1. Preface
In 2023, AICoin brought new vitality and possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Subsequently, in early 2024, Bitcoin set a new historical high of $73,000 and underwent a halving event, once again attracting market attention.
The proven security and network effects of Bitcoin have attracted many developers who view Bitcoin as the foundational layer of blockchain. These developers are working on building various Layer2 projects on top of the Bitcoin base layer. In this article, we will introduce the early and recent Layer2 projects of Bitcoin.
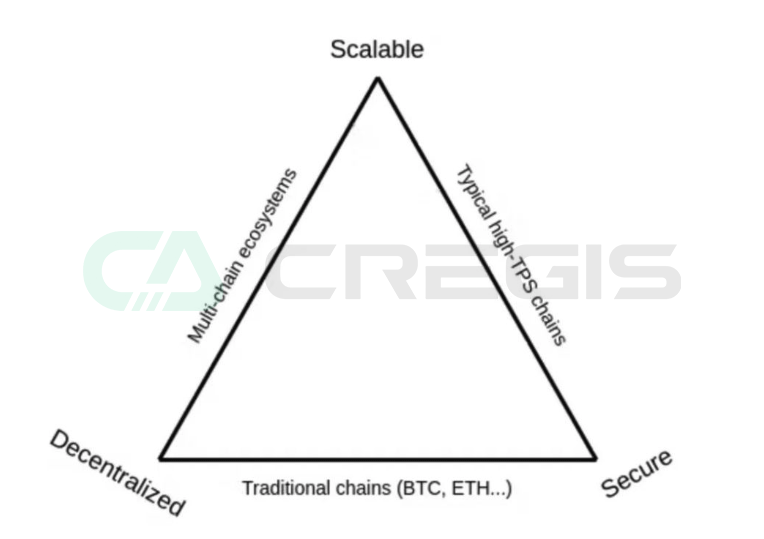
Why Does Bitcoin Need Layer2?
According to the "trilemma of scalability," it is difficult for a distributed network to simultaneously balance decentralization, security, and scalability. The Bitcoin network has over 75,000 core nodes, making it extremely decentralized and widely recognized as the most secure blockchain. However, the Bitcoin network can only process 3-5 transactions per second, making it unable to scale. One potential solution to the scalability issue is Bitcoin Layer2 technology, which aims to improve Bitcoin's scalability, enabling it to handle a large number of transactions without reducing transaction speed or increasing transaction fees.
2. Early Construction Projects of Bitcoin Layer2
Currently, the total locked value (TVL) of Bitcoin's Layer2 (L2) projects is only a small fraction of Bitcoin's market value. The total TVL of the four most well-known L2 projects is approximately $700 million, accounting for only about 0.15% of the entire L2 market. This indicates that the Bitcoin Layer2 ecosystem is still in its early stages, especially compared to the Layer2 market on other blockchains.
However, the situation is quietly changing. The Lightning Network continues to grow steadily, Stacks is committed to major upgrades to drive the development of the Bitcoin smart contract market, and Rootstock is also continuously upgrading. Currently, existing L2 solutions on Bitcoin have different goals, with some aiming to improve Bitcoin network scalability, while others aim to enhance its expressive programmability.
(1) Lightning Network
As a second-layer solution for Bitcoin, the Lightning Network aims to address Bitcoin's scalability issues, increase transaction throughput, and reduce transaction fees. Through payment channels, users can conduct off-chain transactions, avoiding the competition for block space on the Bitcoin blockchain or waiting for L1 consensus, thereby improving efficiency. When users decide to complete transactions conducted through payment channels, they can choose to close the channel and settle off-chain activities on the Bitcoin network. The total locked value of the Lightning Network currently is:
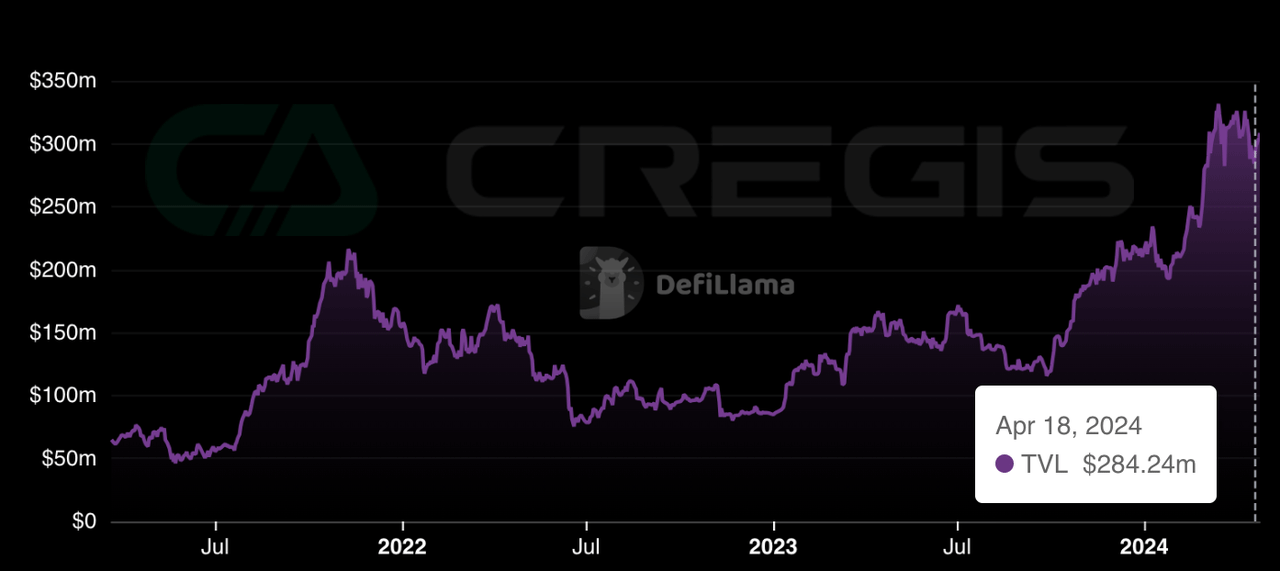
The design of the Lightning Network enables it to facilitate over 40 million transactions per second, far exceeding other blockchains and traditional payment channels. Additionally, the Lightning Network significantly reduces transaction fees, with very low base fees and rates. As the usage of the Lightning Network increases, these fees continue to decrease.
More users and businesses are adopting the Lightning Network to reduce transaction costs and enhance the practicality of Bitcoin. Integration at the government and corporate levels has also driven the application of the Lightning Network, such as the Salvadoran government adopting Bitcoin as legal tender and being compatible with the government-commissioned ChivoWallet. Companies like Twitter and CashApp have also added support for the Lightning Network on their platforms.
The market is optimistic about the future prospects of the Lightning Network, with many projects and investors dedicated to building L2 networks. For example, Block, a Bitcoin startup company under Jack Dorsey, launched a new venture capital firm called "c=", focusing on providing new financing tools and services on the Lightning Network. Meanwhile, companies like Spiral are developing the Lightning Network Development Kit (LDK) to improve the user experience of the Lightning Network and increase its appeal to mainstream users. In addition, the Lightning Network core team Lightning Labs introduced the "Taro" upgrade to leverage the Taproot upgrade for the Bitcoin network, enabling users to issue and transfer synthetic assets, tokens, and NFTs on Bitcoin.
Finally, companies like Zeebeedee and Strike are in discussions with different countries for fiat currency deposits, aiming to attract more users to join the Lightning Network and provide international remittance services, expanding its use cases.
(2) Stacks
Stacks refers to itself as the "Bitcoin layer," meaning it is a second-layer solution running on the Bitcoin blockchain. Although it is not a sidechain, it leverages the security of Bitcoin and incentivizes miners and transaction processing through the introduction of the STX token and a consensus mechanism called PoX. Stacks allows developers to build various DApps, especially in the DeFi and NFT fields. The total locked value of Stacks currently is:
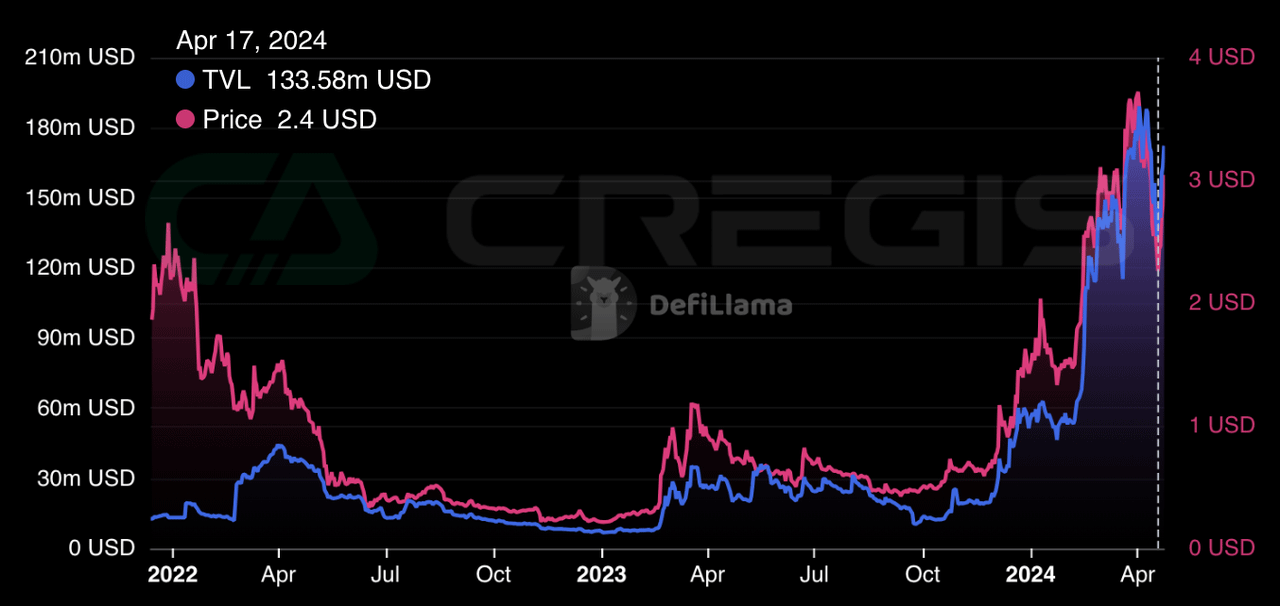
Currently, Stacks has introduced sBTC, an asset pegged to Bitcoin, allowing users to transact with sBTC equivalent to Bitcoin on the Stacks layer. This will further drive the development of DeFi and NFT use cases on Stacks and is expected to unlock capital within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Additionally, Stacks has undergone an upgrade called Nakamoto to fully utilize the security of Bitcoin to confirm transactions on the Stacks layer.
Recently, due to discussions about Ordinals and Runes and Stacks' role in increasing Bitcoin use cases, there has been a noticeable increase in interest in Stacks. Founder Muneeb Ali has also actively participated in top cryptocurrency-related podcasts. Investors may be preparing for the upcoming Stacks upgrade, and everyone is closely watching sBTC and its potential impact on Bitcoin.
(3) Rootstock
Rootstock (RSK) is an EVM-compatible sidechain for general Bitcoin smart contracts. It adopts a unique variant of the Bitcoin Nakamoto consensus called DECOR+, enabling RSK to merge mine with Bitcoin. SmartBitcoin (RBTC) is the native currency within RSK, pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin and used to pay transaction fees. The total locked value of Rootstock currently is:
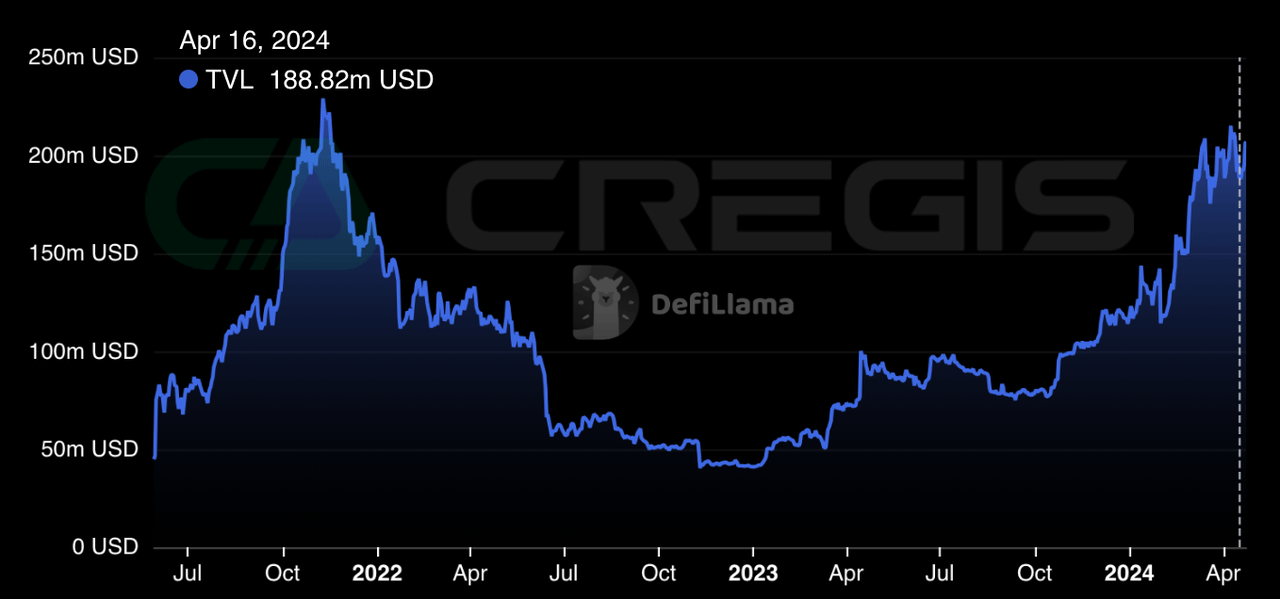
RSK is connected to Bitcoin L1 through Powpeg, allowing BTC to be transferred between the two chains. Initially, Powpeg was managed by an alliance responsible for managing a multi-signature wallet, and RSK further increased the decentralization of Powpeg. However, Powpeg still requires a certain level of trust, as BTC withdrawal requests require approval from at least 51% of the alliance members. Currently, nine members support Powpeg.
One of RSK's key advantages is its virtual machine (RVM) compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), meaning RSK smart contracts can be written in the Solidity language. Sovryn is a relatively well-known RSK project, a non-custodial smart contract platform supporting Bitcoin lending and leveraged trading. RSK recently announced the removal of the supply limit for RBTC, expanding the supply to be equivalent to BTC, i.e., 21 million coins. This move is significant for Bitcoin DeFi, as the previous supply limit restricted activities on RSK. Removing the supply limit may attract more developer attention and encourage them to build more DApps on RSK.
3. New Bitcoin Layer2 Projects
(1) BEVM
BEVM was founded in 2023 and is a decentralized Bitcoin Layer2 compatible with EVM. Based on technologies such as the Schnorr signature algorithm brought by the Taproot upgrade, BEVM allows BTC to cross-chain to the second layer in a decentralized manner from the Bitcoin mainnet. As BEVM is EVM-compatible, all DApps running in the Ethereum ecosystem can run on BTCLayer2 and use BTC as Gas.
On November 29, 2023, BEVM released its whitepaper. Currently, BEVM has launched the testnet ChainX. According to the annual data of the BEVM testnet in 2023, the total transaction volume was 2.77 million, the total number of active addresses was 55,000, and the TVL reached 119.56 BTC (approximately $5.09 million). Recently, the BEVM testnet launched the first script protocol Bevscriptions, processing 3 million transactions in 6 hours, with a tps of around 150.
In December 2023, BEVM initiated the first Odyssey event, which has now ended. BEVM founder Gavin (@gguoss) stated that the second phase is expected to start on January 15 and will invite 10-20 ecological projects to participate. The second phase will be named after the location of the first BTC block mined by Satoshi Nakamoto, "Helsinki," instead of using "Odyssey."
Currently, the BEVM ecosystem includes over 20 projects, such as the BTC full-chain DEX OmniSwap and the decentralized signature protocol BoolNetwork.
(2) B²Network
B²Network was founded in 2022 and is a Bitcoin Layer2 network based on ZK-Rollup, compatible with EVM, allowing seamless deployment of DApps for EVM ecosystem developers. The network participated in the November 2023 ABCDE Bitcoin ecosystem project roadshow and ultimately received investment. According to ABCDE, the core members of the B²Network technical team come from mainstream Web3 open-source communities such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, Cosmos, and Sui, and have received multiple grant support. The team specializes in Web3Infra products such as blockchain Layer1, Layer2, cross-chain, and account abstraction, with mature engineering capabilities.
On December 18, 2023, B²Network announced the launch of the Alpha testnet MYTICA with partners and openly recruited ecological developers. Partners and developers can deploy DApps on the B²Network testnet. The ecological project Meson, a cross-chain protocol supporting stablecoin USDC, has been deployed on the B²Network Alpha testnet. Meson is a cross-chain protocol focused on speed, stability, security, and low fees, supporting the free circulation of mainstream digital assets such as ETH, BNB, USDC, and USDT between B²Network and over 30 mainstream public chains.
(3) Dovi
Dovi was founded in 2023 and is a Bitcoin Layer2 compatible with EVM smart contracts. In November 2023, Dovi officially released its whitepaper, introducing technologies integrated with Schnorr signatures and MAST structures to enhance transaction privacy, optimize data size, and verification processes. Additionally, Dovi has implemented a flexible framework for issuing various asset types beyond Bitcoin and enabling cross-chain asset transfers.
KuCoinLabs announced a strategic investment in Dovi in December 2023, and its native token DOVI was listed on the KuCoin trading platform on December 12 of the same year. The distribution of DOVI tokens followed a fair launch model, with all 15 million tokens claimed within 4 hours of listing. As of January 15, the fully diluted market value of DOVI is approximately $9.4 million. Users can currently stake DOVI on the official website to receive rewards.
The next step for Dovi is to launch the testnet, establish a developer community and ecosystem support, and release DoviV1. This initiative will further develop the Dovi ecosystem, attracting more developers and users to participate.
(4) MapProtocol
MAPProtocol is a promising project, especially in addressing cross-chain interoperability. By leveraging the security of Bitcoin, MAPProtocol provides a seamless interaction for other public chain assets and users with the Bitcoin network, which will enhance the security and interoperability of the entire blockchain ecosystem.
The recent strategic investments from DWFLabs and WaterdripCapital undoubtedly provide strong support for the project's development, indicating market recognition and expectations for the project.
The token burn measures for MAP and MAPO tokens not only help reduce token circulation and increase token scarcity but also contribute to increasing the token's value. The current fully diluted market value is approximately $260 million, demonstrating market recognition of the potential value of MAPProtocol, with the potential to further increase as the project develops and adoption grows.
Overall, MAPProtocol's innovation in cross-chain interoperability and the investment support it has received lay a solid foundation for its future development.
(5) MerlinChain
MerlinChain is a ZKRollup Bitcoin Layer2 network that supports multiple types of native Bitcoin assets and is compatible with EVM, launched by the well-known development team of BRC-420 Blue Box and Bitmap. According to the official website and some research reports, Merlin is a solution that integrates ZK-Rollup network, decentralized oracle, and on-chain BTC anti-fraud module for the Bitcoin Layer2.
From MerlinChain's official website, its Bridge property can transfer assets from BTC to the second layer network, reducing transaction fees, representing a typical solution that addresses pain points.
This integrated solution of ZK-Rollup, oracle, and anti-fraud module is expected to bring more innovation and development to the Bitcoin ecosystem, providing a more efficient and secure trading experience, and attracting more users and developers to participate.
(6) Bison
Bison was founded in 2023 and is a native zk-rollup for Bitcoin, aiming to increase transaction speed while implementing advanced features on native Bitcoin. Developers can use zk-rollup to build innovative DeFi solutions, such as trading platforms, lending services, and automated market makers.
Bison also participated in the ABCDE Bitcoin ecosystem project roadshow. According to the introduction, the Bison solution enables fast and secure transactions using zero-knowledge proofs and Ordinals. All data is anchored back to Bitcoin to enhance security. Bison can achieve 2,200 transactions per second, with fees only 1/36 of Bitcoin's.
The Bison team includes contributors to Starknet's own code, indicating that the team has rich blockchain technology experience and expertise, capable of developing efficient and secure solutions. As Bison continues to develop in the Bitcoin ecosystem, it is expected to bring more innovation and convenience to Bitcoin users and developers.
4. The Next Step in the Bitcoin Ecosystem: Smart Contract Market
For years, Bitcoin has been facing various challenges, including a lack of developer tools, slow and cumbersome infrastructure, and seemingly limited innovation compared to smart contract platforms such as Ethereum, BNBChain, and Solana. However, recent developments suggest a change in the situation. Developers can finally showcase their skills within the Bitcoin ecosystem, working tirelessly to drive updates at an unprecedented pace, all driven by natural demand. This is crucial because when an ecosystem faces real, natural user demands, these demands inherently drive continuous innovation and product development, forming a virtuous cycle and rapidly improving the situation.
(1) BitVM
Robin Linus, the project lead of ZeroSync, announced a paper on BitVM on October 9. In simple terms, BitVM is a virtual machine for the Bitcoin network, achieving Turing completeness through off-chain execution and on-chain validation without changing the consensus rules of the Bitcoin network.
Compared to Ethereum smart contracts, BitVM has significant differences. Ethereum smart contracts can support multi-party transactions, while BitVM's design can only support two-party transaction exchanges. Most of BitVM's transaction processing occurs off-chain, minimizing the impact on the underlying Bitcoin blockchain. Unlike BitVM, EVM is an on-chain engine where all operations take place within the native environment of Ethereum. BitVM is an optional additional engine for the Bitcoin blockchain, and its operations do not require BitVM. In contrast, EVM is an indispensable part of the Ethereum blockchain; without EVM, there would be no Ethereum.
BitVM's functionality is achieved through the Bitcoin Taproot upgrade. BitVM relies primarily on the taproot address matrix (taptree), similar to program instructions in binary circuits. In this framework, the spending condition instructions of UTXOs in each Script script are considered as the smallest unit of a program, generating 0 or 1 through specific code in the taproot address, forming the taptree. The execution result of the entire taptree is the textual effect of a binary circuit, equivalent to an executable binary program. The complexity of the program depends on the number of combined taproot addresses; the more addresses, the richer the pre-set instructions in the Script, and the more complex the programs that taptree can execute.
Most of BitVM's processing occurs off-chain, where off-chain processed transactions are bundled and published to the underlying Bitcoin blockchain using a validity confirmation model similar to that used in optimistic rollups. Additionally, BitVM uses a model that combines fraud proofs with a challenge-response protocol to process and verify transactions between two parties (prover and verifier). The prover initiates the computation task, sends it through a channel established between themselves and the verifier, and the verifier then confirms the validity of the computation. Once verified, the transaction is added to the compiled batch for publication to the underlying Bitcoin blockchain.
(2) RGB
Maintained and updated by the LNP/BP Association, RGB is a smart contract system that supports the Bitcoin network and the Lightning Network. The RGB protocol proposes a more scalable, privacy-focused, and future-oriented solution, with its cornerstone being the concept of client-side validation and single-use seals proposed by Peter Todd in 2017.
The core idea of RGB is to use the Bitcoin blockchain only when necessary, leveraging proof of work and network decentralization to achieve double-spend protection and censorship resistance. All token transfer validation work is removed from the global consensus layer and placed off-chain, verified only by the client of the receiving party.
So how does it work? In RGB, tokens essentially belong to a Bitcoin UTXO (whether an existing UTXO or a temporarily created one), and to transfer tokens, you need to spend this UTXO. When spending this UTXO, the Bitcoin transaction must include a commitment to a message, the content of which is the payment information for RGB, defining the inputs, where the tokens will be sent, the asset's ID, quantity, the spending transaction, and any other required additional data.
The specific payment information for RGB is transmitted off-chain through dedicated communication channels, from the payer's client to the receiver's client, and verified by the latter to ensure it does not violate the rules of the RGB protocol. As a result, blockchain observers will not be able to obtain any information about RGB user activity.
However, verifying the received payment information is not enough to ensure that the sender truly owns the assets they are sending to you. Therefore, to ensure the finality of the received transactions, you must also receive the entire transaction history of these tokens from the payer, from the current one all the way back to their initial issuance. By verifying all transaction histories, you can ensure that the assets have not been inflated, and all spending conditions attached to the assets have been met.
Conclusion
Bitcoin Layer2 is an important part of modern Web3 development. If Bitcoin wants to maintain its position as one of the primary blockchain networks, it needs a fast and cost-effective way to process transactions. Fortunately, many developers have decided to address Bitcoin's scalability challenges, so when people want to reduce transaction fees and expand Bitcoin's capabilities, there are many different Bitcoin Layer2 options to choose from.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




