Author: Algo Rhythmic
Translation: Plain Language Blockchain
My goal is to provide a comprehensive introduction to Solana's liquid staking. I want everyone to not only understand what liquid staking is and how to do it, but also to understand why it is done. What makes a person wake up in the morning and say to themselves, "Today I'm going to stake my SOL for liquid staking? Come on, join me, and I will take you into a whole new world."
I also try to structure this quite lengthy article so that you can skip certain parts if you are already familiar with the topic.
Note: This article focuses on popular science, not investment advice.
1. Staking on Solana
Before we discuss liquid staking directly, let's first understand regular staking. In proof of stake (POS) networks like Solana, staking involves delegating your tokens to a validator who must commit to faithfully validating transactions on the network, or else face penalties. This is the fundamental reason for the consensus between validators and network users. Without this consensus, double spending, censorship, and various other abuses are possible. When you stake "locally," you choose a specific validator and delegate your tokens to them. You can do this through a series of wallet software or using the Solana command-line interface.
Since the launch of the Solana mainnet test version in February 2020, Solana has been following this proposed inflation plan:
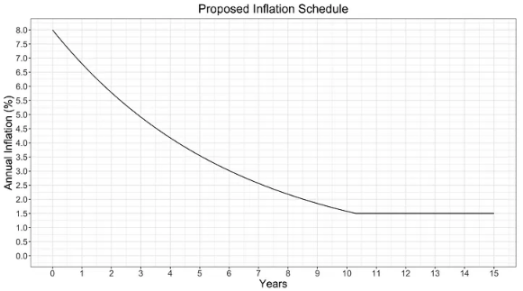
As I write this article, it is already February 2024, four years since that launch, so it is easy to see that the current inflation rate is about 5%. The precise inflation amount is controlled by three parameters: initial inflation rate (8%), deflation rate (-15%), and long-term inflation rate (1.5%). The inflation rate starts at 8% and decreases at an annualized rate of 15% at each epoch boundary, until it stabilizes at 1.5%. This may change in the future, but this is the plan observed since its launch.
Who owns the SOL tokens generated by inflation? Quite simply: the stakers. This means that in each epoch, stakers are increasing their relative ownership of SOL tokens at the expense of non-stakers. In fact, nothing more complex is happening. If all SOL is staked, no one will increase their total value. This results in a high staking rate for the Solana network; at the time of writing this article, about 2/3 of SOL is staked. However, the proportion of liquid staking is still relatively low.
For proof of work (POW) blockchains, validators bear high equipment and energy costs, forcing them to sell some (or possibly all) of the tokens they receive just to break even. In proof of stake networks like Ethereum, these costs are very low, so there is almost no selling pressure. On Solana, the operating costs of validators are slightly higher than Ethereum because validators must execute transactions as part of the consensus, incurring costs, and the cost of validator equipment is slightly higher than Ethereum because it requires higher performance than Ethereum. Therefore, compared to Bitcoin, the selling pressure of validators is still very low, but slightly higher than Ethereum.

Translation: I think "Solana's cheap transactions are artificially subsidized by token inflation" has become a bloody slander against Solana. CT has learned some knowledge about inflation from Bitcoin, and now we can't forget it. There is no strong buying and selling pressure
Next, let's talk about Liquid Staking.
2. LSTs (Liquid Staked Tokens) and Continuous Risk
There are high incentives on Solana for staking to avoid dilution by other stakers. One of the few reasons not to stake is that it locks your capital in each epoch. With liquid staking, you contribute your tokens to a pool that manages the staking rights allocated by the validator and tokenizes the fact that you have committed tokens to the pool. This action returns a new asset representing that fact to the stakers and allows users to exchange it for the original staked SOL. Therefore, in many cases, it can be used as a functional equivalent of SOL.
The most popular liquid staking tokens (referred to as LST) on Solana are almost always "rewarded" tokens. Almost all SOL in the pool is delegated to the validator selected by the pool operator (sometimes minus a small buffer for quick exchange), so these delegated SOL in the pool accumulate rewards in the form of more SOL. Therefore, the quantity of LST increases over time, but the amount of SOL it represents in each epoch increases, causing its price relative to SOL to rise. Another method is "rebasement," where LST holders receive more liquid tokens, each of which can be exchanged 1:1 (with a delay), but this is not commonly used on Solana.
On Solana, each epoch takes about 2.5 days. If a user wants to retrieve the original staked SOL, they must submit a request to retrieve the delegated stake and wait for the epoch to end before they can exchange it. In traditional financial markets, this is known as bearing continuous risk. You are betting that the reward for locking up capital for 2.5 days will exceed the risk of needing it immediately. In terms of duration, the 2.5-day risk is much smaller than a 10-year U.S. Treasury bond. On the other hand, overall, U.S. Treasury bonds… are less volatile than cryptocurrencies.
Therefore, when LST holders want to obtain the underlying SOL tokens, they can redeem them from the staking pool controlled by the Liquid Staking protocol, choose to wait for the end of the epoch for it to be undelegated from the underlying pool, or trade mSOL for SOL on the open market through existing liquidity pools. Here is an example from Marinade Finance:
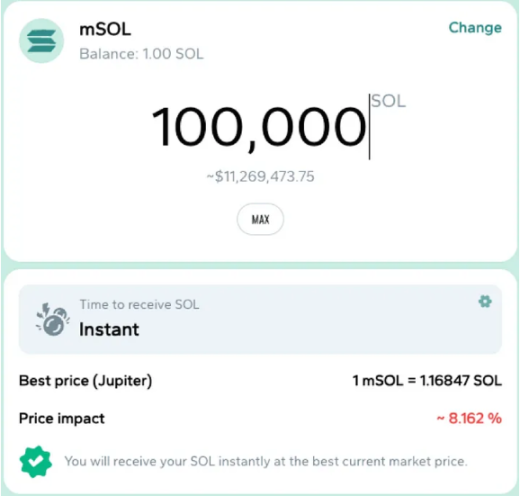
Marinade uses the Jupiter decentralized trading aggregator to trade mSOL for SOL. I did some checks and found that undelegating 10,000 mSOL would have a 0.01% impact on the price, but when the delegation amount increases to 100,000 mSOL, the displayed price impact is 10,000 (in fact, I don't have that much mSOL, but it can be simulated), what does this mean?
This means that if you want to undelegate and immediately obtain SOL, you will receive 8.162% less SOL than waiting for the end of the epoch to undelegate. The above price impact is determined based on current market conditions, depending on the liquidity situation. If rechecked, this number may increase or decrease. This highlights an important fact about LSTs. As I mentioned earlier, they can act as a functional equivalent of SOL in many scenarios, but one important difference is that you will bear a certain degree of continuous risk. If you urgently need funds and need a large amount, you will have to accept a lower price to obtain the required funds.
A simple example can help understand this point. Let's take a look at the "mSOL Decoupling" event that occurred on December 12, 2023. In just 20 minutes, a wallet address 85b5jKkgSuopF3MUA9s4zsBhRANrererBLRx689PqTPA exchanged approximately 68,536 mSOL for SOL in about 9 transactions on the open market. This caused the price of mSOL to drop from around $78 to $66. Here is an analysis from birdeye.so:
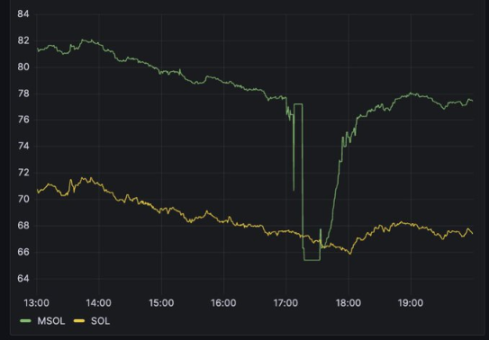
You can see that the price quickly recovered to its previous level. Why did this happen? Because arbitrage bots and other speculators noticed this opportunity and started buying mSOL, as they did not need this capital in the next epoch. The price of underlying SOL did not actually change, so they were essentially buying discounted SOL.
This situation is not limited to mSOL and applies to every LST (with some additional conditions that we will discuss later). The liquidity of any specific LST will inevitably be lower than that of SOL tokens. However, this is mainly a concern when you have a large amount of staked SOL for liquid staking. Overall, having more funds also means facing more challenges.
Therefore, the lesson here is that while liquid staking tokens bear some continuous risk similar to regular staked SOL, it only becomes apparent when there is insufficient liquidity in the market. The stronger the liquidity in the LST market, the smaller the impact of continuous risk. If your holdings are relatively small, you may not feel this continuous risk at all. Nevertheless, understanding the liquidity constraints of tokens is still very important.
3. LST Leaders and Their Incentive Structures
There are three LSTs on Solana with a total locked value of over $100 million, highlighting different adoption incentive methods: Jito (jitoSOL), Marinade (mSOL), and BlazeStake (bSOL). This may change, but you can see approximate numbers here:
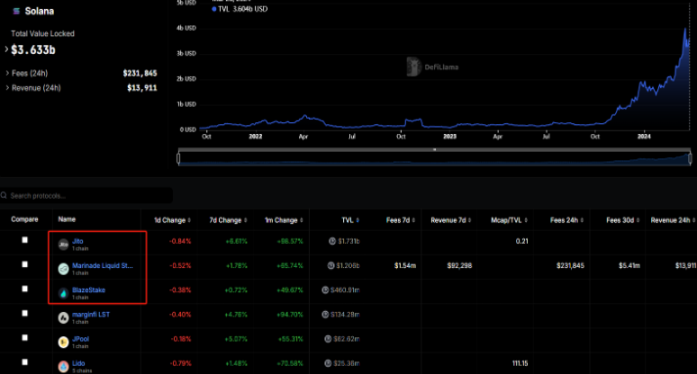
https://defillama.com/protocols/Liquid%20Staking/Solana
Currently, Jito is in the lead, so we will start with it.
1) Value Proposition of Jito
The Jito protocol invites stakers to join the ranks of earning MEV on Solana and offers rewards for minting JitoSOL. JitoSOL is achieved through a secure SPL Stake Pool with optimized validator groups and MEV distribution. The protocol supports efficient transaction processing through the Jito-Solana client and plays a crucial role in Solana DeFi. The use of JitoSOL earns points in the growing Solana ecosystem and provides competitive returns and performance, offering a unique staking experience for the community.
However, a real differentiator is the maximum extractable value (MEV). In short, MEV allows traders to extract value from transactions, but Solana's design makes MEV more difficult to extract. Jito modifies Solana Labs' validator software to increase the ability of validators to accept ordered transactions and charge for them, creating a more orderly and accessible environment for the MEV market. Staking SOL in the liquid staking pool operated by Jito can earn a portion of these profits. Other LSTs can also be staked with validators running Jito-modified validator software to benefit from it.

2) Value Proposition of Marinade
Marinade is the first liquid staking protocol on Solana and leads best practices in the field. When staking directly, you need to choose a validator, but the liquid staking pool automatically allocates you to multiple validators, reducing risk. Last month, Marinade proposed an initiative for validators to create an insurance fund to protect the interests of delegators. Additionally, they introduced "Directed Staking" to allow stakers to support specific validators and earn additional incentives. Marinade's governance is conducted by MNDEToken, allowing holders to vote on the protocol's operation, which is independent of mSOL. They are currently running a campaign where participants can earn additional MNDEToken as a reward to encourage support for the protocol's development.

3) Value Proposition of BlazeStake
The main differentiator of BlazeStake is associated with the BLZE governance token. Similar to MNDE, BLZE can be used to vote on incentive distribution, but it also has independent value. BlazeStake is a relatively young project, so they have only distributed about 80% of the total supply of tokens, while Marinade has fully distributed their tokens and must repurchase them to create MNDEToken incentives. Depending on your perspective and investment time horizon, this may have benefits or drawbacks. Jito also has a governance token JTO, but it is not currently used for incentivizing liquid staking with Jito. Let's quickly compare the top three governance tokens in TVL in the protocol, including market cap, circulating supply, and growth trend:
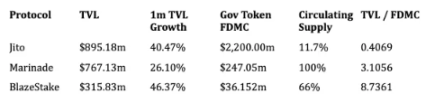
Data as of February 16, 2024, sourced from Defillama, Coingecko, and Birdeye
BLZE performs well in the total locked value to fully diluted market cap ratio of governance tokens. However, several issues need to be noted. First, the high FMDC of JTO is due to a low circulating supply, which may cause FMDC to be less accurate in the short term. Secondly, BLZE has only unlocked 2/3 of the token supply, so new tokens will enter the market. To understand the unlocking schedule, please refer to this: https://twitter.com/solblaze_org/status/1688480225255161856.
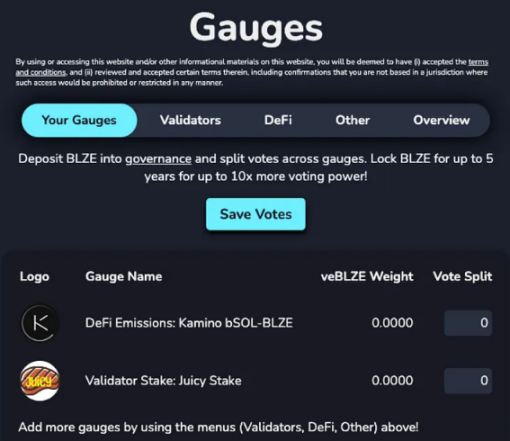
BLZE has some use cases that give it value. Similar to MNDE, you can support specific governance proposals through voting to help bSOL achieve its goals. However, BlazeStake employs a mechanism called "Stake Weight" that allows users to have more sustainable and fine-grained control. You can choose to vote in the decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) on Realms.today to direct additional stake to specific validators or to direct more BLZE rewards to specific liquidity pools in DeFi. BLZE holders can also lock their BLZE for up to 5 years to increase voting power in the DAO. Below is a screenshot of the Stake Weight, showing some example options for directing votes after depositing into the DAO. These features are quite unique within the LSTs.
Some DeFi protocols require you to claim BLZE rewards within their interface, and BLZE rewards are airdropped directly every two weeks. You can check your wallet's current SolBlaze score on rewards.solblaze.org. Attempting to boost your score by creating multiple wallets does not provide a real advantage. The basic formula is: 1 bSOL in your wallet = 1 point, 1 bSOL in a supported lending protocol = 1.5 points, and 1 bSOL in a supported bSOL liquidity pool = 2 points. This roughly aligns with the risk you take with your capital, so it's reasonable that higher risk leads to higher rewards.
It's also worth noting that BlazeStake offers an option to stake your SOL with a single validator, called "Custom Liquid Staking," for liquid staking. Unlike Marinade, 100% of the stake will be directly allocated to that validator. It's important to note that unlike Marinade, Marinade only directly delegates 20% of the stake to the validator of your choice, with the remaining 80% allocated through their delegation strategy algorithm. Marinade details this in their documentation, but it's not immediately apparent in their user interface, which I find a bit less than ideal.
BlazeStake also has some other interesting features. They provide a real SOL faucet, meaning if you mistakenly lock all your SOL on their platform and don't have enough SOL to pay for the unlocking transaction fee, you can use the faucet to get some SOL to cover the fee. This is convenient because you don't need to introduce new funds through a centralized exchange. Additionally, they offer a simple token minting user interface that allows you to easily create an SPL Token and provide an RPC status page and SOL Pay SDK. All of these are beneficial features that help promote the concept of SOL and liquid staking.
If the primary value of BlazeStake comes from the issuance of its governance token, then the price trend of BLZE is the driving factor of its value. The price of BLZE has been rising since the end of November 2023 and has remained stable between 0.002 and 0.004 USD, but based on the data above, there may still be significant room for growth. If it can maintain stability like Marinade, there is still a 2.8x growth potential.
In my opinion, the valuation of BLZE should be comparable to MNDE, or even higher. I'm not sure how to compare the valuation of JTO with the other two. I like this project, and what they are doing with MEV on Solana is fundamentally unique. I look forward to future innovations, but with almost 90% of the token supply still to be issued, it seems a bit high. However, fully diluted market cap doesn't matter… until it does. Anyway, I think all three projects have good potential for appreciation against the USD, as these liquid staking protocols are creating value. In simple terms: liquid staking is good.
In summary, regarding the three most important liquid staking protocols on Solana, they all emphasize the benefits of decentralization on Solana. Liquid staking pools distribute stake to a wide set of validators rather than creating a winner-takes-all situation. They all openly promote their security. Every Liquid Staking protocol has smart contract risk, meaning there is a risk of errors in the operation of the liquid staking pool's smart contracts, but they all have a trusted security awareness. These are all good things, but they don't really differentiate these three methods, which is why I tried to highlight their unique features in the above text.
4. Sanctum and the Future of Infinite Liquid Staking
There are many other Liquid Staking protocols on Solana, and the number of these protocols is set to increase significantly due to the liquidity support pools that sanctum.so is working hard to advance. Their goal is to maximize the liquidity of any Liquid Staking protocol by accepting all of them and providing SOL exchange services. They charge a fee of less than 0.03%, usually 0.01%, which is essentially taking on the epoch risk for you. You can immediately exchange your Liquid Staking tokens for SOL using their pool, which provides a buffer to spread the epoch risk across a wider range.
As of now, Sanctum supports twelve different Liquid Staking protocols, but their goal is to address the liquidity bootstrapping problem for almost all Liquid Staking protocols. The liquidity of Liquid Staking protocols depends solely on the liquidity available in protocols like Orca and Radium, so new Liquid Staking protocols often need to devise strategies to boost liquidity to fulfill their commitment. Sanctum provides a huge additional buffer, allowing new and low-market-share Liquid Staking protocols to have immediate liquidity.
Currently, you can exchange the following Liquid Staking tokens for SOL immediately using Sanctum: bSOL, cgntSOL, daoSOL, eSOL, jitoSOL, JSOL, laineSOL, LST (Marginfi's Liquid Staking Token), mSOL, riskSOL, scnSOL, and stSOL.
Sanctum's universal LSTs liquidity pool makes it possible to conduct larger-scale experiments in the Liquid Staking field.
5. How to Liquid Stake
Now that you have some options, let's briefly go over how to operate. Taking bSOL as an example, simply go to stake.solblaze.org, click on the "Stake" tab, and the following user interface will appear.
Remember, like most LSTs on Solana, bSOL generates returns, so the bSOL you withdraw will be less than the SOL you deposit. Don't be alarmed by this. In the image, you can see that 0.8993 bSOL = 1 SOL. This is because 0.8993 bSOL represents the claim to the BlazeStake liquid staking pool equivalent to 1 SOL, so you won't lose any value. As the amount of SOL in the liquid staking pool grows, this number will continue to decrease, meaning the amount of SOL you receive per bSOL will continue to increase. Currently, 1 bSOL = 1.11 SOL, and this number will continue to rise over time.
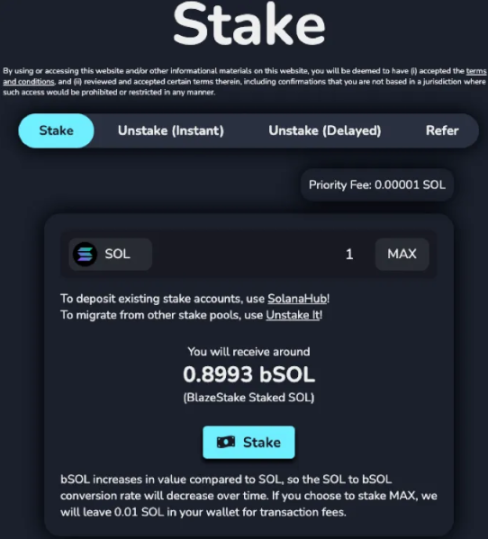
Select the amount, click the button, approve the transaction, and you're done.
6. LSTs and DeFi
Now that we have a fairly good understanding of how LSTs work and the benefits of different methods, let's take a look at the DeFi options. The purpose of all this is to turn your staked tokens into liquidity so that you can use it for various purposes.
Let's start with something relatively simple, like lending.
Lending
One of the simplest and lowest-risk things you can do with LSTs is to lend them out. Platforms like MarginFi, Solend, and Kamino allow users to deposit collateral and borrow other assets of their choice. Cryptocurrencies are typically very volatile, so these platforms only offer over-collateralized lending positions. This means that the value of collateral provided by your counterparty must be higher than the assets they borrow. This usually varies based on the assessment of collateral quality. If the value of the deposited collateral falls below a certain threshold, it will be liquidated to repay the borrower.
The rules for this liquidation process are somewhat complex and vary between different projects. If you are investing a significant amount of funds, it's important to understand these rules.
Generally, the annualized lending rates for LSTs are relatively low because the demand is not very high. The highest and lowest risk-reward opportunities have already been utilized due to the collateral being staked. Nevertheless, you can still lend it out in a relatively safe manner to earn some additional returns, or possibly earn some protocol rewards through lending, so it's worth considering.
Looping
Now that we've discussed lending, let's talk about what lending can achieve. Suppose you have 10 bSOL, currently advertised with an annualized yield of 7.34% (remember, this number will vary slightly with each epoch), plus an additional 0.81% annualized yield in the form of BLZE issuance (depending on the price of BLZE). How can you earn more returns? One way is to deposit these bSOL into a lending protocol, borrow more SOL, and then stake that SOL with BlazeStake. Drift Protocol and Kamino Finance offer a simple product to execute this operation with a configurable leverage. You can also manually execute this operation through protocols like Solend. An important variable to note is the SOL lending rate. The higher the rate, the lower your overall annualized yield. Why? Because you have to deduct it as a cost. Here's a quick example from Drift's SuperStakeSOL UI.
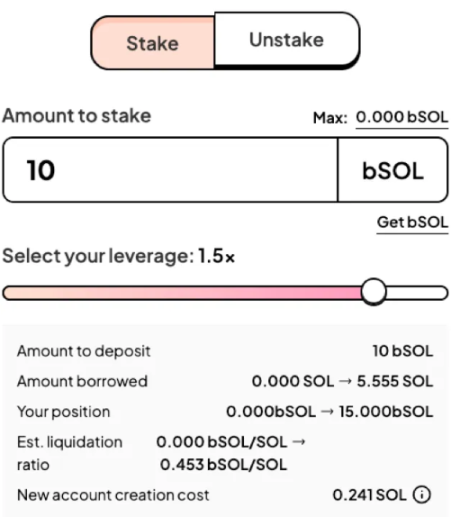
In this example, you use 10 bSOL as collateral to borrow 5 SOL. You have to pay a 0.6% annualized interest rate to borrow SOL, but you can then stake that SOL with bSOL again and earn additional returns. As long as the lending rate is lower than the rewards, this makes sense. Remember, you are taking on risk here. The main risk is the "unpegging" event similar to mSOL mentioned earlier. This can happen at any time because the mechanism that ties its value to SOL has a time component.
Providing Liquidity
Providing liquidity is another way to increase LST returns. Liquidity pools support decentralized trading, allowing you to swap tokens. With enough of these pools, you can exchange any asset through a list of pools via cross-pool swaps. Since USDC and SOL typically have the deepest liquidity, any route usually goes through them. For example, if you want to swap WIF for WHALES, you might first swap WIF for SOL, and then swap SOL for WHALES.
Pools charge fees for swaps, and these fees are returned to liquidity providers (LPs). When trades are balanced, with the same amount of WIF being swapped for the same amount of WHALES, the price remains stable, and LPs just collect fees. However, these fees are reasonable because there is a risk of impermanent loss. If demand starts to significantly favor WHALES, the amount of WHALES in the pool will decrease, while the amount of WIF will continue to increase until LPs only hold WIF, which is now worth less than before. This trend can obviously reverse, which is why it's called impermanent loss, but it's something to keep in mind.
So, which liquidity pools are attractive for LSTs? Firstly, SOL-LST pools are popular because they support instant staking and unstaking operations. Secondly, pools of the LST1-LST2 type are also good because you hold two LSTs, both of which can earn normal staking rewards, while also earning a small portion of trading fees. You know they should be highly correlated in price because they are related to the price of SOL (though not pegged). The risk of impermanent loss is low. Thirdly, for a higher risk, higher reward option, you may want to consider pools that allow you to swap LST for their protocol governance tokens, such as jitoSOL-JTO or bSOL-BLZE. These are usually incentivized with additional governance token rewards to ensure reasonable liquidity.
I cannot emphasize enough the importance of understanding the nuances of providing liquidity. Different pools have differences in how liquidity is allocated and the control LPs have over it. Different methods will be better or worse depending on how tokens are traded, so you need a good mental model to understand how price action will unfold, and thus, you want to place liquidity in pools that will maintain good results. For the first two options (SOL-LST, LST1-LST2), your mental model is basically "they will continue to be highly correlated," which makes everything very simple. If you want to delve deeper than simple options, I suggest starting with a small amount and observing how price action unfolds. Note how the balance in the pool changes as assets are traded, how fees accumulate, and decide if it's worth making a larger investment.
Some DeFi protocols, like Kamino, offer a treasury of automated LP strategy management, so you don't have to do much. They come with a pre-built strategy for deploying funds into the liquidity pools they follow. You should understand what it is before doing this, but it means you don't have to manually enter pools and rebalance your range. Of course, they charge a small fee.
These three combinations of lending, looping, and providing liquidity don't exhaust your options with LSTs, but I don't want to turn this into a thesis. If you haven't tried all three options yet, you may want to try them out before delving deeper.
7. Conclusion
I hope this article has given you a solid understanding of Liquid Staking on Solana. The future of LSTs and DeFi on Solana is promising, and the pace of innovation in this field is remarkable.
If you find any errors in the article that need to be corrected, or if you feel that I have misrepresented something, I am open to feedback and considering making changes.
The amazing thing about Solana is that you can try all of this with just $10. If you are concerned about the risks involved and whether you understand them enough to try all of this, you can start cautiously and get a feel for it. The only person who can assess your risk tolerance and whether it's worth trying any given opportunity is you.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




