# I. Outlook
## 1. Macroeconomic Summary and Future Predictions
Last week, the U.S. stock market began to digest the reality of previously strong employment data and the repeated postponement of interest rate cut expectations after several weeks of high performance. High valuations and high positions quickly turned into sources of pressure in the absence of new positive developments. Market sentiment shifted from "hesitant" to "defensive," with technology and high-growth sectors being the first to face sell-offs. The indices experienced a significant drop in volume, indicating that this was not a normal correction, but rather an emotional sell-off triggered by collapsing expectations and loosening positions.
Looking ahead, this decline seems more like a forced correction of overly optimistic expectations. With no significant deterioration in the macro environment, but policy easing still not materializing, it is difficult for the U.S. stock market to quickly return to its previous one-sided upward trend, and high volatility may become the norm.
## 2. Market Changes and Warnings in the Crypto Industry
Last week, the cryptocurrency market entered a phase of high volatility and extremely weak sentiment. Bitcoin experienced a technical rebound at $60,000 but remains in a clearly weak range. Trading volume remains high, indicating that deleveraging and the long-short battle are still ongoing and have not yet fully cleared.
From a risk perspective, the current market is closer to a consolidation phase after a sharp decline rather than a trend stabilization. As long as Bitcoin cannot quickly return to and stabilize in the key pressure range, any rebound may be seen as a window for reducing positions, and altcoins and high-volatility sectors will continue to face selling pressure. Additionally, the repeated adjustments in macro interest rate expectations may continue to impact the crypto market through sentiment and liquidity channels. Overall, in the short term, caution is warranted regarding the risk of a second dip or prolonged low-level consumption, and true stability signals are still to be observed.
## 3. Industry and Sector Hotspots
Total funding of $2 million, led by CMS and Shimu Capital—River, a liquidity layer for bridge-less cross-chain stablecoins, is building a chain-abstract stablecoin system to connect liquidity between different ecosystems; total funding of $5 million, led by Mint with participation from 90S, DeepNode is a decentralized smart infrastructure platform that supports the deployment, execution, and verification of AI models in a permissionless, low-trust, modular environment with incentive mechanisms.
# II. Market Hotspot Sectors and Potential Projects of the Week
## 1. Overview of Potential Projects
1.1. Analysis of Total Funding of $2 Million, Led by CMS and Shimu Capital—River, a Bridge-less Cross-chain Stablecoin Liquidity Layer
Introduction
River is building a chain-abstract stablecoin system to connect liquidity between different ecosystems. Its core product is the omni-CDP based satUSD: users can deposit collateral on one chain and mint satUSD on another—without cross-chain bridges or asset wrapping.
This design achieves true cross-chain capital efficiency, allowing liquidity to flow seamlessly between multi-chain ecosystems.
Core Mechanism Overview
1. Omni-CDP
River has built the first Omni-CDP (omni-chain collateral debt position) protocol by integrating LayerZero's cross-chain communication technology. Users can deposit BTC on one chain and directly mint satUSD on another, seamlessly connecting liquidity across multiple blockchains without traditional cross-chain bridges or asset wrapping.
2. satUSD+
satUSD+ is the core yield-bearing token in River's yield layer. After users stake satUSD, it automatically converts to satUSD+, allowing them to continuously earn real protocol revenue shares while maintaining liquidity and composability.
satUSD staking mechanism:
Users stake satUSD, supported by over-collateralized assets like BTC, ETH, BNB, and LST, to participate in River's yield layer and proportionally earn fees generated by the protocol.Essence of satUSD+:
A liquidity yield token in ERC-20 format
Automatically accumulates protocol income without manual claiming or reinvestment
Can be redeemed for satUSD at any time
Usable in other DeFi protocols (lending, LP, etc.)
Sources of income (non-inflationary):
Omni-CDP: minting, redemption, and liquidation fees
System-level usage: satUSD's use across multiple chains and applications
Future modules: lending markets, cooperative protocol incentives, on-chain income sharing
3. River4FUN
River4FUN is River's contribution incentive layer, aimed at rewarding influence and participation, not just capital investment.
Core concept:
Most protocols only reward capital; River4FUN incorporates attention, content, and dissemination into the incentive system, converting them into real protocol ownership.Operation method:
Connect wallet with X (Twitter) account
Publish content related to River or cooperative projects (tweets, replies, quotes)
Earn River Points based on exposure, interaction quality, and consistency
Points are updated regularly
All River Points can be exchanged for $RIVER at TGE
System significance:
River4FUN completes River's full flywheel:
Mint → Stake → Post
4. Smart Vault
Smart Vault is a one-click yield module launched by River, focusing on zero liquidation risk + sustainable yield. Users simply deposit assets to continuously earn yields without managing positions or worrying about market volatility and liquidation.
Problem solved:
In traditional DeFi, users often have to choose between "earning yield" and "ensuring safety," frequently managing collateral ratios and monitoring liquidation lines. Smart Vault eliminates these complexities through automation.Core advantages:
Zero liquidation risk: assets will not be forcibly liquidated
No position management required: no need to monitor collateral ratios or health
Sustainable yield: derived from real strategy income rather than inflation
Asset safety: 1:1 deposit and withdrawal, can be retrieved at any time
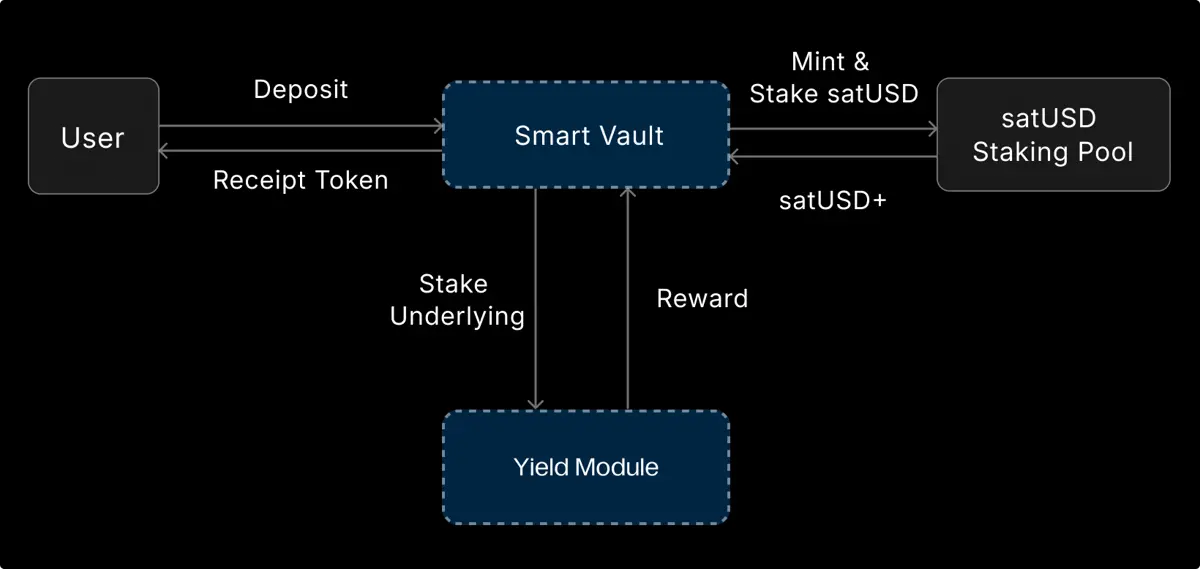
Operation mechanism:
Users deposit BTC, ETH, USDT/USDC → the protocol automatically mints satUSD based on value → satUSD directly enters the staking pool → underlying assets are deployed to DeFi / CeDeFi / RWA yield scenarios by strategy modules → users continuously earn yields.
Throughout the process, satUSD circulates within the protocol and does not enter the user's wallet, thus avoiding liquidation risk.
5. Prime Vault
Prime Vault is an institutional-grade yield vault created by River for institutional users, providing predictable, sustainable stable yields while ensuring the highest level of asset safety and compliant custody, while minimizing operational complexity and risk exposure.
Problem solved:
Eliminating forced liquidation risks due to market volatility
Meeting high standards for compliance custody and asset safety required by institutions
Reducing the technical and operational burden for institutions participating in DeFi
Core advantages:
Institutional-grade security: collaborating with leading custodians and publicly listed companies, assets are always held in regulated custody wallets
Zero liquidation risk: internal automated position management avoids any form of liquidation
No smart contract risk: underlying assets are not exposed to complex DeFi contracts, avoiding code and hacking risks
Predictable returns: continuous returns based on River's stablecoin yield system
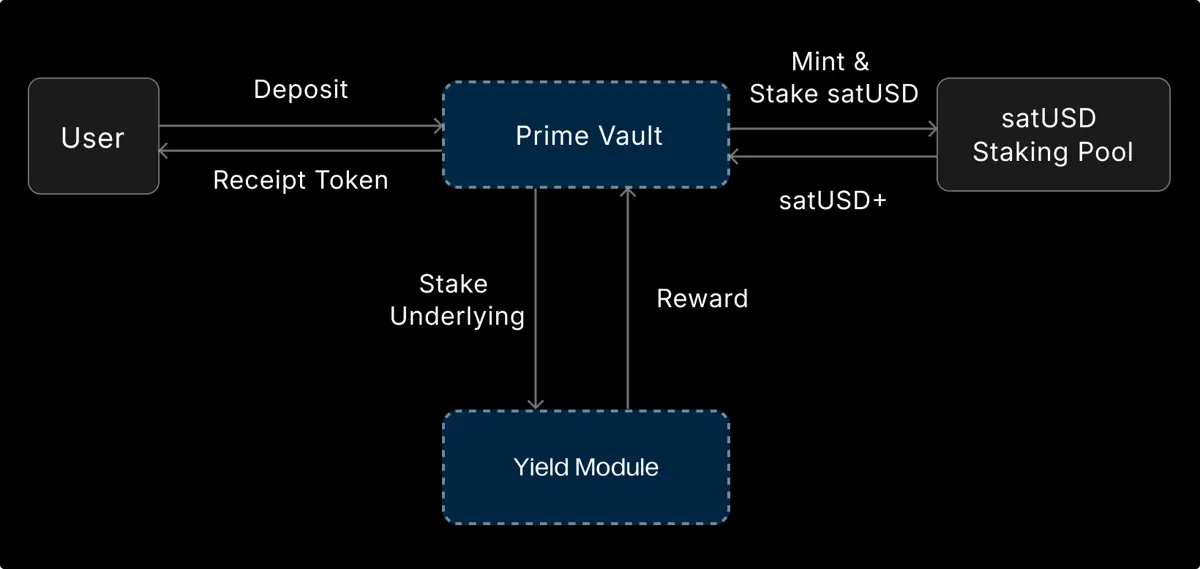
Operation mechanism:
Institutions deposit assets like BTC → custodians lock assets in secure wallets → the protocol internally mints satUSD based on asset value → satUSD enters the staking pool to earn yields → principal + accumulated yields are withdrawn upon maturity.
Throughout the process, users do not incur liabilities, and satUSD does not enter the user's wallet.Structure and risk control parameters:
Custody integration: assets are always held by compliant custodians
Internal satUSD system: used only for staking and yield distribution
Smart position management: automatically adapts to deposits and market fluctuations
Governance parameters: asset-level staking ratios (0–100%) set by $RIVER holders
Regular rebalancing: based on oracle adjustments, ensuring yield operation without affecting principal safety
Tron Comments
River's core advantage lies in its highly differentiated chain-abstract stablecoin system: through Omni-CDP and LayerZero, it achieves "bridge-less, no wrapping" cross-chain minting of satUSD, significantly enhancing multi-chain capital efficiency; satUSD+, Smart Vault, and Prime Vault form a complete yield product matrix from retail to institutional investors, balancing zero liquidation risk, real protocol income, liquidity, and compliant custody; River4FUN incorporates influence and content contributions into the incentive loop, forming a complete flywheel of Mint → Stake → Yield → Contribute.
Potential disadvantages include a relatively complex system structure, high dependence on cross-chain communication and custody partners, and the scale and long-term stability of yields still highly reliant on the cross-chain adoption rate of satUSD and the actual usage of the protocol, posing certain execution and expansion risks before the ecosystem is fully mature.
1.2. Interpretation of Total Funding of $5 Million, Led by Mint with Participation from 90S—DeepNode, a Global Smart and Computing Power Market for Decentralizing AI
Introduction
DeepNode is a decentralized AI network where intelligence no longer belongs to a few giants but to all those who participate in building it. It is an open AI marketplace: developers from around the world can contribute AI models, computing power, and data, and receive fair compensation based on the real value they create.
The goal of DeepNode is to transform AI from a monopolized resource into a democratized public infrastructure—owned and operated collectively by those who truly drive AI development.
Architecture Overview
DeepNode is a decentralized smart infrastructure platform that supports the deployment, execution, and verification of AI models in a permissionless, low-trust, modular environment with incentive mechanisms. The platform connects model developers, computing power providers, validators, and users into a unified AI value network through the $DN token, replacing centralized intermediaries with on-chain coordination.
- Core Design Principles
Open Participation: Anyone can participate as a model creator, executor, validator, staker, or user.
On-chain Transparency: Model registration, task execution, reputation scoring, and reward distribution are all recorded on-chain.
Modular Roles: Participants can choose or combine different roles based on their capabilities.
Built-in Redundancy: The same AI task is executed in parallel by multiple nodes, ensuring results are verifiable and fault-tolerant.
Performance-Oriented Incentives: Rewards are based on quantifiable metrics such as accuracy, execution efficiency, and online rate.
Progressive Decentralization: Starting with an initial whitelist, gradually transitioning to a fully open network governed by a DAO.
- Core Modules of the System Architecture
Model Marketplace
A decentralized model registration and monetization layer that ensures transparent ownership and fair income distribution for models.Execution Layer
A distributed computing power network where nodes run AI models and earn $DN rewards for validating tasks.Validation Layer
Validates and scores model outputs, maintaining network credibility.Reputation Layer
Records participant performance on-chain, influencing task allocation, weights, and earnings.Governance Layer
A community-driven protocol upgrade and key decision-making mechanism.Domain Layer
Supports specialized sub-networks (subdomains) to operate independently while anchoring to the DeepNode main network.
Incentive Mechanism
The incentive mechanism of DeepNode operates around the $DN token, covering staking, bonding, access rights, payments, governance, and incentive distribution. This mechanism is tightly coupled with platform roles and value flows, serving as the economic foundation for the network's efficient operation.
- Domain-Level Incentive Design
DeepNode adopts a Domain-level incentive model.
Each Domain has its own independent incentive configuration.
Domain Owners are responsible for deciding within their domain:
Revenue Distribution
Emission Distribution
2. Incentive Targets (Key Participants)
Domain Owners set incentive rules for the following core roles:
Miners: Execute AI tasks and provide computing power.
Validators: Validate model outputs and maintain network credibility.
Creators & Backers: Provide AI models, data, or early support.
3. Summary of Mechanism Highlights
Incentives are highly modular and configurable.
Different Domains can customize economic models based on application scenarios.
Earnings and token releases are directly tied to real contributions and performance.
Tron Comments
DeepNode's advantage lies in its unification of AI models, computing power, and data into a decentralized marketplace. Through on-chain verifiable execution, multi-node redundancy, reputation systems, and Domain-level configurable incentives, it achieves refined pricing and fair distribution of real AI contributions; the $DN token runs through execution, validation, governance, and payments, avoiding empty incentives, and the modular architecture facilitates rapid expansion into vertical AI scenarios.
Its disadvantage is the high complexity of the system, which places higher demands on execution efficiency, validation costs, and network coordination. In the early stages, it relies on the parameter design and governance capabilities of Domain Owners; if incentive configurations are inappropriate, it may affect the quality of computing power supply and the speed of ecosystem launch.
2. Key Project Details of the Week
2.1. Detailed Analysis of Total Funding of $8.5 Million, Led by DWF and Genesis—Zenchain, a Fully Interoperable Layer 1 Connecting Bitcoin, Ethereum, and the Future Multi-chain World, Guarded by AI
Introduction
Zenchain is a Layer 1 blockchain designed to achieve trustless, low-cost cross-chain interoperability with ecosystems like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Based on the BARK (Blockchain Architect Resource Kit) architecture, Zenchain employs a cross-liquidity consensus mechanism (CLCM) protected by validators, providing cryptoeconomic security for transactions.
At the execution layer, Zenchain natively supports EVM for smart contract deployment and integrates WebAssembly (Wasm) dApps through precompiles, bridging EVM and native Wasm runtimes. Its cross-chain interoperability module (CCIM) supports secure cross-chain asset transfers and interactions; the innovative ZIP-20 token standard offers a more flexible asset management framework.
Additionally, Zenchain integrates Niō (AI-driven on-chain guardian) for real-time threat detection and mitigation, enhancing network resilience and security; it also supports non-fork upgrades, promoting innovation in cross-chain communication and decentralized computing while maintaining stable operation.
Architecture Overview
Zenchain's architecture aims to build a highly secure, scalable, and strongly interoperable Layer 1 blockchain. Based on the BARK framework, Zenchain integrates advanced consensus mechanisms, flexible runtime environments, and comprehensive client support to facilitate smooth cross-chain interactions and decentralized application development.
The cross-liquidity consensus mechanism (CLCM) is Zenchain's core consensus design, aiming to balance security, decentralization, and efficiency. CLCM maintains network integrity through a collaborative mechanism between Validators and Nominators, encouraging broad participation and enhancing overall security through staking and incentive mechanisms.
Validators: Responsible for validating transactions, producing blocks, and confirming block finality, elected based on their own or their nominators' delegated ZTC stake. Validators earn incentives through staking rewards and face penalties (slashing) for malicious behavior or poor performance, making their stable performance crucial for network security.
Nominators: Support one or more validators by staking tokens, sharing their validation rewards, and bearing corresponding risks—if a supported validator is penalized, the nominator's stake will also be reduced, incentivizing them to carefully choose reliable validators.
Overall, CLCM strengthens Zenchain's degree of decentralization and network security through economic incentives and risk-sharing mechanisms, providing a solid consensus foundation for cross-chain and application ecosystems.
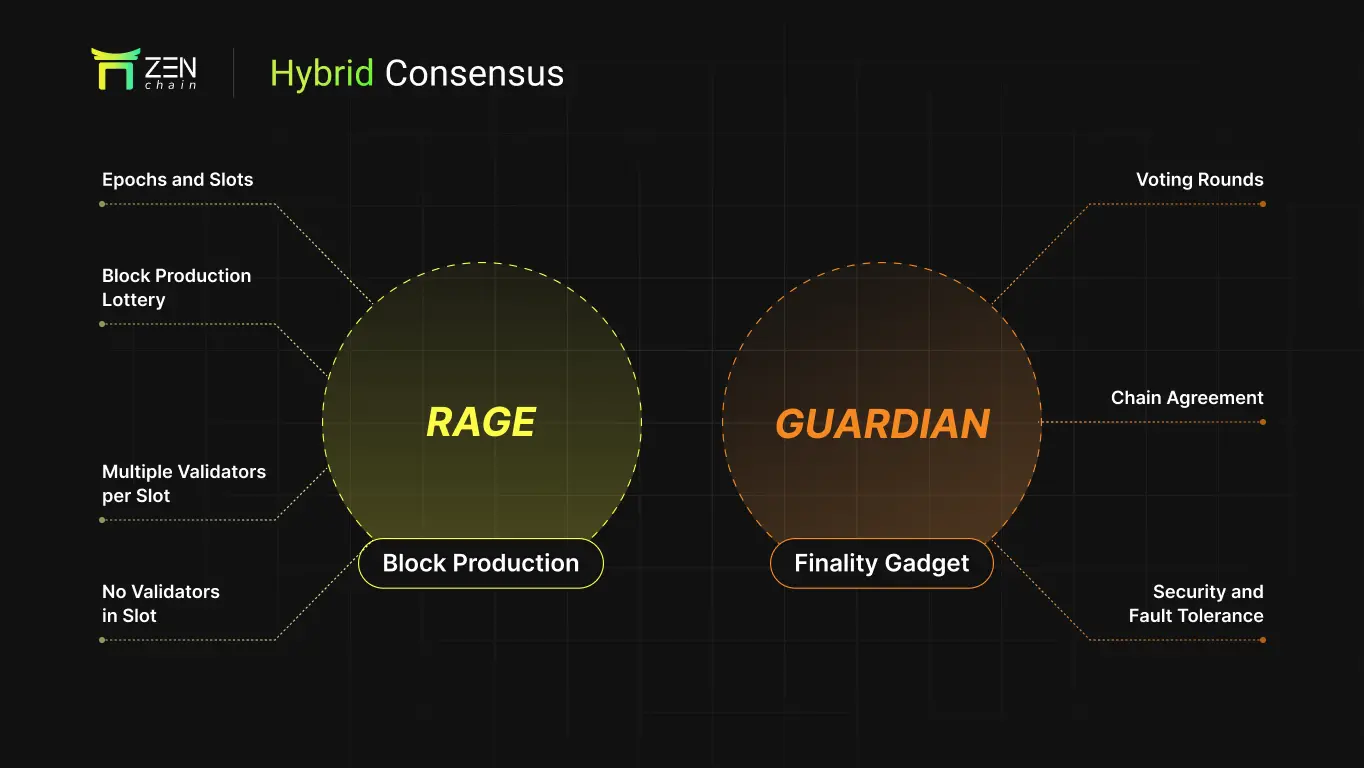
- Block Production and Finality Mechanism
Zenchain adopts a hybrid consensus model, using RAGE for block production and GUARDIAN for finality confirmation, combining the advantages of probabilistic finality and provable finality to achieve irreversible secure consensus while ensuring high performance.
Hybrid Consensus Design
Probabilistic Finality (RAGE): Ensures blocks can be continuously and quickly produced, preventing the network from stalling due to consensus.
Provable Finality (GUARDIAN): Finalizes the blockchain state through validator voting; once a block is finalized, it cannot be rolled back.
This division allows Zenchain to balance high throughput and strong security.
Block Production: RAGE
Epoch and Slot: The network operates in Epochs, each containing multiple slots of about 6 seconds.
Random Block Production: Each slot determines which validators are eligible to produce blocks through a random lottery.
Multi-validator Block Production: If multiple validators are selected in the same slot, they produce blocks simultaneously, with the block that propagates fastest being accepted.
No Validator Backup Mechanism: If no one is selected in a slot, a polling mechanism is activated to ensure continuous block production.
Finality Component: GUARDIAN
Voting Finalization: Validators vote in multiple rounds; when more than 2/3 of validators confirm a chain, that chain and its previous blocks are finalized at once.
Chain-level Finality: Unlike block-by-block confirmation, GUARDIAN reaches consensus directly on the entire chain, allowing for quick recovery even during network fluctuations.
Security: In partially synchronized networks, finality can be achieved as long as 2/3 of validators are honest, tolerating a certain proportion of Byzantine nodes.
Fork Selection and Coordination Mechanism
RAGE continues to produce blocks on top of the chain head finalized by GUARDIAN, forming clear fork selection rules to avoid the network following erroneous forks while overcoming potential stalling issues in purely finality systems.
2. Staking Mechanism
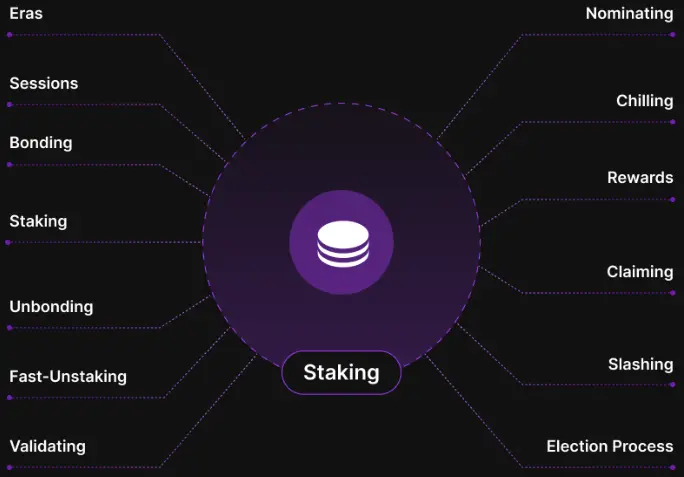
Positioning: Staking is the core of Zenchain's Cross-Liquidity Consensus Mechanism (CLCM), securing the network by locking ZTC tokens and incentivizing participants.
Cycle Structure:
Era: Approximately 6 hours, settling rewards and penalties for validators and nominators.
Session: A sub-cycle within an Era (approximately 1 hour) used for rotating validators and assessing performance.
Participation Methods:
Bonding: Locking ZTC to participate in consensus.
Staking: Participating in the network as a validator or nominator.
Unbonding: Exiting staking, which requires a lock-up period.
Fast-Unstaking: Can exit quickly under specific conditions, requiring a deposit.
Role Division:
Validators: Produce blocks, validate transactions, participate in finality voting, and earn rewards based on performance; violations will result in slashing.
Nominators: Delegate stakes to support validators, share rewards, and bear associated risks.
Auxiliary Mechanisms:
Chilling: Temporarily stop participating in staking without unlocking assets.
Rewards: Distributed based on actual performance within the Era, unrelated to staking size.
Claiming: Rewards must be actively claimed.
Slashing: Punishment for malicious or low-performance behavior.
Election Mechanism:
Uses the Phragmen algorithm to select and balance the validator set at the start of each Era.
3. Runtime Mechanism
Overall Positioning: Zenchain's runtime is compatible with both the Ethereum ecosystem and native BARK modules, supporting the development of various types of dApps.
EVM Compatibility:
Integrates SputnikVM to execute Ethereum-compatible smart contracts.
Supports Ethereum JSON-RPC.
Existing Ethereum dApps can be deployed directly without modification.
Native BARK Modules (Wasm Modules):
BARK modules based on Wasm.
Natively run on-chain, offering high performance and flexibility.
Supports direct integration of complex functions into the runtime.
Precompiles:
Connects EVM with native BARK modules.
Provides native functionality access for EVM.
Achieves efficient cross-VM interaction.
JSON-RPC Interface:
A unified client interaction entry point.
Supports both Ethereum and BARK-specific methods.
Covers operations such as contract deployment, querying, transactions, and state management.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability
Overall Design
Core Module: Cross-Chain Interoperability Module (CCIM).
Features: Chain-agnostic, unified management of cross-chain inbound and outbound transactions.
Goal: Achieve secure and efficient interoperability between Zenchain and multiple chains like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Advantages:
Abstracts the complexity of different chains.
Provides standardized interfaces.
Highly scalable and adaptable.
Incoming Cross-Chain Transactions
Process Overview:
- Transaction Detection and Monitoring
Continuously monitor external chain transactions pointing to Zenchain.
Transaction Validation
Use chain-specific validation methods (light clients, proof mechanisms, etc.).
Data Abstraction and Standardization
Convert to a format that Zenchain can uniformly process.
Transaction Storage and State Recording
Secure on-chain storage to ensure traceability.
Execution and State Transition
Execute corresponding operations on Zenchain (minting, state updates, etc.).
User Transparency
Provide query interfaces to track transaction status.
Outgoing Cross-Chain Transactions
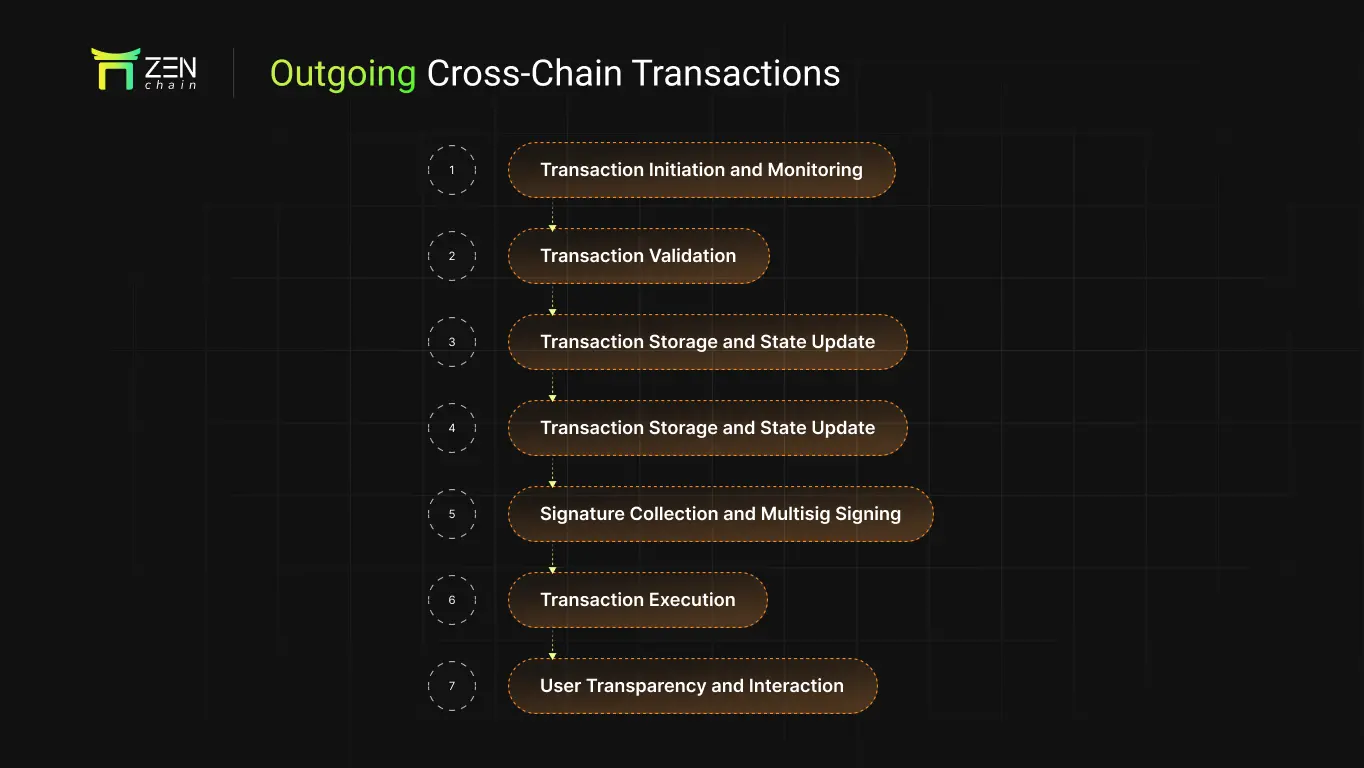
Process Overview:
- Transaction Initiation and Monitoring
Listen for cross-chain triggering events on Zenchain.
Transaction Validation
Verify compliance with cross-chain rules and authorization conditions.
Data Abstraction and Transformation
Convert to a data format recognizable by the target chain.
Transaction Storage and State Recording
Record cross-chain transaction information on Zenchain.
Multi-signature Collection
Signatures completed by Zenchain validators through multi-signature accounts.
Transaction Execution
Complete asset transfer or contract invocation on the target chain.
User Transparency
Support queries for cross-chain execution progress and results.
- Niō AI
Overall Positioning
Niō is Zenchain's built-in AI-driven security guardian system.
Through decentralized AI + real-time monitoring, it identifies and defends against threats before escalation.
The goal is to provide continuous, adaptive chain-level security protection for Zenchain.
Core Capabilities
Real-time Security Monitoring: Continuously scans on-chain activities and ecological behaviors.
Decentralized Security Intelligence: Avoids single points of failure.
Machine Learning + Heuristic Analysis: Responds to evolving attack methods.
Proactive Defense: Intervenes before or at the early stages of an attack.
Niō Guardians (Modular Security Guardians)
Niō adopts a modular design, allowing for flexible expansion of new Guardians based on attack types.
Deployed core Guardians include:
Scam Guardian: Identifies and warns against new types of scams.
Attack Guardian: Real-time detection and mitigation of protocol layer attacks.
Spam Guardian: Filters out spam tokens and NFTs, maintaining ecological quality.
Rug Pull Guardian: Identifies malicious code patterns to prevent rug pulls.
Sybil Guardian: Defends against Sybil attacks, ensuring the integrity of the identity system.
Tron Comments
Zenchain's advantage lies in its integrated Layer 1 design centered on cross-chain interoperability: through CLCM consensus and the hybrid mechanism of RAGE + GUARDIAN, it achieves provable finality while ensuring fast block production. Additionally, its native compatibility with EVM and integration of Wasm/BARK runtimes allow Ethereum applications and native modules to coexist efficiently. CCIM provides standardized, bidirectional cross-chain capabilities, covering multiple ecosystems like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Coupled with Niō AI's real-time security guardianship, the network possesses differentiated advantages in security and maintainability.
Its potential disadvantage is the high complexity of the architecture (multiple consensus components, multiple runtimes, multiple cross-chain modules), which places higher demands on validators, developers, and early governance of the ecosystem. Furthermore, the cross-chain and AI security capabilities still require time to validate their long-term stability and cost efficiency under large-scale real loads.
### Industry Data Analysis
1. Overall Market Performance
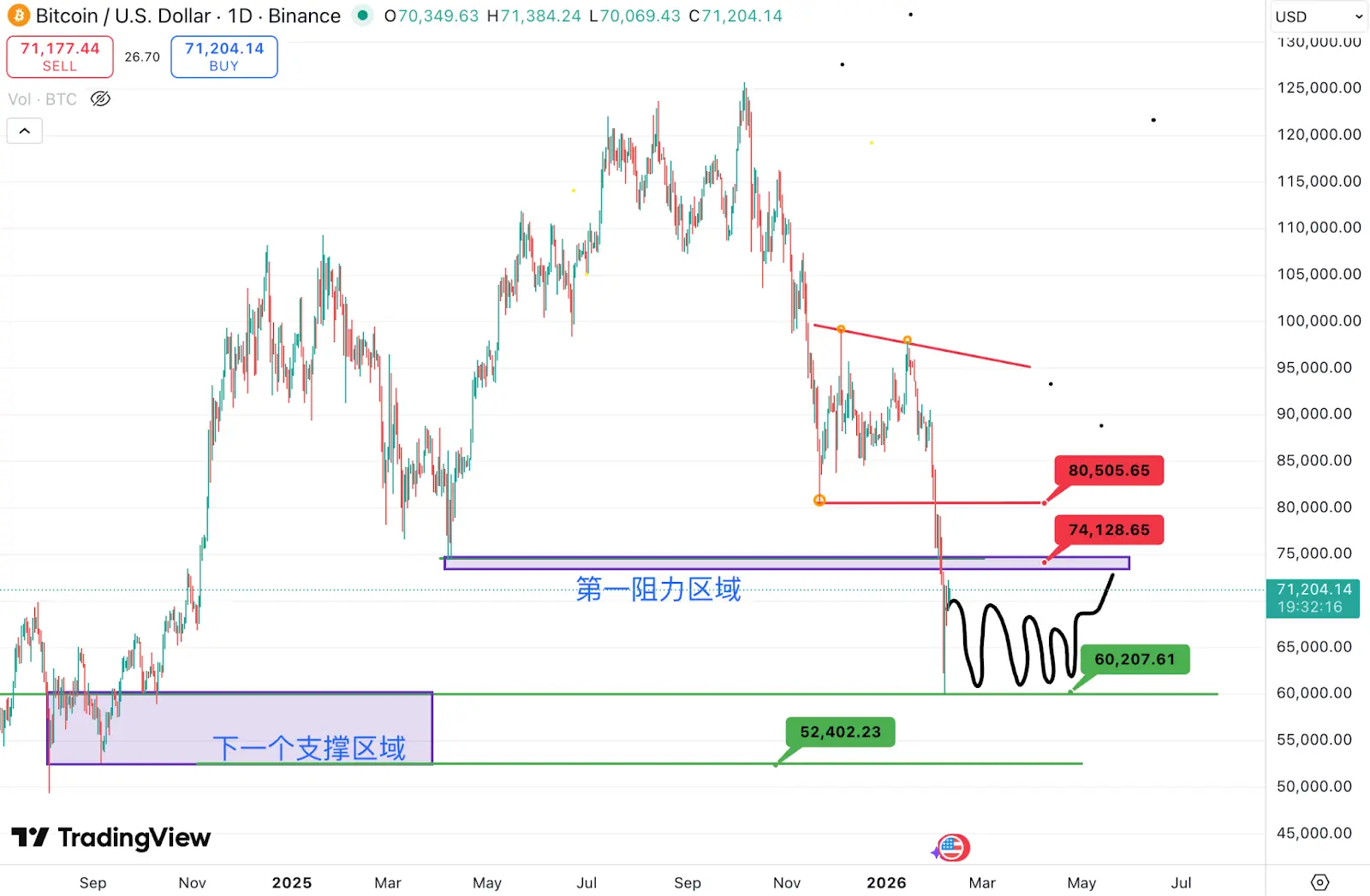
1.1. Spot BTC vs ETH Price Trends
BTC
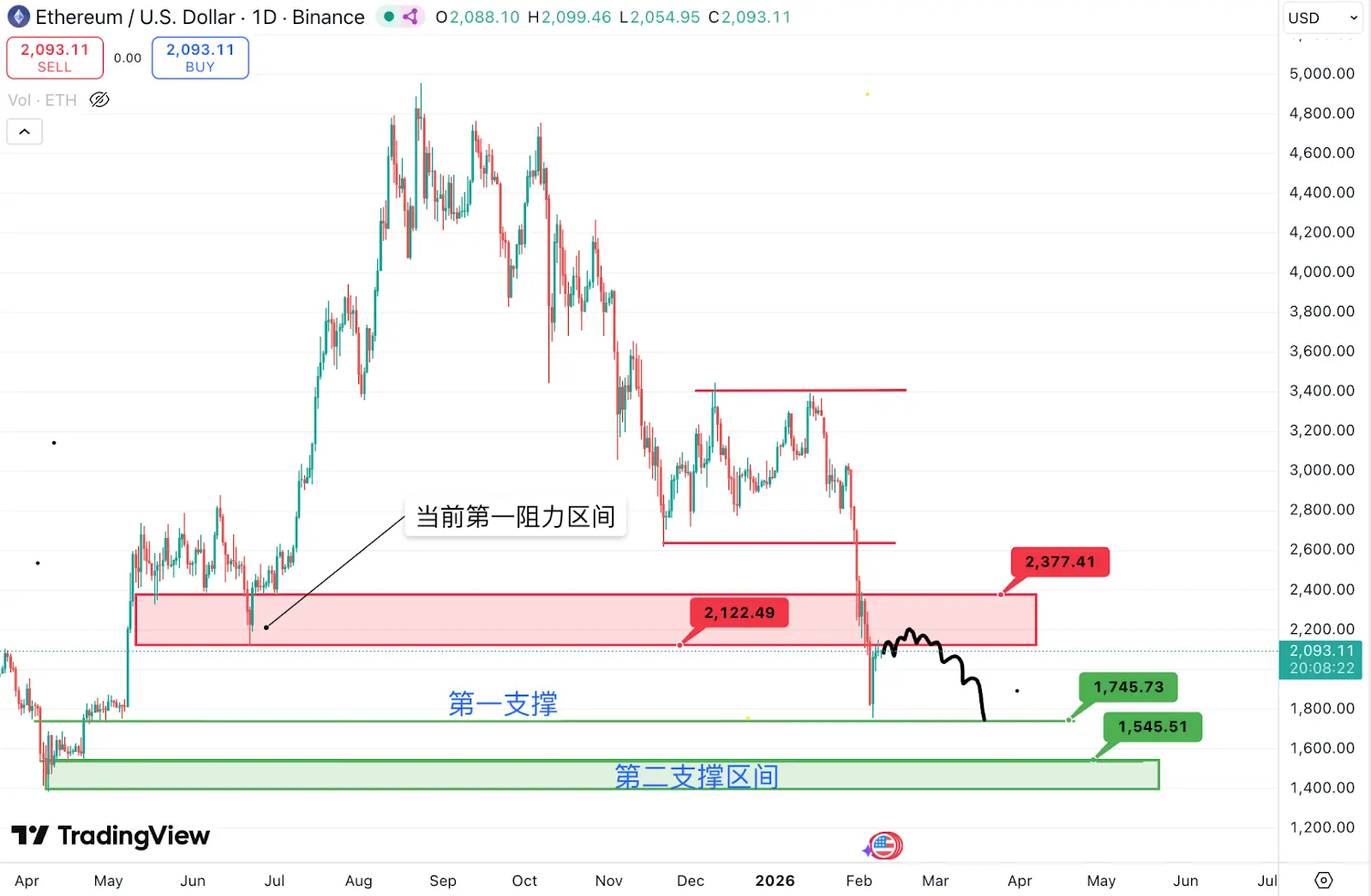
ETH
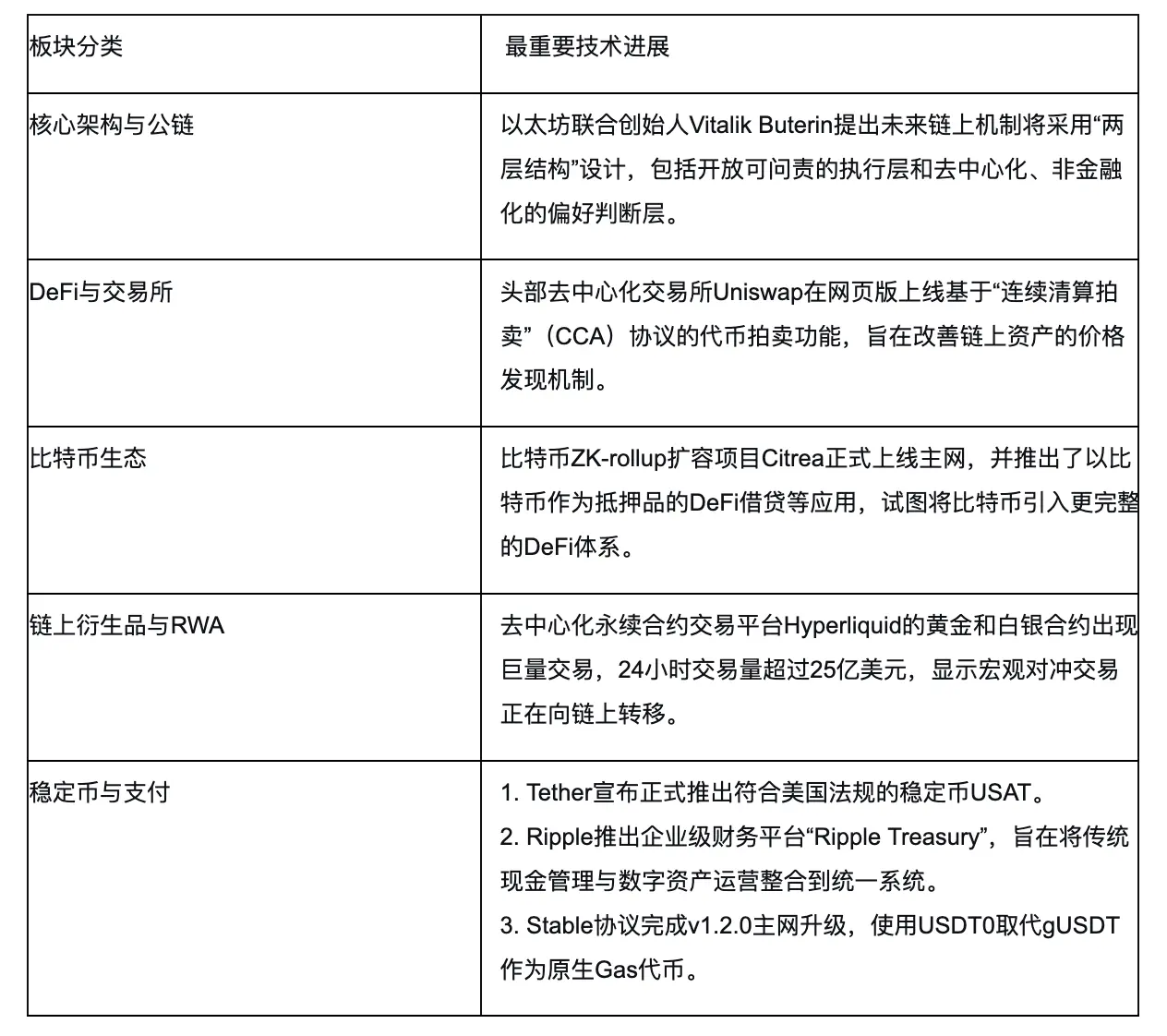
2. Summary of Hot Sectors
### 3. Macroeconomic Data Review and Key Data Release Nodes for Next Week
Important macroeconomic data released this week:
February 10: U.S. December Retail Sales Month-on-Month
February 11: U.S. January Unemployment Rate; U.S. January Seasonally Adjusted Non-Farm Payrolls
February 13: U.S. January Unadjusted CPI Year-on-Year
### 4. Regulatory Policies
China: Comprehensive Risk Prevention Notice Released
On February 5, 2026, eight Chinese ministries jointly issued a notice on further preventing and addressing risks related to virtual currencies, upgrading regulatory measures comprehensively.
Core Policy: The notice explicitly prohibits all virtual currencies and the tokenization of real-world assets, classifying them as illegal financial activities, and requires financial institutions, payment agencies, and internet companies not to provide any related services.
New Regulatory Targets: In addition to virtual currencies, it explicitly includes the tokenization of real-world assets in the comprehensive prohibition scope for the first time and imposes strict regulations on domestic entities conducting related businesses abroad.
Law Enforcement Coordination: Emphasizes the establishment of a collaborative working mechanism between central and local authorities to severely crack down on related illegal financial and criminal activities.
United States: Legislative and Regulatory Coordination Progress
This week, the United States made clear progress in crypto legislation and regulatory coordination.
Legislative Process: On January 29, the Senate Agriculture Committee passed its version of the "Digital Asset Market Structure Act" by a vote of 12 to 11. The bill aims to expand the regulatory authority of the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission over the spot cryptocurrency market and still needs to be coordinated with the Senate Banking Committee's version of the bill.
Executive Coordination: On February 2, the White House Crypto Policy Committee convened representatives from the cryptocurrency and traditional financial sectors to focus on unresolved issues such as market structure legislation and stablecoin yields.
Regulatory Cooperation: The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission announced that they will jointly advance a "crypto project" to coordinate regulatory approaches to the digital asset market and reduce uncertainty arising from jurisdictional ambiguities.
European Union: Advancing Tax Transparency Directive Implementation
At the EU level, efforts are underway to push member states to implement existing cryptocurrency tax transparency rules.
Violation Handling: On January 30, the European Commission confirmed that 12 member states (including Belgium, Spain, the Netherlands, etc.) failed to timely transpose the "DAC8 Directive" into national law. This directive requires cryptocurrency service providers to report customer transaction information to tax authorities. The EU has initiated infringement procedures, demanding that these countries complete the transposition within two months.
Goal: This move aims to ensure the automatic exchange of cryptocurrency tax information across the EU to combat tax evasion.
Global Level: G20 Calls for Multilateral Regulatory Cooperation
- In a joint communiqué issued after the G20 finance ministers and central bank governors meeting held in early February, leaders from various countries called on international standard-setting bodies, such as the Financial Stability Board, to monitor risks associated with cryptocurrency assets and consider taking multilateral response measures. They also emphasized their expectation for the Financial Action Task Force to adopt its new guidelines on cryptocurrency assets by the end of this month.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




