User experience is the most important infrastructure before the wave of large-scale applications.
Written by: Pzai, Foresight News
Since the birth of blockchain, crypto geeks have been committed to building an interactive environment and architecture rich in rebellion and fundamentalism. This environment ensures purity while also creating certain barriers. As more and more ordinary people participate in the interactions within the blockchain ecosystem, the trend towards a more mainstream user experience will determine how the next billion users navigate the ocean of cryptocurrency.
When traditional user experience design collides with the new architecture of blockchain, we need to consider how to dismantle the existing barriers one by one. This article analyzes the user experience architecture step by step and, combined with a glimpse into the history of the development of the crypto field, looks at the formation process of user experience in the future of the crypto domain.
From Personal Homepages to the Paradigm Shift of Free Currency
In the interaction of humans with the information dissemination networks they have built, paradigm shifts have always been calculated in terms of "years." In the early internet, most users hosted their own homepages, building information networks based on individual connections. The experiences gained by users were more based on the implicit social connections and sense of belonging generated through the network (or rather, their participation in the construction of the experience as part of the network). A clear example is that early internet communication was heavily laden with ideology, and the deconstruction of language output (e.g., GM :) ) profoundly influenced the subsequent primary languages of communication on the internet.
Subsequently, with the trend of network clustering, a group of internet companies began to seize territory, and most of the experiences we use today stem from this phase. The paradigm shift has begun to strip users of their dominance in the network, instead providing "services" to users through a series of centralized methods. It was likely during this phase that product designers began to pay attention to user experience, as the smoothness of interactions designed for the masses determined their competitive position, a fact proven by the growth of mobile internet. Zhang Yiming of ByteDance believed that recommendation algorithms could create more personalized content for users, aligning with their psychological expectations, leading to the later emergence of Douyin.
In today's crypto field, the author believes it has simultaneously experienced the aforementioned two phases over the past decade. Initially, it represented the ideology of crypto-punk and free currency, where users could build through various means (e.g., running full nodes or participating in technical proposals). Later, with the influx of giants and a significant increase in asset scale and forms, user experience has increasingly become one of the important considerations in protocol design. If we view these paradigm shifts as a linear process, we can say that the crypto field is a return to past ideologies under the trend of clustering, creating and nurturing new interaction and experience paradigms through this return. As large-scale applications approach, we need to seek the Nash equilibrium point among these elements, thus requiring further analysis of crypto user experience.
What is Crypto User Experience?
The term "user experience" originates from cognitive psychologist Donald Norman, referring to a purely subjective feeling established during the user's interaction with a product. Initially a psychological term, it emerged during the flourishing of usability and human-computer interaction in the last century when computer technology was not yet widespread. People began to study the interaction processes and results between individuals' physiology, psychology, and machines, leading to the birth of user experience. In cognitive psychology, user experience is defined at three levels:
- Instinctive Level: This level reflects human instinctive responses, focusing on appearance design and creating a good initial impression, mainly related to visual experience, brand perception, browsing experience, etc.
- Behavioral Level: This level encompasses the feelings users experience during application interactions, including functional experience, content experience, and interactive experience, primarily related to application usability.
- Reflective Level: The highest level of user experience, aimed at shaping the brand value of the project itself, creating memorable experiences for users, allowing them to feel pleasure and satisfaction during the service process, and achieving a sense of identity and self-worth through interaction.
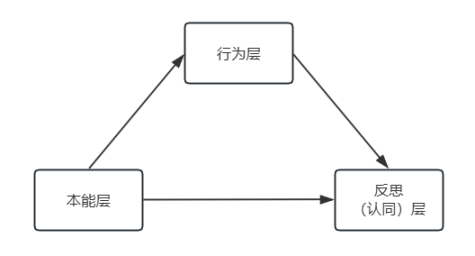
User Experience Hierarchy
Within this research framework, we can abstract the levels of crypto user experience by combining the characteristics of the crypto field:
- Crypto Instinctive Level: As one of the many flowers in the crypto space, a good initial impression for users is reflected in the construction of community atmosphere and front-end presentation, both of which can provide users with initial impressions related to the project while laying the groundwork for the reflective level experience.
- Crypto Behavioral Level: Here, we can break it down into two parts: front-end and contract interaction. The front-end can build more diverse experiences based on contracts, for example, the user interaction optimization of Farcaster Frame combines on-chain experiences with off-chain visualization (rather than just financial transactions on-chain).
- Identity Level: Through the combined effects of the first two levels, users cultivate loyalty in the community by understanding the brand value of the project and are granted emotional value through various incentive forms, gradually involving users in the protocol governance process, thus making them "loyal users" of a project and contributing to the growth of the protocol.
However, before these levels truly form a closed loop of crypto user experience, many projects have not realized the importance of user experience over years of development. Due to some historical legacy issues and the characteristics of the crypto field, they have been unable to complete the construction of user experience. Therefore, the author will explore how crypto user experience needs to transcend itself, even surpassing all other experiences.
How Do We Build It?
The transition from Web2 to Web3 has brought many changes, such as if users want to migrate assets on-chain, they cannot just remember their passwords; or if users want to invest in on-chain products, they must bear the risk of smart contracts being hacked. This learning threshold is vividly reflected in the behavioral level of user experience, and it is precisely this threshold that deters many users. The unique environment derived from the crypto field also brings certain difficulties to the migration of user experience, reflected in the following points:
- Isolation of Circulation Systems: Most existing users' demands for the circulation and transfer of crypto assets need to go through centralized exchanges or onramp/offramp services, severely limiting the circulation within and outside the system. This isolation not only restricts the cross-platform usability of applications (let alone the fact that each chain in the blockchain ecosystem is also fragmented), but also indirectly leads to a gap in user experience at the front end of crypto projects compared to traditional applications, thus limiting the perception of the behavioral level to some extent.
- Cultural Differences: The early cultural origins from crypto-punk brought an extreme pursuit of technology, and the field related to cryptographic technology itself is a very niche circle, with limited outreach weakening the demands for front-end interaction design. The designs related to users' instinctive responses are very limited (assuming users are inherently lazy, the best presentation for a transaction would be one-click processing, but this contradicts the design of self-custody). Additionally, for many front-end design primitives of crypto projects, the strong composability of the underlying layer combined with the complexity of token economic systems leads to a lack of uniformity compared to traditional designs, resulting in fragmentation of user front-end interaction processes, and in many cases, optimal solutions cannot be obtained. (Some DeFi protocols restrict the distribution of their LPs on-chain, and users need to find the corresponding DEX of the protocol to trade for the best depth.)
- Weak User Sustainability: If, during the development of the entire crypto industry, a portion of users can achieve long-term retention, then user experience will become a subset of these users. However, amidst the ebb and flow, many users may completely miss out on crypto projects that could reconstruct their sense of identity. The reality also proves that the product cycles in the existing crypto field cannot build a form of sustainable growth in the traditional sense.
The strong composability unique to the crypto field has also generated many unique interaction layers, which, while intercommunicating, also determine the user interaction experience from zero to one. Former Baidu Chief Product Officer Yu Jun once said: "Essentially, every interaction process between users and products is a transaction. Users may not have incurred monetary costs, but they may have incurred time costs, cognitive and thinking costs, etc. Every interaction and detail design of the experience essentially reduces the transaction costs for users while increasing the benefits they gain during the transaction." Jon Crabb, founder of Web3UX, divides Web3 user experience into four layers: visual layer, functional layer, access layer, and technical layer architecture.
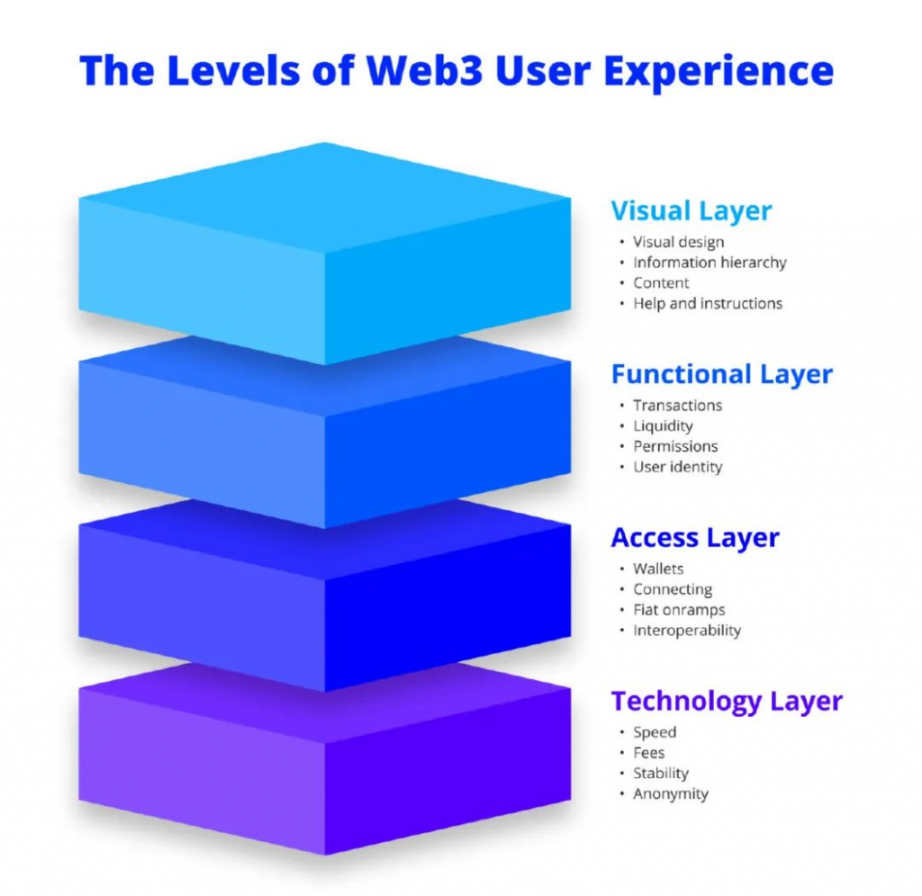
Four Layers of Web3 User Experience Source: Jon Crabb
Visual Layer
At this level, the design related to user experience is relatively similar to Web2 design, but due to the differences in the ecological niches of each protocol, the corresponding design styles can vary greatly. In general, the design at this level should provide maximum accessibility, including reducing the use of jargon and enhancing the prominence of important functions of the protocol.
Functional Layer
In Web3, smart contracts are almost the carriers of all operations. The algorithms and assets derived from smart contracts (such as AMM, NFT, etc.) create experiences different from traditional systems, but such constructions complicate the understanding and execution of transactions. Moreover, the governance derived from this fact allows only a small portion of people to gain entry, which is precisely the key to crypto projects gaining user recognition. Therefore, at the functional level, we can create automated strategies for transactions, unify experiences (e.g., account and asset identity across the entire chain to avoid transaction obstacles caused by asset differences), simplify front-end operations (aggregators), enhance the functionality of governance itself, and enable NFTs to play corresponding roles in certain scenarios.
Access Layer
Users generally access protocols through wallets (software and hardware), and an easy-to-use wallet can greatly simplify the setup process. Many technical solutions are currently working towards this goal (e.g., Passkey login or account abstraction wallets). Additionally, the circulation layer of assets needs enough fiat service providers to build smooth on-chain deposit services. In terms of address readability, on-chain domain services like ENS and 3DNS are creating an increasingly readable environment for users to ensure smoothness. In the future, we may even transcend the existing internet interaction paradigm and participate in various internet activities primarily on-chain.
Technical Layer
In fact, compared to the original payment systems, blockchain can achieve second-level confirmations, but when it merely serves as a settlement layer for on-chain economic activities, it is far from sufficient. The demand for stablecoins is growing in an obvious manner, not to mention that there is already enough depth in on-chain economic activities waiting to be explored. Therefore, the construction of the technical layer of user experience is about "speeding up and reducing costs." As long as a large number of transactions can be processed in seconds, all economic activities will achieve shared prosperity. Additionally, to enhance the connectivity between on-chain and off-chain economic activities, more transaction verification infrastructure (such as ZK proof layers) is needed.
Leveraging Strengths and Avoiding Weaknesses
At this year's EDCON, Ethereum founder Vitalik shared a timeline of the evolution of decentralized Twitter. The former is EtherTweet, built on simple transactions, and it is evident that the entire interaction interface is very rudimentary, lacking any form of social media. The latter is the interface of the decentralized social application Firefly, which shows that the overall front-end presentation can now rival that of Twitter.

Analyzing according to the framework mentioned earlier, the latter has iterated on some key points compared to the former:
- Uniformity of the Front-End: Firefly brings a "unification" to the social media experience, with a standardized interface and interaction model that lowers the interaction threshold for users, while the aggregated experience allows users to manage complex information flows within a single interface.
- Narrowing the Experience Gap: The overall interface benchmarking against X can reduce the learning costs for users in interactions, thereby narrowing the overall experience gap.
- Better Infrastructure: It can be said that without Lens and Farcaster, Firefly could only become X Plus rather than a decentralized social platform. The key lies in the infrastructure laying a foundation that matches and surpasses the original experience for existing users.
Future potential applications for user experience construction can focus on the following points:
- Initial Impression Introduction: Projects can construct a schema for their community (for example, some public chains often use well-known crypto schemas like Pepe, overlaying their main design colors to enhance community vibe), while closely integrating with the community on the front end, allowing users to build their initial understanding of the project through direct community participation.
- Mid-Term Behavioral Construction: Through incentive mechanisms and token economics, while tailoring ecological experience routes for users, a paradigm for overall user interaction can be constructed, along with real-time feedback on user interactions, creating a highly sticky and sustainable interaction mechanism.
- Late-Stage Sense of Identity: Users' sense of self-worth is usually constructed from both behavior and sensory experiences. After the initial user experience construction, reinforcing the sense of participation generated for users (for example, through governance or ecological activities) can enhance users' sense of self-worth while generating sustainable value for the project team.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




