Author: Revc, Golden Finance
I. Preface
The recently popular Bitcoin expansion solution Fractal broke through a fully circulating market value of over 6 billion US dollars on the day of its listing, a feat that took Bitcoin nearly 5 years to achieve. This gives us a new perspective on thinking about the launch mechanism of projects. The market value of POW projects fluctuates dramatically with the project's recognition, while projects with a combination of POW and pre-mining go live with high market value expectations, sparking a series of reflections. Does pre-mining lead to insufficient decentralization at the protocol launch, and further affect the development and mining return expectations of its ecosystem? How to balance the incentives of the ecological community and decentralization?
Within a week of its listing, Fractal supported a fully circulating market value of 6 billion US dollars with an average daily trading volume of 10 million US dollars, in the current sluggish market environment. What exactly allowed Fractal to gain market acceptance, whether it was due to technical innovation or the behavior of market makers? Let's explore Fractal, the Bitcoin expansion solution, with these thoughts in mind.
II. CAT Protocol
The outbreak of CAT20 has once again made Fractal the focus of the market. CAT20 is a token launched by the Fractal network project CAT protocol, which created 4.7 million transactions within two days, with nearly 35,000 holder addresses. As a tokenization protocol, it can define the characteristics and behaviors of tokens using Bitcoin's script language, enabling the creation, transfer, and destruction of tokens.
Key features of the CAT protocol:
- Based on Bitcoin: The CAT protocol uses Bitcoin's UTXO model and script language to implement tokenization, ensuring security, decentralization, and scalability.
- Customizable Tokens: Users can create different types of tokens according to their needs, including transferable, non-transferable, and tokens with specific properties.
- Security Mechanism: The CAT protocol uses a recursive contract mechanism to ensure the security of tokens, preventing malicious behavior and forgery.
- Scalability: The CAT protocol can support a large number of tokens and transactions, with good scalability.
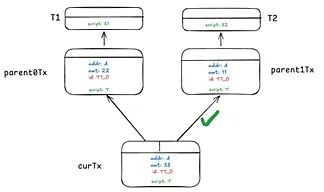
The implementation process of the CAT protocol can be divided into the following steps:
Token Creation: Users can create new tokens by submitting a specific transaction containing the token's attributes and initial state.
Token Transfer: Users can transfer tokens to others by specifying the new owner's address in the transaction.
Token Merge: Multiple tokens of the same type can be merged into one token.
Token Destruction: Users can destroy tokens, making them no longer exist.
The CAT protocol uses a recursive contract mechanism to ensure the security of tokens. This mechanism verifies the legitimacy of token states by embedding conditional statements in each transaction. If the conditional statements are not met, the transaction will be rejected.
The scalability concept of the CAT protocol comes from the Bitcoin opcode OPCAT, which is a proposed opcode in the Bitcoin script aimed at enhancing the functionality of the Bitcoin script by allowing scripts to concatenate two elements from the stack. The current execution mode of the Bitcoin script is linear, lacking loops and basic arithmetic operations, limiting its expressive power. The Bitcoin script cannot directly access certain data in transactions, limiting the complexity of smart contracts. OPCAT enhances the expressive power of the Bitcoin script by concatenating data and performing simple arithmetic operations, enabling Bitcoin to support more complex smart contracts, such as vault contracts, Merkle tree verification, and tree signature. Through OP_CAT, scripts can access more transaction data, enabling finer control and the implementation of recursive restriction clauses that allow constraint conditions to be passed across multiple transactions.
III. Fractal
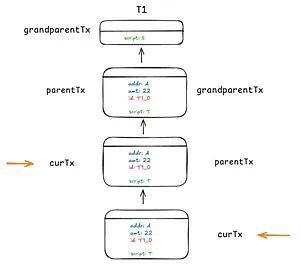
Fractal is a Bitcoin network expansion protocol that encapsulates the Bitcoin core into a deployable software package (BCSP) to run multiple instances on the Bitcoin mainnet. It achieves infinite scalability through nested recursion while maintaining consistency with the Bitcoin core. Similar to virtualization in operating systems, it provides isolation and flexibility.
Fractal ensures that all virtualized instances maintain consistency with the main chain by reusing Bitcoin's consensus mechanism, avoiding consensus disputes caused by forks and enhancing system stability. By instantiating BCSP multiple times, it achieves infinite scalability horizontally and vertically while maintaining structural balance to avoid over-congestion in any specific layer. New instances may require protective mechanisms at startup, such as secure settings at specific block heights. The system's resistance to attacks is enhanced through methods like merged mining. Fractal's distributed on-chain computing can establish a network of multiple BCSP instances, superior to the computational efficiency of a single instance. Unlike on-chain sharding, BCSP instances can be independently deployed and monitored.
Fractal shortens the block confirmation time to 60 seconds or less, improving response speed, increasing storage space, reducing transaction costs, and suitable for applications like ordinal ciphers. The cross-layer elevator can directly transfer assets between different layers without additional relays. Through virtualization and self-replication, Fractal theoretically enhances Bitcoin's processing capabilities and provides new application scenarios for future development, such as optimizing ordinal ciphers and constructing virtual worlds, integrating the cipher community, and allowing the value of ordinal ciphers to overflow into the L1 network.
IV. Reflections
Virtualized instances are relatively easy to understand, but recursion in the application of the Bitcoin network is evidently much more complex. Reusing consensus reduces the complexity of the blockchain system while introducing new entropy. The following are reflections after reading the Fractal Lite paper.
Fractal adopts the same PoW consensus mechanism as Bitcoin. BTC miners can seamlessly switch to mining Fractal blocks using existing ASICs, GPUs, and other hardware. Every 3 blocks, 2 blocks are generated through "permissionless mining," and 1 block is generated through "merged mining." Permissionless mining allows anyone with suitable tools and hardware to mine Fractal blocks, similar to BTC mining. Merged mining is specifically for BTC miners, allowing them to mine BTC blocks and Fractal blocks simultaneously without requiring additional computing power.
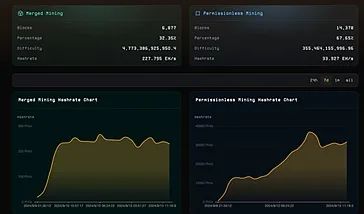
To control the transaction confirmation time to around 30 seconds, Fractal's difficulty adjustment may need to be more frequent than the Bitcoin network. Due to the existence of permissionless and merged mining mechanisms, the network's computing power level is not stable, and the complexity of the difficulty adjustment mechanism may affect network security.
The merged mining mechanism also increases the initial reward burden on the network, requiring Fractal to maintain a coin price of at least $25 to achieve 50% of the mining revenue for 1EH of computing power, compared to the Bitcoin network.
- Bitcoin's revenue for 1EH/10 minutes:
Assuming the block reward for each block is 0.3 BTC, with a price of $60,000 and a total network hash rate of 660EH.
(3.15+0.3)*60000/660≈$313
- Fractal's revenue for 1EH/10 minutes:
Assuming the block reward for each block is 5 FB, with a price of $25, and a merged hash rate of 220E and a permissionless hash rate of 30E
*25*(600/30)/(220*1/3+30*2/3)≈$160
Note: The actual revenue from permissionless mining may be higher. The formula here is for simplified expression only.
The instantiation of BCSP ensures security and consensus through recursion, while the elevator ensures cross-layer asset flow, similar to plug-in ledgers, increasing the network's computing and storage capabilities. However, recursive calls may generate a large number of function call stacks, potentially leading to stack overflow. Debugging recursive code is relatively difficult and requires careful tracking of the function call process. New issues may arise as the network expands and need to be monitored. The early instantiation requires specifying block heights, and whether this process involves centralized operations and the associated risks.
Whether instances can have independent security, i.e., independent difficulty adjustment mechanisms and network rewards to attract computing power, to expand into new use cases beyond ordinal ciphers. But at present, the risks appear to be significant.
V. Comparison of Bitcoin's Expansion Solutions
The following compares the characteristics and challenges of several mainstream expansion solutions. Projects like Fractal aim to enhance the expressive power of the Bitcoin script, enabling Bitcoin to support more complex smart contracts.
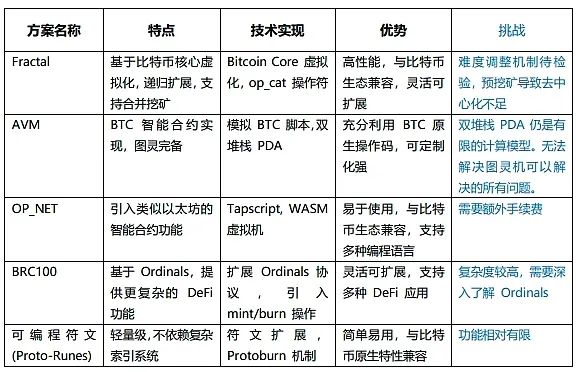
VI. Conclusion
The innovative design of Fractal is commendable. While expanding the Bitcoin network, it leverages existing Bitcoin code and ecosystem. Through recursion, it has created an extension layer compatible with the Bitcoin main chain, significantly improving the network's transaction processing capacity and speed, allowing seamless transition for Bitcoin miners and users. In the future, more expansion solutions will emerge, demonstrating Bitcoin's greater decentralization compared to other ecosystems.
However, as stated in the CAT protocol, mainstream solutions are still in the experimental stage and attention should be paid to network security, especially when it involves changes to core Bitcoin mechanisms such as the difficulty adjustment mechanism, potential hash rate impacts on the Bitcoin shadow chain, and the sustainability of token economic models.
Furthermore, there is a consensus in the market that high market value and low circulation VC tokens should not be brought into the Bitcoin ecosystem. Despite using the POW consensus mechanism, Fractal has 50% of tokens pre-mined, allocated to ecosystem partners, the BRC20 community, large mining pools, and wallet infrastructure, which may pose a high cost of resource integration and limit its development, reducing its decentralization attributes. Cryptocurrency projects should avoid forming crypto oligarchs or crony capitalism and carefully design token distribution mechanisms.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



