EVM Compatibility Can Help Developers Attract Traffic and Expand the Ecosystem, While Non-EVM Compatibility Will Undoubtedly Allow Developers to Experiment and Innovate.
By veDAO Research Institute
On September 12th, the blockchain wallet MetaMask launched a beta feature called Snaps, which will allow third-party developers to customize wallet features and mechanisms, enabling MetaMask to seamlessly operate assets on non-EVM (Non-Ethereum Virtual Machine) blockchains. This version can be seen as another step towards complete premise-free and decentralized MetaMask; another noteworthy point is that MetaMask has also started to be compatible with non-EVM. This article will analyze the differences between EVM and non-EVM to further understand the similarities and differences between these two blockchain virtual machines.
EVM and Non-EVM
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)

The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the first virtual machine created for the blockchain industry, serving as an abstraction layer between physical machines (nodes) and smart contract code. It allows programs running on it to be isolated from each other and separate from the Ethereum main chain. Simply put, it is a chain created based on the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing for rapid development and iteration, reducing development workload, and avoiding starting from scratch. Each Ethereum node runs an instance of EVM, working together to form a network or a global decentralized computer. As Vitalik Buterin said, Ethereum is even referred to as the "world computer."
EVM is the heart and soul of the Ethereum network and is also the platform for deploying and executing smart contracts. The physical instantiation of EVM cannot be described in the same way as clouds or waves, but it does exist as an entity, maintained by thousands of connected computers running Ethereum clients. *EVM is Turing complete, which means it will find an answer if there is a problem. Users can use Ethereum's programming language Solidity to create smart contracts and send them to EVM for interpretation and execution. In simple terms, the benefit of EVM is that it makes it easier to achieve interoperability with the Ethereum ecosystem, inheriting existing dApps on the Ethereum chain; however, the disadvantage is obvious, as it is constrained by the Ethereum roadmap, which may interfere with the plans of project parties, who must follow the pace of Ethereum.
Non-EVM Virtual Machine (Non-EVM)
Other blockchains have chosen a different path from EVM compatibility, known as non-EVM blockchains. Non-EVM means completely independent of the Ethereum ecosystem, with developers and project parties rebuilding the blockchain virtual machine. This means that non-EVM is independent of the Ethereum roadmap, thus offering lower costs and faster speeds. However, it also faces many obstacles, as developers and users have to enter a new ecosystem, resulting in higher entry costs. Despite this, it is clear that non-EVM chains have greater innovation space and can operate without the constraints of Ethereum.
Differences Between EVM and Non-EVM

EVM is compatible with Ethereum, while non-EVM is not compatible with Ethereum. For example, the two are like two different smartphone systems, where the Android system in our phones is EVM, and the Apple system is non-EVM. All applications developed based on the Android system can be used on Android phones, which we collectively refer to as EVM, while software developed based on the Apple system cannot be installed and used on Android systems, which we collectively refer to as non-EVM.
Some well-known EVM chains include Ethereum, Bsc, Arbitrum, Polygon, and Avalanche, while non-EVM chains include Solana, Mixin, DefiChain, Osmosis, and EOS.
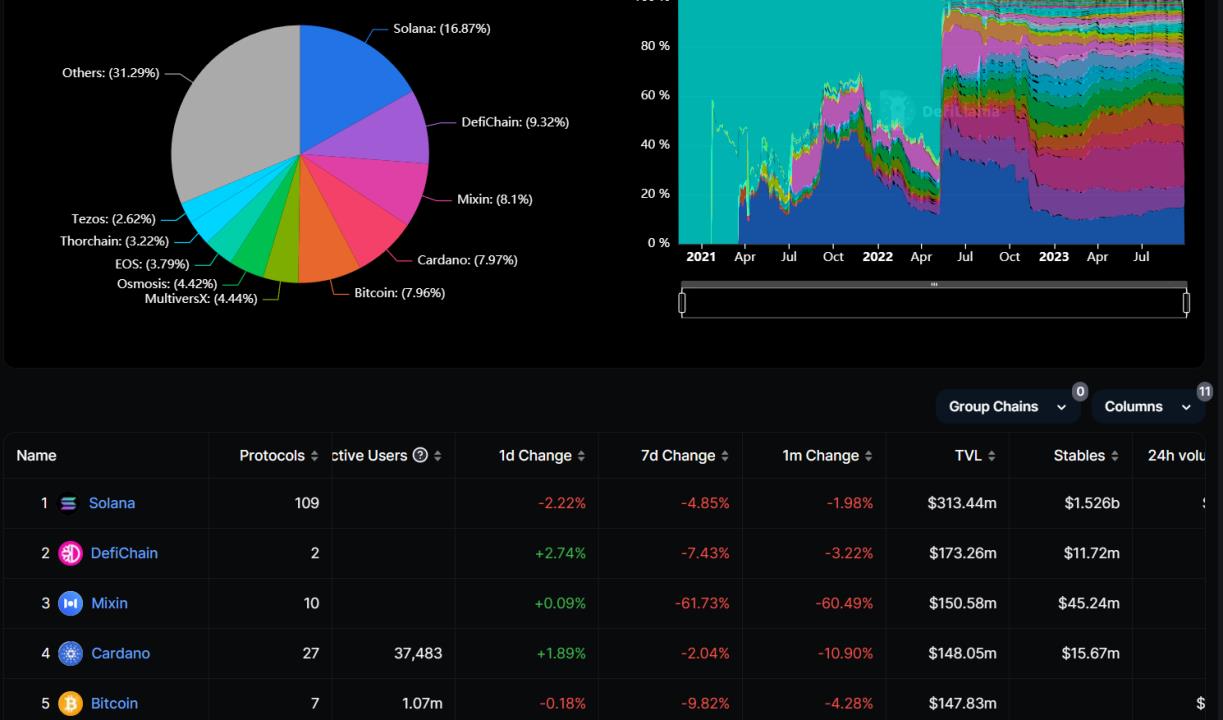
Currently, most of the top ten blockchains are compatible with EVM, and EVM remains the market leader in public chains. However, the growth rate of emerging non-EVM blockchains is also very rapid.
Functions of EVM and Non-EVM
The functions of EVM and non-EVM (hereinafter referred to as blockchain virtual machines) are to determine and track the state of each network block. Although it sounds like a monitoring tool, it actually refers to state changes, which are signals or reasons for actions in various computer systems. For example, when opening or closing certain content, activating or deactivating, sending or receiving certain content, or moving files or documents, state changes occur. These state changes lead to modifications in the data structure of the computing system.
Blockchain virtual machines can review changes in the network and dApp states, addressing issues such as network saturation or operation priority, allowing the public chain and its dApps to work in a decentralized manner. In this way, blockchain virtual machines allow any developer to run code in an ecosystem without the need for third-party trust, and the execution and interaction of the software are guaranteed and predictable.
The Battle Between EVM and Non-EVM
For a long time, there has been a debate between EVM chains and non-EVM chains. Although it seems that the EVM virtual machine is the obvious winner, non-EVM chains like Solana make this battle worth paying attention to. EVM compatibility is the primary requirement for evaluating public chain platforms.
Leveraging the advantages of Ethereum, EVM-compatible public chains can quickly gain customers and grow in the early stages, benefiting from developer friendliness, user experience, and ecosystem incentives, but they must compete with many other chains in the Ethereum ecosystem. Non-EVM-compatible chains are more likely to gain development in trend areas and niche markets where new ideas emerge. At the same time, a variety of public chains can succeed in areas such as NFT, GameFi, and payments.
Overall, it is difficult to say which is better between EVM chains and non-EVM chains. Attracting Ethereum traffic is the fastest way for new chains to grow, and EVM compatibility is the most convenient solution; while non-EVM can choose development directions according to demand, free from the constraints of the main chain.
Let's take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of EVM and non-EVM separately to understand the actual situation of EVM and non-EVM.
Advantages and Disadvantages of EVM and Non-EVM
EVM
Advantages of EVM
As mentioned earlier when introducing EVM, there are no security barriers or restrictions because anyone can develop decentralized applications, making EVM scalable and the process of migrating from the Ethereum ecosystem relatively simple, making it easier for users to access projects. NFT has become one of the most popular contents in the encrypted world thanks to the convenience of EVM.
Disadvantages of EVM
Although decentralized, the EVM network is not completely decentralized. The vast majority of Ethereum nodes are hosted on centralized cloud servers of Amazon Web Services. If the operators of these services decide for any reason that they do not like Ethereum, nodes may be rejected, thereby harming the network.
In times of network congestion, gas fees can be very high. This may cause serious inconvenience for Ethereum users, as while those sending large transactions may not be affected, those sending small transactions may experience network access issues for a period of time. When many users interact with DApp smart contracts and execute a large number of transactions, high gas fees can have many negative impacts on projects.
Due to its bytecode language and rigid native functionality, EVM is overly complex and lacks sufficient virtual machine functionality to achieve security design. Additionally, due to the rules of Ethereum and EVM, designers need to implement many key parts of EVM's functionality and execution model on their own.
Non-EVM
Advantages of Non-EVM Blockchains
Non-EVM allows programmers to expand their user base and application scope. For example, projects like Raydium and Serum on the Solana chain are exclusive to Solana. Terra was once a unique public chain aimed at connecting on-chain and off-chain payments. Additionally, platforms incompatible with EVM can provide fast transaction times and inexpensive transactions for end users.
These advantages make non-EVM blockchains a choice that stands out in specific use cases and markets, providing developers and users with more choices and flexibility.
Disadvantages of Non-EVM Blockchains
High development costs: Chains incompatible with EVM may require additional development work to adapt to their unique ecosystem and rules, which may lead to increased development costs.
High barriers to entry: Non-EVM compatible chains may have a high barrier to entry for developers and users, as they need to adapt to new tools, technologies, and ecosystems.
Difficulty in project migration: Migrating projects from EVM-compatible chains to non-EVM chains may pose some challenges, including the need to rewrite smart contracts and adapt to a new ecosystem.
Due to the significant disadvantage in the number of projects on non-EVM compatible chains, developers are more inclined to choose EVM-compatible chains.
Because they can be quickly replicated and deployed on new chains, which can help save time and costs.
Conclusion
So, who wins in the competition between EVM and non-EVM chains? There is no clear winner between the two, as each situation is unique, and developers must choose a public chain that corresponds to the development path of their project. Different projects and use cases may be better suited to different chains, so no one chain can be absolutely chosen as superior to another; decisions should be based on specific needs and project goals. EVM compatibility can help developers attract traffic and expand the ecosystem, as Ethereum users can quickly migrate to new chains. At the same time, non-EVM compatibility will undoubtedly allow developers to experiment and innovate.
In the blockchain field, no single chain can meet all needs, so developers and project teams must make choices based on their unique goals and use cases to achieve the best results. Therefore, in the long run, the future will not be dominated by EVM alone, but rather the coexistence of multiple chains. After all, the diversity and continuous evolution of the blockchain ecosystem is its essence.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



