
Author: Spike @ Contributor of PermaDAO
Reviewed by: Kyle @ Contributor of PermaDAO
Recently, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) released the "Bond Tokenisation in Hong Kong" report, using the first tokenized bond issued by the Hong Kong government in February, the Evergreen "Green Bond," as an example to detail the theory and practice of bond tokenization. everPay has also collaborated with Asian digital banks to issue offshore RMB stablecoin ACNH, believing that RWA will lead the next wave of DeFi development. Therefore, PermaDAO has specifically summarized the key points of the report to share with readers:
1. It discusses the experience brought by the collaboration between the Hong Kong Monetary Authority and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), and introduces their assistance in the project to issue the first digital bond for the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region government (the Evergreen project);
2. Evergreen demonstrates the possibility of using distributed ledger technology (DLT) within the existing legal framework in Hong Kong to conduct real capital market transactions, and shows the potential of DLT to improve efficiency, liquidity, and transparency in the bond market;
3. The report also discusses the technical and platform design details to be aware of in digital bond trading, and provides guidance and reference opinions for issuers interested in bond tokenization;
4. Finally, the article explores the future development direction and action plan for digital bond tokenization, emphasizing the importance of addressing challenges and adjusting existing legal and regulatory systems.
In terms of timing, the global tokenized bond market is expected to exceed $3.9 billion between 2021 and 2023, which is basically in line with the development during the previous bull market, and the accumulated infrastructure is already sufficient to support large-scale use.
The typical process of issuing bonds can be broken down into the following steps:
1. Preparation and issuance of bonds: including the tokenization and preparation for issuance of bonds, such as the tokenization and initial issuance of bonds;
2. Participant onboarding: existing platforms can only be accessed by specific participants, including issuers, central securities depositories, payment agents, distributors, custodians, and secondary bond traders;
3. Issuance and subscription: bond issuance is divided into off-chain and on-chain processes. In the off-chain stage, standardization and pricing of bonds are required, and after being put on the chain, smart contracts representing the rights of the bonds need to be used for tokenization before subscription work can be carried out;
4. Allocation, settlement, and delivery: on the issuance date, banks will transfer the corresponding cash into the real-time settlement account of the central securities depository; then all parties are brought together to facilitate allocation, settlement, and delivery activities, and efficiency needs to be improved to reduce settlement delays and settlement risks;
5. Application of securities regulations: the issuance of digital bonds needs to comply with the requirements of securities regulations, including provisions for securities issuance and licensing requirements;
6. Credit rating: issuers may consider obtaining credit ratings for digital bonds.
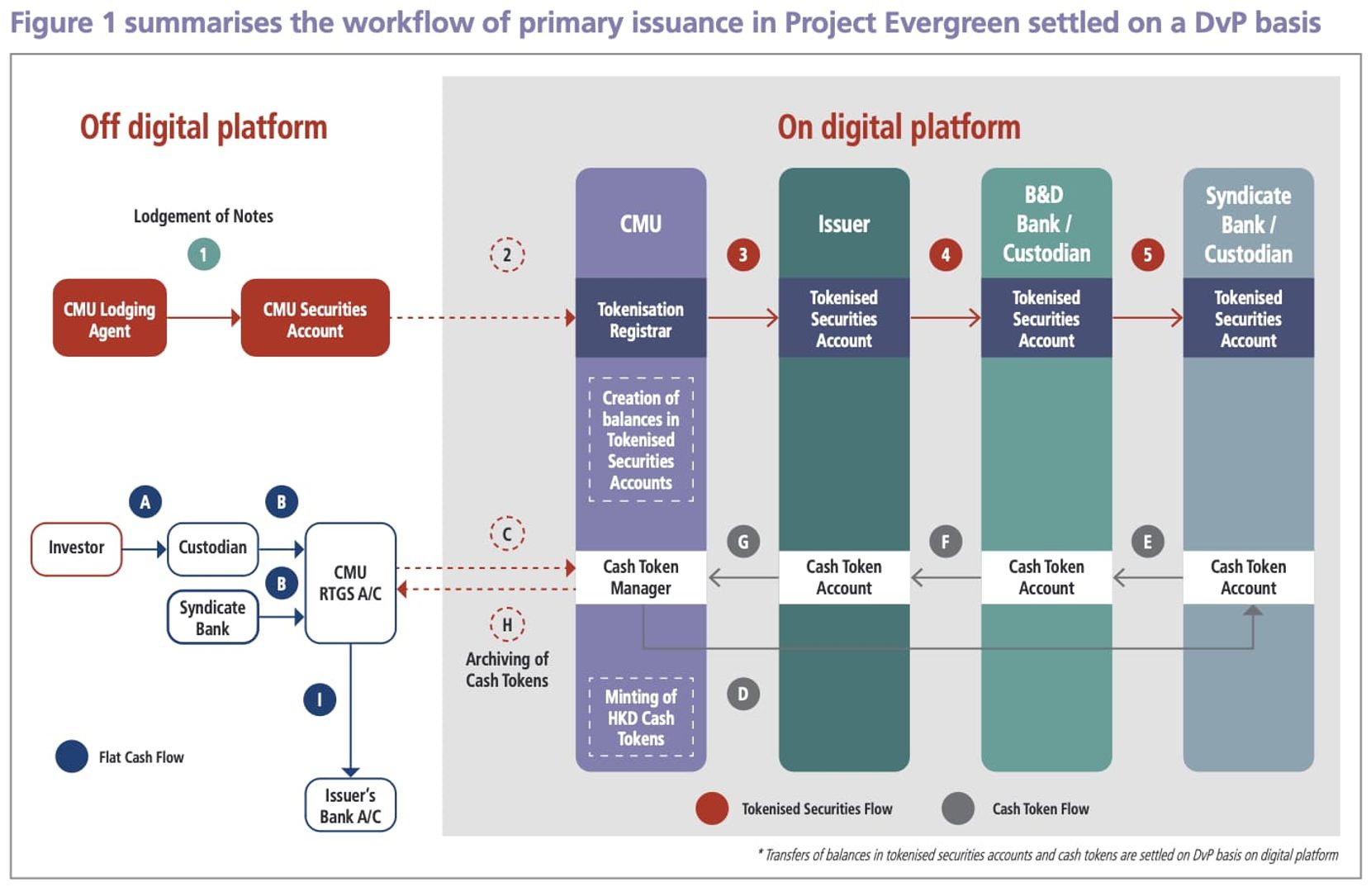
In practice, DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) has once again demonstrated its advantages. In the process of issuing tokenized bonds, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has summarized the following technical advantages of DLT:
- Paperless creation: in the process of creating tokenized bonds, the need for physical certificates and manual marking can be eliminated, saving time and eliminating the risk of manual errors;
- Facilitate interaction between different parties on a common DLT platform: a common DLT platform gathers all different parties on the chain, with specific permissions, real-time verification, and involving multi-party workflows, thereby improving processing efficiency;
- Atomic DvP Settlement: bond transactions and cash payments can be settled instantly on the DLT platform, reducing settlement delays and settlement risks;
- End-to-end DLT adoption across the bond lifecycle: using DLT in primary issuance, secondary trading settlement, coupon payments, and maturity redemption can significantly reduce manual processing, reduce service time and costs, and eliminate the need for synchronization between different channels, achieving significant operational improvements;
- Enhanced transparency: DLT achieves real-time data synchronization between different participants, thereby increasing system transparency.
In terms of system construction, it can be roughly divided into four layers from bottom to top, with Layer 1 and Layer 2 serving as public chain infrastructure, followed by the smart contract layer and user interaction interface. However, this part is more technical, so only a brief introduction is provided.
- Layer 1 blockchain: the digital platform uses Hyperledger Besu 4 as the Layer 1 blockchain, which is a private Ethereum blockchain used for communication between nodes and as a consensus layer;
- Layer 2 blockchain: the digital platform uses Canton as the Layer 2 blockchain, which is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that supports privacy and scalability, used to interpret and execute smart contracts, and maintain consistent execution efficiency among participating nodes;
- Smart contract solution: the digital platform has chosen Digital Asset Modeling Language (Daml) as the smart contract solution. Daml is an enterprise-grade, privacy-focused open-source smart contract language used to define workflows, patterns, semantics, and transaction execution among participants in the Canton DLT network;
- Interaction interface: participants in the digital platform can use node hosting, application programming interfaces (APIs), or user interfaces (UI).
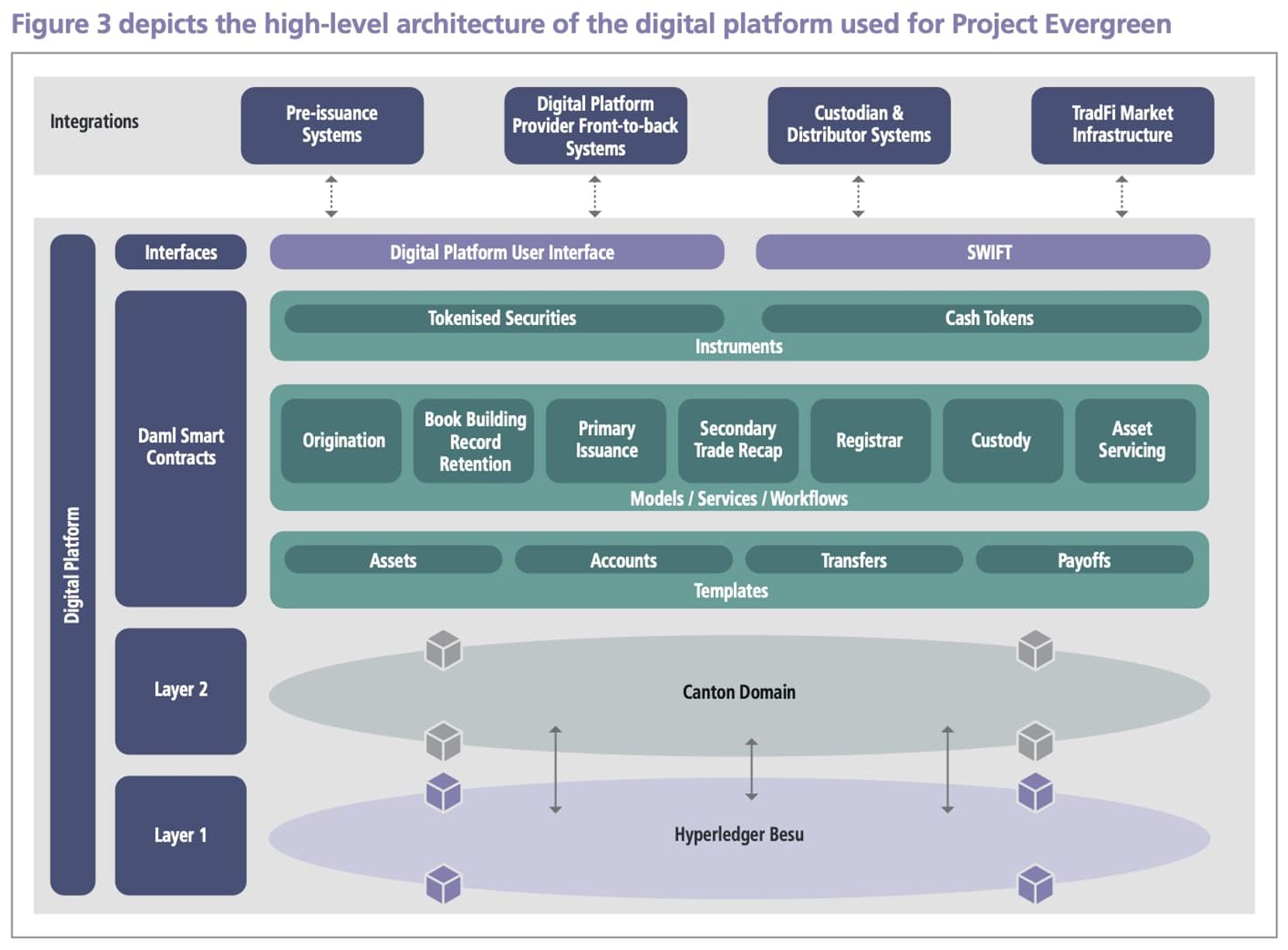
In addition, the DLT platform has also designed secondary trading, which refers to the trading of bond rights outside the digital platform through traditional over-the-counter (OTC) transactions, with only settlement and transfer taking place on the digital platform.
Similar to traditional bonds, OTC trading allows the parties involved to directly negotiate the terms and conditions of the transaction. If the DLT platform can include features such as security token trading, it can enhance the liquidity and transparency of the secondary market, provide standardized and automated processes and protocols, and potentially reduce counterparty and settlement risks by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts for more secure and efficient verification and settlement.
Of course, including such trading features has complex technical and legal requirements, and the impact on costs, time, and infrastructure setup needs to be considered. At the same time, the legal implications of the trading platform's business may be considered in the long term, and may not be truly pushed into the market.
Furthermore, DLT technology is expected to improve the existing market and product status in multiple aspects, such as having application potential in the following areas:
- Cross-platform: establishing interoperability and connectivity across different public chains and DLT platforms, linking assets between different public chains and DLT platforms, and building communication bridges between off-chain and on-chain;
- Stablecoins: supporting not only the digital Hong Kong dollar but also issuing on-chain versions of other fiat currencies, as well as issuing commercial stablecoins, or further integrating with off-chain payment systems;
- Standardization: promoting on-chain standardization of protocols, facilitating the interconnection of assets, and even providing practical references for the classification and regulatory framework of global assets.
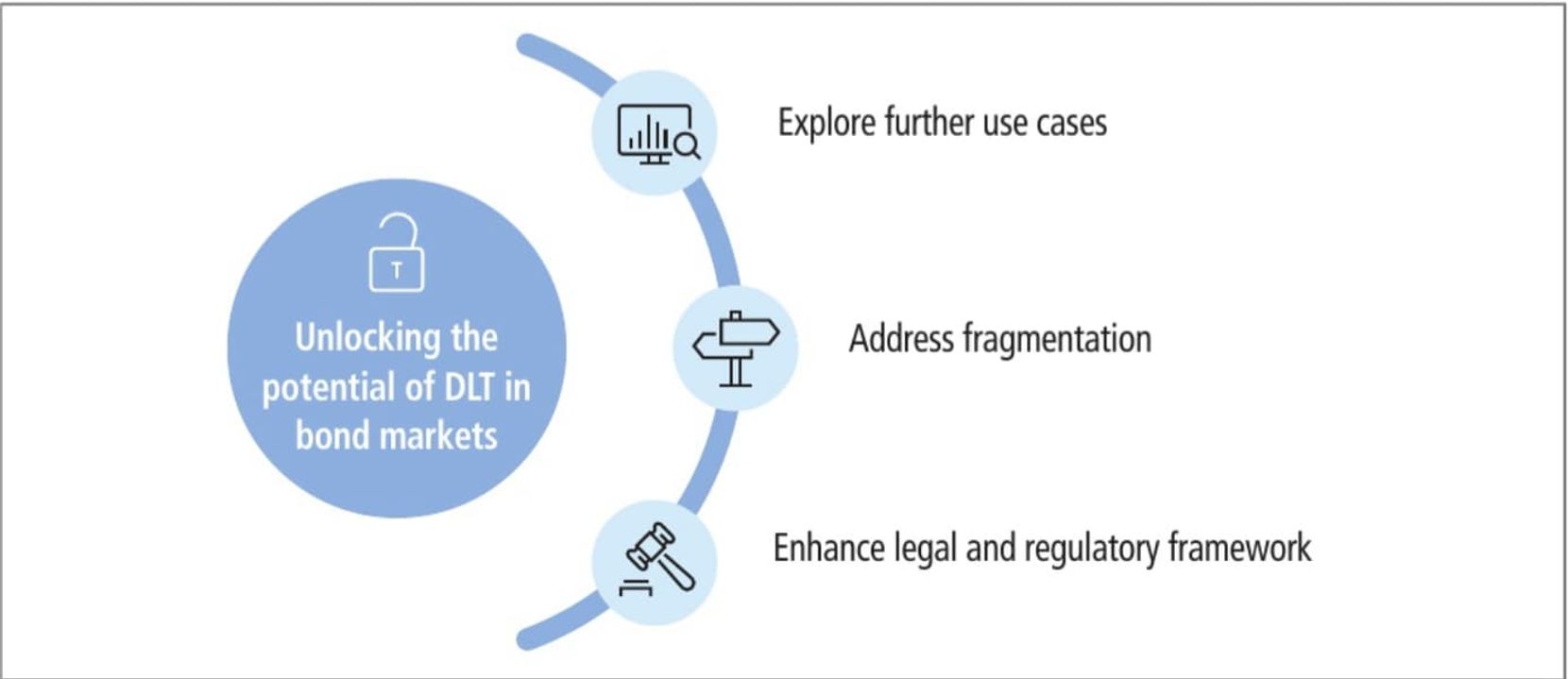
DLT is expected to completely change the operation of the financial market, and this report basically covers the conceptual framework of DLT technology. In the practice of Evergreen, it experimentally verifies the practical application of DLT technology.
As early as July, PermaDAO produced an article titled "Thoughts and Practices of RWA," which used the issuance of green bonds by the Hong Kong government as the most compliant example for introduction. Today, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has issued a report using this as an example, and PermaDAO feels that the future compliance framework will also be built based on this practice. At that time, a truly broad range of off-chain assets will usher in a real application explosion period.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




