This report is written by Tiger Research. In 2025, the U.S. government is implementing a policy that supports cryptocurrency, with a clear goal: to regulate the existing cryptocurrency industry in the same way as traditional finance.
Key Points Summary
The U.S. is working to integrate cryptocurrency into its existing financial infrastructure, rather than simply absorbing the entire industry.
Over the past year, Congress, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have gradually incorporated cryptocurrency into this system by introducing and adjusting rules.
Despite tensions among regulators, the U.S. continues to support industry growth while refining its regulatory framework.
1. U.S. Absorption of the Cryptocurrency Industry
After President Trump was re-elected, the government launched a series of radical pro-cryptocurrency policies. This marked a sharp turn from past positions, where the cryptocurrency industry was primarily viewed as a subject of regulation and control. The U.S. has entered a phase that was once unimaginable, absorbing the cryptocurrency industry into its existing system at an almost unilateral decision-making pace.
The shift in positions of the SEC and CFTC, along with traditional financial institutions venturing into cryptocurrency-related businesses, indicates that broad structural changes are underway.
Notably, all of this has occurred just a year after President Trump's re-election. What specific changes have taken place in the U.S. at the regulatory and policy levels so far?
2. Changes in U.S. Cryptocurrency Stance Over a Year
In 2025, with the Trump administration in power, U.S. cryptocurrency policy reached a significant turning point. The executive branch, Congress, and regulatory agencies acted in concert, focusing on reducing market uncertainty and integrating cryptocurrency into the existing financial infrastructure.
2.1. U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
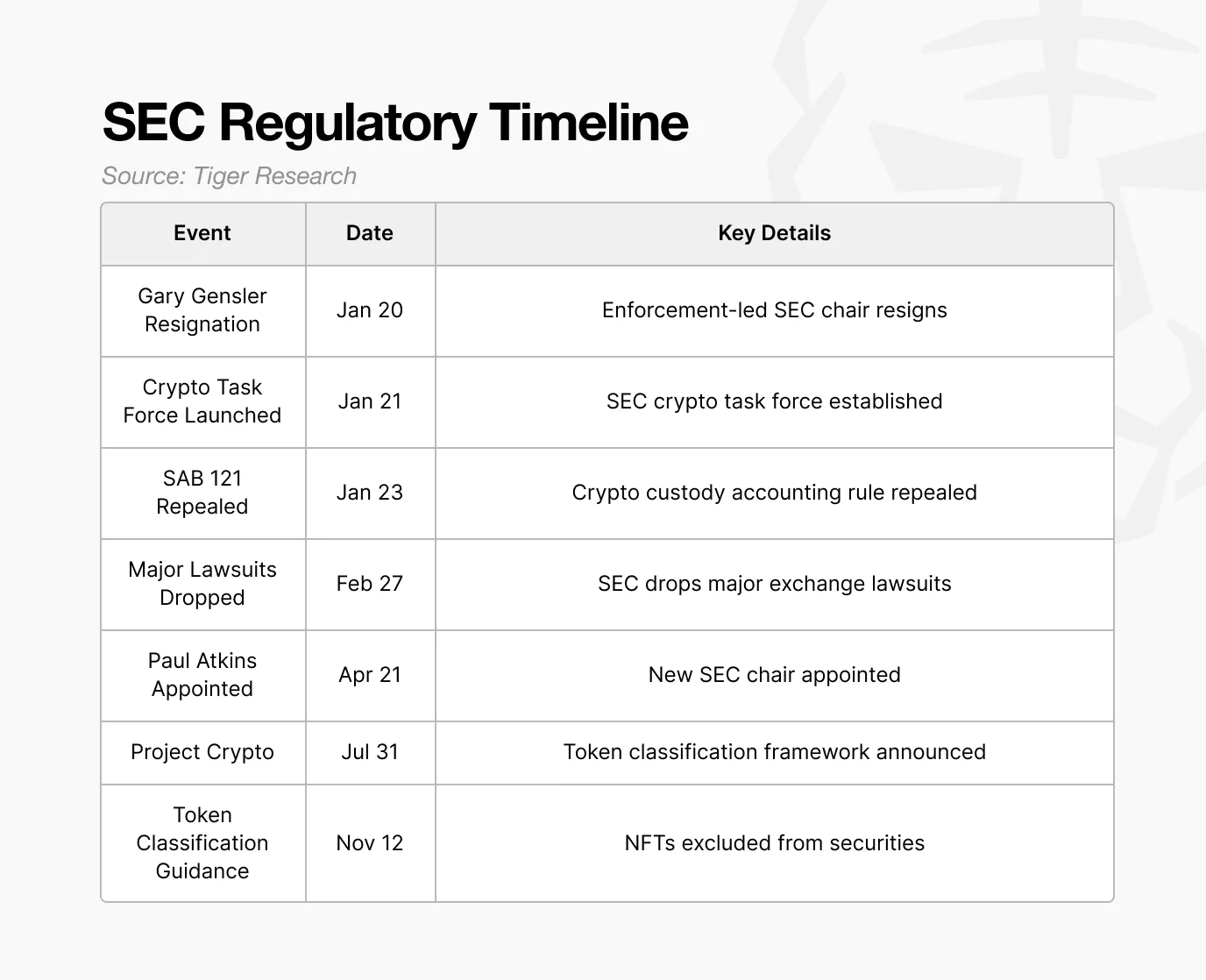
In the past, the SEC primarily relied on enforcement actions to address cryptocurrency-related activities. In major cases involving Ripple, Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken's staking services, the SEC filed lawsuits without providing clear standards regarding the legal status of tokens or what activities were permitted, often basing its enforcement on post hoc interpretations. This led cryptocurrency companies to focus more on managing regulatory risks rather than business expansion.
This stance began to change after the resignation of Chairman Gary Gensler, who held a conservative view of the cryptocurrency industry. Under the leadership of Paul Atkins, the SEC shifted to a more open approach, beginning to establish foundational rules aimed at incorporating the cryptocurrency industry into the regulatory framework rather than relying solely on litigation for regulation.
A key example is the announcement of the "Crypto Project." Through this initiative, the SEC expressed its intent to establish clear standards to define which tokens are considered securities and which are not. This once ambiguous regulatory body is beginning to reshape itself into a more inclusive institution.
2.2. U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission
 Source: Tiger Research
Source: Tiger Research
In the past, the CFTC's involvement with cryptocurrency was largely limited to regulating the derivatives market. However, this year, it has taken a more proactive stance, officially recognizing Bitcoin and Ethereum as commodities and supporting traditional institutions in using them.
The "Digital Asset Collateral Pilot Program" is a key initiative. Through this program, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and USDC are permitted as collateral for derivatives trading. The CFTC applied reduction ratios and risk management standards to treat these assets in the same way as traditional collateral.
This shift indicates that the CFTC no longer views crypto assets purely as speculative tools but is beginning to recognize them as stable collateral assets that can stand alongside traditional financial assets.
2.3. Office of the Comptroller of the Currency
 Source: Tiger Research
Source: Tiger Research
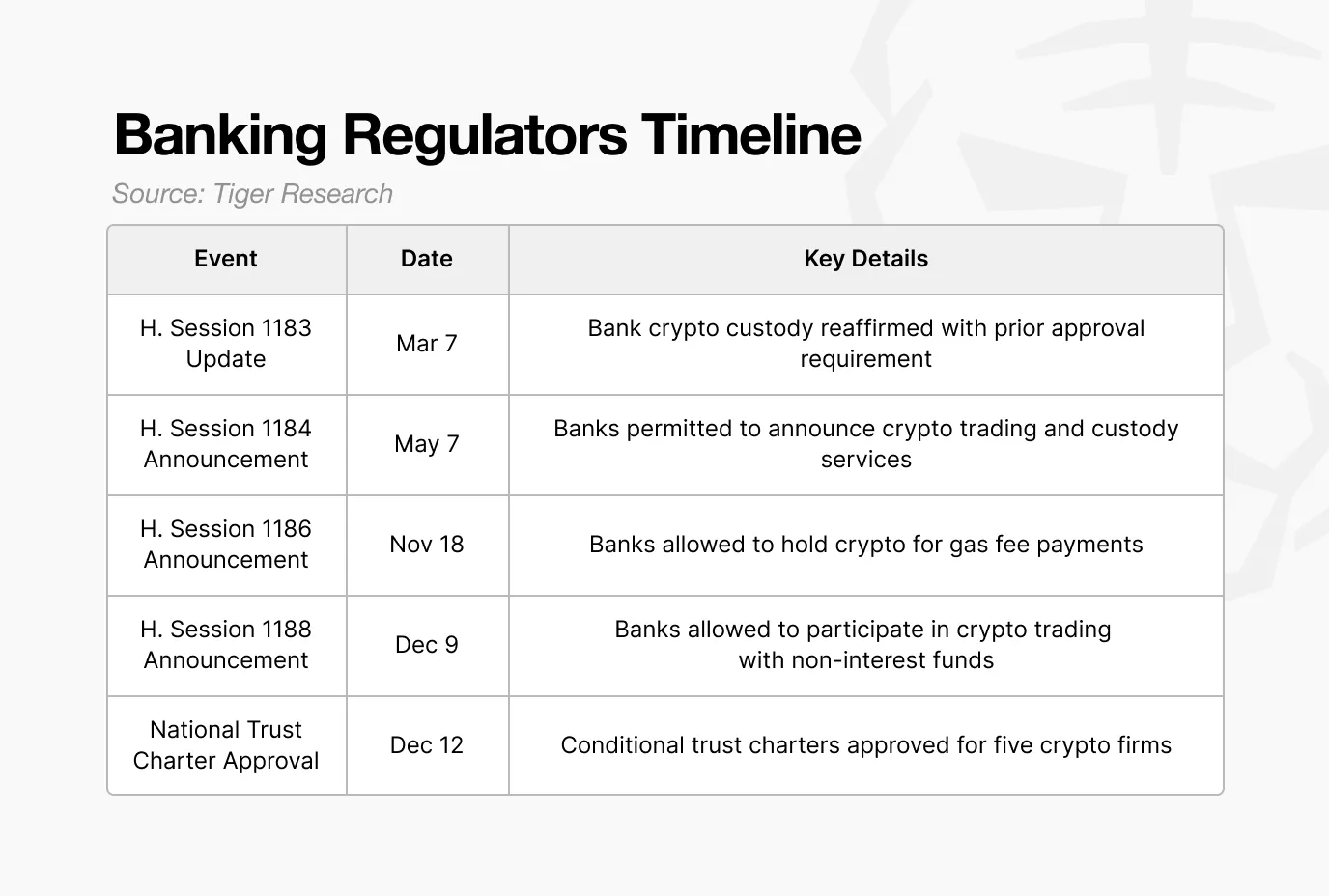
In the past, the OCC maintained a distance from the cryptocurrency industry. Cryptocurrency companies had to apply for licenses on a state-by-state basis, making it difficult to enter the federal banking regulatory system, limiting business expansion, and structurally obstructing connections with the traditional financial system, thus mostly operating outside the regulated framework.
Now, this practice has changed. The OCC has chosen to incorporate cryptocurrency companies into the existing banking regulatory framework rather than exclude them from the financial system. It has issued a series of interpretive letters (formal documents clarifying whether specific financial activities are permitted), gradually expanding the scope of allowed activities, including crypto asset custody, trading, and even bank payment transaction fees on the blockchain.
This series of changes culminated in December when the OCC conditionally approved national trust bank charters for major companies like Circle and Ripple. This is significant because it grants these crypto companies the same status as traditional financial institutions. Under a single federal regulation, they can operate nationwide, and transfers that previously required intermediary banks can now be processed directly like traditional banks.
2.4. Legislation and Executive Orders
 Source: Tiger Research
Source: Tiger Research
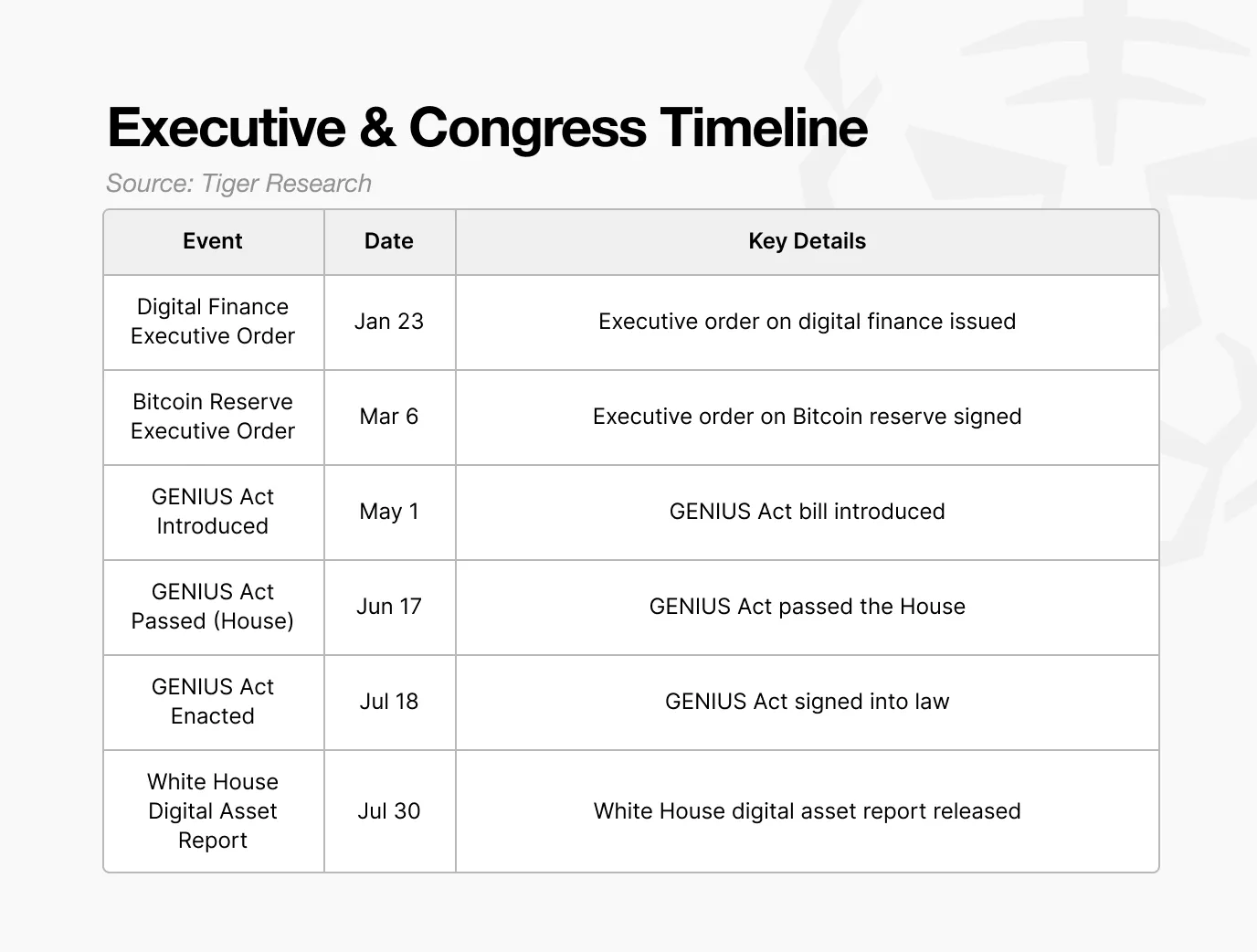
In the past, although the U.S. began to draft stablecoin legislation in 2022, repeated delays led to a regulatory vacuum in the market. There was a lack of clear standards regarding reserve composition, regulatory authority, and issuance requirements, making it difficult for investors to reliably verify whether issuers held sufficient reserves, raising concerns about the transparency of some issuers' reserves.
The GENIUS Act addresses these issues by clearly defining stablecoin issuance requirements and reserve standards. It mandates that issuers must hold reserves equal to 100% of the issued amount and prohibits the rehypothecation of reserve assets, while consolidating regulatory authority under federal financial regulatory agencies.
As a result, stablecoins have become legally recognized digital dollars with guaranteed payment capabilities.
3. Established Direction with Competition and Checks and Balances
Over the past year, the direction of U.S. cryptocurrency policy has been clear: to integrate the cryptocurrency industry into the formal financial system. However, this process has not been uniform or frictionless.
Internal divisions of opinion still exist in the U.S. A typical example is the debate surrounding the privacy mixing service Tornado Cash: the executive branch actively enforces actions to block illegal fund flows, while the SEC chairman publicly warns against overly suppressing privacy. This indicates that there is not yet complete unity within the U.S. government regarding cryptocurrency.
However, these divisions do not equate to policy instability; they are more reflective of the inherent characteristics of the U.S. decision-making system. Agencies with different responsibilities interpret issues from their own perspectives, sometimes publicly expressing dissent, moving forward through mutual checks and persuasion. The tension between strict enforcement and innovation protection may lead to short-term friction, but in the long run, it helps to make regulatory standards more specific and precise.
The key is that this tension has not stalled the process. Even amidst debates, the U.S. continues to advance on multiple fronts: SEC rule-making, CFTC infrastructure integration, OCC institutional absorption, and congressional legislation establishing standards. It does not wait for complete consensus but allows competition and coordination to proceed in parallel, driving the system forward.
Ultimately, the U.S. has neither completely let cryptocurrency run free nor attempted to suppress its development; instead, it has simultaneously reshaped regulation, leadership, and market infrastructure. By transforming internal debates and tensions into momentum, the U.S. has chosen a strategy that directs the global cryptocurrency industry center towards itself.
The past year has been crucial because this direction has transcended mere declarations and has been effectively translated into concrete policies and execution.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




