1. Background
First of all, with the continuous development of the blockchain industry, various forms of chains have emerged, such as Layer1, Layer2, Layer3, sidechains, Rollups, etc. There are homogeneous chains as well as heterogeneous chains, and on each blockchain, there are many different protocols.
These different blockchains and protocols have fragmented the world of blockchain into isolated islands of information, with a large amount of encrypted assets distributed across these different chains and protocols, undoubtedly reducing the efficiency of capital utilization.
The emergence of cross-chain bridges can build bridges between these different chains, allowing assets from one chain to be bridged to other blockchains.
For example, the appearance of the Base cross-chain bridge, a Layer 2 network launched by Coinbase, can bridge encrypted assets from other chains to the Base network, allowing users to enjoy some early benefits of the Base chain. At the same time, through the cross-chain bridge, assets on the Base chain can also be bridged to other blockchains.
The emergence of cross-chain bridges greatly improves the efficiency of capital utilization. 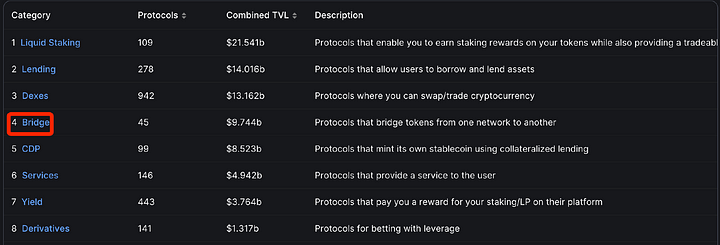
According to data statistics from defillama, the total value locked (TVL) of cross-chain bridge ranks fourth in the current DeFi landscape, reaching a volume of 9.7 billion US dollars, second only to the Dex track.
In addition, in the cross-chain bridge track, there are generally issues such as low security, high fees, and slow cross-chain speeds. Stargate was developed in such a background.
2. Overview of Stargate Protocol

Stargate Finance is a multi-chain cross-chain bridge protocol based on LayerZero, created by LayerZero Labs in March 2022. It is also the first DApp based on the LayerZero protocol, and it is a protocol that can achieve asset transfers between multiple blockchains.
The goal of Stargate is to simplify the process of transferring assets from one blockchain to another, eliminating the cumbersome steps of locking, minting, burning, and redeeming to achieve the convenience of completing transfers in a single transaction.
Since Stargate is a cross-chain protocol built on LayerZero, discussing Stargate requires starting from LayerZero.
What is LayerZero
LayerZero is an omnichain interoperability protocol that builds a new type of ultra-light node mode, providing a secure and reliable infrastructure for various cross-chain protocols. 
In theory, LayerZero can achieve message transmission on any chain that supports smart contracts. For example, when a user sends a message on Chain A, this message can be transmitted to Chain B, allowing the smart contract on Chain B to perform the corresponding operation. LayerZero can achieve information communication between different chains, including asset transfers between different chains.
LayerZero is not a public chain or an application ecosystem, but a more fundamental protocol. The positioning of LayerZero is similar to the TCP protocol in the transport layer of the Internet, upon which many different DApps can be built.
How LayerZero Achieves Omnichain Interoperability
First, let's understand the differences between full nodes, light nodes, and ultra-light nodes.
- Full Node: Nodes that synchronize all blockchain data, storing both block headers and specific transaction information.
- Light Node: Only stores a small part of blockchain data, such as block headers and some other information, without storing specific transaction information within the blocks.
- Ultra-Light Node: Does not retain all block headers, but instead transmits streamable block headers on demand through oracles, thereby synchronizing off-chain entities more efficiently to achieve the required state.
The omnichain interoperability of LayerZero is achieved by deploying an Endpoint (client) on each chain, which runs an ultra-light node (ULN) and then uses an Oracle to transmit block headers containing cross-chain information on demand (rather than transmitting all block headers in sequence to reduce costs), and then uses a Relayer to transmit transaction proofs (Proof information), both of which mutually verify to ensure the correctness of cross-chain information.
The following diagram shows the process of a user application (UA) on Chain A sending a message to a user application on Chain B through LayerZero. 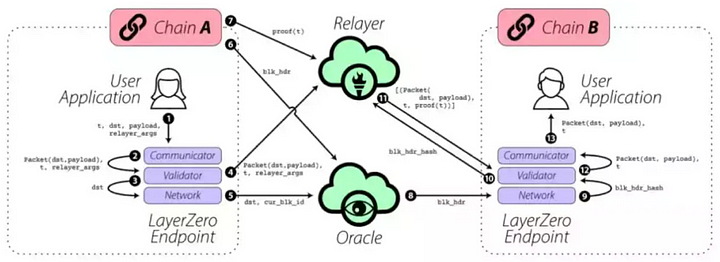
The omnichain interoperability of LayerZero is achieved through the combined action of these three core components: Endpoint, Oracle, and Relayer.
Based on this omnichain interoperability of LayerZero, many previously difficult-to-implement businesses can be realized, such as omnichain cross-chain bridges, cross-chain transactions, and cross-chain lending. Stargate is the official cross-chain bridge of LayerZero, and it is also the first DApp based on the LayerZero protocol, referred to by the LayerZero team as the first solution to the "three difficulties of bridging dilemma".
3. How Stargate Achieves Cross-Chain
It is well known that there exists an "impossible triangle" theory in public chains, referring to the decentralization level, security, and scalability, with a public chain being able to satisfy at most two of these aspects simultaneously.
For example, in the case of Bitcoin, its decentralization level and security are relatively high, but its scalability is relatively poor. For many public chains, although scalability and security have been improved, they sacrifice decentralization.
The "impossible triangle" dilemma in the public chain field can be solved through modular public chains.
Similarly, in the cross-chain field, there is also an "impossible triangle" theory, which includes:
- Ensuring instant guaranteed finality;
- Unified liquidity;
- Native assets.
 In other words, in most cross-chain bridges, at most only one or two of these points can be achieved at the same time, and all three cannot be achieved at their best.
In other words, in most cross-chain bridges, at most only one or two of these points can be achieved at the same time, and all three cannot be achieved at their best.
However, the Stargate cross-chain bridge built on the LayerZero protocol can simultaneously satisfy these three major characteristics of cross-chain bridges, namely ensuring instant guaranteed finality, achieving unified liquidity, and supporting native assets.
In many common cross-chain bridges, the method used is "locking + minting + burning", meaning that assets are first locked in the source chain and synthesized in the target chain, and when the assets need to be transferred back to the source chain, the previously synthesized assets need to be burned, and the original tokens redeemed. This does not actually achieve instant finality.
Stargate has developed a new resource balancing algorithm that can unify the native liquidity of all blockchains, while also providing instant guaranteed finality.
In terms of asset cross-chain, Stargate adopts a liquidity swap approach, which is different from most cross-chain bridges that establish independent liquidity pools for specific networks. Stargate uses a unified liquidity pool to support asset cross-chain operations.
In other words, Stargate can achieve unified liquidity pool management, and each chain can also access the liquidity on other chains.
For example, if there is a USDT liquidity pool on Chain A, then USDT-related transactions initiated on other chains can borrow and return the USDT liquidity on Chain A, thereby allowing the algorithm to maintain liquidity balance in the face of imbalanced transaction volumes, thus improving the efficiency of capital utilization.
However, when multiple chains share a single liquidity pool, there is a risk of transaction failures due to insufficient liquidity depth, as the number of users and parallel transactions will increase, reducing the liquidity in the pool and causing some cross-chain transactions to fail.
For example, if there is 100 USDT liquidity on Chain A, and Chain B requests 60 USDT liquidity, while Chain C requests 50 USDT liquidity, the total USDT liquidity on Chains B and C exceeds the total USDT liquidity on Chain A, causing one of the cross-chain requests to fail.
To address this, Stargate has introduced a "resource balancing algorithm" to solve the above problem. Stargate divides the liquidity pool on each chain into multiple intervals, also known as soft partitions.
For example, the 100 USDT on Chain A is soft partitioned into 50 USDT on Chain B and 50 USDT on Chain C.
To ensure that liquidity can more likely meet cross-chain demands, the protocol allows for the "borrowing" and "returning" of liquidity between different chains, thereby balancing liquidity in the face of imbalanced transaction volumes.
When a cross-chain request is received, the resource balancing algorithm examines the liquidity of each interval and allocates the assets deposited by users to supplement intervals with insufficient liquidity, thereby avoiding transaction failures caused by liquidity depletion.
If cross-chain requests on Chain B are more frequent, it can be assigned a higher weight. When new liquidity comes in, in addition to filling the liquidity gap of each chain, the excess liquidity will be virtually allocated to other chains according to pre-assigned weights.
1. Background
Furthermore, Stargate has introduced Equilibrium Fees (incentivizing the even distribution of liquidity across different chains).
For example, when there is an excessive outflow of funds from Chain A, continuing to transfer funds from Chain A will incur higher fees, allowing the liquidity on each chain to be maintained through users' spontaneous trading behavior.
Overall, Stargate improves the efficiency of capital utilization through a "resource balancing algorithm," utilizing the liquidity of single-coin assets as a complete liquidity pool on each chain, minimizing the risk of depletion on a single chain, and achieving timely allocation and on-demand mobilization under a unified liquidity pool.
4. Team
The specific number of team members at Stargate Finance is currently unknown. However, given that Stargate Finance is the first application on LayerZero Labs, it is known from early community feedback that Stargate Finance has a close relationship with LayerZero and has a certain overlap in development personnel. The whitepaper for Stargate was jointly written by the three co-founders of LayerZero.
Therefore, in terms of the team, we can start with the team members of LayerZero.
The team has three co-founders, with Bryan Pellegrino serving as CEO, Ryan Zarick as CTO, and Caleb Banister as another member.
All three graduated from the University of New Hampshire with a degree in Computer Science, and they have had significant professional intersections after graduation.
The specific profiles of the founding team members are as follows:
Ryan Zarick:
Co-founder and CTO of LayerZero Labs, with a master's degree in Computer Science from the University of New Hampshire.
From 2011.11 to 2013.03, he served as the CTO of BuzzDraft; from 2010.09 to 2020.13, he was a co-founder of Coder Den; from 2018.01 to 2020.03, he was a co-founder of 80Trill; from 2019.06 to 2021.01, he was a co-founder of Minimal AI; and in 2021, he founded LayerZero and served as CTO.
Bryan Pellegrino:
Co-founder and CEO of LayerZero Labs, with a degree in Computer Science from the University of New Hampshire.
From 2010.10 to 2013.01, he was a co-founder and COO of Coder Den; from 2011.06 to 2013.01, he was the CEO of BuzzDraft; from 2017.10 to 2019.08, he was a co-founder of OpenToken; from 2016.06 to the present, he has been the Chief Engineer of Rho AI; and in 2021, he founded LayerZero.
Before founding LayerZero, Pellegrino was a professional poker player and co-founded a machine learning company with Ryan Zarick, successfully selling a set of machine learning tools to an MLB team.
Caleb Banister:
Founder of LayerZero Labs, with a degree in Computer Science from the University of New Hampshire.
From 2005.06 to 2010.12, he served as a software developer at the UNH Interoperability Lab; from 2010.09 to 2021.02, he was a co-founder of Coder Den; from 2018.03 to 2021.02, he was a co-founder of 80Trill; from 2019.06 to 2021.02, he was a co-founder of Minimal AI; and in 2021, he founded LayerZero.
From the resumes of the three core members of the team, it can be seen that in 2021, the three of them reunited and co-founded LayerZero Labs, and the team has outstanding innovative capabilities in machine learning algorithms and blockchain development, as well as long-term cooperation and years of development experience and successful entrepreneurial experience.
Additionally, 0xmaki, co-founder of Sushiswap, has joined the team full-time and serves as the Chief Strategic Advisor, helping to build the cross-chain ecosystem of LayerZero.
5. Basic Products
1. Cross-Chain Functionality (Transfer)
The cross-chain functionality is the most important feature of Stargate, and it is very intuitive in the user interface. It can achieve 1:1 cross-chain exchange of native assets and ensure instant finality.
Currently, the available chains include Ethereum mainnet, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, Fantom, Metis, Polygon zkEVM, zkSync Era Mainnet, and the recently supported Base network.
The supported cross-chain assets on the Stargate platform include stablecoins, ETH, as well as tokens such as CAKE, STG, CRV, and RDNT.
2. Providing Liquidity (Pool)
Liquidity providers can add liquidity to Stargate and receive rewards in each cross-chain (transfer) transaction.
Users can choose different liquidity pools to add liquidity. Currently, the main pools are stablecoin pools. After providing liquidity, users receive LP tokens and earn rewards from the protocol's cross-chain transaction fees.
3. Liquidity Mining (Farming)
Liquidity providers on Stargate can stake their LP tokens to earn STG rewards.
After obtaining LP tokens from providing liquidity, users can use them for liquidity mining and earn STG rewards. The current APY can be as high as over 12%, which is considered a very good return for stablecoin mining.
4. STG Staking (Stake)
Users can stake their STG tokens and choose the staking duration. The longer the staking period, the more veSTG tokens the staker can receive.
veSTG will serve as the governance token of the Stargate platform, and holding more veSTG tokens will provide more governance weight.
6. Token (STG) Economic Model
The token of the Stargate platform is STG, with a total supply of 1 billion tokens, distributed as follows:
- 17.50% — Stargate Core Contributors (fully locked for 1 year, followed by linear unlocking over 2 years);
- 17.50% — Investors (fully locked for 1 year, followed by linear unlocking over 2 years);
- 65.00% — Allocated to the community, dedicated to realizing the vision of the protocol: making cross-chain liquidity transfer a seamless single transaction process.
The community allocation details are as follows:
1) 15.00% — Stargate Protocol Launch;
a. 10.00%: STG launch auction purchases (snapped up by two addresses from Alameda).
b. 5.00%: STG-USDC pool on Curve.fi.
2) 15.95% — Joint curve auction, post-release;
3) 2.11% — Initial emission plan;
4) Up to 1.55% increase on DEX on BNB, Avalanche, Matic, Arbitrum, Optimism, and Fantom;
5) Remaining 30.39%: Dedicated to future community initiatives and the long-term success of Stargate.
Token release schedule:
STG tokens can be staked to obtain governance tokens veSTG, and holding these tokens can be used for voting. The longer the staking period, the greater the voting power the staker will receive.
7. Current Development and Competitive Landscape
1. Trading Volume
According to data from defillama, the total trading volume of cross-chain bridges in the last 24 hours has reached 170 million USD, and the total cross-chain trading volume of Stargate has exceeded 72 million USD, accounting for nearly 50% of the cross-chain trading volume, far higher than the trading volume of other cross-chain protocols.
Additionally, in all cross-chain bridges on Polygon, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Fantom, and BSC chains, Stargate's trading volume ranks first, indicating Stargate's industry position. 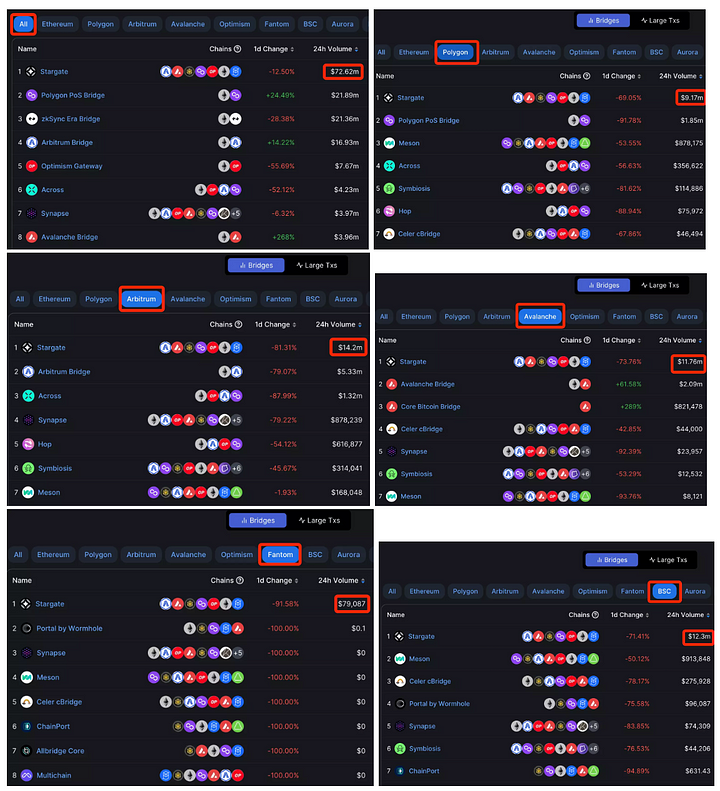
2. TVL
Stargate's total value locked (TVL) across all chains exceeds 300 million USD, far surpassing the TVL of other cross-chain bridges such as Hop. 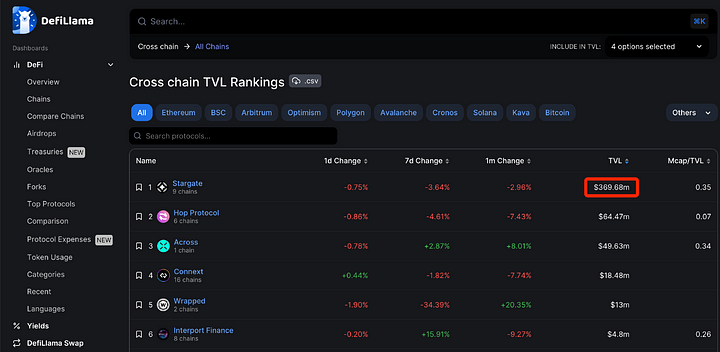
Even within the entire DeFi protocols, Stargate's TVL ranks 30th. 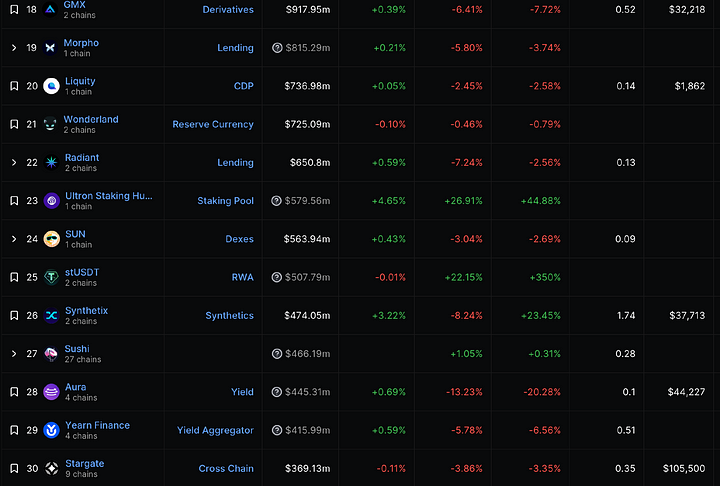
3. Active Users
According to data from tokenterminal, Stargate has reached a daily active user count of 48,000, which is nearly ten times the daily active user count of other cross-chain bridges. The trend chart shows a significant increase in Stargate's active users starting from the end of March. 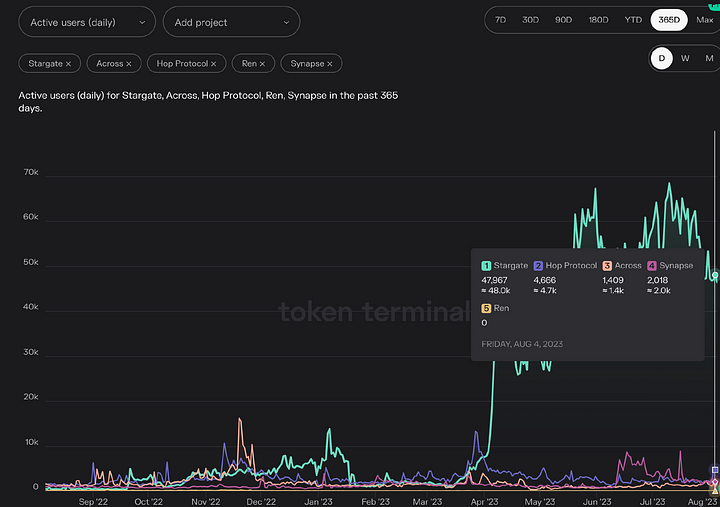
4. Fees
Over the past year, Stargate's generated fees have been continuously increasing, with a surge of over 400% in the past six months, indicating a relatively fast growth rate. 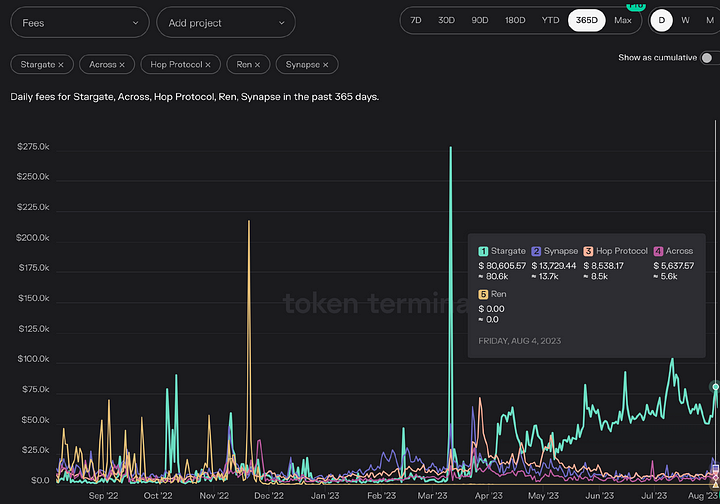
In comparison to other cross-chain bridges, Stargate's daily generated fees have exceeded 80,000 USD, far surpassing the daily generated fees of other cross-chain bridges.
5. Financial Analysis
From Stargate's financial situation, it can be seen that earnings have been continuously increasing in recent months, with significant monthly increases, especially in July, where earnings have exceeded 1 million USD.
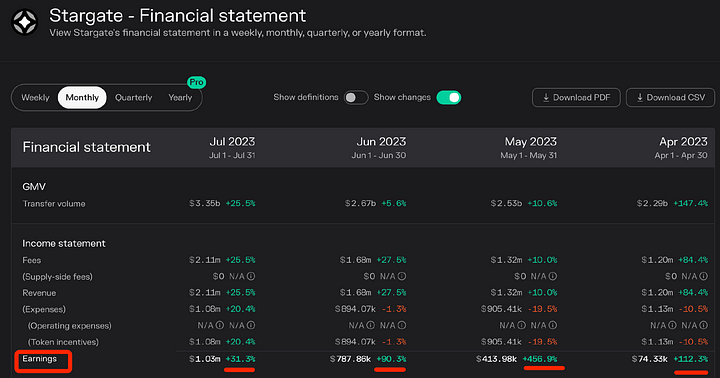 The trading volume in recent months has also been increasing, with the trading volume reaching over 900 million USD in March, and reaching 2.6 billion USD in June, nearly three times the volume in March.
The trading volume in recent months has also been increasing, with the trading volume reaching over 900 million USD in March, and reaching 2.6 billion USD in June, nearly three times the volume in March. 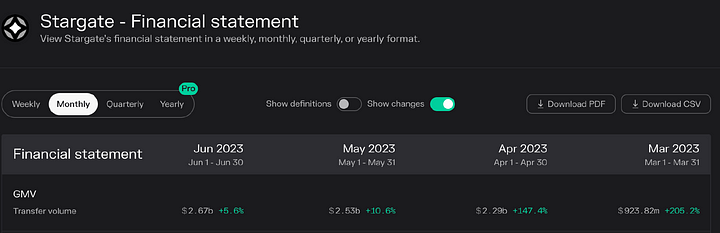
The number of active users each month has also been continuously increasing. 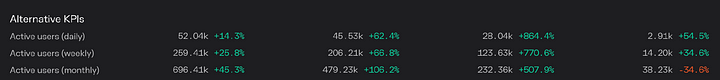
From Stargate's financial data, it can be observed that metrics such as active users, trading volume, and earnings are all continuously increasing, indicating that Stargate is experiencing rapid growth to a certain extent.
Eight, Future Potential
The native token of the Stargate platform is STG, and its functionality is similar to Curve. Users can lock their tokens to obtain veSTG for voting, with the weight of veSTG allocated based on the lock-up period.
The platform primarily generates profits by collecting transfer fees. Each non-STG token transfer incurs a platform fee of 0.06%.
In addition to the 0.06% fee for non-STG token transfers, cross-chain transactions may also incur pool rebalancing fees, with the specific fees depending on the imbalance of pool weights between the source and target chains.
From the analysis data above, it can be seen that all indicators of Stargate are continuously increasing.
Moreover, as the official cross-chain bridge of LayerZero, Stargate benefits from the official endorsement of LayerZero, which greatly promotes its development and can bring in a large number of users. Stargate is a leader among multi-chain cross-chain protocols.
The future is inevitably an era of coexistence of multiple chains, and there will be more diverse forms of blockchains emerging. With a valuation of over 3 billion USD, LayerZero, as a full-chain interoperability protocol, will connect assets from more diverse chains.
As LayerZero supports more chains, Stargate will also support more chains and tokens for cross-chain transactions, continuously increasing Stargate's trading volume, user count, TVL, and driving its development.
Furthermore, as a direct descendant of LayerZero, Stargate's role extends beyond just being a cross-chain bridge. From Stargate's documentation, it is evident that Stargate aims to be a technology provider for asset cross-chain transactions, enabling more projects to easily utilize Stargate for cross-chain functionality.
Therefore, in addition to 2C business, Stargate also has 2B and even 2B business models that have more imaginative space than 2C. Based on Stargate, more complex DApps can be built.
Currently, the market value of STG is only slightly over 100 million USD, ranking 173rd in market value. STG has significant potential for future growth. Hot Air Balloon will continue to monitor the latest developments of Stargate and share them with everyone in a timely manner.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




