The Surge upgrade of Ethereum will significantly enhance scalability through second-layer Rollups and improvements in data availability, achieving a processing capacity of over 100,000 transactions per second while maintaining decentralization and security.
Author: Kucoin
Translation: Blockchain in Plain Language
Learn about Ethereum's next major upgrade—The Surge, which focuses on achieving a processing capacity of over 100,000 transactions per second (TPS) through second-layer rollup solutions and improvements in data availability. Dive into how this phase enhances scalability, reduces gas fees, and maintains decentralization, providing a secure and efficient foundation for the future of blockchain.
Ethereum is continuously evolving, with the next major upgrade being The Surge. This phase aims to enhance scalability without sacrificing decentralization and security. As part of Ethereum's long-term vision, The Surge will elevate the network's processing capacity on both the first and second layers to over 100,000 transactions per second. This article will explain in detail the next steps Ethereum is taking towards becoming the most scalable and efficient blockchain.
1. What is The Surge?
The Surge refers to Ethereum's transition towards scalability, primarily achieved through second-layer (L2) solutions and rollup schemes. This concept was introduced by Ethereum's founder Vitalik Buterin in the Ethereum roadmap, aiming to make the network faster and more efficient. Its main goal is to process more transactions while maintaining decentralization, security, and interoperability.
Currently, Ethereum processes about 15 to 30 transactions per second on the base layer. While this meets the needs of many applications, it can lead to network congestion during peak times and drive up gas fees. The Surge aims to address these bottlenecks and enhance Ethereum's ability to serve global applications.
1) Key Features of The Surge
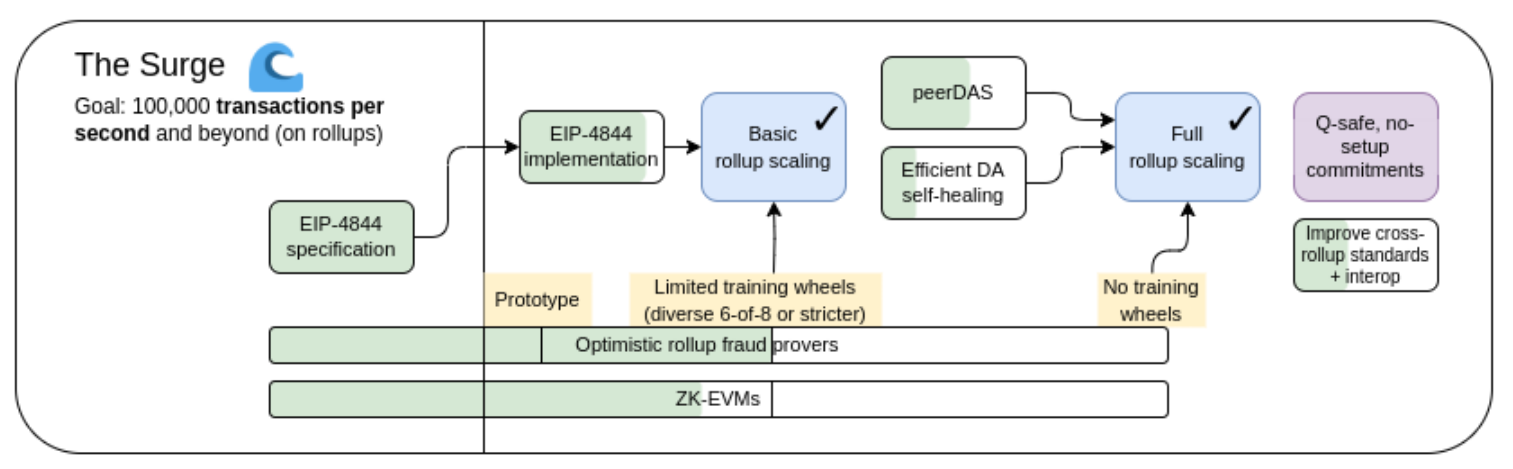
The Surge Roadmap | Source: Vitalik Buterin
Over 100,000 transactions per second processing capacity on L1 and L2 networks: Through second-layer rollup solutions, Ethereum can handle over 100,000 transactions per second. Rollups bundle multiple transactions and submit them to the Ethereum blockchain, increasing throughput and reducing gas fees.
Decentralization and security: The Surge ensures that Ethereum remains decentralized, allowing users to run nodes with minimal resources. Enhanced cryptographic proofs (such as SNARKs) will further strengthen Ethereum's trustless mechanisms.
Improved data availability through Data Availability Sampling (DAS): DAS allows nodes to verify information without downloading all data, enhancing efficiency and supporting the scalability of second-layer solutions.
2) Ethereum's Path to 100,000 Transactions per Second
Currently, Ethereum's processing capacity on the first layer is about 15 to 30 transactions per second. However, with the help of rollups and DAS, the network is expected to reach a processing capacity of over 100,000 transactions per second. Vitalik Buterin emphasizes that Ethereum should be viewed as a holistic ecosystem rather than a collection of disparate blockchains.
This means that cross-chain interoperability between L2s will improve, leading to a smoother user experience. The Ethereum roadmap focuses on creating a network where transferring assets between different layers is as convenient as sending ETH between wallets.
2. Timeline of The Surge
The Surge of Ethereum includes multiple phases, focusing on continuous upgrades on both the first and second layers. Here is the expected timeline based on the latest updates and roadmap:
Q1 2024 - Dencun Upgrade (Proto-Danksharding Launch)
Introduction of Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844), improving data availability through data "blobs." This lays the groundwork for further rollup expansion. Ethereum's second-layer solutions will begin to utilize improved data availability for faster and cheaper transactions.
2024-2025 - Rollup Expansion and Maturation of Proof Systems
Rollups such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync will undergo updates to enhance scalability. New cryptographic proofs (like SNARKs) will strengthen the trustless nature of rollups. Data availability sampling (DAS) systems like PeerDAS and 2D DAS will expand to support higher transaction throughput.
End of 2025 - Gas Price Optimization and First Layer Enhancements
Introduction of EOF (Ethereum Object Format) to improve smart contract execution efficiency. Multi-dimensional gas pricing may be adopted to differentiate costs for computation, data, and storage. Rollup solutions may be directly integrated into the Ethereum protocol.
2026 and Beyond - Full Launch of Danksharding
Transitioning from Proto-Danksharding to full Danksharding, dividing Ethereum into multiple shards to further enhance scalability. Ethereum aims to achieve a processing capacity of 100,000 transactions per second across the L1 and L2 ecosystems.
Post-2026 - Continuous Monitoring and Upgrades
Introduction of advanced consensus mechanisms, including post-quantum cryptography, to ensure network security. Ethereum will continue to optimize and integrate cross-L2 interoperability to enhance user experience.
This timeline reflects Ethereum's phased approach, ensuring stability and smooth adoption during the transition. Each step of The Surge builds on the previous phase, with the ultimate goal of creating a blockchain that can support global-level applications while maintaining decentralization and security.
3. Key Components Potentially Affected by The Surge
Here are the key elements in the Ethereum 2.0 roadmap that will be impacted during The Surge upgrade:
Proposal for "Division of Labor" between L1 and L2 | Source: Vitalik Buterin
1) Second Layer Rollup: The Core of The Surge
Second-layer rollup solutions are crucial tools for making Ethereum faster and more economical. They bundle multiple transactions off-chain (i.e., outside the Ethereum mainnet) and submit summaries of these transactions to the Ethereum blockchain. This alleviates the load on the mainnet, making transactions faster and cheaper.
There are two main types of rollups:
OP-rollup: Assumes all transactions are valid unless an error is reported within a specified time. This method does not require immediate verification of each transaction, allowing for faster processing.
ZK-rollup: Utilizes an advanced mathematical method—zero-knowledge proofs—to instantly confirm the validity of transactions. This method provides immediate and secure verification.
The impact of rollups has already been significant. According to L2Beat, the total value locked (TVL) in Ethereum's second-layer networks has grown by 216% over the past year, exceeding $38 billion. As more individuals and projects adopt rollup solutions, Ethereum is becoming more scalable and accessible, laying the groundwork for the arrival of The Surge.
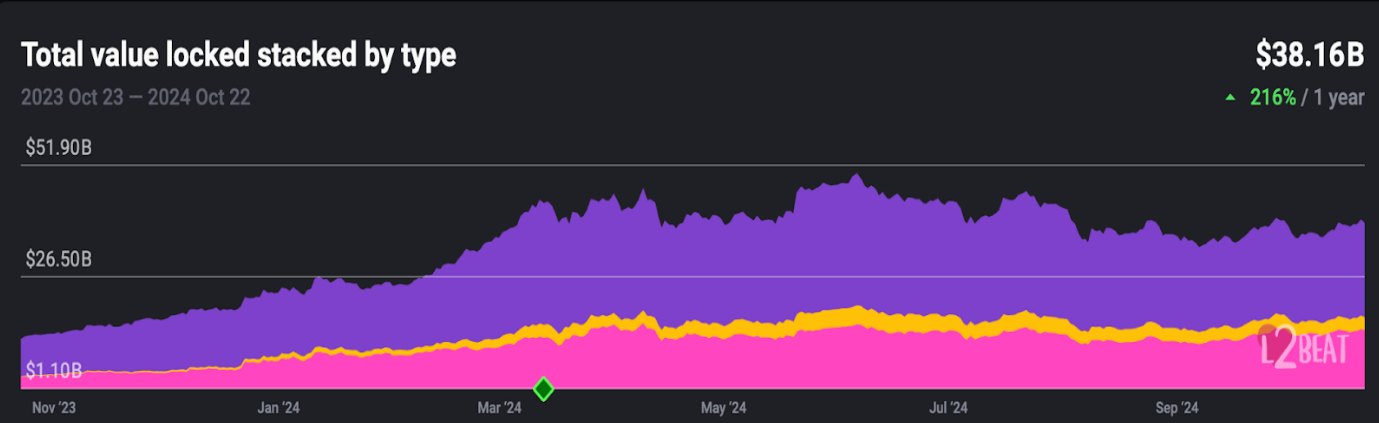
Ethereum Second Layer TVL | Source: L2Beat
2) Data Availability Sampling (DAS)
Data Availability Sampling (DAS) is a method that helps Ethereum process large amounts of data more efficiently. In decentralized networks like Ethereum, each node must confirm the availability of all transaction data. However, it is not practical for every node to store all data. DAS addresses this issue by allowing nodes to verify data without downloading and storing everything.
There are two main types of DAS:
PeerDAS: This system utilizes a peer-to-peer network to distribute the workload. Each node in the network checks only a small portion of the data, and all nodes collectively confirm the entire dataset. This method ensures efficient data verification without requiring large storage.
2D DAS: This is an improved version of PeerDAS that further enhances verification efficiency. It not only verifies individual data fragments but also checks how these fragments combine, making Ethereum more scalable while maintaining decentralization and ensuring higher security.
With DAS, rollups can handle more transactions without increasing the burden on the Ethereum network. This keeps the system fast, economical, and decentralized, supporting Ethereum's goal of scaling without sacrificing security.
Plasma and Data Compression Solutions
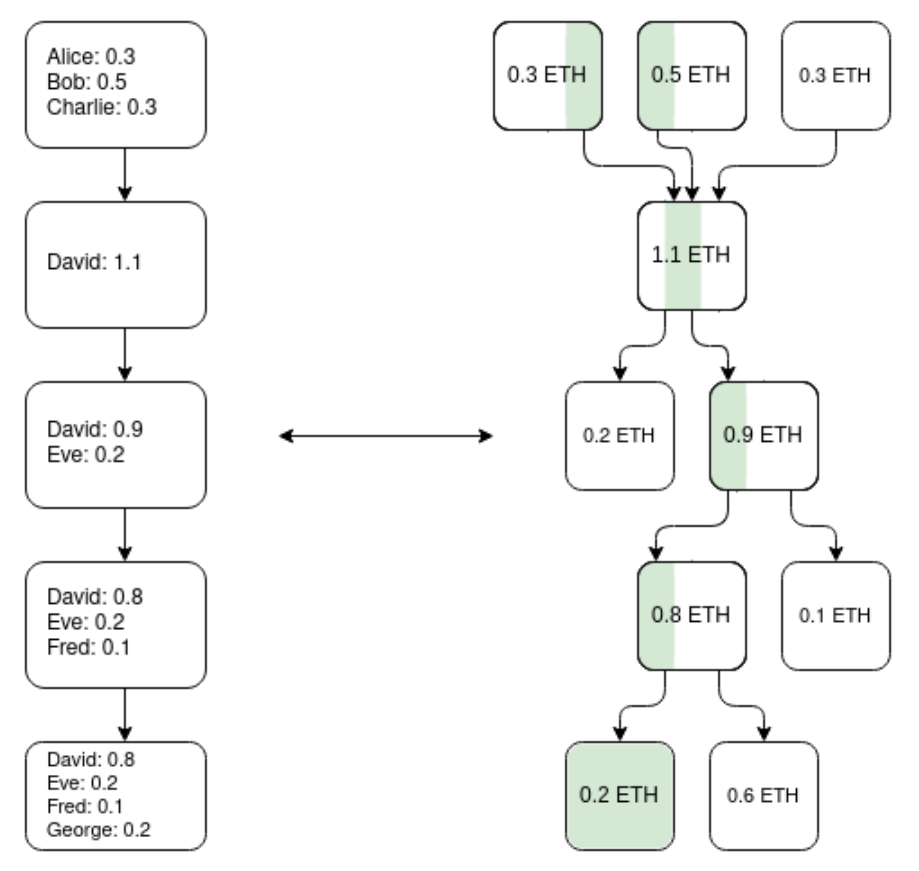
One way to build an EVM Plasma chain (not the only method) is to use ZK-SNARK to construct a parallel UTXO tree that reflects the balance changes generated by the EVM and defines a unique mapping of the "same coin" at different points in time. Based on this, a Plasma solution can be constructed. Source: Vitalik Buterin
In addition to Rollups, Plasma and data compression technologies also help Ethereum achieve efficient scaling. Let's take a closer look at how they work:
Plasma: Plasma processes transactions off-chain, meaning transactions occur outside the Ethereum mainnet. Plasma does not submit every transaction to the blockchain but only submits summaries of these transactions. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be stored on the main chain, increasing speed and lowering costs. You can think of it as summarizing many small tasks into a report, saving time and resources.
Data Compression: Compression makes transactions smaller by reducing the amount of data required by the transaction platform. For example, Ethereum can switch from standard signatures to BLS signatures, allowing multiple signatures to be combined into one. This not only saves space on the blockchain but also makes transactions more efficient, especially in systems handling large volumes of transactions, such as second-layer networks.
3) Collaboration between Plasma and Rollups
One way to build a Plasma system is to use ZK-SNARK (a cryptographic technology) to track the flow of tokens. This system creates a "parallel ledger" that records the movement of each token over time. Plasma ensures efficiency without sacrificing accuracy and security by only submitting necessary information summaries to the main chain.
Plasma and data compression technologies further enhance the effectiveness of Rollups. These solutions help Ethereum reduce gas fees, process more transactions, and support large-scale applications while maintaining decentralization.
4. Layer 1 Improvements in The Surge
While Rollups handle a large number of off-chain transactions, Ethereum's main blockchain (Layer 1) still needs upgrades to accommodate the growing ecosystem. These upgrades will ensure that Ethereum's base layer remains scalable, efficient, and accessible. Here are the key improvements coming to Layer 1:
1) Increased Gas Limit: The gas limit determines the amount of data that can be processed in a single block. Increasing the gas limit means Ethereum can handle more transactions in each block, reducing wait times and alleviating network congestion. However, raising the gas limit also carries risks. If the limit is set too high, the cost of running nodes may increase, which could limit the number of participants securing the network, thereby reducing decentralization. Ethereum's goal is to find a balance—processing more transactions while keeping the network open and decentralized.
2) EVM Bytecode Improvements: The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is where smart contracts run. Ethereum will introduce a new bytecode format called EOF (Ethereum Object Format) to improve the efficiency of smart contract execution. This update will reduce gas fees, making transaction and contract interaction costs lower for developers and users.
3) Multi-dimensional Gas Pricing: Ethereum will also implement multi-dimensional gas pricing, categorizing gas fees based on the type of resources used—computation, data, or storage. This approach ensures that users pay reasonable fees based on the actual needs of their transactions, optimizing cost structures and improving user experience.
4) Native Rollups: Native Rollups are Rollups that run directly on the Ethereum protocol. This means Ethereum will support multiple parallel versions of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Native Rollups will enhance Ethereum's ability to process transactions without overloading the network. You can think of it as a train station with multiple tracks, where each track independently handles trains, making the entire system faster and more efficient.
These Layer 1 improvements ensure that even as Rollups take on most of the transaction load, Ethereum can still remain scalable and efficient. Together, they help Ethereum continue to grow as a secure, decentralized platform that supports complex applications and millions of users.
5. The Surge's Impact on Users and Developers
Ethereum's The Surge upgrade promises to make the network more efficient and affordable, benefiting both regular users and developers. While some of the technical details may be complex, here’s a simple explanation of how these changes will affect you:
1) Lower Gas Fees: One of the most significant improvements will be the reduction of gas fees, especially on second-layer networks like Arbitrum and Optimism. These networks already offer cheaper transactions, with current ETH transfer fees around $0.24 to $0.78. After The Surge, transaction fees may decrease further, making it more affordable to send ETH or interact with decentralized applications (dApps). Lower gas fees mean users can transact more frequently without worrying about high costs during network congestion.
2) Improved dApp Performance: Developers will benefit from faster transaction speeds, enabling them to build more complex and feature-rich dApps. Whether you are developing a DeFi platform, a blockchain game, or an NFT marketplace, the scalability improvements brought by The Surge will make operations smoother. Faster transactions will also reduce latency, enhance user satisfaction, and encourage innovation across various fields, including decentralized finance (DeFi) and gaming.
3) Stronger Interoperability: The ability for different networks to work together will also be enhanced. Moving tokens and assets between second-layer networks and the Ethereum mainnet will become more seamless. Users will no longer need to rely on complex cross-chain bridges to transfer assets. Instead, Ethereum will feel like a unified ecosystem, where interacting with dApps or transferring funds between different layers will be as simple as using a single network.
These improvements make Ethereum more user-friendly for both users and developers, fostering an ecosystem where both regular users and developers can thrive. Whether you are transferring funds, developing applications, or exploring new projects, The Surge will bring faster, cheaper, and more convenient blockchain services to the Ethereum community.
6. Security Considerations
As the Ethereum network expands, the complexity of maintaining security also increases. With the widespread use of Rollups, ensuring their trustlessness and robustness is crucial. Rollups rely on cryptographic proofs to confirm transactions, and these proofs must remain secure to guard against potential vulnerabilities.
Vitalik Buterin has also emphasized the long-term risks posed by quantum computing. Ethereum developers are already exploring post-quantum cryptographic technologies to ensure the future security of the network.
7. The Future After The Surge
After The Surge, Ethereum will continue its comprehensive Danksharding roadmap. This phase will introduce complete data sharding, further enhancing scalability. Other upcoming upgrades include:
The Splurge: Focused on other improvements, such as better gas pricing and transaction formats.
The Verge: Improving the efficiency of Ethereum's consensus mechanism by implementing stateless clients.
The Purge: Optimizing the network by reducing unnecessary data and enhancing node performance.
Ethereum's long-term vision is to create a blockchain capable of supporting millions of users globally while not sacrificing security and decentralization.
Learn more about Danksharding—the complete sharding upgrade for Ethereum.
8. Conclusion
Ethereum's The Surge marks a significant step towards becoming a global decentralized platform. By focusing on Rollups, data availability, and Layer 1 improvements, Ethereum aims to handle over 100,000 TPS while maintaining decentralization and security.
With the rollout of these upgrades, users will benefit from faster transactions and lower fees, while developers can build more innovative dApps. However, rapid scalability also brings risks. Potential challenges include vulnerabilities in second-layer solutions, temporary network disruptions, and fluctuating gas fees during the transition. Developers and users must stay informed and adapt to changes as Ethereum continues to evolve.
With the arrival of The Surge, Ethereum lays the groundwork for a scalable, efficient, and secure blockchain future. But like any major upgrade, careful monitoring and ongoing adjustments will be key to ensuring long-term success. This is just the beginning of Ethereum's ambitious development journey.
Article link: https://www.hellobtc.com/kp/du/10/5490.html
Source: https://www.kucoin.com/learn/crypto/what-is-the-surge-the-next-phase-in-ethereum-2-0-upgrade
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




