Each region assigns different meanings to Bitcoin based on its own needs.
Authors: Vaish Puri & Joey Campbell
Translation: Deep Tide TechFlow
When historians look back at 2024, they may view it as a significant year for Bitcoin's move into the mainstream. This year, Bitcoin reached an all-time high, became a hot topic in the U.S. presidential election, 11 Bitcoin ETFs were approved for listing, and it experienced a halving event. Meanwhile, the global economy struggled under the pressure of inflation.
This year, Bitcoin showcased its unique charm in its multifaceted nature. In countries facing severe economic difficulties (such as Argentina and Turkey), it was seen as a safe haven against high inflation; in the eyes of Wall Street elites, it became an investment tool recognized by financial giants like BlackRock; for crypto-punks and developers, it was a new canvas for innovation; and for governments around the world, it transformed from a threat that needed to be controlled into an opportunity that could be leveraged.
Bitcoin's technology is also continuously evolving. The Bitcoin network, which once centered on "simplicity," began to experiment with more new features. The re-enabled opcodes (such as OP_CAT) and revolutionary research (like BitVM) injected programmability and self-custody possibilities into Bitcoin's base layer. Layer 2 networks rapidly developed, providing solutions for transaction scalability; at the same time, the emergence of liquid staking derivatives brought potential for yield generation to Bitcoin.
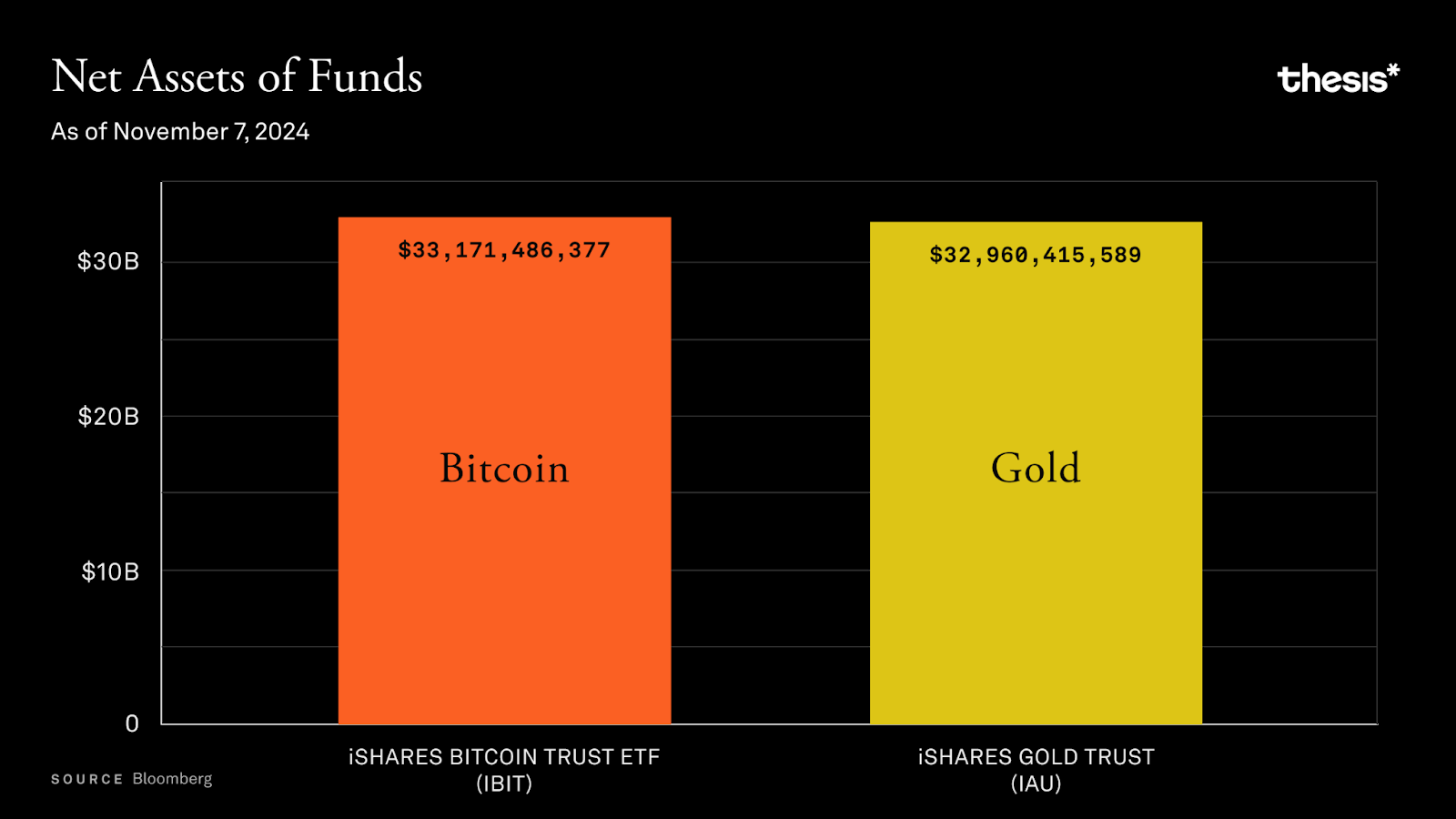
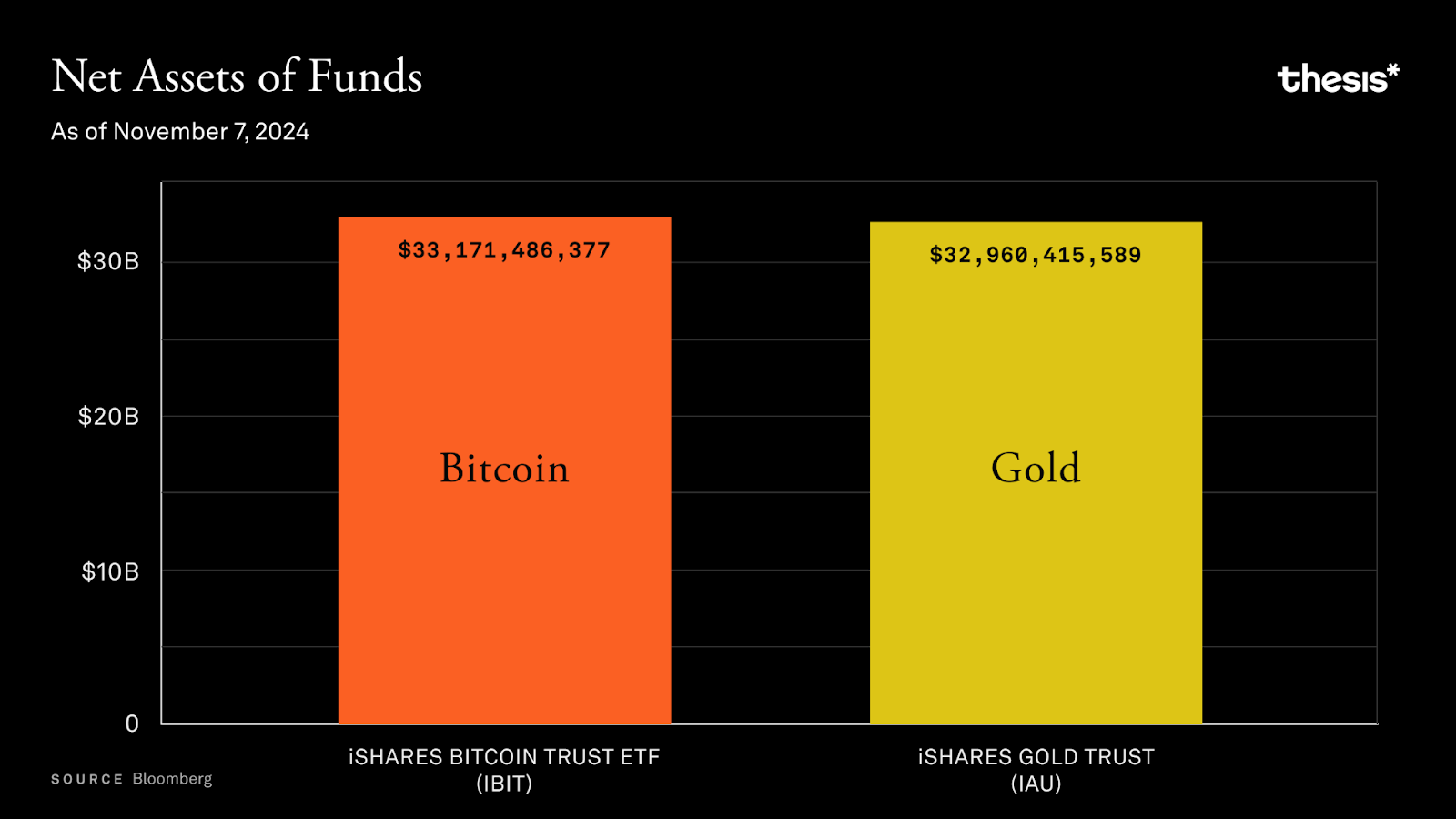
BlackRock's iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) set a record, achieving $10 billion in assets under management (AUM) in just a few weeks, a pace far exceeding that of its gold ETF. With a flood of institutional funds pouring in, Bitcoin gradually entered retirement portfolios. This phenomenon excited Wall Street while causing concern among Bitcoin purists. The popularity of ETFs made Bitcoin more accessible than ever—now, 62% of Americans can easily purchase Bitcoin through brokerage accounts, just like buying Apple stock. However, this convenience also brought problems. The Bitcoin ethos of "not your keys, not your coins" was gradually overshadowed by the clamor of institutional trading.
However, Bitcoin always finds vitality in contradictions. In the U.S., Trump's crypto-friendly policies made Bitcoin a legitimate institutional asset; in India, despite regulatory pressure, 75 million users have adopted Bitcoin as a tool for financial empowerment; in Turkey, with a 50% inflation rate, Bitcoin became a savings choice for millions; and in Argentina, as the currency rapidly depreciated due to a 140% inflation rate, citizens had no time to worry about custody methods and instead used Bitcoin to protect their savings. In Latin America and Africa, Bitcoin is not an investment tool but a means of survival.
This adaptability has run through Bitcoin's development in 2024. Each region has assigned different meanings to Bitcoin based on its own needs. This flexibility has not weakened Bitcoin's core objectives; rather, it has proven its strong vitality. Bitcoin acts like a mirror, reflecting the needs of different users while maintaining its core characteristics.
As 2024 draws to a close, Bitcoin faces significant choices. It has gained the legitimacy that early supporters hoped for, but this legitimacy may not have been achieved in the way they originally envisioned. The rise of ETFs has brought about tremendous changes but also introduced risks that Bitcoin's design initially sought to avoid. Meanwhile, the network's scalability issues are finally being taken seriously, and the future of 2025 is filled with hope and possibilities.
Are Bitcoin ETFs a bridge to mass adoption or a risk of centralization? Can Bitcoin staking enhance the network's functionality, or will it further divide its core principles? With the emergence of Layer 2 solutions and tokenized Bitcoin, can Bitcoin truly achieve scalability, or are we merely repeating past debates? Does Trump's victory and the end of the Gensler era mark a new chapter for cryptocurrency in the U.S.? From the revival of OP_CAT to record ETF inflows, from MEV on Bitcoin to explorations of recursive contracts, the story of Bitcoin in 2024 is still being written.
Institutional Adoption: ETFs and MicroStrategy
- ### Bitcoin ETFs: Institutional Demand
Bitcoin ETFs (such as BlackRock's IBIT) achieved $20 billion in assets under management (AUM) in just 137 days, setting a historical record. In contrast, the previously fastest-growing ETF (JEPI) took 985 days to reach the same scale.
Currently, the total amount of Bitcoin held by ETF custodians has surpassed 1 million coins, accounting for over 5% of the current total Bitcoin supply.
Hedge funds and financial advisors make up a significant portion of the investors in these ETFs, indicating strong interest from institutional investors in Bitcoin.
- ### The Decline of Grayscale
- Due to management fees as high as 1.5% and inefficiencies in the redemption mechanism, Grayscale's GBTC is no longer the market leader. A large number of users have shifted to lower-fee ETFs, leading to a significant reduction in GBTC's assets under management, with a decrease of 152,000 Bitcoins in just one month.
- ### MicroStrategy's Strategy
Under Michael Saylor's leadership, MicroStrategy has accumulated 402,100 Bitcoins, valued at approximately $39.8 billion. They have raised funds by issuing convertible bonds and increasing stock offerings to continuously increase their Bitcoin holdings.
Although this strategy has sparked some controversy, MicroStrategy remains one of the largest holders of Bitcoin globally and is also seen as an indirect way to invest in Bitcoin, with its stock trading at a threefold premium compared to pure Bitcoin exposure.
- ### Broader Impact
With the entry of institutional investors, Bitcoin's price volatility has gradually decreased. ETF options trading further solidified Bitcoin's position as a long-term store of value, becoming an important component of many portfolios.
ETFs provide retail investors and financial advisors with convenient investment channels but have also been criticized for being overly reliant on custodial models, contradicting the self-custody ethos that Bitcoin advocates.
BRC-20, Ordinals, and Runes
Through the Taproot and SegWit upgrades, the Bitcoin network introduced Ordinals and Runes, making NFTs and fungible tokens possible. These innovations have driven an increase in network activity but have also sparked controversy. Critics argue that they add to the network's burden, while supporters believe they help improve the sustainability of transaction fees and demonstrate Bitcoin's permissionless innovation capabilities.
- ### Trends and Network Impact
Due to the popularity of Ordinals collectibles, Bitcoin transaction activity surged, leading to an increase in network transaction fees. In May 2024, at the peak of the Ordinals craze, transaction fees accounted for over 75% of miner revenue, setting a historical high.
The size of the mempool peaked at 350 million bytes at the end of 2023 before gradually returning to normal, while the introduction of Runes improved the management efficiency of UTXOs.
Throughout the year, Ordinals, Runes, and BRC-20 took turns becoming the main drivers of transaction activity, with Runes having the highest transaction share.
- ### Market and Adoption
Platforms like Magic Eden and OKX dominate the trading market, accounting for over 95% of transaction volume. With the optimization of user experience and cross-chain bridging with Solana, the adoption rate of Bitcoin NFTs has significantly increased.
Although Ordinals collectibles performed well at the beginning of the year, their prices have dropped over 50% from their peak after the halving.
Protocols like Liquidium allow users to use Ordinals and Runes as collateral for loans, further expanding the application scenarios of Bitcoin's native DeFi. Meanwhile, stablecoins (such as USDh launched by Hermetica) attempt to use Bitcoin as collateral, although they still face technical limitations.
- ### Cultural and Economic Shifts
Memecoins, digital art, and decentralized markets are redefining the ways Bitcoin is used. Although these trends are speculative, they also showcase the core values of Bitcoin's censorship resistance and permissionless innovation.
Tokenized Bitcoin: BTC on EVM Chains
Currently, using tokenized Bitcoin on EVM chains (Ethereum Virtual Machine chains) is the most popular way to unlock Bitcoin's utility, rather than relying on Layer 2 networks. Due to changes in the custodial model of WBTC, the market landscape for tokenized Bitcoin has undergone significant changes this year.
- ### Tokenized Bitcoin and DeFi Applications
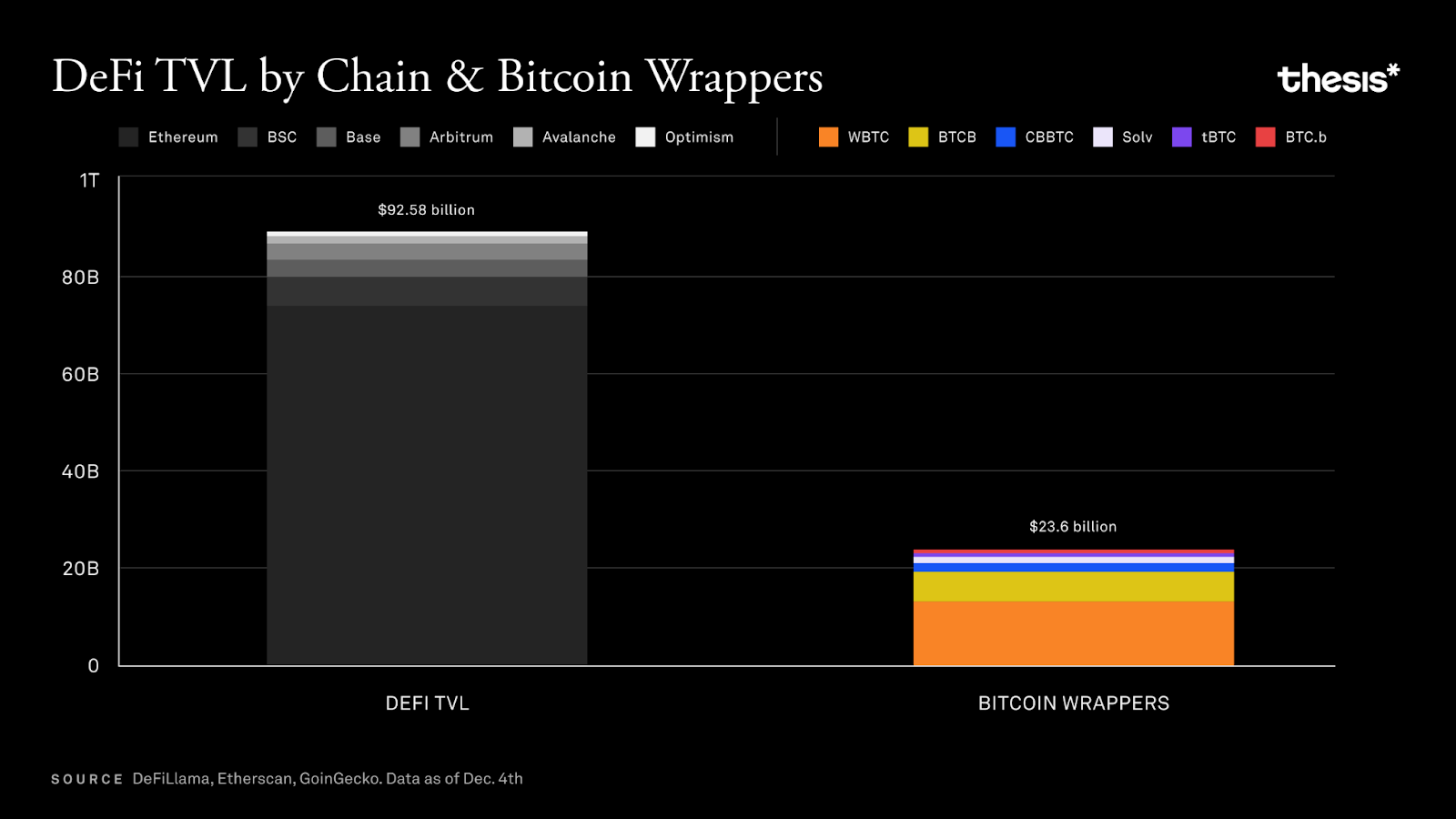
Tokenized Bitcoin (such as WBTC, tBTC, and the emerging cbBTC) accounts for over 25% of the total value locked (TVL) in decentralized finance (DeFi).
While Ethereum is the primary testing ground for DeFi innovation, some Bitcoin-centric solutions (such as Bitcoin Layer 2 networks) are attempting to reduce reliance on custodians, better aligning with Bitcoin's decentralization ethos. However, these Layer 2 networks still have a long way to go before official launch.
- ### Failures and Lessons Learned
Early tokenized Bitcoin projects (such as renBTC, imBTC, and HBTC) failed due to low adoption rates, hacking incidents, or centralization risks. We summarize these failures, referring to them as the "Bitcoin Wrapper Graveyard," to analyze their key vulnerabilities.
With changes in BitGo's custodial model, WBTC's dominance has been challenged, and user trust has declined. Meanwhile, cbBTC launched by Coinbase has rapidly risen, with a total value locked (TVL) exceeding 20,000 BTC.
- ### tBTC and Decentralized Alternatives
tBTC offers a decentralized tokenized Bitcoin model, avoiding the risks of centralized custody. With widespread application in protocols like Aave and GMX, tBTC's supply increased fourfold in 2024, demonstrating strong market demand for decentralized solutions.
- ### Bitcoin-Backed Stablecoins
Bitcoin-collateralized stablecoins (such as USDe and crvUSD) are gradually gaining popularity, with 30-60% of the collateral assets being Bitcoin. However, these stablecoins may introduce risks that Bitcoin users are unwilling to accept.
Fully Bitcoin-backed stablecoins remain an important development direction, as they align more closely with Bitcoin's spirit of decentralization and openness.
- ### Dominance of EVM
Despite the attention on Bitcoin's Layer 2 networks, the EVM ecosystem and its mature applications currently dominate Bitcoin's use in the DeFi space.
While Bitcoin's Layer 2 networks have great potential, they are primarily used for speculative activities (such as airdrop arbitrage) at present. Future solutions need to better align with Bitcoin's core protocol to achieve more meaningful application scenarios.
Bitcoin Staking
In 2024, Bitcoin staking experienced rapid development. Numerous new protocols leverage Bitcoin as the "hardest currency" to support Proof of Stake (PoS) systems. Staking platforms have released Bitcoin's liquidity through native staking, liquid staking derivatives, and re-staking innovations, with total locked value (TVL) exceeding $10 billion.
- ### Native Staking
The Babylon protocol allows Bitcoin holders to stake Bitcoin on PoS chains while retaining custody on the Bitcoin network.
Currently, 34,938 Bitcoins have been staked, with a total value of approximately $3.53 billion, and the number of active stakers has reached 82,440.
Through contracts and penalty mechanisms, the protocol effectively ensures the security of the PoS chain.
- ### Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs)
Lombard: Users can receive LBTC after staking Bitcoin, earning Babylon's staking rewards while using it in DeFi applications (such as Curve and Uniswap). The platform's current locked value is $1.68 billion.
Solv Protocol: Unifies Bitcoin staking operations through a Staking Abstraction Layer (SAL). Its liquid staking tokens (LSDs) like solvBTC can aggregate Bitcoin liquidity across chains, with total locked value exceeding $3 billion.
Example tokens include solvBTC.BBN (Babylon), solvBTC.CORE (CoreDAO), and solvBTC.ENA (Ethena).
- ### Re-Staking
Platforms like Lombard and Solv utilize re-staking to generate additional DeFi yields (such as liquidity provision and lending) from staked Bitcoin. Lombard's re-staking locked value alone has exceeded $1.04 billion.
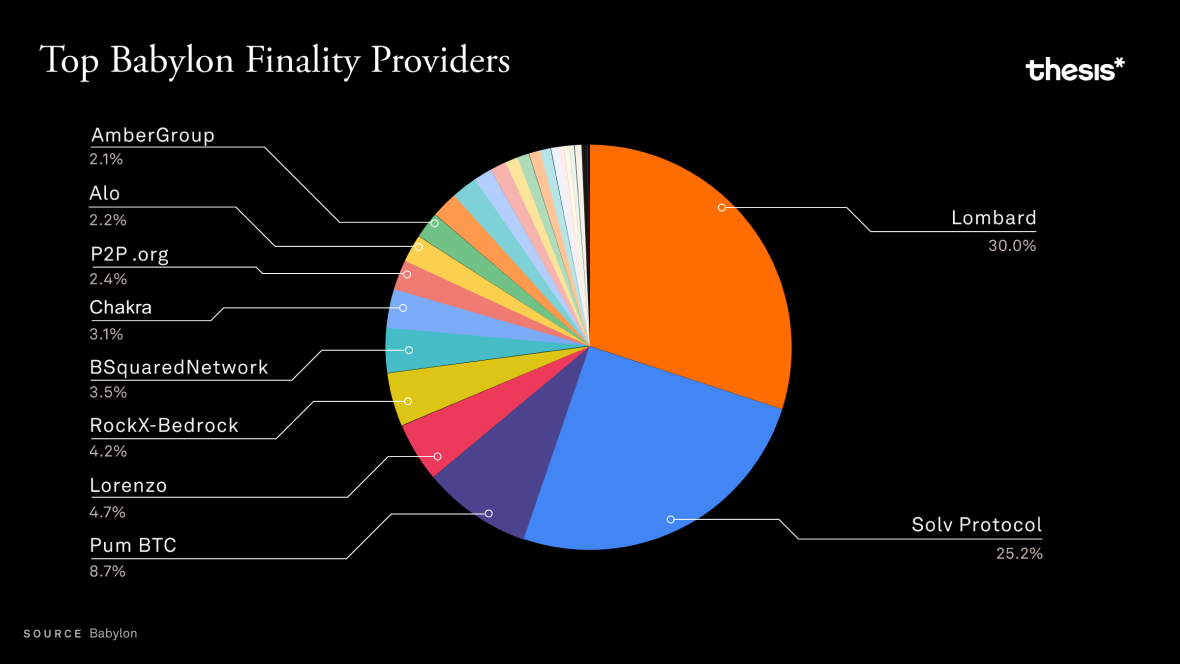
Bitcoin staking is still in its early development stage, primarily relying on reward mechanisms and high yields to attract users. In the long run, its sustainability depends on the growth of real demand. However, major players like Lombard and Solv dominate the market, which may trigger centralization risks. The total locked value of these two platforms in Babylon has reached $1.32 billion.
While liquid staking offers users greater flexibility, it also introduces more trust assumptions. The future direction of Bitcoin staking still requires further observation.
Scalability: Sidechains, Rollups, and Layer 2 Networks
- ### New Developments
Taproot and Opcode Revival: Taproot (launched in 2021) and proposals like OP_CAT enhance Bitcoin's programmability and privacy, supporting contract functionality.
BitVM: Introduces Turing-complete contract functionality without altering Bitcoin's consensus mechanism, supporting more complex off-chain computations.
- ### Layer 2 Solutions
Sidechains:
For example, Rootstock (RSK), Liquid Network, and Mezo.
Sidechain technology introduces smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin network and enhances transaction throughput. However, these projects typically rely on federated security models or merged mining to ensure blockchain security.
Rollups:
ZK-Rollups: Provide fast transaction confirmations through zero-knowledge proofs while maintaining strong cryptographic security.
Optimistic Rollups: Assume transactions are valid by default and verify their authenticity through fraud-proof mechanisms. This method can significantly enhance network scalability, but transaction confirmation times may experience some delays. Example: The Citrea project utilizes zk-STARKs technology and the Clementine bridging solution to build a trustless Bitcoin cross-chain bridge.
State Channels (e.g., Lightning Network):
State channel technologies like the Lightning Network allow users to make nearly instant payments off-chain with very low fees.
The total capacity of the Lightning Network has reached 5,380 BTC, achieving an annual growth rate of 11%.
Trends indicate a decrease in the number of channels in the network, but an increase in the capacity of individual channels, raising concerns about network centralization.
In developed countries (such as the U.S. and Germany), the Lightning Network is primarily used for large payments, while in emerging markets, it is more commonly used for small payments and microtransactions.
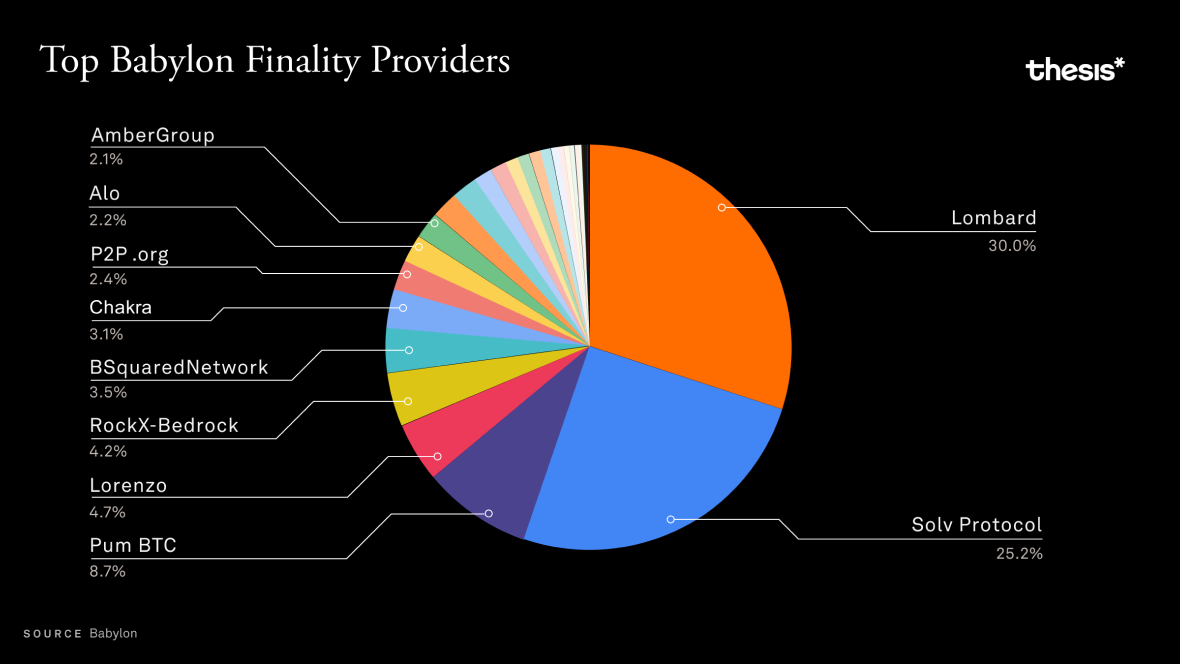
- ### Build on Bitcoin (BOB):
The BOB project, while using Ethereum as a settlement layer, aims to build a Bitcoin-centric economic system, utilizing tokens like WBTC and tBTC to achieve this vision.
In 2024, BOB's total locked value (TVL) grew from $1.5 million to $238.27 million, primarily due to deep integration with Uniswap V3 and Avalon Finance.
- ### CoreDAO and Ecosystem Growth
CoreDAO combines Bitcoin's security with DPoW (Delegated Proof of Work) and DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake) technologies through the Satoshi Plus mechanism.
The ecosystem has launched a core token, coreBTC, supported by Bitcoin for DeFi applications, further expanding Bitcoin's functionality.
In 2024, CoreDAO achieved significant growth: the network growth rate reached 95%, adding 13.3 million addresses, with daily transaction peaks exceeding 500,000.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




