Author: Eli5DeFi
Compiled by: Tim, PANews
PANews Editor's Note: On November 25, Google's total market value reached a historic high of $3.96 trillion. Factors boosting the stock price include the newly released AI Gemini 3 and its self-developed chip TPU. Beyond the AI field, TPU will also play a significant role in blockchain.
The hardware narrative of modern computing is essentially defined by the rise of GPUs.
From gaming to deep learning, Nvidia's parallel architecture has become the industry standard, gradually shifting CPUs to a co-processing role.
However, as AI models encounter scaling bottlenecks and blockchain technology moves towards complex cryptographic applications, a new competitor, the Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), has emerged.
Although TPU is often discussed within the framework of Google's AI strategy, its architecture unexpectedly aligns with the core needs of the next milestone in blockchain technology: post-quantum cryptography.
This article explains why TPU (rather than GPU) is more suitable for the intensive mathematical computations required by post-quantum cryptography when building decentralized networks resistant to quantum attacks, by reviewing the evolution of hardware and comparing architectural characteristics.
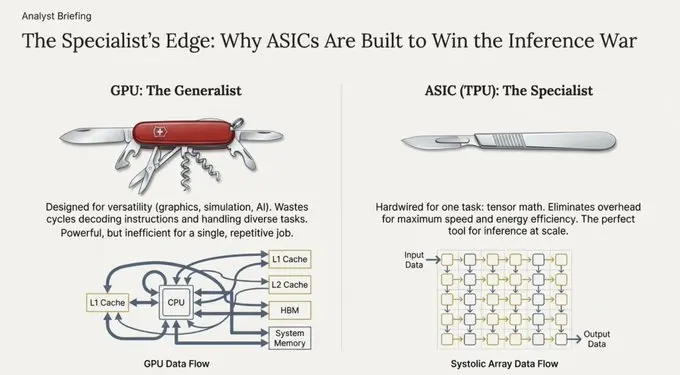
Hardware Evolution: From Serial Processing to Pulsed Architecture
To understand the importance of TPU, one must first grasp the problems it addresses.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): As a versatile player, it excels at serial processing and logical branching operations but is limited when it comes to executing massive mathematical computations simultaneously.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): As a parallel processing expert, it was originally designed for rendering pixels, thus excelling at executing many identical tasks simultaneously (SIMD: Single Instruction, Multiple Data). This characteristic made it a cornerstone during the early explosion of artificial intelligence.
- Tensor Processing Unit (TPU): A specialized chip designed by Google specifically for neural network computation tasks.
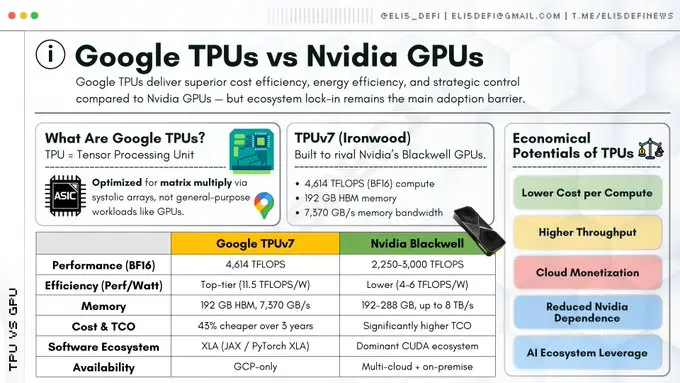
Advantages of Pulsed Architecture
The fundamental difference between GPU and TPU lies in their data processing methods.
GPUs repeatedly access memory (registers, caches) for computations, while TPUs utilize a pulsed architecture. This architecture functions like a heart pumping blood, allowing data to flow through a grid of large-scale computing units in a rhythmic manner.
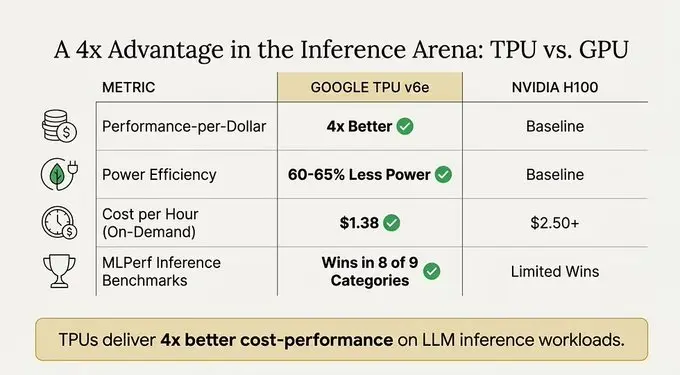
https://www.ainewshub.org/post/ai-inference-costs-tpu-vs-gpu-2025
The computation results are directly passed to the next computing unit without needing to write back to memory. This design significantly alleviates the von Neumann bottleneck, which is the delay caused by the repeated movement of data between memory and the processor, thus achieving an order of magnitude increase in throughput for specific mathematical operations.
The Key to Post-Quantum Cryptography: Why Does Blockchain Need TPU?
The most critical application of TPU in the blockchain field is not mining, but cryptographic security.

Current blockchain systems rely on elliptic curve cryptography or RSA encryption systems, which have fatal weaknesses when facing Shor's algorithm. This means that once sufficiently powerful quantum computers emerge, attackers could derive private keys from public keys, potentially emptying all encrypted assets on Bitcoin or Ethereum.
The solution lies in post-quantum cryptography. Currently, mainstream PQC standard algorithms (such as Kyber, Dilithium) are based on lattice cryptography.
TPU's Mathematical Compatibility
This is where TPU has an advantage over GPU. Lattice cryptography heavily relies on dense operations involving large matrices and vectors, primarily including:
- Matrix-vector multiplication: As+e (where A is a matrix, and s and e are vectors).
- Polynomial operations: Algebraic operations based on rings, typically implemented using number-theoretic transforms.
Traditional GPUs treat these operations as general parallel task processing, while TPUs achieve dedicated acceleration through hardware-level fixed matrix computation units. The mathematical structure of lattice cryptography almost perfectly maps to the physical construction of TPU's pulsed array.
The Technical Competition Between TPU and GPU
Although GPUs remain the universal king in the industry, TPUs have a clear advantage when handling specific mathematically intensive tasks.
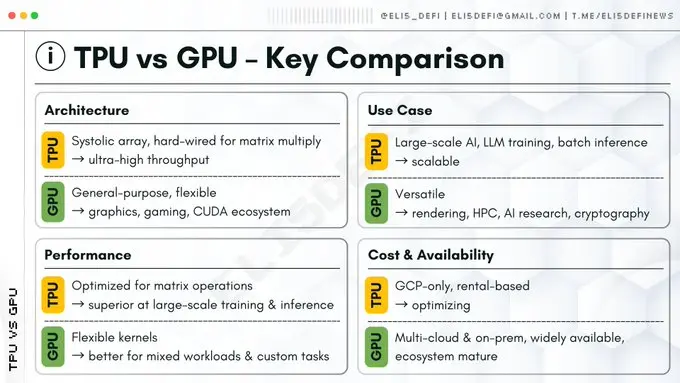
Conclusion: GPUs excel in versatility and ecosystem, while TPUs dominate in the efficiency of dense linear algebra computations, which are the core mathematical operations relied upon by AI and modern advanced cryptography.
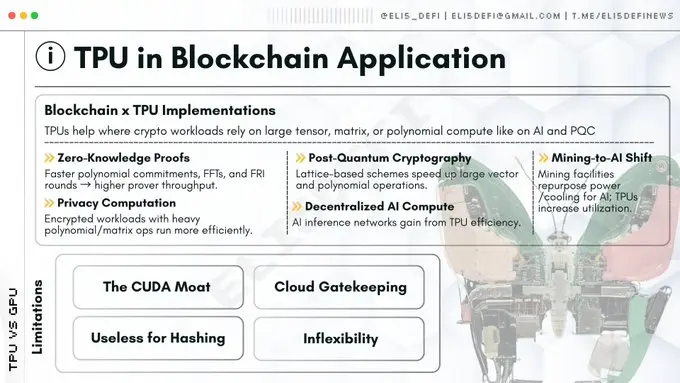
Expanding the TPU Narrative: Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Decentralized AI
In addition to post-quantum cryptography, TPUs also show application potential in two other key areas of Web3.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
ZK-Rollups (such as Starknet or zkSync) serve as scalability solutions for Ethereum, and their proof generation process requires massive computations, primarily including:
- Fast Fourier Transform: Achieving rapid transformation of data representation.
- Multi-scalar multiplication: Combining point operations on elliptic curves.
- FRI protocol: A cryptographic proof system for verifying polynomials.
These operations are not hash computations that ASICs excel at, but rather polynomial mathematics. Compared to general CPUs, TPUs can significantly accelerate FFT and polynomial commitment operations; due to the predictable data flow characteristics of these algorithms, TPUs typically achieve higher efficiency than GPUs.
With the rise of decentralized AI networks like Bittensor, network nodes need to be capable of running AI model inference. Running general large language models essentially involves executing massive matrix multiplication operations.
Compared to GPU clusters, TPUs enable decentralized nodes to handle AI inference requests with lower energy consumption, thereby enhancing the commercial viability of decentralized AI.
TPU Ecosystem Landscape
Although most current projects still rely on GPUs due to the prevalence of CUDA, the following areas are poised for TPU integration, especially under the narrative framework of post-quantum cryptography and zero-knowledge proofs.

Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Scalability Solutions
Why choose TPU? Because ZK proof generation requires large-scale parallel processing of polynomial operations, and under specific architectural configurations, TPUs far exceed general GPUs in handling such tasks.
- Starknet (Layer 2 scalability solution): STARK proofs heavily rely on fast Fourier transforms and fast Reed-Solomon interactive oracle proofs, which are computationally intensive operations that align closely with TPU's computational logic.
- zkSync (Layer 2 scalability solution): Its Airbender prover needs to handle large-scale FFT and polynomial operations, which are the core bottlenecks that TPU can address.
- Scroll (Layer 2 scalability solution): It uses the Halo2 and Plonk proof systems, where the core operations of KZG commitment verification and multi-scalar multiplication perfectly match TPU's pulsed architecture.
- Aleo (Privacy-preserving public chain): Focused on zk-SNARK zero-knowledge proof generation, its core operations rely on polynomial mathematical characteristics that align well with TPU's dedicated computational throughput.
- Mina (Lightweight public chain): Utilizing recursive SNARKs technology, its mechanism of continuously regenerating proofs requires repeated execution of polynomial operations, highlighting the value of TPU's efficient computation.
- Zcash (Privacy coin): The classic Groth16 proof system relies on polynomial operations. Although it is an early technology, high-throughput hardware can still significantly benefit from it.
- Filecoin (DePIN, storage): Its replication proof mechanism verifies the validity of stored data through zero-knowledge proofs and polynomial encoding techniques.
Decentralized AI and Agent-Based Computing
Why choose TPU? This is precisely the native application scenario for TPU, designed to accelerate neural network machine learning tasks.
- Bittensor: Its core architecture is decentralized AI inference, which aligns perfectly with TPU's tensor computing capabilities.
- Fetch (AI agents): Autonomous AI agents rely on continuous neural network inference for decision-making, and TPUs can run these models with lower latency.
- Singularity (AI service platform): As a marketplace for AI service transactions, Singularity significantly enhances the speed and cost-effectiveness of underlying model execution by integrating TPUs.
- NEAR (Public chain, AI strategic transformation): Transitioning to on-chain AI and trusted execution environment agents, the tensor operations it relies on require TPU acceleration.
Post-Quantum Cryptography Networks
Why choose TPU? The core operations of post-quantum cryptography often involve the shortest vector problem in lattices, which requires dense matrix and vector operations, sharing a high degree of similarity in computational architecture with AI workloads.
- Algorand (public chain): Adopts quantum-safe hashing and vector operation solutions, highly compatible with TPU's parallel mathematical computation capabilities.
- QAN (quantum-resistant public chain): Utilizes lattice cryptography, with its underlying polynomial and vector operations having a high degree of isomorphism with TPU's specialized mathematical optimization domain.
- Nexus (computing platform, ZkVM): Its preparations for quantum-resistant computing involve polynomials and lattice-based algorithms that can be efficiently mapped to TPU's architecture.
- Cellframe (quantum-resistant public chain): The lattice cryptography and hash encryption technology it employs involves tensor-like operations, making it an ideal candidate for TPU acceleration.
- Abelian (privacy token): Focuses on post-quantum cryptography lattice operations. Similar to QAN, its technical architecture can fully benefit from TPU's high throughput characteristics in vector processing.
- Quantus (public chain): Post-quantum cryptographic signatures rely on large-scale vector operations, and TPU's parallel processing capabilities for such computations far exceed those of standard CPUs.
- Pauli (computing platform): Quantum-safe computing involves a large number of matrix operations, which is precisely the core advantage of TPU architecture.
Development Bottlenecks: Why Hasn't TPU Been Fully Popularized?
If TPU is so efficient in post-quantum cryptography and zero-knowledge proofs, why is the industry still scrambling for H100 chips?
- CUDA Moat: Nvidia's CUDA software library has become the industry standard, and the vast majority of cryptographic engineers program based on CUDA. Porting code to TPU's required JAX or XLA frameworks not only has a high technical threshold but also requires significant resource investment.
- Cloud Platform Access Barriers: High-end TPUs are almost exclusively monopolized by Google Cloud. If decentralized networks overly rely on a single centralized cloud service provider, they will face risks of censorship and single points of failure.
- Architectural Rigidity: If cryptographic algorithms need fine-tuning (such as introducing branching logic), TPU performance can drop sharply. GPUs far surpass TPUs in handling such irregular logic.
- Limitations in Hash Computation: TPUs cannot replace Bitcoin mining machines. The SHA-256 algorithm is a bit-level computation rather than a matrix computation, rendering TPUs useless in this domain.
Conclusion: Layered Architecture is the Future
The future of Web3 hardware is not a winner-takes-all competition but is evolving towards a layered architecture.
GPUs will continue to play a leading role in general computing, graphics rendering, and tasks requiring complex branching logic.
TPUs (and similar ASIC accelerators) will gradually become the standard configuration for the "mathematical layer" of Web3, specifically used for generating zero-knowledge proofs and verifying post-quantum cryptographic signatures.
As blockchain transitions to post-quantum security standards, the massive matrix operations required for transaction signatures and verification will make TPU's pulsed architecture not just an option but a necessary infrastructure for building scalable quantum-safe decentralized networks.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




