Author: Yinliang (Former Researcher at BlockBooster, Lead Author) and Caiya (From BlockBooster, Supporting Author)
This research received support from the Kaspa Ecosystem Foundation regarding the development of the Kaspa ecosystem.
Grayscale has released a list of cryptocurrencies under consideration for future investment products and a list of cryptocurrencies for already published products, categorized into currencies, smart contract platforms, finance, consumer and culture, utilities and services. Among the cryptocurrencies that Grayscale is considering for future investment products is: Kaspa (KAS).

(Source: grayscale)
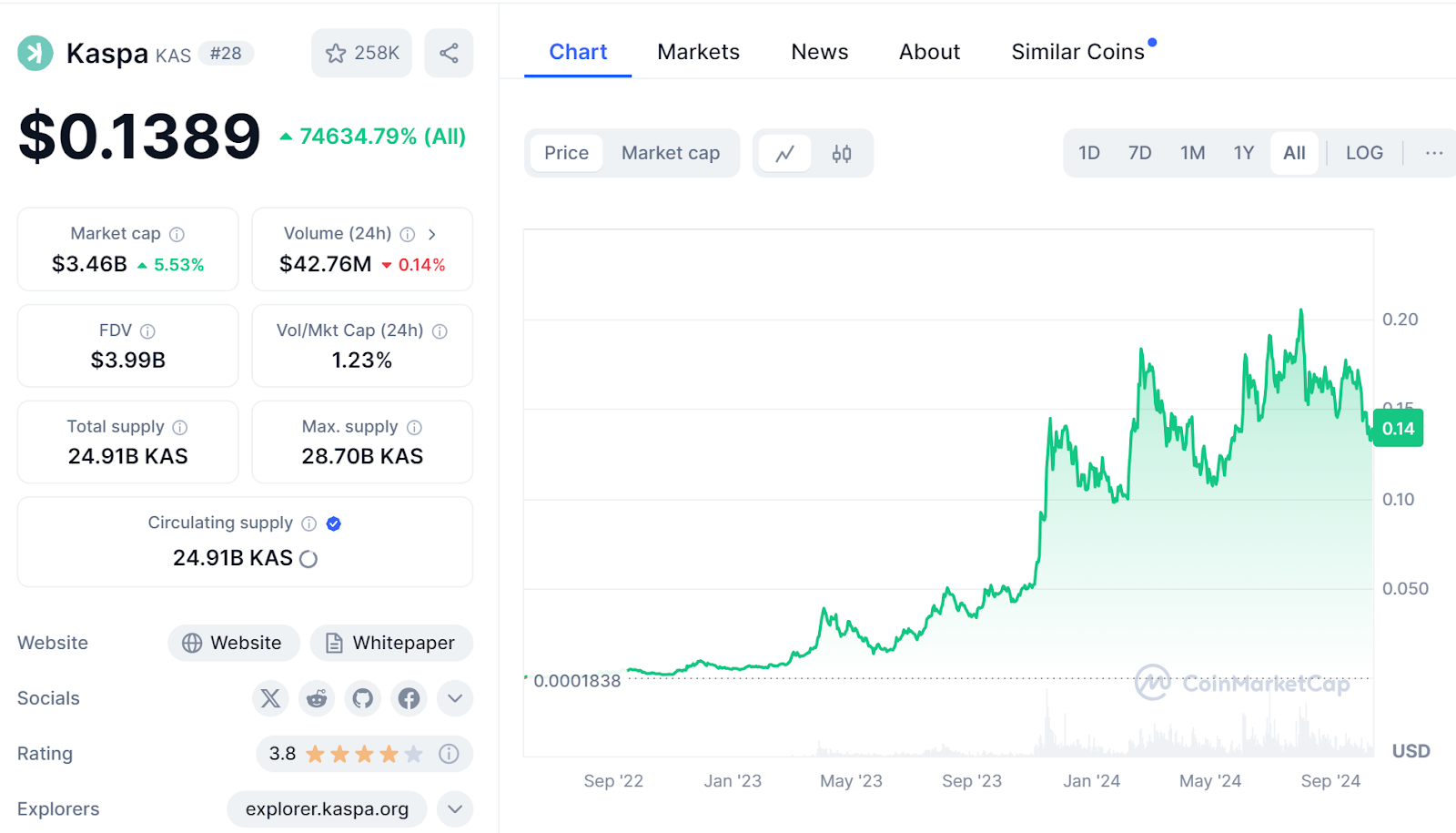
Since the mainnet launch in 2021, Kaspa has a total supply of 28.7 billion KAS, with a current market cap of approximately $3.4 billion. With a strong and supportive community, Kaspa's position in the blockchain industry continues to rise.
As part of its ongoing efforts to strengthen its ecosystem and community, Kaspa has hosted a series of developer-focused events, including the Advances in Financial Technologies in September 2024, the Kaspa Innovation Summit scheduled for October 27 in Hong Kong, and the Australian Crypto Convention in November.
Additionally, the Kaspa Ecosystem Foundation plays a key role in nurturing and expanding the Kaspa ecosystem, providing funding support and strategic guidance, and recently announced a series of plans to promote ecosystem development: Kasplex and KEF Katalyst Program Season 1.
Kasplex is a comprehensive solution aimed at enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of the Kaspa network, integrating data insertion protocols, open-source indexers, and powerful APIs. It currently supports seamless creation and management of KRC-20 tokens and will soon release standards for NFTs. By leveraging Kaspa's high block rate and decentralized proof-of-work (PoW) Layer-1, Kasplex lays the foundation for a diverse ecosystem of decentralized applications.
The KEF Katalyst Program Season 1 is a series of initiatives aimed at accelerating the growth of the Kaspa ecosystem. The first phase of the program received $10 million in funding, covering grants, infrastructure development, and educational activities, aimed at promoting Kaspa, encouraging developer collaboration, and providing a platform for innovative projects.
These recent initiatives launched by Kaspa are all preparations for building the expansion and application of the ecosystem. Next, let’s take a closer look at the current status of Kaspa's projects and technological advancements.
Overview
Kaspa is a Layer-1 blockchain based on a blockDAG structure, utilizing the GHOSTDAG consensus protocol, which is an evolution of the PHANTOM mechanism. The main difference between Kaspa and Bitcoin lies in its structural approach. Bitcoin uses a single-chain structure, while GHOSTDAG employs a directed acyclic graph (DAG), where one block can point to multiple other blocks.
This design improves transaction finality and accelerates block generation speed through parallel processing. Unlike traditional PoW chains, Kaspa uses the KHeavyHash proof-of-work consensus algorithm, optimizing energy efficiency while enhancing hashing power to ensure blockchain security and decentralization. Through innovative pruning techniques, Kaspa minimizes storage requirements, retaining only about three days of transaction history. However, to support future transaction outputs, certain key blocks may still need to be pruned under specific conditions. Kaspa currently operates at a block generation speed of one per second, with plans to scale up to ten per second, and even one hundred per second. Notably, in 2024, Kaspa's smart contracts will transition from GoLang to Rust, and mining nodes began migrating to Rust earlier this year, marking a significant advancement in its technological ecosystem.
Migration from GoLang to Rust
Rust is known for its high performance and safety, aligning with Kaspa's goals of enhancing transaction speed and network capacity. This migration involves rewriting Kaspa's full nodes and related libraries in Rust to leverage modern computing potential and benefit from Rust's active developer community.
Reasons for Kaspa's transition from GoLang to Rust include:
Performance Optimization: Rust is renowned for its exceptional performance, featuring advanced parallel processing capabilities that allow concurrent processing of multiple blocks across CPU threads. This functionality is crucial for Kaspa's blockchain network, especially as it aims to handle a large number of transactions and blocks per second.
Modern Computing Potential: By adopting Rust, Kaspa aims to maximize the capabilities of modern computing hardware and optimize energy efficiency.
Safety and Reliability: Rust prioritizes safety, reducing security vulnerabilities caused by common programming errors. Security is paramount in blockchain networks, and Rust's compile-time safety checks provide additional protection against potential threats.
Community and Ecosystem: The Rust developer community is rapidly expanding. Kaspa's migration to Rust allows it to integrate into this ecosystem and gain access to the rich knowledge, tools, and libraries contributed by Rust developers.
The impact of this migration on the Kaspa network is profound:
Increased Transaction Throughput: By enhancing transaction processing speed, Kaspa aims to significantly increase its transaction throughput, which is essential for the widespread application of its technology. This migration lays the groundwork for Kaspa's future goal of processing 100 blocks per second.
Energy Efficiency: Rust's energy-efficient execution model aligns with Kaspa's commitment to achieving sustainability in blockchain technology. This shift supports a more environmentally friendly approach compared to traditional proof-of-work systems.
Scalability: The efficiency and performance improvements expected from Rust are anticipated to enhance Kaspa's scalability, enabling the network to handle increasing transaction volumes without sacrificing speed or security.
Attracting Developers: The adoption of Rust may attract more developers to the Kaspa project. Rust is highly regarded among developers for its performance and safety features, which could expand the talent pool contributing to the Kaspa ecosystem and innovation.
As of the publication date, over 96.49% of nodes have completed the migration from GoLang to Rust.
Hash Rate
Hash rate is a metric used to measure computational power in a blockchain network, indicating the number of hash calculations that a miner or network can perform per second. A higher hash rate means more calculations are completed per second, thereby increasing the chances of successfully mining and receiving rewards. Miner performance is measured in h/s (hashes per second).
1 Kh/s = 1,000 h/s
1 Mh/s = 1,000 Kh/s = 1,000,000 h/s
1 Gh/s = 1,000 Mh/s = 1,000,000 Kh/s = 1,000,000,000 h/s
1 Th/s = 1,000 Gh/s = 1,000,000 Mh/s = 1,000,000,000 Kh/s = 1,000,000,000,000 h/s
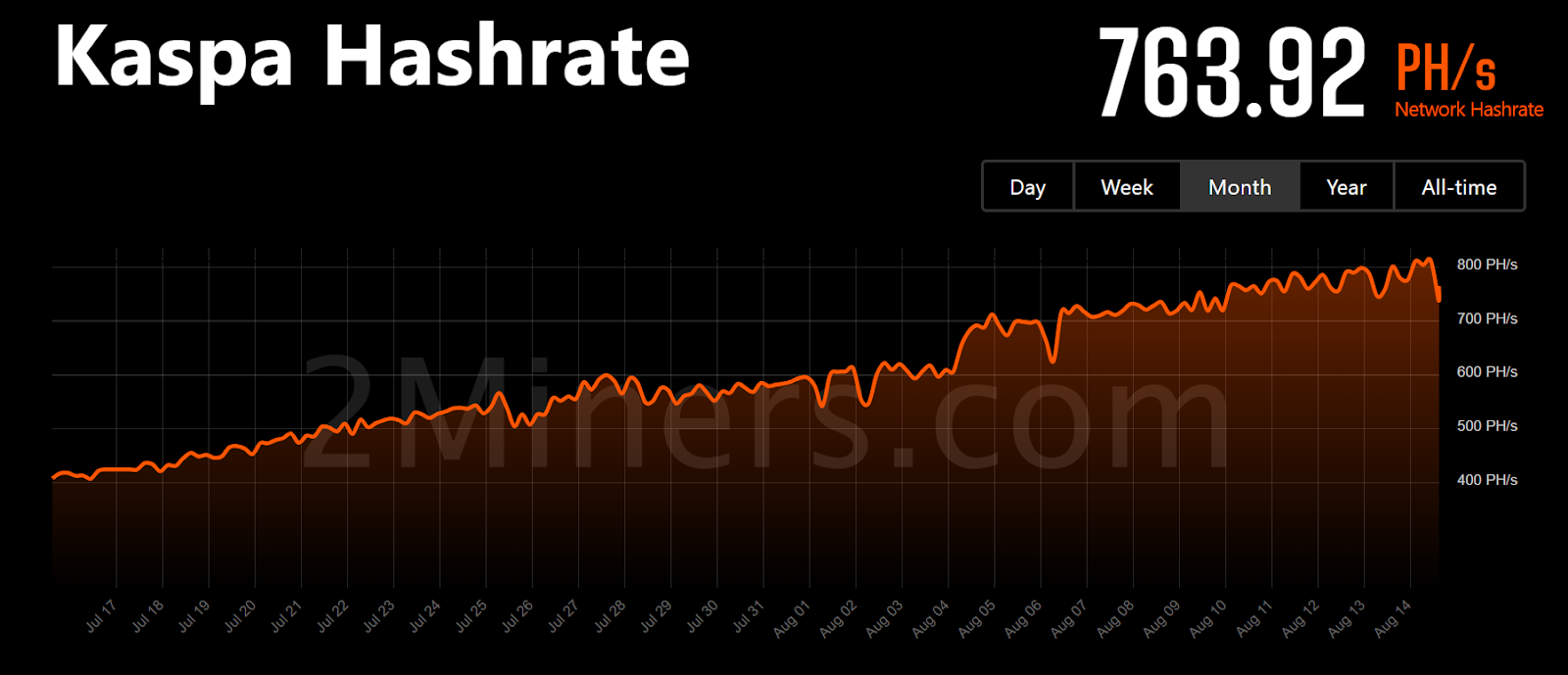
The hash rate of the Kaspa network reflects the overall performance of all miners. Currently, the hash rate of the Kaspa network is 763.92 PH/s, with a peak of 843.44 PH/s on August 13, 2024.
Architecture
Bitcoin operates on the "longest chain" principle, ensuring the integrity of the blockchain by linking honest blocks together, thereby securing the network. However, this approach limits network throughput and scalability due to its sequential processing nature.
Structural Model: Directed Acyclic Graph
Kaspa introduces the PHANTOM protocol based on a directed acyclic graph (DAG), which is a permissionless ledger protocol. Unlike Bitcoin's single-chain structure, PHANTOM allows referencing multiple predecessor blocks, achieving a total ordering of all blocks and transactions while ensuring a consistent set of accepted transactions. The core of PHANTOM lies in the parameter K, which adjusts the protocol's tolerance for simultaneously created blocks, accommodating higher throughput scenarios. When K=0, the protocol resembles Bitcoin's fork-free structure.
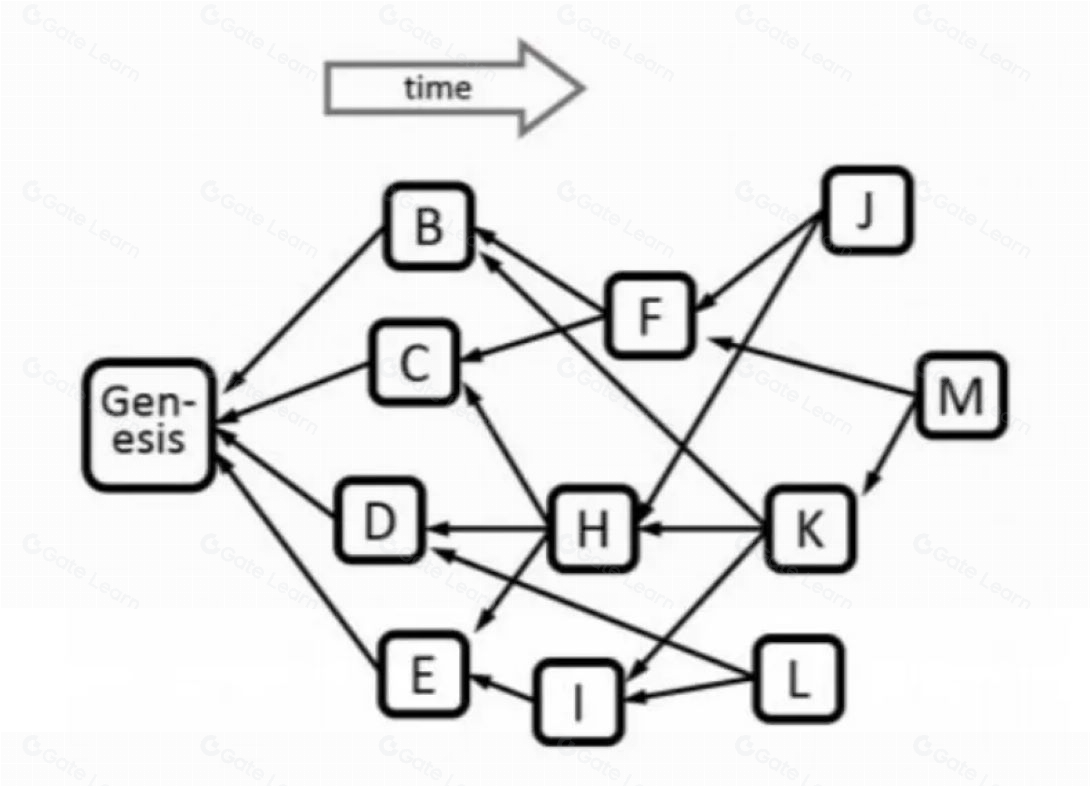
Linear Ordering
To address the double-spending problem, Kaspa employs the GhostDAG protocol. GhostDAG evaluates each block's connectivity within the past block set, selecting the highest-scoring blocks to form the main chain. This main chain constitutes the initial subset, and subsequent blocks vote in order based on this main chain. The entire network votes according to a trend of connectivity from high to low.
Traditional blockchain systems often generate competing blocks when encountering simultaneously created blocks, leading to wasted orphan blocks. GhostDAG resolves this issue by adopting a DAG structure, where blocks can reference multiple parent blocks, forming a BlockDAG rather than a linear chain. This design supports parallel block creation, significantly enhancing system throughput without sacrificing security.
Additionally, the GHOSTDAG protocol includes several sub-protocols, such as block data pruning, SPV proofs, and proof-of-work enhancements, all of which collectively improve performance. Block data pruning reduces the size of the blockchain by discarding unnecessary data, while SPV proofs allow lightweight clients to verify transaction validity without downloading the entire blockchain. These innovations enhance Kaspa's scalability and efficiency in blockchain operations.
Token Economics
Kaspa was fairly launched in November 2021, without pre-mining, pre-sale, or token distribution. Kaspa is fully decentralized, open-source, and community-managed. The total supply cap of the protocol's tokens is 28.7 billion, with a current circulation of 24.9 billion. Kaspa's current total market cap and fully diluted valuation stand at $4 billion.
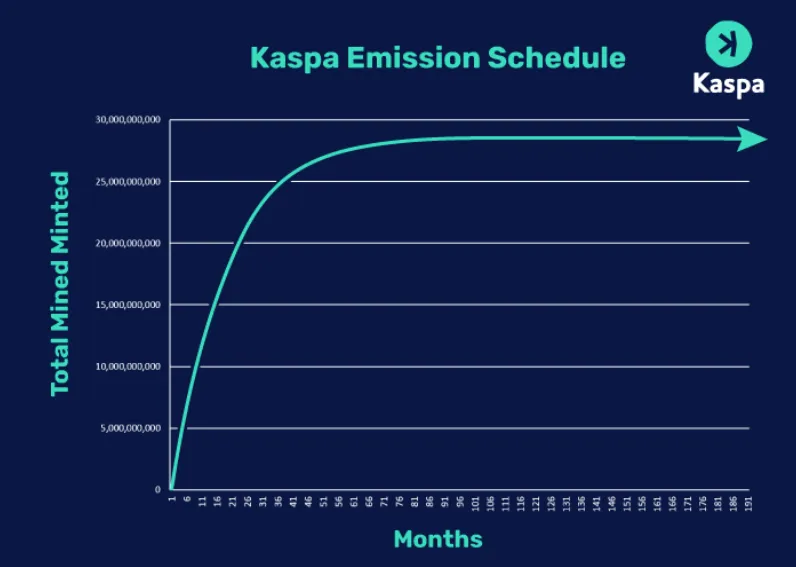
The token issuance design of Kaspa is set to decrease year by year, with a smooth monthly reduction leading to halving each year. Initially, mining could be done through CPU, and the network gradually integrated GPU and ASIC mining capabilities. Kaspa follows a carefully designed issuance plan to manage the growth of token supply.
Mining Collaboration
On June 26, 2024, Marathon Digital announced that its Kaspa mining operations have mined 93 million KAS, valued at approximately $15 million, since launching in September last year.
In May 2023, Marathon began evaluating Kaspa as a potential avenue to diversify its revenue sources while continuing to leverage its existing infrastructure and expertise in digital asset computing. After successfully deploying its first Kaspa ASIC miners in September 2023, the company began scaling its operations. Marathon has purchased approximately 60 PH of KS3, KS5, and KS5 Pro ASIC miners, with profit margins for each unit reaching up to 95% in certain cases, based on current network difficulty and KAS prices. Currently, 30 PH of Kaspa ASIC miners are operating in the company's owned facility in Texas, with the remainder expected to be fully operational by the third quarter of 2024.
"By mining Kaspa, we are able to create a revenue stream that is distinct from Bitcoin, and this stream is directly associated with our core competencies in digital asset computing," said Adam Swick, Chief Growth Officer of Marathon. "With our existing infrastructure, unique relationships with hardware manufacturers, strong balance sheet, and the expertise of our team, Marathon has a unique advantage in mining Kaspa and capitalizing on the high profit margins currently available with Kaspa ASICs. We look forward to continuing to support innovation in the proof-of-work ecosystem while expanding our position as a leader in digital asset computing."
Once fully deployed, Kaspa will account for 1% of Marathon's 1,100 megawatt data center portfolio.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。