
Introduction
Hello to all friends who care about Polkadot, we are the Polkadot Ecological Research Institute. We focus on researching the development opportunities and prospects of Polkadot and its ecosystem, and have received support from the Polkadot Treasury six times in a row.
As a team that has been dedicated to researching Polkadot for nearly five years, we have heard more and more voices of discouragement from the community about Polkadot recently. Many people cannot see hope and have even left the Polkadot ecosystem, which is something we do not want to see. With the recent launch of OpenGov on Polkadot, we see that governance rights are increasingly being transferred to the community, and we can now become a driving force for the development of Polkadot. Therefore, we have decided to change from our previous passive research role to an active participant role. This article is a Polkadot growth strategic planning report that we have launched on how we believe Polkadot should grow, and many of the viewpoints in it are the results of our research over the years.
This article will directly address the market rather than just technology and ideals. We are facing the most real problems and proposing improvement ideas and suggestions. Of course, we also see that many teams are actively proposing solutions to some of the current issues with Polkadot in the official forums and community. However, often these solutions are singularly targeted at a specific problem, without taking a more comprehensive approach or unifying multiple problems under a strategic ideological system.
We welcome everyone to point out the shortcomings in this article, and we also welcome everyone to provide constructive feedback and suggest practical modifications as much as possible. Our only hope is to make Polkadot better, so let's work together.
Current Situation of Polkadot
In the past six months, Polkadot has made significant progress, successfully achieving two important milestones in its roadmap. Among them, the launch of OpenGov introduced an advanced governance model, providing a broader participation and decision-making power for community members; the release of XCM V3 improved the message transmission format, enhancing the functionality and interoperability of Polkadot, laying a solid foundation for future development.
The infrastructure construction of the Polkadot network remains strong, and the level of developer activity has increased significantly, currently ranking first in public chains, and the total number of developers has also risen to second place. This indicates that the number of developers attracted by Polkadot is continuing to grow, and their contributions to its technical ecosystem are also increasing.
However, despite the remarkable progress, Polkadot still faces some challenges. The price trend of the DOT token is unstable, with significant fluctuations, which may bring some uncertainty to investors and ecosystem builders. At the same time, user activity is declining, the development of ecosystem projects is sluggish, and there are also some urgent issues in treasury governance.
Overall, although Polkadot is full of innovation on its path of continuous progress, it has also been facing challenges.
1. Technical Update Situation
Polkadot has been committed to continuously improving its technology and functionality. In the first half of this year, Polkadot has achieved two important technical updates, with the release of OpenGov and XCM V3 on June 15. Currently, Polkadot has announced the formal completion of version 1.0, and at Polkadot Decoded 2023 at the end of June, Dr. Gavin proposed the vision for Polkadot 2.0.
OpenGov: The new governance model introduced by Polkadot, achieving decentralization through community voting and power balance, adopting a structured implementation lifecycle, the Technical Fellowship has replaced the old technical committee and acts as a developer DAO.
XCM V3: As the latest version of the cross-consensus message format XCM, it has been launched on Kusama through governance. The release of XCM V3 brings innovative designs, supporting external network bridging, NFT transfers, and asset locking functions.
With the complete delivery of Polkadot 1.0, Polkadot will usher in a new development stage. Polkadot 2.0 is a multi-core computer that will transition from a chain-centric to an application-centric model, and proposes many new concepts and technologies.
- Accord: A voluntary treaty across multiple chains, where chains voluntarily adhere to the treaty and ensure its faithful execution. In the process of implementing Accord, Polkadot has introduced two key technologies: SPREE and Project CAPI.
- SPREE technology: Based on relay chain runtime logic segments, it acts like a secure tunnel, ensuring safe transmission of information and value between different parallel chains.
- Project CAPI: A middleware project aimed at driving the development of decentralized applications (DApps) based on Polkadot. It provides developers with a lightweight client solution, enabling developers to create cross-chain applications with good user interfaces.
In the vision of Polkadot 2.0, Polkadot reiterates its commitment to building a resilient application platform. Polkadot will focus on building a ZK primitives library, and the first library is about to be completed, providing privacy protection for on-chain collectives (Fellowship). Polkadot will also invest in the update of several technologies such as Hermit Relay, Smoldot lightweight client, Sassafras consensus, and Internode Mixnet.
In addition, technologies developed by Parity such as parallel threads, system parallel chains, and asynchronous support are also under full support and yet to be implemented.
2. On-chain Situation
As of the writing of this article, according to Messari's report on Polkadot's second quarter of 2023, the on-chain progress of Polkadot has experienced some ups and downs. Here is a brief overview of the on-chain situation of Polkadot in the second quarter:
Development activity:
- The participation of developers in Polkadot and Kusama has maintained a good upward trend, reaching peak active developers of 613.71 and 600.29 on May 28 and June 16, respectively.
- The number of core active developers reached a historical high of 181 on March 22 and has remained relatively stable.
- Polkadot ranks first in terms of the number of submissions and active developers in terms of protocols and ecosystem.
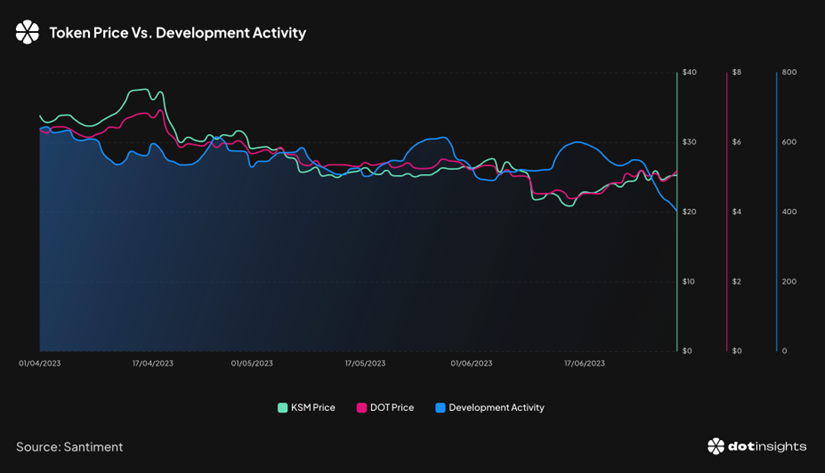
Source: dotinsights
User activity and financial situation:
- The daily active accounts of Polkadot in the second quarter decreased from 6,290 in the first quarter to the current 5,810.
- Polkadot's revenue in the second quarter decreased from over $120,000 to nearly $81,000.
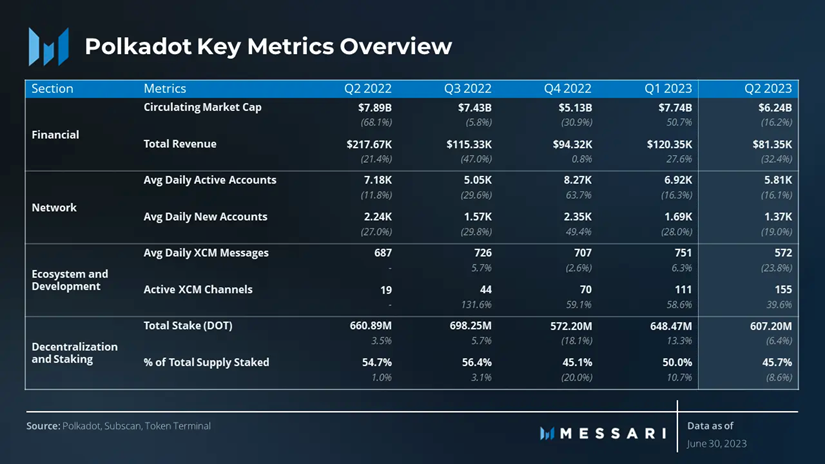
Source: Messari
Total Value Locked (TVL) of parallel chains:
- In the Polkadot ecosystem, the top 6 parallel chains focusing on DeFi, Moonbeam, Astar, Parallel, Acala, Moonriver, and Karura, dominate.
- The total locked value of parallel chains experienced a rise followed by a downward trend in the second quarter, decreasing from a peak of $236.12 million on April 14 to $146.77 million on June 30.
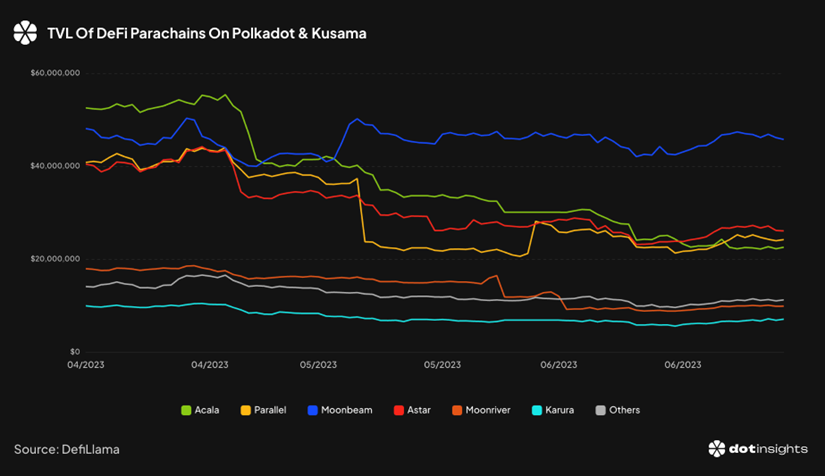
Source: dotinsights
DOT staking rate and return rate:
- The staking rate of DOT in the second quarter of 2023 was 46%, lower than the ideal staking rate.
- The current return rate is approximately 9%, but it changes with the staking rate.
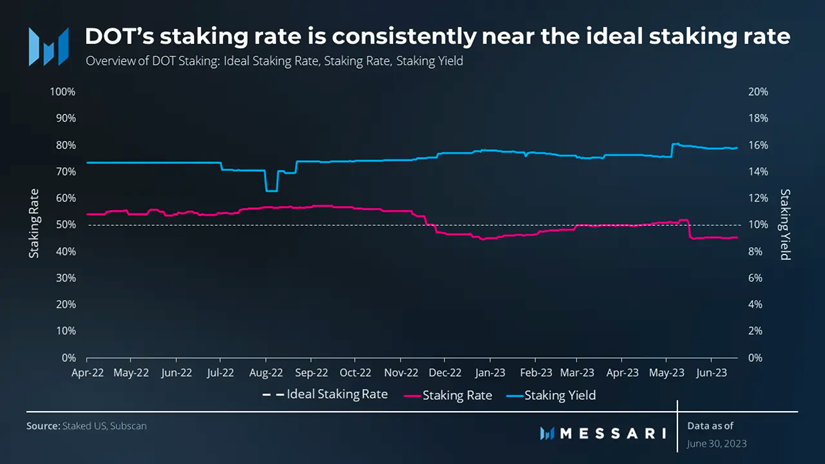
Source: Messari
Please see:
Dotinsights Polkadot Q2:
https://dotinsights.subwallet.app/polkadot-report-q2-2023-en/
tokenterminal: https://tokenterminal.com/terminal/projects/polkadot
https://www.newsbtc.com/news/polkadot-price-slumps-in-q2/
3. Developer Situation
According to data released by Electric Capital, in the first half of 2023, Polkadot has a large developer base in the industry. As of September 17, Polkadot currently has 645 full-time developers, ranking second in the number of full-time developers; the total number of developers is 1923, rising from third place to second place, and maintaining a relatively stable proportion compared to last year, with full-time developers accounting for approximately 33.54% of the total. These data indicate that the developer community of Polkadot is continuously expanding and playing an important role in the development of the Polkadot ecosystem.
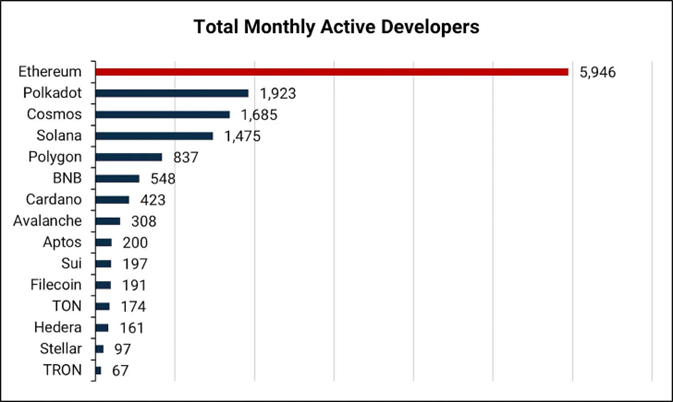
Source: Electric Capital
4. Ecosystem Situation
The Polkadot ecosystem is a rapidly growing and diverse blockchain ecosystem aimed at providing cross-chain interoperability and innovative solutions.
According to PolkaProject statistics, there are currently 580 Polkadot-related ecosystem applications, including DeFi, infrastructure, NFT, browsers, wallets, forums, etc., developed based on Substrate.
The launch of XCM V3 on June 15 has attracted widespread attention, providing advanced programmability, bridging capabilities with external networks, cross-chain locking, improved fee payment mechanisms, and support for non-fungible tokens (NFTs). In terms of Total Value Locked (TVL) in parallel chains, Moonbeam and Nodle are the two projects with the most active accounts, with Moonbeam consistently leading in TVL, and the TVL of parallel chains such as Acala, Astar, and Parallel also maintained at a high level.
Slot auctions are the process of allocating access rights to relay chains, and the winners will obtain the permission to operate parallel chains. In addition, Polkadot ecosystem projects are attracting more and more attention and collaboration, and significant progress has been made by projects such as Mythical Games, Kilt, Frequency, Composable Finance, Aventus Network, etc.
Overall, the Polkadot ecosystem is continuously growing and developing, the Roadmap is progressing smoothly, and some key projects have been successfully implemented.
5. Market Value Situation
As of the current date (October 11), the market value of Polkadot is approximately $3.375 billion, ranking 14th in the Crypto market. Over the past few months, it has been on a downward trend, with the price relatively stable from early May to mid-June. Overall, the price of DOT has dropped by 31.87% in the past few months.
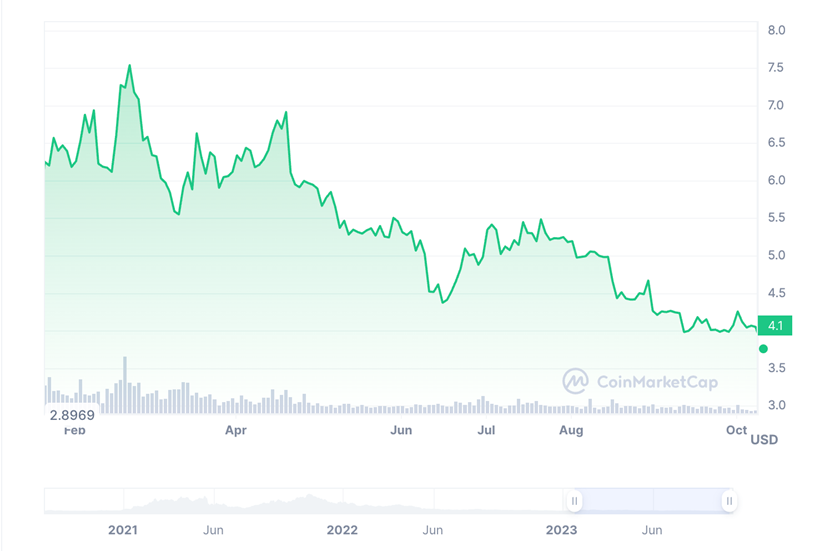
Source: CoinMarketCap
Polkadot and Cosmos are both committed to solving cross-chain communication issues but have taken different technological paths. Compared to Cosmos, the price of ATOM is relatively low, with a decrease of approximately 27.42% so far this year (except for a brief rebound in June). However, overall, the market value of Cosmos has declined, with the current market value being approximately $2.598 billion.
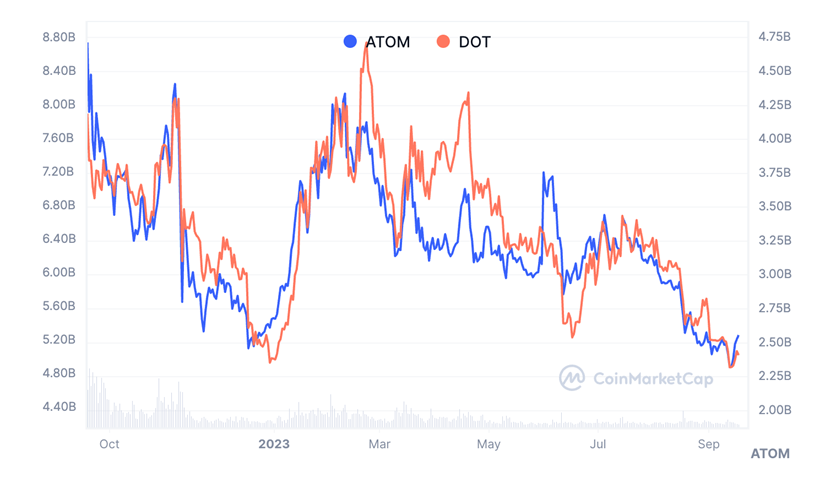
Source: CoinMarketCap
The migration of stablecoins to Layer2 solutions has been a highlight of 2023, such as Optimism. OP is one of the best-performing Crypto projects in 2023, with a surge of up to 227% at the beginning of the year, and Optimism's current market value is approximately $1 billion.
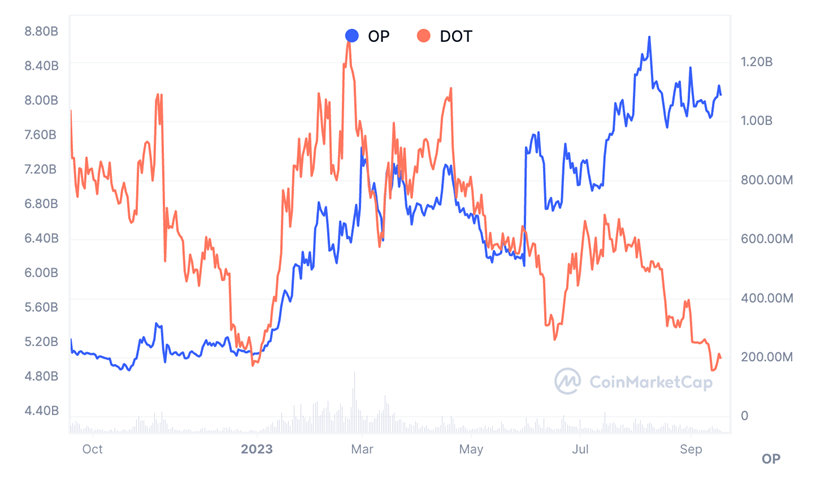
Source: CoinMarketCap
Arbitrum (ARB) is another highly anticipated Layer2 solution, with a trading volume exceeding $17 billion and a current market value of $1 billion.
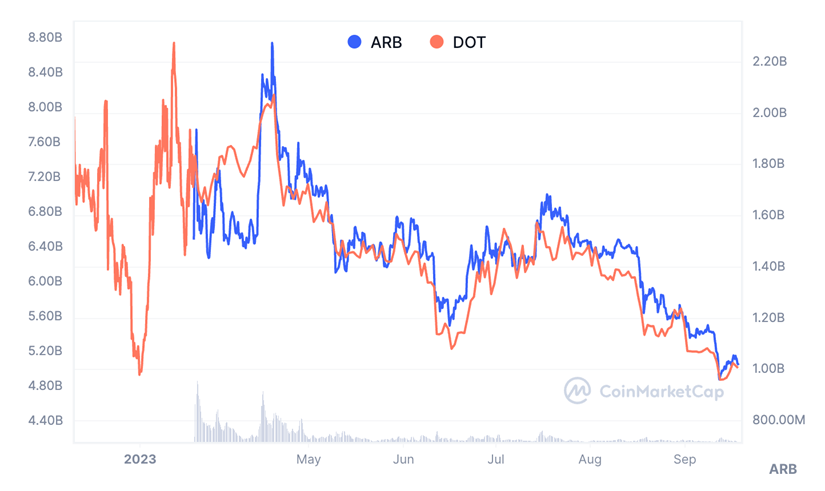
Source: CoinMarketCap
6. Social Media Situation
The official media of Polkadot mainly includes the Polkadot official website, Kusama network, Polkadot Twitter, Web3 Foundation Twitter, Reddit, YouTube, etc. The official website provides detailed information about the Polkadot project, including technical documentation, news, community governance, ecosystem development, etc.; Twitter, Reddit, Medium, and other social media platforms are used to release the latest Polkadot developments and important events, engage with the community, and expand influence; YouTube provides some video resources of Polkadot team speeches, technical sharing, community activities, etc., to help users better understand the Polkadot ecosystem.
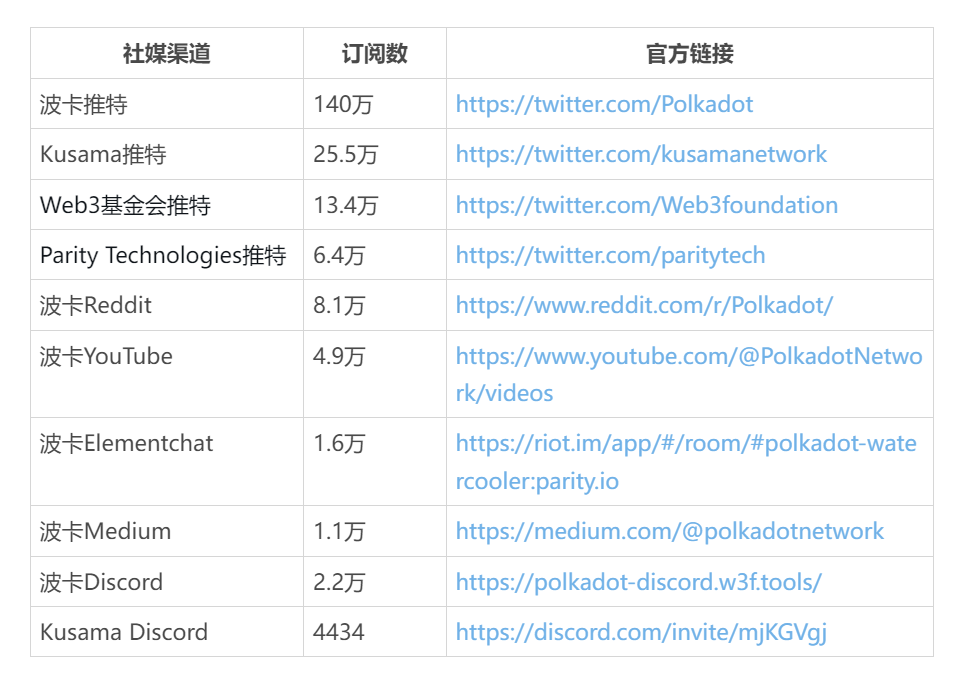
In addition, there are platforms for technical discussions and the future of Polkadot, such as the Polkadot forum, Polkadot GitHub, and the Polkadot Support Knowledgebase providing tutorial support and help for Polkadot. Overall, the official social media of Polkadot is quite rich, providing users with various forms of participation and communication, which is very important for strengthening community consensus and expanding influence.
7. Treasury Governance Situation
OpenGov is a new governance system introduced by Polkadot, launched on the Kusama network in November 2022. It has significant advantages in improving governance efficiency and promoting community participation. However, OpenGov also faces some challenges, such as uneven voting rates and excessive treasury spending.
Efficient governance processing: Compared to the original governance system Gov1, OpenGov has improved the operation efficiency of the governance system, and referenda can be processed in parallel, greatly improving governance efficiency.
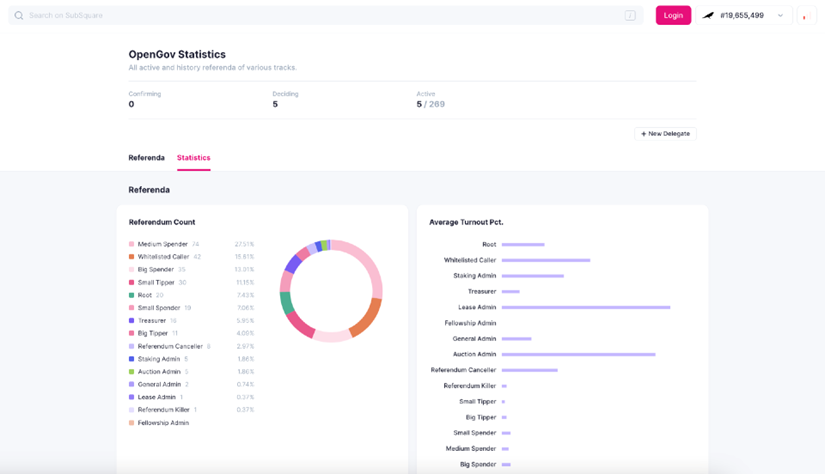
Source: https://kusama.subsquare.io/referenda
Currently, OpenGov governance has several issues:
Issues Faced by Polkadot
1. Economic Model Issues
Many users and the community have provided feedback on issues with Polkadot's economic model, including a relatively high inflation rate, limited use cases for DOT tokens, and concerns about the token's value.
Polkadot's DOT token adopts an inflationary monetary policy, with the current inflation rate at around 7.38% (according to data from Subscan.io), which is considered relatively high. Polkadot uses a mechanism based on Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS), where validators and nominators participate in network validation and receive rewards in the form of tokens, leading to a certain level of inflation. The design intention of Polkadot is to maintain moderate inflation to incentivize participants and ensure network security. However, some observers believe that the relatively high inflation rate may have a negative impact on the value of the DOT token.
In contrast, the inflation rates of other blockchain projects are relatively low. For example, Ethereum's inflation rate has gradually decreased over time and is currently at around -0.21% after the Merge phase (according to data from https://ultrasound.money/), indicating a deflationary state. Similarly, Bitcoin's inflation rate is also decreasing and is currently around 1.7%, with the next halving expected to further reduce this rate.
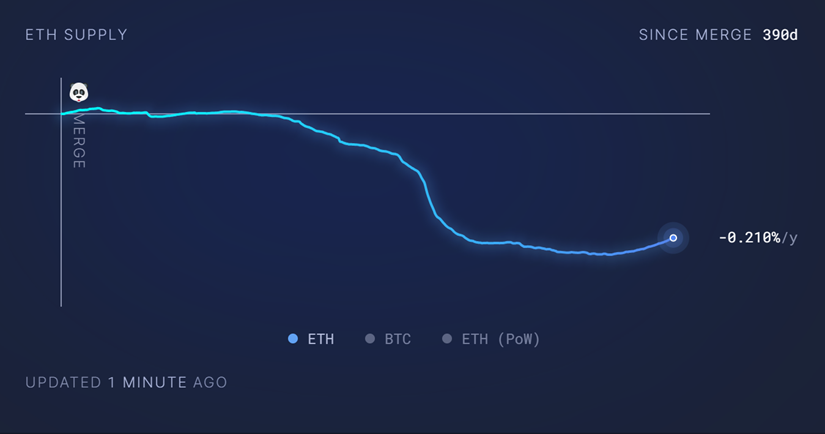
As one of the largest smart contract platforms, Ethereum has a wide range of use cases, including DeFi, NFTs, and decentralized applications, providing more practical utility and demand for its token.
In contrast, the current use cases for the DOT token are relatively limited, mainly focusing on governance, staking, and parachain bonding. However, compared to other blockchain projects, the use cases for the DOT token are relatively limited, which may lead to doubts among some users and investors about the actual utility and long-term value of the DOT token.
2. Operational Issues
① Poor On-Chain Data Performance
Polkadot's on-chain data has shown relatively weak performance over the past 6 months. According to Chainalytics Labs' statistics on the activity levels of major blockchains in May of this year, Polkadot ranks relatively low in terms of user activity, developer activity, financial status, and social activity, with the exception of developer participation. Its user activity index even ranks the lowest, and its overall ranking is third compared to BNB and Solana.
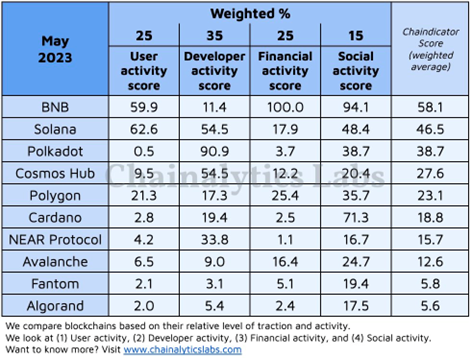
Source: Chainalytics Lab
In terms of transaction volume and active addresses, Polkadot lags behind other major blockchains. In the DeFi field, the number of DeFi projects and the total locked value on Polkadot are relatively low, indicating a weaker performance compared to other blockchains.
Overall, Polkadot is currently facing some challenges, especially in terms of user activity and financial performance, but it is worth noting that developer participation remains strong.
② Poor Social Media Data Performance
The official social media platforms of the Polkadot community are not particularly outstanding. The discussion activity and topic engagement on official social media platforms, such as Polkadot Twitter and Polkadot Discord, are relatively low.
On Polkadot Twitter, the official account @Polkadot currently has approximately 1.4 million followers. Despite the high number of followers, the average views per tweet are below 50,000, and interactions and comments are even fewer than 50. Although the Twitter account maintains a high frequency of posting news about the Polkadot ecosystem, technical progress, and important events, the level of interaction and discussion is relatively low compared to other large projects.
Similarly, apart from Polkadot's official Twitter, the number of followers on other social media platforms is relatively low, such as the official Twitter account of Polkadot's Canary Network Kusama, which has only 250,000 subscribers, and the Web3 Foundation, which has 130,000 subscribers. The social media platforms are relatively fragmented and fail to attract a sufficient number of users to participate in discussions and interactions.
Observations show that the discussion and participation in the Polkadot community are relatively low, as evidenced by the relatively low activity on the Reddit platform, with an average of fewer than 5 discussions per day over the past month. Although there are some in-depth technical discussions, the level of discussion on Polkadot is still much lower compared to other blockchain projects, such as Solana's performance on Reddit.
③ Lack of Data Presentation
The current situation mainly involves two issues. Firstly, poor social media data performance, which fails to attract sufficient attention and participation; secondly, a lack of comprehensive websites presenting the overall situation of the Polkadot ecosystem.
Even though Polkassembly mentioned in the Roadmap that it will launch an ecosystem overview, there is still a lack of a detailed and comprehensive website presenting the overall situation of the Polkadot ecosystem. This makes it difficult for users and industry professionals to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Polkadot ecosystem.
For example, the Polkadot ecosystem lacks a data presentation website similar to L2beat in Layer2, and also lacks a website like DeFillama that provides detailed information on the development of different parachain ecosystem projects. After all, those who are interested in the Polkadot ecosystem do not have a comprehensive and unified place to understand the most authentic situation of Polkadot, making it difficult to conduct research.
To better understand industry trends and compare with other ecosystems, the Polkadot community can exchange data with other projects, further improve data analysis and visualization capabilities, and launch an ecosystem overview website (the previous one has stopped updating), providing in-depth analysis and a comprehensive overview of the Polkadot ecosystem, which will help increase community attention, awareness, and provide more resources and support for ecosystem development.
3. User Accessibility Issues
Polkadot's high level of specialization is currently not very user-friendly for new users, posing challenges in terms of usability and learning difficulty.
Using Polkadot's features and tools may be operationally challenging for the average user. For example, interacting and managing using Polkadot's official tool Polkadot.js, creating and managing wallets, transferring funds, and participating in governance all require a certain level of technical knowledge and familiarity with the operational processes of the tools. This may be challenging for non-technical users and may require a significant amount of time and effort to learn and understand.
Next, Polkadot's ecosystem is relatively complex. To fully understand the workings and technical details of Polkadot, users need to learn basic blockchain concepts, consensus algorithms, cross-chain communication, and related knowledge. Additionally, Polkadot's technical documentation and tutorials may be overly specialized and difficult for ordinary users to understand. The technical documentation and tutorials for Polkadot are typically aimed at developers and technical professionals, containing a large amount of technical terminology and complex concepts, which undoubtedly increases the learning curve for ordinary users to understand Polkadot-related knowledge.

From the perspective of user perception and promotion, there is a disconnect in information dissemination and feedback between Polkadot and its users. On one hand, as an actively evolving blockchain project, Polkadot's latest developments, such as new concepts, technologies, and community activities, are not always effectively communicated to users in a timely manner. This may result in a lack of understanding among users, especially new users, about Polkadot's new technologies and project developments, making it difficult for them to join the ecosystem and potentially leading to a lack of participation.
On the other hand, Polkadot's promotional materials are often too technical and specialized, making them difficult for ordinary users to understand. This results in many users having insufficient understanding and awareness of new technologies and concepts. For example, even though the OpenGov governance mechanism has been live for nearly three months, a large portion of users still do not have a detailed understanding of OpenGov, such as how to participate and its significance.
4. Treasury Governance Issues
Polkadot's treasury governance mechanism is considered one of the most advanced in the blockchain industry; however, due to its forward-looking nature, it currently faces some challenges, including low voter participation, game theory attacks, and non-representativeness (whales).
Although Polkadot has adopted the decentralized governance model of OpenGov, allowing community members to participate in the decision-making process, in reality, very few voters actively participate in voting and proposals. This may lead to centralization of the decision-making process and a lack of broad community participation. In public referendums related to treasury spending, the voter turnout is low, raising questions about the reasonableness of treasury fund payments. Currently, low voter participation is a serious challenge.

Game theory attacks are also a pressing issue. Due to the incentive mechanism in Polkadot's treasury mechanism, individual holders may attempt to influence voting results through exploiting system rules, bribery, and other means to gain benefits, potentially leading to distorted and unfair decision-making, affecting governance outcomes.
Another challenge facing Polkadot's treasury governance is non-representativeness, where a small number of large token holders (whales) may have an outsized influence on decision-making. This may lead to decision outcomes that favor the interests of a few individuals rather than the entire community, weakening the democratic and fair nature of governance.
SWOT Analysis of Polkadot
Taking into account the current situation and issues, we attempt to use the classic strategic analysis SWOT to understand the overall development status of Polkadot.
Strengths:
- Technological innovation: Polkadot has made significant progress in technology, including the introduction of the new OpenGov governance model and XCM V3 message format. Meanwhile, Gavin has proposed the vision of Polkadot 2.0, continuing to introduce more new technologies to enhance Polkadot's functionality and efficiency, providing a unique technological advantage.
- Strong developer base: Polkadot has a large and active developer community, with a significant increase in developer activity, and the total number of developers has risen to second place, providing solid support for the development of Polkadot's ecosystem.
- Relatively rich multi-chain ecosystem: Thanks to the high degree of customization provided by the Substrate framework, Polkadot has various types of parachains, making its ecosystem richer in project categories compared to other multi-chain ecosystems.
Weaknesses:
- Token price below expectations: The price fluctuation of DOT is significant, which may be one of the reasons for the decrease in user activity and unclear financial status.
- High user barriers: For new users, there are certain barriers to using and understanding the technology and functionality of Polkadot, which may limit the growth of Polkadot's user base and adoption rate.
- Immature DeFi ecosystem: The Polkadot ecosystem lacks a mature DeFi ecosystem similar to Ethereum, not only in terms of a lack of diverse DeFi projects but also a relatively low total value locked (TVL).
Opportunities:
- Increase user participation: Through the OpenGov governance mechanism and increased user participation, Polkadot can further strengthen decentralization and community involvement, enhancing the transparency of decision-making.
- Innovative concepts and technologies: Polkadot has proposed a new vision for 2.0 development, introducing multiple innovative concepts and technologies, providing opportunities for Polkadot's future development.
- Abundant available treasury funds in the Polkadot ecosystem: As an NPoS public chain, Polkadot has a significant amount of staking funds deposited, which can be utilized by some DeFi projects and reinvested in the ecosystem. Additionally, Polkadot's unique treasury mechanism can continuously provide development funds for Polkadot's operations.
Threats:
- Treasury governance challenges: Polkadot's treasury governance faces challenges such as low voter participation, game theory attacks, and non-representativeness, potentially leading to centralization of decision-making, a lack of broad community participation, and unfair decision outcomes.
- Competition: Polkadot faces pressure from various aspects in a competitive market, compared to Ethereum, leading multi-chain ecosystems, and Layer2 cross-chain protocols. Polkadot is at a disadvantage in terms of user numbers, community activity, and ecosystem application scenarios, making it easier for new projects or users to be attracted to other projects with stronger network effects.
- Pessimistic market conditions: Despite the rapid development of the Web3 industry in recent years, it is currently in a low period, posing a challenge for Polkadot as well.
In summary, Polkadot has strengths in technological innovation and a strong developer base, but faces weaknesses and threats in token price fluctuations, technological barriers, treasury governance challenges, and a pessimistic market environment. However, through the introduction of innovative concepts and technologies, increased user participation, and effective utilization of treasury funds, Polkadot has the opportunity to further develop and consolidate its position in the Web3 industry.
Macro Analysis of Polkadot from Two Perspectives
In addition to considering the current state of Polkadot, we should also take a high-level view of the entire crypto industry to understand Polkadot's position and infer its future development direction. We will conduct a macro analysis from two perspectives.
1. Endgame Perspective
When formulating strategies, it is important to consider what the ultimate form of the industry will be, as having a clear endgame can guide current development. For the public chain sector where Polkadot operates, there are various opinions in the market. However, with many public chains performing poorly recently and Layer2 gaining more traction, more and more people are discussing whether Ethereum will continue to dominate in the future.

On the other hand, Layer2 solutions are issuing their own tokens and building their own multi-chain networks to capture value, indirectly draining Ethereum. Additionally, DYDX has completely migrated to Cosmos and achieved new highs in its performance, making the future public chain landscape seem uncertain.
However, if we take a higher-dimensional view of how the public chain landscape will ultimately take shape, our perspective may become clearer.
Firstly, different public chains represent different technical communities, each with corresponding resources for support. Even if they are not performing well at present, it does not necessarily mean they will disappear, but rather may be influenced by market cycles.
Next, there are indeed some public chains with their own unique characteristics, and many application chains and decentralized infrastructure public chains are gradually developing. Ethereum cannot fulfill all blockchain use cases. The future is definitely multi-chain.
Furthermore, in addition to multi-chain ecosystems represented by Polkadot and Cosmos, Layer2 projects are also gradually building their own multi-chain ecosystems.
Moreover, more and more cross-chain protocols such as Layerzero, Celer Network, Wormhole, Circle's CCTP, and Chainlink's CCIP are emerging like mushrooms after the rain, connecting different public chains/Layer2 solutions.
Therefore, we can roughly outline a (future medium to long-term) endgame form.
Different public chains/Layer2 solutions can be seen as points, and different cross-chain methods can be seen as lines. Multi-chain ecosystems such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and Ethereum + various Layer2 solutions can be seen as a whole composed of many points and lines.
In the end, all points will be connected by various lines, and this kind of landscape can be called the "full-chain landscape," which is also the endgame form of public chains, Layer2, etc.
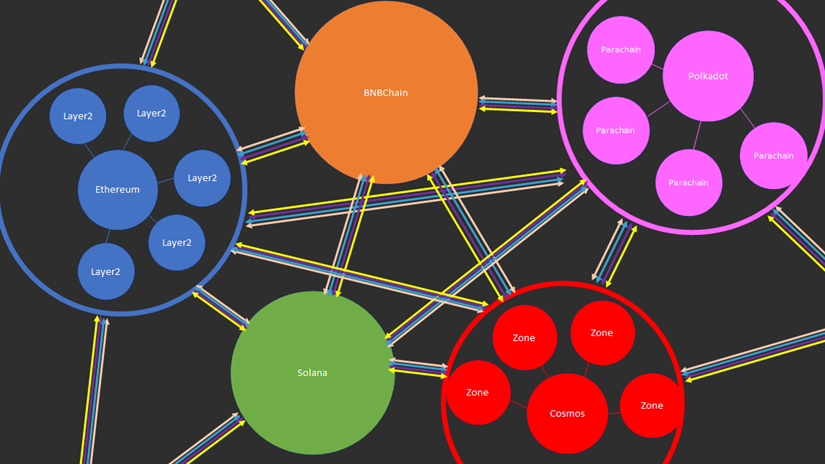
Based on this endgame, we need to consider the role that Polkadot plays in it.
We can see that different points (chains) and lines (cross-chain solutions) have different attribute values in terms of security, decentralization, performance, and fees, and different attributes will attract different types of users.
Observing Polkadot, we can see that, thanks to its unique relay chain + parachain architecture, the parachains can enjoy the security level of a public chain, and the security level between the parachains is the same. Additionally, the security of cross-chain communication within Polkadot's parachains is higher than other types of cross-chain solutions.
Therefore, we can conclude that Polkadot is the multi-chain ecosystem with the highest internal security coefficient in the full-chain landscape, and the security between its parachains is the same.
Blockchain is inherently good at facilitating multi-party collaboration among untrusted entities, but previously, such collaboration required multiple entities to maintain a ledger on the same chain (in the form of a consortium chain) or to participate in an application on the same chain in order to achieve mutual trust.
However, in recent years, we have seen that crypto applications tend to operate independently on their own chains, because chains can independently control security and even develop their own ecosystems. However, at present, there is a lack of mutual trust solutions between chains, especially the need for these chains to have the same level of security. After all, different levels of security will always entail certain risks for the party with higher security, which can hinder cooperation. If everyone has the same level of security, many collaborations become easier to achieve without having to consider security issues.
At present, it seems that only Polkadot can solve this problem, as the security between its parachains is equal, and this level of security is equivalent to that of a public chain. Additionally, its inter-chain messaging has a high level of security. Dr. Gavin's Accord proposed in Polkadot 2.0 is more suitable for solving this problem. This is a very important solution for physical enterprises or organizations that want to achieve fair mutual trust on the network, as everyone hopes to collaborate under equal security.
In other words, there are indeed some scenarios that only Polkadot can solve, and these scenarios are very in line with the trend of traditional sectors entering the blockchain world, which means that Polkadot will definitely have a place in the full-chain landscape.
Now that we have outlined the possible endgame of public chains and the role that Polkadot plays in it, our strategy should focus on how Polkadot needs to develop in order to transition into its future role.
2. Cyclical Perspective
Cycles have always been an eternal topic of discussion, as the development of anything is inseparable from cycles. For public chains like Polkadot, it is necessary to study two cycles: the macroeconomic cycle and the development cycle of public chains. We need to understand what stage Polkadot is currently in to accurately formulate its development plan.
Macroeconomic Cycle
The development of any industry depends on the influx of capital into that industry. If we compare the industry to a container and the influx of capital to water entering the container, then the change in water volume will determine the overall height of the industry. In 2020, due to the economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States had to adopt an exaggerated quantitative easing approach to counter the economic impact of the pandemic. At the same time, traditional institutions and enterprises represented by Grayscale and MicroStrategy began to invest a large amount of capital in the crypto industry, rapidly expanding the crypto market with a huge influx of incremental capital, directly triggering the last bull market.
However, quantitative easing is a double-edged sword, as it subsequently led to terrible inflation. To curb inflation, the Federal Reserve began a lengthy process of raising interest rates, prompting funds with traditional financial attributes to leave the crypto market. As a result, the prices of crypto assets fell, and many core assets used in DeFi depreciated, leading to a withdrawal of liquidity and the start of a bear market.
During this process, we can see that the same incentive mechanism or the same play in a bull market environment will be more optimistic about the future, and funds will further participate in the incentive mechanism or play. Conversely, in a bear market environment, fund sentiment will be more panicked, and funds will tend to cash out after participating in the incentive mechanism, or choose not to participate in many plays.
This means that the same incentive scheme will have the opposite effect in a bad market, but at the right time, it will be more effective. Therefore, we cannot blindly provide incentives but must take different measures in different cycles.
Public Chain Development Cycle
In 2021, emerging public chains such as Solana, Polygon, and Avalanche experienced varying degrees of growth. By observing the early development of these public chains, we can outline a set of common growth logic for public chains and then see what stage Polkadot is in. This will help us understand why Polkadot is in its current state and what measures it can take to develop rapidly.
The following sections will focus on breaking down what Polkadot can learn from the development cycle of public chains.
What Innovations Have Occurred in Public Chain Development in Recent Years?
1. Ecosystem Empowerment + Public Chain Incentives
Public chains can empower projects within their ecosystems in various ways, and these projects can generate demand for the public chain's tokens in their business models, thereby achieving reverse empowerment of the public chain by the ecosystem. Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom, and other public chains have collaborated with mature DeFi projects to jointly launch incentive programs, attracting users to participate in DeFi and receive corresponding incentives.
This approach originated from Polygon. On April 14, 2021, Polygon announced liquidity mining rewards for the lending protocol Aave, with rewards of 1% of the total supply of MATIC (approximately $40 million). Subsequently, the amount of locked assets in Polygon rapidly increased. The successful implementation of the incentive program allowed Polygon to take a gamble and subsequently provided liquidity mining rewards for well-known DeFi projects such as Sushiswap and Curve. The amount of locked assets in Polygon quickly surpassed $5 billion in just over a month, increasing more than 30 times.
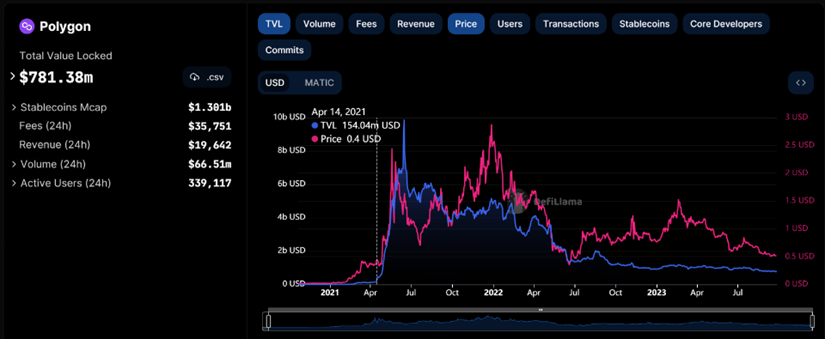
And then on August 18, 2021, the Avalanche Foundation announced the launch of a $180 million liquidity mining reward program called Avalanche Rush, encouraging more applications and assets to join the thriving Avalanche DeFi ecosystem. Following Polygon's explosive growth, Avalanche's activities quickly gained traction, and its Total Value Locked (TVL) also soared like Polygon's.
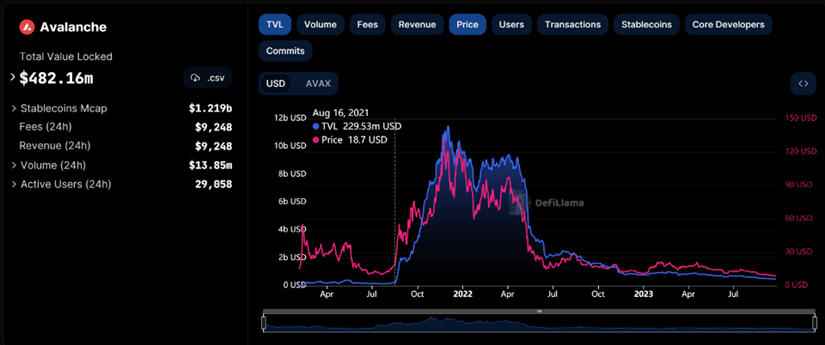
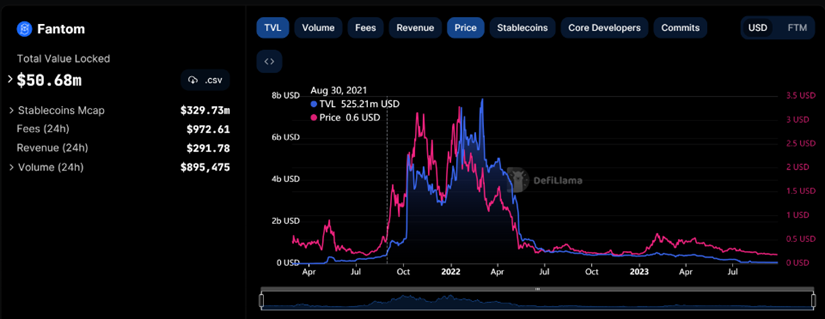
Avalanche's performance once again validated the effectiveness of public chain incentive programs, at least in the prevailing environment at the time. Subsequently, on August 30, 2021, the Fantom team announced the allocation of 370 million FTM tokens to better incentivize users, builders, and the network, also achieving similar results.
2. Exchange Empowerment + Ecosystem Empowerment
In addition to the above-mentioned public chains, BNBChain (formerly known as BSC, later unified as BNBChain) and Solana also experienced an explosive growth in their ecosystems in 2021. While the development of their ecosystems also relied on DeFi and attracted a large amount of capital, their ecosystem explosion was mainly supported by a special external force, namely exchange empowerment.
Exchanges themselves have a large user base, abundant capital flow, and to some extent, the endorsement of trust institutions. Because they are centralized institutions, they can freely create various marketing or promotional methods to empower an ecosystem. Furthermore, exchanges are upstream institutions in the crypto ecosystem, not only familiar with how to empower projects at the secondary market trading level but also heavily investing in the ecosystem at the primary market level. For example, in the entire crypto market, the investments made by Coinbase and Binance, the two major exchanges, in early-stage projects are among the top.
For empowering a public chain, exchanges can invest in projects or applications on the public chain at the primary market level, then list these projects on their exchanges, and through a series of market activities, guide their large user base and capital to empower these projects. After successfully exiting the secondary market, the new capital can be reinvested in other projects on the public chain.
This strategy is likely to occur in a favorable market environment: projects empowered on the public chain will have better market performance, and exchanges will attract more users and capital as a result. These users and capital will pay more attention to newly empowered projects, and exchanges will have a higher probability of attracting more teams to the public chain empowered by the exchange, building new projects, or deploying existing projects on this public chain, ultimately achieving a win-win situation for both the exchange and the public chain ecosystem.
This strategy was initially implemented by BNBChain and gained momentum in 2021, leading BNBChain's development to surpass other public chains besides Ethereum. Subsequently, FTX exchange also discovered this strategy, and in this strategy, the public chain does not have to be one issued by the exchange itself; any public chain can be supported as long as the exchange is willing to implement this strategy.
As a result, the subsequent story was FTX fully supporting the Solana ecosystem, and both parties formed a flywheel effect under this strategy. Even without quickly replicating mature projects from Ethereum to Solana through EVM compatibility, Solana still achieved considerable success.
3. Empowerment Missteps
However, not all ecosystem applications that perform well can empower the public chain in return. During this period, some public chains lagged behind, such as Flow. Flow is a public chain launched by the team behind the once-popular NFT project Crypto Kitties, Dapper Labs, and they also launched the well-known NFT project NBA Top Shot based on Flow, attracting millions of users and achieving monthly revenue of up to hundreds of millions at one point.

Despite having such excellent applications on the Flow chain, Flow's performance was not satisfactory, and we can identify some possible influencing factors.
First, the well-known projects on the Flow chain, such as NBA Top Shot, are mostly projects launched by Dapper Labs, and these projects are more based on traditional business models that have been blockchainized. Most of the users attracted to these projects are traditional Web2 users, and these users use traditional Web2 login and payment methods such as email and credit cards. Therefore, these users attracted are not truly knowledgeable about and engaged in Web3 operations; they only stay within these applications and do not interact with assets in other projects like true Web3 users would.
Second, these projects' business models do not directly use the FLOW token, resulting in minimal demand for the FLOW token. Therefore, even with a large user base and considerable revenue, and even though Flow is used, it does not empower FLOW token holders and is difficult to empower other projects on the Flow chain. It only allows the operating team of the project to generate substantial revenue from the business model.
Third, Flow chain has not developed a comprehensive DeFi ecosystem, and therefore has not been able to experience rapid ecosystem development through linkage with DeFi and cooperation with public chain incentives, as other public chains have.
What is the Growth Logic of Public Chains?
1. Public Chain Value-Added Logic: Transformation of Public Chain Tokens
After reviewing the experiences of some successful and unsuccessful public chains, it is easy to see that public chains that have successfully developed robust ecosystems have collaborated with DeFi. This has led to a significant change. If we consider a public chain as a Web3 computer, the original role of the public chain token was to provide a resource that anyone using this computer needed to pay, namely gas fees.
However, during the rise of DeFi, public chain tokens have taken on a new role as the most trusted Web3 native asset on the public chain, widely used in DeFi as the underlying asset. This process has brought about an important transformation, similar to the transformation of gold from an industrial raw material to a financial asset, which has greatly increased the value of gold.

With this transformation, we can more intuitively understand that the rise of public chains is inseparable from the development of DeFi. This is because as the most trusted asset on the chain, the tokens of these public chains will be in high demand with the development of DeFi and will be locked in these applications in large quantities.
The resulting demand is enormous, enough to drive the initial development of public chains. This is also why the market value of BNB entered the top ten, as it transformed from a platform token of the exchange to a public chain token in high demand by the DeFi ecosystem. On the other hand, one of the major reasons for Flow's poor performance is the lack of DeFi development, and the lack of FLOW being locked in DeFi.
2. Understanding Token Value-Added Logic from a Different Perspective
Since DeFi can bring considerable demand for public chain tokens, does this have the same effect for all types of applications? In fact, it does not. This brings us to the question of how we should judge the value-added logic of tokens.
First, let's review the relationship between stocks and listed companies. The business operations of a listed company are reflected to some extent in the stock price, but the stock price generally does not affect the business operations, which is why Luckin Coffee was able to make a comeback.
Similarly, if we consider a Web3 project as a company, the project's own operations and token prices are related. However, crypto projects are much more unique.
First, Web3 projects have various business models. A project may operate well and generate significant revenue, but this revenue may have little or no direct impact on the token, as exemplified by Uniswap. Uniswap's primary business model is to collect trading fees, and the team and liquidity providers (LP) have earned significant revenue through this model. However, this revenue has no connection to UNI token holders, and Uniswap's business model does not require the use of UNI tokens (governance demand is weak).
Second, if a Web3 project has many token-use scenarios in its operations, a well-operated project will create more demand for the project's token, which can affect the token price. However, there is an irrational aspect of Web3 projects: once operations are linked to the token, not only can operations affect the token price, but the token price can also affect normal operations.
For example, in a bullish market, the market sentiment is aggressive, and many DeFi or gaming projects' incentive measures will attract users to participate and invest more funds. Conversely, in a bearish market, the market sentiment is conservative, and users may not participate in these mechanisms or invest less. Once they receive incentives, they may immediately sell off.
Therefore, normal project operations are also affected by market conditions, and market conditions are directly influenced by the macro performance of traditional finance.
In addition, we mentioned that if a Web3 project has many token-use scenarios in its operations, does this necessarily lead to a rise in token price?
Not necessarily. It depends on the specific circumstances. Let's take the most common scenario of using tokens for payments as an example. For instance, a project may have a core function that requires the use of its token for payment. However, in this scenario, A buys tokens and then trades them to B, who can then sell the tokens, generating revenue.
Fundamentally, in this process, the buyer will give the seller the same amount of tokens as they purchased. On the trading level, the supply and demand between buyers and sellers are balanced. In this situation, even if there is an increasing demand for payments, it may not lead to an increase in token price because the supply and demand between buyers and sellers are balanced.
Therefore, not all token uses in operations can empower the value of the token. Only when the token use in operations results in the buyer purchasing more tokens than the seller, can the value of the token show an increasing trend as operations improve.
In summary, to increase the value of a token, the project's operations must involve token-use scenarios, and the token price can be enhanced from two aspects. Firstly, on the operational level, efforts can be made to improve project operations, which will increase the demand for the token and thereby boost the price.
Secondly, at the trading market level, the focus is mainly on the project's expectations, aiming to enhance the project's future prospects as much as possible.
Finally, it is necessary to wait for an improvement in the macro performance of traditional finance to achieve the best timing. This will allow for a combination of favorable conditions, enabling the project to achieve maximum growth potential in both operations and trading.
3. What Kind of Public Chain Ecosystem Can Better Drive Its Development?
In the previous section, we described a general token value-added strategy, which can also be applied to public chains. Many people mistakenly believe that public chain tokens have a usage scenario for paying gas fees, and as long as there are enough applications on the public chain, there will be a high demand for gas fees, leading to an increase in value.
However, the logic of gas fees is similar to the payment logic mentioned earlier. Users need to purchase public chain tokens to pay gas fees for certain functions, but ultimately, these gas fees go to miners. As sellers, miners receive the same amount of gas fees as the buyers purchased, so this does not inherently lead to an increase in value due to increased usage.
However, Ethereum has now introduced EIP-1559, which has redefined the allocation of gas fees. A portion of the gas fees will be burned, causing the amount purchased by buyers to exceed the amount received by sellers. Today, Ethereum can indeed be said to become more valuable due to the development of its ecosystem, as the increasing usage of applications leads to more gas fees being burned, resulting in a greater amount purchased by buyers than received by sellers.
However, the difference between buyers and sellers in terms of gas fees is relatively slow and imperceptible. The more tangible effect comes from public chain tokens being widely used as underlying collateral assets in DeFi, leading to a significant difference between buyers and sellers.
The business models of DeFi are generally mature and involve locking up assets. Following this line of thought, let's consider which types of ecosystem projects, apart from DeFi, can have a similar effect. In fact, other types of projects such as NFTs, Web3 applications, and blockchain games have diverse business models and require specific analysis.
For example, most PFP NFTs use public chain tokens for minting or direct sales, and the revenue goes to the NFT team. This is similar to trading and does not have a significant empowering effect on public chain tokens. However, a few NFT projects like NounsDAO allocate funds to their treasury and govern them through a DAO. This approach results in a large amount of public chain tokens being locked up, providing a better empowering effect on public chain tokens.
The situation with blockchain games is even more unique, as their economic models are the most complex and do not have fixed design methods. They often involve projects having multiple tokens or a combination of NFTs and tokens. However, their economic models usually form an internal loop, combining gameplay with their own NFTs and tokens to create a complete closed-loop system. The connection between public chain tokens and their economic models is usually minimal, and public chain tokens are typically used to purchase or mint NFTs or tokens for blockchain games. This logic still follows the trading logic, resulting in limited empowering effects on public chain tokens for this type of project.
Therefore, DeFi, which naturally involves locking up assets, will be the most important application category for the development of public chains. A public chain with a rich DeFi ecosystem can attract and retain a large amount of funds, validating the public chain's ability to handle a large amount of funds and verifying the stability of products in extreme scenarios such as liquidation, as well as the security of smart contract languages.
Furthermore, DeFi can empower other projects on the chain in the same way traditional finance empowers entities. It can increase the composability of other project assets and their asset utilization, as well as leverage more funds for the entire public chain. DeFi for public chains is like important financial infrastructure, similar to banks and other financial institutions for cities. Therefore, with limited resources and time, prioritizing the development of DeFi is the primary goal for public chains.
4. Why Didn't Polkadot Develop During the Last Bull Market?
Based on the previous discussion, we can gradually outline a clear logic regarding why Polkadot did not develop well during the last bull market.
First, the unfavorable timing caused Polkadot, which was just getting started, to stumble. As mentioned earlier, the crypto industry is highly influenced by traditional finance, and most of the public chains that emerged in 2021 did so against the backdrop of the US beginning a large-scale quantitative easing, rising with a large influx of funds from outside the crypto industry, particularly in DeFi.
Polkadot itself does not support smart contracts, and it was not until December 2021 that the first batch of parachain slots were successfully auctioned. By early 2022, parachains in the Polkadot ecosystem that support smart contracts began to go live. Polkadot was half a year late, and then several events led the entire market into the prelude of a bear market.
First, the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine war in February 2022 stimulated the return of the US dollar. Then in March 2022, the Federal Reserve began a tightening cycle, laying the groundwork for a setback in the industry's development. The most significant blow came in May 2022 with a series of black swan events caused by Luna, leading to a rapid outflow of funds from the crypto industry and the subsequent bear market.
Polkadot encountered a bear market at a time when it should have been vigorously developing. Some parachains at this time still adopted public chain incentive measures similar to Avalanche, but the effect was greatly reduced because the sentiment in the entire crypto market had become conservative. The funds participating in the incentives decreased, and even those who received incentives tended to sell off. Many Polkadot DeFi projects we have communicated with also reported that some incentive measures organized during the bear market phase had the opposite effect. Therefore, going against the trend is very difficult, and Polkadot's development needs to go with the flow.
Secondly, DOT has not undergone a transformation in the nature of the public chain token, and its financial value has not been fully realized. Although market expectations for Polkadot pushed its price to a relatively high level before the parachain auctions, at that time, Polkadot's ecosystem had not yet developed, and it was unable to translate this advantage into an actual ecosystem or create a mature DeFi ecosystem with DOT as the core asset. However, this is both a current shortcoming and a key factor for Polkadot's potential resurgence in the future.
Ethereum's current prominence is largely due to its rich DeFi ecosystem. Among the top five projects in terms of Total Value Locked (TVL) on Ethereum, Lido, as represented by LSD, is far ahead. The stETH derivative of ETH generated by Lido is widely used in other DeFi applications. For example, the ETH/stETH pool on Curve is one of the largest pools on Curve, and there are over 600,000 stETH in Aave. LSD is the most important DeFi category on Ethereum.
In contrast, Polkadot itself has a rich staking asset. If a project on Polkadot can capture half of the market for LSD on Polkadot, with Polkadot's current staking ratio at around 50%, its TVL could reach an astonishing 681 million DOT, equivalent to a TVL worth $2.72 billion, quickly becoming the 7th largest TVL project in the crypto industry.
Once a project achieves this goal, it also means bringing $2.72 billion in new funds to the Polkadot ecosystem, which can then help drive the development of other DeFi projects. Therefore, the Polkadot ecosystem still has enormous potential, and at the right time, developing Polkadot's LSD project and incentivizing more DOT staking derivatives for use in other DeFi applications will be key to Polkadot's resurgence in the future.
In this process, timing is the most important factor. It is crucial to develop in sync with the rhythm of the cycle, meaning that spending resources in what kind of environment can achieve the maximum utility of resources. The second most important factor is when to adopt what kind of incentives, but for now, the timing is not right, and we will not discuss it in this article.
How Can Polkadot Break Through in the Current Market?
1. Overall Strategy: Harnessing the Power of Governance
To make Polkadot more resilient, it needs to become more decentralized, which can give it some advantages when facing regulatory uncertainty. For example, when the US SEC strengthened regulations on exchanges such as Coinbase and Binance.US, many public chain tokens were delisted, but DOT was not, which is one of DOT's advantages. Therefore, we must fully understand the Polkadot team's desire to operate Polkadot in a decentralized manner.
However, with the launch of OpenGov on Polkadot, we see some opportunities for change. OpenGov takes a more open approach, allowing many DOT holders to participate in governance, decentralizing power and providing greater freedom and potential for on-chain governance on Polkadot. Although some negative events have occurred on OpenGov, on-chain governance is still in its early stages of exploration, and some chaos is acceptable. However, we should also see the other side of the coin, as it allows non-official roles to actively drive the operation of Polkadot.
Therefore, we can view decentralized governance as an unofficial force driving the development of Polkadot. Managing Polkadot well depends on the synergy between official and decentralized governance.
One of Polkadot's core advantages is its treasury, which ensures a continuous flow of funds for ecosystem development. However, the use of treasury funds in the past has been relatively broad, without clear goals or only some vague goals, such as supporting hackathons and some tools. Essentially, it is up to the voters to judge which proposals among all proposals are beneficial for Polkadot's development and then support them, hoping they will achieve the desired results.
However, this approach tends to be more random, or development relies more on luck, and it is difficult to form effective synergy with only incentives that do not have a clear and consistent goal. Therefore, governance of the Polkadot treasury must also have a strategic development plan. Only by operating all treasury funds more clearly around the development plan is it more likely to promote the development and evolution of Polkadot's governance.
Therefore, for Polkadot to improve, we need to drive Polkadot's development in synergy with official and decentralized governance. The official roadmap and management style for Polkadot should be complemented by a treasury governance roadmap and management style. The official Polkadot raises the upper limit, and treasury governance lowers the lower limit for Polkadot.
2. Emphasizing the Balance Between Price and Development
First, we need to respect the consensus reached between the Web3 Foundation and the SEC: the native digital asset of the Polkadot (DOT) blockchain has undergone a transformation in nature, and it is no longer a security but software. Therefore, at least at the official level, it is not possible to discuss issues related to DOT price, as this may touch on sensitive areas for the SEC, potentially subjecting DOT to regulation. Therefore, we need to understand the difficulties faced by the official team.
However, as unofficial participants, understanding DOT can be a different matter. Therefore, we need to be clear that as participants in decentralized governance in the Polkadot ecosystem, we are not subject to the influence of the SEC, and we must also value the worth of DOT.

Because DOT is not just an asset, it is also an important indicator of people's confidence in the Polkadot ecosystem. Furthermore, the previous discussion has detailed how the price can affect operations. If we only focus on operations without considering the impact on the price, it is likely that we will take the wrong actions at the wrong time, resulting in suboptimal outcomes. Therefore, the strategies and solutions outlined in our strategic report are designed to focus on how to achieve growth for Polkadot.
Many projects have worked very hard, but their efforts have not aligned with a growth logic, and they have overlooked the issue of how project operations are related to the price. As a result, the project teams have struggled, the project prices have not risen, and the projects have not been able to thrive. The level of technical prowess and the quality of the token are not directly related, and there are many such cases, which can be deeply felt by anyone who delves into the crypto industry.
3. Strategic Positioning and Objectives
The positioning of Polkadot should not only be viewed as a multi-core computer, but should be positioned from the perspective of the entire chain as a multi-core computer.
To achieve this positioning, a goal needs to be realized: to attract genuine users and funds to Polkadot, thereby creating network effects. However, this means that the value of DOT needs to increase. Growth can solve most problems, so our strategic goal is singular: to achieve growth for Polkadot. The core element here is that the token price needs to rise, and the market value needs to be attractive enough to draw more people to participate. Otherwise, if the market value is not sufficient, existing users will leave, and those outside will be unwilling to build and participate in Polkadot.
The author has had in-depth discussions with dozens of startup teams or teams deeply involved in Polkadot. Many startup teams carefully consider which chain to deploy on, and an important indicator is where there are more users, more funds, and where it is easier for projects to succeed.
Therefore, despite Polkadot's strong support for startup teams, many teams still choose Ethereum and Layer2, which have more users, funds, and a richer ecosystem. These are the network effects of the Ethereum ecosystem.
At the same time, many teams that originally deployed on Polkadot are also considering entering Layer2. Because Polkadot has not formed a mature ecosystem, and the current price has discouraged many users from leaving Polkadot, teams building on Polkadot are seeking other ecosystems that can bring growth.
Therefore, Polkadot has only one goal—growth.
As for how to achieve growth, we need to split it into two categories of tasks: one is to maintain stability, to ensure that Polkadot can steadily develop, in order to retain existing users, assets, and applications on Polkadot. The other is to build a more attractive development prospect for Polkadot.
We, the Polkadot Ecosystem Research Institute, hope to propose some suggestions and work with organizations and individuals who want to see better development for Polkadot, to build a stable and promising future for Polkadot.
Solutions or Approaches
In response to some common issues or areas for improvement in Polkadot, we have proposed several solutions or approaches for discussion.
Polkadot's current treasury governance model essentially allows anyone to propose ideas, and DOT holders can only vote for or against these proposals. However, this situation involves spending money to seek development, but the outcome is somewhat random, and it is likely that money is spent without achieving the desired results, or it leads to the awkward situation of duplicated efforts or a lack of synergy.
Success is difficult to achieve by chance. Only through strategic planning, concentrating all resources and efforts around a common goal, is it more likely to achieve the desired results.
Therefore, we need to establish a strategic development plan for "How Polkadot's Treasury Should Be Governed." The governance process of Polkadot's treasury can be decentralized, but it needs to have a strategic central idea. Governance should not passively wait for people to propose ideas, but should have a strategic development plan in place to actively promote better governance for development.
1. Polkadot's "Governance Framework"
So how can this be achieved? We hope that treasury governance ultimately aims to enable Polkadot to develop better. This goal is consistent with the project's objectives. Therefore, just as a project requires various departments to operate, we can also establish a similar system based on treasury governance. For example, there could be a dedicated technical department responsible for research and development, and a marketing department responsible for publicity.
However, the author prefers to view this entire governance as a logic of national governance, because not only should the work be divided into departments, but the author will also introduce a new role in the Polkadot ecosystem—“citizen.”
Why should there be citizens? In China, there was an incident from 1991 to 1993 when Hainan experienced a gold rush due to reform and opening up, leading to a rapid rise in real estate prices. However, after the introduction of regulatory policies, real estate prices in Hainan plummeted, leaving a large number of unfinished buildings and bad debts, ultimately causing suffering for local residents.
Similar situations also occur in the crypto industry. Many new projects have attracted attention through airdrops, drawing in a large number of speculative investors. However, after the airdrop ends, these investors immediately sell their tokens. Once these people leave, there is little left, casting a shadow over the initial development of new projects and causing frustration for those who genuinely support the projects.
In the same way, we should also grant a citizen identity to DOT holders who are committed to participating in the Polkadot ecosystem, to distinguish them from those who are only speculating on DOT without contributing to the development. Citizens will have a corresponding credit system and citizen rights.
This framework, similar to national governance, is an important reference proposed by the author for the decentralized governance of the Polkadot treasury.
This framework treats the governance of the Polkadot treasury as the governance of a national government, and establishes different government departments, including: the technical department, the marketing department, the investment department, the governance department, and the events department.
Each department will evaluate proposals related to it (new proposals must be submitted to the corresponding department and apply for funding), and each department will have a corresponding share of treasury funds. (Additional input is welcome)
- Technical Department: Guides technical experts and members of the Technical Fellowship to develop more technical products, tools, and projects needed for Polkadot. (Including support for technical training)
- Marketing Department: Organizes and manages media and community activities funded by the treasury, and sets some mainline tasks for publicity to promote wider dissemination of Polkadot. (Including support for media and community)
- Investment Department: Attracts more outstanding projects to emerge or migrate to Polkadot through strategic investments and by establishing funds similar to government industry funds.
- Governance Department: Upgrades and iterates governance-related policies, and encourages users to actively participate in Polkadot governance.
- Events Department: Mainly supports hackathons or events needed by the official and ecosystem.
This approach ensures that various aspects have corresponding treasury funds for Polkadot's development, and ensures that the use of treasury funds is planned and controllable, avoiding situations where excessive treasury funds are used due to a lack of planning or imbalanced fund allocation.
2. Ten Strategic Objectives for Polkadot Treasury Governance
So, how should these departments execute specific strategic objectives? As emphasized in the previous text, we aim to build a stable and promising future for Polkadot in order to make it more attractive. Therefore, our strategic objectives are formulated around the directions of "stability" and "development potential." The specific strategic objectives are as follows:
① Introduce policies to support the development of LSDFi projects and other DeFi projects (lending, AMM, decentralized stablecoins) within the Polkadot ecosystem.
② Introduce a public chain incentive program at the appropriate time.
The growth of DOT's price is not an unknown factor. As detailed in the previous text, many emerging public chains rapidly developed in 2021 using similar methods, and more than one public chain has validated this approach. Therefore, by taking the same measures during a favorable macro environment, we can replicate the rapid development of these public chains in the past. This is a deterministic opportunity and a goal to achieve "stability" for Polkadot's development.
To achieve this, Polkadot needs to have DeFi projects that can support the use of DOT as collateral in advance. However, since Polkadot's relay chain does not support smart contracts, for DOT to be used in DeFi, it must enter various DeFi platforms through the issuance of derivative DOT assets, which is why LSDFi projects need to be encouraged.
③ Introduce policies to encourage the development of RWA, Web2.5, and DePIN.
Some may say that the second objective essentially requires waiting for a bull market to be effectively implemented. However, if a bull market is delayed, how will Polkadot continue to develop?
As discussed earlier, the bull market in 2021 was fueled by a large influx of external funds into the crypto industry. Similarly, attracting more external funds into the ecosystem will also bring growth, and the best ways to achieve this are through RWA and Web2.5.
RWA can attract a large amount of traditional assets or financial products into the crypto industry. Additionally, based on the example of introducing U.S. Treasury yield rates from MakerDAO, it can effectively increase the yield rates of some projects or products on the chain.
Furthermore, the on-chain functionality of RWA is also practical for traditional use. For example, on-chain funds are permissionless and can reach global funds, making it very convenient for participation and withdrawal.
Additionally, RWA on-chain can further utilize other DeFi components to create more high-yield products, and this process is transparent and avoids packaging bad products with good ones, preventing problems similar to the subprime mortgage crisis.
In the traditional financial sector, business interactions between different entities are cumbersome. However, using blockchain technology can solve the issue of mutual trust, greatly reducing the cost of trust (reducing processing time and transaction costs, etc.). The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) has collaborated with central banks in France, Singapore, and Switzerland to release a new report exploring how central bank digital currencies (CBDC) and automated market maker (AMM) technology are changing foreign exchange trading.
Therefore, the development of RWA is not only needed in the crypto industry, but also in the traditional sector, making it a two-way street. Since the development of RWA is an inevitable trend, it indicates that a large amount of funds will enter the crypto industry through this method, and Polkadot needs to prepare in advance for this trend to capture the influx of funds and achieve growth.
The logic behind Web2.5 is similar. Web2.5 refers to projects where traditional enterprises use Web3 technology. Even in a bear market, we can still see many traditional enterprises exploring Web3 marketing methods using blockchain technology. This is because fundamentally, such projects are closely integrated with business and are not heavily influenced by market conditions. However, Web2.5 will still bring a large amount of funds into the crypto industry.
However, whether it is RWA or Web2.5, it is important to design mechanisms that empower projects and their underlying public chains, without repeating the mistakes of Flow.
DePIN projects can bring more decentralized storage, computing, network transmission, and other network resources to the crypto industry, expanding the hardware capabilities of the crypto industry, and potentially bringing more innovative projects beyond DeFi, blockchain games, and NFTs.
Many DePIN projects require the construction of an additional resource network, and determining how to incentivize participants providing resources to the network often requires a consensus mechanism designed specifically by the project. The Substrate framework behind Polkadot can support projects in adopting their own consensus mechanisms, a feature that is not available in other Layer2 launch tools such as Cosmos SDK and OP Stack.
Therefore, by carefully observing the composition of ecosystem projects in different multi-chain ecosystems, it is evident that Polkadot has the most diverse ecosystem projects among all multi-chain ecosystems, and Polkadot also has the most DePIN projects, such as the decentralized computing network Phala and the decentralized storage CESS. Therefore, DePIN is not only an advantage for Polkadot, but also an important track for the future development potential of the crypto industry, and Polkadot should further support DePIN to maximize its advantages.
This objective is to provide a promising future for Polkadot.
④ Continuously build public goods.
An enterprise has multiple departments, but among them, there are departments responsible for making money, while the remaining departments are responsible for spending money. It is not realistic to expect all departments to be profitable, and the same applies to project operations.
The teams supported by Polkadot's treasury play a very important role, but they do not have the ability to independently generate profits and achieve a balanced budget. It is extremely challenging to require these teams to be self-sufficient. However, without the support of these projects, it will affect the basic operations. Therefore, for those necessary and important activities, they should be classified as public goods.
This includes data websites, tool projects, community and media organizations in different languages, and technical training organizations. These will provide necessary support for the basic operations of Polkadot. The Polkadot treasury should also provide long-term support for these types of projects to ensure the improvement and stability of Polkadot's basic operations.
This objective is to provide a stable foundation for the continuous operation of Polkadot.
⑤ Establish a citizen system.
In addition to establishing the ways to obtain and exit citizen identities, corresponding rights and credit systems should be provided to citizens. These rights can include the ability for citizens with a certain credit rating to navigate the Polkadot ecosystem with 0 gas fees, or to have priority participation in certain reward opportunities, and so on.
⑥ Design a long-term plan for Polkadot's Odyssey.
Continuously incentivize projects and citizens who are genuinely willing to stay in the Polkadot ecosystem, and incentivize their participation in governance, participation in Polkadot-related promotion and discussions, and participation in projects within the Polkadot ecosystem.
⑦ Make Polkadot more open and become a perennial technology leader.
Polkadot needs to be more open to accepting and investing in new technologies. Through investments, incentive policies, and other means, all new technologies in the existing crypto industry should be able to join the Polkadot ecosystem, even those that have emerged in other public chains, or to ensure that these new technologies are linked to Polkadot, ensuring that the technology on Polkadot remains up-to-date. For example, ZK technology, account abstraction, and more.
Polkadot doesn't need to reinvent the wheel; it just needs to collaborate with the best wheel makers, explore, and promote these technologies within the Polkadot ecosystem. The ultimate goal is to have what other chains don't have (technology), what other chains have, Polkadot can also have, and Polkadot can also have the new technologies that emerge in the future.
⑧ Make Polkadot the core of the entire chain.
As the multi-chain ecosystem with the highest internal security in the entire chain map, Polkadot's parallel chains all enjoy the same level of security as Polkadot, which is a unique advantage of Polkadot. Therefore, we can consider the Polkadot ecosystem as the safest neutral area in the entire chain map, allowing any organization to interact fairly on the Polkadot chain. Therefore, any project on any chain that wants to interact fairly with a project on another chain at the same level of security can choose to move to Polkadot for interaction.
Of course, some may think that such a scenario is very rare. However, we can see more and more traditional enterprises entering Web3, and these enterprises may be more inclined to build their own application chains, or some DApps/DeFis may also start migrating to their own independent application chains, so application chains will definitely be a future trend. When two different application chains want to interact fairly, or even form an alliance to collaborate within a governance framework on one chain, this requires fair interaction based on consistent security, and such fairness and collaboration are common requirements in traditional business. Therefore, Polkadot will definitely become the ecosystem that all these application chains want to participate in.
To achieve this goal, the most important first step is to open up pathways for Polkadot, raise the flag of the entire chain, and link almost all cross-chain technologies (such as Layerzero, Circle's CCIP, Chainlink's CCTP, etc.) with the Polkadot ecosystem, making it easy for other ecosystems to link with the Polkadot ecosystem.
And introduce policies to encourage Polkadot ecosystem projects to expand outside the Polkadot ecosystem and encourage projects from other ecosystems to enter the Polkadot ecosystem (can be understood as encouraging imports and exports), while creating zero-gas fee transactions within Polkadot and zero fees for XCM. Ultimately, achieve seamless connectivity and zero fees for Polkadot in the entire chain map. This will make other projects not have to worry about fees and channel issues when they need to move to Polkadot for collaboration, thereby making Polkadot the largest secure and fair trading center in the entire chain map.
⑨ Mobilize all ecosystem participants to jointly promote Polkadot.
Currently, the promotion of Polkadot mainly relies on the official channels, and each ecosystem project is basically fighting on its own, without forming a united front. Therefore, a way needs to be designed to unite investors, public chains, ecosystem projects, and users to jointly promote and empower Polkadot, creating a win-win situation.
⑩ Establish a feedback and iteration mechanism.
During the development of Polkadot, there are definitely many areas that need improvement, but often feedback cannot be obtained in a timely manner, and some problems persist for a long time, which is not conducive to the rapid iteration of Polkadot. Therefore, there needs to be a complete feedback and iteration mechanism that allows all participants to provide their opinions on certain aspects, and ultimately summarize the urgent problems that Polkadot needs to solve at a certain stage. Consider regularly posting a summary of opinions on the Polkadot Forum, and after a period of time, conduct a vote on the collected opinions to identify the most pressing issues for users at the current stage, and then propose targeted solutions to address them.
And, as much as possible, let the discussions related to Polkadot's governance, such as the Polkadot forum and polkassembly, be more widely spread on social media, allowing more people to participate in the feedback.
There are many areas for improvement in Polkadot's governance. For example, feedback in the governance process needs further optimization, and preliminary rules (or on-chain laws) can be established for some obvious behaviors, and a secondary vote can be conducted for certain behaviors, such as proposing an audit for potential bribery or governance interference (and setting up a supervision bonus, anyone who questions can choose and mark their behavior, similar to a reporting mechanism, and set up a reporting bonus, if the report is successful, someone will receive a portion of the reward), to prevent malicious disruption of elections or whale operations.
Of course, there are many governance issues, but we should not continue to let many problems persist until a perfect solution is developed. We should first propose some urgent solutions and address some obvious and tricky problems. For example, there can be a secondary vote for projects with a lot of opposition, and measures to determine malicious opposition, among others.
Note:
Regarding these strategic objectives, some can be specifically implemented, some can be further discussed, and some are just proposed solutions that need further exploration. Some of these we have some ideas about, but due to space limitations, we will not elaborate further here. Additionally, some issues still require further research. We will, in the future, based on these strategic objectives, develop a series of roadmaps for the Polkadot treasury governance to accelerate the decentralization of Polkadot governance.
3. Three areas for improvement
① Improve inflation: dynamically adjust inflation
According to data from subscan.io, Polkadot's inflation is approximately 7.38%. In late August 2023, we conducted a survey on Polkadot, and the participants were mostly loyal users who had been involved in Polkadot for over 2 years, with an average holding of over 10,000 DOT. Only about 11% of users believed that Polkadot's current inflation is reasonable, indicating that at least from the community's perspective, inflation is indeed the most common concern.
In reality, inflation has a profound impact on projects, especially on project tokens. Although Polkadot's staking can earn double the inflation, this means that participating in staking can definitely resist inflation. However, this perspective does not consider the impact on the token price itself.
For those who hold DOT but do not use it for staking, they may feel that the inflation of DOT is too high, causing their DOT to depreciate too quickly, leading them to choose to sell DOT, causing the price to decline. At this time, those who persist in staking and maintaining the Polkadot network, despite the staking rewards, may suffer losses to their principal due to the decline in token price.
As a result, those who support the Polkadot network may suffer similar losses to those who do not support the network due to the perception of high inflation and the sale of DOT, which is unreasonable and against human nature. Therefore, we need to find a way to prevent such occurrences from continuing.
Furthermore, inflation also affects the development of the entire ecosystem. For example, the high inflation of Polkadot currently results in staking rewards of over 10%, and when staking rewards are too high and other DeFi rewards are unlikely to exceed this reward, it encourages users to participate more in staking rather than in other DeFi projects, which means they are not participating in the market economy of the public chain, hindering the development of the public chain's ecosystem. Controlling the inflation rate within a more moderate range would be more conducive to the development of DeFi projects.
As we have seen in the rise of public chains, chains like Avalanche, Polygon, and others have had a good wave of development in collaboration with DeFi. Therefore, for Polkadot to rise, it still needs to rely on DeFi and ecosystem projects, rather than relying on staking to attract users. Reducing the current inflation rate also aligns with the well-known view that "moderate inflation can stimulate the economy."

Therefore, the inflation rate of Polkadot definitely needs to be adjusted. The next question is, how much should the inflation rate be adjusted, and how should it be adjusted? This is a topic that needs to be discussed collectively, but please allow me to provide some ideas for discussion:
a. Polkadot's design itself has an inflation rate of 10%, but due to non-optimal Staking ratios, a portion of the inflation funds flow into the treasury, and a portion of transaction fees and slashed funds are also collected in the treasury. Additionally, 1% of the treasury funds are burned every 24 days, allowing Polkadot to have an inflation rate lower than 10% (according to subscan.io, the inflation rate at the time of writing this article is 7.38%).
So, we can directly divide the upper limit of the inflation rate of 10% by 2, which can directly control the upper limit of Polkadot's inflation to 5%, and combined with the continuous burning of treasury funds, it can probably control Polkadot's inflation rate to around 2-3%. The Staking rewards will also not be too high, and will be controlled within 10%. This means modifying the original inflation rate formula to change the ideal Staking annualized return to 10% (assuming the ideal optimal Staking ratio is 50%, attached is the official token inflation design formula: link).
 (Model of inflation when the ideal Staking annualized rate is 10%)
(Model of inflation when the ideal Staking annualized rate is 10%)
- x-axis: DOT staking ratio
- y-axis: Annualized inflation percentage
- Blue line: Annual inflation rate of NPoS, representing the total amount of DOT minted for validators and nominators
- Green line: Annualized reward rate for stakers
b. Secondly, in the future development, Polkadot will cancel slot auctions and use time-based sales to allocate block space. However, there is no clear conclusion on how to handle the DOT involved in time-based buying and selling. The author's view is that this portion of DOT should still be aggregated into the treasury, similar to slashed funds and a portion of transaction fees, and then burned at a rate of 1% of the total treasury every 24 days, which can reduce the need for parameter adjustments.
c. Why make these adjustments? Because developed countries generally consider 2% to be a moderate inflation rate, and the Federal Reserve also hopes to keep inflation between 2% and 3%, which is a suitable proportion that can slightly stimulate the economy. In addition, by making these adjustments, the Staking yield can be reduced, providing more room for project development. This makes it more likely for projects with lower returns to develop, and also provides space for more traditional funds to enter Polkadot, which is very important. For example, if the returns of some RWA projects are lower than the Staking yield, it will hinder the development of RWA projects on Polkadot.
d. Of course, this adjustment method is not the final proportion that the author believes. The author hopes to keep the inflation rate within ±2%. On the one hand, if the inflation is within 2%, DOT holders will not sell due to excessively high inflation, as it is within an acceptable range for them. On the other hand, the logic of public chain tokens is not entirely the same as traditional fiat currencies, because when public chain tokens have a certain degree of deflation, they will be more stable in transactions, attracting more buyers. However, excessive deflation, such as exceeding 2%, is also not conducive to the development of applications other than DeFi.
So, how to adjust the inflation rate to within ±2%? Currently, all burning of Polkadot is done in the treasury, and the current parameter is to burn 1% of the total treasury every 24 days. We can change this fixed value of 1% to a burn parameter that can be adjusted at any time, let's call it "b".
The adjustment rule is as follows: starting from the first burn after a cycle, record the total DOT quantity after this burn as M1, and a cycle consists of 15 treasury burns (15 times 24 days is approximately one year). The Nth burn is denoted as An (n=1,2,…15), and the total DOT quantity before the Nth burn is denoted as Kn (n=1,2,…15). So, when An is about to start, calculate (Kn-M1)×15÷n, let's call this value H. If H > 2%, then b=b0; if -2% ≤ H ≤ 2%, then b=b1; if H ≤ -2%, then b=b2, where b0, b1, and b2 should satisfy b0 > b1 > b2.
In simple terms, this formula aims to calculate the approximate annual inflation rate based on the current total DOT quantity before each burn. If the inflation rate is greater than 2%, then more should be burned in this cycle, and if the inflation rate is within ±2%, then less should be burned. If the inflation rate is less than -2%, then even less should be burned.
By dynamically adjusting the burn parameter in this way, the annual inflation rate can be kept within ±2%. As for the specific value of parameter "b", it can be calculated after the official launch of time-based sales, as the DOT obtained from time-based sales will be aggregated into the treasury and change the total treasury burn, so the specific value of parameter "b" can be calculated at that time.
② Improve Operations and Lower Barriers
This is a suggestion for the official team. In terms of promoting Polkadot, consider increasing the level of activity and user engagement of Polkadot on traditional media platforms (especially on Twitter). Also, increase the frequency of feedback on the latest developments in Polkadot, such as sharing key updates and expected launch dates.
Additionally, there is too much for new and existing users to learn about Polkadot, which creates a long learning curve that is not conducive to dissemination. Consider taking measures to reduce the learning curve for users, such as summarizing many of Polkadot's new technologies and mechanisms in a simple and easy-to-understand manner, and introducing non-technical content that is easier for non-technical individuals to understand and more concise. Alternatively, establish a continuously updated set of content that allows Polkadot novices to quickly understand the past, present, and future of Polkadot, or use activities such as Q&A sessions to disseminate important information.

Currently, some projects are addressing these issues, such as the ongoing discussion on the Polkadot forum about the Polkadot App (details can be found here: link), but this is far from enough. In the future, it is hoped that users can further simplify the operational aspects, ultimately allowing users to simply state their intentions and have an application execute directly, without the need for cumbersome on-chain operations.
③ Improve Governance Functions
For example, the voting process for proposals is too simplified. For a proposal, in addition to voting for or against, it should be further divided into specific aspects, such as feasibility, cost, etc., so that the proposer can know whether their proposal is difficult to accept in terms of feasibility or cost based on this feedback, and can optimize it accordingly, and further propose more feasible suggestions.
Similarly, there should be a standardized format for how proposals are written and what content they should include. The approval of proposals should also have a standardized inspection and feedback mechanism, such as adding more feedback indicators for feasibility, cost, and more, and having a richer set of options to show how the proposal performs in each indicator.
4. Potential Questions about the Proposal
① How to ensure that treasury support does not affect the price of DOT?
After OpenGov, many DOT holders felt that the treasury's support for many proposals caused a large amount of selling pressure, leading to a significant number of opposing votes for numerous proposals. However, this approach is undoubtedly self-defeating. Limiting treasury spending means limiting development, which will only make Polkadot's development worse. But this sentiment is not limited to just a few individuals, so simple preaching cannot convince a large number of people with such thinking. Therefore, the only way to alleviate this situation is to address the issue of treasury support potentially causing selling pressure through mechanisms. Here, the author provides two approaches:
a. All treasury support is extended over time, with rewards distributed in parts for each block within a certain period. This can extend the redemption period, ensuring that all reward recipients continue to receive rewards, making it difficult for them to immediately receive and sell their rewards, and instead requiring them to wait for a period of time to receive all rewards, thereby increasing participant retention. It can also spread out selling pressure over a long period, avoiding panic-induced sharp declines.
b. Vigorously develop decentralized stablecoins similar to MakerDAO and distribute rewards in the form of stablecoins generated through over-collateralization. This way, treasury funds will not create selling pressure, and if proposal proponents further believe in Polkadot and are willing to buy the stablecoins received into DOT, it will create buying pressure. However, the drawback of this approach is the lower utilization of funds, as the mechanism of MakerDAO requires over-collateralization, meaning that when the treasury support is $10,000, it may require collateralizing over $10,000 worth of DOT to generate $10,000 worth of decentralized stablecoins.

In this way, both approaches can to some extent address the situation where treasury support may cause significant selling pressure.
② Aren't these strategies too proactive and contrary to the decentralized ethos?
Decentralization does not mean the inability to take proactive action, and proactive action does not mean centralization. All the strategies in this article require governance voting to be executed, and this article only provides strategic references. Furthermore, Polkadot needs to take proactive intervention now. This is because the current landscape of public chains is dominated by Ethereum and its Layer 2 solutions, which has the largest network effect, including users, projects, and funds. When Ethereum was first launched, there was no other public chain with strong support for smart contracts, so Ethereum was sufficient as a market pioneer.
However, for other public chains today, Ethereum is already mature with a rich ecosystem and a strong network effect, so they cannot simply attract users, projects, and funds by just excelling in technology, as new projects are more likely to succeed in a mature market. Therefore, including Polkadot, other public chains must adopt more proactive strategies to attract users, funds, and developers.
③ These strategies have a lot of incentives. What if there is rent-seeking behavior?
First, it is impossible to achieve absolute fairness and justice. No matter how clever the measures, there will still be areas that can be manipulated. Second, compared to not making mistakes and just doing research, we, the Polkadot Ecological Research Institute, hope to continuously explore future possibilities through trial and error, even if we may be criticized for making mistakes. Finally, these strategies can be rapidly iterated. Rather than reducing the iteration speed by 50% for the sake of 5% more fairness, we hope that the entire mechanism is characterized by rapid trial and error and rapid iteration, in order to evolve more quickly into a stable and error-free mechanism.
Afterword
After completing this nearly 30,000-word content, the author is deeply moved. For Polkadot, some may consider it a successful representative, having once been ranked in the top ten in global market capitalization and even being dubbed as "surpassing Ethereum" at one point. However, the actual development process is much more difficult than we imagine, and it will face many criticisms and doubts, just like many entrepreneurial teams.
Over the past few years, we have witnessed the construction of Polkadot from scratch. Although it is still in the early stages of development (as we believe), compared to many other Web3 entrepreneurial teams, it has already made a name for itself and even received a lot of praise.
However, there are still many challenges in development. As a participant in this ecosystem, we do not want to play the role of a "bystander" or a "complaining spectator," but rather, we want to immerse ourselves in it, starting from the spirit of Web3, to explore new possibilities. This is a road that few people have traveled, but we are still moving forward, together with that small group of people.
Once again, thank you for patiently reading through this lengthy report. I believe you must be full of concern and expectations for the current and future of Polkadot, which is our honor and also the driving force for Polkadot's progress. It has been almost 10 years since Dr. Gavin proposed the concept of Web3, and we are still on the road to progress. Please continue to be patient and persevering.
"Pessimists are always right, optimists always move forward."
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




