In-depth Analysis of the Ethereum Fusaka Upgrade and Its Impact
Author: Tanay Ved
Translation: Baihua Blockchain

Key Points:
Fusaka expands Ethereum's scalability through higher Blob capacity and a more powerful PeerDAS efficient data availability system.
L1 throughput significantly increases with a higher 60M Gas limit and execution layer optimizations.
Improved fee mechanisms and user experience (UX) upgrades lay the foundation for a more unified and cost-effective L1-L2 ecosystem.
Overview of Fusaka
Ethereum plans to undergo its next upgrade, codenamed “Fusaka” hard fork, on December 3, 2025, at 21:49 UTC (slot 13,164,544). Fusaka combines the execution layer upgrade Osaka and the southern layer upgrade Fulu, following the architecture of past forks.
Following the Pectra upgrade in May, Fusaka takes an important step in Ethereum's scalability roadmap, as it enhances Layer-1 performance, expands Blob capacity, improves Rollup cost efficiency, and brings UX upgrades. It also introduces the Blob Parameter Specific (BPO) fork, which safely increases Blob capacity as Rollup demand grows. Earlier this year, the Ethereum Foundation outlined its “Protocol Strategy”, centered around three long-term goals: scaling L1, scaling Blobs, and improving UX. Fusaka is the first upgrade fully aligned with this unified vision, marking a turning point in how Ethereum plans to scale and improve accessibility in the future.
Scalability Highlights
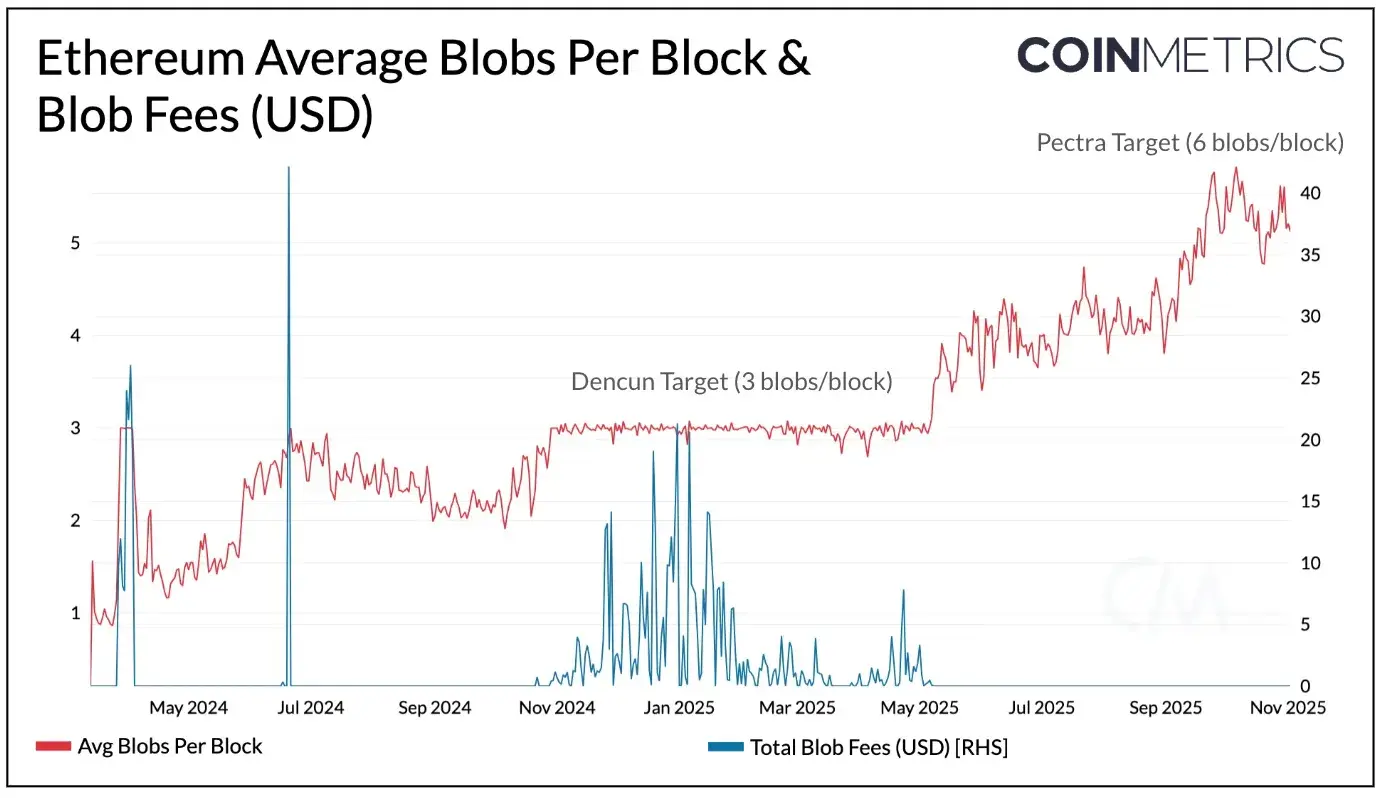
Last year's Decun upgrade introduced efficient “Blobs”, an economical way to store transaction data on the Ethereum mainnet for Rollups. Since then, Blobs have gained significant traction driven by Rollups like Base, Arbitrum, and Lighter. This has led to Blob usage nearing peak levels (currently close to the target of every 6 Blob blocks), creating a risk of exponential surges in Rollup demand. The higher demand for data availability (DA) has made Blob space a critical bottleneck in Ethereum's scalability path, and Fusaka directly addresses these limitations.
PeerDAS: Peer Data Availability Sampling
PeerDAS (EIP-7594), or peer data availability sampling, can be considered the most significant upgrade in Fusaka, as it directly aligns with the goals of scaling L1 and Blobs. PeerDAS introduces a more efficient way for Ethereum nodes to check the availability of Blob data. Instead of requiring full nodes to download the entire Blob, it verifies data availability by sampling small fragments of the data content, providing the same security guarantees without increasing the load on L1 relay nodes.
Expected Impacts:
Nodes only store about 1/8 of each Blob, enabling greater Blob throughput without increasing hardware requirements.
Allows Ethereum to safely increase Blob capacity, which is a core driver of Rollup capacity.
Lower internal data availability costs lead to cheaper L2 transactions and more reliable batch releases.
Lays the groundwork for full Danksharding and higher overall transaction throughput across the ecosystem. For example, Base stated in a blog post that post-Fusaka L2 scalability improvements will be able to “double its chain throughput within 2 months.”
Blob Parameter Specific (BPO) Fork
As PeerDAS reduces the bandwidth and storage required for nodes to validate Blob data, Ethereum can now safely increase Blob capacity. Fusaka introduces the Blob Parameter Specific (BPO) fork, aimed at gradually increasing the number of Blobs per block over time. This allows Ethereum to adjust Blob parameters while waiting for a complete hard fork, providing a more flexible and responsive scaling tool for the protocol.
Upcoming BPO Forks:
Early 2026: Increase from 6 to 12 (slot 14,000,000)
End of 2026: Increase from 12 to 25 (slot 15,500,000)
Early 2027: Increase from 25 to 50 (slot 16,300,000)
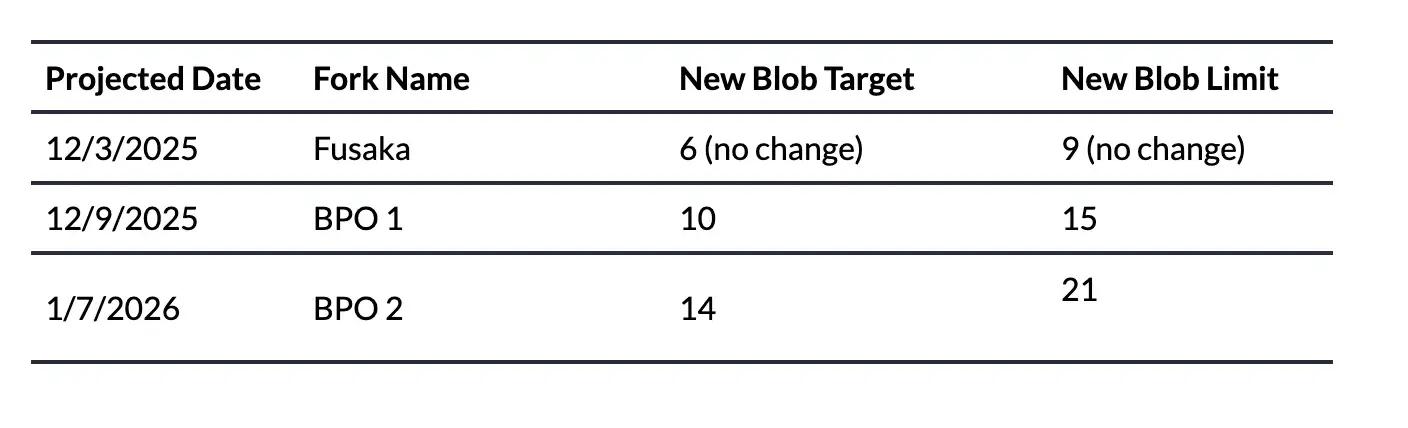
Expected Impacts:
More DA bandwidth: Increases Rollup capacity from 6 Blobs per block to 128 Blobs, reducing L2 transaction fees.
Flexible scaling: Blob parameters can be dynamically adjusted as demand grows.
Gradual development path: Aligns with Ethereum's roadmap for achieving cheaper Rollup execution and scalable data availability.
Blob Base Fee Adjustment
As Blob capacity expands, Ethereum's Blob fee market will play a larger role in aligning with Rollup demand. Currently, Rollup consumption on Blobs is nearly zero. Since Blob prices typically remain at a minimum of 1 wei, demand is relatively price-insensitive and does not always adjust smoothly with usage changes. This has led to the fee mechanism remaining in a “non-elastic” range, limiting its responsiveness to changes in usage.
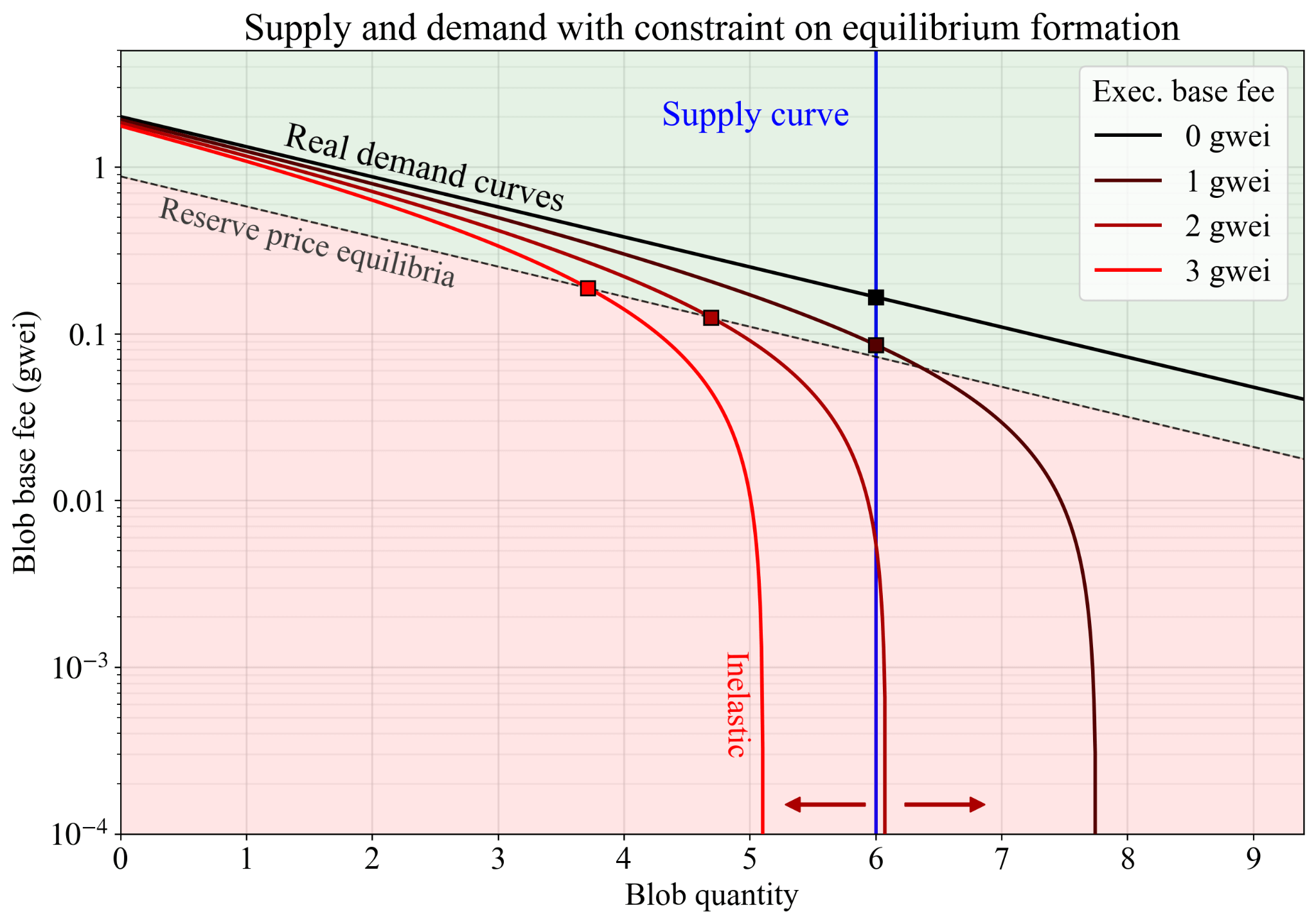
Fusaka introduces a minimum for Blob base fees by partially linking them to L1 base fees. This can prevent Blob prices from dropping to zero and maintain compatibility of the fee adjustment mechanism as Blob space expands.
More stable Blob pricing: Prevents the fee market from falling to the lowest price.
Predictable economics for Rollups: Ensures Rollups pay a reasonable baseline fee for data availability without sudden or unstable fee jumps.
Minimal impact on user costs: Even with the new minimum, L2 data costs remain as low as a few cents, with negligible impact on user experience.
Sustainable long-term economics: Increases node processing of the added Blob throughput, with Blob fees today contributing to ETH's adaptability, potentially expanding over time and capacity.
Scaling L1
Fusaka also places significant emphasis on L1 scaling. It enhances Ethereum's Layer-1 execution capabilities by raising the protocol's default Gas limit to 60M through EIP-7935. This directly increases the number of transactions that can fit into a block, resulting in higher throughput, less congestion, and cheaper Gas fees.
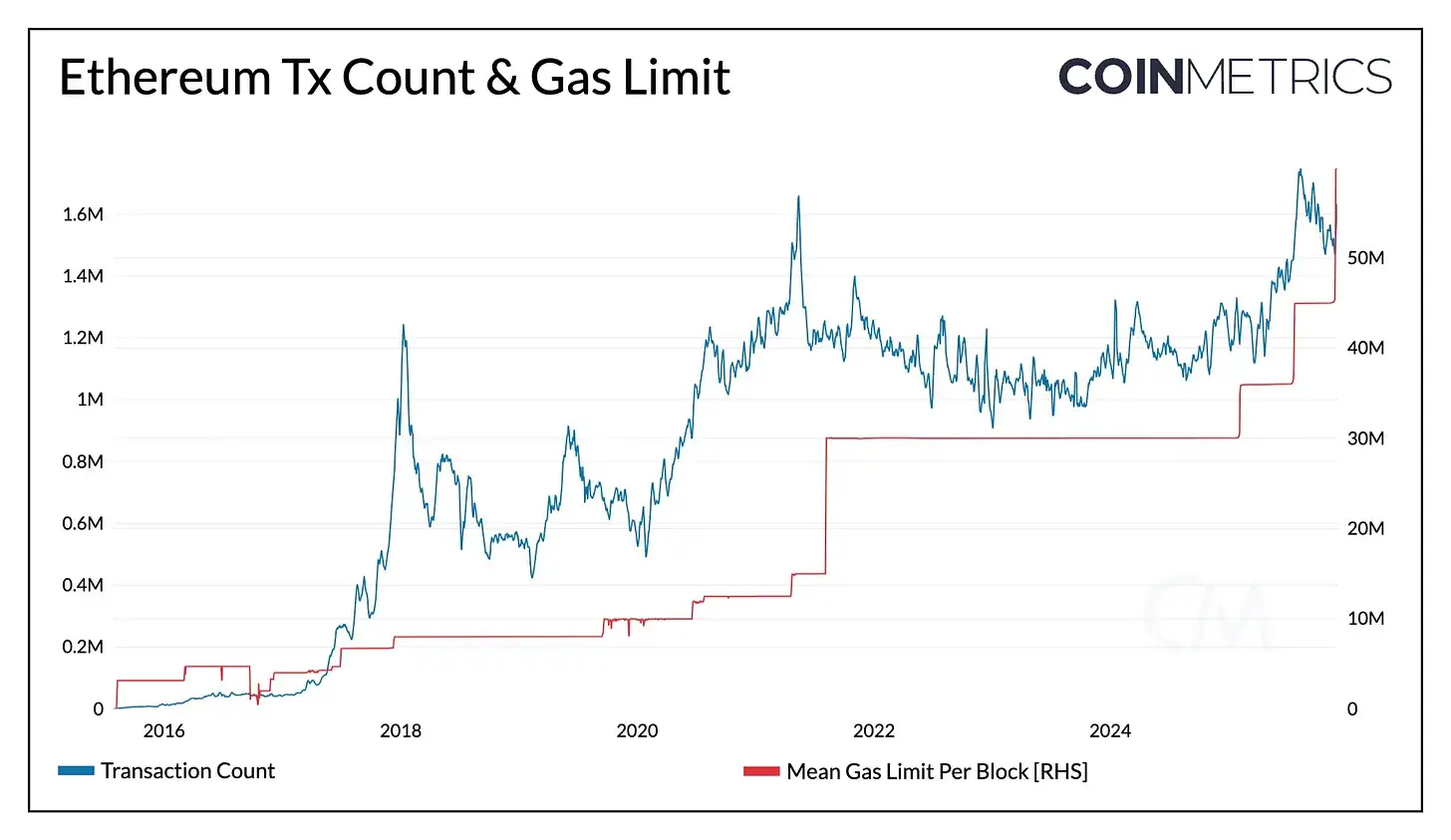
Expected Impacts:
Higher throughput: More computation per block increases total L1 capacity.
Supports more complex applications: A larger Gas limit supports complex contract executions.
Less pre-block congestion under load: Additional space reduces pre-block congestion during demand peaks.
Helps maintain low fees: Additional capacity supports the current low fee environment (0.4 gwei).
In addition to the increase in Gas limits, Fusaka also introduces improvements that make L1 execution clearer and prepare the network for future scaling. The new per-transaction Gas usage cap prevents any single transaction from dominating a block and solidifies the foundation for wood execution. Updates to the ModExp precompile readjust Gas costs and set clearer boundaries for operations, maintaining predictable resource usage as goods grow. The network layer is also simplified by removing outdated pre-merge fields, making synchronization of Ethereum nodes faster and more convenient.
Improving User Experience
Fusaka also introduces updates to improve user and developer usability. EIP -7951 adds native support for secp256r1 elliptic curves, which is the signature standard used by Apple Secure Enclave, Android Keystore, and most consumer hardware. This allows wallets and applications to directly integrate similar authentication processes (Face ID, Touch ID, WebAuthn) into Ethereum, thereby reducing onboarding friction and enhancing security for retail and institutional users.
These contribute to upgrading the developer and user interface of modern Ethereum, making it easier to build secure, mainstream applications.
Conclusion
With the activation of Fusaka, the most immediate impacts will be seen in lower Rollup costs, higher Blob throughput, and significant expansion of L1 execution capabilities. Combined with larger Blob space, overhead, and ongoing improvements in L1 performance, this will shape the financial dynamics of L2 settlements, influencing related dynamics and clearing the broader Ethereum ecosystem's sense of internal aggregation.
While the long-term value impact ultimately depends on demand and adoption, Fusaka lays a clearer and more scalable foundation for the next phase of Ethereum, where L1 and L2 functionalities will work more seamlessly together, and the network will be better positioned to support higher capacities of users, assets, and on-chain activities.
Article link: https://www.hellobtc.com/kp/du/12/6151.html
Source: https://coinmetrics.substack.com/p/state-of-the-network-issue-340
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




