Stock Rating: Positive
Analyst: Bread
Likaixin@bbtcresearch.com
Investment Highlights
In the Bitcoin investment boom, the development of the holding stock industry is attracting attention. This article will answer two main questions: 1) What is the competitive landscape of the Bitcoin asset management industry, and will it be concentrated or differentiated in the future? 2) How can listed companies in the holding stock industry become an important force in the financial sector, and what are the challenges of active asset management?
Note: The discussion focuses on listed companies in the holding stock industry as the mainstream of the sector.
Envisioning the competitive landscape of the Bitcoin asset management industry: Competition in quantity and scenarios
The global Bitcoin asset management industry will show differentiation but with a high concentration. Leading companies maintain their advantages, while emerging companies also participate in competition with unique strengths. The main reasons are:
1) Why is the concentration high? The asset management industry requires substantial capital and professional teams, but the cost of use is low and declines rapidly, leading large companies to leverage their financial and resource advantages to stay ahead, making it difficult for small and medium-sized companies to participate.
2) How is differentiated competition achieved? The competition among Bitcoin listed companies can be divided into three dimensions: quantity, scenarios, and functions. Giants are similar in scenarios and functions, but differ in quantity. The key to quantity competition lies in speed and scenarios; companies that quickly accumulate Bitcoin can optimize their models, and those with suitable scenarios have stronger strategies. First-mover advantage is also important, as early companies can gain more experience and resources.
Envisioning the development space of the holding stock industry: Future transformations in the holding stock industry
Bitcoin investment brings development opportunities and transformations to listed companies. Its low correlation helps to diversify risks and optimize asset portfolios; at the same time, Bitcoin aids companies in exploring new technologies and business models. It is expected that in the next three years, over 200 companies globally will hold more than 1,000 Bitcoins. By 2025, a holding stock ETF index will be released, and holding stock investments will become mainstream, injecting new vitality into the industry.
Investment Recommendations
We believe that Bitcoin investment is expected to bring new growth momentum to listed companies, and the holding stock industry has enormous development potential. We closely monitor the disruptive opportunities arising from the combination of the holding stock industry and Bitcoin investment.
1) Opportunities for Industry Pioneers: Aggressive investors may focus on companies like MicroStrategy. During Bitcoin market adjustments, they can build positions at low prices and share in their growth potential; at the same time, pay attention to emerging technology and financial companies' Bitcoin layouts to capture early opportunities, but set stop-loss measures to mitigate risks.
2) Opportunities for Mature Enterprises: Conservative investors should focus on large, mature companies like Tesla with Bitcoin holdings. Once market trends become clear and policies stabilize, they can participate moderately when Bitcoin prices are reasonable, emphasizing long-term holding, leveraging corporate management and diversified businesses to buffer against price fluctuations, and achieving asset appreciation; at the same time, pairing with traditional safe-haven assets like gold and high-quality bonds to optimize investment portfolios.
3) Indirect Investment Opportunities: Conservative investors may focus on Bitcoin-related financial products, such as compliant Bitcoin ETFs. When market sentiment is optimistic, capital inflows are strong, and technical indicators are favorable, they can make small exploratory investments, control investment exposure, ensure principal safety, and share in the industry's growth dividends.
Risk Warnings
1) Bitcoin Price Volatility: Bitcoin prices are highly volatile, as seen in the significant fluctuations during 2017-2018 and 2021-2022, leading to fluctuations in the value of listed companies' Bitcoin assets, affecting financial statements and market value management, and undermining investor confidence, resulting in uncertain investment returns.
2) Regulatory Policy Risks: The global regulatory stance on cryptocurrencies varies and changes dynamically. For example, some U.S. states recognize Bitcoin, but federal agencies impose strict regulations; China prohibits related businesses, and the EU continues to improve its regulatory framework. Tightening regulations may lead to impairment and sell-offs of listed companies' Bitcoin assets, obstructing business operations and affecting investment value.
3) Market Acceptance and Application Risks: Bitcoin faces issues such as long transaction confirmation times and significant price volatility as a payment method, with cross-border transactions subject to policy and regulatory restrictions. This limits Bitcoin's application in listed companies' businesses and market penetration, hindering its market value's full realization, potentially affecting the industry's development process.
Table of Contents
1 Industry Overview
1.1 Review of Bitcoin's Development History
1.2 Background of Listed Companies Involved in Bitcoin
2 In-Depth Analysis of Typical Cases
2.1 MicroStrategy: Pioneer in Bitcoin Investment
2.2 Tesla: Disruptor Across Industries
2.3 Meitu: Representative of Emerging Forces
3 Insights into Investment Motivations
3.1 Demand for Asset Diversification
3.2 Considerations for Hedging Inflation
3.3 Intentions for Strategic Layout
4 Outlook on the Development Trends of the Holding Stock Industry
4.1 Market Size Forecast
4.2 Evolution of Industry Structure
4.3 Integration Prospects with the Blockchain Ecosystem
5 Development Trends of the Holding Stock Industry
5.1 We answer two key questions regarding the current revolution in the holding stock industry: structure and space
5.1.1 Competitive landscape of holding listed companies: future showing high fixed and low marginal cost structure leading to high concentration
5.1.2 Industry space aspects
5.2 Financial Performance of Bitcoin-Holding Listed Companies
5.3 Valuation Models for Holding Listed Companies
5.3.1 Market Capitalization Premium Rate
5.3.2 Net Asset Value (NAV) Premium Model
5.3.3 Bitcoin Price Sensitivity Model
6 Conclusion and Recommendations
6.1 Research Summary
6.2 Investment Recommendations
6.3 Identification of Risk Factors
6.4 Industry Outlook
Charts Directory
Chart 1 Overview of Trump's Bitcoin Conference Promises and Fulfillment
Chart 2 Trend Chart
Chart 3 Asset Allocation Chart
Chart 4 Prediction Chart for Bitcoin Holding Companies' Listings
Chart 5 Asset Allocation Chart
Chart 6 Asset Allocation Chart
Chart 7 Market Premium Rates of MSTR, NANO, MARA, and Boya Interactive
Chart 8 Company Values of MSTR, NANO, MARA, and Boya Interactive
Table 1 Overview of Trump's Bitcoin Conference Promises and Fulfillment
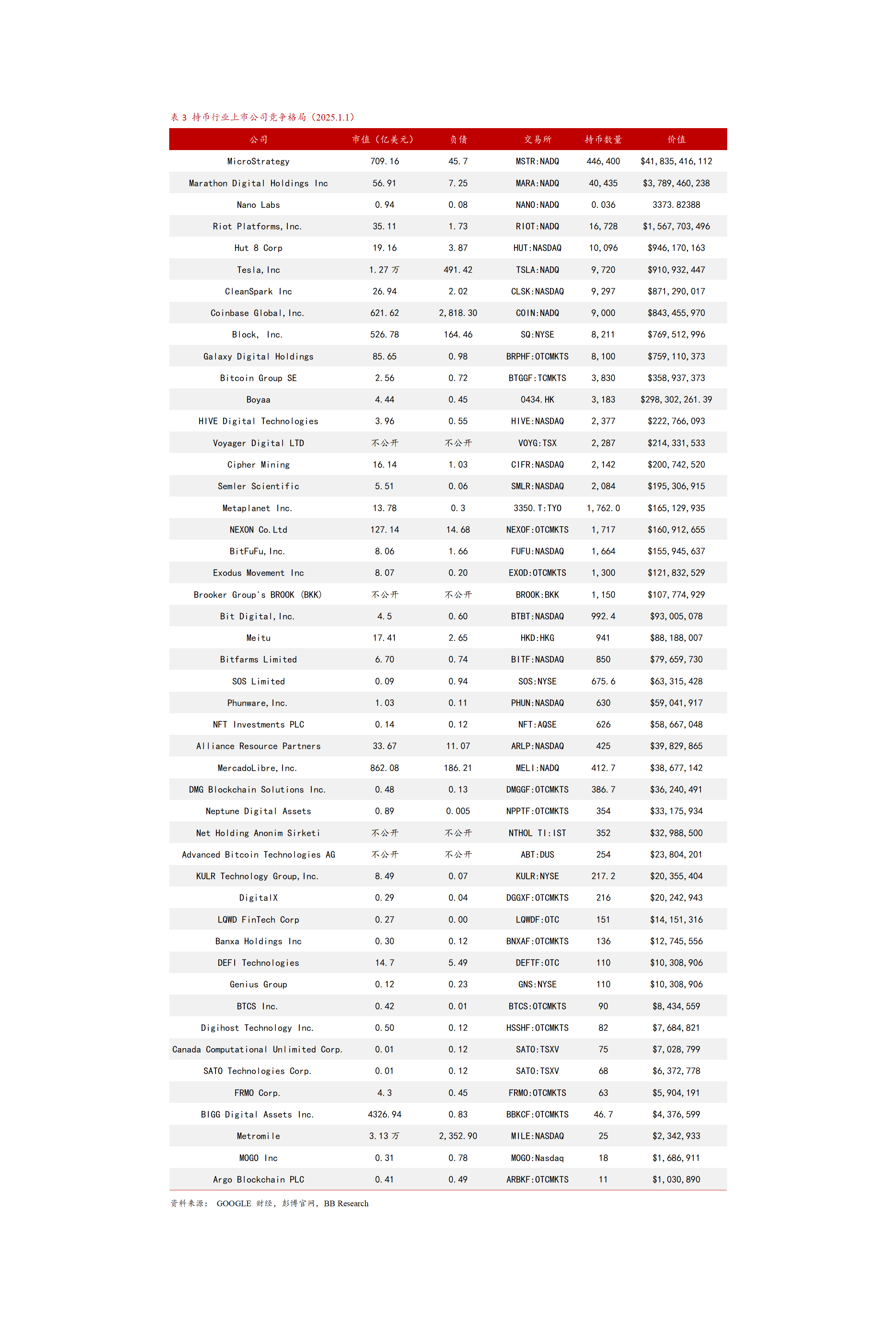
Table 2 Main Categories of Bitcoin-Holding Listed Companies
Table 3 Competitive Landscape of Listed Companies in the Holding Stock Industry (List of Holding Companies)
Table 4 NB Bitcoin Holding ETF Index
Table 5 Market Premium Rate
Table 6 Median Market Capitalization Premium Rate in the Industry
Table 7 Company Value
Table 8 Company Value
Table 9 Market Capitalization Increase
Table 10 Market Capitalization Increase
1 Industry Overview
1.1 Review of Bitcoin's Development History
Bitcoin was born against the backdrop of the 2008 global financial crisis, conceived by Satoshi Nakamoto, and the genesis block was mined on January 3, 2009, marking its official emergence. Initially, Bitcoin circulated only within a small circle of cryptography enthusiasts and tech aficionados, with a value close to zero. In May 2010, American programmer Laszlo Hanyecz purchased two pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoins, marking Bitcoin's first commercial transaction, with the price at that time around $0.003. Subsequently, with the rise of Bitcoin trading platforms like Mt. Gox, its price was gradually determined by the market. In 2013, Bitcoin's price broke through $1,000, attracting global attention; by December 2017, it soared to nearly $20,000, drawing the focus of numerous investors and media. Although it later experienced significant corrections and volatility, Bitcoin's market capitalization and influence continued to rise, gradually integrating into mainstream investment perspectives, becoming an undeniable force in the financial sector, and prompting more listed companies to consider its strategic significance and potential value.
The development history of Bitcoin is marked by numerous key milestones and significant events, which profoundly influence its price trends and market perceptions. The period from 2009 to 2010 was the nascent stage of Bitcoin, with the birth of the genesis block opening a new era of decentralized cryptocurrency. At this time, transactions were extremely niche, with no clear market price, circulating only in small amounts among tech enthusiasts for testing and experimentation, primarily as a proof of concept. The period from 2011 to 2013 saw early growth and volatility, with Bitcoin's price first breaking through key psychological price points of $1, $10, and $100, attracting tech innovators and early investors, while trading platforms like Mt. Gox emerged, providing venues for price discovery and market trading. The 2013 Cyprus debt crisis prompted European citizens to seek Bitcoin as a safe haven, pushing the price above $1,000, and mainstream media began to pay attention and report.
From 2014 to 2016, Bitcoin entered a corrective bear market, with the theft of 850,000 Bitcoins from Mt. Gox severely damaging market confidence. Bitcoin's price significantly retreated from its highs, regulatory uncertainties increased, and many countries expressed intentions to strengthen regulations or even ban Bitcoin trading. Market trading activity plummeted, and investor sentiment turned cautious, while the mining industry faced a reshuffle due to low prices and rising difficulty, reshaping the hash power landscape. The period from 2017 to 2018 saw another frenzied bull market followed by deep corrections, with the ICO (Initial Coin Offering) craze emerging, leading to a massive influx of capital into the crypto market. Bitcoin, as the benchmark for "digital gold," saw its price soar from around $1,000 at the beginning of the year to nearly $20,000, but by the end of the year, with the ICO bubble bursting and countries imposing strict regulations, the price collapsed, falling back to the $3,000 to $4,000 range within months, leaving many investors with significant losses and spreading panic in the market.
From 2019 to 2021, Bitcoin entered a phase of recovery and new prosperity, oscillating between $3,000 and $10,000 before starting a new round of increases. Institutional investors rushed in, Grayscale Bitcoin Trust continued to accumulate, and companies like MicroStrategy made significant allocations. Bitcoin's status as an emerging alternative asset gradually stabilized, with its price breaking through $60,000 in April 2021, and market enthusiasm surged, accelerating the expansion of payment, lending, and derivative applications. From 2022 to 2024, Bitcoin has shown a volatile consolidation trend, with the earlier bull market's accumulated bubble bursting, and the price significantly dropping due to factors such as the Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes and concerns over global economic recession, briefly falling below $16,000. However, with a shift in macro policies, clearer industry regulations, and advancements in technological innovation, such as the rising expectations for Bitcoin spot ETF approvals and improvements in scaling solutions like the Lightning Network, the price gradually stabilized and rebounded. In 2024, it oscillated in the $30,000 to $70,000 range, breaking through $100,000 in one go, with Bitcoin's price increasing by 120.88% throughout the year. Within a month after Trump's victory, it successively broke through the $80,000, $90,000, and $100,000 thresholds, and after reaching a peak of $109,000, it gradually retreated, currently hovering around $105,000. Market participants are becoming more rational, and the industry is developing towards compliance and diversification.
Chart 1 Overview of Trump's Bitcoin Conference Promises and Fulfillment

Source: PA News
As shown in Table 1, it reached $93,500 on January 1, 2025, approximately 297 times the value on January 1, 2015.
Chart 2 Trend Chart
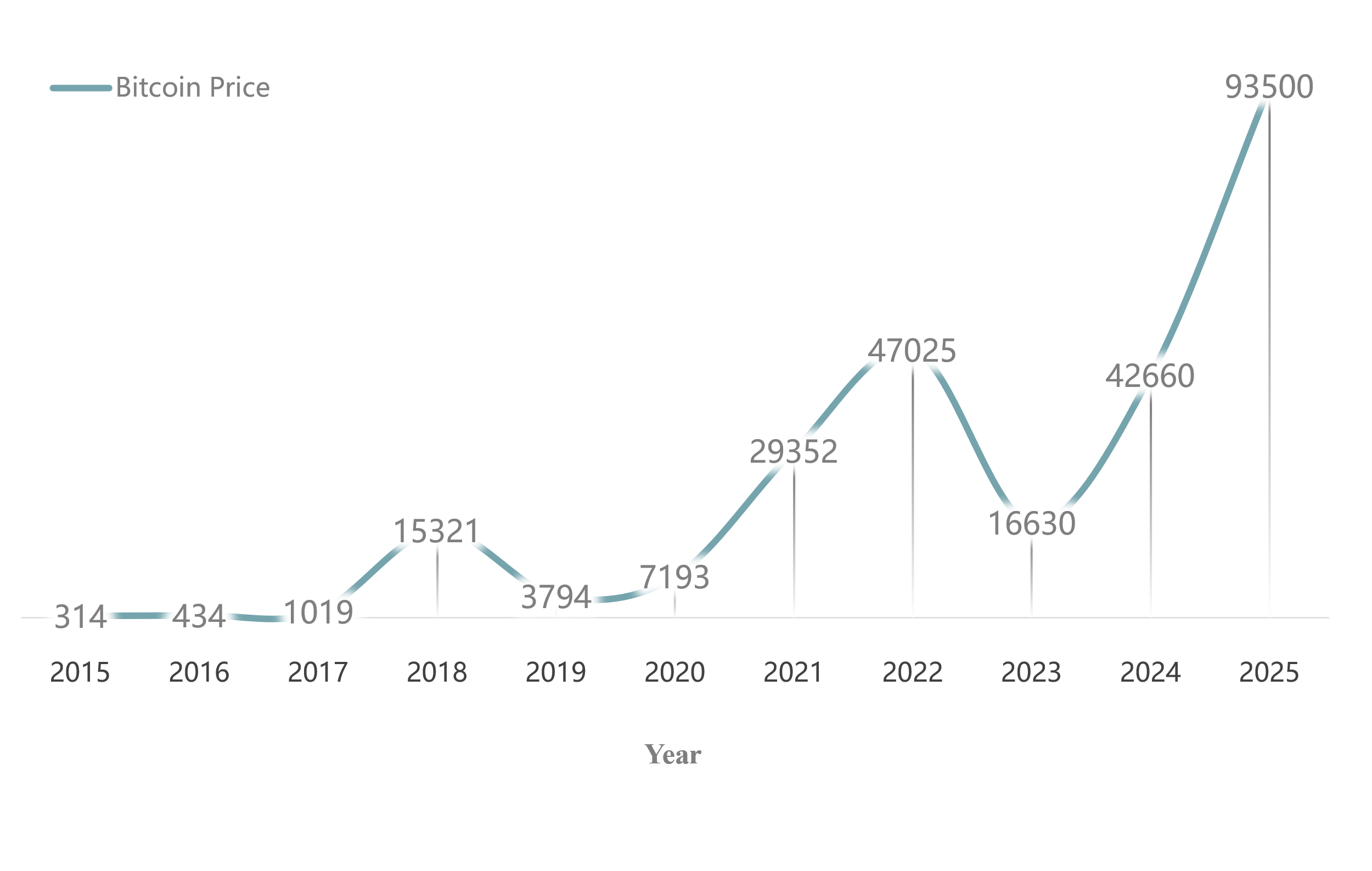
Source: BB Research
From a price characteristic perspective, Bitcoin's early price was highly susceptible to minor supply and demand changes and dynamics within the technical community due to a small number of participants and shallow market depth, resulting in extreme volatility and unpredictability. During its growth phase, it was driven by a mix of macroeconomic events, regulatory policies, and technological innovations, exhibiting cyclical large fluctuations. In bull markets, the price surged rapidly and dramatically, while in bear markets, it retracted swiftly. In recent years, as the market has matured and institutional participation has increased, although volatility remains, the price trend is increasingly dominated by long-term factors such as macroeconomic fundamentals, monetary policy, and industry supply and demand, enhancing its correlation with traditional financial markets. However, the unique halving mechanism still introduces special variables into its price cycle, as the halving every four years reduces the supply of new Bitcoins, providing momentum for price increases from a supply-demand fundamental perspective and stimulating periodic surges in market expectations and investment enthusiasm.
Recently, several key figures in the U.S. political and business sectors have expressed their positions on Bitcoin, influencing market trends and investor sentiment. After Trump was re-elected as President of the United States in November 2024, he promised to make the U.S. the "global cryptocurrency capital" and considered including Bitcoin in the national reserves. On January 21, 2025, he was sworn in, and Bitcoin broke through $109,000, setting a new historical high. The "Trump meme coin" saw its market value exceed $20 billion in a single day. Musk has been an active supporter of cryptocurrencies and backs Trump's cryptocurrency-friendly policies, believing they will promote technological innovation and economic growth. Federal Reserve Chairman Powell recently stated at a press conference that the Fed has no intention of holding Bitcoin and emphasized that, under the Federal Reserve Act, the Fed is prohibited from holding such assets. He also noted that the Fed would not seek to change this law, and Powell's stance on monetary policy is considered to have an indirect impact on the Bitcoin market.
Gold is a mature reserve asset with a long history and stable prices but has physical limitations. Bitcoin is an emerging reserve value tool with scarcity, convenience, and technological potential, but it has high volatility and uncertainty. In the future, Bitcoin and gold may coexist: gold will continue to serve as a traditional reserve asset, while Bitcoin will carve out a niche in the digital economy and among younger investors. The specific choice depends on investors' balance between stability and growth potential. If more central banks and institutions globally begin to adopt Bitcoin, its status as a reserve asset may significantly increase over the next decade.
1.2 Background of Listed Companies Involved in Bitcoin
From a macroeconomic perspective, global economic growth is unstable, traditional monetary policies are volatile, and inflation concerns are the main reasons. For example, after the 2008 financial crisis, long-term quantitative easing in Europe and the U.S. led to excessive money supply, raising doubts about the value storage function of fiat currencies. Due to its fixed total supply of 21 million and decentralized characteristics, Bitcoin is viewed by some listed companies as a new choice for hedging against inflation and preserving asset value. For instance, MicroStrategy has publicly stated that it purchased Bitcoin to combat the risk of U.S. dollar depreciation.
In the financial market, on one hand, traditional investment areas such as the stock and bond markets have seen significant fluctuations in returns in recent years. In a low-interest-rate environment, bond yields are meager, and the stock market has been frequently impacted by trade frictions and geopolitical tensions, leading to large swings. On the other hand, there is an urgent need for portfolio diversification. Bitcoin has a low correlation with traditional assets, effectively diversifying risks. According to statistics, from 2015 to 2020, the average correlation between Bitcoin and assets like stocks and bonds was only 0.11. To pursue stable returns and optimize asset allocation, listed companies have begun to explore new opportunities in the Bitcoin space.
2 In-Depth Analysis of Typical Cases
2.1 MicroStrategy: Pioneer in Bitcoin Investment
MicroStrategy, as one of the publicly listed companies holding the most Bitcoin globally, began its Bitcoin investment journey in August 2020. At that time, the global economy was impacted by the pandemic, traditional financial markets were turbulent, and expectations of U.S. dollar depreciation were rising. The company purchased Bitcoin as inventory assets for $250 million, accurately capturing the macroeconomic turning point. Since then, its holding strategy has remained aggressive, with multiple large purchases in September 2020 and the first quarter of 2021. During this process, the company's stock price has shown significant correlation with Bitcoin prices. In the Bitcoin bull market, the expectation of substantial unrealized gains attracted a large influx of investors, causing the stock price to soar, with an increase of over 500% in 2024. Conversely, during periods of deep Bitcoin price adjustments, the stock price also fluctuated significantly. For example, in 2022, as Bitcoin prices retracted, the company's market value evaporated by billions, highlighting the high-risk, high-reward characteristics that profoundly influenced investor sentiment and capital flows in both the crypto and traditional financial markets.
2.2 Tesla: The Cross-Industry Disruptor
In early 2021, Tesla entered the Bitcoin market with a massive investment of $1.5 billion, instantly igniting market enthusiasm. The influx of such a large amount of capital caused Bitcoin prices to surge significantly in the short term, and Musk's tweets became a "catalyst" for price fluctuations. On one hand, investing in Bitcoin provided a way for the company to seek value for idle funds, alleviating the challenges of low returns in a low-interest-rate environment. On the other hand, in March of the same year, Tesla announced it would accept Bitcoin for car purchases, attempting to create a closed loop between crypto payments and car sales. Although this was later canceled due to controversies over Bitcoin's energy consumption and price volatility, it successfully shaped Tesla's image as a technological pioneer willing to innovate, spilling the heat of the crypto sector into its automotive business, attracting attention from young tech enthusiasts and stimulating vehicle order growth. At its peak, Bitcoin-related business contributed impressive earnings to its financial reports. Although the strategy has since turned cautious, Tesla still maintains its voice in the crypto space through its remaining holdings.
2.3 Meitu: Representative of Emerging Forces
In March to April 2021, Meitu made three significant investments totaling $100 million, purchasing over 940 Bitcoins and 31,000 Ether, forcefully entering the crypto space. From a business perspective, as an imaging technology company, Meitu faced fierce competition in its traditional business and sought to embrace new technological trends through crypto investments, exploring intersections between digital content and blockchain, such as launching blockchain-based copyright protection applications for creative works. From a financial perspective, the initial appreciation of crypto assets helped optimize its balance sheet, resulting in substantial unrealized gains and a short-term rise in stock prices. However, the bear market in 2022 led to asset impairments, putting pressure on performance and causing net losses to soar. After weathering the winter, the market rebounded in 2023-2024, allowing Meitu to seize the opportunity to sell and profit approximately $79.63 million, successfully recouping funds to return to its core imaging business. The crypto investment served as a "springboard" for transformation, accumulating experience in emerging fields and paving new paths for business diversification and financial stability.
3 Insights into Investment Motivations
3.1 Demand for Asset Diversification
Within the traditional investment portfolio theory framework, asset diversification is key to reducing non-systematic risk. Listed companies typically concentrate their asset allocations in areas such as stocks, bonds, and cash. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, stock markets plummeted, and bond markets experienced turbulence, leading to significant asset shrinkage for many companies. Bitcoin, due to its unique properties, has become a "new favorite" for risk diversification. According to Bloomberg data, from 2010 to 2020, the average correlation between Bitcoin and the S&P 500 index was only 0.08, with its correlation to bonds nearly zero. Before entering the Bitcoin market, MicroStrategy's asset allocation heavily relied on business software-related assets, facing cyclical industry risks and concentrated market competition. After introducing Bitcoin, its asset portfolio became diversified, with multiple revenue streams. For example, during the 2021 crypto bull market, Bitcoin investment returns exceeded those from its core software business, smoothing out the volatility of a single business and reducing overall risk exposure without sacrificing too much expected return, thereby solidifying the foundation for the company's financial stability.
Chart 3 Asset Allocation Chart
Source: OPEN AI Official Website, BB Research
3.2 Considerations for Hedging Against Inflation
In the context of global economic cycles, inflation is a "sword of Damocles." Especially after 2020, under the quantitative easing measures taken by various countries due to the COVID-19 pandemic, excessive money supply has led to high inflation, with the U.S. CPI exceeding 9% in 2022. Traditional anti-inflation assets such as gold and real estate face limitations; gold is affected by geopolitical factors and central bank sell-offs, while real estate faces regulatory constraints and liquidity bottlenecks. Bitcoin, with its fixed total supply of 21 million and decentralized nature, theoretically possesses strong anti-inflation properties. Empirical data from 2009 to 2023 shows that, in the long term, Bitcoin's price increase far exceeds the inflation rate when compared to U.S. inflation data. During certain periods, such as from 2013 to 2017, when inflation was rising moderately, Bitcoin's annualized growth rate exceeded 200%. Companies purchasing Bitcoin can, to some extent, hedge against the erosion of purchasing power due to rising prices on their balance sheets, safeguarding shareholder rights. Many resource-based and consumer-oriented companies are significantly impacted by inflation driven by upstream cost pressures and are exploring Bitcoin as a hedge to seek new paths for cost control and profit stability.
3.3 Strategic Layout Intentions
In the wave of emerging technologies, blockchain and the crypto economy are seen as frontiers of future transformation. Some listed companies are proactively positioning themselves in Bitcoin to seize opportunities. The tech company Reddit purchased Bitcoin to strengthen community recognition of the crypto ecosystem, exploring new models that combine "community points + Bitcoin" to attract user participation and inject vitality into platform development. Financial institutions like Grayscale entered the market through Bitcoin trusts, attracting capital, accumulating experience, and shaping standards to transition from traditional asset management to digital asset management. Traditional companies like Tesla invested in Bitcoin, linking it to crypto payments, integrating into a collaborative ecosystem across multiple fields, expanding business boundaries, and leveraging the hype for marketing to attract customers and enhance brand image. Pioneers in various industries are using Bitcoin as a "test stone" for related strategies, exploring new "colonies."
4 Outlook on the Development Trends of the Holding Stock Industry
4.1 Market Size Forecast
Based on the rapid growth of publicly listed companies holding Bitcoin in recent years, the future expansion momentum is strong. In terms of market capitalization of holding stocks, although currently only a few companies have large holdings, with the central price of Bitcoin rising and more companies entering the market, it is expected to increase exponentially. According to OKG Research, if approximately $2.28 trillion flows into the Bitcoin market within the next year, pushing the price to $200,000, the market capitalization of listed companies holding Bitcoin will surge correspondingly, with leading companies like MicroStrategy potentially surpassing $100 billion in asset scale. In terms of the number of holding companies, the penetration of emerging markets and traditional industries is accelerating, with a growth rate of about 15% over the past five years. It is expected that in the next five years, the number of new companies will increase at a rate of 20%, especially in the financial and technology sectors, where new startups are attracted by crypto culture and investment returns, rapidly entering the market, increasing from the current 80 to 200 companies, fundamentally reshaping the industry landscape. Bitcoin is transitioning from a "niche embellishment" to a "mainstream weight" on corporate balance sheets.
Chart 4 Prediction Chart for Bitcoin Holding Companies
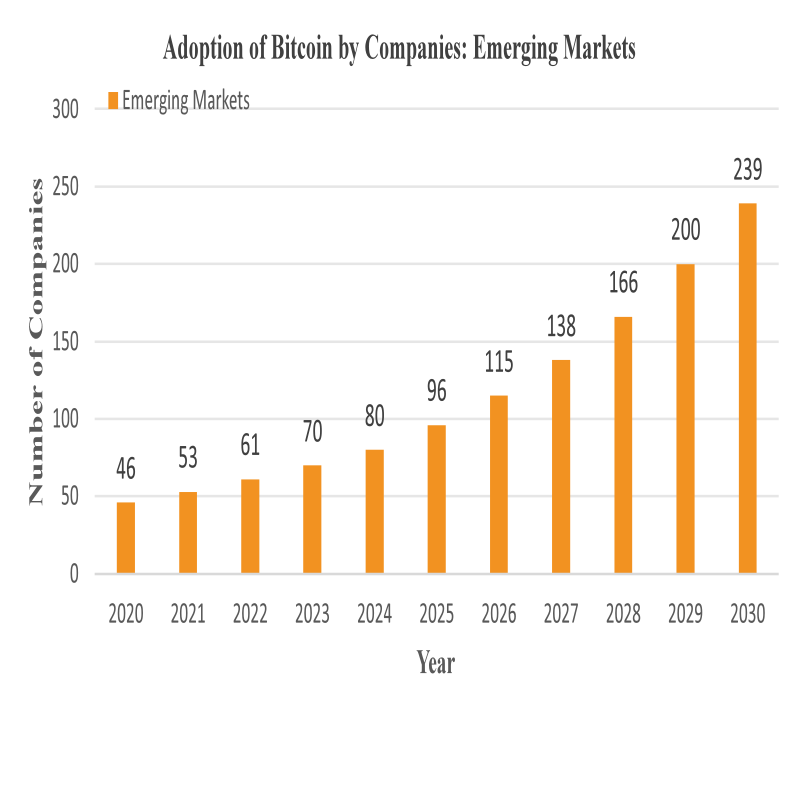
Source: OPEN AI Official Website, BB Research
4.2 Industry Pattern Evolution
Competition among old and new players will intensify. Established giants like MicroStrategy and Tesla will continue to solidify their positions due to their first-mover advantage, capital, and brand strength. MicroStrategy may leverage its specialized crypto investment team to expand Bitcoin-related financial services, creating a "Bitcoin asset management empire." Tesla, utilizing cash flow from its automotive business, may seek to increase its holdings and strengthen the synergy between crypto and automotive ecosystems. Emerging forces should not be underestimated; fintech startups are competing for market share with innovative products and flexible strategies, such as launching Bitcoin yield optimization financial products to attract retail investors indirectly. Traditional industry giants are also entering the fray, with energy and retail companies exploring Bitcoin payments and supply chain financial innovations using upstream and downstream resources. In the short term, the industry concentration may dilute due to new players, but in the long term, comprehensive strengths in resources, technology, and branding will allow the strongest players to emerge, reshaping the top tier of the industry and forming a new multi-polar competitive landscape.
4.3 Integration Prospects with the Blockchain Ecosystem
The deep involvement of listed companies in building blockchain infrastructure is an inevitable trend. Tech companies are investing in R&D to optimize Bitcoin-centric blockchain performance, reducing transaction costs and shortening confirmation times. For example, they are exploring the commercialization of the Lightning Network to normalize small, high-frequency payments and expand Bitcoin's everyday consumption scenarios. Financial institutions are building compliant Bitcoin custody and clearing platforms based on blockchain technology to facilitate institutional entry, promoting Bitcoin's transition from "wild" to "tamed." In terms of application development, companies are exploring the value of Bitcoin beyond its "currency" aspect, such as in traceability and copyright fields, combining it with NFTs to anchor value, enabling digital asset rights confirmation and circulation, and achieving a dual approach of virtual economy materialization and real economy virtualization. Riding the wave of blockchain, Bitcoin is stepping out of the realm of mere investment products and integrating into the core of the global business value creation network, empowering the digital transformation of various industries.
5 Trends in the Holding Stock Industry
5.1 We Address Two Key Questions of This Round of the Holding Stock Industry Revolution: Structure and Space
5.1.1 Competitive Landscape of Bitcoin Holding Listed Companies: Future Direction Towards High Concentration with High Fixed and Low Marginal Cost Structure
Bitcoin holding listed companies refer to enterprises that incorporate Bitcoin into their balance sheets and are publicly traded in the capital markets. They may view Bitcoin as a reserve asset, part of their investment portfolio, or a strategic technological asset. The cryptocurrency industry revolution brought about by foreseeable policies such as the U.S. National Reserve Strategy Act series is becoming the factual starting point for the next technological revolution, altering the financial landscape and breaking the arms race pattern.
The asset management industry of Bitcoin holding companies requires high fixed cost inputs, but the marginal usage cost is relatively low and shows a rapid downward trend. This indicates a high level of industry concentration, gradually developing into a competitive landscape dominated by leading players.
We believe that the global competitive landscape will trend towards a flourishing competition. On one hand, the high concentration of the market due to Bitcoin trading creates certain industry barriers. On the other hand, the initial homogenization of Bitcoin asset management methods exists, but the accumulated industry experience shows some differences. The ability to manage Bitcoin assets will become the core competitiveness of enterprises, and leading players mastering Bitcoin-enhanced yield strategies will gain this advantage.
(1) Competitive Factors for Bitcoin Holding Listed Companies: Homogenization of Value Storage, Quantity of Bitcoin Held as Core Competitiveness
We can break down the competition among Bitcoin holding listed companies into three dimensions: quantity, scenario, and function. For giants, scenarios and functions exhibit high homogeneity, with significant differentiation only in the quantity dimension. We believe that in the ultimate competition, quantity will reign supreme, followed by first-mover advantages and unique scenarios.
Chart 5 Asset Allocation Chart

Source: OPEN AI Official Website, BB Research
(2) Homogenization of Value Storage Competition
a. Scenario Level: The core reason is that the Bitcoin blockchain cannot support the deployment of new financial applications like Ethereum, making it difficult to become an ideal financial infrastructure.
b. Function Level: Early Bitcoin holders tend to be risk-averse in their investment philosophy, lacking proven complex structures and risk hedging strategies, making it difficult to meet investors' diverse needs for returns and risks.
(3) Quantity Competition: First-Mover Advantage and Scenario Advantage
Quantity differentiation will become the core competitive factor determining the outcome among competitors. We believe that the essence of quantity competition lies in the competition of speed and scenarios. First, whether one can quickly hold a large quantity of Bitcoin to enjoy the model optimization brought by quantity flywheel; second, whether there are suitable scenarios to support the accumulation of sufficient Bitcoin quantity strategy enhancement applications.
a. The Flywheel Effect of Holding Quantity: The Positive Cycle of Bitcoin Quantity and Asset Management Models
The more Bitcoin held, the more interactive feedback between investors and asset management models, allowing for better model optimization. Theoretically, 1) the larger the data volume, the richer and more comprehensive the investment levels and dimensions, and the more timely the updates, the better the investment model performance; 2) for large models of Bitcoin-enhanced investment strategies (with market feedback reinforcement learning), this is a core link for model tuning. It can be considered that the quantity held affects the actual usage scenarios of asset management models, and the scale of holdings is crucial for promoting the optimization of asset management models.
b. The Uniqueness of Data and Scenarios Creates Differentiated Opportunities
Bitcoin Enhanced Strategy Application Scenarios: 1) Improving the robustness of strategies under extreme market conditions through AI-optimized model adaptability; 2) Designing innovative enhancement strategies using tools provided by decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms (such as AMM, decentralized lending); 3) Large-scale development of security usage scenarios, along with new ecological revenue sources. For a long time, Bitcoin applications and yield aspects have been lacking, leading leading listed companies to only use Bitcoin as a value storage tool.
(4) Number of Holding Companies and Geographic Distribution
According to data from institutions such as CoinGecko and OKG Research, as of 2024, there are approximately 80 publicly listed companies globally holding Bitcoin. North America dominates, accounting for over 60% of related enterprises, with the U.S. leading with more than 50 companies, including well-known industry players like MicroStrategy and Tesla. Europe follows closely, accounting for about 20%, with companies from countries like the UK and Germany participating due to a more lenient financial regulatory environment. The Asian region accounts for about 15%, with Japan and South Korea as representatives. Japan has about 10 companies investing in Bitcoin, driven by the legalization of cryptocurrency trading, while South Korean companies purchase Bitcoin to expand payment and asset appreciation channels due to the developed internet and gaming industries. The participation of listed companies from other continents is relatively low, mainly limited by financial infrastructure and regulatory uncertainties.
Chart 6 Asset Allocation Chart
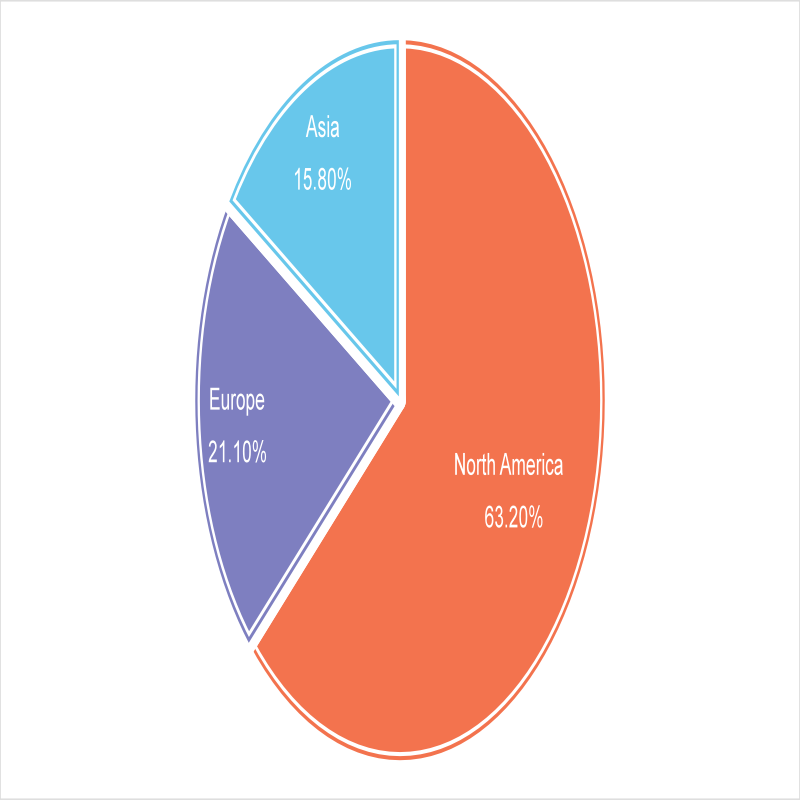
Source: OPEN AI Official Website, BB Research
(5) Industry Category Differences
Several listed companies invest in Bitcoin, with tech companies leading, accounting for over 40%. Software giant MicroStrategy has continuously purchased Bitcoin since 2020 to optimize its asset structure, holding over 440,000 Bitcoins by 2024, viewing Bitcoin as a tool against inflation and for digital wealth storage. Payment companies like Square and PayPal are exploring new settlement methods through Bitcoin payment ecosystem construction. Internet and e-commerce companies like Rakuten and Meitu seek new business opportunities and traffic monetization by purchasing cryptocurrencies.
The financial industry accounts for 30%, with asset management institutions holding Bitcoin on a large scale through GBTC trusts. Crypto hedge funds and quantitative investment companies use algorithms to arbitrage during price fluctuations, while some banks are researching digital currency-related businesses to explore compliant participation in the Bitcoin financial ecosystem.
Mining companies account for 20%, such as Marathon and Riot Platforms, which leverage their computing power advantages to reserve large amounts of Bitcoin in addition to operations and debt repayment. Their strategies are influenced by various factors and jointly affect Bitcoin supply with mining machine manufacturers and mining pools.
Traditional industries such as manufacturing and consumer goods account for a smaller proportion, less than 10%. For example, although Tesla primarily focuses on automotive manufacturing, Musk's forward-looking vision led to a $1.5 billion investment in Bitcoin aimed at asset diversification and brand marketing. Despite adjustments in strategy, Tesla still holds over 10,000 Bitcoins, providing a model for new manufacturing enterprises to integrate into the crypto economy. Investments in Bitcoin across various industries reflect differing views on industry transformation, asset appreciation, and user demand.
(6) Holding Scale and Asset Allocation Proportion
There is a significant disparity in the holding scale of listed companies. MicroStrategy holds 446,400 Bitcoins, with a market value exceeding $50 billion, far surpassing other companies. Tesla, Galaxy Digital, Hut 8, and others hold thousands to tens of thousands of Bitcoins, with market values ranging from hundreds of millions to billions. More than half of the companies hold fewer than 1,000 Bitcoins.
In terms of asset allocation, over 70% of MicroStrategy's assets are in Bitcoin, with a strategic depth tilted towards the crypto ecosystem. Mid-sized companies like Meitu have about 10% - 20% of their assets in Bitcoin as an emerging investment supplement. Small or cautious companies have Bitcoin allocations below 5%, using it only as a trial. The holding scale and asset allocation reflect companies' differing attitudes towards crypto assets and indicate the diversity of Bitcoin's future role in enterprises.
5.1.2 Industry Space Aspects
(1) Bitcoin ETFs and actively managed Bitcoin strategies covering staking, CeDeFi fee arbitrage, and DeFi may be replaced by other recommendations to maximize the release of Bitcoin's intrinsic value. Here, we define all entry points for passive Bitcoin ETFs and active asset management, including Coinbase (ETF), MARA (mining companies), and MSTR (Bitcoin holding listed companies), which may be replaced by multiple competitive entrants in the industry;
(2) Some established Bitcoin holders generally have a conservative investment philosophy and a high degree of risk aversion;
(3) Although Bitcoin is a powerful value storage tool, it is difficult to meet investors' diverse needs for returns and risks in terms of financial management.
5.2 Financial Performance of Bitcoin Holding Listed Companies
5.2.1 Impact on Balance Sheet: Bitcoin is typically recorded as "intangible assets" in financial statements, and its value is subject to accounting standards. In a bear market, companies may face asset impairment; in a bull market, the increase in asset value may not be fully reflected in financial reports.
5.2.2 Correlation Between Stock Prices and Bitcoin Prices: The stock price fluctuations of companies holding Bitcoin are usually highly correlated with Bitcoin prices. For example, MicroStrategy's stock price surged during Bitcoin bull markets and retreated in bear markets.
5.2.3 Investor Sentiment and Market Value: Companies holding Bitcoin attract specific investors due to their exposure to digital assets, but they also bear more market volatility risk.
5.3 Valuation Models for Bitcoin Holding Listed Companies
Based on global data of Bitcoin holding companies as of December 31, 2024, four Bitcoin holding listed companies are selected to build a company valuation model.
5.3.1 Market Capitalization Premium Rate
This model relies on the market capitalization premium rate, which increases Bitcoin holdings through equity dilution financing, enhancing the per-share BTC holdings and thereby boosting the company's market value.
Market Capitalization Premium Rate Model = (Market Price - Intrinsic Value) / Intrinsic Value × 100%
Using formula (1), we calculate the market premium rates for MSTR, NANO, MARA, and Boya Interactive.
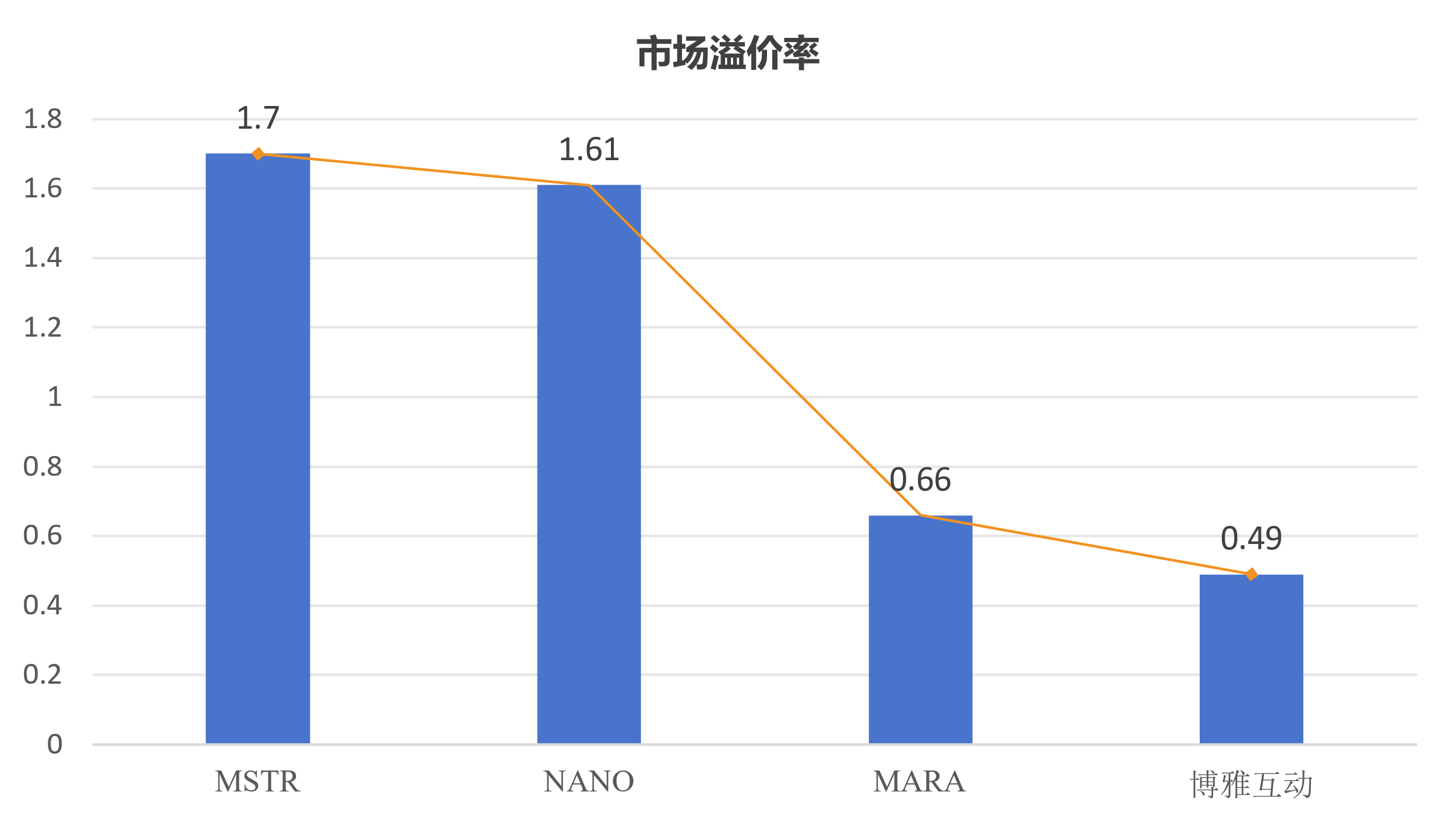
Chart 7 Market Premium Rates for MSTR, NANO, MARA, and Boya Interactive
Source: BB Research
As shown in Table 4, in 2024, MSTR's Bitcoin holdings amount to 402,100, with each Bitcoin priced at $82,100, giving an intrinsic value of $33 billion, and its market capitalization is $89 billion, resulting in a market premium rate of 1.70 according to formula 1;
In 2024, NANO's Bitcoin holdings amount to 300, with each Bitcoin priced at $99,700, giving an intrinsic value of $0.36 million, and its market capitalization is $0.94 million, resulting in a market premium rate of 1.61 according to formula 1;
In 2024, MARA's Bitcoin holdings amount to 40,400, with each Bitcoin priced at $87,205, giving an intrinsic value of $3.526 billion, and its market capitalization is $5.866 billion, resulting in a market premium rate of 0.66 according to formula 1;
In 2024, Boya Interactive's Bitcoin holdings amount to 3,183, with each Bitcoin priced at $57,724, giving an intrinsic value of $29.8 million, and its market capitalization is $44.4 million, resulting in a market premium rate of 0.49 according to formula 1.
The competitive landscape of the holding stock industry envisions a contest of speed and premium rates: the leading MSTR has a market premium rate of 1.70;
The emerging NANO has a market premium rate of 1.61.
The median market premium rate is 1.82, serving as the central valuation for the holding stock index.
Reviewing the volatility of holding companies, it can be seen that when marginal net buying increases, the premium rate can remain high; when marginal net buying weakens, the premium rate begins to decline; during marginal net selling, the premium rate will quickly turn negative.
The extent to which the premium rate of Bitcoin holding companies like MSTR can be maintained depends on: 1) the height and duration of the BTC bull market; 2) the sustainability of marginal BTC net buying; 3) the ongoing marketing ability of the company's founders.
5.3.2 Net Asset Value (NAV) Premium Model
This model estimates company value based on the net value of Bitcoin assets held by the company, combined with the premium multiple given by the market.
Company Value = Premium Multiple × Bitcoin Net Assets
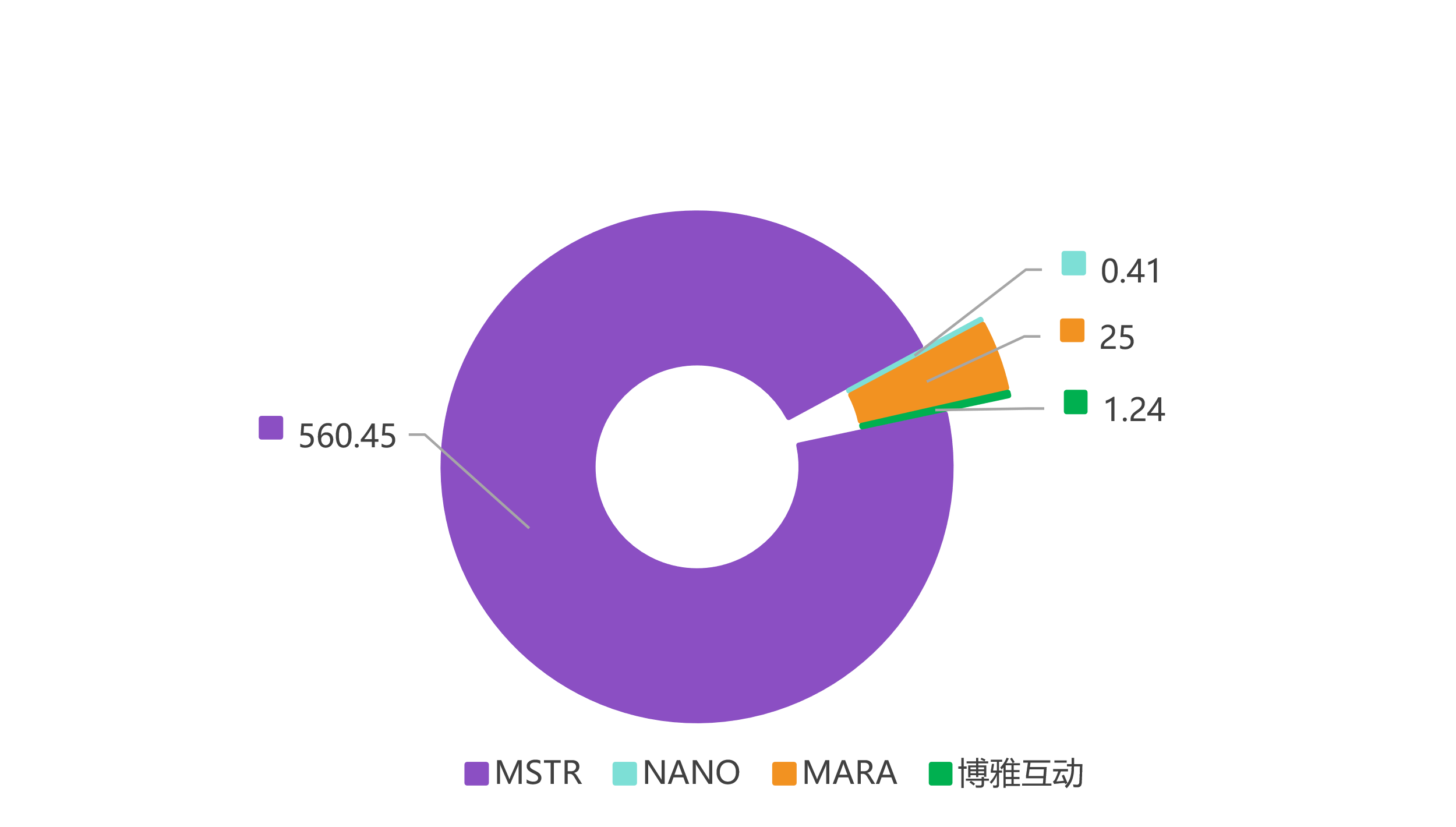
Chart 8 Company Values for MSTR, NANO, MARA, and Boya Interactive
Source: BB Research
As shown in Table 5, in 2024, MSTR's Bitcoin value is $37.59635 billion, with liabilities of $4.57 billion, resulting in Bitcoin net assets of $33.026 billion, a premium multiple of 1.70, and a company value of $56.045 billion;
In 2024, NANO's Bitcoin value is $0.03366 million, with liabilities of $0.0008 million, resulting in Bitcoin net assets of $0.026 million, a premium multiple of 1.61, and a company value of $0.041 million;
In 2024, MARA's Bitcoin value is $3.7815 billion, with liabilities of $0.013 billion, resulting in Bitcoin net assets of $3.768 billion, a premium multiple of 0.66, and a company value of $2.500 billion;
In 2024, Boya Interactive's Bitcoin value is $0.298 million, with liabilities of $0.046 million, resulting in Bitcoin net assets of $0.252 million, a premium multiple of 0.49, and a company value of $0.124 million.
The median company value is $0.27, serving as the central valuation for the industry.
5.3.3 Bitcoin Price Sensitivity Model
This model values the company based on the impact of a certain change in Bitcoin price on the company's market capitalization.
Market Capitalization Change = Sensitivity Coefficient × Bitcoin Price
As shown in Table 6, in 2024, MSTR's price sensitivity coefficient is 1.51%, meaning that for every 1% increase in Bitcoin price, the company's market capitalization increases by $861 million;
In 2024, NANO's price sensitivity coefficient is 2.96%, meaning that for every 1% increase in Bitcoin price, the company's market capitalization increases by $0.01 million;
In 2024, MARA's price sensitivity coefficient is -0.53%, meaning that for every 1% increase in Bitcoin price, the company's market capitalization decreases by $0.13 million;
In 2024, Boya Interactive's price sensitivity coefficient is 1.04%, meaning that for every 1% increase in Bitcoin price, the company's market capitalization increases by $0.01 million.
The median increase in market capitalization is $0.01 million, serving as the central valuation for the industry.
Buying holding stocks is equivalent to gaining the expected appreciation of Bitcoin and the performance multiplier of the listed company. First, holding stock companies can leverage debt; second, they can leverage the PE Ratio, with MSTR maintaining around 2x leverage during Bitcoin bull markets.
Currently, there is no perpetual motion machine for holding companies. Once MSTR's BTC holdings reach a certain limit (Grayscale is 200,000), the premium rate will inevitably decline. A reasonable allocation of Bitcoin holding ETFs is more beneficial for obtaining long-term stable returns.
Finally, the research finds that when the historical turnover rate of MSTR exceeds 30%, it signals a potential peak.
6 Conclusion and Recommendations
6.1 Research Summary
The global group of publicly listed companies holding Bitcoin is still in the development stage but has already shown vigorous vitality and enormous potential.
From a developmental perspective, the region is concentrated in North America, spanning diverse fields such as technology, finance, and mining. The holding scale and asset allocation strategies are diversely differentiated, with some companies aggressively embracing Bitcoin while others cautiously test the waters.
In terms of opportunities, Bitcoin provides listed companies with asset diversification and a new tool for hedging inflation, aligning with strategic transformation needs, and is expected to seize opportunities in the emerging technological wave. However, challenges should not be underestimated, as the rollercoaster price fluctuations, unclear regulatory policies, and limited market acceptance all introduce uncertainties to the companies' finances, operations, and strategic implementation.
By 2025, the launch of a Bitcoin holding stock ETF index is expected, with mainstream institutions covering Bitcoin holding stock investments. All holding stocks will issue tokens, and all tokens will issue stocks. The combination of holding listed companies and Bitcoin-enhanced strategies will bring disruptive investment opportunities.
Overall, Bitcoin investment has become a key path for listed companies to explore new growth and respond to complex economic environments, but careful weighing of pros and cons and meticulous risk management are necessary.
6.2 Investment Recommendations
For risk-tolerant aggressive investors, attention can be directed towards industry pioneers like MicroStrategy and emerging players like Nano, especially during Bitcoin market adjustments, when panic sentiment spreads, or when prices hit key support levels. Gradually build positions on dips to share in their high growth potential; at the same time, closely track the dynamics of emerging technology and financial companies' Bitcoin derivative products and Bitcoin holding stock index ETF layouts to capture early entry opportunities, leveraging industry growth dividends for asset appreciation, but strict stop-loss measures must be set to guard against black swan impacts.
Conservative investors should prioritize focusing on the Bitcoin holding dynamics of large, mature listed companies, such as Tesla, and wait for market trends to clarify and policy environments to stabilize. Combining technical analysis with fundamental research, they should participate moderately with a small proportion of funds when Bitcoin prices pull back to reasonable valuation ranges, emphasizing long-term holding. By leveraging the professional management and diversified business of enterprises to buffer against Bitcoin price fluctuations, they can achieve steady asset appreciation; at the same time, pairing with traditional safe-haven assets like gold and high-quality bonds can optimize the risk-return ratio of the investment portfolio.
Cautious investors can participate indirectly by focusing on Bitcoin-related financial products, such as compliant Bitcoin ETFs (if approved in their regions), tracking the movements of professional asset management institutions. When market sentiment is optimistic, funds continue to flow in, and technical indicators improve, they can make small exploratory investments while strictly adhering to asset allocation discipline, keeping Bitcoin investment exposure at a very low level to ensure principal safety while gently sharing in the industry's growth dividends.
6.3 Risk Factor Identification
Since its inception, Bitcoin's price has fluctuated dramatically, causing severe impacts on publicly listed companies holding Bitcoin. Taking MicroStrategy as an example, when Bitcoin prices fell in 2022, the company's asset impairment losses significantly increased, leading to a widening net loss in financial reports and a sharp decline in market capitalization and stock price. The sharp price changes create uncertainty in financial and market capitalization management for listed companies, which in turn affects investor confidence.
There is a significant disparity in global regulatory attitudes towards Bitcoin, and these attitudes are constantly changing. Some U.S. states recognize Bitcoin as legal, but federal agencies impose strict regulations, making it difficult for Bitcoin ETFs to be approved. Companies holding Bitcoin face stringent compliance reviews and information disclosure requirements; since 2017, China has banned virtual currency-related businesses, limiting domestic companies' Bitcoin investments; the European Union is continuously improving its regulatory framework for crypto assets. The direction of regulatory policies affects the legality and operational models of listed companies holding Bitcoin. If regulations tighten, the Bitcoin assets of listed companies may depreciate, facing selling pressure, and their business and strategic layouts may also be hindered.
In everyday business scenarios, Bitcoin faces numerous challenges as a payment method. Its transaction confirmation time can take 10 to 60 minutes, making it difficult to meet the immediate transaction needs of retail fast-moving consumer goods. The significant price volatility also exposes merchants to high foreign exchange risks. In cross-border transactions, although Bitcoin theoretically can bypass foreign exchange controls and reduce remittance costs, practical operations are limited by various countries' foreign exchange policies and anti-money laundering regulations, leading to difficulties in fund inflows and outflows, complex exchange rate conversions, and insufficient liquidity. This restricts Bitcoin's role in the expansion of cross-border business and capital circulation for listed companies, hindering its market penetration.
6.4 Industry Outlook
Looking ahead, globally listed companies holding Bitcoin are expected to continue expanding the boundaries of financial innovation. On one hand, they will promote the diversification of Bitcoin financial products, moving from simple holding to complex derivative innovations such as Bitcoin futures, options, and structured notes, catering to different risk preferences. On the other hand, they will deepen integration with blockchain technology, aiding in the upgrade of Bitcoin's underlying technology, accelerating the implementation of applications like the Lightning Network, enhancing transaction efficiency, and expanding commercial use cases. In terms of market leadership, leading companies, leveraging their resources, technology, and brand accumulation, will become industry standard setters, guiding the improvement of regulatory policies; emerging companies will stimulate a catfish effect with their innovative vitality, promoting diverse competition and healthy development within the industry, collectively pushing Bitcoin from the margins to the mainstream, integrating into the core of the global financial ecosystem, reshaping the landscape of asset allocation, payment settlement, and value storage, and injecting lasting momentum into the digital transformation of the economy.
In the future, "all holding stocks will issue tokens, and all tokens will issue stocks," leading to the formation of a new industry—capital market WEB 3.0 carnival, soaring high and reaching great heights, with a promising future.
Investment Rating Explanation for Holding Stocks
Within six months after the report date, the performance relative to the holding stock ETF index's rise and fall is defined as follows:
- Buy: Performance relative to the holding stock ETF index is +20% or more;
- Add: Performance relative to the holding stock ETF index is +10% to +20%;
- Neutral: Performance relative to the holding stock ETF index fluctuates between -10% to +10%;
- Reduce: Performance relative to the holding stock ETF index is -10% or less.
Industry Investment Ratings:
Within six months after the report date, the performance of the industry index relative to the holding stock index's rise and fall is defined as follows:
- Bullish: Industry index performance relative to the holding stock index is +10% or more;
- Neutral: Industry index performance relative to the holding stock index is -10% to +10% or more;
- Bearish: Industry index performance relative to the holding stock index is -10% or less.
We remind you that different securities research institutions use different rating terminologies and standards. We employ a relative rating system, indicating the relative weight of the investment.
Recommendation: The decision for investors to buy or sell holding stocks depends on individual circumstances, such as the current holding structure and other factors to consider. Investors should not rely solely on investment ratings to draw conclusions.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




