Author: Rhythm Worker, Blockbeats
On December 5, 2024, the value of a single Bitcoin reached $100,000, a historic high, with a market capitalization of $2.1 trillion. It officially entered the six-figure range. The once unattainable and seemingly fantastical $100,000 is now history.
Any asset that grows from zero to a market value of trillions of dollars inevitably has a grand story behind it, and Bitcoin is no exception. For those of us in the midst of it, Bitcoin's journey over the past decade seems almost magical. The Bitcoin network was officially launched on January 3, 2009, with an initial trading price of $0.0008.
At a price of $100,000, Bitcoin's increase exceeds 125 million times. Let us return to the starting point of cryptocurrency, commemorating the release of the Bitcoin white paper.
The 2008 Financial Crisis, The Starting Point
Compared to Bitcoin's current glory, its birth was almost insignificant.
In November 2008, a paper authored by Satoshi Nakamoto was published online, titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System." The paper detailed how to create a "trustless electronic transaction system" using a peer-to-peer network.

The birth of Bitcoin directly reflected Satoshi Nakamoto's profound disappointment with the financial system at the time. In September 2008, the financial crisis, triggered by the collapse of Lehman Brothers, erupted in the United States and quickly spread globally. To save the economy on the brink of collapse, the U.S. government took unprecedented intervention measures: massive public funds to rescue the market and monetary overexpansion caused by quantitative easing policies. Although these measures alleviated the crisis in the short term, they also brought a series of side effects such as inflation, market turmoil, and exchange rate fluctuations.
As a result, Satoshi Nakamoto conceived a bold idea: to create a currency system independent of governments and financial institutions. In the traditional system, currency is issued by central banks, and transactions are recorded and confirmed by banks. Bitcoin broke this model, making peer-to-peer transactions possible through decentralized blockchain technology, without the need for third-party intervention.
The core design of Bitcoin also reflects its philosophy: its total supply is limited to 21 million coins, avoiding the devaluation risk caused by unlimited issuance of traditional currencies. This design ensures Bitcoin's scarcity, allowing it to serve as "digital gold" in an inflationary environment. This characteristic attracted widespread attention from cryptography enthusiasts and economists.
However, there is controversy in the economics community regarding Bitcoin's quantitative design. Keynesian scholars argue that a fixed total supply deprives monetary policy of flexibility, and the deflationary effect may hinder economic development. In contrast, supporters of the Austrian school believe that a fixed money supply helps reduce human intervention, and deflation may actually encourage market efficiency.
Two months after the release of Nakamoto's paper, on January 3, 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto personally mined the Genesis Block on a small server in Helsinki, Finland. As a reward, he received the first 50 Bitcoins, marking the birth of the first Bitcoin.
Silk Road, The Dark Demand
For a long time after Bitcoin's emergence, it went unnoticed. People wondered: what is the practical use of this invention? Even Satoshi Nakamoto, the genius founder, did not provide a clear answer. In December 2010, he left his last message online and mysteriously disappeared.
In the early years of Bitcoin's birth, its value hovered around $0.1 per coin. The most famous transaction during that time was someone purchasing a pizza for 10,000 Bitcoins. Despite Bitcoin's design being nearly perfect, it was like a script without a performance, deemed to lack practical significance—until it encountered another "genius."
Ross Ulbricht, born in 1984, was involved in drug trafficking since his college days. Limited by the government's strict control over drugs, his business could never scale. The turning point came in 2010 when he heard about Bitcoin from a customer.
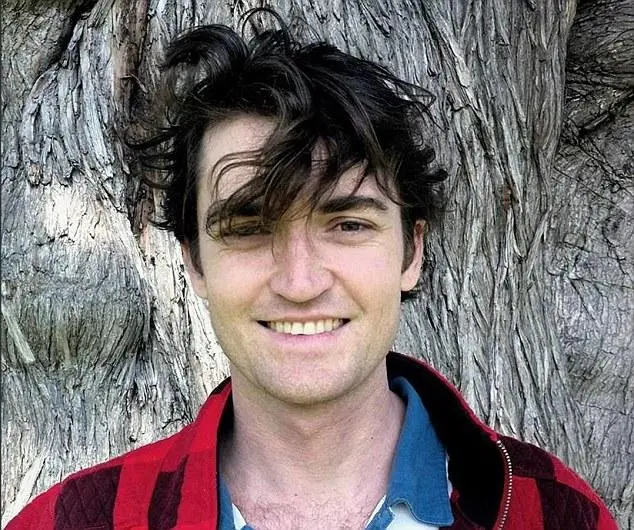

Ross Ulbricht
The government's crackdown on illegal activities hinges on monitoring the flow of funds, which relies on the traditional banking system. However, Bitcoin, as a decentralized and hard-to-trace payment tool, is naturally suited to evade regulation. Ross keenly realized that this was the tool he needed. In January 2011, 26-year-old Ross created a deep web platform—commonly referred to as the dark web. He named this platform "Silk Road," symbolizing a market for free trade.
However, the transactions on "Silk Road" were not for tea, silk, or porcelain, but for illegal goods such as drugs, human trafficking, child pornography, hired killers, weapons, and fake documents. This platform quickly became the most notorious dark web market globally, attracting a large number of illegal traders.
With the rise of "Silk Road," Bitcoin finally found its first large-scale application scenario: a payment tool for illicit transactions. Statistics show that Silk Road circulated over 9.5 million Bitcoins, accounting for 80% of the Bitcoin circulation at that time. This undoubtedly pushed Bitcoin into the spotlight of public opinion.
Ross's criminal activities ultimately backfired. He not only engaged in drug trafficking through "Silk Road" but also attempted to resolve business disputes by hiring hitmen. In August 2013, he was arrested in a public library in San Francisco. In 2015, Ross was sentenced to life in prison without the possibility of parole.
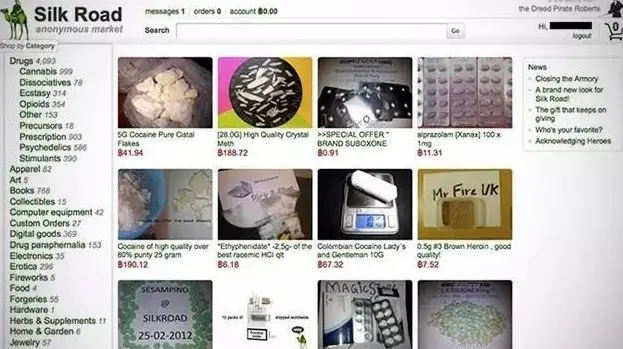
Screenshot of the Silk Road website
Just like the consensus of fools, it is also a consensus. Dark demand is still demand.
Driven by criminal transactions, Bitcoin experienced its first surge, reaching $31 in June 2011. Two months after Ross's arrest, Bitcoin soared to $1,100 per coin. It can be definitively stated that Ross is an important figure in the history of Bitcoin's development. Just as Bitcoin was about to be overlooked by the world, he ended Bitcoin's history as a toy and gave it real-world significance—serving crime.
"Criminals are the most capable of embracing new technologies," summarized Xu Zhihong, a partner at CoinU. Law enforcement agencies gradually mastered the technology to trace Bitcoin transactions, weakening its appeal in illegal markets. More and more criminal transactions began to shift to harder-to-trace cryptocurrencies, such as Monero, leading Bitcoin into a prolonged bear market for several years.
The Block Size War and Forking Crossroads
Fast forward to 2015, the Bitcoin community faced its most intense controversy ever—the block size war. This "block size war" not only caused a split in the community but also led to the largest hard fork in Bitcoin's history.
Since Satoshi Nakamoto designed Bitcoin in 2009, the block size has been limited to 1 megabyte. This design was intended to prevent meaningless transactions and network data inflation. However, as the number of users increased, this limitation gradually became inadequate: transaction congestion, soaring fees, and delayed confirmation times. In 2013, core developer Jeff Garzik proposed increasing the block size to 2 megabytes, sparking intense discussions in the community about scaling.
By 2015, the rapid growth in transaction volume made the scaling issue urgent. The Bitcoin developer camp split into two factions: one supporting larger blocks advocated for direct scaling to solve congestion issues; the opponents argued that decentralization was more important and advocated for improving transaction efficiency through technical optimization.
Developers supporting scaling, Gavin Andresen and Mike Hearn, believed that Bitcoin's goal was to serve as an efficient "electronic cash system," rather than merely a store of value. To this end, they proposed the BIP-101 proposal, suggesting increasing the block size to 8 megabytes. They argued that Bitcoin transfers were becoming increasingly slow, and the fees for transfers were rising correspondingly; if this continued, Bitcoin would become as mundane as bank card transactions.
Opponents, including core developers Greg Maxell, Luke-Jr, and Pieter Wuille, warned that larger blocks could increase the hardware costs for running nodes, reducing the number of full nodes and weakening the decentralization of the Bitcoin network. They preferred to adopt second-layer solutions like "Segregated Witness" and "Lightning Network" to optimize transactions without changing the block size.
This dispute directly led to the birth of Ethereum. Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin was a staunch supporter of larger blocks, and when he realized that Bitcoin might struggle to adopt larger blocks, he took a different path, shifting the scalability issue to a new chain, allowing for larger blocks and flexible smart contract designs to reduce transaction fees, enabling Ethereum to do more.
On February 20, 2016, both sides reached an agreement known as the "Hong Kong Consensus." The agreement included the implementation of Segregated Witness technology and subsequent scaling plans, which were seen as a significant breakthrough to quell the controversy. However, the agreement was soon denied due to the lack of participation and clear statements from Bitcoin Core's core developers. The collapse of the Hong Kong Consensus intensified community conflicts, and trust between miners and developers was nearly obliterated.
With the failure of the Hong Kong Consensus, the controversy escalated into a philosophical confrontation over Bitcoin's future direction. One side emphasized transaction efficiency, while the other insisted on decentralization. This divergence ultimately led to the hard fork in 2017. Bitmain founder Wu Jihan became the representative of the larger block faction, advocating for creating a new chain through forking to support the 8-megabyte block proposal.
On a day in March 2017, Wu Jihan tweeted, "I believe the economic majority is not important; I ignored the so-called majority when I started investing in Bitcoin in 2011." He decided to start anew and no longer play with Bitcoin Core.
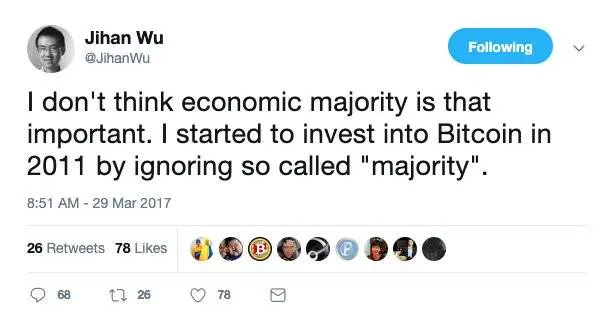
At that time, Wu Jihan, as one of the founders of Bitmain, the world's largest cryptocurrency mining machine manufacturer, was ranked among the top 50 self-made entrepreneurs born in the 1980s by Hurun, with assets of 16.5 billion RMB at the age of 32. Bitmain controlled over 60% of the Bitcoin network's computing power, and Wu Jihan was considered "the only person with a chance to destroy and control Bitcoin" at that time. Therefore, Wu Jihan's forking plan received support from miners and some developers.
On August 1, 2017, the fork officially occurred, and Bitcoin Cash (BCH) was born. BCH was designed to support larger blocks and was incompatible with the Segregated Witness technology, allowing it to handle more transactions. Meanwhile, the Bitcoin Core camp insisted on the small block solution of 1 megabyte and optimized transaction efficiency through Segregated Witness and the Lightning Network.
After the fork, Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash developed along different paths. Wu Jihan sought market recognition for BCH by driving up its price and weakening BTC's hash power. In the short term, BCH's price soared from $200 to nearly $900, triggering a wave of miners switching over. However, Bitcoin's brand effect and vast ecosystem kept it in a dominant position. Over time, BCH's price and market capitalization gradually shrank, and its hash power share continued to decline.
But with the arrival of the bear market in 2018, BCH's price plummeted, causing significant losses for Bitmain, which had heavily invested in the BCH sector. Subsequently, BCH maintained a rough 1:20 ratio with Bitcoin in terms of both price and hash power. Due to its heavy holdings in BCH, Bitmain faced scrutiny during its Hong Kong IPO in 2018, with questions raised about relying on BCH sales for revenue.
Looking back two years after the Bitcoin fork, the BTC fork event had long settled, and BCH had taken a parallel route. However, this fork had a profound impact on the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
The Story of Miners
If I told you today that Bitcoin had a chance to be controlled by Chinese people ten years ago, would you believe it?
On a night in May 2010, a hungry programmer exchanged 10,000 Bitcoins for two pizzas worth $30, giving Bitcoin its first valuation—$0.003. This intangible protocol thus gained real value, leading to a bull market filled with wealth creation myths and the rise of cryptocurrency mining.
In the early days, Bitcoin had no value, and there were few participants in the network; mining only required a computer CPU. Hal Finney was among the earliest miners, and within a week or two, he mined thousands of Bitcoins with his computer, eventually stopping the mining software due to overheating and the annoying noise of the computer fan.
However, this $0.003 valuation changed everything. Seeing that Bitcoin mining was profitable, more and more people joined the network, and soon, various geeks began writing their own GPU mining programs and building targeted mining machines, which we now know as mining rigs.
Quickly, this technological craze spread to domestic geek forums, sparking enthusiastic discussions among a small group. In 2011, Wu Jihan funded Changsha and established the earliest Bitcoin forum in China, Babit, where discussions on mining began. Zhang Nangen, studying integrated circuit design at Beihang University, gained fame for creating FPGA mining machines and was nicknamed "Pumpkin Zhang" by netizens. Another notable figure was a software engineer from Guilin, "Watermelon Li," who developed the popular "Watermelon Miner."
Just as GPUs were gaining popularity, a small American company called Butterfly Labs announced that it was developing a machine specifically for Bitcoin mining—ASIC. This machine discarded all other computing functions and was designed solely for the Bitcoin SHA-256 algorithm, achieving speeds far exceeding those of GPU mining rigs.

Butterfly miner, image sourced from the internet
Once the concept of ASIC miners reached China, action was quickly taken. Besides the previously mentioned "Pumpkin Zhang," another legendary figure in the mining circle emerged: Jiang Xinyu from Kuaimao. Jiang entered the University of Science and Technology of China at 15 and later pursued a PhD in computer science at Yale. He was captivated by Bitcoin's ideology upon first hearing about it and returned to China to become a miner before finishing his studies, becoming the second person in China to develop an ASIC miner after Zhang Nangen.
In August 2012, Jiang established a company in Shenzhen and conducted an IPO online, issuing 160,000 shares at a price of 0.1 Bitcoins per share, with the code ASICMINER. He then used the funds raised to open a mining farm in Shenzhen, mining Bitcoin with his own machines, reportedly earning 200 million yuan in three months.

One of the few public photos of Kuaimao (left), image sourced from the internet
Seventeen days after Kuaimao's ASIC prototype was announced, Zhang Nangen also formed his Avalon team and delivered the first mining machine, Avalon 1. While Kuaimao and Zhang Nangen were rapidly developing, another competitor entered the scene. In the first half of 2013, Wu Jihan founded Bitmain, launching three types of computing chips in just 13 months, forming a three-way competition with Kuaimao and Zhang Nangen. After the winter season, Bitmain's Antminer S1 swept away many competitors, allowing its mining rig distributors to earn substantial profits.
Kuaimao and Zhang Nangen also faced high demand and thriving businesses, heralding the arrival of the Bitcoin ASIC mining era.
The enormous wealth effect attracted countless entrepreneurs to enter the market, producing various Bitcoin mining machines, with names like Chrysanthemum Miner, Cockroach Miner, and Silverfish Miner in abundance. Manufacturers competed fiercely, and the iteration of mining rigs accelerated to the point where early pre-ordered futures mining rigs became outdated by the time they were delivered. Eventually, manufacturers realized that while their mining rigs were still on the production line, their competitors' customers had already received better-performing machines. Companies like Bitmain, which entered the market early, began deploying larger-scale hash power in petabytes, leading to over 70% of Bitcoin's hash power being firmly rooted in China.
On the other hand, under the leadership of geek miners, a large number of fortune seekers flooded into China's Bitcoin market. Driven by "Chinese aunties," Bitcoin's price skyrocketed, breaking through the 4,000 yuan mark and approaching 7,000 yuan within days, while at the beginning of the year, Bitcoin was still below 80 yuan. In just a few months, approximately 10 billion yuan of capital was injected into the market, making China the most enthusiastic market for mining and trading Bitcoin in the world.
In 2013, Bitcoin created one wealth myth after another, with Li Xiaolai being the most typical example. This former New Oriental English teacher purchased 100,000 Bitcoins in 2011 and has since become China's "Bitcoin billionaire," founding the Bitcoin Fund and Yunbi.com. Another example is "Old Cat," who, ten years ago, saw a report about Bitcoin in a newspaper kiosk while on a business trip with his boss, changing the trajectory of his life.
The Great Migration
Time quickly moved to 2021, and the dark moment for miners arrived.
At midnight on June 20, all Bitcoin mining farms in Sichuan were forced to shut down due to a directive. Previously, domestic Bitcoin miners had been continuously relocating their machines from Inner Mongolia, Qinghai, to Xinjiang and Yunnan, with Sichuan becoming the last gathering place. However, the shutdown directive from Sichuan completely dashed miners' hopes and marked the theoretical end of mining farms within China, with the 75% of the Bitcoin network's hash power that once came from China disappearing from the map.
After that unforgettable night, the domestic crypto mining capital—Chengdu—was filled with distressed and confused miners.
On June 22, in a jazz bar on the top floor of a five-star hotel in Chengdu, young men with serious expressions sat together in small groups, smoking and talking. Their T-shirts sporadically bore slogans like "Bitcoin" and "To Da Moon," and their conversations were filled with keywords like "mining rigs," "going overseas," and "overseas resource connections." In the bar's entrance hallway, a few people were scattered about, pacing back and forth while making phone calls to sell mining rigs, lighting one cigarette after another.
On the same day, a "Global Mining Resource Connection Conference" was quietly held at another five-star hotel in Chengdu, where miners from various parts of Sichuan who had already lost power gathered to systematically learn about the overseas process from various companies, hoping to salvage a "Noah's Ark" to venture across the ocean through collective wisdom and support.
From the miners' state, it was clear that the halted Chinese Bitcoin mining industry was engulfed in confusion and panic.
Fifty kilometers from Chengdu, in Dujiangyan, the mighty Min River surged down, where the father and son of Li Bing from the Warring States period witnessed the world-renowned water conservancy project. Contemporary Bitcoin miners, however, saw the electric resources essential for their mining rigs in the rushing waters.
Old Wu's mining farm is located in the mountains of Dujiangyan, covering about 1,000 square meters, relying on the flow of water to maintain the day-and-night roar of thousands of mining rigs.

Bitcoin mining farm in the deep mountains, image from a miner
"When the policy to shut down mining farms in Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang was announced in May, I wasn't panicking," Old Wu told BlockBeats. "Having been in this industry for a long time, since 2013, there has been a crackdown on mining policies roughly every one or two years, especially in Inner Mongolia, which relies on thermal power. We are used to it."
So when the mining farms in Inner Mongolia began shutting down, Old Wu continued to purchase second-hand mining rigs online and attracted more machines to his farm for hosting. At that time, he calmly told his friends, "Don't panic."
As June approached, even Old Wu began to feel restless. The mining farm was on the front lines, and he had received wind of the situation from various channels, but Old Wu still held out hope. "Sichuan is different from Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang; there is a lot of wasted water and electricity here, all of which are clean resources. If we don't use these resources, they will just go to waste."
The unsettling news initially came from Ya'an. On June 17, market news indicated that Ya'an, Sichuan, would implement a "one-size-fits-all" policy for mining farms, requiring all to shut down by the 25th, including those consuming electricity and wasted water. On June 18, a notice issued by the Sichuan Provincial Development and Reform Commission and the Sichuan Provincial Energy Administration began circulating in the community, demanding the shutdown of 26 suspected virtual currency "mining" projects by June 20.
On the evening of the 19th, Old Wu finally set aside his hopes, lamenting, "I have to change careers again," and turned off the continuously roaring mining rigs, beginning the process of transferring the mining farm.
Compared to miner Old Long, Old Wu was considered lucky, as his mining farm had been operational for several years, and the profits from previous years were still considerable.
"In March of this year, I started building a hosting mining farm in Ganzi Prefecture, which was completed in May, with a capacity of 50,000 kilowatts, capable of accommodating over 30,000 mining rigs, but it was blocked by policy just before it started operating," Old Long told BlockBeats. "The total investment in this mining farm was close to 20 million yuan, which means I lost everything. After all, the profit from a hosting mining farm comes from the difference in electricity costs and management fees."
The speed and decisiveness of the government's policy this time left Old Long feeling somewhat hopeless. "I've been in this industry for five years, and there has been a policy crackdown every one or two years, but this time it is just too severe. Mining farms, miners, mining pools—every mining group has been affected."
In the mining circle, Old Long's experience is not the worst. "I have a friend who also runs a hosting mining farm that was already in operation. His mining farm had an investment of 160 million yuan, with the total value of the mining machines reaching 400 million yuan. However, after the policy was implemented, not only did the mining farm lose power and the machines shut down, but the roads in and out of the farm were also blocked, making it impossible to transport the machines out. It was a complete mess."
In the face of the mining crisis, selling mining machines has become a forced choice for many miners.
Unlike the famous mining machine sales point "Seg Plaza" in Shenzhen, although Chengdu is an important city for miners, the computer city, known as Chengdu's "Zhongguancun," does not show a bustling scene of selling mining machines.
BlockBeats' on-site visit found that there were no stalls related to mining machines in Chengdu's computer city. When further inquiring with merchants, it was discovered that they were not unfamiliar with mining machines. "Currently, there are very few Bitcoin mining machines flowing through offline channels. We also need to inquire with suppliers; instead, there are more graphics card mining machines," a salesperson in the computer city told BlockBeats.
In stark contrast to the quiet offline market, online Bitcoin mining machines are experiencing a 50% clearance sale.
In the miner community, which values reputation and privacy, information from strangers easily raises their suspicions. They prefer to trade with familiar miners and mining farms within the same circle, so the main trading market during this round of mining crisis remains large online intermediaries and communities.
Mr. Tu from CoinCore Technology told BlockBeats, "The price of mining machines has already dropped by more than half, and it has entered a buyer's market where the price is determined by the buyers." Taking the commonly seen Antminer S19 Pro 95t as an example, its price could reach 60,000 to 70,000 yuan at the peak of the bull market, while the current domestic price is only over 30,000 yuan.
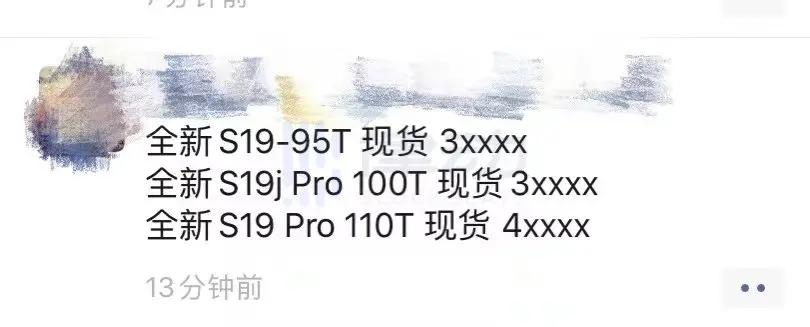
Online quote for Antminer S19 at the time of publication, image from miners
BlockBeats also discovered that while foreign mining companies and farms are taking advantage of the domestic "mining crisis" to acquire mining machines at low prices, they are pushing the prices even lower. A foreign buyer expressed, "We hope to receive S19j Pro at $40/T," which converts to only 252 yuan/T, making the total price for a 100T machine only 25,200 yuan, which can be considered the "floor price" in recent months.
Such low prices indicate that the second-hand mining machine market has become saturated. Previously, Bitmain also announced a suspension of spot mining machine sales. However, some miners believe the prices are too low and choose to wait and see.
"Maybe because I have experienced multiple rounds of policy crackdowns, I always believe that the mining industry has prospects," Old Long told BlockBeats. "Now that the prices of mining machines are too low, I would rather shut down and wait than sell at a loss."
Senior mining industry insider Ahao also told BlockBeats that most mining farms are currently shut down and waiting, not selling, and are waiting for clearer policies. "Most are struggling like this now."
With the domestic survival space continuously shrinking, miners unwilling to sell their machines and leave the industry are looking to go overseas for a glimmer of hope.
Currently, there are about 10 million loads of mining machines in Sichuan that need to go overseas. Ahao told BlockBeats that if these machines remain stagnant in China, their owners and investors will face significant financial costs. Just like using leverage to speculate in real estate, many miners also use borrowed funds to buy machines and build farms, carrying the pressure of millions of yuan. "They need to supplement funds every day and are very anxious," Ahao said.
In the face of overseas demand, mining machine companies with long-term overseas layouts see opportunities and have designed customized "overseas module containers" to address miners' difficulties. These containers include equipment for thermal and cold isolation, fans, networks, monitoring, and distribution cabinets, essentially creating mobile mining farms built from containers.
Such designs naturally come at a high price. For example, with Bit Deer, the minimum price for each container is 142,000 yuan, accommodating 180 units of the 19 series mining machines. Given that domestic mining farms often have thousands of machines, the cost of just the container for a small to medium-sized mining farm can reach nearly a million, while large farms may require tens of millions.
Currently, the main directions for mining overseas are North America and the Middle East. In North America, represented by the United States and Canada, local policies are relatively stable, and the legal system is relatively sound, with many large mining companies already stationed there. However, the comprehensive costs of mining farms in North America are high, and the U.S. imposes a 25% tariff on Chinese electronic products.
Another relatively cheaper option is Kazakhstan. This region has abundant energy resources, is closer to China, and has lower labor and construction costs, with tariffs far below those of the U.S. However, the level of legal governance is not high, the business environment needs improvement, and like China, policy remains the biggest risk.
The road to going overseas is long, and on the path to "seeking true scriptures," there is not only no "Sun Wukong" to protect them but also countless pitfalls to encounter.
Recently, industry insiders reported that at a mining farm in Kazakhstan, as soon as the mining machines arrived locally, they were robbed clean, leaving miners in tears.
"There are too many pitfalls in going overseas; it's not that easy," Ahao also believes. "Initially, Kyrgyzstan attracted mining farms with investment promotion, but in the end, the military directly seized the Chinese mining farms, resulting in total loss."
In legal countries like the U.S. and Canada, building factories overseas faces extremely high costs. Ahao told BlockBeats that building a mining farm with a load of 10,000 in China requires about 3.5 to 5 million yuan. For the same scale abroad, it requires 18 to 40 million yuan. Currently, Bitmain quotes 18 million, while Bit Deer quotes 40 million.
It is worth noting that despite various resource connections and one-stop services during the overseas process, the ultimate losses are often "fully borne by the miners."
Western Development
Since the comprehensive ban on Bitcoin mining activities in inland areas in June 2021, the Bitcoin hash power center has shifted from China to North America.
By the end of 2021, this change was visibly apparent. According to the Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index from Cambridge, if we use the average monthly hash rate share as a standard, the global Bitcoin mining center was still in China in January 2021, but by December 2021, this center had moved to North America.
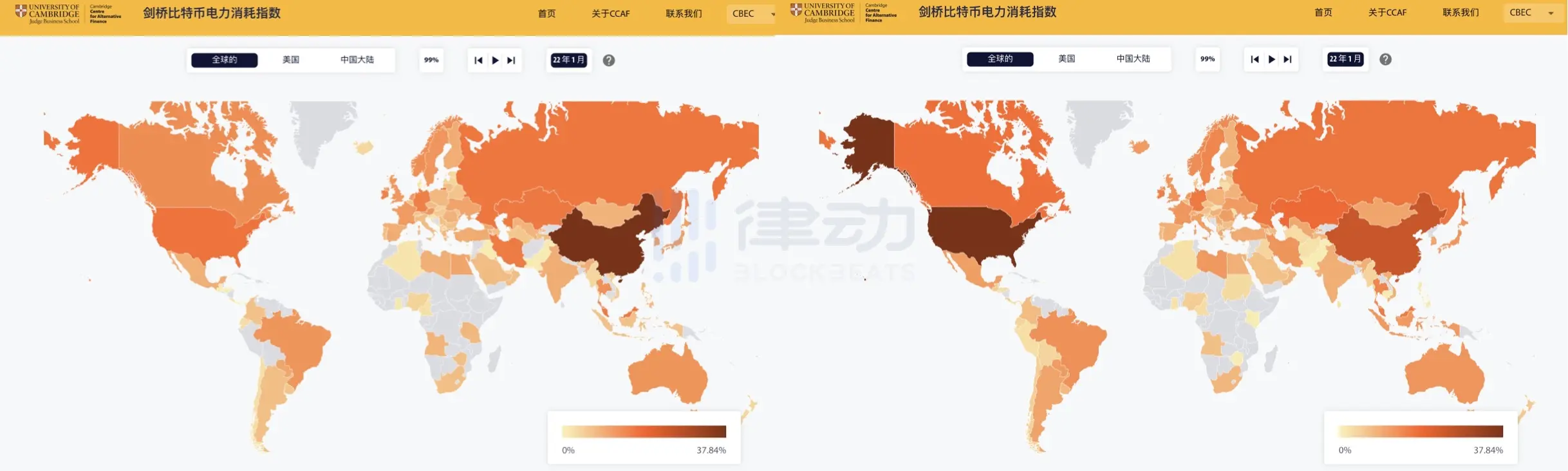
Left image: January 2021; Right image: December 2021. Source: Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index
Behind this change is the continuous rise of mining companies in North America. Since 2020, North American mining companies led by Core Scientific (NASDAQ: CORZ), Riot Platform (NASDAQ: RIOT), Bitfarms (NASDAQ: BITF), and Iris Energy (NASDAQ: IREN) began purchasing mining machines in large quantities and subsequently went public in North America, embarking on a path of compliant operations.
In February 2020, Bit Digital (NASDAQ: BTBT) went public; in June 2021, Bitfarms, Hut 8 (TSE: HUT), and HIVE Digital (CVE: HIVE) went public; in November 2021, Iris Energy went public; in January 2022, Core Scientific went public; Riot Platform, originally a biopharmaceutical company, also took off after entering the mining wave.
These mining companies primarily engage in Bitcoin mining, so their development is highly correlated with Bitcoin prices. During the bull market from January 2021 to May 2022, the stock prices of these companies soared. According to Nasdaq data, compared to their initial public offering prices, the stock prices of Core Scientific, Bitfarms, Hut 8, and HIVE Digital rose by as much as 57%, 707%, 371%, and 228%, respectively, during the crypto market bull run.
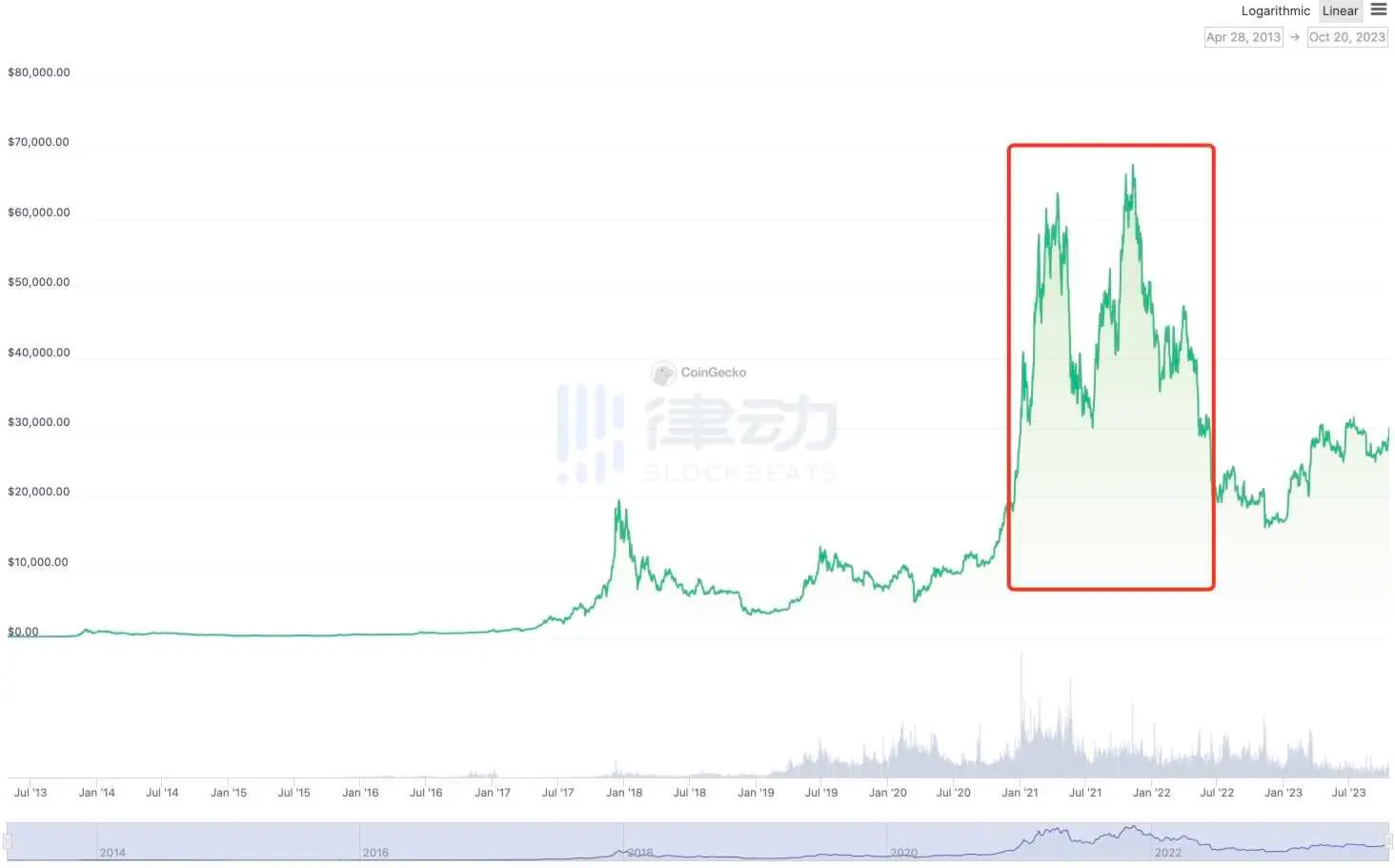
Bull market conditions from January 2021 to May 2022. Source: Coingecko
During this period, most mining companies achieved profitability through a combination of hash power mining and debt/equity financing. Taking Marathon Digital (MARA) as an example, its main business is self-operated Bitcoin mining, with a strategy of financing to purchase mining machines and deploy mining farms, holding Bitcoin as a long-term investment after covering cash operating costs. Data shows that in 2021, Marathon Digital spent $120 million to purchase 30,000 Antminers from Bitmain in one go and obtained a $100 million revolving credit line from Silvergate Bank, planning to raise $500 million in debt through the issuance of senior convertible notes to continue purchasing mining machines, becoming the largest Bitcoin holder among North American mining companies.
Coincidentally, Core Scientific was even more extravagant, operating over 200,000 Bitcoin mining machines across five states in the U.S. and producing over 7,000 Bitcoins in just June 2022. Additionally, Core Scientific received a $54 million investment from Celsius and signed a $100 million equity investment agreement with investment bank B. Riley.
However, due to their high-leverage business nature, the sudden bear market caught these mining companies off guard.
First, Marathon Digital recorded a net loss of $686.7 million for the entire year of 2022; Riot Platform had a net loss of $509.6 million in 2022; Bitfarms reported a net loss of $239 million in 2022; Core Scientific lost over $1.7 billion in just the first nine months of 2022, leading to Core Scientific being on the brink of bankruptcy by the end of 2022.
According to a report from Hashrate Index, the total collective debt of mainstream centralized mining companies exceeded $4 billion by the end of 2022. Among them, Core Scientific had the highest debt, owing creditors $1.3 billion as of September 30, 2022; Marathon Digital owed about $851 million, most of which was in convertible notes; the third debtor was Greenidge Generation, with a debt of $218 million.
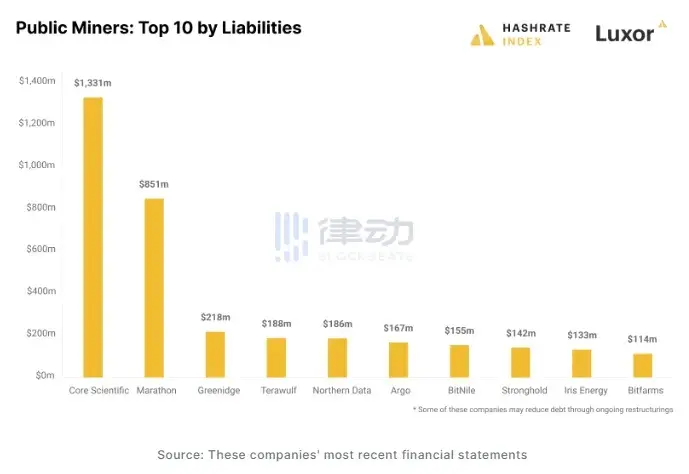
Source: Hashrate Index
Many institutions believe that the development of centralized mining companies is highly correlated with Bitcoin prices, thus "the business model of financing to purchase Bitcoin mining machines is a significant test of a company's cash flow management ability during a bear market," and it is also easy to face the risk of insolvency.
Regular Army
In 2017, Bitcoin experienced an epic bull market, and the cryptocurrency craze quickly swept the globe. In China, a Bitcoin trading platform called OKCoin was quietly established, which later became known as the "Huangpu Military Academy of the cryptocurrency circle." Its founder, Xu Mingxing, was originally a technical expert in the internet field and served as the CTO of Douyin. Xu Mingxing had a clear goal: to make it easier for ordinary people to access and purchase Bitcoin.
There were many others who shared his vision. From miners to mining machine manufacturers, and blockchain developers to tech enthusiasts, more and more people joined this emerging industry. They realized that Bitcoin is not just a decentralized currency; its growth also requires a deep connection with the traditional fiat currency world. Electricity costs, equipment R&D costs, technology development expenses… all of these need support from the fiat economy, making trading platforms an essential bridge.
With the arrival of the first wave of the bull market, the wave of Bitcoin trading platforms also quickly rose. A batch of platforms such as OKCoin, Huobi, Binance, Coinbase, BitMEX, and Bitfinex emerged. These platforms not only provided investors with a pathway to enter the cryptocurrency world but also injected a continuous flow of funds into the Bitcoin ecosystem. Through these platforms, investors could trade Bitcoin as easily as opening a stock account. At that stage, trading platforms almost became the only entry point for ordinary people to access Bitcoin.
Although Bitcoin prices fluctuated, the continuous inflow of traditional capital helped its price steadily rise. Meanwhile, the prosperity of trading platforms also spurred innovation in more fields. From infrastructure construction to the exploration of payment methods, Bitcoin was gradually moving from a niche experiment to the mainstream market through these platforms.
However, merely relying on investors' interest was far from enough for Bitcoin to truly enter mainstream society. Bitcoin needed to be understood and used by more people, even entering daily payment scenarios. In February 2021, Bitcoin's price broke through $50,000, setting a new historical record.
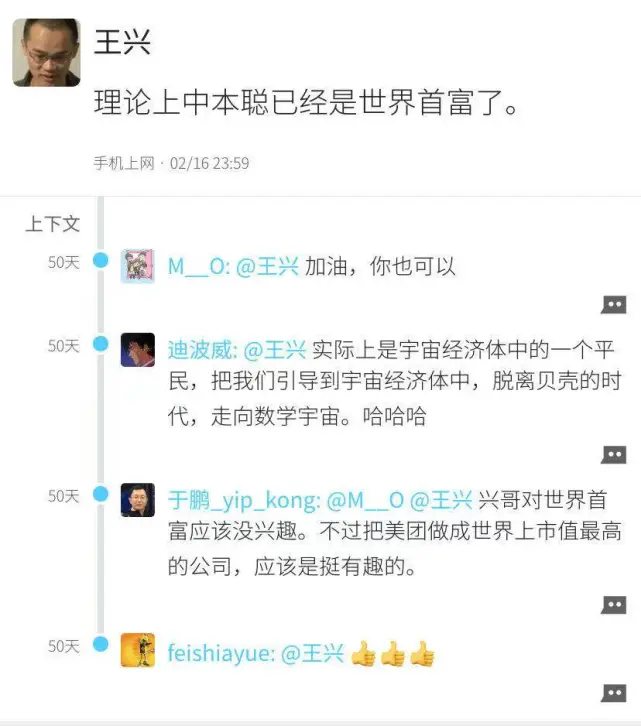
At this juncture, Meituan founder Wang Xing expressed his high recognition of Bitcoin on the social platform Fenfu. As an early investor in 2013, Wang Xing had bought Bitcoin at a very low price and regarded it as a "highly imaginative creation."
Few Bitcoin supporters in China come from the financial industry. Most supporters, like Wang Xing, are from the internet sector.
Xu Zhihong, a partner at Biyou, once gave a Bitcoin as a wedding gift to a friend. At that time, the value of that Bitcoin was only $300, but he repeatedly advised the recipient: "Keep it; when your child gets married, it might be able to buy a house in Beijing." Today, ten years later, such a gift has become a rare luxury.
"Bitcoin will quickly approach 80% of gold's market value (within 1.5-2 years), which is $400,000 per coin," predicted Chen Weixing, founder of Kuaidi. After merging with Didi, Chen Weixing ventured into blockchain and founded Dache Chain. As Bitcoin rose, similar predictions became more frequent.
At that time, there were two larger peaks in front of Bitcoin—how to enter the investment portfolios of mainstream financial institutions and how to enter the balance sheets of publicly listed companies.
"Currently, most financial institutions and banks cannot buy Bitcoin, and it will take a long time to form further consensus," said Zhu Xiaohu from Jinsha River Ventures in an interview with Tencent Technology. He had previously invested in a series of cutting-edge technology companies such as Didi, ofo, and Yingke. Wherever there is a windfall, he is there.
"The biggest limitation for institutions participating in Bitcoin investment is still the financial regulations of various countries," said Yuan Yuming, CEO of Huolien Technology. In 2018, Yuan Yuming, who was the chief analyst for TMT at Industrial Securities, announced his move to join Huobi China, which caused a stir in the circle.
And today, with Bitcoin at $100,000, both of these peaks have been achieved.
MicroStrategy, Silicon Valley, and Wall Street
When asked why there is this new market trend, almost all cryptocurrency practitioners gave the same answer—America.
"The center of blockchain innovation has always been in the United States, and in the past two years, blockchain innovation, particularly Ethereum's innovation, has basically had nothing to do with China," said Chen Yong, founder of Biyou, who was previously a senior vice president at Cheetah Mobile before entering the cryptocurrency space. "This situation of being based on American financial innovation still cannot be changed."
Also purchasing Bitcoin is the American company MicroStrategy. As the first publicly traded company to adopt Bitcoin as a primary reserve asset, MicroStrategy was founded in November 1989 and went public on June 11, 1998.
As of the time of writing on November 21, MicroStrategy's Bitcoin holdings reached a new all-time high: 331,200 Bitcoins, with an average purchase price of $49,874.
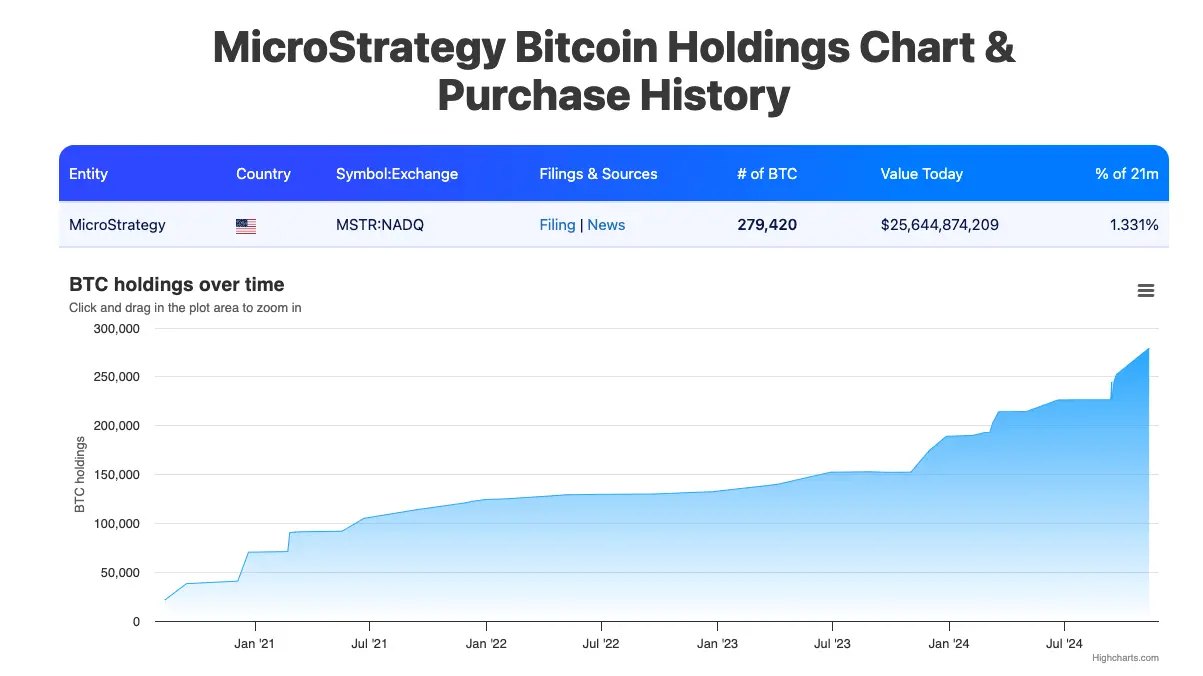
MicroStrategy founder Michael Saylor stated that MSTR and BTC have a cooperative relationship and released MicroStrategy's nine BTC principles, including: 1. Purchase and hold BTC indefinitely, exclusively, and securely; 2. Prioritize the long-term value creation of MSTR common stock; 3. Treat all investors with respect, consistency, and transparency; 4. Build MSTR through smart leverage to surpass BTC; 5. Continuously purchase BTC while achieving positive BTC returns; 6. Grow quickly and responsibly based on market dynamics; 7. Issue innovative fixed-income securities backed by BTC; 8. Maintain a healthy, robust, and clean balance sheet; 9. Promote global adoption of BTC as a fiscal reserve asset.
Under such strategies and principles, MicroStrategy has also benefited significantly from the price increase of Bitcoin.
"This year, MicroStrategy's capital operations achieved a 26.4% BTC yield, bringing approximately 49,936 BTC in net gains to shareholders," Michael Saylor posted on social media on November 12, 2024. After "Bitcoin President" Trump confirmed his return to the White House, MicroStrategy's after-hours price briefly surpassed $360, currently reported at $355.43, setting a new historical high.
On the other hand, Silicon Valley, the innovation hub, is also caught up in the FOMO. Twitter's founder Jack Dorsey is a well-known tech leader in the U.S. and a more steadfast supporter of cryptocurrency than Musk, believing that cryptocurrency will become the "single currency" of the world.
Although Twitter is widely known, it is not Dorsey's most successful business venture. Dorsey's Square is a pioneer in the Bitcoin innovation field, currently valued at $120 billion, twice that of Twitter. If Grayscale is like a pump, drawing water from the fiat world into the Bitcoin world, Silicon Valley tech companies have invented new tools that gradually consume Bitcoin inventory like ants moving a mountain.
In January 2018, Square's Cash App launched a new feature allowing users to purchase Bitcoin. "In 2020, 3 million people purchased Bitcoin through Cash App, and in January 2021, an additional 1 million people joined." Data disclosed by Square's CFO indicates that Bitcoin is entering the wallets of the general public in various ways.
Under pressure from competitors, in October 2020, the world's leading online payment tool PayPal announced support for purchasing Bitcoin, Litecoin, and other digital currencies.
Research shows that the number of Bitcoins stored on trading platforms decreased from 3 million to 2.2 million over the past year, a reduction of 800,000. The number of Bitcoins stored on trading platforms continues to decline.
In February 2021, Tesla announced that it had purchased $1.5 billion worth of Bitcoin and announced that customers could buy Tesla cars with Bitcoin. Bitcoin's price instantly surged by 10%. Musk also announced that customers would be able to purchase Tesla cars with Bitcoin, and Tesla would not sell these Bitcoins.
Tesla was not the first tech company to take the plunge; in 2020, Square invested about $50 million to purchase 4,709 BTC. Square's attempt brought Bitcoin onto the balance sheets of publicly listed companies in the U.S. for the first time and was recognized by accounting standards.
The limited supply of Bitcoin and the increasing demand are creating a more severe supply-demand contradiction. The approval of Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024 directly expanded this supply-demand contradiction.
Spot ETF
On January 11, 2024, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) finally approved the application for Bitcoin ETFs, with 11 Bitcoin ETFs listed simultaneously.
"Bro, no longer just a stinky coin trader, but a serious U.S. stock trader," was a joke at the time, but it truly reflected Bitcoin's changed status in the financial circle.
Among these listed entities, Grayscale (GBTC) stands out with approximately $46 billion in assets under management, while BlackRock's iShares leads the industry with a massive $9.42 trillion in assets under management. Following closely is ARK 21Shares (ARKB), managing about $6.7 billion in assets. In comparison, Bitwise (BITB), although smaller in scale, still has around $1 billion in assets under management.
Other significant participants include VanEck, managing approximately $76.4 billion in assets; WisdomTree (BTCW) with $97.5 billion in assets under management; Invesco Galaxy (BTCO) and Fidelity (Wise Origin), managing $1.5 trillion and $4.5 trillion in assets, respectively.
Among them, BlackRock's spot ETF application has been the most talked about in the market. Looking back at 2023, BlackRock's application for a Bitcoin spot ETF was seen as a crucial turning point in the crypto market's bull-bear trends. As an asset management company with over $10 trillion in assets under management, BlackRock's managed assets even exceed Japan's GDP of $49.7 trillion in 2018. BlackRock, Vanguard, and State Street Bank were once referred to as the "Big Three," controlling the entire index fund industry in the U.S.
More importantly, BlackRock has an impressive track record of success with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in getting its ETF applications approved. According to historical data, BlackRock's success ratio for SEC-approved ETFs is 575 to 1, meaning that out of the 576 ETFs it applied for, only one was rejected. Therefore, when BlackRock submitted its spot Bitcoin ETF filing to the SEC in June 2023, it sparked considerable discussion in the community, which generally believed that BlackRock's entry signified the inevitable approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs.
The importance of the approval of the spot Bitcoin ETF mainly manifests in two aspects.
First, it enhances accessibility and popularity. As a regulated financial product, Bitcoin ETFs provide a pathway for a broader group of investors to access Bitcoin. With a Bitcoin spot ETF, financial advisors can start guiding their clients to invest in Bitcoin, which is significant for the wealth management sector, especially for capital that has been unable to invest in Bitcoin directly through traditional channels.
More directly, this opens up an easy purchasing channel for many "old money" investors without worrying about the potential risks of crypto trading platforms. In contrast, spot Bitcoin ETFs are listed on strictly regulated securities exchanges, allowing investors to hold them through traditional stock accounts and gain exposure to Bitcoin prices without the complexities and risks of directly holding Bitcoin.
Moreover, the ETF structure also increases the likelihood of institutional investors accessing Bitcoin, some of whom are prohibited from directly investing in alternative assets. This type of product will attract large-scale capital into the market, thereby driving the Bitcoin market to continue to grow.
The approval of the spot Bitcoin ETF signifies regulatory recognition and enhances market acceptance. SEC-approved ETFs will alleviate investors' concerns about safety and compliance, as they provide more comprehensive risk disclosures. A more mature regulatory framework will attract more investment, and this regulatory clarity is crucial for market participants, helping them conduct business in the cryptocurrency industry.
The legitimacy of the cryptocurrency industry has been elevated, and Bitcoin is further moving into the mainstream. This is also a step that changes the game rules in the cryptocurrency industry, with continuous capital inflow leading to a new surge in the entire crypto circle. Consequently, after briefly dropping from $49,000 to $38,500, Bitcoin's price gradually rebounded and successfully broke through the $53,000 mark.
Ten months have passed, and Bitcoin's price has risen significantly due to multiple driving forces. As of now, according to Trader T's monitoring, the total holdings of Bitcoin ETFs worldwide have surpassed the holdings in Satoshi Nakamoto's wallet address. Nate Geraci, president of The ETF Store, also revealed that BlackRock's Bitcoin ETF asset size has exceeded that of its gold ETF, achieving this in just 10 months.
At this point, it is necessary to mention the "first Bitcoin president" of the United States, Donald Trump.
"Bitcoin President" to Return to the White House
Once upon a time, Trump was a staunch opponent of cryptocurrency. In early 2019, during his presidency, Trump publicly criticized Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, calling them "worthless" and suggesting that crypto assets could be used as tools for illegal activities. He stated that Bitcoin "is not money" and is highly volatile.
After leaving the White House, Trump continued to hold a reserved attitude in interviews, labeling Bitcoin as a "scam" and insisting that the U.S. dollar should be the world's only reserve currency. During this period, Trump's attitude toward cryptocurrency was largely negative. However, the NFT craze in 2021 soon began to influence Trump's perspective.
The story begins in 2022. At that time, the cryptocurrency market was in a "winter," with many crypto projects on the brink of bankruptcy and market confidence low. It was during this time that Trump's long-time advisor, Bill Zanker, appeared in his life with a suggestion that would change Trump's mind: to issue Trump-themed NFTs.
Trump expressed unexpected interest in this idea—though he preferred to call them "digital trading cards" rather than "NFTs." Despite seeming quirky, these cards became immensely popular, selling for $99 each and quickly selling out after their release. Trump's NFTs allowed the former president to "stand in front of the crypto community" for the first time, bringing him tens of millions of dollars in revenue and introducing him to a new, powerful support group.
As a result, Trump's attitude toward crypto underwent a complete turnaround over the years.
On November 1, 2024, the 16th anniversary of the Bitcoin white paper's release, Trump tweeted his blessings for Bitcoin and stated that if elected, he would end the Harris administration's crackdown on cryptocurrency, even calling on supporters to help him realize the vision of "Bitcoin made in America." At this point, he was no longer an opponent, nor just a bystander, but a "presidential candidate" who supported cryptocurrency.
One of the most iconic events was his attendance at the Bitcoin 2024 conference in Nashville, where Trump announced that he would become a staunch supporter of cryptocurrency. He even clearly understood the biggest pain points in the crypto community, promising to fire the current SEC chairman Gary Gensler and replace him with a "regulator who understands crypto."
He candidly stated that "opposing crypto is the wrong policy" and that he would make the U.S. a "Bitcoin superpower," hoping to lead the global crypto industry through a more friendly regulatory environment. He even praised Bitcoin as the core of the modern economy, stating that if Bitcoin were to "moon," he hoped the U.S. could be its leader.

Trump attends the Bitcoin 2024 conference, source: WSJ
In his speech, Trump vigorously positioned himself against the Democratic Party's harsh stance on crypto, especially contrasting himself with Elizabeth Warren, known for her crypto regulation. He also pointed out that if elected, he would create a "Presidential Crypto Advisory Committee," which immediately elicited enthusiastic applause and cheers from the audience. More shockingly, he suggested that Bitcoin's market value could one day surpass gold and publicly criticized the Biden and Harris administration's anti-crypto policies.
During the conference, Trump seemed to experience a "public awakening," no longer the former president who was skeptical of cryptocurrency, but rather an enthusiastic defender of Bitcoin and free markets. The audience was inspired by his change in attitude, viewing him as a "hero" in the crypto community.

Trump attends the Bitcoin 2024 conference, source: The New York Times
Another detail behind this transformation reveals the subtle connection between Trump and cryptocurrency. At the conference, he looked at the crypto supporters in the crowd and mentioned that Bitcoin had risen 3900% during his previous presidential term, skyrocketing from under $1,000 to over $30,000. His remarks not only ignited the audience but also garnered support from crypto industry giants, such as Elon Musk, the Winklevoss twins, and Marc Andreessen, founder of venture capital firm A16Z, who all expressed their support for his crypto policies.
Beyond Bitcoin itself, Trump has also gradually recognized the importance of Bitcoin mining in U.S. energy security and economic sovereignty. In June 2024, he met with executives from several large Bitcoin mining companies in the U.S. and promised to strongly support cryptocurrency mining activities through policy. He even posted on Truth Social that Bitcoin mining is the "last line of defense" against central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and expressed the hope that "all remaining Bitcoins are made in America." In Trump's view, Bitcoin mining is not just an economic activity; it symbolizes America's will to resist central banks.
As September approached, Trump used Bitcoin to purchase a cheeseburger at a Bitcoin-themed bar, PubKey, in New York. This action also pushed Bitcoin back from being seen solely as a financial investment to a potential everyday transaction currency, becoming a symbol of his crypto stance.
Trump also made larger commitments to the crypto community, publicly stating that he would retain Bitcoin as a strategic reserve and even planned to pardon Ross Ulbricht, who was sentenced to life in prison for operating a dark web platform. Through these radical moves, Trump successfully positioned himself as the "savior" of the crypto community, promising to protect Bitcoin from excessive government regulation and pledging to make the U.S. the center of global cryptocurrency.
As the dust settled from the U.S. elections, Trump won the votes in swing states, sweeping both houses and confirming his election as the next U.S. president, returning to the White House. Bitcoin could no longer contain its surge. On November 14, according to HTX market data, Bitcoin briefly surpassed $93,000, setting a new historical high.
According to data from the Stand With Crypto website initiated by Coinbase, a total of 247 pro-cryptocurrency candidates won seats in the House of Representatives, while only 113 members opposed cryptocurrency. The Stand With Crypto website also showed that the Senate leaned toward supporting cryptocurrency, with 15 supporters and 10 opponents.
Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong praised the results of this congressional election as a watershed moment for cryptocurrency, writing on Twitter: "Welcome to the new members of Congress who are the most pro-cryptocurrency in U.S. history."
With more members in the House of Representatives, representing a diverse range of interests, they typically initiate legislation, while the smaller, more conservative Senate usually reviews proposals initiated by the House. Since both the House and Senate tend to support cryptocurrency, the path for favorable legislation may be smoother, and crypto insiders are optimistic about the potential for supportive regulation from the U.S. Congress in the future.
Bitcoin has traversed 16 years of ups and downs, with its price rising from zero to $100,000. This is not only a victory for technological innovation but also a bold attempt by humanity to reconstruct the trust system. From the white paper born out of the financial crisis to the current financial giant with a global market value exceeding $2 trillion, Bitcoin has changed our understanding of currency, wealth, and power in an unforeseen way.
Behind all this are the efforts of countless evangelists: early miners, platform founders, and developers who ignited the spark of belief amid uncertainty; as well as ordinary investors who maintained their faith through extreme volatility, navigating the bull and bear markets. This revolution, spanning technology, philosophy, and economics, is not merely a transfer of wealth but a transformation of ideas.
And the story of Bitcoin is far from over. It continues to evolve, attracting more institutions and individuals to participate, pushing for a new balance between regulation and the market. From Satoshi Nakamoto's original intention to today's brilliance, Bitcoin is not only writing a legendary past but also the prologue to the future. As many supporters firmly believe, Bitcoin is not the end but the starting point for redefining global finance.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




