As venture capital flows into fields such as artificial intelligence infrastructure, healthcare, finance, and defense, the AI market is expected to reach $13 trillion by 2030, with future investment opportunities focusing on innovative areas like automated robotics, energy systems, and quantum drug discovery.
Author: Raman Rai
Translation: Blockchain in Plain Language
TL;DR:
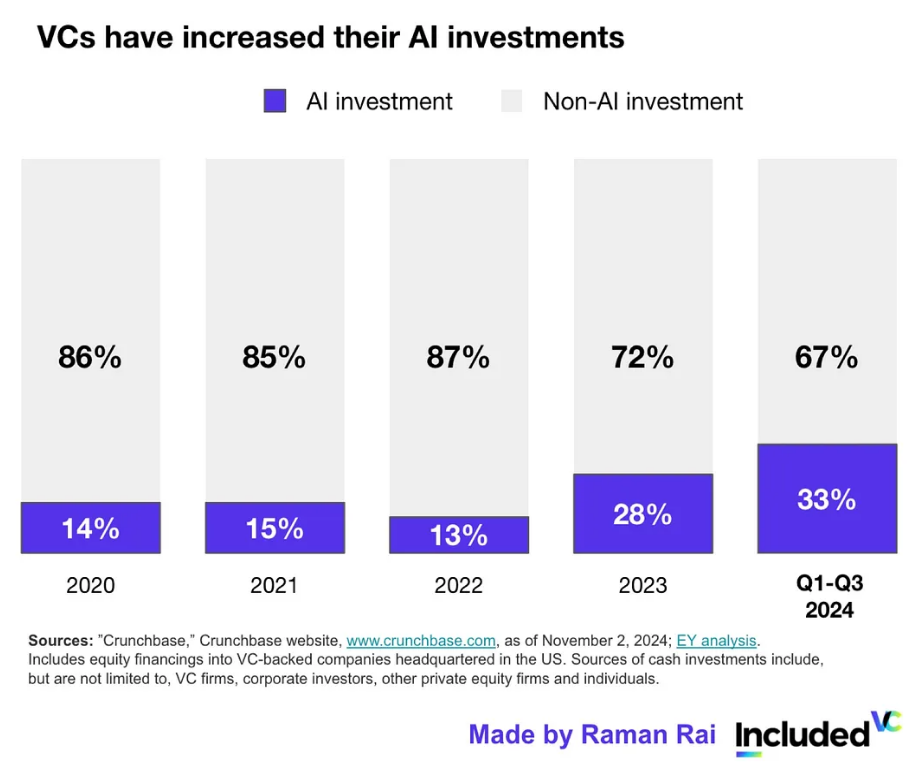
AI investment hits new highs: The global AI market is expected to reach $13 trillion by 2030. As venture capital firms bet on startups reshaping industries, AI investment is experiencing explosive growth.
One of the key investment areas for 2024 is AI infrastructure: As the demand for computing power from AI models continues to rise, venture capital firms are increasing their investments in AI infrastructure, including dedicated chips and data centers.
Notable funding trends: Late-stage financing and AI infrastructure investments dominate, while AI applications in healthcare, finance, and defense attract significant investment as investors seek projects with real impact.
The next billion-dollar startups: The future of AI investment will focus on areas like automated robotics, energy, and entertainment, where collaboration between humans and AI has paved the way for groundbreaking startups.
Overview: This article will discuss:
Introduction of AI in the venture capital ecosystem
Part One: How to navigate the noise in a competitive market
Part Two: Top AI funding rounds of 2024
Part Three: Five key opportunities leading to the next billion-dollar AI startups
Challenges and ethical considerations
1. Introduction of AI in the venture capital ecosystem
With billions of dollars flowing into the AI sector, it can be said that the "AI craze" has not subsided—and it will only grow larger.
AI has become one of the most heavily invested industries in the venture capital space.
According to Pitchbook, global AI investment has reached $290 billion over the past five years, with private investment firms completing over 15,400 deals since 2022. This intense activity reflects a high level of confidence in the future of AI. Opinions vary on how large the AI market will become by 2023.
According to McKinsey:
“AI has the potential to contribute $13 trillion to the global economy by 2030, equivalent to a cumulative GDP that is 16% higher than now. This means an additional 1.2% GDP growth per year.”
Statista and Bloomberg Intelligence both predict that the AI market could grow to $2 trillion by 2030, covering various fields from AI software to hardware and services. PwC estimates that AI will contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, primarily through increased productivity and heightened consumer demand for AI-enhanced products.
It is safe to say—AI has become a part of our daily lives, and the hype has passed. However, with excitement comes noise—investors now face thousands of AI companies, each claiming to be the next "blockbuster star." Data privacy issues, talent shortages, ethical AI, and centralization risks add more challenges to this already competitive industry.
2. Part One: How to navigate the noise in a competitive market
Today, over 100 venture capital funds are actively investing in the AI market, covering horizontal applications (like infrastructure) as well as vertical applications in specialized industries such as healthcare, finance, and agriculture.
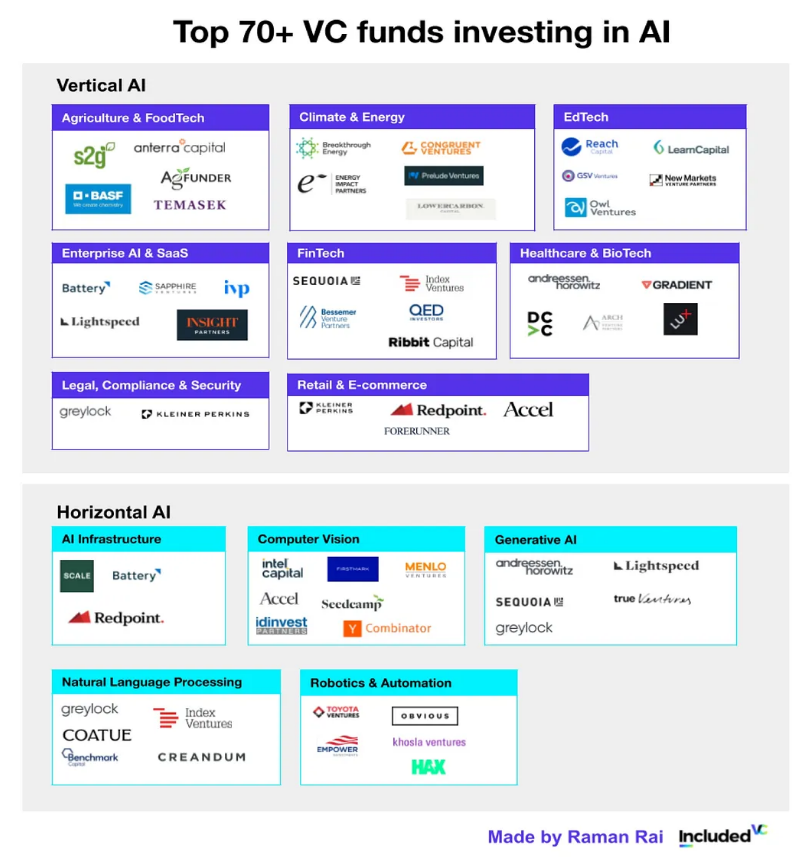
To understand the current state of venture capital in the AI field, I will introduce two types of investors:
Pioneers: Active investors who boldly bet on multiple AI fields. Pragmatists: Conservative funds that see potential in AI but are more selective or cautious in their investments.
1) Pioneers: The most active venture capital firms
Pioneers are known for their willingness to take risks and lead trends, playing a key role in shaping the future of AI investment. Here are some notable players:
Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) has made 29 investments since 2023, covering multiple fields, including a $100 million investment in Character.AI and a $224 million investment in Genesis Therapeutics, with a16z making significant bets at the intersection of AI, biotechnology, and consumer technology.
Sequoia Capital has taken a particularly aggressive approach, leading funding rounds for several well-known startups, such as Cohere (language models) and Viz.ai (medical imaging). In 2023, about 60% of Sequoia's new investments were focused on AI, a significant increase from just 16% the previous year.
General Catalyst has invested $750 million in the healthcare AI sector, including companies like Commure, Sword Health, and Overjet. They have made 19 AI investments, with less than half involving generative AI (GenAI) projects.
Alumni Ventures has made several investments in AI and machine learning, covering consumer and enterprise applications, including SenseTime, Dataminr, and Iterative Health.
As Stephanie Zhan, a partner at Sequoia Capital, who focuses on seed and early-stage investments, said:
“In the past year, AI has injected new life into the investment ecosystem.”
2) Pragmatists: Conservative venture capital firms
While pioneers rush in, pragmatists choose to wait and see.
These funds see the potential of AI but prefer a more selective approach, focusing on sustainable returns and more stable market conditions. Here are some typical examples:
Kleiner Perkins tends to choose relatively safe AI investments, such as Together AI ($102.5 million Series A), which supports the development of AI in a wide range of applications.
Benchmark Capital is known for its anti-hype philosophy; they led an 11x $24 million Series A round in September 2024 for a startup aiming to create automated digital employees to streamline go-to-market (GTM) operations. Benchmark Capital prefers to focus on practical solutions rather than speculative technologies.
Bessemer Venture Partners has invested about $250 million in AI, focusing on applications that solve real problems rather than chasing hype. Their support for EvenUp ($50.5 million Series B) reflects their cautious investment strategy; EvenUp is an AI startup that helps personal injury lawyers automate medical documentation.
Union Square Ventures has invested about $150 million in AI, primarily focusing on applications driven by network effects. Their investment in Recursion Pharmaceuticals aligns with their belief that network effects outweigh high-risk technologies, as the company uses AI for drug discovery.
GGV Capital has invested about $180 million in AI, preferring mature fields like SaaS and enterprise software, using AI as an additional technology rather than a core technology. Their strategy supports growth without venturing into experimental technologies.
So, what causes these funds' hesitation?
Pragmatists remain cautious about the challenges posed by AI:
High capital demands: Developing AI is costly—from data to computing power—these venture capital firms are cautious about large upfront investments.
Regulatory uncertainty: As AI regulation lags behind its rapid development, pragmatic funds prefer to wait for clearer rules before making decisions, especially in areas like autonomous driving and healthcare.
Market volatility: The soaring valuations of AI startups have led some investors to worry about a potential "AI bubble" bursting. Pragmatic funds avoid over-investing during market overheating until the hype subsides.
Ethical and privacy issues: With tightening global data regulations, the ethical issues facing AI increase risks. Pragmatic funds remain cautious, avoiding investments in areas where privacy concerns may overshadow returns.
3) Are pragmatists missing out on opportunities?
Conservative funds like Kleiner Perkins, Bessemer Venture Partners, Benchmark Capital, Union Square Ventures, and GGV Capital may be seen as missing out on AI investment opportunities due to their cautious investment strategies. However, this conservative stance is not necessarily a disadvantage. While their selective investment strategies provide stability and allow them to capitalize on the rapid growth of AI, they may also miss out on some transformative opportunities in the long run.
Pioneers like Sequoia and a16z (Andreessen Horowitz) have made significant investments in foundational AI and generative technologies, ultimately paving the way for the next era of technological transformation. If AI continues to grow at its current pace, the pragmatists' cautious stance may leave them on the sidelines in this potentially defining industry for the next decade.
3. Part Two: Major AI Funding Rounds in 2024
Now that we understand which large venture capital funds are dominating the AI space, let’s take a look at the startups that received the most funding in 2024.

Significant Deals in Q4 2024 in Europe and the U.S.:
Glean (Series E funding of $260 million): An AI-based enterprise search engine, valued at $4.34 billion.
Codeium (Series C funding of $150 million): An AI programming platform that enhances developer productivity, valued at $1.1 billion.
Opkey (Series B funding of $47 million): A company providing an AI testing automation platform for finance, HR, and enterprise planning.
Butlr (Series B funding of $38 million): Focused on providing anonymous people sensing and occupancy solutions using physical AI.
These deals showcase the broad range of AI applications attracting investor interest, from logistics to automation.
So, what are the key themes driving AI funding in 2024?
1) Generative AI Continues to Attract Significant Investment
Despite the cost and scalability challenges posed by generative AI, it remains a focal area for investment. Over the past five years, generative AI startups have raised a total of $26 billion, particularly in content creation, healthcare, and enterprise solutions, including companies like QuizGecko, Writesonic, and Tome.
2) AI Infrastructure and Hardware Receive the Most Funding
As the demand for computing power from generative AI models continues to rise, venture capital firms are betting on the "pillars" of AI—AI infrastructure. Companies focused on developing specialized chips, data centers, and platforms are receiving more funding:
Groq, an AI semiconductor and software startup, completed a $640 million Series D funding round led by BlackRock, achieving a valuation of $2.8 billion. Groq's success highlights the growing attention on companies that support the "engine" of AI (from chip design to large-scale computing).
- BlackRock and Microsoft jointly launched a $30 billion AI investment fund aimed at building AI infrastructure, including data centers and energy projects, to meet the demands of AI. This trend reflects a fundamental shift: as AI advances, venture capital firms recognize that supporting AI infrastructure (such as chips, servers, and data platforms) is as important as the algorithms themselves.
3) Large Late-Stage Funding Rounds Become the Focus
Venture capital firms are pouring significant funds into AI companies with established business models, pushing some funding rounds into the billions. While early-stage investments are still occurring, late-stage funding rounds are dominating. In just the third quarter of 2024, the following major funding events occurred:
Waymo (Alphabet's autonomous driving division) raised $5 billion.
Safe Superintelligence, an AI research lab founded by OpenAI co-founder Ilya Sutskever, secured $1 billion from top investors like Andreessen Horowitz and Sequoia Capital.
Cohere completed a $500 million Series D funding round, bringing its valuation to $5.5 billion.
If you think these amounts are not large enough, OpenAI raised $6.6 billion in an October 2024 funding round, led by Thrive Capital, Microsoft, and Nvidia, achieving a valuation of $157 billion.
4) Rise of AI in Specific Domains
Venture capital firms are increasingly inclined to invest in startups applying AI in healthcare, finance, and defense:
Healthcare: AI is transforming drug discovery and diagnostics, and investors are taking note of this trend, with companies like Insilico Medicine (drug development) and Ainnocence (drug discovery).
Finance: AI is reshaping decision-making processes, such as Taktile using machine learning to help banks create customized credit scoring decision flows, recently raising $20 million; PolySign applies AI to digital asset security, demonstrating how machine learning permeates various aspects from lending practices to financial security.
Defense: Europe's Helsing completed a $488.2 million Series C funding round, focusing on AI-driven military intelligence and defense systems; the U.S. Shield AI specializes in military drones. Both startups showcase the expanding role of AI in defense technology, where real-time insights and automation are becoming increasingly important.
5) Decrease in Seed Stage Deals, Investors Become More Selective
Due to stricter screening by venture capital firms, seed stage deals have slowed down.
For early-stage AI startups, securing funding is becoming increasingly difficult, especially without clear potential. Venture capital firms prefer to invest in later-stage companies that already have a clear path to profitability, which may include companies with strong historical growth, a stable customer base, and ample market space, such as Cognigy (Series C funding of $100 million).
4. Part Three: Five Key Opportunities to Lead the Next Billion-Dollar AI Startups
Generative AI and foundational models are the biggest trends of 2024. So, what can we expect to see next in the AI field that may give rise to the next billion-dollar AI startups?
My Key Predictions
The next AI revolution will not be about making technology smarter but fundamentally changing how humans live—how we live, work, and even age.
Here are my three major predictions for the future:
1) The Internet as We Know It Will Disappear.
Say goodbye to Google Search, Bing, and Yahoo. The next evolution of the internet will no longer be a simple search box but a dynamic realm composed of digital agents that complete browsing tasks for us. Imagine billions of personal AI agents handling everything from research to filtering out spam ads and bots. The era of "do-it-yourself" searches may soon become a relic of the dial-up internet age.
2) We Will Be Closer to Human Immortality.
From breakthroughs in anti-aging to AI-driven health diagnostics, we are moving toward a future where living to 100 may become the norm. Advances in AI in molecular biology and regenerative medicine could turn aging into a solvable problem.
3) Human-AI Collaboration Will Become the Norm.
Forget the notion of "AI taking jobs"; we are entering a new era where human intuition, creativity, and moral judgment combine with AI's data processing and analytical capabilities to help solve problems that neither humans nor AI could tackle alone. This collaboration will become a defining trend of the next decade.
These changes lay the groundwork for the rise of the next wave of billion-dollar startups.
Here are the five major opportunities that will create the next billion-dollar startups:
1) Automated Robotics: The Rise of Home and Industrial Assistants
Collaboration between humans and AI could fundamentally change robotics, creating automated systems that support rather than replace us. Automated robots are beginning to enter our homes and workplaces, providing hands-free assistance in areas where humans are present but limited.
Consumer Applications: Figure and Tesla's Optimus are leading this transformation, launching affordable humanoid robots for home use. Imagine a future where middle-class families have robot assistants at home to help care for children and do household chores, just like owning a washing machine or dishwasher.
- Industrial Applications: Companies like Agility Robotics, Sanctuary AI, and Co.bot are advancing collaborative robots in industrial environments. Co.bot recently raised $100 million in Series B funding, showcasing the growing demand for "collaborative robots" (cobots) that can safely work alongside humans, handling heavy or repetitive tasks. As robots take on labor-intensive work, humans can focus on strategic tasks, enhancing productivity and safety.
2) Energy Grids: Building Sustainable and Efficient Energy Systems
The energy sector remains an underdeveloped area in the field of artificial intelligence, with immense potential for optimizing and autonomously managing energy usage. The vision for the future is for every household and business to utilize smart energy management systems, creating a resilient and efficient power grid.
Autogrid (now part of Schneider Electric) leverages AI to optimize energy distribution in real-time, minimizing waste and enhancing the reliability of renewable energy. Grid AI and Stem Inc. have also made strides in demand forecasting and energy storage solutions, supporting smart grids that could significantly reduce carbon footprints.
3) Quantum Molecular Modeling in Drug Discovery
In healthcare, quantum molecular modeling offers unprecedented potential for drug discovery and materials science. By combining quantum computing with artificial intelligence, we can accelerate the screening of promising drug candidates, saving time and costs, and potentially saving lives.
Insilico Medicine uses AI to predict molecular behavior, significantly shortening the time required to find new drug candidates. Schrodinger employs quantum modeling for precise drug interaction simulations, while Atomwise uses deep learning to design compounds targeting diseases.
4) AI in the Entertainment Industry: The Rise of Synthetic Media and Hyper-Personalized Content
The entertainment industry is witnessing a creative transformation driven by AI, with synthetic media and personalized content redefining storytelling. AI can now not only generate media content but also collaborate with creators to produce innovative and high-quality experiences.
In a conversation with Farid Haque, a partner at AlphaQ Venture Capital and an investor in AI and deep tech, he shared the vision of AI creating films and series where live actors become part of a "high art" experience. As AI-driven production processes handle routine content creation, live performances will become scarce and highly sought after, adding a layer of uniqueness to live-action productions.
Actors can authorize the use of their voice and facial expressions for AI-generated films, creating new revenue streams while retaining the "high art" characteristics of human-led performances. As AI technology evolves, economic models are changing, allowing studios to utilize digital profiles of actors, while traditional live performances become a premium experience.
DeepBrain AI allows actors to authorize the use of their digital "clones," opening up new revenue models. Flawless AI makes cross-language voice and lip-sync seamless, driving a transformation in global media distribution.
5) Gaming and Advanced NPCs (Non-Player Characters)
Gaming is one of the most natural fields for human-AI collaboration, as AI enables deeper interactions, more realistic NPCs, and highly personalized gaming experiences. Here, AI is not just a tool; it is a co-creative partner with players, capable of adapting and evolving based on player behavior.
Inworld AI is developing NPCs that can remember past interactions with players, creating a more immersive and responsive gaming world. This collaboration between players and AI characters opens up a new dimension of interactivity.
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As AI systems continue to advance, ensuring their ethical and responsible use becomes crucial. It is necessary to build systems that avoid discrimination against specific groups or exacerbate potential biases in human data. AI is fundamentally a social equity issue.
Currently, over 3 billion people worldwide still lack internet access, with a significant proportion being women—this makes it possible for AI to exacerbate the digital divide. For AI to be a truly benevolent force, people need reliable internet access and digital literacy. Today, nearly 40% of the global population cannot access the internet, and many more have very limited experience using digital tools. This imbalance could lead to AI systems favoring privileged groups, further exacerbating bias and exclusion.
Therefore, investing in inclusive AI to cover underserved communities is essential. From AI-driven remote education to accessible healthcare and digital tools that promote rural development, venture capitalists, tech leaders, and policymakers need to address the digital divide and advocate for inclusive AI models that benefit everyone.
6. Conclusion
As AI becomes ubiquitous from our search engines to various aspects of home life, it is clear that this technology has deeply penetrated human society and is here to stay. The "hype" around AI is over; we are tired of companies and marketing gimmicks that tout "AI." It is not a trend from the 90s but has become a reality in our daily lives. Venture capital is spawning a wave of new startups that will change how we live and work, from robotics to energy to media.
For investors and innovators, the challenge lies in moving beyond the hype and focusing on real impact. AI is not just a trend—it is a transformation destined to last. This is just the beginning; more changes await us in the future.
Article link: https://www.hellobtc.com/kp/du/12/5588.html
Source: https://medium.com/included-vc/the-hype-is-over-ai-landscape-in-venture-capital-2024-4eedd7f352ff
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




