Author: J1N, Techub News
The new bullet for MicroStrategy has arrived, using collateralized Bitcoin to borrow $130 million. Without selling coins, they can obtain cash flow.
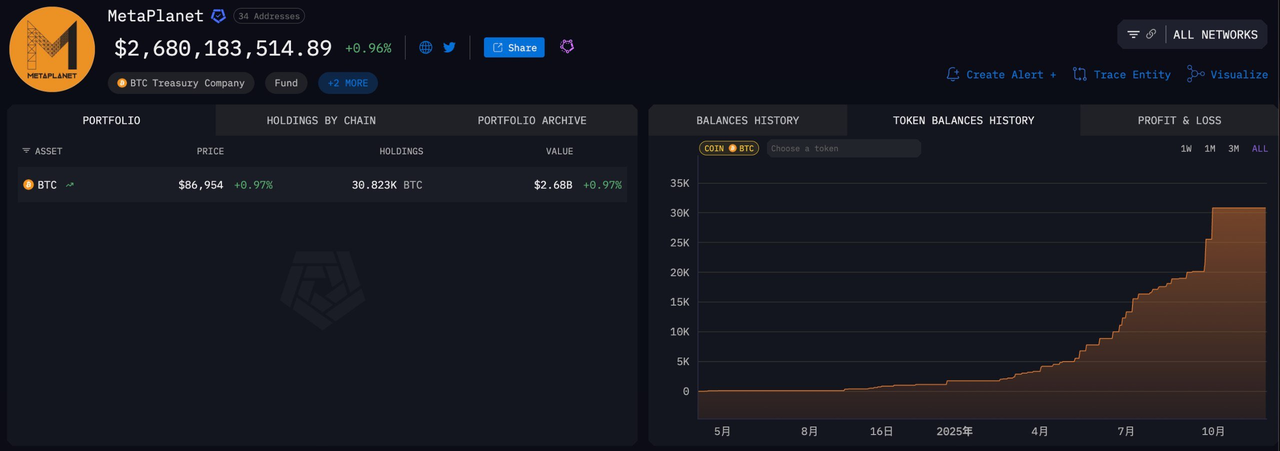
Source: Arkham
On November 25, Metaplanet, a publicly listed company in Japan, announced that it has executed a new loan of $130 million based on a credit limit contract, using its held Bitcoin as collateral. The total credit limit is $500 million, and with this loan, a total of $230 million has been borrowed to purchase more Bitcoin in the market. In simple terms, they are collateralizing Bitcoin, obtaining cash, and then buying more Bitcoin, in a continuous cycle. Currently, the company still holds 30,823 Bitcoins, which is sufficient to cover the collateral requirements. The funds raised are planned for additional Bitcoin purchases, advancing Bitcoin revenue operations, and even repurchasing stocks when the market allows. Metaplanet also emphasized that this loan will have a minor impact on its performance for the fiscal year 2025.
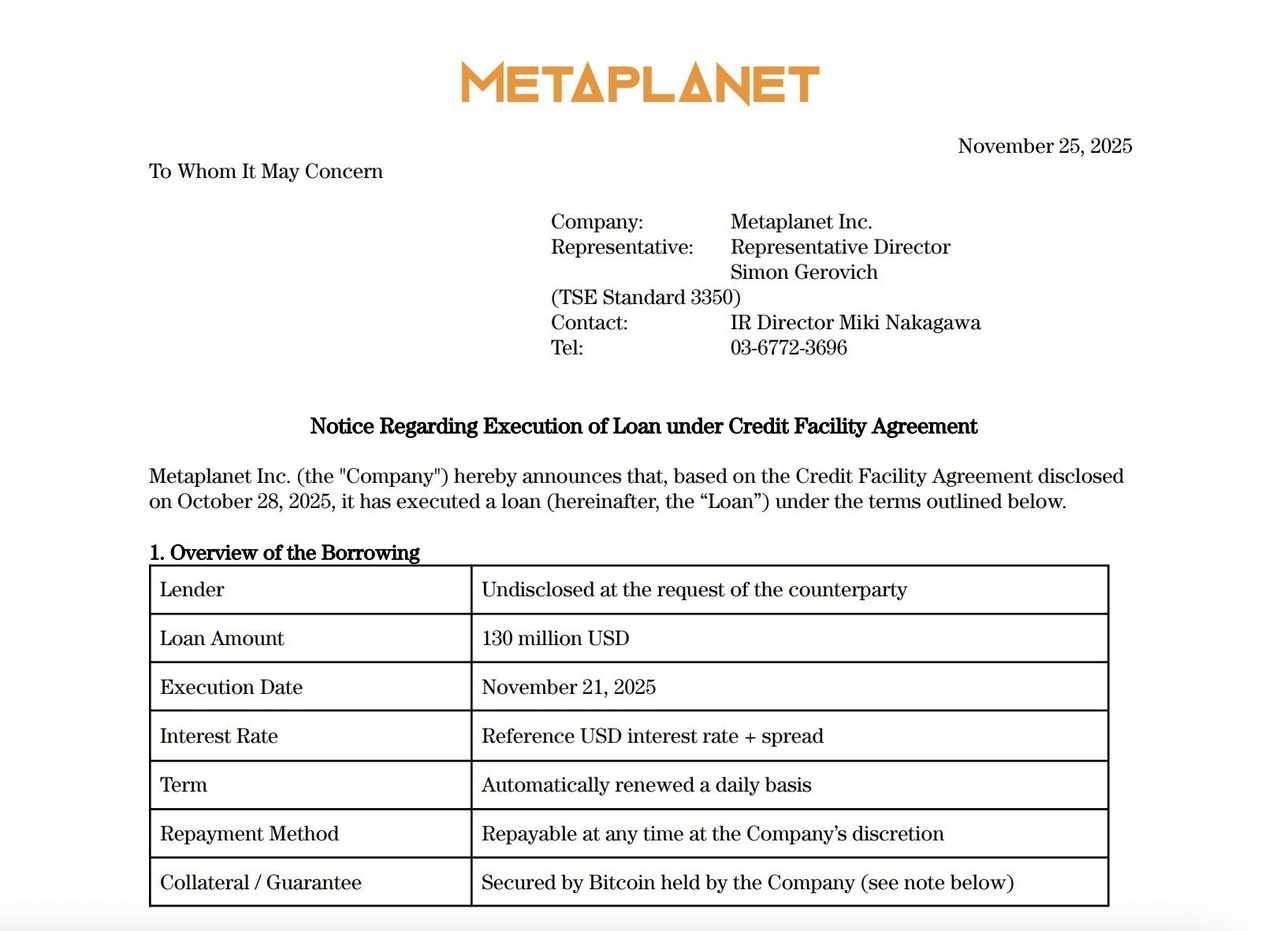
Source: Metaplanet
The next wheel of MicroStrategy begins to turn
Before understanding the advanced version of "MicroStrategy," let's first clarify the logic and valuation methods of "the first Bitcoin stock," MicroStrategy, so that we can better understand Metaplanet.
MicroStrategy's funds for buying Bitcoin mainly come from three sources.
Convertible bonds, accounting for about 60% to 70%. For example, it's like using a credit card to buy Bitcoin first and possibly paying off the debt later with the Bitcoin in hand. This part of the debt has low costs and high flexibility, making it the main source of funds for MicroStrategy.
Corporate bonds, accounting for about 20% to 25%. This is similar to taking out a mortgage from a bank, using a house or Bitcoin as collateral, and then buying more Bitcoin. The collateral ensures the safety of the debt, but it also means that if risks are triggered, additional collateral may be required or liquidation may occur.
Stock issuance, accounting for about 10% to 15%. This is like selling a piece of your cake to someone else for money and then using that money to buy Bitcoin. However, the existing shareholders' cake becomes smaller, and their equity is diluted.
After understanding these three logical sources, we can look at the stock value of MicroStrategy. When MSTR's value dropped from $450 to $179, this decline far exceeded the drop in Bitcoin itself. From this perspective, if MSTR's price rises, it is likely to move in tandem with Bitcoin. Let's calculate the stock's net value in the simplest way.
The formula is actually quite simple: stock price ≈ Bitcoin holdings ÷ shares outstanding. According to their latest disclosed data, they hold 649,870 Bitcoins, with the current price at $89,000, and shares outstanding at 284,380,000. Calculating this gives: 649,870 × 89,000 ÷ 284,380,000 ≈ $203.5 per share. This means that last night, MSTR's stock at $179 was below the net value of $203.5. This theoretically indicates that the stock price is undervalued, suggesting a potential opportunity to buy at a low price.
Of course, the stock's net value only reflects the value of the Bitcoin portion. There are several factors not included: first, the intrinsic business value of the company, which is the premium it can create; second, the cost of debt. The interest on convertible bonds is usually less than 1%, while corporate bond interest is about 6% to 8%, which does not constitute a large proportion of total assets. In other words, the debt will not significantly burden the holdings.
Next, let's look at Metaplanet, which is a typical case of the advanced version of MicroStrategy. It has not sold any coins, nor diluted its equity, but instead used its held Bitcoin as collateral to obtain cash and continue buying Bitcoin, treating Bitcoin as a financial tool to amplify its position. This strategy is somewhat like mortgaging a house to borrow money and then using that money to buy a second house. Metaplanet's latest loan of $130 million, combined with the previously borrowed $230 million, still leaves them with approximately 30,823 Bitcoins on their balance sheet, valued at about $3.5 billion at that time. This means they have turned their held Bitcoin into a leveraged funding pool and are using cash to increase their Bitcoin holdings.
This operation appears stable on the surface and serves as a catalyst for driving up Bitcoin prices, but the downside risks are much more apparent. Once risks are triggered, it could instantly amplify market volatility.
The risks of "revolving loans"
The biggest fear of revolving loans is severe market fluctuations. Looking back at the history of Web3, the collapse of Iron Finance's TITAN/IRON is a typical case where collateralized lending + leverage + market panic led to a chain liquidation, causing users to suffer heavy losses; similarly, Three Arrows Capital (3AC) leveraged loans led to significant drops in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and LUNA, ultimately triggering liquidation and bankruptcy. When users collateralize assets to borrow and leverage, if prices hit the liquidation threshold, it can lead to a chain reaction of liquidations, causing instant liquidity depletion in the market and a sharp drop in token prices.
Although Metaplanet is a publicly listed company, and its leverage and liquidation mechanisms are more stable than those of retail investors or DeFi projects, the logic remains the same: as long as Bitcoin's price drops and triggers liquidation, they may face additional collateral requirements or forced liquidation. Assuming Metaplanet holds 30,823 Bitcoins and has borrowed a total of $230 million. If Bitcoin's price drops to trigger a safe collateral ratio of about 50% to 60%, the value of the collateral would equal the principal of the loan, which is the "trigger risk" price level. In other words, if Bitcoin drops more than about 40% from the current price, it could trigger the liquidation boundary. For the market, this is why retail investors need to keep a close eye on the leverage operations of large institutions, rather than just focusing on coin prices.
Additionally, revolving loans have a psychological effect. If institutions continue to take out loans and increase their positions, the market may follow suit, thinking "someone is always buying, it should be safe." Once panic sets in, the leveraged positions will lead to a selling speed that exceeds expectations, and the risks at the end of a bull market are hidden within these seemingly stable operations. Although Metaplanet's strategy appears quite stable, the potential impacts should not be underestimated, which is also where the undercurrents of the second-generation MicroStrategy lie.
Summary
Metaplanet's operations tell us that the second-generation MicroStrategy has indeed increased the demand for Bitcoin hoarding, while also making price increases more scarce, but it is also indirectly inflating a bubble.
What the market fears most is not that someone is buying, but that leverage is quietly increasing at the end of a bull market. Metaplanet's revolving loans are a typical "bull tail cycle." Unlike retail investors who directly impact prices with short-term buying and selling, they continuously roll over leverage, turning Bitcoin into a reusable funding pool. Each round of collateralization and each increase in position gradually alters the market supply and demand structure, subtly pushing prices higher. Bitcoin does not cash out; funds come in to buy more coins, and positions grow larger. As long as prices do not trigger liquidation, everything remains stable.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



