Author: Ash Li
Recently, the total supply of 112,383 Runestones has attracted widespread attention in the market since its issuance, with a total trading volume exceeding an astonishing 1,400 bitcoins. The average price has also been on the rise, and the increasing number of airdrops has kept the heat on Runestone, giving a feeling of a "golden shovel." What kind of project is Runestone? What is its relationship with the Runes protocol? This article will delve into the Runes protocol and ecosystem, and look ahead to the future ecosystem.
I. Overview of the Bitcoin Inscription Ecosystem
Background
From the "ORDI" effect that started in March last year, to the first wave of inscriptions in May, and then the second wave of inscriptions in November-December, everyone is discussing the soaring emotions of what to invest in today and tomorrow. Returning to the blockchain itself, what is the Bitcoin inscription that is made every day, what is the Ordinals protocol, and various protocols ending in "20" are emerging one after another, such as BRC-20, ARC-20, SRC-20, and so on. What are they, what are their connections and differences, and why is there suddenly a Runes protocol? Today, let's explore the colorful Bitcoin ecosystem protocols with these questions in mind.
Protocol Introduction
Ordinals Protocol
First released by Casey (@rodarmor) in December 2022, this protocol allows data to be inscribed on the smallest unit of Bitcoin, the satoshi, including text, images, audio, video, and other data information. The Bitcoin inscription we have been talking about is a piece of metadata inscribed (Inscribe) on satoshis using the Ordinals protocol, which is what we commonly refer to as NFTs on Bitcoin. For more detailed information, you can refer to the previously written introduction to the Ordinals protocol: https://www.spectrumlab.io/zh/reports/看完這篇,你對於ordinals銘文的了解將超過99,which provides a detailed introduction.
BRC-20 Protocol
The BRC-20 protocol was introduced by the anonymous developer @domodata on March 8, 2023, and is based on the Ordinals protocol introduced earlier. This protocol writes the token's name, quantity, and other information in a specific JSON format into satoshis to achieve the functions of token deployment, minting, and transfer. More than 30,000 inscriptions were minted on the second day of its release, with the number of text-type inscriptions approaching 27,000. Following the naming convention of Ethereum's ERC-20 token standard, the BRC-20 protocol is equivalent to a token issuance protocol based on the Ordinals protocol. The first token under the BRC-20 protocol is $ORDI, which saw astonishing gains in both the first and second waves of inscriptions. Recently, @domodata and his creation, @L1Fxyz, proposed an upgrade at block height 837,090 to support self-issuance mode, 5-character token names, and a method to burn BRC-20 assets. The original link is https://l1f.discourse.group/t/brc-20-proposal-for-issuance-and-burn-enhancements-brc20-ip-1/621。
ARC-20 Protocol
ARC-20 is a colored coin model, different from the Ordinals protocol, where each ARC-20 token must have a supporting satoshi, unlike BRC-20, which is distinguished by ordering. Information is inscribed into the transaction script, and the balance is represented using the satoshi amount of UTXO, with the transfer function being processed entirely by the Bitcoin mainnet. Artomicals operates through instructions, making each ARC-20 token the first "output" of a transaction to avoid being spent as a miner fee. When various wallets did not support this protocol initially, there was a phenomenon of burning assets.
SRC-20 Protocol
SRC-20 utilizes the BTC STAMPS protocol, the Bitcoin postage protocol, instead of the Ordinals protocol. We can also tell from the addresses used for inscribing and transferring that SRC-20 uses addresses starting with "bc1q" instead of the commonly used "bc1p" addresses. The main difference between Stamps and Ordinals lies in the architecture. The Stamps protocol stores metadata in multi-signature UTXOs, while the Ordinals protocol stores metadata in the SegWit part of Bitcoin transactions.
II. Runes Protocol
Timeline Background
On May 8, 2023, BTC's core developers published an article claiming that the excessive garbage and frequent transactions caused by the BRC-20 protocol were causing network congestion on BTC, and the BTC community should take action to stop it. On September 1, Casey publicly opposed the BRC-20 protocol and hoped to stop minting BRC-20. On September 26, 2023, Casey Rodarmor developed a protocol called Runes as a replacement for BRC-20. This protocol is a UTXO-based alternative token protocol that allows Bitcoin users to have a good user experience. Casey believes that the improved Runes, which can reduce the phenomenon of creating a large number of garbage UTXOs, is a better, lighter, and more concise asset issuance solution than the experimental BRC-20 protocol. At least, the popularity of BRC-20 has already created a large number of "garbage" UTXOs.
Runes Implementation
The balance of Runes tokens is directly contained within UTXOs. If a transaction contains an output with a pubkey script containing an OP_RETURN followed by data output representing the ASCII uppercase letter R, then the transaction contains a protocol message. Runes in transactions with invalid protocol messages will be burned, allowing future upgrades to change the allocation or creation of Runes balances, avoiding the previous client's incorrect allocation of Runes balances.
Transfer
The first data output in the protocol message is decoded into an integer sequence, which will contain three pieces of information: ID, OUTPUT, and AMOUNT. ID specifies which Runes token the transfer is for. Each token is assigned an ID when created, starting from 1, with lower values for tokens created earlier. OUTPUT determines which output the transfer is allocated to. AMOUNT represents the quantity of the transfer.
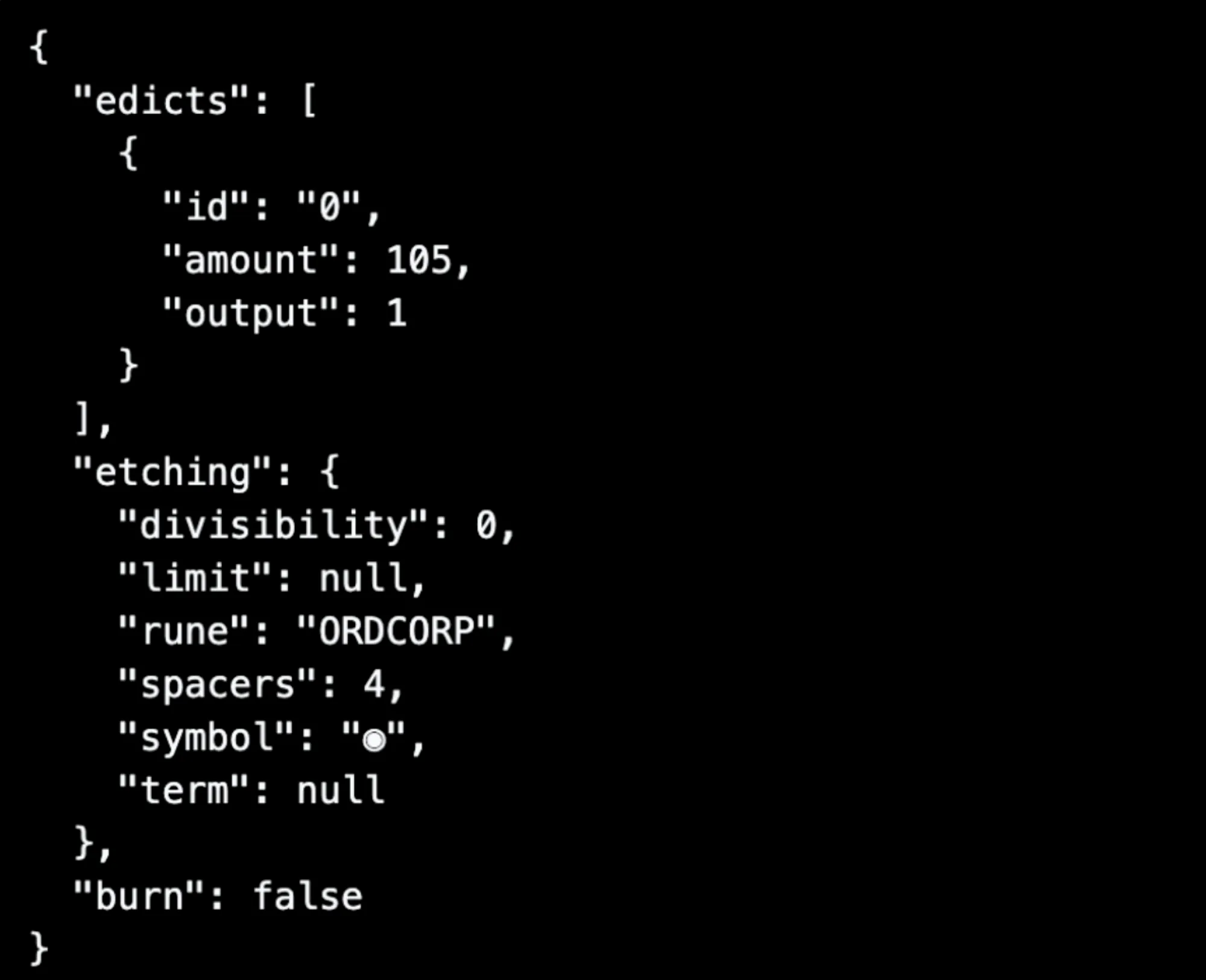
Creation
If there is a second data output after the protocol message, the transaction is considered a Runes token creation transaction. This part of the data output will be decoded into two integers, SYMBOL and DECIMALS. If there are more integers, they are considered invalid. SYMBOL is equivalent to the Ticker in BRC-20, which represents the token name and supports a maximum of 26 characters, using only A-Z. DECIMALS refers to the precision, determining how many decimal places Runes tokens can support. If SYMBOL has not been used, the Runes token will be assigned an ID value. The first created "rune" token has an ID value of 1. The names BITCOIN, BTC, and XBT are prohibited, and the Runes protocol still does not support the creation of tokens with the same name.
Comparison with Other Protocols
In a blog post, Casey compared the Runes protocol with other existing Bitcoin inscription protocols in four aspects:
Complexity: How complex is the protocol? Is it easy to implement? Is it easy to be widely adopted? User Experience: Are there any implementation details that may have a negative impact on the user experience? Especially for protocols that rely on off-chain data. State Model: UTXO-based protocols are more naturally suited for Bitcoin and minimize the creation of "garbage" UTXOs. Native Tokens: The process of obtaining native tokens required for protocol operations is cumbersome and less likely to be widely adopted.
In comparison to existing Bitcoin token protocols:
BRC-20: Not UTXO-based and quite complex, as it requires the use of the Ordinals protocol for certain operations. RGB: Very complex, relies on off-chain data, and has not been widely adopted despite a long development time. Counterparty: Requires native tokens for certain operations, rather than being UTXO-based. Omni Layer: Requires native tokens for certain operations, rather than being UTXO-based. Taproot Assets: Somewhat complex, relies on off-chain data.
According to Casey, the Runes protocol is a better and simpler choice for creating alternative tokens on the Bitcoin network, compared to the experimental BRC-20 token standard, which has led to a large number of UTXOs and network congestion. Unlike other Bitcoin token standards, Runes does not rely on off-chain data to operate. Instead, it uses a UTXO-based model and tracks Runes balances using UTXOs. Each transfer transaction is split into different UTXOs, each holding a different quantity of Runes.
Technical Features
UTXO Model
Firstly, the Runes protocol demonstrates outstanding compatibility and scalability, seamlessly integrating with Bitcoin's UTXO model and second-layer protocols based on it, such as the Lightning Network and CKB. Compared to other homogeneous token protocols like BRC-20, Runes significantly improves operational efficiency and user experience through a simplified transaction process and token balance management directly tied to UTXOs.
Token Issuance
Runes offers greater flexibility in token issuance, allowing token names of 1 to 28 characters in length and employing various innovative issuance mechanisms, including but not limited to fixed total issuance and public inscription issuance, and even considering more expressive issuance methods. The fixed total issuance method is more centralized, with the issuer directly inscribing all Runes and distributing them. The public inscription method is based on specific parameters, such as block height or timestamp, where the quantity of assets inscribed by users within a specified time determines the final total of that Runes token.
In UTXO management, Runes avoids the complexity and security risks that the witness part of transactions may bring by using the OP_RETURN script, reducing unnecessary UTXO generation and improving the overall health and efficiency of the network. The design philosophy of the Runes protocol is to minimize on-chain "footprints," encourage optimized UTXO usage, and seamlessly integrate with Bitcoin's underlying infrastructure. It promotes the development and innovation of the Bitcoin ecosystem through a more concise and intuitive approach.
User Experience
The Runes protocol supports Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) wallets, providing users with a lightweight transaction experience, which traditional BRC-20 has not been able to achieve. By providing reference implementations and emphasizing compatibility with existing Bitcoin scripts and address types, it offers developers a more friendly and accessible development environment. Further analysis of undisclosed details or more innovative aspects can be conducted after the official release of the Runes protocol.
III. Potential Opportunities of the Runes Protocol
Many projects utilizing the Runes protocol have started to gain attention in the market. Strictly speaking, there are currently no Runes in any form, as the official Runes protocol has not been released. Many are still being released in the form of Bitcoin NFTs. After the official protocol is launched, they will be distributed in the form of airdrops or 1:1 exchanges into Runes. Below are some early projects expected to utilize the Runes protocol.
RSIC
RSIC utilizes a pre-mining mechanism and can only be minted after the Runes protocol is launched. RSIC has four reward distribution methods, including fixed rewards, enhanced rewards, random rewards, and halving rewards. The issuance process uses techniques such as parent-child inscriptions, Metaprotocol fields, and recursive inscriptions. This project has rich gameplay and advanced technology, increasing its playability. Different RSIC rarities also add to the randomness. Holding RSIC through the mining mechanism will yield the Runes tokens that the project will issue in the future. After the Runes protocol is officially launched, the project will airdrop the self-issued Runes tokens to these pre-mined addresses based on the pre-mined quantity. Twitter user @wutaner created an RSIC_DATA table to calculate mining quantities, available at: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1xlAS5-_XS5aCHSozkcF_SCW8M1Kl2SDeolLWEvK4Sgg/edit?pli=1#gid=308398888
Runestone
Following RSIC, another highly anticipated project is Runestone, also in the form of pre-mining. It is led by @LeonidasNFT, the founder of Ord.io. The airdrop rule is simple and transparent: at block height 826,600, Bitcoin wallets need to hold 3 inscriptions, excluding text-based and JSON format inscriptions, such as those of BRC-20.
The Rune Guardians
The total supply of The Rune Guardians is 10,000, and different attributes will have different effects on mining. It is worth mentioning that this project will become a true PFP series during the Bitcoin halving. The gameplay of The Rune Guardians is similar to RSIC, and it will airdrop to holders of Ordinals blue-chip NFTs, with the project bearing all gas costs.
Rune Alpha
Rune Alpha is an early practical project based on the Runes protocol, which has released an experimental platform in advance. Initially, it offers a time-limited and unlimited casting method based on block height intervals and introduces the first trading market based on PSBTS technology. Additionally, RuneAlpha's dragon token $COOK will seamlessly migrate at a perfect 1:1 ratio after the launch of the Runes protocol. The latest airdrop plan and roadmap have also been announced, outlining many future development directions for the runes.
Unicross
$RUFI is the first runic token on @merlinlayer2 and can be converted from BRC-20 to runes at a 1:1 ratio. Unicross is dedicated to supporting Runes Asset casting and protocol indexing. The token is fairly launched, with 25% airdropped to Merlin chain users, and the remainder is in the minting phase.
Participation Method
There are many other Runes concept projects currently, and we have only selected some of the more popular projects. Additionally, founder Casey recently decided to deploy tokens 0-9, with the specific names still being collected from the community. When Runes first launches, all token names will be 12 characters or longer, and token lengths under 12 characters will be gradually released, allowing projects in need to pay for shorter tokens. Therefore, after the official launch, participation can be done through the following methods:
- Directly mint the first 10 tokens deployed by the Casey team. Since the infrastructure of Ordinals is relatively complete, there are also many conditional tools available, and those who are able can also synchronize with the Ordinals full node for early participation.
- Hold NFTs or other credentials from the aforementioned pre-mining projects. After the corresponding tokens are deployed on the Runes protocol by the project, you can directly receive the corresponding airdrop or exchange the tokens at a 1:1 ratio.
IV. Introduction to the Runestone Project
Among the recent Rune protocol-related projects, the most talked-about is likely the Runestone. On March 9th of this year, a 3.97MB-sized Runestone, the largest Ordinals inscription to date, was successfully auctioned for 8 BTC. Its creator, @LeonidasNFT (Ordinals OG and founder of Ord.io), stated that all proceeds from the auction, along with the previously raised 2.25 BTC through Twitter donations, will be used to pay for the mining fees of the Runestone airdrop plan, targeting over 112,383 Bitcoin addresses. This can be considered one of the largest-scale Ordinals airdrop projects in history, and it has generated high expectations within the global Bitcoin community for the upcoming launch of the Runes protocol.
When Leonidas initially proposed the idea for this airdrop, Casey also commented below the tweet, discussing ways to reduce gas consumption. The name "Runestone" also comes from a tweet by Casey, where he mentioned the development of a feature called Runestone under the Runes protocol. This has added to the meme-like nature and the founder's soft support, creating a strong buzz.
The Runestone project's ability to gain traction is also attributed to its mining of the largest block on the Bitcoin blockchain, thanks to collaborations with @ordinalsbot and @MarathonDH. The previously mentioned Runestone, auctioned for 8 BTC, left its mark on Block 832,947: the largest Bitcoin block, the largest Bitcoin transaction, and the largest Ordinals inscription in history. The proceeds from the auction used to pay for the airdrop's mining fees also demonstrate the commitment of the Runestone project to the entire community.
The rapid development of the inscription ecosystem is largely due to its fairness, and Runestone has added the "fairness" feature from the start. The narrative characteristics of "airdrop" + "fairness" + "Runes" can also be seen in the FOMO sentiment in the secondary market. Unlike previous inscriptions, Runestone has gained consensus from both the Eastern and Western communities, while previous BRC-20 inscriptions were more popular in the Chinese-speaking community. Leonidas also tweeted in Chinese, stating, "Runestone plays a role as a bridge between the East and the West, which is remarkable. I have noticed the efforts and contributions of the Eastern Runestone community. Although I only understand English, it does not prevent me from seeing your contributions. Without the joint efforts of the East and the West, the achievements of Runestone today would definitely not have been possible."
Currently, over a dozen projects have conducted airdrops for Runestone holders, positioning Runestone as a new catalyst for the Rune ecosystem. Twitter user @0xquqi has created a comprehensive spreadsheet to record the summary information of Rune Stone airdrops, available at: [https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1F27vFEzlJsJtvuaOpgX5YyXEOwfhDDvf4KOSA5m0_5M/edit#gid=0. Reminder: High-quality projects will directly airdrop, so be careful to discern wallets linked or requiring authorized signatures.
V. Future Prospects
Both Runestone and other Rune protocol-related projects have recently attracted widespread attention from both Eastern and Western communities. This not only demonstrates the new technical potential of Ordinals but also reflects the market's expectations for this runic protocol. With the Bitcoin halving and the launch of the new protocol, will it usher in a new round of rotation in the Bitcoin ecosystem? Can the long-awaited third wave of inscriptions also arrive smoothly with the wind of the runes? Let's all wait and see!
Who We Are
Bitcoin Square is an alpha community established in May 2023, dedicated to providing the latest market dynamics, professional market analysis, and a research-oriented community environment. Follow us on Twitter: Bitcoin Square.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




