Project Introduction
Dark Forest is a real-time strategy game based on the Ethereum and Gnosis (XDAI) chains, and it is also the world's first incomplete information game based on zero-knowledge proof technology. The game released its first test version in August 2020 and received recommendations from well-known figures such as Vitalik Buterin. Inspired by Liu Cixin's science fiction novel "The Three-Body Problem 2: The Dark Forest," the specific gameplay allows players to discover and conquer planets in an infinite, cryptographically specific universe generated by the program, while avoiding being destroyed by enemies hidden in the darkness.
Dark Forest is a pioneer in full-chain games, providing not only an interesting and challenging gaming experience, but also an experimental platform for exploring the application and innovation of blockchain technology in the gaming field, as well as a model showcasing the potential and prospects of a decentralized digital world. When considering the value of the project itself (while also taking into account the current stagnation in the development of the Dark Forest game), we should expand our thinking to consider the investment value of the entire full-chain gaming track. Whenever full-chain games are mentioned now or in the future, it is inevitable to refer to Dark Forest, and perhaps its core investment logic lies therein.
Considerations for the investment logic of the full-chain gaming track are as follows:
The growth of on-chain users is facing bottlenecks, and it is expected that full-chain games can bring more active users to the blockchain sustainably. As of today in 2023, there are over 2500 chain game projects, with continuous growth, yet the daily active users are only around 800,000, and the ratio of human to machine is difficult to estimate, and the market value of game tokens is also very low. Gamefi is facing a crisis of industry decline and urgently needs to find a new narrative to inject vitality into the industry. Full-chain games represent the highest form of blockchain technology in the gaming field and may be an effective entry point. The inherent tamper-proof nature of full-chain games also provides a fair and perpetually growing soil for narratives, which is urgently needed by encrypted VCs, WEB3 players, and the industry as a whole.
Full-chain games are the inevitable path of technological evolution. Every technological revolution in history has been driven by the interaction of several underlying technologies, rather than a single "from 0 to 1" innovation. The current on-chain games may be a branch on the path of technological development. In the context of blockchain infrastructure innovation, on-chain games may also be the prototype of the next generation of killer applications. In any case, it is worth paying attention to and exploring because it may have strong relevance to future killer applications.
Full-chain games are beneficiaries of blockchain scaling and acceleration. New blockchain infrastructure, such as new public chains, zkEVM/VM, modularity, etc., provide higher performance and lower costs for on-chain games, as well as more features and possibilities. On low-performance and high-cost Ethereum, only applications with low TPS requirements and high unit returns, such as DeFi, NFT, etc., can survive and develop, while on high-performance and low-cost new networks, applications with high TPS requirements and low unit returns, such as complex on-chain applications, can emerge. On-chain games are representatives of complex on-chain applications, requiring a large number of user transactions and interactions to realize their business models and token economies. These applications are similar to low ARPPU (average revenue per paying user) games/applications in the Web2 era, and they need to constantly enter other fields and scenes to build their own business ecosystems.
The openness and composability of full-chain games bring about imaginative space. As players, we will always yearn for greater openness, more freedom of composition, and more unique narrative structures. This is why "The Legend of Zelda" can become a classic, and why LEGO, as a simple building block game, can be popular worldwide for 90 years. Perhaps no one can imagine how many combinations can be created with just 6 simple LEGO bricks and 8 studs, the answer is an astonishing 900 million. Full-chain games release the potential to build a "game LEGO," with highly composable and scalable characteristics, the imagination it can inspire in the future is worth the anticipation of all game players.
In summary, Dark Forest and full-chain games are projects and tracks worthy of attention.
1.2. Valuation
Dark Forest has not yet issued tokens or conducted financing, making it difficult to evaluate. It is not a typical commercial project, but rather an experimental artistic project.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Basic Information
Dark Forest was founded by Gubsheep (pseudonym) in 2020. The core innovation of the game lies in using zkSNARKS technology to create a fully decentralized, privacy-protecting, scalable, fair, open, composable, and programmable game world, opening up new possibilities and space for on-chain games. It is not only an interesting and challenging game, but also an experimental field for exploring blockchain technology and cryptographic frontiers, as well as a platform for building decentralized communities and ecosystems.
The current game version of Dark Forest has been updated to v0.6 Round 5, with each round introducing new features and improvements, as well as different challenges and rewards. The game mode is by invitation only, meaning that only users with an invitation code (invite key) can enter the game. Invitation codes can be obtained by completing the objectives of the previous round or contributing outstanding works, and can also be purchased through auctions or lotteries.
Dark Forest currently does not have its own native token, but plans to launch one in the future. The game tokens used in previous versions were xDai and ETH, used for paying fees in the game and purchasing NFTs (non-fungible tokens). xDai is a sidechain network compatible with Ethereum, providing fast and low-cost transactions.
2.2. Team Situation
2.2.1. Overall Situation
Dark Forest's development team is led by Gubsheep (Brian Gu). The project can be traced back to the end of 2019, when Brian Gu and Jacob Rosenthal came up with the idea of using zkSNARKs technology to build a hidden information game while participating in a cryptography hackathon. They spent two days creating a prototype and won the first prize. Afterward, they decided to continue improving the project and invited Philip Daian, Ariana Chaikin, Sam Matson, and Scott Moore to join the team.
2.2.2. Core Members
Brian Gu: He is the game designer of Dark Forest, responsible for the overall conceptualization, gameplay design, and rule formulation of the game. He is a senior blockchain developer who has worked at Cornell Tech and the IC3 lab, participating in multiple blockchain-related research and projects. He is also a science fiction enthusiast with a profound understanding and insight into the "Three-Body" series of novels.
Jacob Rosenthal: He is the front-end developer of Dark Forest, responsible for the interface design, interaction implementation, and user experience optimization of the game. He is an experienced full-stack developer who has worked at several well-known internet companies such as Google, Facebook, and Twitter. He is also a game enthusiast with a strong interest and professional insights in RTS games.
Philip Daian: He is the back-end developer of Dark Forest, responsible for the logic writing, data storage, and security of the game, and is also a top-notch cryptographer and blockchain expert. Currently pursuing a doctoral degree at Cornell University and serving as a researcher at the IC3 lab, Philip Daian has in-depth research and mastery of zkSNARKS technology, providing strong support for the technological innovation of Dark Forest.
2.2.3. Team Development
In the process of operating Dark Forest, Brian Gu discovered broader prospects for the application of zero-knowledge proof technology in other fields. Therefore, in early 2021, he established a new organization called 0xPARC, mainly focusing on research in the field of zero-knowledge proofs, supporting experimental application projects such as Lattice, ZKonduit, Index Supply, Zupass, and ZFT. 0xPARC aims to promote the innovation and development of cryptographic technology in gaming, social, financial, and other fields.
Lattice is a full-chain gaming platform supported by 0xPARC, aiming to provide developers and players with a high-performance, low-cost, highly secure, and highly scalable gaming environment on the blockchain, allowing them to create and experience various types of games and virtual worlds. The core technology of Lattice is a virtual machine (VM) based on zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP), which can achieve complete decentralization of game logic and state while ensuring the correctness and privacy of the game. Lattice's VM can interact with any EVM-compatible blockchain network, such as Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, etc., thereby realizing the possibility of cross-chain games.
Lattice aims to become an open gaming ecosystem, providing not only a gaming platform but also a series of tools and services such as game engines, editors, SDKs, markets, and communities, making it easier for developers and players to participate in the development and experience of full-chain games. Lattice is currently hosting an online hackathon called Autonomous Worlds Hackathon, inviting builders, hackers, and artists interested in full-chain games to explore the forefront of on-chain games and virtual worlds and use Lattice's tools and platform to realize their creativity.
Mud is an important product of Lattice and a full-chain game engine inspired by Dark Forest. Because Dark Forest is directly written on the blockchain, it is very difficult to develop and modify. Therefore, Brian Gu felt that it was necessary to abstract the experience of Dark Forest into a framework or engine for more people to use, allowing them to more easily develop their desired full-chain games. Thus, Mud was born, allowing developers to write their game logic and interface in JavaScript and deploy it to run on the blockchain.
Since Brian Gu has a deep interest and research background in zero-knowledge proof technology, he has decided to divide the focus of 0xPARC into two directions: on one hand, continue to support full-chain game projects such as Lattice and Mud, and collaborate with other blockchain networks and projects; on the other hand, continue to explore the application and innovation of zero-knowledge proof technology in other fields, such as ZKonduit, Index Supply, Zupass, and ZFT.
As a result, starting from 2022, the Dark Forest game has been in a maintenance state with few updates and improvements. However, Dark Forest remains a game with a rich plugin ecosystem and a loyal player community, providing valuable experience and inspiration for subsequent full-chain game projects.
2.3. Financing Situation
The Dark Forest team has received support and sponsorship from some well-known investment institutions and individuals, such as Y Combinator, Paradigm, Naval Ravikant, and Balaji Srinivasan. The Dark Forest team has stated that they are not doing this project to make money, but to explore the potential and possibilities of cryptography, blockchain, and gaming, and to provide users with a meaningful and enjoyable gaming experience. They have expressed their intention to continue developing and improving the project, and welcome more investors, partners, and community members to join and support them.
2.4. Code Situation
Dark Forest's smart contracts are completely open source and can be viewed and verified for their logic and security on GitHub. From GitHub, it can be seen that the code repository has been established for a long time, starting development in 2019, and after its official launch in May 2020, the code has been continuously updated, indicating a good project development process.
The total number of commits is 1,414, with the most frequent code commits and problem resolutions occurring between May 2020 and January 2021. Code commits were also relatively concentrated between January and April 2022, mainly to support the start of the fifth round of the game. The number of code commits in April 2023 was relatively low, possibly because the project has matured and stabilized, or because the team's focus has shifted to other projects.
The main developer of Dark Forest is @jacobrosenthal, responsible for writing and testing smart contracts, clients, subgraphs, and packages. There are also other contributors to the project, mainly involved in writing and optimizing plugins and documentation.
2.5. Past Development and Roadmap
2.5.1. Past Development
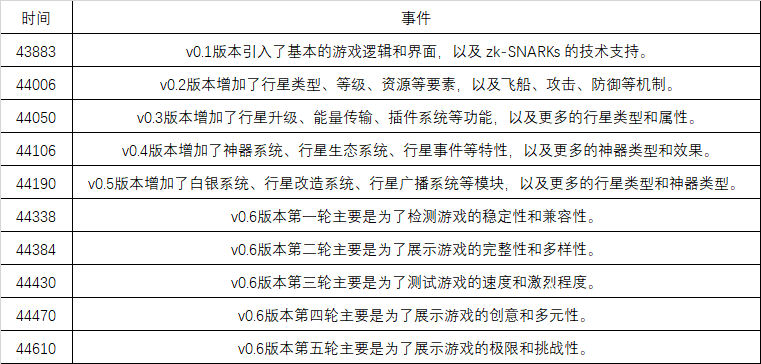
2.5.2. Development Plan and Roadmap
In the future, Dark Forest plans to continue improving game features and experiences, and explore more possibilities combining blockchain technology and the community. For example, Dark Forest has already supported players using NFTs as in-game items, and plans to collaborate and interact with other projects. They also plan to open up more game data and interfaces to encourage players and community members to develop their own plugins, tools, and content, creating a richer game ecosystem.
The upcoming test plans for Dark Forest are as follows:
v0.7 Lemon Small: This is the seventh round of testing for Dark Forest and the first test to introduce planet upgrades. Planet upgrades are a mechanism that can enhance the abilities and characteristics of planets, such as increasing energy, defense, speed, etc. The goal of this round of testing is to increase the strategic and complexity of the game, and enhance player challenges and satisfaction.
v0.8 Orange Medium: This is the eighth round of testing for Dark Forest and the first test to introduce planet types. Planet types are a factor that can affect the appearance and behavior of planets, such as some planets being volcanoes, glaciers, deserts, etc. The goal of this round of testing is to increase the diversity and aesthetics of the game, and enhance player exploration and surprise.
v0.9 Banana Large: This is the ninth round of testing for Dark Forest and the first test to introduce planet ecosystems. Planet ecosystems are a factor that can affect the resources and life of planets, such as some planets having water, oxygen, plants, animals, etc. The goal of this round of testing is to increase the depth and realism of the game, and enhance player engagement and empathy.
v1.0 Pineapple Extra-Large: This is the tenth round of testing for Dark Forest and the first test to introduce the DARK token. The DARK token is the native token of Dark Forest, which will be used for governance, staking, rewards, and in-game transactions. The goal of this round of testing is to increase the value and fairness of the game, and enhance player motivation and loyalty.
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
The background of Dark Forest mainly consists of two aspects: game background and technical background.
Game Background: The inspiration for Dark Forest comes from the science fiction novel "The Dark Forest," the second book in Liu Cixin's "Three-Body" trilogy, and its eponymous thought experiment, which posits that the universe is a dark forest, and every civilization is an armed hunter, stealthily seeking and destroying other civilizations like ghosts to ensure their own survival.
Dark Forest transforms this theory into a unique and interesting game mechanism, allowing players to explore and conquer in a universe of hidden information, while also experiencing the charm of science fiction and philosophy. To achieve this mechanism, Dark Forest utilizes zero-knowledge proof (ZK) cryptographic technology, which is a technology that can prove a statement to be true without revealing any information.
Technical Background: Zero-knowledge proof technology made a leap in development in 2019, with new tools like iden3's SnarkJS (SnarkJS is a JavaScript and WebAssembly library for implementing zero-knowledge proofs) for the first time achieving efficient, in-browser ZK proof and verification. Based on the latest developments in these technologies, Dark Forest has established a hidden information game based on zkSNARKs.
3.2. Project Principles
Dark Forest uses zkSNARKs technology to implement a hidden information game. zkSNARKs is a special type of zero-knowledge proof technology that enables non-interactive, verifiable, and scalable proofs. To understand the impact zkSNARKs can have on the digital world, it is important to understand the difference between two types of games: complete information games and incomplete information games.
1) Complete Information Games:
These are games where all players know the complete state of the game universe. For example, checkers and chess are complete information games, where all players always know the positions of all pieces on the board. Participants make decisions based on the same information.
2) Incomplete Information Games:
Also known as "hidden information games," these are games where players may not know the complete state of the world. For example, in Texas Hold'em, in addition to the five cards openly placed on the table, players also have their own two hole cards, which increases the challenge of decision-making. Strategic games like "Firewatch" and "EVE Online" also fall into this category. In these games, information is hidden through a "fog of war" - on a game map, you can only see nearby people, not the entire map, and you don't know exactly where your enemies are, so you have to explore for yourself. While centralized games can easily implement this, it is difficult to do so in a decentralized manner, because everything on the chain is open and transparent. Incomplete information games provide players with the opportunity to explore a richer and more dramatic strategic space. Asymmetric information may trigger complex behaviors such as deception, ambush, reconnaissance, counter-reconnaissance, etc., making incomplete information games generally more challenging and interesting than complete information games.
However, most blockchain-based games are currently complete information games, because the blockchain itself is a publicly transparent ledger, and anyone can view all transactions and states. This means that players can easily obtain information about other players' positions, resources, actions, etc., disrupting the balance and fun of the game. For example, in a blockchain-based RTS game, if you want to ambush your enemy, you have to broadcast your movement transaction on the blockchain and wait for it to be confirmed. This gives your enemy enough time to discover your plan and react.
How does Dark Forest do it?
In Dark Forest, players can submit the position and status of their planets to smart contracts using zkSNARKs, without worrying about being discovered or attacked by other players. At the same time, smart contracts can verify the proofs submitted by players using zkSNARKs to ensure their correctness and validity, without knowing the specific details or data. This enables a completely decentralized, secure, private, fair competition game world.
Specifically, the game process of Dark Forest is as follows:
Universe Generation: The positions and attributes of all planets in the universe are generated by a cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (PRNG), and are only revealed when players explore them. This PRNG is based on Ethereum block hashes and a fixed seed value, making it deterministic, verifiable, but unpredictable. In other words, anyone can reproduce the entire universe by providing a block hash and a seed value, but no one can know the position and attributes of any planet in the universe without a block hash.
Planet Exploration: When a player explores a new planet, they generate a zkSNARK proof to prove that they indeed own this planet, and submit it to the smart contract. The smart contract verifies this proof and assigns the planet to the player. However, the smart contract does not know the specific location or attributes of the planet, as this information is encrypted. Only the player can decrypt this information and store it in their local browser.
Planet Attack: When a player wants to launch an attack on another player, they also need to generate a zkSNARK proof to prove that they have enough resources and energy to execute the attack, and submit it to the smart contract. The smart contract verifies this proof and executes the attack. However, the smart contract does not know the specific locations of the attacker and the target, or the result of the attack, as this information is also encrypted. The details of the attack are only revealed when the attack reaches the target planet, and the statuses of both parties are updated.
Using zkSNARKs, players can publicly submit verifiable and valid operations while maintaining private states.
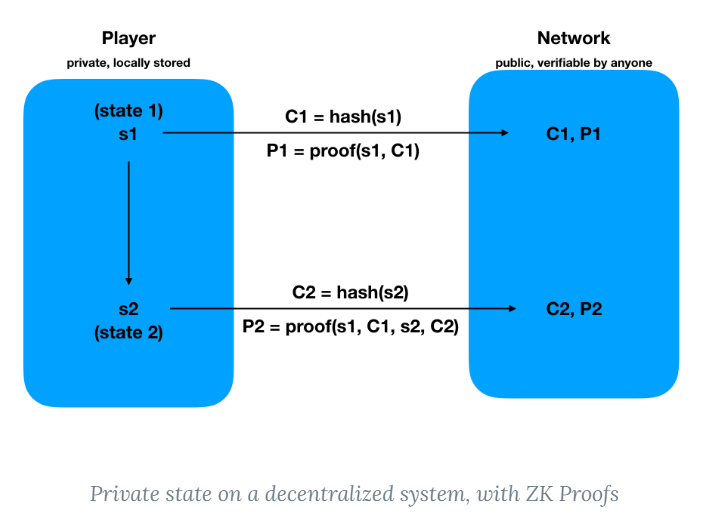
In this way, Dark Forest has implemented a blockchain-based incomplete information game, protecting players' privacy and security, while also increasing the strategic and entertaining aspects of the game. Players need to explore, expand, compete, and cooperate in a dark universe, while also carefully hiding their existence to avoid being discovered and eliminated by other players.
3.3. Core Gameplay
Resource Management
In Dark Forest, resources are at the core of the game, with the most essential resource being the energy of celestial bodies. Players use energy to guard and invade celestial bodies, exploring the entire randomly generated universe. In addition to energy, there are other types of resources such as silver and artifacts. Different types of resources have different uses; for example, silver can be used to upgrade planets or purchase artifacts, and artifacts can be used to enhance the attributes or effects of planets or fleets.
Scoring Rules
In Dark Forest, each round of the game has different scoring rules, commonly based on the conversion of the total resources obtained by players according to specific logic. For example, in v0.6.2, a player's score is calculated using the following formula:
$$Score = \sqrt{Energy + 10 \times Silver + 100 \times Artifacts}$$
There are also special rules, such as in v0.6.3, where a player's score is determined based on the closest distance of their owned planets to the center of the universe. For example, in v0.6.3, a player's score is calculated using the following formula:
$$Score = \frac{1}{MinDistance + 1}$$
Where $MinDistance$ is the closest distance of all the planets owned by the player to the center of the universe.
Based on the final scores, rankings and rewards are determined. The duration of each round of the game varies, generally lasting from a few weeks to several months. Players can view the specific rules and rewards for each round of the game on the game's official website or blog.
3.3.1. Core Elements
In Dark Forest, players need to master the following core elements:
Fog of War: This is a core feature of the incomplete information game, preventing players from seeing the entire universe and requiring them to explore to discover new planets and fleets. The fog of war is presented as a gray area, and players can place their exploration cursor in a designated area, which will expand exploration based on the hash rate of the CPU or GPU. Explored areas turn black, indicating that the player knows the situation there, but over time, black areas gradually turn back to gray, indicating that the player needs to re-explore the area. The fog of war adds difficulty and interest to the game, and provides players with more strategies and gameplay.
Planets: Planets are the basic units in the game, serving as players' bases and sources of resources. Planets have different levels, types, and attributes, affecting their energy, silver mines, defense, speed, and range. Players can discover and occupy planets in the universe, and can also use their fleets to attack other players' planets. Planets can also produce or use special NFT assets, such as artifacts and relics, to enhance their abilities or effects.
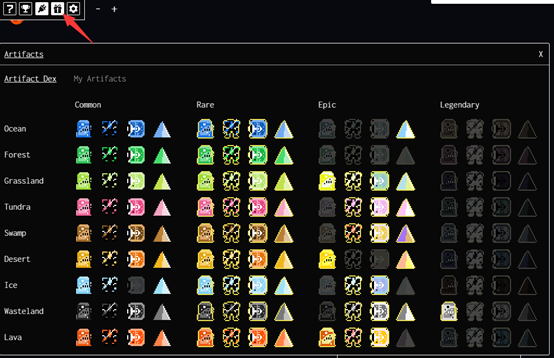
Artifacts: Artifacts are special NFT (ERC-721) items with powerful abilities, which can only be obtained from the Foundry or through secondary trading. There are nine types of artifacts, including Spaceship, each with one-time use and reusable types.
Scores: The basis for determining player rankings, composed of the energy and silver mine quantities of all celestial bodies occupied by the player.
3.3.2. Game Interface
Dark Forest's game interface features a clean and visually appealing black theme, allowing players to feel the vastness and mystery of the universe, and to focus on the game's strategy and gameplay. The game interface of Dark Forest mainly consists of the following components:
Map: The map is the main part of the game interface, displaying the universe area where the player is located, as well as the planets and fleets within it. Planets and fleets on the map are represented by different colors and shapes, such as blue circles representing the player's own planets, and red triangles representing enemy fleets. The map also has a layer of gray fog, indicating areas that the player has not explored or does not have visibility into. Players can move and zoom the map using the mouse or keyboard, and can select and operate planets and fleets by clicking or dragging.
Data Panel: Located in the bottom right corner of the map, the data panel displays detailed information about the currently selected planet or spaceship, such as position, level, attributes, resources, and artifacts. The data panel also contains buttons and options for performing actions, such as transferring energy or silver, upgrading planets, and using artifacts.
Score Panel: Located in the top left corner of the map, the score panel displays the player's current score and ranking, as well as the remaining time and rules of the game. The score panel also has a button to switch to the leaderboard view, to view other players' scores and statuses.
Plugin Panel: Located on the left side of the map, the plugin panel displays a list and interface of the plugins installed or enabled by the player. Plugins are extensions developed by community developers or players, providing additional functionality or optimizations for the game. Plugins can be downloaded or installed from the official or community plugin library.
3.3.3. Game Process
The game process of Dark Forest can be divided into the following stages:
① Preparation Stage: In this stage, players need to purchase an invite key to enter the game. Invite keys can be found on platforms selling them, or players can find others willing to share invite keys in the community. Then, download and install the game client, and use the invite key to register an account.
② Exploration Stage: In this stage, players will see a black universe map with planets and fleets. Players can move and zoom the map using the mouse or keyboard, and can select and operate planets and fleets by clicking or dragging. The goal of the game is to discover and occupy more planets in the universe, while protecting their own planets from attacks by other players. Players can use energy to take various actions, such as moving fleets, attacking planets, and broadcasting their positions. Energy is a limited resource and needs to be allocated and transferred between planets and fleets in a reasonable manner.
③ Development Stage: In this stage, players can start collecting, trading, and using special NFT assets such as artifacts and relics to enhance the abilities or effects of their planets or fleets. NFT assets are scarce and valuable, and can be found on some special planets or traded within or outside the game.
④ Competition Stage: In this stage, players can deploy different tactics according to their style, whether they are explorers longing for the stars, artifact merchants looking to make a profit, or aggressive players advocating for conflict. Players can interact with other players in a friendly or hostile manner, such as through cooperation, competition, alliances, etc. They can also publicly broadcast their positions or actions, but need to be mindful of protecting their privacy and security.
At the end of the game, based on the scoring rules of different rounds, the system will calculate the final scores of players based on the planets and resources they have occupied, and rank them according to their scores. Players with higher rankings may receive rewards or honors, such as special artifacts, NFT badges, invite keys, etc.
3.3.4. Lobby System
The Lobby system is a revolutionary new feature developed by the core team of Dark Forest to support third-party developers and mod makers after the end of v0.6. It allows players to create and configure their own Dark Forest Universe without waiting for official or community rounds, and without needing to be developers to launch it. It has the following characteristics and functions:
It is a fully on-chain configuration and deployment system for the player's own Dark Forest Universe. Players can use over 30 different configuration parameters to initialize the Universe, and choose whether to enable a whitelist.
It allows players to experiment with different game parameters, such as game speed, space type, occupation area, space debris, world radius, etc., to adapt to different game styles and needs.
It also allows developers to add or replace contract functions to implement custom features and scoring mechanisms, such as scores based on energy quantity or minimum step challenges.
It allows the community to express themselves more and create interesting universes and game modes.
3.4. Project Features
3.4.1. Technical Aspect
- 3.4.1.1. Fully On-Chain, FOC
Dark Forest is a full-chain game based on Ethereum, meaning that all game logic and data are run and stored on the blockchain through smart contracts, without relying on any centralized servers or databases. This design gives the game decentralized, tamper-proof, and publicly transparent characteristics, and allows players to freely create and use various plugins and tools to expand the game's functionality and experience.
However, the feasibility of full-chain games has always been a challenging issue because games are different from other applications, especially when it comes to implementing real-time multiplayer online games, which have high requirements for network latency and interaction frequency. Putting the entire game on the chain means that these interaction programs need to be deployed in the form of smart contracts, which imposes significant limitations on the choice of game types and the design of game logic.
Dark Forest is the first project to implement this conceptual idea, deploying all game rules and logic in the form of contracts on the chain, ensuring that the state of players and the universe is updated in real-time on the chain after any interaction.
- 3.4.1.2. zk-SNARK Implementation of Incomplete Information Games
One of the core applications of zk-SNARK in Dark Forest is the implementation of a mechanism for incomplete information games. In incomplete information games, players make decisions without knowing all the relevant information, and can only make the best choices based on their observations and reasoning. This mechanism increases the strategic and entertaining aspects of the game, and is consistent with the Dark Forest theory in the game background. In Dark Forest, players can only see planets they have explored and need to consume energy to continue exploring new planets. The positions and statuses of other players' planets are hidden, unless they voluntarily submit proof to the smart contract to disclose their actions. This creates a balance between exploration and concealment, as well as a strategic and tactical gameplay.
3.4.2. Experiential Aspect
Dark Forest not only follows encryption principles at the technical level, but also embodies the spirit of encryption at the experiential level. The game design of Dark Forest is very open and flexible, without fixed goals or rules, allowing players to freely explore and create their own ways of playing the game. Essentially, Dark Forest is an Ethereum smart contract, like a protocol or rule, which means it is not limited by a specific client (Client Agnostic), and anyone with the ability can create a front-end client to access the backend contract in their preferred visual form. It also means that any address can interact with it, whether the address behind it is a person, a bot, or another smart contract. This not only expands the boundaries of game strategy, but also fosters a thriving plugin ecosystem.
The openness and flexibility of Dark Forest allow players to freely combine various elements to create different gameplay and experiences. In this ecosystem, players spontaneously combine, build, and experiment with various things and gameplay, forming an organic community. The things created during the process far exceed the official expectations, such as the artifact trading market, celestial body trading market, planet bounty system, and even battle AI, among others. The emergence of these plugins adds more game objectives and gameplay, allowing more types of players to participate. The introduction of the Lobby system and the development of the on-chain engine have further unleashed the rules, allowing players to freely set the rules of the universe to conduct the game.
This open and highly combinable attribute undoubtedly greatly expands the boundaries of game possibilities, allowing players themselves to participate in the construction of the game experience, and enabling players to enjoy different fun and challenges, no longer relying solely on the official team.
3.5. Dark Forest Ecosystem
The community ecosystem of Dark Forest is an important part of the game, consisting of different players, teams, organizations, and platforms, all working together to drive the development and innovation of the game. Here, we will introduce some of the more active and influential community members and projects to showcase the diversity and vitality of Dark Forest.
3.5.1. Community Ecosystem
Dark Forest: Firstly, the official community, which serves as a concept incubator and ecological square, has minimal operational activities apart from specific event announcements, issue resolutions, and daily problem-solving. The official community mainly uses Discord as a platform for communication and interaction, and also utilizes Twitter and Blog for promotion and updates.
Project Sophon: This is a highly professional and excellent American team that has a close cooperative relationship with the official team and is an indispensable part of the Dark Forest ecosystem. They have strong technical capabilities, focusing on the technical infrastructure of the game, and have provided many useful tools and services for Dark Forest. For example, they developed a Dark Forest local library that allows users to start a game on-chain or off-chain by themselves; they also developed the Broadcast Market and NightMarket, two zk-based coordinate trading markets; in addition, they provide useful tools and services such as DF-CLI, DF-Stats, and DF-Notify.
Orden_GG: This is a very hardcore Ukrainian game organization with high standards in both coding and game technology. They consecutively topped the leaderboard for four rounds in version 0.6, and are also high-quality builders within the ecosystem, demonstrating strong initiative and execution. They have built an artifact trading market with added liquidity, and are core players of Aavegotichi (Little Ghost), even creating an open-source client for the game.
D_F DAO: This early DAO, mainly composed of Americans, was established during version 0.6 and is an organization that focuses on innovative game experiences. They also have excellent development capabilities and have created many interesting things in the Dark Forest universe, including the Star Realm Colossus, a sacrificial flow method (a smart contract that allows members to contribute their star systems to the contract to win collectively), and the modified version of Dark Forest Arena (a MOBA-style DF competitive game), among others. They are also good at organizing and trying new strategies in the game. Overall, they have good brand promotion and operations, making them a very dynamic community within Dark Forest.
MarrowDAO|GuildW: This is a Chinese-speaking DAO that actively assists in expanding and promoting the Dark Forest ecosystem, especially within the Chinese-speaking community. MarrowDAO has produced many high-quality articles and strategy sharing within the organization, and also has decent development capabilities, creating several plugins including the artifact trading market and GPU mapping tools. They were also the first to organize a community round in the entire Dark Forest ecosystem. At that time, since the Lobby system was not yet available, the community had to modify the client and contract code on their own, which required a considerable amount of work and technical expertise.
277DAO: This is a Chinese-speaking community focused on blockchain games, specializing in organizing events. After the launch of the Lobby system in Dark Forest, they held five consecutive Dark Forest community events. They are also the main promoters in the Chinese-speaking community, translating and writing many Dark Forest-related tutorials and materials, and developing some interesting small plugins.
DF Archon: This is a small group of developers focused on full-chain games, mainly involved in the development and integration of many plugins within the Dark Forest ecosystem. They have also made the tool functions in DF more user-friendly, creating DF-Gaia to better serve developers and players. They also created the first celestial bounty system, DF-ARTEMIS, in the Dark Forest game.
P DAO: This is a relatively mysterious small-scale Chinese organization that appeared in round v0.6.5. Unlike large-scale DAOs with extensive plugin usage and group expansion strategies, P DAO focuses more on efficient collaboration among team members. Through a strategy of full-time voice communication and shift rotation, they achieved excellent results with seven members dominating the top ten in round v0.6.5.
3.5.2. Plugin Ecosystem
The plugin ecosystem of Dark Forest refers to a series of tools created by community developers and players to extend and optimize the game experience. These plugins allow players to more conveniently explore and conquer the universe, and also increase the fun and challenge of the game.
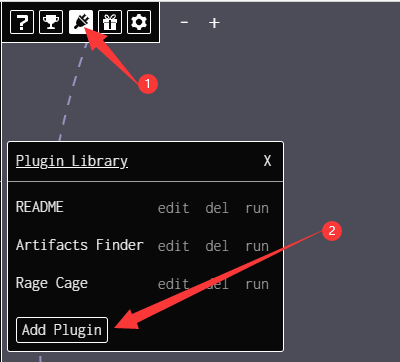
Dark Forest officially encourages and supports community developers and players to participate in the development and use of plugins. To this end, the official team holds a community plugin competition in each game version to select the best plugins and provide rewards and recognition. Currently, the official team has released some commonly used plugins on GitHub and provided documentation and tutorials for plugin development.
Plugins are a very important part of the entire Dark Forest ecosystem, with 55 open-source plugins included in the official plugin library. Here, we will provide a brief overview of the plugins.
Plugins are divided into six categories: Artifacts, Casual, Diplomacy, Productivity, Strategic, and Utilities.
1) Artifacts
There are currently 7 plugins in this category, which are related to the artifacts in the game. These plugins help players discover, extract, install, and manage artifacts to enhance different attributes of planets. For example, Hunt Artifacts and Artifactory are two commonly used artifact plugins.
2) Casual
There are currently 6 plugins in this category, which allow players to enjoy some relaxed and fun experiences in the game, such as listening to music, watching movies, and playing mini-games. For example, Dark Forest Radio and Dark Forest Cinema are two commonly used casual plugins.
3) Diplomacy
There are currently 2 plugins in this category, which allow players to interact with other players in a friendly or hostile manner, such as gifting or attacking planets. For example, Gift Empire and Gift Planet are two commonly used diplomacy plugins.
4) Productivity
There are currently 16 plugins in this category, which allow players to more conveniently control and manage their planets, such as upgrading, distributing, and attacking. For example, Crawl Planets and Distribute Silver are two commonly used productivity plugins.
5) Strategic
There is currently 1 plugin in this category, which allows players to better formulate and execute their own strategies, such as analyzing the enemy situation, planning routes, and optimizing resources.
6) Utilities
There are currently 23 plugins in this category, which provide some practical functions, such as displaying a mini-map, calculating travel time, and exporting maps. For example, Mini-Map and Voyage Time are two commonly used utility plugins.
3.6. Project Data
3.6.1. Social Media Data
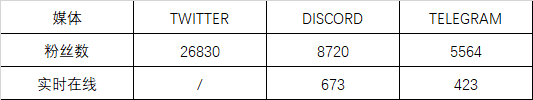
Twitter: The official Twitter account of Dark Forest is @darkforest_eth. As of August 2023, the account has approximately 26,000 followers and has posted about 500 tweets, receiving about 200,000 likes and retweets. However, the account has had a low posting frequency this year, with only 5 tweets, mainly retweeting information from other accounts.
Discord: Dark Forest's Discord account has 8,720 followers. However, the community activity on the server is very low, with very little communication and interaction.
Overall, the social media data for Dark Forest shows a lack of effective operation and maintenance of the game project this year, with overall low community activity. This may affect the development and promotion of the game, and may also lead to a loss of interest and confidence among players. The specific data for each platform is as follows:
4. Industry Space and Potential
4.1. Track Situation
4.1.1. Project Classification
Dark Forest is classified as a blockchain game, specifically a full-chain game.
Blockchain Game Classification
1) On-Chain Assets (OCA)
Most current blockchain games mainly involve the modification of economic models, where currency and some assets are put on the chain. However, the core game logic, computation, narrative, and governance are still centralized. While putting currency and assets on the chain increases circulation efficiency, it may not have the significant impact we imagine, as centralized control policies can still lead to instant asset loss for players.
2) Optional Cosmetic Mints (OCM)
Early traditional games that wanted to quickly enter the web3 often chose the OCM model. In the OCM model, everything is the same as traditional web2 games, and the issuance of assets and currency is centrally managed. However, players have the option to mint some of the assets they hold in the game as NFTs to achieve free circulation. The game developer may also sell certain rights or functionalities in the form of NFTs.
3) Fully On-Chain (FOC)
Fully on-chain games refer to putting all behaviors, interactions, and target states of the game on the chain. This means that the core game logic and asset economic model are processed through the blockchain, using the chain as the game server. All player operations are completed through interaction with smart contracts, and even the game's narrative and governance can be decentralized through DAOs, achieving true decentralized gaming.
4.1.2. Market Size
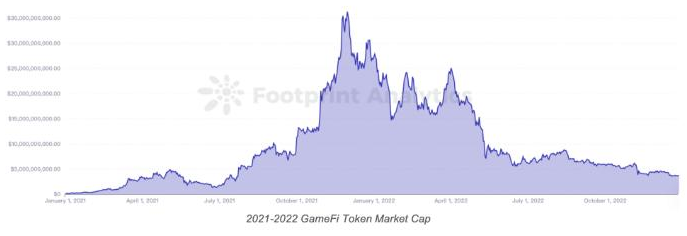
With the wealth effect of the NFT boom in 2021 and the development of the BSC ecosystem, the entire blockchain game market has attracted a lot of attention from project teams and users. According to statistics, the market value of tokens related to blockchain games reached as high as $30 billion in 2021, but has since fallen to around $8.5 billion. Currently, there are 2,519 blockchain game projects, with approximately 820,000 daily active wallet addresses.
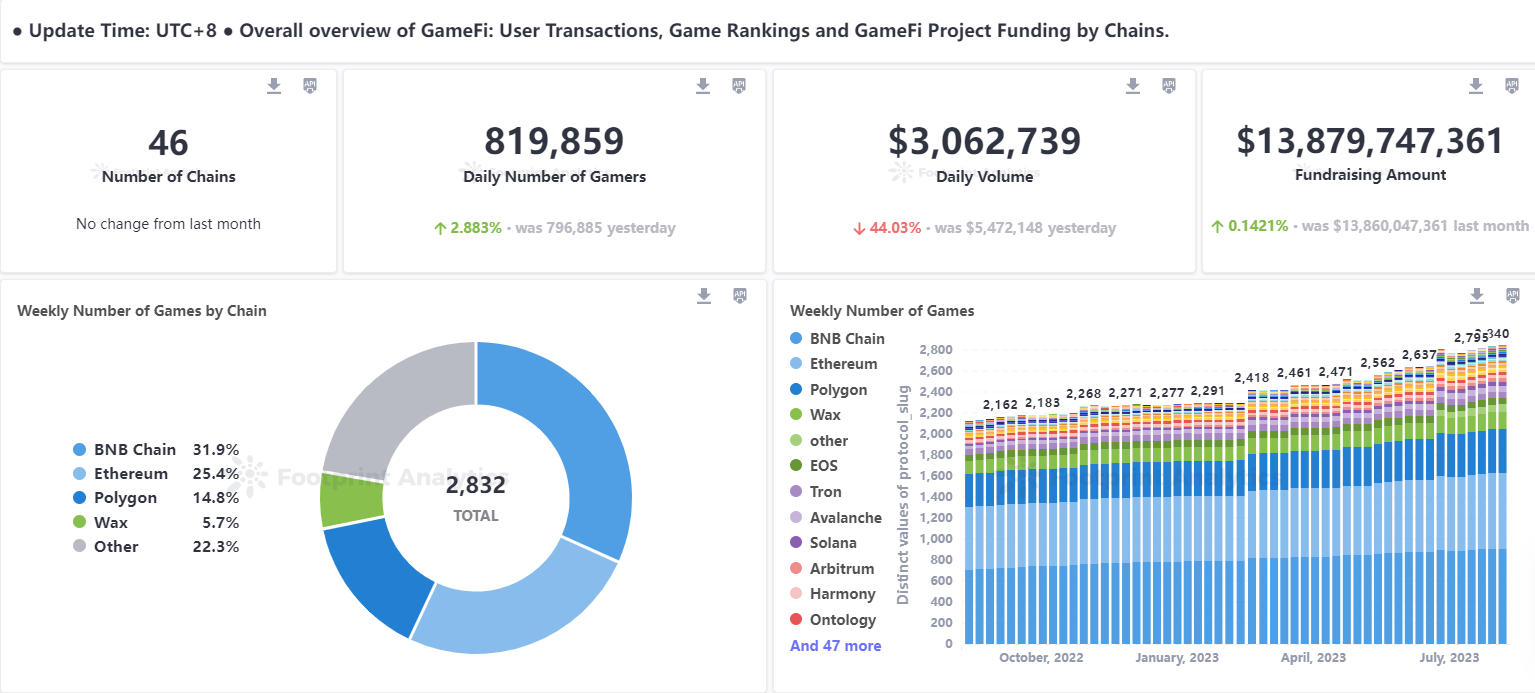
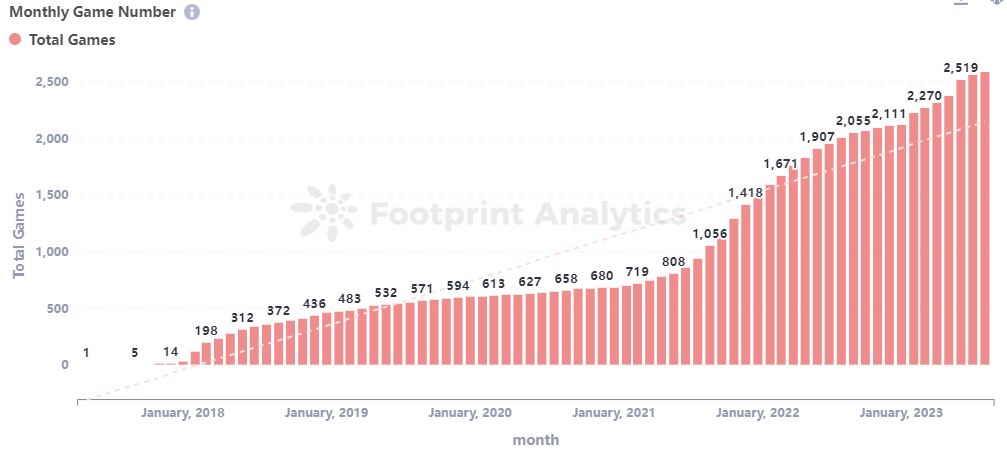
Full-chain games are an emerging and rapidly growing market with tremendous potential and space. Based on the collected data, it can be roughly estimated that the current full-chain game market is still relatively small, but is growing rapidly. Currently, there are approximately 100 projects in the full-chain game market, with about 20 projects having released official or test versions, attracting around 100,000 users and generating approximately $10 million in revenue. These numbers are still relatively small compared to the traditional game market or some on-chain game markets, but they also demonstrate the activity and potential of the full-chain game market.
Currently, full-chain games are a relatively new field, with not many mature and successful cases. They are still in the exploration and experimentation stage and have not yet formed a large scale and influence compared to other types of blockchain games. However, with technological advancements and user acceptance, full-chain games are expected to capture a larger market share in the future.
4.2. Development History of Full-Chain Games
The development and evolution of Dark Forest and Loot, the two pioneering full-chain game types, almost constitute the entire development history of full-chain games. Understanding their birth and maturation process can provide a clearer understanding of why full-chain games exist, their significance, value, and audience.
The first stage is the birth and development of Dark Forest. This stage was mainly driven by the core team of Dark Forest, who used zero-knowledge proof technology to solve the problem of running complex logic on the blockchain and created a unique and captivating space exploration game. The later development of the team has been detailed in the previous section on the Dark Forest team and will not be repeated here.
The second stage is the emergence and derivation of Loot. This stage was mainly driven by the founder of Loot and the community, who used NFT technology to create a novel and open game format, giving rise to a series of related projects and forming a vast and diverse game ecosystem. Loot is a full-chain game based on blockchain and NFT technology. It is an abstract and open role-playing game inspired by traditional RPG games, where players can build their characters by acquiring different equipment, items, and skills, and participate in various adventures and quests. Loot was released in its initial version in August 2021 and was issued on the Ethereum network. It is characterized by providing only abstract text descriptions, without any restrictions on the worldview and rules, completely leaving the interpretation of the text to each participant. Loot is also considered a new way of world-building, somewhat like an epic work similar to Romance of the Three Kingdoms.
The third stage is the competition and cooperation of Mud and Dojo, the two major full-chain game engines. This stage was mainly driven by the developers and users of Mud and Dojo, which are full-chain game engines developed based on the experience and inspiration of Dark Forest and Loot. These engines aim to lower the threshold for full-chain game development and usage, attracting more developers and players to participate in full-chain games.
The timeline of the development of the Dark Forest and Loot camps is as follows:
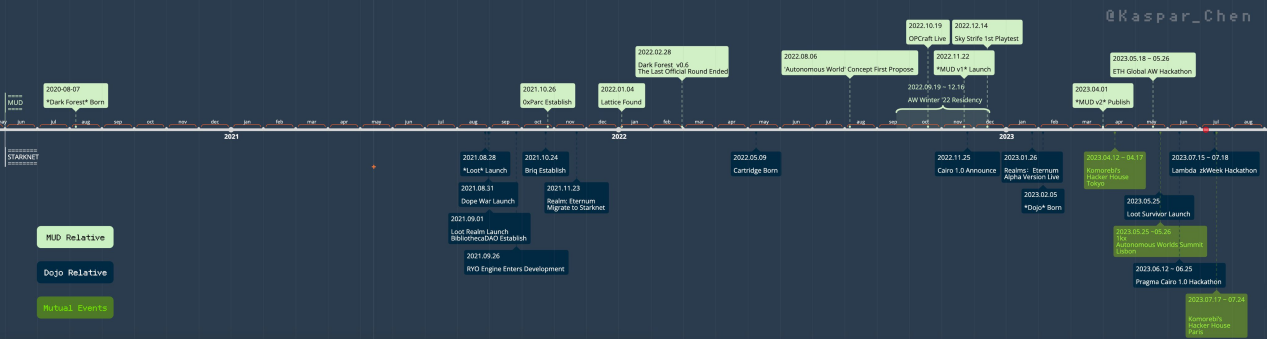
Based on the entire development history of full-chain games, the ecosystems of the Dark Forest and Loot camps can be summarized as follows:
1) Dark Forest Ecosystem:
The Dark Forest ecosystem consists of the 0xPARC, Lattice, and Mud full-chain game engines. These components collaborate to build a powerful Dark Forest ecosystem.
2) Loot Ecosystem:
The Loot ecosystem consists of Loot itself, Genesis adventurer, Realms, and the Dojo full-chain game engine. Loot is a unique NFT, Genesis adventurer is a role generator based on Loot, Realms is a map generator based on Loot, and Dojo is a full-chain game engine. These components complement each other to build a rich Loot ecosystem.
4.2.1. Current Landscape of Full-Chain Games
Currently, based on the entire development history of full-chain games, it is evident that full-chain games are still in a relatively early stage. Limited by the performance and scalability of blockchain, they often cannot achieve complex game content and exquisite artistic expression, but instead focus more on gameplay and technological innovation. As the two starting points of the extension of full-chain games, Dark Forest and Loot, the subsequent full-chain games are inheritors of their will and practitioners of their ideas. Based on the evolution of full-chain games, the existing full-chain game ecosystem can be roughly divided into two categories based on the type of full-chain game engine:
1) Mud-based on Ethereum.
1) Mud is developed on Ethereum by the 0xPARC team, abstracting the core logic and framework of Dark Forest, making it easier for developers to write complex game logic on the chain. Mud released its V2 version in May 2022 and hosted a hackathon, attracting 109 submissions. Mud has also released two demonstration games: OPCraft and Sky Strife. Other representative works in the Mud ecosystem include Autonomous Game of Life, Netherscape, and Realm of Pepe.
2) Another type is the Dojo ecosystem based on StarkNet, abbreviated as the StarkNet series.
Dojo is developed on StarkNet by the Realm, Cartridge, and Briq teams. It is fully compatible with ZK technology and can automatically help developers generate the proofs needed for ZK. Dojo released its first version at the end of 2022 and has three flagship projects: Kakarot, Madara, and Dojo itself. Dojo also released its first game: Loot Survivor, which inherits Loot's text style and open world, allowing players to freely create and explore. Representative works in the StarkNet series include BibliothecaDAO, Cartridge, Briq, Influence, and Topology.
Mud and Dojo, as full-chain game engines, provide powerful tools and platforms for developers, promoting the further development of the game ecosystem. The formation of these ecosystems has brought new possibilities to the blockchain gaming field and has driven the development of NFTs and full-chain games.
4.2.2. Comparison of Mud Series and StarkNet Series
In terms of style, Mud is more like the Ethereum school, with a pure lineage, strong ideological consciousness, solid product concepts, and a strong ability to attract developers. It aims to build underlying infrastructure and combines ideology and practice through narrative construction, idea dissemination, product display, and hackathons, attracting the participation and contributions of many developers and players. On the other hand, Dojo is more like the grassroots and unconventional school, inheriting Loot's bottom-up philosophy and leaning towards mutual cooperation and alliance between different projects and communities.
In terms of ecosystem infrastructure, the EVM ecosystem's infrastructure system is more complete, with more tools and reference content available for development. However, due to the broader development of the EVM ecosystem, attention has not yet focused on the relatively early field of full-chain games. The StarkNet ecosystem is more concentrated and places relatively more emphasis on full-chain games. Founder Eli Ben-Sasson has mentioned full-chain games multiple times in his speeches, indicating that StarkNet will undoubtedly invest a higher proportion of resources in supporting full-chain games in terms of infrastructure and resources.
In terms of content resources, the Mud ecosystem has fewer available resources, making it difficult to produce larger and deeper games in the short term. However, it is known that CCP Games, the developer behind EVE Online, has shown great interest in Mud and has already started developing a Web3 version of EVE. The StarkNet ecosystem, on the other hand, has the strong content IP of Loot, as well as some independent projects such as Dope War and Influence, which have deeper and more complete content narratives. However, the Cairo language is still in a phase of frequent updates and iterations, bringing considerable uncertainty to development work.
In summary, both sides have their own strengths. The Mud ecosystem has a larger number of developers and a more mature infrastructure system but lacks sufficiently attractive content resources. The Dojo ecosystem has richer content IP and a more concentrated community atmosphere but lacks stable and complete development tools and documentation. I believe that full-chain games still have great potential and space, and they can bring new innovation and change to the gaming industry.
5. Token Economy Model Analysis
5.1. Total Token Supply and Distribution
As a project with a strong crypto spirit, Dark Forest is currently mainly operated and maintained by the community and has not issued its own tokens yet, but may do so in the future. In previous test versions, xDAI was used as the universal currency in the game. xDAI is the native token of the xDAI sidechain, which is compatible with and interoperable with the Ethereum mainnet, aiming to provide fast, cheap, and stable transaction services. The main role of xDai is to serve as the fuel token in the Dark Forest game, used to pay for various fees in the game, with specific functions including:
- Incentivizing players to engage in more game activities and interactions, increasing the game's activity and interest.
- Maintaining the security and stability of the game by charging reasonable fees to prevent malicious behavior and network congestion.
- Promoting the scalability and composability of the game by supporting cross-chain interactions and contract calls to achieve more game functions and possibilities.
5.2. Token Value Capture
Dark Forest may issue its own tokens in the future. According to the official blog, it has several goals:
- Incentivizing participation: Rewarding in-game activities and contributions with tokens to increase the game's activity and stickiness, cultivate and expand the game's community and ecosystem.
- Distributing rights: Implementing decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) governance through tokens, allowing token holders to participate in the governance and profits of the game, increasing the transparency and fairness of the game, and inspiring a sense of responsibility and belonging among players and community members.
- Creating value: Implementing metacoin and culture token through tokens, allowing players to freely transfer and use their assets and data between different virtual worlds, expressing and showcasing their identity and personality, increasing the diversity and personalization of the game, shaping and spreading the game's brand and culture.
6. Preliminary Value Assessment
Dark Forest has not yet officially launched or issued its own tokens, making it difficult and subjective to assess its value. However, we can conduct a preliminary value assessment of Dark Forest based on some basic principles and methods to understand its potential market value and competitiveness. Here are some principles and methods that may be used:
What stage is the project in? Is it in the mature stage or in the early to middle stage of development?
According to the information found, Dark Forest is currently in the development stage, not yet officially launched, and has undergone multiple rounds of public testing. It has not generated stable income and profits, and there are many features and optimizations that need to be improved. There are also many new gameplay and creative ideas to explore. Dark Forest has not yet formed a stable and large user base, nor has it formed a complete and active community and ecosystem.
Does the project have reliable competitive advantages? Where do these competitive advantages come from?
Dark Forest has strong competitive advantages, mainly derived from its technology, culture, and community aspects.
Technological innovation: Dark Forest is the first blockchain project to use zkSNARKs to implement hidden information games, demonstrating high technological innovation and complexity. To this day, Dark Forest can still be considered one of the most complex applications in the entire blockchain.
Cultural influence: Dark Forest is inspired by Liu Cixin's science fiction novel "The Dark Forest," which has a wide readership and fan base globally. The game's setting and gameplay resonate with the Dark Forest principle described in the novel, allowing players to experience the cosmic adventures and civilization conflicts depicted in the novel. Dark Forest has attracted not only science fiction and blockchain enthusiasts but also some novel authors and critics, adding cultural value and influence to the game.
Community participation: Dark Forest is a completely open-source and open project, allowing anyone to participate in the game's development and improvement.
What are the main variable factors in the project's operations? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
The main variable factors in Dark Forest's operations are user numbers, user satisfaction, user retention rates, and user activity. These factors can be quantified and measured using various data indicators, such as registered users, daily active users, monthly active users, average online time, average transaction volume, average invitation code price, average NFT price, and more.
What is the project's management and governance approach? How is the level of DAO governance?
Dark Forest's management and governance approach is decentralized and community-driven. Dark Forest welcomes players to participate in the game's creation and improvement through developing plugins and tools, creating art and literary works, showcasing planets and fleets, engaging in warfare and diplomacy, and more.
7. Project Challenges and Risks
Dark Forest is highly innovative and cutting-edge in the blockchain gaming field, but it also faces some challenges and risks:
1) Stagnation in Dark Forest's development, in a maintenance state:
This point has been detailed in the team development introduction section. Since 2022, the team's focus has shifted from game development and construction to community development and governance, led by Brian Gu's deep interest and research background in zero-knowledge proof technology. While this approach aligns with cryptographic principles in terms of technology and user experience, it also brings a degree of uncertainty to the project's future, requiring further examination and evaluation.
2) Incomplete underlying infrastructure and ecosystem:
Dark Forest relies on the performance and stability of the Ethereum network. However, Ethereum still faces issues such as congestion, high fees, and scalability challenges, which can affect the game's smoothness, playability, and sustainability. For example, when the Ethereum network is congested, player actions may be delayed or fail, leading to a decrease in the game experience. When Ethereum fees are too high, players may be unwilling to engage in on-chain interactions, leading to a decrease in game activity. When Ethereum faces scalability challenges, the game may encounter bottlenecks, limiting its scale. Additionally, due to the immaturity of blockchain game development tools, the Dark Forest development team needs to spend more time and effort writing and maintaining smart contract code, increasing development costs and risks.
3) Choice of game genre and game logic design:
Dark Forest is a strategy game that adapts to the characteristics of blockchain by extending energy transmission time, setting planet levels, and introducing a plugin system to increase the game's interest and strategic elements. However, these designs also bring some challenges. For example, the long energy transmission time may slow down the game pace, potentially causing some players to feel bored or lose patience. The differences in planet levels may affect game balance, leading to the marginalization or abandonment of some players. The open nature of the plugin system may lead to cheating or unfair situations, causing dissatisfaction or loss of trust among some players.
4) Challenges inherent in full-chain properties:
As a full-chain game, Dark Forest faces challenges related to the performance, scalability, and user experience of blockchain technology, as well as the integration of game logic and economic models on the chain. These challenges include technical complexity, user adoption, and regulatory considerations.
Dark Forest has placed the entire game logic and data on the chain, giving the game advantages such as fairness, transparency, immutability, and composability. However, this also means that the development team has almost completely lost control and adjustment capabilities over the game. For example, if the game encounters a bug or vulnerability, the development team may not be able to fix or roll back it in a timely manner, leading to game disruption or loss. If the game needs to be updated or iterated, the development team may not be able to easily modify or replace smart contract code, making it difficult for the game to adapt to changes or meet demands. If the game involves economic models or token distribution, the development team may not be able to effectively manage or adjust the game's supply-demand relationship or incentive mechanism, leading to issues such as inflation or collapse.
8. References
https://zkga.me/ Dark Forest Project Official Website
https://0xparc.org/ 0xparc Project Official Website
https://blog.zkga.me/ Dark Forest Project Blog
https://plugins.zkga.me/ Dark Forest Official Plugin Library
https://twitter.com/darkforest_eth Dark Forest Twitter
https://www.panewslab.com/zh/articledetails/o7rpu2qh.html Dialogue with Mask Network: Why is Full-Chain Gaming Suddenly Popular?
https://medium.com/dfdao/dark-forest-community-new-years-round-7cb16dd7b575 Dark Forest Medium
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vMwnVLJ8Yyo Dark Forest Introduction Video
Investment Risk and Disclaimer
The content analysis provided in this report is for reference only and does not constitute any form of investment advice or decision-making basis. We strongly advise against making any investment decisions based on this report to avoid potential risks. WJB and the report authors are not responsible for the investment results based on this report.
The preparation time of this report is as of the date shown, and subsequent changes in market or economic conditions may result in changes to the content. The graphics, charts, and other visual aids in the report are for reference only and cannot be used as the basis for making investment decisions. Any graphics, charts, or other visual aids in the report cannot cover all the factors and variables needed to make such decisions. Please note that WJB will not assist anyone in making specific investment decisions.
Some of the discussions in this report may be WJB's assumptions about future expectations and other forward-looking views. However, these assumptions and views are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties that may result in significant differences between actual results, performance, or events and the stated views and assumptions.
All speculations, forecasts, and estimates contained in this report are based on certain assumptions and are speculative in nature. These forward-looking statements may prove to be incorrect and may be affected by incorrect assumptions or known or unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, most of which are beyond control. It is expected that some or all of these forward-looking assumptions will not be realized, or there will be significant differences from actual results.
Copyright Information
This report is copyrighted by WJB only. Without written permission, no organization or individual may infringe on WJB's copyright through reprinting, copying, quoting, or redistributing in any form.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



