Original Source: IceTech Research Institute

Image Source: Generated by Wujie AI
It has been nearly a year since the release of ChatGPT3.5, and the enthusiasm for large models is gradually cooling down: the fact of GPU embargo and long-term burning of money has forced domestic large model enterprises to accelerate commercial considerations.
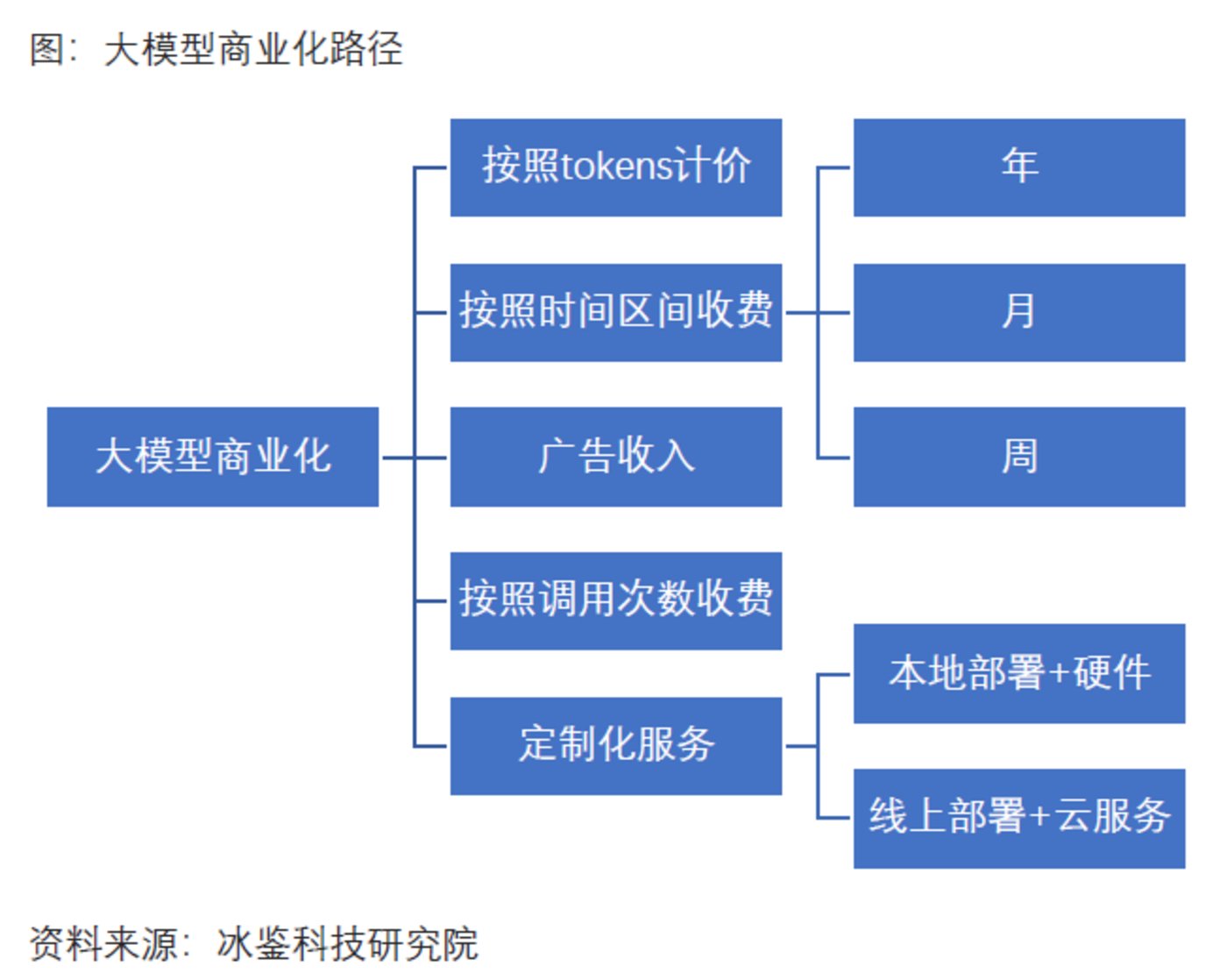
Currently, various pricing methods have emerged for B-end applications of large models, including charging based on time periods, charging based on call volume, and various all-in-one solutions including hardware. Among them, pricing based on call volume for large models can be divided into token billing and charging based on the number of queries.
Meanwhile, foreign pioneers in large models have seen a significant increase in revenue. For example, Microsoft's monthly revenue from large model applications has reached tens of millions of RMB, maintaining a monthly average growth rate of over 20%. OpenAI's revenue growth has also exceeded expectations. The Information cited sources as saying that based on OpenAI's current revenue growth rate, the company is expected to generate over $1 billion in revenue from selling AI software and computing power in the next 12 months, exceeding the revenue forecast previously reported to shareholders by the company.
However, the commercialization of large models in China is slower than that of foreign counterparts, and the path to commercialization, imitating the latter, may be full of obstacles.
ChatGPT can charge a monthly fee for C-end customers, but it is not easy for domestic large models to charge C-end customers. Building a large C-end user base first and then charging advertisers is the golden rule for internet companies; as for demanding B-end customers, whether large model manufacturers can persuade them to pay and form a stable SaaS subscription revenue model, there is still a long way to go.
Charging by Token
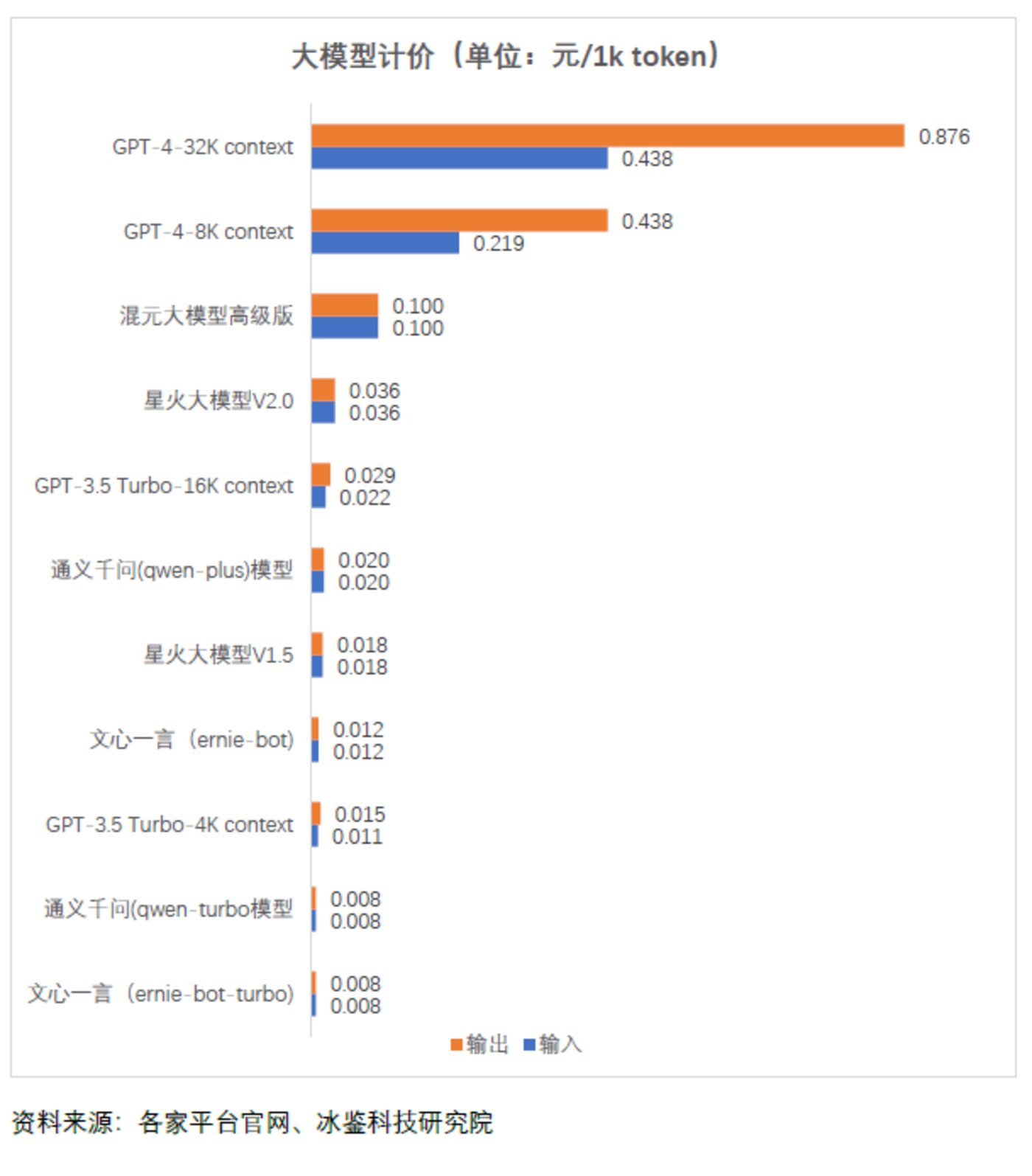
Currently, general large model platforms prefer to charge by token, but the token standards vary between China and abroad. In China, some large model platforms define 1 token as 1 Chinese character, while others understand it as 1.5 Chinese characters or 1.8 Chinese characters. In addition, the charging calculation methods of each company also vary, with the price difference for every 1000 tokens reaching up to hundreds of times, with charges ranging from 0.008 to 0.876 RMB per 1000 tokens.
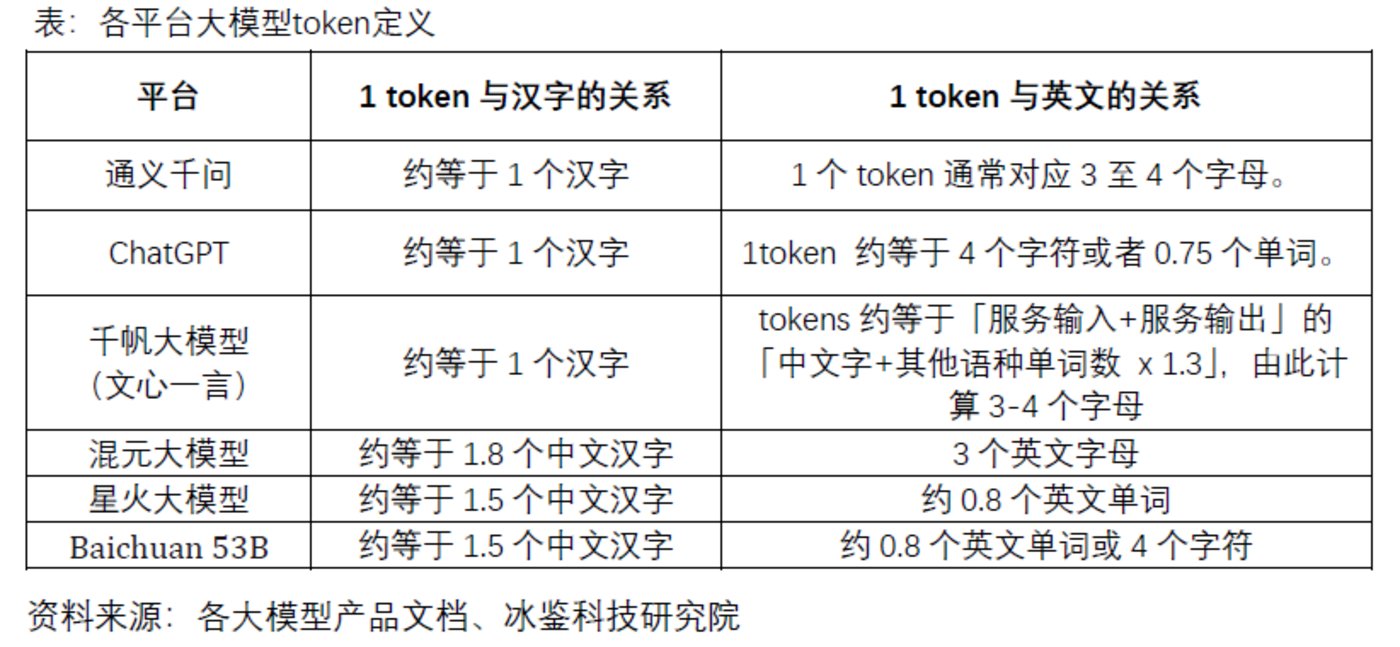
1. What is a token?
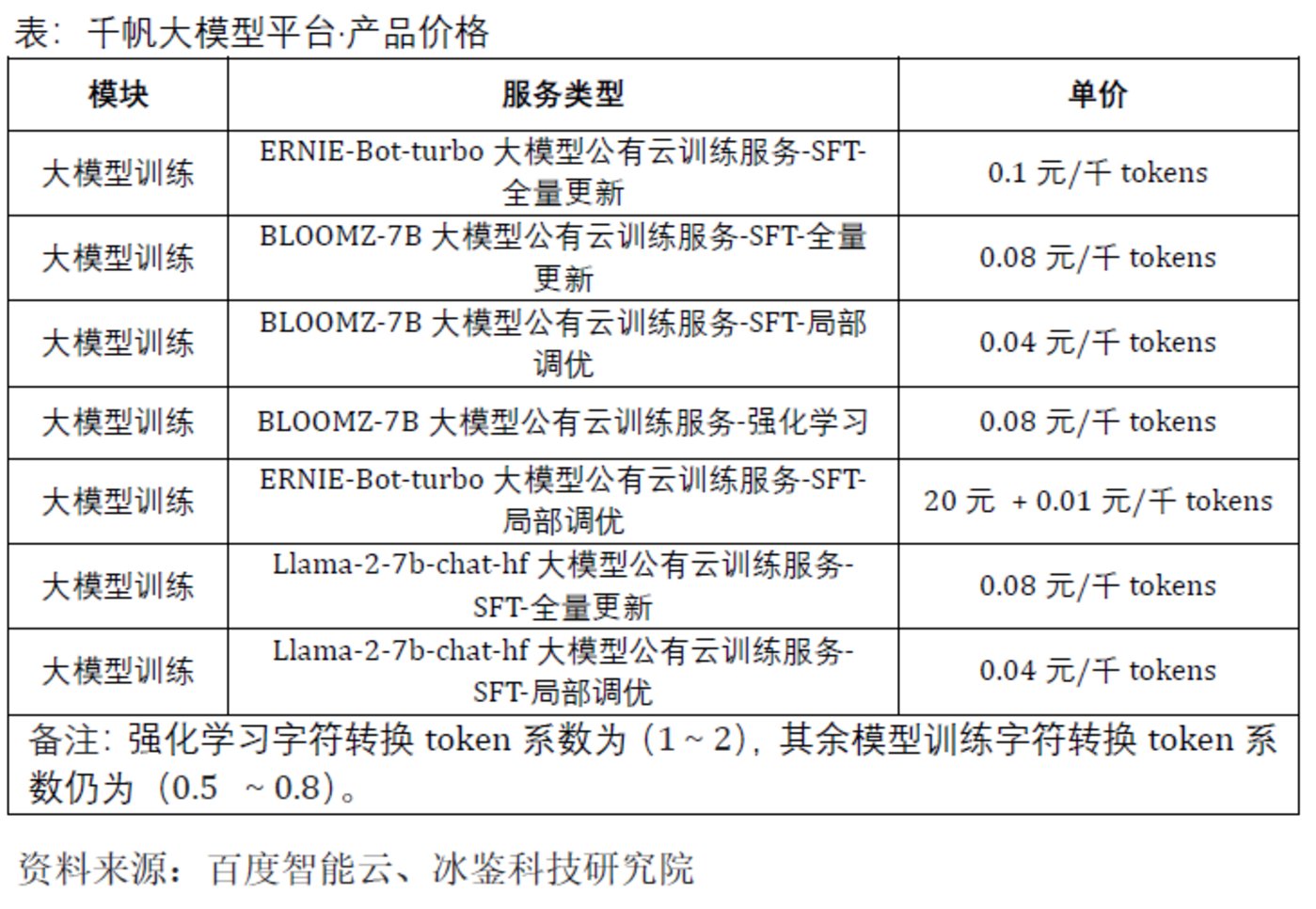
A token is the basic unit used to measure the input and output of large models, and can be intuitively understood as a "word" or "term." However, there is currently no unified measurement standard, and each large model platform "arbitrarily" defines it according to its own preference. For example, Tencent defines 1 token as approximately 1.8 Chinese characters, while Tongyi Qianwen and Qianfan large models define 1 token as 1 Chinese character. For English text, 1 token usually corresponds to 3 to 4 letters. There is an urgent need for a unified standard in the market.
Specifically, large models are charged based on tokens, and both input and output services are charged. Currently, ChatGPT charges different fees for input and output, while domestic large models charge the same fee for input and output. For example, Baichuan 53B by Baichuan Intelligence charges 0.01 RMB per 1000 tokens from 00:00 to 8:00, and 0.02 RMB per 1000 tokens from 8:00 to 24:00.
1.2 Token Pricing
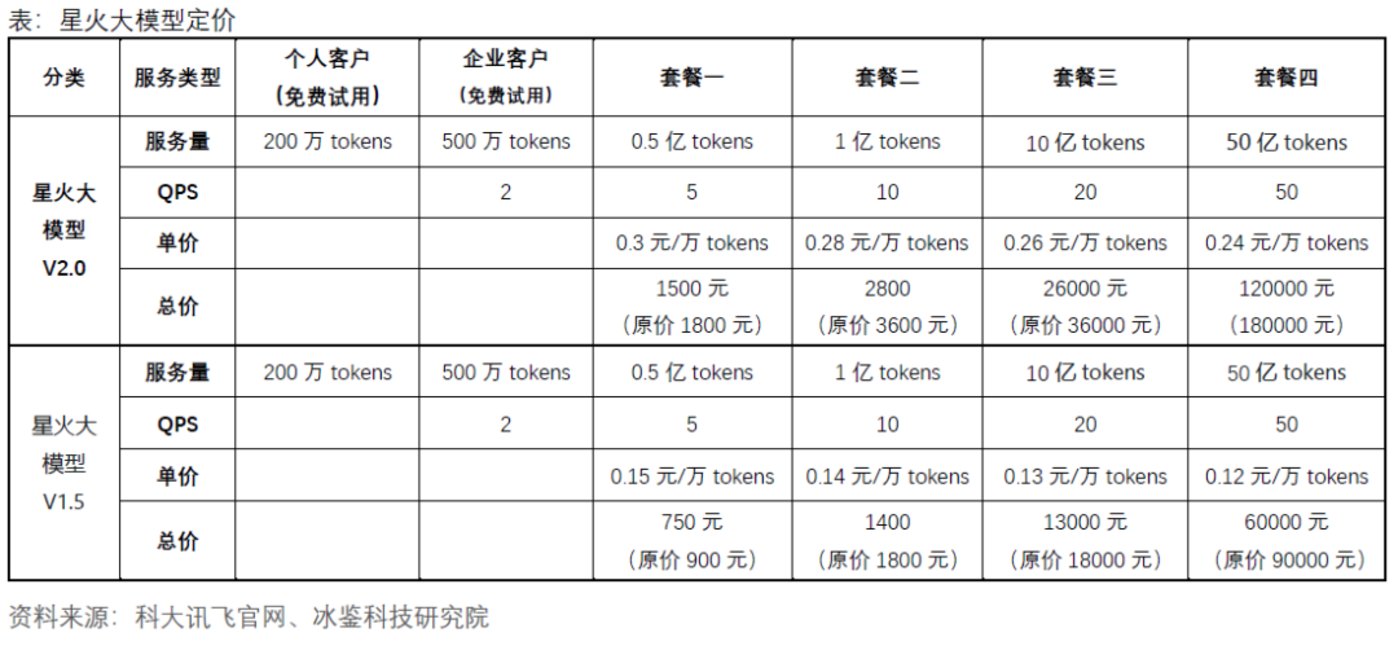
The token pricing of various companies' large models varies, and the charges for different products from the same company also differ. Additionally, the charges vary for usage during different time periods. For example, iFLYTEK currently offers three versions of its Xinghuo large model V1.5, V2.0, and V3.0, with list prices of 0.18 RMB per 10,000 tokens, 0.36 RMB per 10,000 tokens, and 0.36 RMB per 10,000 tokens, respectively. Currently, individual customers can use 2 million tokens for free, while enterprise customers can use 5 million tokens for free. For enterprise customers, iFLYTEK has introduced four charging packages for each version of the large model, with the prices as follows:
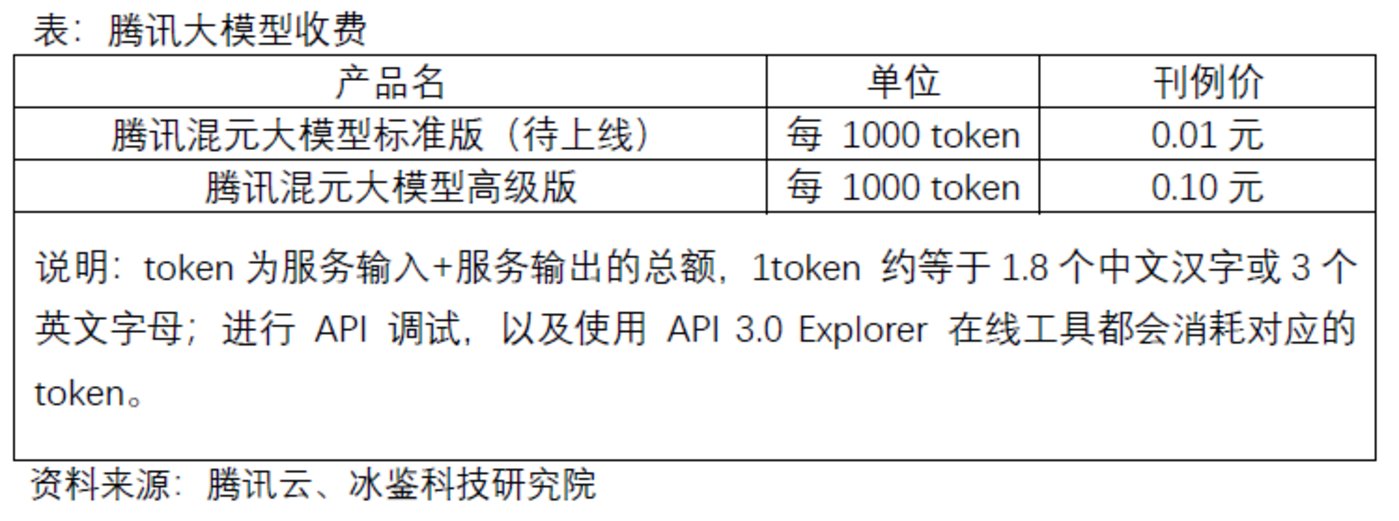
Tencent's Hunyuan large model provides API access and adopts a postpaid daily settlement model: it provides a cumulative free call quota of 100,000 tokens to each Tencent Cloud enterprise account that is in the whitelist and has been real-name authenticated; it is distributed to the Tencent Cloud account in the form of a resource package and is deducted on a priority basis. After the free quota is used up, the following prices are charged:
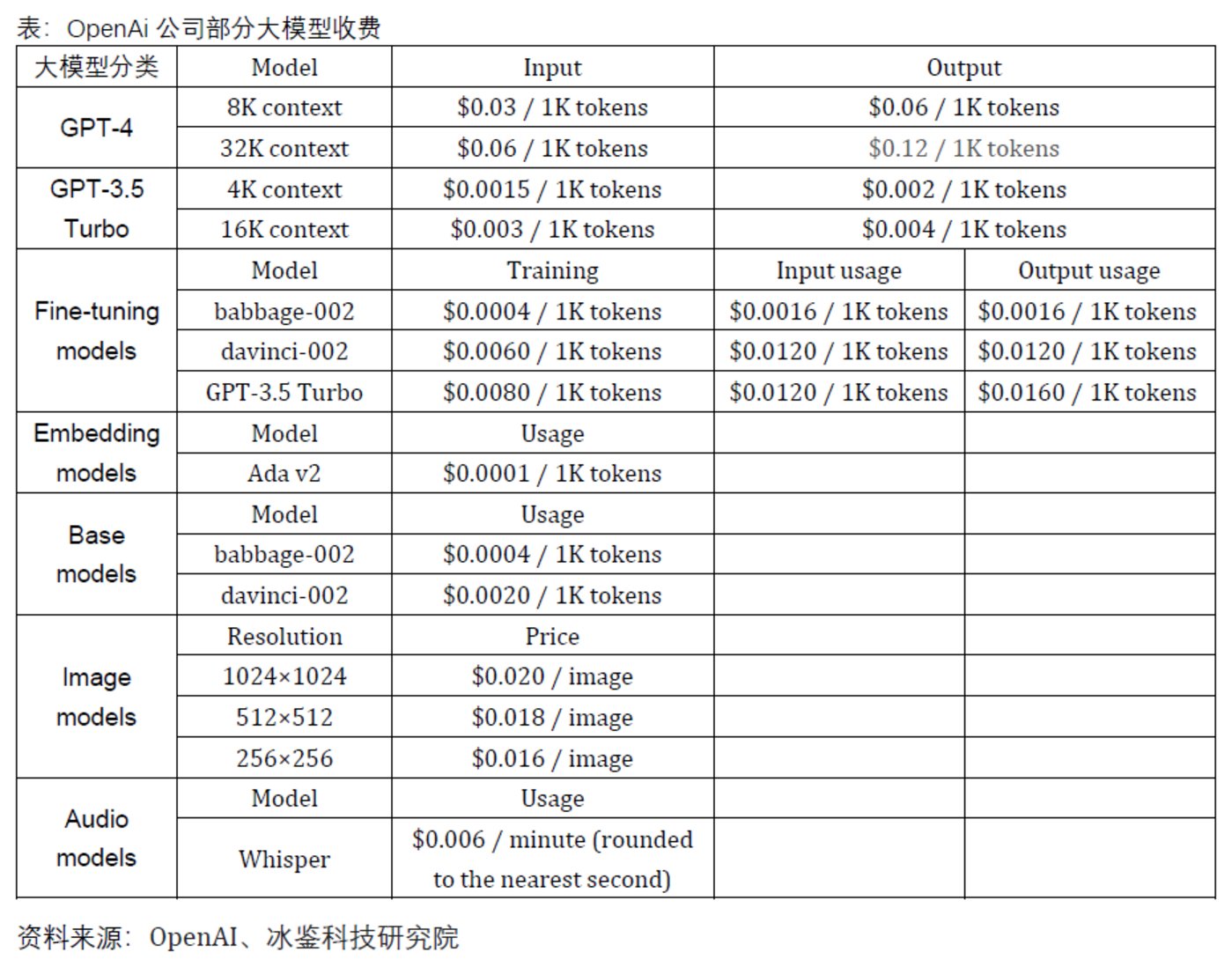
OpenAI has launched multiple commercial large models, including GPT-4, GPT-3.5 Turbo, Fine-tuning models, and Embedding models. The pricing of OpenAI's various large models varies, with the output service of GPT-4-32k context being the most expensive, charging 0.12 USD per 1000 tokens, equivalent to 0.876 RMB.
The pricing of large models in China and abroad differs by a factor of 100, with Wenxin Yiyuan and Tongyi Qianwen (qwen-turbo) charging only 0.008 RMB per 1,000 tokens.
Based on token calculation, the pricing for input and output of some large models from various companies is as shown in the following figure:
Monthly Charging
In addition to token-based billing, some AI assistants charge monthly fees. For example, GitHub Copilot, an AI programming tool developed by Microsoft, currently has 1.5 million users. For individual customers, GitHub Copilot charges $10 per month or $100 per year; for enterprise customers, the corresponding charge is $19 per month. According to Microsoft's latest financial report, internet giants have seen significant revenue growth in surrounding businesses such as Office, Bing search engine, and Azure cloud services, driven by large models, which is also a commercialization model.
In addition, OpenAI's ChatGPT also offers monthly subscription services for customers, currently at $20 per person per month. Furthermore, OpenAI's analysis based on customer registration accounts using corporate email addresses found that 80% of the world's top 500 companies' employees have started using ChatGPT for work.

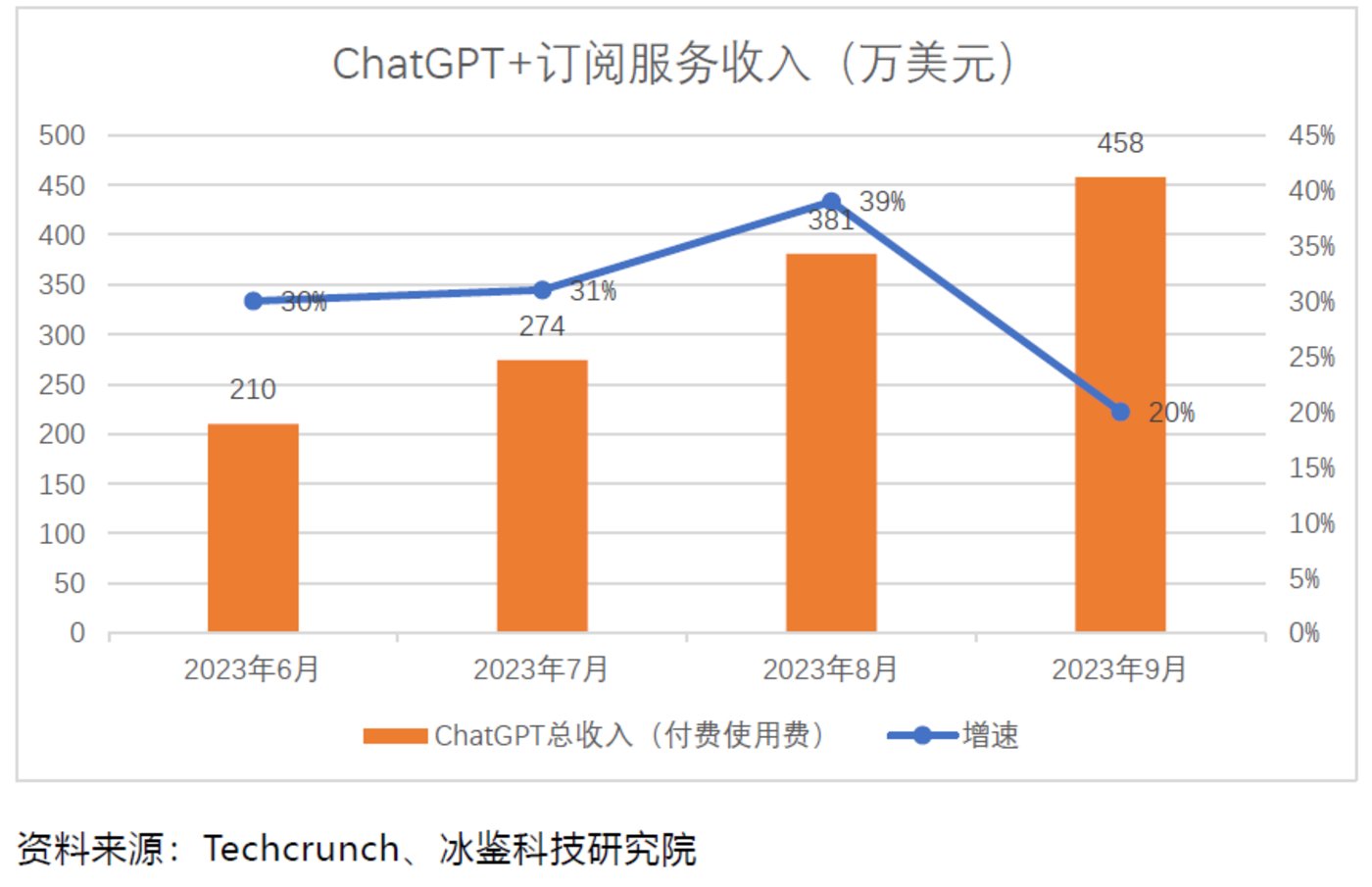
According to Techcrunch, data shows that in September, ChatGPT's downloads on iOS and Android reached 15.6 million times, with a total monthly revenue of $4.58 million.
On November 1st, Wenxin Yiyuan launched a membership model, with a single-month purchase priced at 59.9 RMB/month, and a continuous monthly subscription priced at 49.9 RMB/month. After becoming a member, paying members can use the Wenxin large model 4.0. In addition, Wenxin Yiyuan has a joint membership - "Wenxin Yiyuan Member + Wenxin Yige Silver Member" priced at 99 RMB/month, with Silver members enjoying AI editing, image editing, and more benefits. However, the monthly charging model is costly for C-end users, and even Microsoft is still heavily in the red. In the first few months of this year, Microsoft averaged a monthly loss of over $20 per user in this project, with some users causing losses of up to $80. However, GitHub Copilot's overall revenue continues to increase. Surprisingly, although ChatGPT is the most well-known, it is not the largest revenue-generating AI application in the app store, but a competitor called Ask AI. According to the app's description in the App Store, Ask AI aims to simplify users' work and expand knowledge, providing accurate answers to help users complete tasks. The app not only charges a weekly subscription fee of $4.99 but also, due to its huge number of downloads, exceeding 25 million, it has attracted advertisers and earns millions of dollars in revenue each month. According to Appfigures data, Ask AI's subscription and advertising revenue has exceeded $16 million, rising from $6.48 million in May to $8.55 million in August, with a slight decrease in September to $5.51 million, but still higher than ChatGPT's revenue in the app store. Therefore, as long as the download or usage volume is large enough, future advertising revenue will also become the main source of revenue for large model commercialization. According to Data.ai App IQ statistics, as of August 2023, more than 1,000 generative AI function applications have been released on the iOS App Store and Google Play, with a total global download volume exceeding 800 million. Among them, a new application called Artimind, with the main function of generating AI images, has obtained nearly 1.5 million installations. In China, there are also similar products being launched, which may also achieve advertising revenue in the future, such as iFLYTEK's large model-based product Xinghuo, which surpassed 1 million users within 14 hours of its launch and quickly climbed to the top of the App Store's free overall rankings. Different from token pricing, some large model products charge based on the number of calls. At the DingTalk Ecological Conference in 2023, DingTalk integrated the commercialization of large models with its existing services, and the commercialization solution for landing application scenarios is based on the number of calls. Specifically, on top of the annual fee of 9,800 RMB for DingTalk Professional Edition, adding 10,000 RMB will provide 200,000 times of large model calls; adding 20,000 RMB will provide 450,000 times of large model calls, equivalent to an average of about 5 cents per call. In addition, large model products such as Ask AI have also launched on-demand purchasing services for C-end customers. For large enterprises and institutions such as banks, insurance companies, trusts, and universities, they prefer large model enterprises to provide customized services or all-in-one services. The service content includes not only large model systems but also hardware products such as servers, providing all-in-one solutions. For example, Tsinghua University recently prepared to spend 7 million RMB to publicly procure a large model system teaching and practice platform. This procurement includes not only the large model system but also 24 servers (GPU FP32 computing precision ≥80 TFLOPS), 4 servers (GPU FP32 computing precision ≥35 TFLOPS), and a programmable switch. Shandong Business Vocational and Technical College's Cloud Computing Industry College released a procurement project for the large model technology empowerment center, with a budget of 1.16466 million RMB, also requiring the provision of related hardware products. At the same time, some companies in the market have also released all-in-one AI solutions, such as Huawei's release of the FusionCube A3000 training/inference super-converged integrated machine. This product supports two business models: the Ascend all-in-one solution and the third-party GPU all-in-one solution. In addition to the self-developed OceanStor A300 high-performance storage node, the rest of the GPU servers, switches, and AI platform software are open to partners, providing large model partners with a plug-and-play deployment experience and achieving all-in-one delivery. In summary and looking ahead, the urgency of commercializing large models is evident due to the burning of money, but whether the current revenue can cover all costs remains unknown. The IceTech Research Institute believes that in terms of product pricing, large model enterprises charging C-end customers on a monthly basis and charging B-end customers based on usage (tokens, number of calls) may be a wise choice. Although C-end customers have weak willingness to pay, large model companies can compensate from advertisers as long as the user base is large enough, similar to Ask AI. Enterprise customers have stronger payment capabilities due to work requirements and large daily usage, and charging based on usage can better cover costs. In addition, as large enterprises have stronger payment capabilities, providing customized all-in-one services to banks, large central enterprises, state-owned enterprises, and listed companies can bring more revenue to large model enterprises. For example, some large banks, when announcing the procurement of large model services, not only include AI software and model development services but also include the procurement of large model GPU servers, GPU dedicated storage servers, IB switches, and other hardware. However, the pressure faced by domestic large model enterprises is even greater. As the United States continues to tighten the export of AI chips, they not only face the dilemma of difficult and expensive chip purchases. On October 17, the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) of the U.S. Department of Commerce further tightened export controls on advanced artificial intelligence chips, strictly limiting Nvidia and other chip manufacturers from selling high-performance semiconductors to China. According to the new regulations, controlled Nvidia chips include A100, A800, H100, H800, L40, and even RTX4090. At the same time, the prices of related chip inventories have doubled, with A800, H100, and others each exceeding 1.5 million RMB, and the price of the RTX 4090 graphics card has soared from the original 15,000 RMB to over 30,000 RMB, and other chips are in short supply. The soaring prices of chips have led to a doubling of research and development expenses for domestic large model enterprises, and the profitability of enterprises continues to deteriorate. In the third quarter of this year, iFLYTEK's net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies decreased by 81.86% year-on-year, with the main reason being the firm's firm investment in general artificial intelligence cognitive large models. All these unfavorable conditions have led to the dilemma of domestic large model enterprises, which are just starting out, facing insufficient computing power, lagging large model optimization and upgrades, and thus causing insufficient willingness to pay from customers compared to their foreign counterparts. Facing the huge costs, in addition to waiting for chip prices to drop, large model enterprises are also trying to manufacture chips. For example, OpenAI is not only considering self-developed chips but has also invested in three chip companies, including the American computing chip company Cerebras. This company has created the world's largest chip, with 12,000 transistors and an area larger than an iPad. The pressure faced by domestic large model enterprises is even greater. As the United States continues to tighten the export of AI chips, they not only face the dilemma of difficult and expensive chip purchases. On October 17, the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) of the U.S. Department of Commerce further tightened export controls on advanced artificial intelligence chips, strictly limiting Nvidia and other chip manufacturers from selling high-performance semiconductors to China. According to the new regulations, controlled Nvidia chips include A100, A800, H100, H800, L40, and even RTX4090. At the same time, the prices of related chip inventories have doubled, with A800, H100, and others each exceeding 1.5 million RMB, and the price of the RTX 4090 graphics card has soared from the original 15,000 RMB to over 30,000 RMB, and other chips are in short supply. The soaring prices of chips have led to a doubling of research and development expenses for domestic large model enterprises, and the profitability of enterprises continues to deteriorate. In the third quarter of this year, iFLYTEK's net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies decreased by 81.86% year-on-year, with the main reason being the firm's firm investment in general artificial intelligence cognitive large models. All these unfavorable conditions have led to the dilemma of domestic large model enterprises, which are just starting out, facing insufficient computing power, lagging large model optimization and upgrades, and thus causing insufficient willingness to pay from customers compared to their foreign counterparts. Facing the huge costs, in addition to waiting for chip prices to drop, large model enterprises are also trying to manufacture chips. For example, OpenAI is not only considering self-developed chips but has also invested in three chip companies, including the American computing chip company Cerebras. This company has created the world's largest chip, with 12,000 transistors and an area larger than an iPad. Looking ahead, training costs and chip procurement costs continue to rise, severely hindering the upgrade and iteration of large models, with AI chip costs accounting for the largest proportion. How to reduce chip costs has become the top priority for large model enterprises! According to Bernstein analyst Stacy Rasgon's analysis, if ChatGPT's query scale grows to one-tenth of Google search, OpenAI's GPU procurement costs will reach $48 billion, and an additional $16 billion will be needed annually for chip maintenance costs.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




