Analysis of the BTCFi Infrastructure Layer: Which Assets Are Worth Attention?
Written by: Tiger Research
Translated by: AididiaoJP, Foresight News
TL;DR
- Bitcoin L1 as a Trust Anchor: The BTCFi infrastructure revolves around Bitcoin's security, using it for final settlement and verification while keeping complex logic off-chain. Concepts like BitVM can expand Bitcoin's smart contract capabilities without altering the consensus mechanism.
- Multi-layer Execution Ecosystem: From Bitcoin-anchored blockchains (like Stacks) to BTC staking chains (like Botanix and BounceBit), and systems inspired by Rollup (like Merlin and Bitlayer), each approach balances scalability, programmability, and trust in different ways while maintaining Bitcoin as the core of security and value.
- Complementary Systems like the Lightning Network: While the Lightning Network excels at fast, low-cost payments rather than DeFi, its liquidity and routing yield potential can connect Bitcoin's transaction layer with BTCFi's capital markets, opening hybrid use cases as bridging technology matures.
As mentioned in the first part, BTCFi aims to unlock idle capital in Bitcoin and transform it into productive assets. However, achieving this requires robust infrastructure.
In this section, we will explore the infrastructure layer supporting Bitcoin DeFi: from Bitcoin's base layer to emerging Layer 2, sidechains, and new execution environments. These infrastructure components enable DeFi applications to build around Bitcoin without compromising its core principles.
Bitcoin L1: Settlement, Finality, and Trust
The Bitcoin blockchain is the most secure and decentralized financial ledger in existence. With over a decade of nearly zero downtime and a deliberately conservative upgrade history, Bitcoin L1 is widely regarded as the ultimate settlement layer for cryptocurrencies.
This foundational advantage gives Bitcoin a unique role: as the cornerstone of trust in a multi-layer DeFi system. The BTCFi protocol anchors Bitcoin L1 not for computation but for settlement, serving as the "final court of arbitration" for validating transaction outcomes.
Crucially, BTCFi typically avoids modifying Bitcoin's base layer to implement DeFi logic. The mainstream design philosophy is to build around Bitcoin's simplicity and durability, placing execution logic off-chain or on Layer-2 and sidechains, while always reverting to Bitcoin L1 for settlement and security.
Nevertheless, some experimental designs, particularly certain zk-rollup implementations, may benefit from new opcodes (like OP_CAT), which require a soft fork. These proposals remain speculative, with most BTCFi infrastructure focusing on expanding its utility without altering Bitcoin's core consensus rules.
Looking ahead, proposals like BitVM further advance this concept. BitVM is an early idea that allows complex programs to run off-chain while still permitting Bitcoin to verify the results. It can be imagined as solving a complex math problem on paper and publishing the answer; unless someone challenges it, the answer is considered valid. If challenged, proof must be submitted on-chain within a set time window, enforced by Bitcoin.
This could enable fully functional smart contracts on Bitcoin without modifying the core system. While still in the experimental stage, it reflects a broader trend: using Bitcoin as a foundation of trust while moving advanced features and logic to external layers.
Overall, Bitcoin L1 remains simple and conservative, which is precisely why it has succeeded. It serves as a settlement layer and value anchor for a growing modular ecosystem. The goal of BTCFi is not to turn Bitcoin into Ethereum but to expand its utility while maintaining its integrity.
The next section will explore the structure of the execution layer, design differences, and how they enable Bitcoin to support a broader range of financial applications.
Bitcoin-Anchored Blockchains
Bitcoin-anchored blockchains are independent execution environments that gain partial legitimacy or security through Bitcoin's hash power or on-chain transactions. These chains operate their own consensus mechanisms but benefit from Bitcoin's security by "anchoring" to it, without executing logic directly on Bitcoin L1.
One can imagine it as building a closed community next to a tightly protected national reserve. The closed community (sidechain) has its own roads and houses (smart contracts and consensus mechanisms), but it ensures tamper-proofing by being close to Bitcoin's infrastructure (utilizing the reserve's monitoring system, i.e., Bitcoin miners or block hashes).
Anchoring methods include:
- Merge mining: Bitcoin miners simultaneously validate blocks on the sidechain.
- Proof of Transfer (PoX): Bitcoin transactions are used as inputs to elect block producers.
- Timestamps or checkpoints: The state of the chain is periodically recorded on Bitcoin.
These chains are not inherently trustless. Some require custodians to manage BTC deposits or withdrawals, while others establish indirect economic or timestamp links with Bitcoin.
Stacks: A PoX Sidechain with Bitcoin Finality

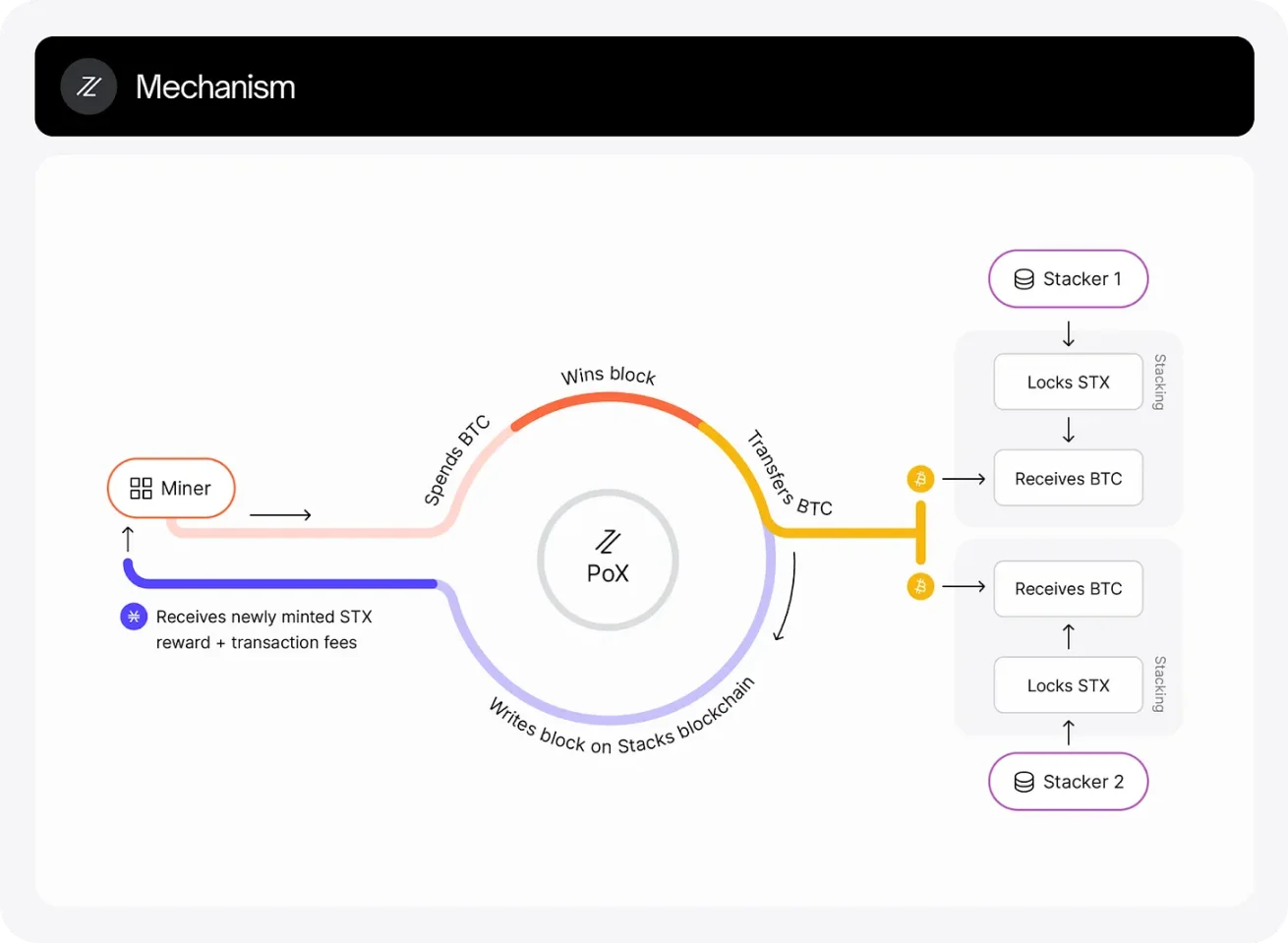
Stacks is the most well-known example of a Bitcoin-anchored blockchain, connecting to Bitcoin using its own consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Transfer (PoX). In PoX, Stacks miners submit Bitcoin transactions and "bid" BTC for the right to produce blocks on the Stacks chain.
By recycling Bitcoin's proof of work as a resource, Stacks links to Bitcoin's economic layer. Similar to hybrid PoS chains, Stacks also anchors its state to Bitcoin by including the hash of Stacks blocks in Bitcoin's PoX block submission transactions, ensuring its chain history is timestamped and tamper-proof on the Bitcoin layer.
Source: Stacks
Stacks employs a Turing-incomplete smart contract language called Clarity, designed with a focus on predictability and security. Developers can read Bitcoin's state and trigger contract logic based on Bitcoin transactions, making it one of the earliest and most mature adjacent DeFi platforms for Bitcoin.
Source: Stacks
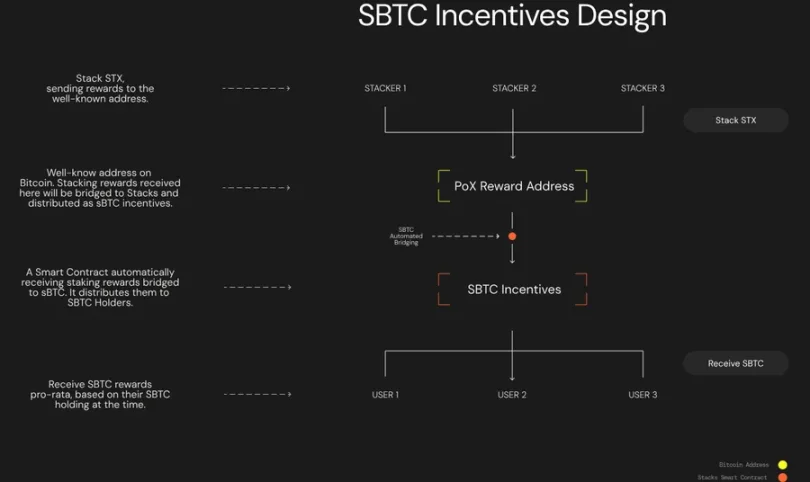
The BTC asset bridge on Stacks is realized through sBTC, an asset maintained at a 1:1 peg to BTC by threshold signers. These signers are also validators protecting the Stacks network by staking STX, reducing the likelihood of malicious behavior since any attack could affect their staked assets. Although the bridge design still involves some trust assumptions, as long as the majority of signers act honestly, exits are permissionless.
Stacks inherits Bitcoin's settlement security, anchoring its state to Bitcoin and using Bitcoin transactions as proof. However, execution and bridge custody are protected by the Stacks network itself, offering greater flexibility compared to strictly defined Bitcoin L2. The network has its own native token (STX) and consensus rules, technically not a Layer-2, but its entire ecosystem revolves around Bitcoin's value.
BTC Staking or Hybrid PoS Chains
BTC staking or hybrid PoS (Proof of Stake) chains are execution environments that directly incorporate Bitcoin into their security model, either requiring users to stake actual BTC or anchoring their state back to Bitcoin. These chains typically offer high throughput, fast finality, or EVM compatibility while still relying on Bitcoin in some form as a trust backstop.
Unlike traditional sidechains that depend on fixed mechanisms, BTC staking chains pursue greater decentralization and transparency through:
- Requiring validators to stake BTC on L1 as collateral.
- Utilizing Bitcoin block entropy (randomness of block hashes) to fairly select node operators.
- Anchoring checkpoints back to Bitcoin to create tamper-proof audit trails.
One can imagine it as renting a safe deposit box at a secure state-owned bank while running one's own business elsewhere. The bank (Bitcoin) does not oversee your business, but it publicly holds your collateral, and you must adhere to the rules, or you risk losing your deposit. Customers (users) trust you not only because of your service but also because their funds are ultimately backed by Bitcoin's security.
This design balances performance and decentralization. It avoids the pitfalls of static multi-signatures while not reaching the fully trustless level of Rollup. These chains are particularly attractive to institutional users as they combine:
- Familiar smart contract interfaces.
- Direct BTC staking mechanisms.
- Permissionless exit paths back to Bitcoin L1.
Each implementation varies in staking mechanisms, governance, and token design, but they share the common goal of transforming BTC into productive, security-bearing assets rather than merely idle reserves.
Botanix: Spiderchain and PoS Anchoring
Source: Botanix
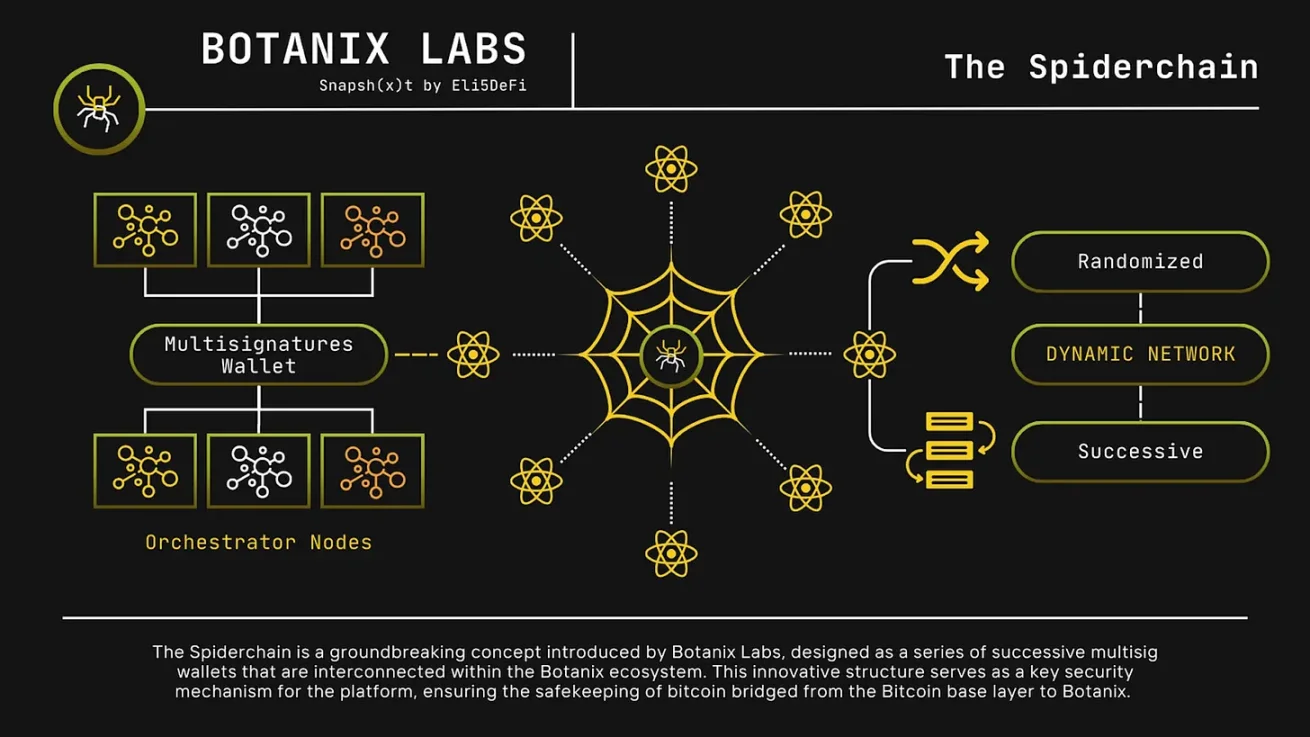
Botanix is a newly launched Bitcoin L2 that combines proof of stake validation with Bitcoin anchoring through a novel architecture called Spiderchain.
At its core, it uses a set of rotating coordinator nodes to manage a multi-signature BTC bridge. These nodes are selected using Bitcoin block hashes as random entropy and require actual BTC to be staked on Bitcoin L1. The network regularly submits state hashes to Bitcoin, making Bitcoin the ultimate checkpoint for the Botanix chain.
This architecture eliminates the need for a fixed federation and allows users to withdraw BTC at any time, creating a permissionless exit path. On-chain activities are EVM compatible, with all gas fees paid in BTC rather than wrapped tokens or separate gas assets.
Botanix also supports native DeFi applications, such as Rover (a liquidity staking protocol that allocates earnings from network fees). Its security assumptions rely on the majority of honest PoS coordinators and fraud visibility on Bitcoin L1, striking a balance between performance and decentralization.
With updates and future developments, Botanix positions itself as a reliable infrastructure layer for Bitcoin-native finance.
BounceBit: CeDeFi and Institutional Yield Layer
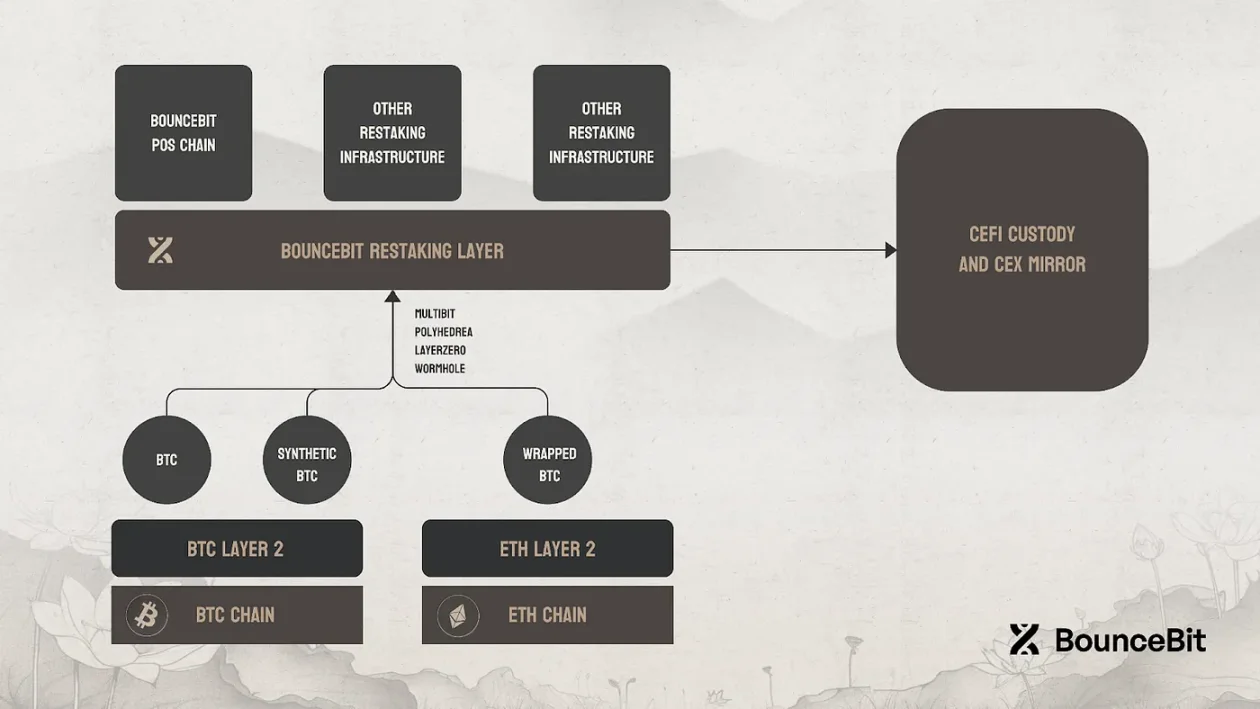
BounceBit takes a different approach by merging CeFi infrastructure with DeFi access, targeting institutional users with Bitcoin as the primary source of liquidity and trust.

Source: BounceBit
Its consensus model is a dual-token PoS, combining the native BB token and BBTC (a tokenized representation pegged 1:1 to BTC). Validators are selected based on the combined staking amount of both assets. Users are required to deposit real BTC into a regulated custodian and receive BBTC on-chain, which is a centralized bridge designed with a focus on auditability and legal compliance.
Source: BounceBit
Once on-chain, BounceBit users can access a range of "one-click yield" strategies through automated CeDeFi infrastructure. These strategies include arbitrage, basis trading, and potentially tokenized RWA yields (such as government bonds) in the future. The ecosystem is modular, with oracles, liquidity strategies, and validator sets revolving around Bitcoin as productive capital.
Despite the apparent trade-offs (custodial risks and permissioned components), BounceBit's focus on usability, compliance, and stable returns makes it attractive to institutions looking to deploy BTC into yield strategies without directly managing complex DeFi tools.
BounceBit embodies one path of BTCFi: prioritizing real-world integration over strict decentralization, providing infrastructure to connect traditional finance with Bitcoin-native capital markets.
Protocols Inspired by Rollup
Protocols inspired by Rollup aim to bring Ethereum-like scalability and programmability to Bitcoin without altering Bitcoin itself. These systems execute transactions off-chain and submit proofs back to Bitcoin, achieving high throughput and smart contract support while still relying on Bitcoin as the ultimate trust arbitrator.
There are two core designs:
- Optimistic rollups: Assume transactions are valid unless disputed, at which point fraud proofs must be submitted.
- ZK-Rollup: Generate zero-knowledge proofs that mathematically confirm the validity of each batch of transactions.
Bitcoin presents practical technical challenges for these designs:
- Lack of native support for complex verification logic or recursive proofs.
- Limited scripting language makes real-time fraud detection difficult.
- No built-in Rollup framework like that in Ethereum's roadmap.
To overcome these challenges, developers build off-chain execution environments and submit streamlined data (proofs, state roots, or transaction hashes) back to Bitcoin L1. These Rollups can be imagined as containers passing through customs checkpoints. The off-chain systems handle all the packaging, sorting, and logistics.
Bitcoin acts as the customs officer; it does not open every box but requires a manifest (proof) to pass inspection. If issues arise, escalation can occur (fraud proofs or challenge periods). As long as the manifest is credible and the inspection system is effective, this process is fast, efficient, and scalable.
These designs provide strong theoretical guarantees and offer a high-performance path for Bitcoin-native smart contracts. However, they are also the most complex and relatively new in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Trust assumptions vary based on bridges, proof models, and whether participants actually challenge invalid behavior.
Despite the risks, Rollup-style systems represent the closest scalable solution to trustlessness for Bitcoin and have quickly attracted the attention of developers and capital allocators.
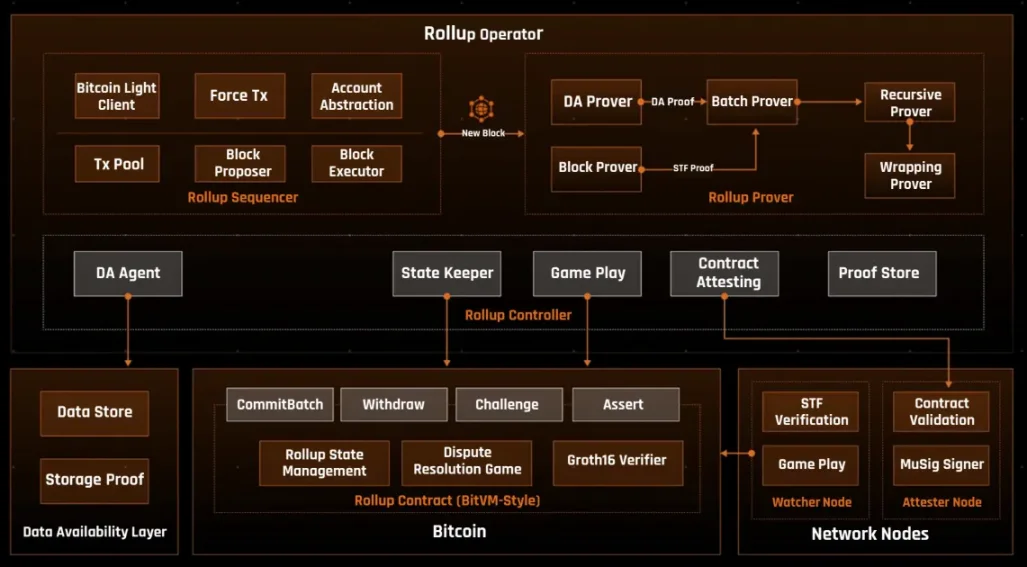
4.1. Merlin: zkEVM Rollup Supporting BTC Staking

Merlin Chain is one of the earliest attempts to build a zkEVM Rollup for Bitcoin, combining zero-knowledge proofs, BitVM-based Bitcoin security, and a decentralized oracle network.
It batches off-chain transactions, generates ZK proofs of state transitions, and submits these proofs to Bitcoin L1 for finality. To handle data availability (which Bitcoin cannot provide natively), Merlin uses a Data Availability Committee (DAC) composed of oracle nodes that store and prove off-chain data. In its proposed architecture, these DAC nodes must stake BTC, and if they sign an invalid state update that is later disputed, they will be penalized.
Merlin offers a smooth EVM experience, supporting assets like Ordinals and BRC-20, and uses MBTC (wrapped Bitcoin on Merlin) as the base currency. It bridges BTC from L1 through Cobo's multi-party computation (MPC) custody setup and mints MBTC on the network.
The Rollup model here is not entirely trustless; users must assume that at least one honest party will challenge fraudulent states, and the bridge introduces custodial risks. However, it provides high performance, Ethereum-level composability, and cryptographic guarantees of correctness.
Merlin has attracted significant attention, with its TVL peaking over $3 billion, indicating that for many users, actual DeFi yields outweigh theoretical purity.
4.2. Bitlayer: BitVM + ZK Rollup Hybrid

Bitlayer addresses the critical gap between Bitcoin's security and modern blockchain demands for scalability and programmability. By leveraging the advantages of Bitcoin's base layer, Bitlayer inherits the same level of trust, decentralization, and resilience as Bitcoin.
At the same time, Bitlayer extends Bitcoin's functionality by introducing Turing-complete programmability, enabling developers to create complex decentralized applications and smart contracts that were previously impossible within the Bitcoin-native framework.
Source: Bitlayer
Bitlayer introduces smart contract functionality while respecting Bitcoin's fundamental principles, and its full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) allows Ethereum applications and tools to migrate seamlessly without major modifications. Its development is rapid, with clear milestones:
- Bitlayer PoS (Mainnet - V1): Launching in April 2024, establishing the initial validators and execution environment for the network.
- Bitlayer Rollup (Mainnet - V2): Currently in development, including a BitVM Bridge mainnet testnet for secure BTC asset bridging.
- Bitlayer Rollup (Mainnet - V3): Planned upgrade to achieve lightning-level confirmations and unparalleled execution performance.
At the core of the architecture is the BitVM Bridge, sometimes referred to as the "third-generation Bitcoin bridge," which replaces traditional multi-signature custodians with a cryptographic challenge-response model. This ensures that even if the majority of participants fail, a single honest validator can protect user funds and ensure correct execution.
By 2025, as partnerships and infrastructure integrations accelerate, the ecosystem is rapidly expanding:
- Strategic alliances with Sui, Base, Starknet, Arbitrum, Sonic SVM, Cardano, and Plume Network.
- API support from major Bitcoin mining pools like Antpool, F2Pool, and SpiderPool, enabling real-time processing of non-standard transactions (NST) through the BitVM Bridge.
- Deployment of YBTC.B (wrapped BTC from Bitlayer) on BSC, Sui, Avalanche, Ethereum, and Plume.
This growth has translated into measurable impact:
- Over 65 million transactions processed since March 2024.
- Peak TVL on Bitlayer reached $850 million.
- YBTC.B asset TVL exceeds $350 million (according to DeFiLlama).
By combining Bitcoin's security with next-generation scalability and programmability, Bitlayer is poised to fundamentally redefine Bitcoin Layer-2 capabilities and shape the future of Bitcoin DeFi.
Hybrid Consensus Chains Aligned with Bitcoin
Hybrid consensus chains aligned with Bitcoin are independent Layer-1 blockchains that combine multiple security models, typically incorporating elements of Proof of Stake (PoS) and Bitcoin's Proof of Work (PoW), creating execution environments that benefit from Bitcoin's reputation and economic weight without relying on its direct state settlement or consensus.
These chains do not submit data to Bitcoin or settle transactions on it. Instead, they:
- Incentivize Bitcoin miners and holders to participate in network security, not by directly using Bitcoin's hash power, but by economically aligning their incentives through staking mechanisms or validator influence.
- Allow BTC holders to non-custodially stake assets through time-locks or smart contract-based methods.
- Design validator economics and governance systems to attract participants from the Bitcoin ecosystem, from miners to long-term holders.
They can be imagined as special economic zones established to attract Bitcoin capital. They have their own laws (governance), infrastructure (consensus), and services (dApps), but provide rewards and influence for participants aligned with Bitcoin. You do not have to give up Bitcoin; these zones are specifically designed to make your BTC work for you.
What makes them unique is that Bitcoin becomes part of their validator economy, influencing who protects the chain and how rewards are distributed. While Bitcoin is not part of the cryptographic consensus engine, its holders and miners are invited to protect the system through economic mechanisms, creating a powerful combination of autonomy and alignment.
This structure attracts BTC holders looking to earn yields without relinquishing custody, as well as miners seeking to maximize capital efficiency without leaving the Bitcoin ecosystem. Hybrid chains do not compete with Bitcoin; they expand its influence by transforming its stakeholders into active participants in adjacent ecosystems.
Compared to true L2s, this is a looser coupling, but more integrated than generic alternative L1s. These chains reflect a broader trend in BTCFi: building for Bitcoin without needing to construct on Bitcoin itself, as long as incentives, architecture, and user bases remain aligned with Bitcoin.
Core: Satoshi Plus and BTC Hash Power Delegation
Core (CoreDAO) is a fully EVM-compatible Layer-1 blockchain launched in 2023, utilizing a unique hybrid consensus mechanism called Satoshi Plus. This model combines:
- Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW): Bitcoin miners delegate their hash power to secure Core blocks.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): CORE token holders stake to select validators.
- Non-custodial BTC staking: BTC holders can lock BTC on L1 to support validators without relinquishing custody.
In this model, Bitcoin miners are incentivized to contribute hash power to the validator selection process for Core, earning additional rewards without interfering with their regular Bitcoin mining activities. At the same time, BTC holders can participate in network consensus through time-locked transactions on Bitcoin L1, achieving what Core calls "trustless Bitcoin staking."
Core offers fast block times, low fees, and complete Ethereum compatibility. It provides DeFi, NFT, and dApp infrastructure similar to Ethereum, but its validator set is tied to Bitcoin's economic and mining capabilities, creating a rare alignment that few chains attempt.
Although Core has its own token (CORE) and governance process and does not directly anchor its state to Bitcoin, it positions itself as a complement to Bitcoin rather than a competitor. Its vision is not to become a narrowly defined Bitcoin L2 but to serve as a Bitcoin-aligned smart contract chain from which BTC users and miners can benefit from on-chain activities.
With the deployment of over 125 dApps and a growing user base, Core demonstrates a BTCFi strategy that blurs the lines between alternative L1s and Bitcoin infrastructure, providing an Ethereum-level ecosystem based on Bitcoin's reputation and capital.
Lightning Network: A Parallel Path
When discussing Bitcoin's scaling architecture, one cannot overlook the Lightning Network, a Layer-2 solution built specifically for fast, low-cost payments. Unlike BTCFi protocols that focus on lending, yield generation, or tokenization, the Lightning Network has taken a different path, successfully fulfilling its original mission: enabling Bitcoin to operate as peer-to-peer cash.
The Lightning Network works by establishing state channels between users. By locking BTC in a channel, both parties can transact off-chain with near-zero latency and extremely low fees, settling only the net results on the Bitcoin base layer. This model significantly increases transaction throughput, theoretically allowing the Lightning Network to process millions of transactions per second and reducing transaction costs to fractions of a cent.
As of 2025, the Lightning Network protects $400 million to $500 million in BTC liquidity and supports real payment applications like Strike, especially in emerging markets where fast remittances and low fees are crucial.
However, despite its strengths in payments, the architecture of the Lightning Network is not designed for DeFi. Its smart contract capabilities are extremely limited, optimized for simple channel scripts rather than complex financial logic. You can buy coffee or make micro-payments, but you cannot launch lending protocols or deploy decentralized exchanges on the Lightning Network. Liquidity is also dispersed across thousands of channels, making it difficult to aggregate capital for pooled DeFi strategies.
While the Lightning Network remains specialized with limited DeFi integration, its strategic importance is evident. It complements BTCFi protocols by enabling BTC to flow cheaply and instantly, while BTCFi platforms unlock value by locking BTC in yield strategies. As bridging technologies improve, liquidity from the Lightning Network may increasingly flow into BTCFi, connecting Bitcoin's payment side with its productive capital layer.
New Ideas and Infrastructure Development
The infrastructure layer is unlocking Bitcoin's idle capital by moving complexity off-chain while anchoring trust back to L1.
New entrants are further advancing these ideas. Plasma is an emerging Bitcoin-pegged sidechain built for fee-less, stablecoin-friendly settlements, combining EVM compatibility with privacy features. Meanwhile, Arch Network is pioneering a bridge-less execution layer on Bitcoin, enabling high-throughput dApps without relying on wrapped assets. Despite differing designs, both reflect the same idea: innovating around the advantages of Bitcoin rather than at their expense.
The path forward for BTCFi will be modular and diverse. But infrastructure is only one side of the equation; in the third part, we will turn to the asset and custody layer, focusing on how Bitcoin moves, holds, and represents itself within the network.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




