We are still in the early stages of the artificial intelligence (AI) era, especially in the deAI era.
Author: Delphi Labs
Translation: Deep Tide TechFlow

This article is written by Luke Saunders (lukedelphi) & Jose Macedo (ZeMariaMacedo).
Artificial intelligence represents the largest technological revolution in history and has sparked an unprecedented technological arms race. Current AI models have entered the top tenth percentile in most standardized university exams and have surpassed humans in many tasks, including AI research itself. Even at the current level, this has had a transformative impact on many industries such as search, customer service, content creation, programming, and education.
We expect that the capabilities, funding, and impact of artificial intelligence will continue to accelerate. All major tech companies are aware of the critical importance of AI to their businesses and are making corresponding investments. NVIDIA's revenue, as the best indicator of AI capital expenditure, is expected to exceed $100 billion in 2024, more than double that of 2023 and more than four times the revenue of the previous year.
Google CEO Sundar Pichai's view on AI investment is:
"For us, the risk of underinvesting in AI is far greater than the risk of overinvesting."
Meanwhile, startups are realizing that AI is a disruptive force that can replace long-standing companies. In the past 18 months, an estimated 830 billion US dollars have been invested in AI startups.
Given that the capabilities of artificial intelligence often grow exponentially with computing power, we are likely to achieve goals similar to general artificial intelligence (AGI) within a decade.
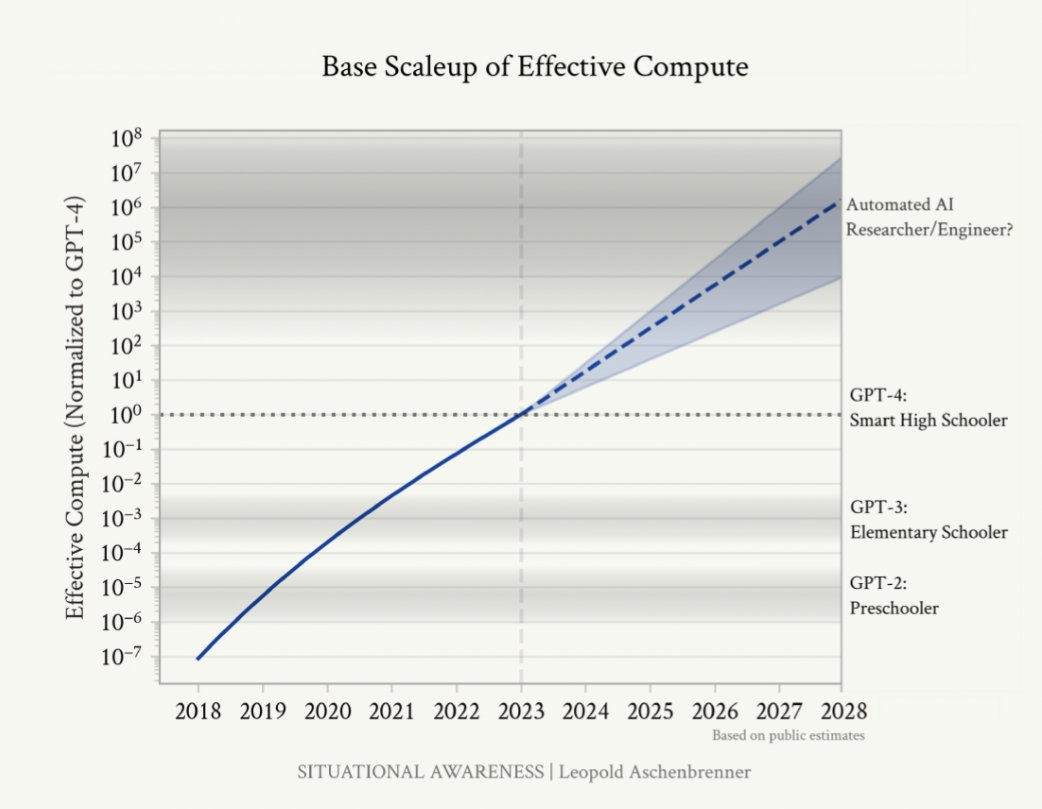
Source: Situational Awareness, Author: leopoldasch
In this article, we believe that the competitive environment will lead to a world with millions of models, and encryption technology is the ideal support for this multi-model world. We will first discuss why we believe a multi-model world is an inevitable result of artificial intelligence. Then, we will introduce the unique advantages that encryption technology provides for artificial intelligence. Finally, we will introduce the technology stack of encryption and artificial intelligence that we believe in and provide case studies of projects that interest us.
The combination of open-source AI and encryption technology has many strong philosophical and ethical reasons, which have been well discussed elsewhere. We fully agree with these views, which is also one of the driving forces behind our development in this field. However, in this article, we will focus on the practical reasons why the combination of encryption technology and AI is likely to succeed, rather than discussing the ethical reasons for its success.
Super Models and Multi-Models
We are now moving towards a world where a few large vertically integrated tech companies produce "super models" that dominate everything else.
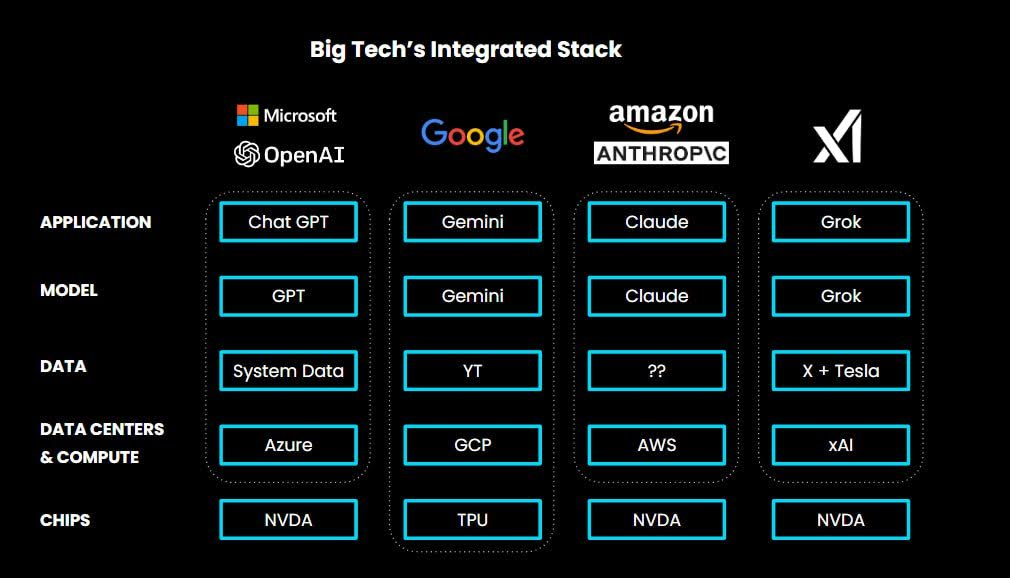
However, we believe this is not the ultimate outcome for several reasons:
Risk Issue: Organizations, entrepreneurs, and developers building AI-based experiences do not want to rely on a single closed-source company, as that company can change models, modify terms of use, or even stop providing services at any time.
Cost-Performance Trade-off: The extremely large, general models favored by large tech companies are inevitably more expensive to train and run. This makes them appear overpriced and overly powerful in many use cases. Although this is not a major consideration at present because profitability is not a concern, as AI develops, people will optimize to achieve the lowest cost for the required performance level. In many tasks, large models are not competitive in this regard. There is a wealth of research supporting this view, showing that smaller, more specialized models can outperform general models in multiple tasks: medical image diagnosis, fraud detection, speech recognition, and more.
Vertical Integration: As Apple has repeatedly demonstrated, the best products often come from vertical integration of the entire technology stack. Ambitious entrepreneurs building AI-driven products will seek to gain a competitive advantage by using their own specialized models. This allows these products to capture more value, attracting more investment.
Privacy Issue: AI will become the core technology in organizational workflows to an extent that no other technology can compare. Many organizations are unwilling to entrust sensitive data to these models.
For these reasons, we believe it is more likely that we will enter a world with many smaller, specialized models that are customized for specific use cases and cost-effective. Application developers and users will use open-source models, such as LLaMA or MistralAI provided models, as a foundation, fine-tuning their own dedicated models, often using proprietary data. Many models will continue to run on servers, but smaller, more privacy-focused applications will run locally on client devices, and other applications that need to resist censorship may use decentralized computing platforms.
This is a world of modular AI building blocks, where developers and entrepreneurs compete to provide value to users, who can choose and combine different services according to their specific needs. Routing, orchestration, synthesis, payment, and various other infrastructure need to be built to dismantle the "God model" technology stack and serve this emerging AI economy. This is also a world of thriving cryptocurrency.
Encryption and Artificial Intelligence
Intuitively, cryptocurrency seems to be an area where practicality can be found in this multi-model world. However, this hype has led to a large allocation of capital in this field by many under-informed investors. Like previous infrastructure bubbles, many projects are receiving funding and being built, and these projects may not necessarily deserve to exist. Therefore, it is difficult to determine which sub-industries in the cryptocurrency and AI fields truly have value, leading many to view the entire field as a meme without fundamental value.
We do not believe this is a Meme, but indeed this multi-model world can theoretically exist without cryptocurrency. Therefore, focusing on the unique differentiating features of cryptocurrency is crucial in helping us create more revolutionary products, or ideally those that cannot be built without cryptocurrency. To do this, we first identify the unique properties of cryptocurrency and how they can be applied to the field of artificial intelligence in a way that produces better products. Then, we will discuss the technology stack of encryption and artificial intelligence, and provide examples of use cases that we believe are relevant.
Coordination Layer: Cryptocurrency rails excel in facilitating collective coordination without the need for centralized control. It is particularly effective in overcoming the inherent "chicken and egg" problem in most markets, and can rapidly attract a large number of new users through encrypted native incentives.
- Small teams building internal models may not have direct access to all the resources they need. For example, while large tech companies' AI labs may have their own computing resources, small teams do not have the same computing resources. Similarly, these teams need to access data and may need to recruit a diverse group of people to provide human feedback. These needs are well suited to be met through specialized markets, and we believe that markets utilizing encrypted infrastructure will have a competitive advantage over those that do not.
Open, Permissionless APIs: Cryptocurrency rails as an open, permissionless API that anyone can access from anywhere without the need for KYC, credit cards, or any other form of approval. This is crucial for AI agents, as they need to be able to access services, deploy code, and transfer value without human intervention in order to act autonomously. This enables science fiction-like behaviors, such as agent collectives, agents paying each other for services, incurring debts, and even raising funds.
Trustlessness: Cryptocurrency rails are typically trustless, meaning you can obtain cryptographic guarantees that they will not change, access will not be unexpectedly revoked, and you can verify that execution meets expectations. This is crucial for modular AI architectures, as builders need to combine a series of primitives they cannot control, unlike integrated approaches, and users essentially need to trust many services, many of which users may not even be aware of.
Resistance to Censorship: Applications running on encrypted rails as immutable contracts are unstoppable. Even if they are upgradeable, they are typically governed by a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that requires consensus. Assuming the capabilities of artificial intelligence are as powerful as we expect, governments are likely to attempt to control and influence it. In fact, we have already seen this happen. Just as Bitcoin and cryptocurrency provide a currency/financial infrastructure outside the system, the combination of encryption and artificial intelligence provides unstoppable intelligence.
Intersection of Encryption and Artificial Intelligence
Given these benefits, what applications do we find particularly interesting at the intersection of encryption and artificial intelligence?
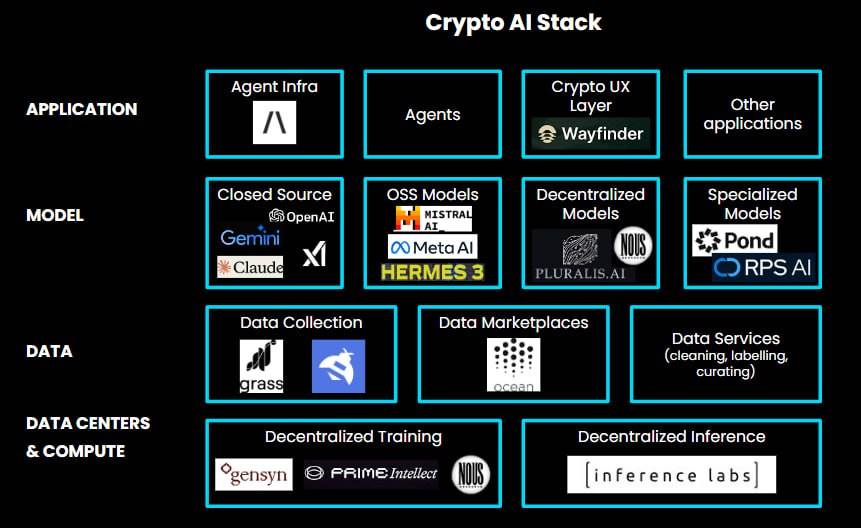
Data Centers and Computing
The use of model computation can be broadly categorized into two types: training and inference. We believe that using decentralized computing in both of these aspects is significant, and we will discuss each separately.
Decentralized Training
Distributed computing currently faces challenges because communication and latency requirements between nodes during the training process are very strict. Many teams are trying to solve this problem, and given the potential scale of the rewards and the talent of the participants, we believe this problem is likely to be solved. Some noteworthy approaches include DisTrO by NousResearch and OpenDiLoCo by PrimeIntellect.
In addition to solving the technical challenges of distributed training and building a product that simplifies this complexity, the winners must figure out:
How to ensure quality and accountability on a permissionless network
How to incentivize the supply side, ideally data centers and clusters rather than consumer-grade hardware. Token incentives may be a fundamental strategy to incentivize the supply side, and more creative approaches may include giving computational providers ownership of the final model.
Fundamentally, the advantage of the distributed computing market is the ability to leverage the lowest marginal cost of compute globally. As existing service providers' costs rise, more and more companies and organizations are starting to push back and look for cheaper alternatives, making this increasingly important. Disadvantages include latency, heterogeneous hardware, and the lack of optimizations and economies of scale that come with building and operating proprietary data centers. The future situation remains to be seen.
Verifiable Inference
Overall, we view use cases for verifiable inference as expanding trust-minimized systems with AI capabilities. Embedding models into smart contracts is not practical, but models can be run off-chain, and proofs of their expected operation can be published on-chain. For example, projects can delegate governance decisions (e.g., decisions about risk parameters in money markets) to off-chain models without the need for trust.
This concept can also be more generally applied to open-source or closed-source models, providing users with assurances that the output comes from the model they expect. As applications and users increasingly use AI for more critical tasks, this may become increasingly important. There are many projects addressing this challenge in different ways, such as Inference Labs (inference_labs), an investment project of Delphi Ventures.
Data
Today, training large language models (LLMs) is a multi-step process that requires various types of data and human intervention. This process begins with pre-training, where large language models are trained using cleaned and curated public crawl data and other freely available datasets. In the fine-tuning phase, these models are trained on smaller, more specific labeled datasets to master domain-specific knowledge (e.g., chemistry), often requiring expert assistance.
To ensure fresh or proprietary data, AI labs typically collaborate with owners of large data sources. For example, OpenAI signed a rumored $60 million deal with Reddit. Similarly, The Wall Street Journal reported that the five-year deal between News Corp and OpenAI is valued at over $250 million. Clearly, the value of data has never been greater.
We believe that encrypted networks can effectively help teams access the data and resources they need at each stage. One of the most interesting areas may be data collection, and we believe that encrypted incentive mechanisms are well suited to drive the supply side of data collection and uncover a wealth of important long-tail data sources.
For example, Grass AI (getgrass_io) encourages users to share their idle internet bandwidth to help crawl data on the web, which is then structured, cleaned, and provided for AI training. If Grass can establish enough supply, it can effectively serve as an API key to provide the latest internet data for models.
Hivemapper is another good example—launched in November 2022, the network collects millions of kilometers of road images every week, covering 25% of the global area. It is evident that similar models can be applied to other forms of multimodal data and monetized by selling to AI labs.
As demonstrated by the NewsCorp and Reddit deal, many companies possess valuable data, but either lack the scale or connections to AI labs to monetize it. Similarly, AI labs may find it not worthwhile to transact with individual small-scale suppliers. A well-designed data market can mitigate this issue by connecting suppliers with AI labs in a unified manner. There are challenges, primarily addressing data quality and the substitutability of APIs and data.
Finally, data preparation is a series of important tasks, including labeling, cleaning, data augmentation, transformation, etc. A small team may not have all these skills and may seek outsourcing. Scale AI (scale_AI) is a centralized company providing these services—currently estimated to have an annual revenue of about $700 million and growing rapidly. We believe that well-designed markets and workflow systems based on encryption technology will be effective here. Lightworks is a company invested in by Delphi Ventures, along with several other companies—all in the early stages.
Models
According to Delphi Digital's report The Tower & The Square, the production and control of AI models are almost entirely controlled by "big companies" and governments. This is a more dystopian state than government-controlled currency, as it allows them not only to control one of the most important economic resources, but also to control the narrative by censoring and manipulating information, excluding certain "undesirable" people, using private AI interactions against them, or simply maximizing ad revenue using AI.
Many smart people are working hard to create a "square"—a decentralized network aimed at producing a completely neutral, censorship-resistant model accessible to everyone. Therefore, just as Bitcoin and cryptocurrency provide a currency/financial infrastructure outside the system, crypto x AI will provide an intelligent system outside the system.
Such projects aim to create a powerful model that competes with GPT and LLaMA by decentralizing every step of the model creation process—networks responsible for acquiring and preparing data, training on their own decentralized computing, running inference on the same computing, and coordinating the entire process through decentralized governance. None of the parts of this process are centralized, so the model is truly owned by the community and cannot be controlled by the "tower".
Clearly, creating a decentralized model that comes close to cutting-edge models in any aspect will be very challenging. We cannot expect most users to accept a lower-quality product for ethical reasons. We view these projects as a "moonshot," unlikely to succeed, but if successful, extremely valuable—we sincerely hope they succeed.
It is worth mentioning that centralized AI labs, embracing the idea of cryptocurrency, may have tokens or use encryption technology in other ways.
NousResearch and PondGNN are some examples of projects invested in by Delphi Ventures. Finally, model creation infrastructure such as opentensor's Bittensor is part of this model architecture. Bittensor has been discussed in depth elsewhere, so we will not discuss its pros and cons further.
Use Cases
In a recent speech, Eric Schmidt mentioned:
"If TikTok is banned, I suggest that each of you do this: tell your large language model (LLM), 'Make me a copy of TikTok, steal all the users, steal all the music, customize it to my preferences, make this program in the next 30 seconds, release it, and if it doesn't go viral within an hour, take similar measures.'"
This statement illustrates the immense capabilities we expect intelligent agents to have. But to autonomously carry out these tasks, these agents need to be able to use various services without human intervention—transfer value and establish economic relationships, deploy and execute code without permission.
Traditional banking apps, KYC (Know Your Customer), and registration processes are not suitable for these intelligent agents. Inevitably, they will encounter a system designed for humans and inaccessible without help.
Encryption technology infrastructure provides the perfect platform. It offers a foundation for the operations of intelligent agents that is permissionless, trustless, and resistant to censorship. If they need to deploy an application, they can do so directly on the chain. If they need to pay for certain fees, they can send tokens. The code and data of on-chain services are open and consistent, so intelligent agents can understand and interact without the need for APIs or documentation.
Intelligent agents can also act as catalysts for on-chain activities in multiple ways. Shifting the user experience (UX) paradigm from people clicking buttons on a website to interacting through our AI personal assistant can simplify the notorious onboarding complexity of the crypto space, thus mitigating one of the major barriers to attracting new users.
Projects like Wayfinder (AIWayfinder), Autonolas (Autonolas), DAIN (dainprotocol), and Almanak (Almanak__) are moving towards this future.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become the most powerful and important resource of the 21st century, profoundly impacting society. A future controlled entirely by large tech companies and nations is a dystopian future we do not want to see. In this article, we have attempted to demonstrate a path where encryption technology prevents this monopoly, not by expecting people to use solutions for philosophical reasons, but by providing truly better solutions for developers and users.
We are still in the early stages of the AI era, especially in the deAI era. There is still much work to be done to guide us from the current state to the future discussed in this article. At Delphi Labs, we are passionate about the future of encryption technology and AI, and we hope to actively shape this future by collaborating with top developers in the field.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




