more opportunities to create more valuable applications and services.
However, the implementation of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade also faces some potential risks and challenges. Firstly, due to the significant changes required for the upgrade, there may be issues with different node versions not being unified, leading to reluctance or inability to upgrade. Secondly, the upgrade's impact on the Ethereum ecosystem is uncertain, and for applications already in the Ethereum ecosystem, the upgrade may lead to a series of compatibility issues. Finally, the upgrade schedule also has uncertainties, and technical challenges and delays in the upgrade process may affect the upgrade process.
The upgrade from Ethereum 1.0 to 2.0 is an important milestone for the Ethereum ecosystem, but its development never stops. With a clear roadmap, the development team is advancing the implementation of upgrades to unleash the full potential of Ethereum and realize the ideal decentralized network. In the near future, we can expect to see a more powerful and efficient Ethereum ecosystem. The flourishing development of Layer 2 will continue to inject new momentum into the Ethereum ecosystem, enabling more applications (including games) and data to be put on-chain. In future articles, we will delve into the Optimistic Rollups and ZK Rollups, providing in-depth analysis of the two Layer 2 public chain projects. Stay tuned!
Disclaimer:
The information in this material is derived from public information or other sources that we believe to be reasonably reliable, and Guatian Lab makes no express or implied warranties as to its accuracy, sufficiency, completeness, and suitability for use.
The information, introductions, and data in this material are for reference only. Under no circumstances should any content of this material be considered as an invitation or recommendation, and it does not constitute investment advice. Investors are responsible for the various risks that may be faced by investment-related project assets (including but not limited to: investment risk, management risk, legal risk, tax risk, liquidity risk, credit risk, policy risk, economic cycle risk, interest rate risk, operational risk, risk caused by force majeure, etc.). Guatian Lab and/or its affiliates do not assume any legal liability for any consequences resulting from the reliance on or use of this material.
Without the written consent of Guatian Lab, any institution or individual may not copy, disseminate, or modify the content of this material in any form.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




