The third quarter of 2025 is of key significance for the cryptocurrency market as it bridges the previous and upcoming periods: it carries forward the rebound of risk assets since July and further confirms the macro turning point after the interest rate cut in September. However, entering the fourth quarter, the market simultaneously suffers from shocks of macro uncertainty and the outbreak of structural risks within the cryptocurrency market, leading to a sharp reversal in market rhythm and breaking the original optimistic expectations.
As the pace of inflation recedes, coupled with the longest government shutdown in U.S. history in October and escalating fiscal disputes, the latest FOMC meeting minutes clearly signal "caution against premature rate cuts," causing the market's judgment on policy paths to swing dramatically. The previously clear narrative of "the rate cut cycle has begun" is quickly weakened, and investors start to reprice potential risks such as "higher rates lasting longer" and "soaring fiscal uncertainty," significantly increasing the volatility of risk assets. In this context, the Federal Reserve also deliberately suppresses excessive market expectations to avoid premature loosening of financial conditions.
As policy uncertainty rises, the prolonged government shutdown further exacerbates macro pressures, creating a dual squeeze on economic activity and financial liquidity:
- GDP growth is significantly dragged down: The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the government shutdown will lower the annualized growth rate of real GDP in Q4 2025 by 1.0% - 2.0%, equivalent to billions of dollars in economic losses.
- Key data missing and liquidity contraction: The shutdown prevents the timely release of key data such as non-farm payrolls, CPI, and PPI, leaving the market in a "data blind spot," increasing the difficulty of policy and economic judgments; at the same time, the interruption of federal spending tightens short-term liquidity passively, putting pressure on risk assets.
Entering November, discussions within the U.S. stock market about whether the AI sector has reached a phase of overvaluation continue to heat up, with the volatility of high-valuation tech stocks rising, affecting overall risk appetite and making it difficult for crypto assets to gain spillover support from the U.S. stock market's Beta side. Although the financial market's early pricing of rate cuts in the third quarter significantly boosted risk appetite, this "liquidity optimism" was clearly weakened in the fourth quarter due to the government shutdown and repeated policy uncertainties, leading risk assets into a new round of repricing.
Alongside rising macro uncertainties, the cryptocurrency market also faces its own structural shocks. Between July and August, Bitcoin and Ethereum both broke historical highs (Bitcoin surged above $120,000; Ethereum reached about $4,956 at the end of August), and market sentiment became temporarily positive.
However, the large-scale liquidation event at Binance on October 11 became the most severe systemic shock to the cryptocurrency industry:
- As of November 20, both Bitcoin and Ethereum experienced significant pullbacks from their highs, weakening market depth and expanding the divergence between bulls and bears.
- The liquidity gap caused by the liquidation weakened overall market confidence, with a noticeable decline in market depth in early Q4, while the spillover effect of the liquidation intensified price volatility and increased counterparty risk.
At the same time, the inflow of funds into spot ETFs and crypto stocks (DAT) significantly slowed in the fourth quarter, with insufficient institutional buying power to offset the selling pressure from liquidations, leading the cryptocurrency market to gradually enter a phase of high turnover and volatility since late August, ultimately evolving into a more pronounced adjustment trend.
Looking back at the third quarter, the rise in the cryptocurrency market was partly due to the overall rebound in risk appetite and partly influenced by the positive impact of listed companies promoting DAT (Digital Asset Treasury) strategies. These strategies improved institutional acceptance of cryptocurrency asset allocation and enhanced the liquidity structure of certain assets, becoming one of the core narratives of the quarter. However, as the liquidity environment tightened and price corrections intensified in the fourth quarter, the sustainability of DAT-related buying began to weaken.
The essence of the DAT strategy lies in companies incorporating part of their token assets into their balance sheets, enhancing capital efficiency through on-chain liquidity, yield aggregation, and staking tools. As more listed companies and funds attempt to collaborate with stablecoin issuers, liquidity protocols, or tokenization platforms, this model is gradually transitioning from the conceptual exploration stage to the practical implementation stage. In this process, assets such as ETH, SOL, BNB, ENA, and HYPE exhibit trends of "token-equity-asset" boundary integration across different dimensions, reflecting a certain bridging role of digital asset treasuries in the macro liquidity cycle.
However, in the current market environment, the valuation framework of innovative assets related to DAT (such as mNAV) generally falls below 1, indicating a market discount on the net value of on-chain assets. This phenomenon reflects investors' concerns about the liquidity, yield stability, and sustainable valuation of related assets, and also suggests that the asset tokenization process faces certain adjustment pressures in the short term.
At the sector level, several segments demonstrate sustained growth momentum:
- The stablecoin sector continues to expand in market capitalization, surpassing $297 billion, further strengthening its role as a funding anchor in a macro uncertainty environment.
- The Perp sector, represented by HYPE and ASTER, has achieved significant increases in activity through trading structure innovations (such as on-chain matching, funding rate optimization, and tiered liquidity mechanisms), becoming the main beneficiary of capital rotation during the quarter.
- The prediction market sector has reactivated under macro expectation fluctuations, with Polymarket and Kalshi achieving record-high transaction volumes, becoming immediate indicators of market sentiment and risk appetite.
The rise of these sectors indicates that capital is shifting from a single price game to a structured allocation around three core logics: "liquidity efficiency—yield generation—information pricing."
Overall, the rhythm of the cryptocurrency and U.S. stock markets in the third quarter of 2025 was misaligned, transforming in the fourth quarter into concentrated exposure of structural risks and a comprehensive rise in liquidity pressure. The government shutdown led to delays in the release of key macro data and exacerbated fiscal uncertainty, weakening overall market confidence; debates in the U.S. stock market surrounding AI valuations increased volatility, while the cryptocurrency market faced more direct liquidity and depth shocks following the Binance liquidation event. Meanwhile, the slowdown in DAT strategy fund inflows and the general drop of mNAV below 1 indicate that the market remains highly sensitive to the liquidity environment during the institutionalization process, showing clear vulnerabilities. Whether the market can stabilize going forward will largely depend on the speed of digestion of the liquidation event's impact and whether the market can gradually restore liquidity and emotional stability in an environment of increasing divergence between bulls and bears.
Rate Cut Expectations Realized, Market Enters Repricing Phase
In the third quarter of 2025, the key variable in the global macro environment is not the event of "rate cuts" itself, but the generation, trading, and consumption of rate cut expectations. The market's pricing of the liquidity turning point began in July, with actual policy actions becoming nodes to validate existing consensus.
After two quarters of contention, the Federal Reserve lowered the target range for the federal funds rate by 25 basis points to 4.00%–4.25% at the September FOMC meeting, and then made another slight rate cut in October. However, since the market's bets on rate cuts had already become highly consistent, the policy actions themselves had limited marginal impact on risk assets, and the signaling effect of the rate cuts had already been largely priced in. Meanwhile, as the pace of inflation's decline slowed and economic resilience exceeded expectations, the Federal Reserve began to express clear concerns about "the market's early pricing of consecutive rate cuts next year," leading to a significant decrease in the probability of further rate cuts in December after October. This communication stance became a new variable dragging down market risk appetite.
Macro data in the third quarter exhibited characteristics of "moderate cooling":
- The annual core CPI rate fell from 3.3% in May to 2.8% in August, confirming the downward trend in inflation;
- Non-farm payrolls added fewer than 200,000 jobs for three consecutive months;
- The job vacancy rate fell to 4.5%, the lowest level since 2021.
This set of data indicates that the U.S. economy has not fallen into recession but has entered a phase of moderate slowdown, providing the Federal Reserve with policy space for "controllable rate cuts." Thus, the market had formed a consensus of "certain rate cuts" as early as the beginning of July.
According to the CME FedWatch tool, the probability of a 25 basis point rate cut in September exceeded 95% by the end of August, meaning the market had almost completed the expectation realization in advance. The bond market also reflected this signal:
- The yield on 10-year U.S. Treasuries fell from 4.4% at the beginning of the quarter to 4.1% at the end of the quarter;
- The decline in the 2-year yield was even greater, about 50 basis points, indicating that market bets on policy shifts were more concentrated.
The macro turning point in the third quarter was more about "the digestion of expectations" rather than "policy changes." The pricing for liquidity recovery had largely been completed between July and August, and the actual rate cut in September was merely a formal confirmation of existing consensus. For risk assets, the new marginal variable shifted from "whether to cut rates" to "the pace and sustainability of rate cuts."
However, when the rate cuts were actually implemented, the marginal effect of expectations had been completely consumed, and the market quickly entered a "vacuum phase with no new catalysts."
Since mid-September, the changes in macro indicators and asset prices have shown a clear dulling:
- The U.S. Treasury yield curve has flattened: As of the end of September, the spread between 10-year and 3-month Treasuries was only about 14 basis points, indicating that while term premiums still exist, the risk of inversion has been alleviated.
- The U.S. dollar index fell back to the 98–99 range, significantly weakening from the year's high (107), but the dollar financing costs remained tight during the quarter-end settlement period.
- The marginal contraction of funds in the U.S. stock market: The Nasdaq index continued to rise, but ETF inflows slowed, and trading volume growth was weak, indicating that institutions had begun to adjust their risk exposure at high levels.
This "vacuum period after expectation realization" became the most representative macro phenomenon of the quarter. The market traded on "certainty of rate cuts" in the first half, while in the second half, it began to price in "the reality of slowing growth."
The dot plot (SEP) released by the Federal Reserve at the September meeting showed significant internal divergence among decision-makers regarding future interest rate paths:
- The median expectation for the policy rate at the end of 2025 was lowered to 3.9%;
- The range of committee predictions fell between 3.4% and 4.4%, reflecting differing opinions among decision-makers on inflation stickiness, economic resilience, and policy space.
After the rate cut in September and another slight cut in October, the Federal Reserve's communication gradually shifted to a more cautious tone to avoid premature loosening of financial conditions. As a result, the probability of a further rate cut in December, which had been highly bet on, has significantly receded, and the policy path has returned to a "data-dependent" framework rather than a "preset rhythm."
Unlike previous rounds of "crisis-style easing," this round of rate cuts belongs to a controllable policy adjustment. While cutting rates, the Federal Reserve continues to advance balance sheet reduction, sending signals to "stabilize capital costs and curb inflation expectations," emphasizing the balance between growth and prices rather than actively expanding liquidity. In other words, the interest rate turning point has been established, but the liquidity turning point has yet to arrive.
In this context, the market exhibits clear differentiation characteristics. The decline in financing costs provides valuation support for some high-quality assets, but broad liquidity has not significantly expanded, and capital allocation has become cautious.
- Sectors with robust cash flow and profit support (AI, tech blue chips, some DAT-related U.S. stocks) continue the trend of valuation recovery;
- Assets with high leverage, high valuations, or lacking cash flow support (including some growth stocks and non-mainstream crypto tokens) have seen weakened momentum after expectation realization, with trading activity significantly declining.
Overall, the third quarter of 2025 is a "period of expectation realization" rather than a "period of liquidity release." The market priced in the certainty of rate cuts in the first half, then shifted to reassessing growth slowdown in the latter half. The premature consumption of expectations has kept risk assets at high levels but lacking sustained upward momentum. This macro pattern laid the foundation for subsequent structural differentiation and explains the "breakout—pullback—high-level oscillation" trend observed in the cryptocurrency market in Q3: funds flowed into relatively stable, cash flow-verifiable assets rather than systemic risk assets.
The Explosion and Structural Turn of Non-Bitcoin Assets' DAT
In the third quarter of 2025, Digital Asset Treasury (DAT) transitioned from a peripheral concept in the cryptocurrency industry to the fastest-spreading new theme in global capital markets. This quarter marked the first instance of public market funds entering cryptocurrency assets simultaneously in terms of scale and mechanism: through traditional financing tools such as PIPE, ATM, and convertible bonds, billions of dollars in fiat liquidity directly entered the cryptocurrency market, forming a structured trend of "coin-stock linkage."
The starting point of the DAT model can be traced back to the pioneer in traditional markets, MicroStrategy (NASDAQ: MSTR). Since 2020, the company has been the first to incorporate Bitcoin into its corporate balance sheet, accumulating approximately 640,000 Bitcoins through multiple rounds of convertible bonds and ATM issuances from 2020 to 2025, with total investments exceeding $47 billion. This strategic move not only reshaped the company's asset structure but also created a paradigm where traditional stocks became the "secondary vehicle" for cryptocurrency assets.
Due to systemic differences in valuation logic between the equity market and on-chain assets, MicroStrategy's stock price has long been above its Bitcoin net value, with mNAV (market cap / on-chain asset net value) consistently maintaining in the range of 1.2–1.4 times. This "structural premium" reveals the core mechanism of DAT:
Companies hold cryptocurrency assets through public market financing, creating a two-way communication and valuation feedback between fiat capital and cryptocurrency assets at the corporate level.
Mechanically, MicroStrategy's experiment laid the three pillars of the DAT model:
- Financing channels: Introducing fiat liquidity through PIPE, ATM, or convertible bonds to provide funding for on-chain asset allocation;
- Asset reserve logic: Incorporating cryptocurrency assets into financial reporting systems, forming a corporate-level "On-Chain Treasury";
- Investor entry: Allowing traditional capital market investors to gain indirect exposure to cryptocurrency assets through stocks, reducing compliance and custody barriers.
These three elements together constitute the "structural cycle" of DAT: financing—holding—valuation feedback. Companies utilize traditional financial tools to absorb liquidity, forming reserves of cryptocurrency assets, and then create capital enhancement through the premium in the equity market, achieving dynamic rebalancing between capital and tokens.
The significance of this structure lies in its realization of digital assets entering the traditional financial system's balance sheet in a compliant manner, endowing the capital market with a new asset form—"tradable on-chain asset mapping." In other words, companies are no longer just on-chain participants but have become structural intermediaries between fiat capital and cryptocurrency assets.
As this model was validated by the market and rapidly replicated, the third quarter of 2025 marked the second phase of the DAT concept's diffusion: extending from a "store of value treasury" centered on Bitcoin to productive assets such as Ethereum (ETH) and Solana (SOL) (PoS yields or DeFi yields). This new generation of DAT models, centered on the mNAV (market cap / on-chain asset net value) pricing system, incorporates yield-generating assets into corporate cash flow and valuation logic, forming a "yield-driven treasury cycle." Unlike the earlier Bitcoin treasury, assets like ETH and SOL possess sustainable staking yields and on-chain economic activities, making their treasury assets not only store value but also cash flow characteristics. This change marks the transition of DAT from mere asset holding to a stage of capital structure innovation centered on productive yields, becoming a key bridge connecting the value of productive cryptocurrency assets with the valuation system of traditional capital markets.
Note: Entering November 2025, a new round of declines in the cryptocurrency market triggered the most systematic revaluation of the DAT sector since its inception. With core assets like ETH, SOL, and BTC experiencing rapid pullbacks of 25–35% in October and November, along with the short-term dilution effects brought about by some DAT companies accelerating balance sheet expansion through ATM, the mNAV of mainstream DAT companies generally fell below 1. BMNR, SBET, FORD, and others experienced varying degrees of "discounted trading" (mNAV ≈ 0.82–0.98), and even MicroStrategy (MSTR), which had long maintained a structural premium, saw its mNAV briefly drop below 1 in November for the first time since the launch of its Bitcoin treasury strategy in 2020. This phenomenon marks the market's transition from a previous period of structural premium to a defensive phase of "asset dominance, valuation discount." Institutional investors generally view this as the first comprehensive "stress test" for the DAT industry, reflecting that the capital market is reassessing the sustainability of on-chain asset yields, the rationality of treasury expansion pace, and the long-term impact of financing structures on equity value.
SBET and BMNR Lead the Ethereum Treasury Wave
In the third quarter of 2025, the market landscape for Ethereum treasury (ETH DAT) was initially established. Among them, SharpLink Gaming (NASDAQ: SBET) and BitMine Immersion Technologies (NASDAQ: BMNR) emerged as two leading companies defining the industry paradigm. They not only replicated MicroStrategy's balance sheet strategy but also achieved a leap from "concept to institution" in financing structure, institutional participation, and information disclosure standards, building a dual pillar for the ETH treasury cycle.
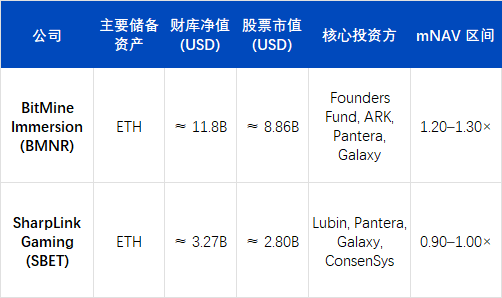
BMNR: Capital Engineering of Ethereum Treasury
As of the end of September 2025, BitMine Immersion Technologies (BMNR) has established its position as the world's largest Ethereum treasury. According to the company's latest disclosure, it holds approximately 3,030,000 ETH, corresponding to an on-chain net asset of about $12.58 billion (based on the October 1 closing price of $4,150/ETH). If accounting for the company's cash and other liquid assets, BMNR's total cryptocurrency and cash holdings amount to approximately $12.9 billion.
Based on this estimate, BMNR's holdings account for about 2.4–2.6% of Ethereum's circulating supply, making it the first publicly listed institution in the market to hold over 3 million ETH. Corresponding stock market capitalization is approximately $11.2–11.8 billion, implying an mNAV of approximately 1.27×, the highest valuation among all publicly listed companies in the digital asset treasury (DAT) category.
BMNR's strategic leap is closely related to its organizational restructuring. After Tom Lee (former co-founder of Fundstrat) took full control of capital operations in mid-2025, he proposed the core assertion: "ETH is the future institutional sovereign asset." Under his leadership, the company completed a structural transformation from a traditional mining enterprise to one that "uses ETH as the sole reserve asset and PoS yields as the core cash flow," becoming the first U.S. publicly listed company to use Ethereum staking yields as its main operating cash flow.
In terms of financing, BMNR has demonstrated rare intensity and execution efficiency. The company has expanded its funding sources through both public markets and private placements, providing long-term ammunition for its Ethereum treasury strategy. This quarter, BMNR not only refreshed the financing rhythm of traditional capital markets but also laid the institutionalized prototype of "on-chain asset securitization."
On July 9, BMNR registered a Form S-3 statement and signed an "At-the-Market (ATM)" issuance agreement with Cantor Fitzgerald and ThinkEquity, with an initial authorized amount of $2 billion. Just two weeks later, on July 24, the company disclosed in an SEC 8-K filing that it would raise this amount to $4.5 billion in response to the market's positive reaction to its ETH treasury model. On August 12, the company submitted a supplemental statement to the SEC, increasing the total ATM amount to $24.5 billion (an additional $20 billion), explicitly stating that the funds would be used to purchase ETH and expand the PoS staking asset portfolio.
These amounts represent the upper limit of sustainable market price issuance of stocks approved by the SEC and do not equate to actual cash raised.
In terms of actual funding, the company has completed several specific transactions:
- In early July 2025, completed a $250 million PIPE private placement to provide funds for initial ETH accumulation;
- ARK Invest (Cathie Wood) disclosed on July 22 that it purchased approximately $182 million of BMNR common stock, of which $177 million in net fundraising was directly used by the company to increase its ETH holdings;
- Founders Fund (Peter Thiel) filed with the SEC on July 16 to report a 9.1% stake, which, while not new financing, reinforced institutional consensus in the market.
Additionally, BMNR has cumulatively sold approximately $4.5 billion worth of stock under its early ATM authorization, significantly exceeding the initial PIPE amount. As of September 2025, the company has utilized several billion dollars through multiple channels, including PIPE and ATM, and continues to advance its long-term expansion plan under the total authorized framework of $24.5 billion.
BMNR's financing system presents a clear three-tier structure:
- Deterministic funding layer— Completed PIPE and institutional directed subscriptions, approximately $450–500 million;
- Market expansion layer— Phase-wise sale of stocks through the ATM mechanism, with actual fundraising reaching several billion dollars;
- Potential ammunition layer— The $24.5 billion total ATM amount approved by the SEC, providing upper limit flexibility for subsequent ETH treasury expansion.
With this layered capital structure, BMNR has quickly established a reserve scale of approximately 3.03 million ETH (valued at about $12.58 billion), achieving a transformation of its treasury strategy from "single holding experiment" to "institutionalized asset allocation."
BMNR's valuation premium primarily stems from two layers of logic:
- Asset layer premium: PoS staking yields maintain an annualized rate of 3.4–3.8%, forming a stable cash flow anchor;
- Capital layer premium: As a "compliant ETH leverage channel," its stock price typically leads ETH spot by 3–5 trading days, becoming a forward indicator for institutions tracking the ETH market.
In market behavior, BMNR's stock price reached historical highs in sync with ETH in the third quarter and repeatedly drove sector rotation. Its high turnover rate and the speed of circulating shares indicate that the DAT model is gradually evolving into a tradable "on-chain asset mapping mechanism" in the capital market.
SBET: A Transparent Sample of Institutionalized Treasury
Compared to BitMine Immersion Technologies (BMNR)'s aggressive balance sheet expansion strategy, SharpLink Gaming (NASDAQ: SBET) chose a more robust and institutionalized path for treasury management in the third quarter of 2025. Its core competitiveness lies not in the scale of funds but in the transparency of governance structure, disclosure standards, and auditing systems, establishing a replicable "institutional-level template" for the DAT industry.
As of September 2025, SBET holds approximately 840,000 ETH, with an estimated on-chain asset value of about $3.27 billion based on the average quarterly price, corresponding to a stock market capitalization of about $2.8 billion, resulting in an mNAV of approximately 0.95×. Although the valuation is slightly below net assets, the company's quarterly EPS growth reached 98%, demonstrating its strong operational leverage and execution efficiency in ETH monetization and cost control.
The core value of SBET is not in aggressive position expansion but in establishing the first compliant and auditable governance framework in the DAT industry:
- Strategic advisor Joseph Lubin (co-founder of Ethereum and founder of ConsenSys) joined the company's strategic committee in Q2, promoting the inclusion of staking yields, DeFi derivatives, and liquidity mining strategies into the corporate treasury portfolio;
- Pantera Capital and Galaxy Digital participated in PIPE financing and secondary market holdings, providing institutional liquidity and on-chain asset allocation advice to the company;
- Ledger Prime offers on-chain risk hedging and volatility management models;
- Grant Thornton serves as an independent auditing agency, responsible for verifying the authenticity of on-chain assets, yields, and staking accounts.
This governance system constitutes the first "on-chain verifiable + traditional audit parallel" disclosure mechanism in the DAT industry.
In the 10-Q report for the third quarter of 2025, SBET publicly disclosed for the first time:
- The company's main wallet addresses and on-chain asset structure;
- Staking yield curves and node distribution;
- Risk limits for collateral and restaking positions.
This report made SBET the first publicly listed company to simultaneously disclose on-chain data in SEC filings, significantly enhancing institutional investors' trust and financial comparability. The market generally views SBET as a "compliant ETH index component": its mNAV is close to 1×, and its price maintains a high correlation with the ETH market, yet it exhibits relatively low volatility due to information transparency and robust risk structure.
Dual Main Lines of ETH Treasury: Asset-Driven and Governance-Driven
The divergent paths of BMNR and SBET form the two core backbones of the ETH DAT ecosystem development in the third quarter of 2025:
- BMNR: Asset-driven—centered on financing expansion, institutional holdings, and capital premiums. BMNR rapidly accumulates ETH positions using PIPE and ATM financing tools and creates a market-driven leverage channel through mNAV pricing, promoting the direct coupling of fiat capital and on-chain assets.
- SBET: Governance-driven—focused on transparent compliance, structured treasury yields, and risk control. SBET incorporates on-chain assets into its auditing and information disclosure system, establishing a governance framework that parallels on-chain verification with traditional accounting, thereby defining the institutional boundaries of DAT.
The two represent the two poles of the transition of ETH treasury from "reserve logic" to "institutional asset form": the former expands capital scale and market depth, while the latter establishes governance trust and institutional compliance foundations. In this process, the functional attributes of ETH DAT have transcended "on-chain reserve assets," evolving into a composite structure that encompasses cash flow generation, liquidity pricing, and balance sheet management.
Institutional Logic of PoS Yields, Governance Rights, and Valuation Premiums
The core competitiveness of PoS cryptocurrency asset treasuries like ETH comes from the triple combination of interest-bearing asset structure, network-level discourse power, and market valuation mechanisms.
High Staking Yields: Establishing Cash Flow Anchors
Unlike Bitcoin's "non-productive holdings," ETH, as a PoS network asset, can earn an annual yield of 3–4% through staking and form a compound yield structure (Staking + LST + Restaking) in the DeFi market. This allows DAT companies to capture real cash flows on-chain in a corporate form, transforming digital assets from "static reserves" to "yield-generating assets" with stable endogenous cash flow characteristics.
Discourse Power and Resource Scarcity under PoS Mechanism
As the staking scale of ETH treasury companies expands, they gain governance rights and ranking power at the network level. BMNR and SBET currently control a combined ETH staking scale of about 3.5–4% of the entire network, entering the marginal influence zone of protocol governance. This type of control possesses a premium logic similar to "systemic status," and the market is willing to assign a valuation multiple above net asset value.
Formation Mechanism of mNAV Premium
The valuation of DAT companies reflects not only the net value (NAV) of their held on-chain assets but also incorporates two types of expectations:
- Cash flow premium: Expectations of distributable profits from staking yields and on-chain strategies;
- Structural premium: The equity of the company provides traditional institutions with a compliant ETH exposure channel, thus forming institutional scarcity.
At the market peak in July-August, the average mNAV of ETH DAT maintained in the range of 1.2–1.3 times, with some companies (BMNR) even reaching 1.5 times. This valuation logic is similar to the premium of gold ETFs or the NAV discount/premium structure of closed-end funds, serving as an important "pricing intermediary" for institutional funds entering on-chain assets.
In other words, the premium of DAT is not driven by sentiment but is formed based on a composite structure of real yields, network power, and capital channels. This also explains why ETH treasuries achieved higher funding density and trading activity than Bitcoin treasuries (MSTR model) in just one quarter.
Structural Evolution from ETH to Multi-Chain Asset Treasury
Entering August-September, the expansion speed of non-Ethereum DAT significantly accelerated. The new wave of institutional allocation represented by Solana treasury marks a shift in market themes from "single asset reserves" to "multi-chain asset layering." This trend indicates that the DAT model is transitioning from an ETH core to multi-ecosystem replication, forming a more systematic cross-chain capital structure.
FORD: A Model of Institutionalized Solana Treasury
Forward Industries (NASDAQ: FORD) has become the most representative case in this phase. The company completed a $1.65 billion PIPE financing in the third quarter, with all funds used for Solana spot accumulation and ecological collaborative investments. As of September 2025, FORD holds approximately 6.82 million SOL, with an on-chain treasury net value of about $1.69 billion based on the average quarterly price of $248–$252, corresponding to a stock market capitalization of about $2.09 billion, resulting in an mNAV of approximately 1.24×, ranking first among non-ETH treasury companies.
Unlike early ETH DAT, FORD's rise is not driven by a single asset but is a product of multi-capital and ecological resonance:
- Investors include Multicoin Capital, Galaxy Digital, and Jump Crypto, all of which are long-term core investment institutions in the Solana ecosystem;
- The governance structure incorporates members of the Solana Foundation advisory committee, establishing a strategic framework of "on-chain assets as corporate production materials";
- The SOL assets held remain fully liquid, with no staking or DeFi configurations yet, preserving strategic flexibility for future restaking and RWA asset linkage.
This "high liquidity + configurable treasury" model positions FORD as the capital hub of the Solana ecosystem and reflects the market's structural premium expectations for high-performance public chain assets.
Structural Changes in the Global DAT Landscape
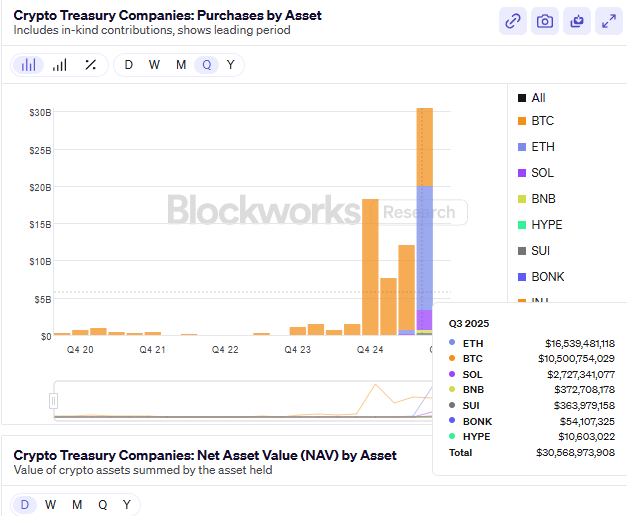
As of the end of the third quarter of 2025, the total disclosed non-Bitcoin DAT treasury scale globally has surpassed $24 billion, representing a quarter-on-quarter growth of about 65%. The structural distribution is as follows:
- Ethereum (ETH) still dominates, accounting for about 52% of the total scale;
- Solana (SOL) accounts for about 25%, becoming the second-largest allocation direction for institutional funds;
- The remaining funds are mainly distributed among emerging assets like BNB, SUI, and HYPE, forming the horizontal expansion layer of the DAT model.
The valuation anchor of ETH DAT lies in the PoS yield and governance rights value, representing a combination logic of long-term cash flow and network control; SOL DAT, on the other hand, emphasizes capital efficiency and scalability as its core premium sources, focusing on ecological growth and staking efficiency. BMNR and SBET established the institutional and asset foundations during the ETH phase, while FORD's emergence propels the DAT model into the second stage of multi-chain and ecological development.
Meanwhile, some new entrants are beginning to explore the functional extension of DAT:
- Ethena (ENA) launched the StablecoinX model, combining government bond yields with on-chain hedging structures, attempting to create a "yield-based stablecoin treasury" to generate stable yet cash flow-rich reserve assets;
- BNB DAT is led by the exchange system, relying on asset collateralization and reserve tokenization of ecological enterprises to expand liquidity pools, forming a "closed treasury system."
Phase Stagnation and Risk Repricing After Valuation Overextension
After the concentrated upward movement in July-August, the DAT sector entered a rebalancing phase following valuation overextension in September. Secondary treasury stocks once pushed the overall premium of the sector higher, with the median mNAV exceeding 1.2×, but as regulatory tightening and financing slowed, valuation support quickly retreated at the end of the quarter, and the sector's heat noticeably cooled.
Structurally, the DAT industry is transitioning from "asset innovation" to "institutional integration." ETH and SOL treasuries have established a "dual core valuation system," but the liquidity, compliance, and real yield of expansionary assets are still in the verification stage. In other words, the market driving force has shifted from "premium expectations" to "yield realization," and the industry has entered a repricing cycle.
After entering September, core indicators weakened in unison:
- The ETH staking yield has fallen from 3.8% at the beginning of the quarter to 3.1%, while the SOL staking yield has decreased by over 25% quarter-on-quarter;
- Several second-tier DAT companies have seen their mNAV drop below 1, indicating diminishing marginal capital efficiency;
- The total amount of PIPE and ATM financing has declined by about 40% quarter-on-quarter, with institutions like ARK, VanEck, and Pantera pausing new DAT allocations;
- At the ETF level, net inflows have turned negative, with some funds replacing ETH treasury positions with short-duration government bond ETFs to reduce valuation volatility risk.
This pullback exposes a core issue: the capital efficiency of the DAT model has been overextended in the short term. Early valuation premiums stemmed from structural innovation and institutional scarcity, but as on-chain yields decline and financing costs rise, the speed of corporate balance sheet expansion has outpaced yield growth, leading to a "negative dilution cycle"—where market capitalization growth relies on financing rather than cash flow.
From a macro perspective, the DAT sector is entering a "valuation internalization period":
- Core companies (BMNR, SBET, FORD) maintain structural stability through robust treasuries and information transparency;
- Marginal projects face deleveraging and liquidity contraction due to single capital structures and insufficient disclosure;
- On the regulatory front, the SEC requires companies to disclose major wallet addresses and staking yield disclosure standards, further compressing the space for "high-frequency balance sheet expansion."
Short-term risks primarily stem from valuation compression caused by liquidity reflexivity. As mNAV continues to decline and PoS yields struggle to cover financing costs, market confidence in the "on-chain reserves + equity pricing" model will be undermined, leading to a systemic valuation correction similar to that seen after the summer of DeFi in 2021. Nevertheless, the DAT industry has not entered a recession but is transitioning from an "expansion-driven" to a "yield-driven" phase. In the coming quarters, ETH and SOL treasuries are expected to maintain their institutional advantages, with their valuation core increasingly relying on:
- Staking and restaking yield efficiency;
- On-chain transparency and compliance disclosure standards.
In other words, the first phase of the DAT boom has ended, and the industry is entering a "consolidation and validation period." The key variables for future valuation recovery will be the stability of PoS yields, the integration efficiency of restaking, and the clarity of regulatory policies.
Prediction Markets: The "Barometer" of Macro Narratives and the Rise of Attention Economy
In the third quarter of 2025, prediction markets have transitioned from "crypto-native fringe plays" to "a new market infrastructure at the intersection of on-chain and compliant finance." In an environment of frequent macro policy changes and significant fluctuations in inflation and interest rate expectations, prediction markets have gradually become important venues for capturing market sentiment, hedging policy risks, and discovering narrative prices. The integration of macro and on-chain narratives has evolved them from speculative tools into market layers that aggregate information and signal prices.
Historically, crypto-native prediction markets have demonstrated significant foresight during various macro and political events. During the 2024 U.S. presidential election, Polymarket's total trading volume exceeded $500 million, with the contract for "who will win the presidential election" alone reaching $250 million, and a single-day trading peak surpassing $20 million, setting a record for on-chain prediction markets. In macro events such as "Will the Federal Reserve cut interest rates in September 2024?", the price changes of contracts have clearly led the expected adjustments of CME FedWatch interest rate futures, indicating that prediction markets have, at times, exhibited leading indicator value.
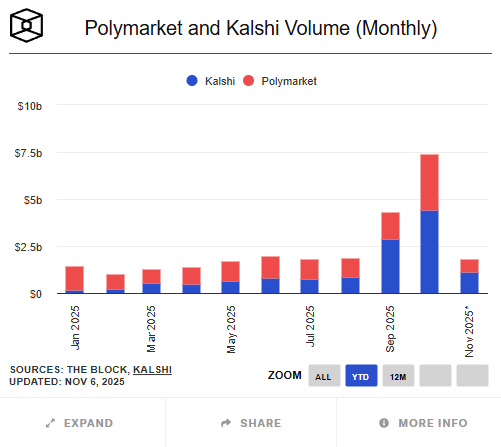
Despite this, the overall scale of on-chain prediction markets remains far smaller than traditional counterparts. Since 2025, the global crypto prediction market (represented by Polymarket, Kalshi, etc.) has accumulated approximately $24.1 billion in trading volume, while traditional compliant platforms like Betfair and Flutter Entertainment have annual trading volumes in the hundreds of billions. The scale of on-chain markets is still less than 5% of traditional markets, but they show higher growth in user growth, thematic coverage, and trading activity compared to traditional financial products.
In the third quarter, Polymarket became a phenomenon of growth. Contrary to rumors of a "billion-dollar valuation financing" earlier in the year, the latest news in early October indicated that ICE, the parent company of the New York Stock Exchange, plans to invest up to $2 billion for about a 20% stake, corresponding to a valuation of approximately $8-9 billion for Polymarket. This suggests that its data and business model have gained recognition at the Wall Street level. By the end of October, Polymarket's annual cumulative trading volume was approximately $13.2 billion, with September's monthly trading volume reaching $1.4-1.5 billion, significantly up from the second quarter, and October's monthly trading volume even hitting a historic high of $3 billion. Trading themes focused on macro and regulatory events such as "Will the Federal Reserve cut rates at the September FOMC meeting?", "Will the SEC approve an Ethereum ETF before the end of the year?", "Winning probabilities in key states for the U.S. presidential election", and "Stock performance of Circle (CIR) after listing." Some researchers noted that the price fluctuations of these contracts often lead U.S. Treasury yields and FedWatch probability curves by about 12-24 hours, becoming forward-looking indicators of market sentiment.
At the same time, Kalshi has achieved institutional breakthroughs along compliance paths. As a prediction market exchange registered with the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Kalshi completed a $185 million Series C financing in June 2025 (led by Paradigm), with a valuation of about $2 billion; the latest disclosure in October has raised its valuation to $5 billion, with an annualized trading volume growth rate exceeding 200%. The platform launched contracts related to crypto assets in the third quarter, such as "Will Bitcoin close above $80,000 by the end of this month?" and "Will the Ethereum ETF be approved before the end of the year?", marking the formal entry of traditional institutions into the speculative and hedging market for "crypto narrative events." According to Investopedia, its crypto-related contracts have exceeded $500 million in trading volume within two months of launch, providing institutional investors with a new channel to express macro expectations within a compliant framework. Thus, prediction markets have formed a dual-track pattern of "on-chain freedom + compliance rigor."
Unlike early prediction platforms that leaned towards entertainment and political themes, the mainstream market focus in the third quarter of 2025 has significantly shifted towards macro policy, financial regulation, and events linking cryptocurrencies and stocks. The cumulative trading volume of macro and regulatory contracts on the Polymarket platform has exceeded $500 million, accounting for over 40% of the total quarterly trading volume. Investors have shown high participation in themes such as "Will the ETH spot ETF be approved before Q4?" and "Will Circle's stock price break key levels after listing?" The price trends of these contracts have, at times, even led traditional media sentiment and derivatives market expectations, gradually evolving into a "pricing mechanism for market consensus."
The core innovation of on-chain prediction markets lies in their ability to achieve liquidity pricing of events through tokenization mechanisms. Each prediction event is priced in a binary or continuous manner (e.g., YES/NO Token) and maintains liquidity through automated market makers (AMM), enabling efficient price discovery without the need for matching. Settlement relies on decentralized oracles (such as UMA, Chainlink) for on-chain execution, ensuring transparency and auditability. This structure allows almost all social and financial events—from election results to interest rate decisions—to be quantified and traded as on-chain assets, constituting a new paradigm of "financialization of information."
However, alongside rapid development, risks cannot be overlooked. First, oracle risk remains a core technical bottleneck for on-chain prediction markets; any delay or manipulation of external data could lead to contract settlement disputes. Second, unclear compliance boundaries still restrict market expansion, as the U.S. and EU have not fully unified their regulatory stance on event-based derivatives. Third, some platforms still lack KYC/AML processes, potentially triggering compliance risks regarding the source of funds. Finally, liquidity is overly concentrated on leading platforms (with Polymarket accounting for over 90% of the market), which could lead to price deviations and amplified market volatility in extreme conditions.
Overall, the performance of prediction markets in the third quarter indicates that they are no longer marginalized "crypto plays" but are becoming an important carrier layer for macro narratives. They serve as an immediate reflection of market sentiment and as intermediary tools for information aggregation and risk pricing. Looking ahead to the fourth quarter, prediction markets are expected to continue evolving along the "on-chain × compliance" dual-loop structure: the on-chain segment of Polymarket will rely on DeFi liquidity and macro narrative trading for external expansion; the compliant path of Kalshi will accelerate the attraction of institutional capital through regulatory recognition and dollar-denominated mechanisms. With the proliferation of data-driven financial narratives, prediction markets are transitioning from the attention economy to decision-making infrastructure, becoming a rare new asset layer in the financial system that reflects collective sentiment while possessing forward-looking pricing capabilities.
Reference Links
https://www.strategicethreserve.xyz/
https://blockworks.com/analytics/treasury-companies
https://www.theblock.co/data/decentralized-finance/prediction-markets-and-betting
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




